High Land-Use Intensity Diminishes Stability of Forage Provision of Mountain Pastures under Future Climate Variability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
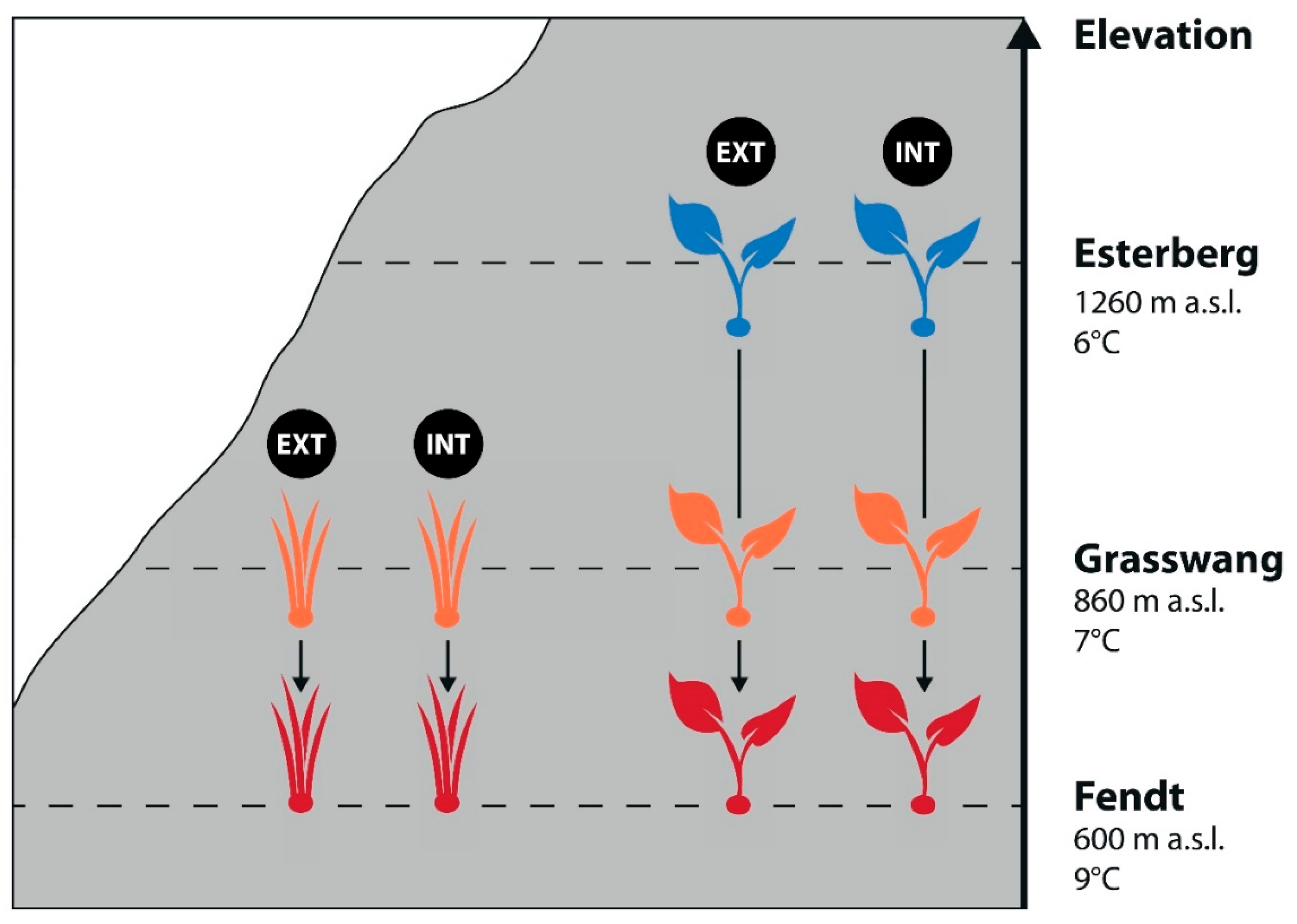
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
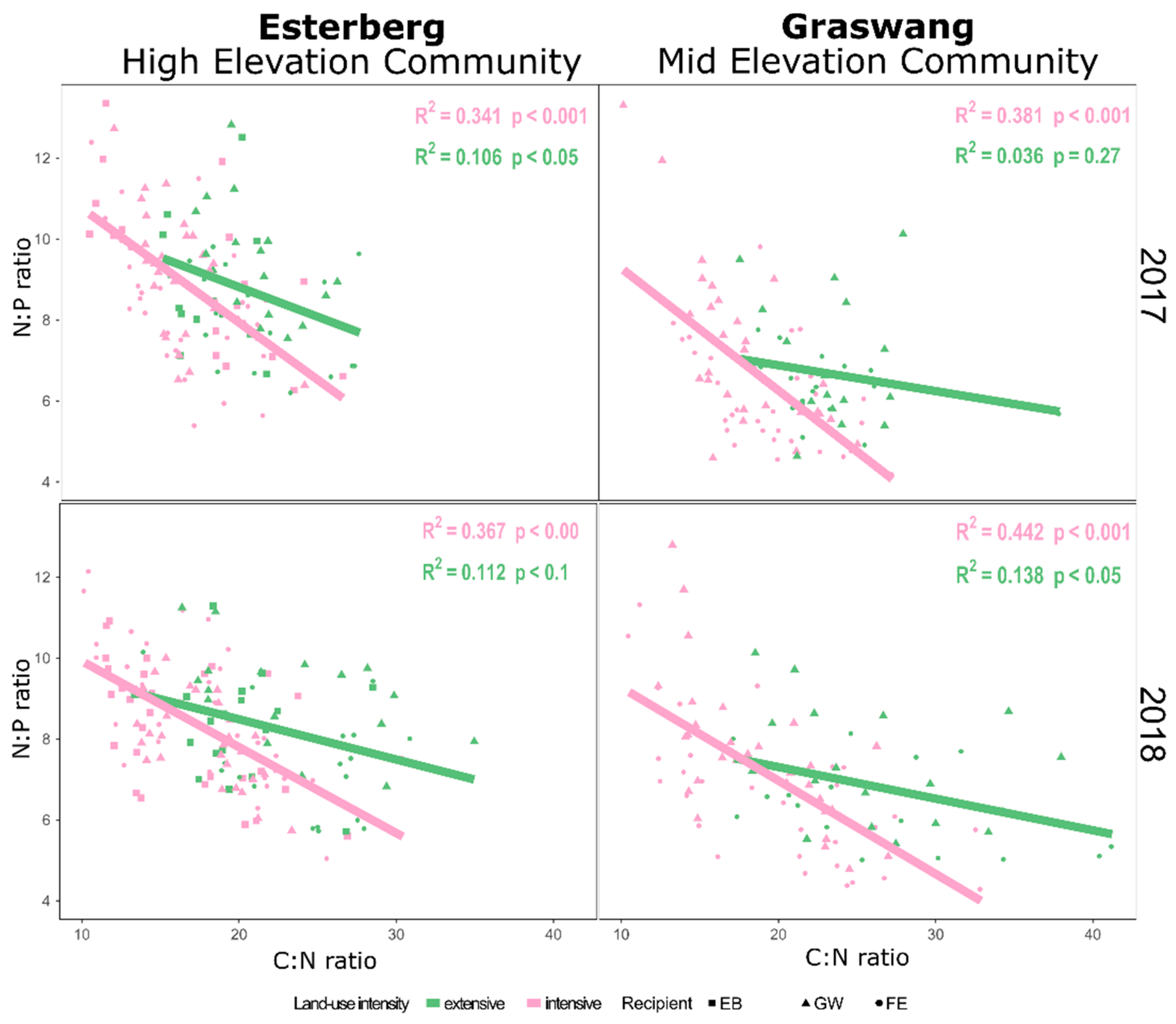
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Formulas
References
- Dixon, A.P.; Faber-Langendoen, D.; Josse, C.; Morrison, J.; Loucks, C.J. Distribution mapping of world grassland types. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 2003–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramankutty, N.; Evan, A.T.; Monfreda, C.; Foley, J.A. Farming the planet: 1. Geographic distribution of global agricultural lands in the year 2000. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.; Knutti, R.; Arblaster, J.; Dufresne, J.-L.; Fichefet, T.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gao, X.; Gutowski, W.J.; Johns, T.; Krinner, G.; et al. Chapter 12. In Long-Term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pepin, N.; Bradley, R.S.; Diaz, H.F.; Baraer, M.; Caceres, E.B.; Forsythe, N.; Fowler, H.; Greenwood, G.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Liu, X.D.; et al. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobiet, A.; Kotlarski, S.; Beniston, M.; Heinrich, G.; Rajczak, J.; Stoffel, M. 21st century climate change in the European Alps—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schär, C.; Vidale, P.L.; Lüthi, D.; Frei, C.; Häberli, C.; Liniger, M.A.; Appenzeller, C. The role of increasing temperature variability in European summer heatwaves. Nature 2004, 427, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntingford, C.; Jones, P.D.; Livina, V.N.; Lenton, T.M.; Cox, P.M. No increase in global temperature variability despite changing regional patterns. Nature 2013, 500, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanca, P. Climate change and drought occurrence in the Alpine region: How severe are becoming the extremes? Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.; Kreyling, J.; Dienstbach, L.F.H.H.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Jentsch, A. Water stress due to increased intra-annual precipitation variability reduced forage yield but raised forage quality of a temperate grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 186, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicke, M.; Alessio, G.A.; Thiery, L.; Falcimagne, R.; Baumont, R.; Rossignol, N.; Soussana, J.-F.; Picon-Cochard, C. Lasting effects of climate disturbance on perennial grassland above-ground biomass production under two cutting frequencies. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silveira Pontes, L.; Maire, V.; Schellberg, J.; Louault, F. Grass strategies and grassland community responses to environmental drivers: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1297–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Estiarte, M.; Prieto, P. Warming and drought alter C and N concentration, allocation and accumulation in a Mediterranean shrubland. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2304–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.M. Effects of water deficits on carbon assimilation. J. Exp. Bot. 1991, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernakovich, J.G.; Hopping, K.A.; Berdanier, A.B.; Simpson, R.T.; Kachergis, E.J.; Steltzer, H.; Wallenstein, M.D. Predicted responses of arctic and alpine ecosystems to altered seasonality under climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 3256–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C. Alpine Plant Life: Functional Plant Ecology of High Mountain Ecosystems; With 47 Tables; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Asam, S.; Callegari, M.; De Gregorio, L.; Jacob, A.; Notarnicola, C.; Zebisch, M.; Matiu, M.; Menzel, A.; Fiore, G. Spatiotemporal variations of alpine climate, snow cover and phenology. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multitemporal Remote Sensing Images (MultiTemp), Brugge, Belgium, 27–29 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ergon, Å.; Seddaiu, G.; Korhonen, P.; Virkajärvi, P.; Bellocchi, G.; Jørgensen, M.; Østrem, L.; Reheul, D.; Volaire, F. How can forage production in Nordic and Mediterranean Europe adapt to the challenges and opportunities arising from climate change? Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 92, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, D.E.; Chapin, K.J.; Kueppers, L.M. Soil moisture mediates alpine life form and community productivity responses to warming. Ecology 2016, 97, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berauer, B.J.; Wilfahrt, P.A.; Arfin-Khan, M.A.S.S.; Eibes, P.; Von Heßberg, A.; Ingrisch, J.; Schloter, M.; Schuchardt, M.A.; Jentsch, A. Low resistance of montane and alpine grasslands to abrupt changes in temperature and precipitation regimes. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2019, 51, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Lützow, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition-what do we know? Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustad, L.E.; Campbell, J.L.; Marion, G.M.; Norby, R.J.; Mitchell, M.J.; Hartley, A.E.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Gurevitch, J.; Alward, R.; Beier, C.; et al. A meta-analysis of the response of soil respiration, net nitrogen mineralization, and aboveground plant growth to experimental ecosystem warming. Oecologia 2001, 126, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Unteregelsbacher, S.; Lu, H.; Gschwendtner, S.; Gasche, R.; Kolar, A.; Schloter, M.; Kiese, R.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; et al. Climate change amplifies gross nitrogen turnover in montane grasslands of Central Europe in both summer and winter seasons. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 2963–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, R.; Chen, W.; Luo, Y.; Niu, S. Global patterns and controlling factors of soil nitrification rate. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, gcb.15119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Chen, H.Y.H. Decoupling of nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial plants associated with global changes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Hübner, R.; Barthold, F.; Spörlein, P.; Geuß, U.; Hangen, E.; Reischl, A.; Schilling, B.; von Lützow, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Amount, distribution and driving factors of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in cropland and grassland soils of southeast Germany (Bavaria). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Venterink, H. Productivity increase upon supply of multiple nutrients in fertilization experiments; co-limitation or chemical facilitation? Plant Soil 2016, 408, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L. Chemical Equilibria in Soils; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Manning, P.; Rist, J.; Power, S.A.; Marsh, C. A global comparison of grassland biomass responses to CO2 and nitrogen enrichment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, P.A.; Prober, S.M.; Harpole, W.S.; Knops, J.M.H.; Bakker, J.D.; Borer, E.T.; Lind, E.M.; MacDougall, A.S.; Seabloom, E.W.; Wragg, P.D.; et al. Grassland productivity limited by multiple nutrients. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirpke, U.; Kohler, M.; Leitinger, G.; Fontana, V.; Tasser, E.; Tappeiner, U. Future impacts of changing land-use and climate on ecosystem services of mountain grassland and their resilience. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P. Nutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency. Am. Nat. 1982, 119, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veen, G.F.; Sundqvist, M.K.; Metcalfe, D.; Wilson, S.D. Above-Ground and Below-Ground Plant Responses to Fertilization in Two Subarctic Ecosystems. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2015, 47, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogianni, V.G.; Wilson, S.D.; Vaness, B.M.; Macdougall, A.S.; Pinno, B.D. Different root and shoot responses to mowing and fertility in native and invaded grassland. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 67, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sistla, S.A.; Schimel, J.P. Stoichiometric flexibility as a regulator of carbon and nutrient cycling in terrestrial ecosystems under change. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågren, G.I. The C:N:P stoichiometry of autotrophs—Theory and observations. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Chen, H.Y.H. Negative effects of fertilization on plant nutrient resorption. Ecology 2015, 96, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Gastal, F. N uptake and distribution in plant canopies. In Diagnosis of the Nitrogen Status in Crops; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 3–43. [Google Scholar]
- Nevens, F.; Rehuel, D. Effects of cutting or grazing grass swards on herbage yield, nitrogen uptake and residual soil nitrate at different levels of N fertilization. Grass Forage Sci. 2003, 58, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Wan, S.; Zhou, X.; Subedar, A.A.; Wallace, L.L.; Luo, Y. Plant nitrogen concentration, use efficiency, and contents in a tallgrass prairie ecosystem under experimental warming. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; Callaghan, T.V.; Dorrepaal, E.; van Logtestijn, R.S.P.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. Seasonal climate manipulations result in species-specific changes in leaf nutrient levels and isotopic composition in a sub-arctic bog. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, T.A.; Ruhland, C.T.; Xiong, F.S. Warming increases aboveground plant biomass and C stocks in vascular-plant-dominated Antarctic tundra. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1827–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.S.; Andresen, L.C.; Beier, C.; Jonasson, S.; Albert, K.R.; Ambus, P.; Arndal, M.F.; Carter, M.S.; Christensen, S.; Holmstrup, M.; et al. Reduced N cycling in response to elevated CO2, warming, and drought in a Danish heathland: Synthesizing results of the CLIMAITE project after two years of treatments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 1884–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. N:P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Poulter, B.; Sardans, J.; Ciais, P.; Van Der Velde, M.; Bopp, L.; Boucher, O.; Godderis, Y.; Hinsinger, P.; Llusia, J.; et al. Human-induced nitrogen-phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.R. Stoichiometrically Explicit Food Webs: Feedbacks between Resource Supply, Elemental Constraints, and Species Diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, A.C.; Austin, A.T.; Cleland, E.E.; Frey, S.D.; Houlton, B.Z.; Wallenstein, M.D. Responses and feedbacks of coupled biogeochemical cycles to climate change: Examples from terrestrial ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.A.; Davis, A.P.; Chagunda, M.G.G.; Manning, P. Forage quality declines with rising temperatures, with implications for livestock production and methane emissions. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berauer, B.J.; Wilfahrt, P.A.; Reu, B.; Schuchardt, M.A.; Garcia-franco, N.; Zistl-Schlingmann, M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Kühnel, A.; Jentsch, A. Predicting forage quality of species-rich pasture grasslands using vis-NIRS to reveal effects of management intensity and climate change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 296, 106929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Peng, F.; Xue, X.; You, Q.; Lai, C.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, Y. Productivity and Quality of Alpine Grassland Vary with Soil Water Availability Under Experimental Warming. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Cao, G.; Zhao, X.; Schmid, B.; He, J.-S. Experimentally simulating warmer and wetter climate additively improves rangeland quality on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfried, M.; Pauli, H.; Futschik, A.; Akhalkatsi, M.; Barančok, P.; Benito Alonso, J.L.; Coldea, G.; Dick, J.; Erschbamer, B.; Fernández Calzado, M.R.; et al. Continent-wide response of mountain vegetation to climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbauer, M.J.; Grytnes, J.-A.; Jurasinski, G.; Kulonen, A.; Lenoir, J.; Pauli, H.; Rixen, C.; Winkler, M.; Bardy-Durchhalter, M.; Barni, E.; et al. Accelerated increase in plant species richness on mountain summits is linked to warming. Nature 2018, 556, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossner, M.M.; Lewinsohn, T.M.; Kahl, T.; Grassein, F.; Boch, S.; Prati, D.; Birkhofer, K.; Renner, S.C.; Sikorski, J.; Wubet, T.; et al. Land-use intensification causes multitrophic homogenization of grassland communities. Nature 2016, 540, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.E. Species composition determines forage quality and medicinal value of high diversity grasslands in lowland England. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, S.C. Life history evolution: Successes, limitations, and prospects. Naturwissenschaften 2000, 87, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B. The world-wide “fast-slow” plant economics spectrum: A traits manifesto. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.L.; Töpper, J.P.; Skarpaas, O.; Vandvik, V.; Klanderud, K. From facilitation to competition: Temperature-driven shift in dominant plant interactions affects population dynamics in seminatural grasslands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbritter, A.H.; De Boeck, H.J.; Eycott, A.E.; Reinsch, S.; Robinson, D.A.; Vicca, S.; Berauer, B.; Christiansen, C.T.; Estiarte, M.; Grünzweig, J.M.; et al. The handbook for standardized field and laboratory measurements in terrestrial climate change experiments and observational studies (ClimEx). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Tank, A.K.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.W. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Zeng, F.J.; Ducharne, A.; Morrill, J.C.; Koster, R.D. The sensitivity of surface fluxes to soil water content in three land surface schemes. J. Hydrometeorol. 2000, 1, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, K.E.; Rawls, W.J. Soil Water Characteristic Estimates by Texture and Organic Matter for Hydrologic Solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; Swenson, N.G.; Enquist, B.J. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R package Version 3.1-140; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R.V.; Herv, M. Least-Squares Means: The Package. J. Stat. Soft. 2016, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xia, J.; Wan, S. Climate warming and biomass accumulation of terrestrial plants: A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Quesada, B.; Xia, L.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Goodale, C.L.; Kiese, R. Effects of climate warming on carbon fluxes in grasslands—A global meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1839–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, M.; Gerstner, K.; Akin-Fajiye, M.; Ceaușu, S.; Kambach, S.; Kinlock, N.L.; Phillips, H.R.P.; Verhagen, W.; Gurevitch, J.; Klotz, S.; et al. Conventional land-use intensification reduces species richness and increases production: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1941–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socher, S.A.; Prati, D.; Boch, S.; Müller, J.; Baumbach, H.; Gockel, S.; Hemp, A.; Schöning, I.; Wells, K.; Buscot, F.; et al. Interacting effects of fertilization, mowing and grazing on plant species diversity of 1500 grasslands in Germany differ between regions. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2013, 14, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautier, Y.; Tilman, D.; Isbell, F.; Seabloom, E.W.; Borer, E.T.; Reich, P.B. Anthropogenic environmental changes affect ecosystem stability via biodiversity. Science 2015, 348, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, D.; Isbell, F.; Manning, P.; Connolly, J.; Bruelheide, H.; Ebeling, A.; Roscher, C.; van Ruijven, J.; Weigelt, A.; Wilsey, B.; et al. Plant diversity effects on grassland productivity are robust to both nutrient enrichment and drought. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, H.; Mi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Jiang, L.; He, J.-S. Climate warming reduces the temporal stability of plant community biomass production. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ramanathan, V.; Victor, D.G. Global warming will happen faster than we think. Nature 2018, 564, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R. Perception of climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2415–E2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 2012, 486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, J.M. The pace of biodiversity change in a warming climate. Nature 2020, 580, 460–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchslueger, L.; Kastl, E.-M.; Bauer, F.; Kienzl, S.; Hasibeder, R.; Ladreiter-Knauss, T.; Schmitt, M.; Bahn, M.; Schloter, M.; Richter, A.; et al. Effects of drought on nitrogen turnover and abundances of ammonia-oxidizers in mountain grassland. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2014, 11, 9183–9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F.M. The Vegetation N:P Ratio: A New Tool to Detect the Nature of Nutrient Limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zistl-Schlingmann, M.; Feng, J.; Kiese, R.; Stephan, R.; Zuazo, P.; Willibald, G.; Wang, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Dannenmann, M. Dinitrogen emissions: An overlooked key component of the N balance of montane grasslands. Biogeochemistry 2019, 143, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, F.; Bünemann, E.K.; Huguenin-Elie, O.; Jeangros, B.; Frossard, E.; Oberson, A. Plant phosphorus nutrition indicators evaluated in agricultural grasslands managed at different intensities. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 44, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussana, J.-F.; Tallec, T.; Blanfort, V. Mitigating the greenhouse gas balance of ruminant production systems through carbon sequestration in grasslands. Animal 2010, 4, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soussana, J.-F.F.; Lemaire, G. Coupling carbon and nitrogen cycles for environmentally sustainable intensification of grasslands and crop-livestock systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Simons, N.K.; Jung, K.; Prati, D.; Renner, S.C.; Boch, S.; Fischer, M.; Hölzel, N.; Klaus, V.H.; Kleinebecker, T.; et al. Land use imperils plant and animal community stability through changes in asynchrony rather than diversity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, E.; Manning, P.; Alt, F.; Binkenstein, J.; Blaser, S.; Blüthgen, N.; Böhm, S.; Grassein, F.; Hölzel, N.; Klaus, V.H.; et al. Land use intensification alters ecosystem multifunctionality via loss of biodiversity and changes to functional composition. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berauer, B.J.; Wilfahrt, P.A.; Schuchardt, M.A.; Schlingmann, M.; Schucknecht, A.; Jentsch, A. High Land-Use Intensity Diminishes Stability of Forage Provision of Mountain Pastures under Future Climate Variability. Agronomy 2021, 11, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050910
Berauer BJ, Wilfahrt PA, Schuchardt MA, Schlingmann M, Schucknecht A, Jentsch A. High Land-Use Intensity Diminishes Stability of Forage Provision of Mountain Pastures under Future Climate Variability. Agronomy. 2021; 11(5):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050910
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerauer, Bernd Josef, Peter Allan Wilfahrt, Max Anatol Schuchardt, Marcus Schlingmann, Anne Schucknecht, and Anke Jentsch. 2021. "High Land-Use Intensity Diminishes Stability of Forage Provision of Mountain Pastures under Future Climate Variability" Agronomy 11, no. 5: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050910
APA StyleBerauer, B. J., Wilfahrt, P. A., Schuchardt, M. A., Schlingmann, M., Schucknecht, A., & Jentsch, A. (2021). High Land-Use Intensity Diminishes Stability of Forage Provision of Mountain Pastures under Future Climate Variability. Agronomy, 11(5), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050910





