Geographical Distribution and Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Tributaries of the Han River Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review of VOCs in Water
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals Used
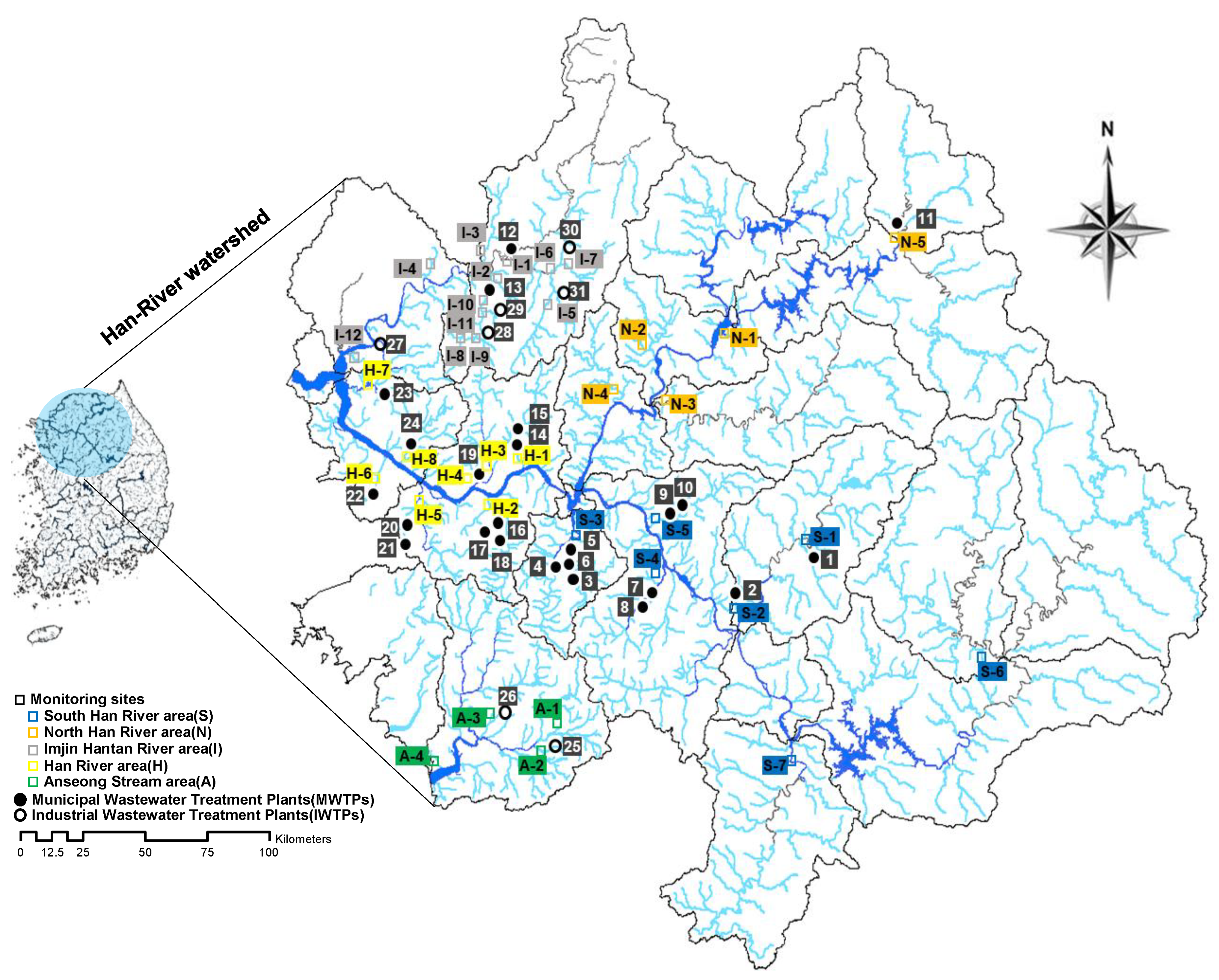
3.2. Sample Collection
3.3. Analytical Method and Quality Analysis
3.4. Data Analyses
3.5. Evaluation of Ecological Risks
4. Results and Discussion
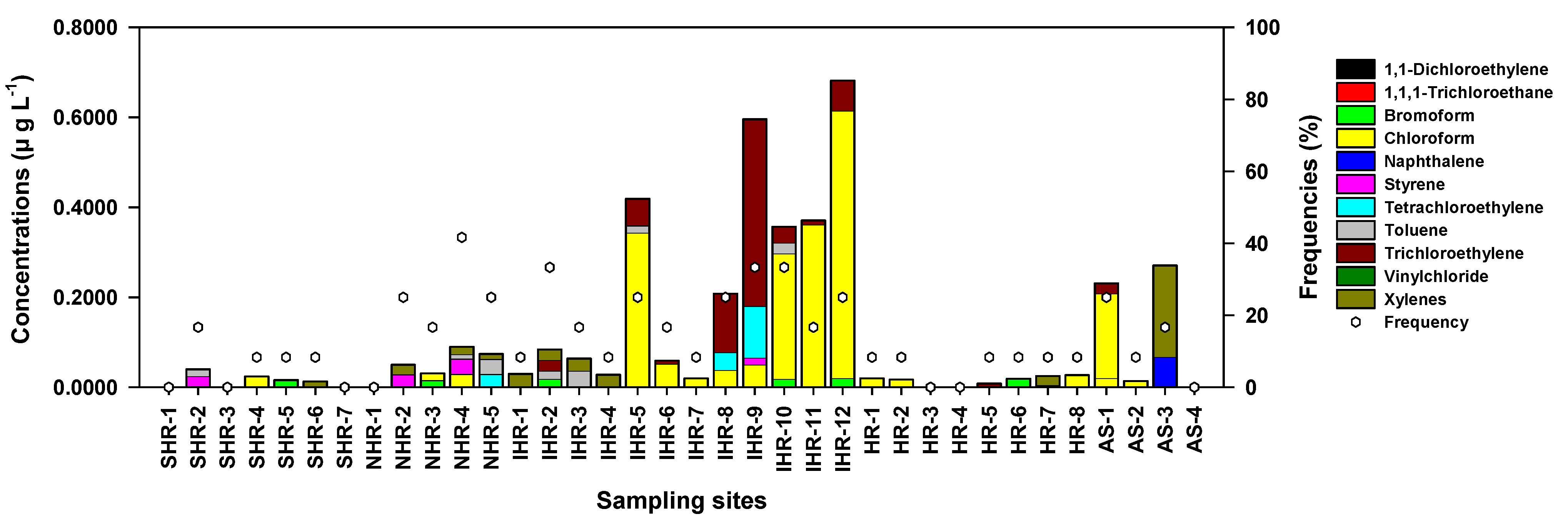
4.1. General Trends
4.2. Halogenated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons (HAHs)
4.3. Aromatic Hydrocarbons (AHs)
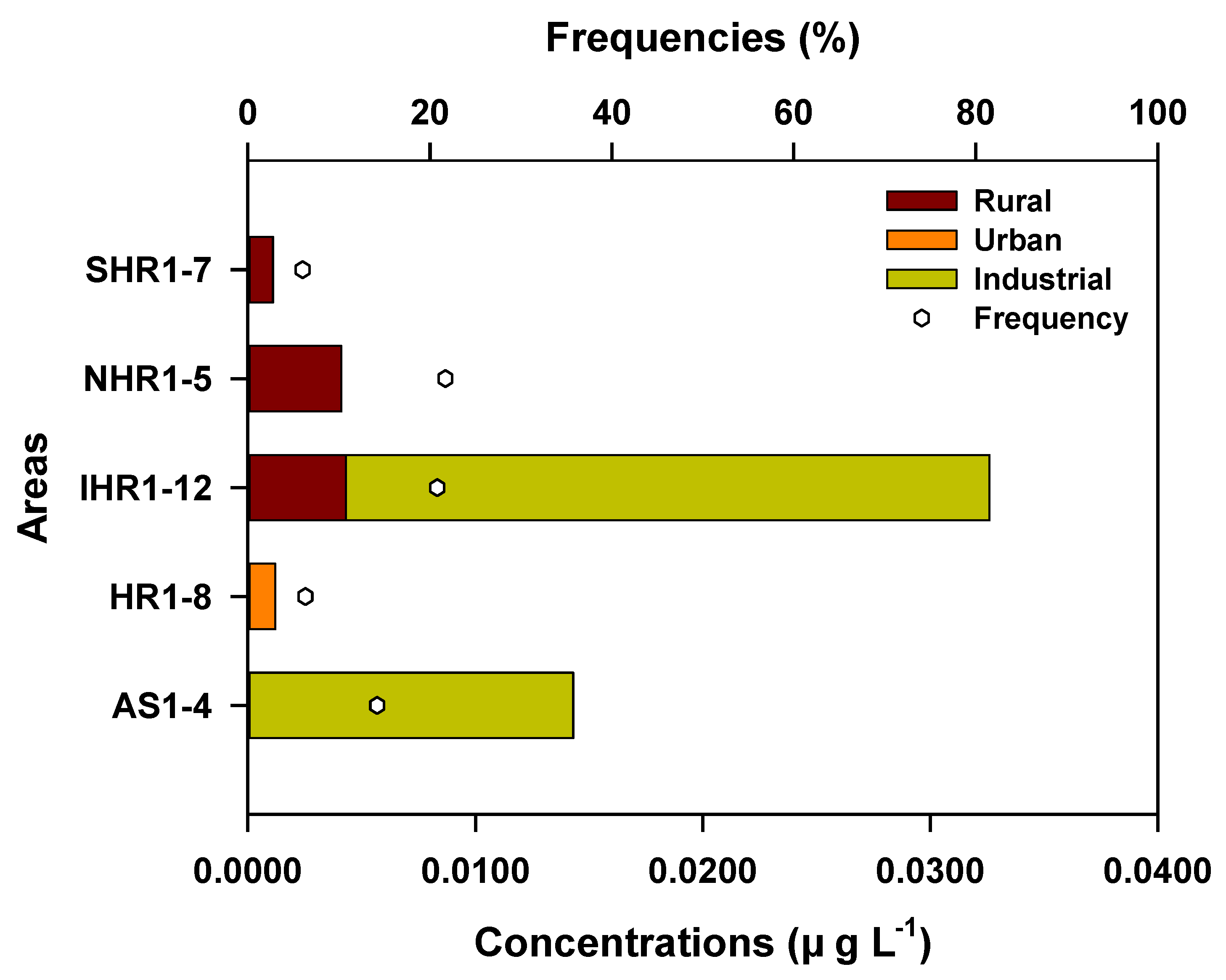
4.4. Geographic Distribution and Sources of VOCs
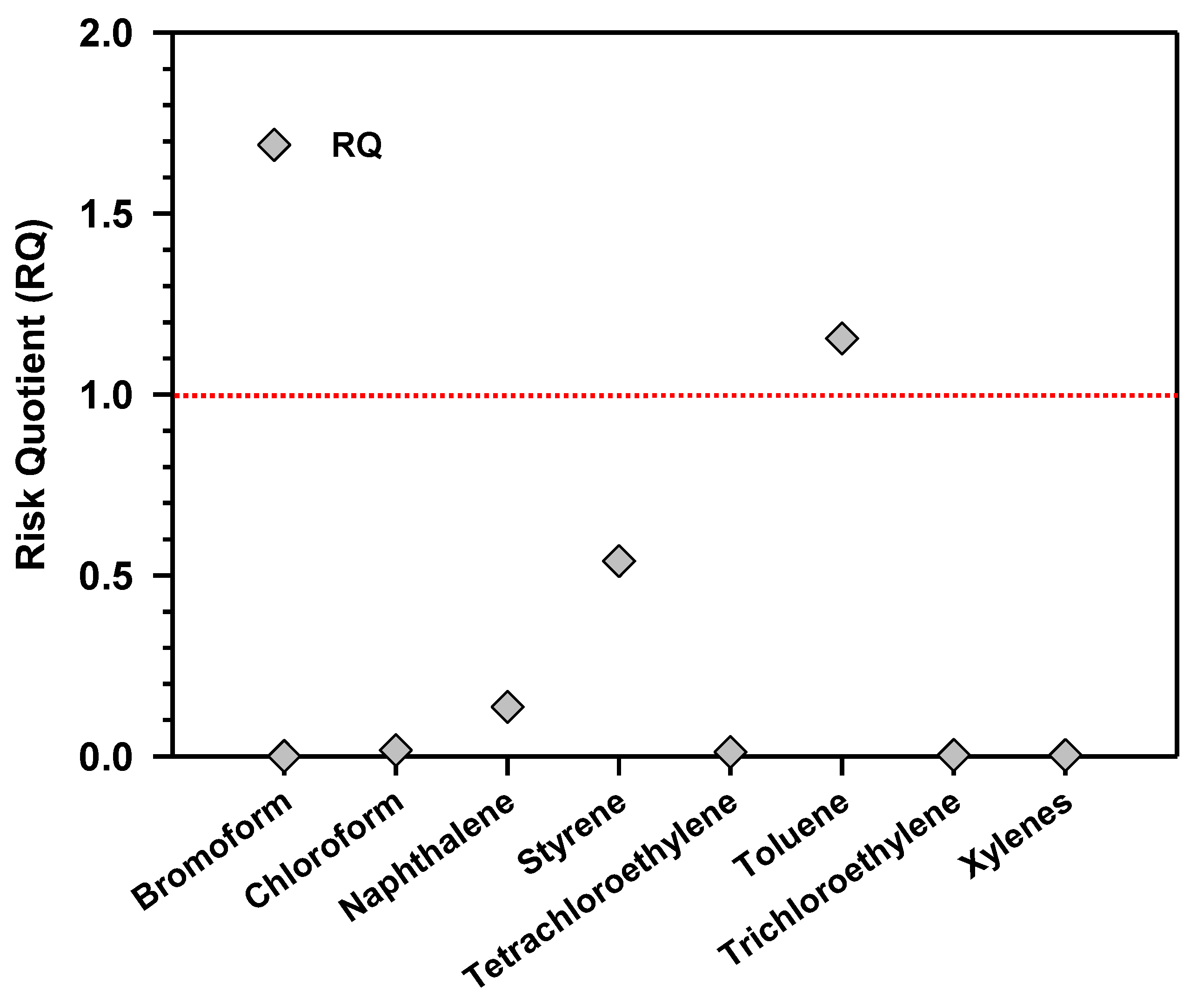
4.5. Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.-Z.; Guan, Y.-F.; Ni, H.-G.; Luo, X.-L.; Zeng, E.Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta (China): Concentrations, fluxes, and fate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5614–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Liang, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, N.; Duan, H. Occurrence, spatial distribution, historical trend and ecological risk of phthalate esters in the Jiulong River, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, W.; Licha, T.; Nödler, K. Qualitative and quantitative use of micropollutants as source and process indicators. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ya, M.; Li, Y.; Hong, H. Seasonal variation and spatial transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water of the subtropical Jiulong River watershed and estuary, Southeast China. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Khim, J.; Chung, S.; Seo, D.; Son, Y. Occurrence of micropollutants in four major rivers in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 491, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Lei, C.; Wei, C.; Zeng, G. Chlorinated volatile organic compounds (Cl-VOCs) in environment—sources, potential human health impacts, and current remediation technologies. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, P.M.; Ward, L.M.; Woytowitch, L.M.; Wolfe, N.L. Homogeneous hydrolysis rate constants for selected chlorinated methanes, ethanes, ethenes, and propanes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinicola, R.S.; Cox, S.E.; Bradley, P.N. Natural Attenuation of Chlorinated Volatile Organic Compounds in Ground Water at Area 6, Naval Air Station Whidbey Island, Washington; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Comprehensive screening and priority ranking of volatile organic compounds in Daliao River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y. Disinfection Byproducts in Drinking Water: Formation, Analysis, and Control; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barceló, D. Emerging Organic Pollutants in Waste Waters and Sludge; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.J.; Pal, V.K.; Kannan, K. A review of environmental occurrence, toxicity, biotransformation and biomonitoring of volatile organic compounds. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 3, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Cao, F.; Lu, S.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, B.; Wan, Z.; Bi, B. Occurrence and health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in the surface water of Poyang Lake in March 2017. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 22609–22617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Luo, Q.; Wang, D.; Gao, J.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Mazumder, A. Simultaneous assessments of occurrence, ecological, human health, and organoleptic hazards for 77 VOCs in typical drinking water sources from 5 major river basins, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Kadokami, K.; Wang, S.; Duong, H.T.; Chau, H.T.C. Monitoring of 1300 organic micro-pollutants in surface waters from Tianjin, North China. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsikowitzky, L.; Sträter, M.; Ariyani, F.; Irianto, H.; Schwarzbauer, J. First comprehensive screening of lipophilic organic contaminants in surface waters of the megacity Jakarta, Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Qin, P.; Lu, S.; He, Q.; Wu, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Measurement of volatile organic compounds and associated risk assessments through ingestion and dermal routes in Dongjiang Lake, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asejeje, G.I.; Ipeaiyeda, A.R.; Onianwa, P.C. Occurrence of BTEX from petroleum hydrocarbons in surface water, sediment, and biota from Ubeji Creek of Delta State, Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 15361–15379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Qiao, X.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zheng, B. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in the groundwater of Lanzhou City, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3609–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selden, T.M.; Forrest, A.S.; Lockhart, J.E. Analyzing the reductions in US air pollution emissions: 1970 to 1990. Land Econ. 1999, 75, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.J.; Hamilton, P.A.; Zogorski, J.S. Volatile Organic Compounds in the Nation’s Ground Water and Drinking-Water Supply Wells: A Summary; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Miermans, C.; Van der Velde, L.; Frintrop, P.C. Analysis of volatile organic compounds, using the purge and trap injector coupled to a gas chromatograph/ion-trap mass spectrometer: Review of the results in Dutch surface water of the Rhine, Meuse, Northern Delta Area and Westerscheldt, over the period 1992–1997. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkas, T.; Kolokythas, G.; Nikolaou, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Kotrikla, A.; Gatidou, G.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Golfinopoulos, S.; Makri, C.; Babos, D. Evaluation of the pollution of the surface waters of Greece from the priority compounds of List II, 76/464/EEC Directive, and other toxic compounds. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, E.; Lacorte, S.; Llobet, I.; Viana, P.; Barceló, D. Multicomponent analysis of volatile organic compounds in water by automated purge and trap coupled to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 959, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huybrechts, T.; Dewulf, J.; Van Langenhove, H. Spatial and temporal variability of priority volatile organic compounds in the Scheldt estuary. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3241–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E. Determination of volatile organic compounds in rainwater and dew water by head space solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Bunseki Kagaku 2010, 59, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okochi, H.; Sugimoto, D.; Igawa, M. The enhanced dissolution of some chlorinated hydrocarbons and monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rainwater collected in Yokohama, Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4403–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullaugh, K.M.; Byrd, J.N.; Avery, G.B., Jr.; Mead, R.N.; Willey, J.D.; Kieber, R.J. Characterization of carbohydrates in rainwater from the Southeastern North Carolina. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, P.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Prediction of the wash-off of traffic related semi-and non-volatile organic compounds from urban roads under climate change influenced rainfall characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Šoštarić, A.; Stojić, A.; Stojić, S.S.; Gržetić, I. Quantification and mechanisms of BTEX distribution between aqueous and gaseous phase in a dynamic system. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-Z.; Feng, T.-Z.; Sree, U.; Chiu, K.-H.; Lo, J.-G. Sampling and analysis of volatile organics emitted from wastewater treatment plant and drain system of an industrial science park. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 576, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Mao, W.-M.; Nadim, F. Forensic investigation of BTEX contamination in the Houjing River in Southern Taiwan. J. Environ. Eng. Manag. 2007, 17, 395–402. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances, Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances, and Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Biocidal Products on the Market; European Commission Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2003; p. 20418. [Google Scholar]
- Mattice, J.; Tsai, S.; Burch, M.; Beauchamp, J. Toxicity of trihalomethanes to common carp embryos. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1981, 110, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, G.A. Acute toxicity of priority pollutants to water flea (Daphnia magna). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1980, 24, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.A.; Birge, W.J.; Westerman, A.G.; Francis, P.C. Comparative aquatic toxicology of aromatic hydrocarbons. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1983, 3, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, J.; Rausina, G.; Cruzan, G.; Gilbert, J.; Williams, E.; Harrass, M.; Sousa, J.; Putt, A.; Garvey, N.; Laurent, J.S. Ecotoxicity hazard assessment of styrene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1997, 37, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Benoit, D.; Brooke, L.; Call, D.; Carlson, A. Aquatic Toxicity Tests to Characterize the Hazard of Volatile Organic Chemicals in Water: A Toxicity Data Summary. Parts 1 and 2; NTIS: Springfield, VA, USA, 1984.
- Black, J.A.; Birge, W.J.; McDonnell, W.E.; Westerman, A.G.; Ramey, B.A.; Bruser, D.M. The Aquatic Toxicity of Organic Compounds to Embryo-Larval Stages of Fish and Amphibians; University of Kentucky, Kentucky Water Resources Research Institute: Lexington, KY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Niederlehner, B.; Cairns, J., Jr.; Smith, E.P. Modeling Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Nonpolar Narcotic Chemicals and Mixtures toCeriodaphnia dubia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 39, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, H.C.; Liu, D.H.; Javitz, H.A. Time/toxicity relationships in short-term static, dynamic, and plug-flow bioassays. In Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Assessment: Eighth Symposium; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch, A. Chloroform in the environment: Occurrence, sources, sinks and effects. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1291–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzioch, I.; Stoll, C.; Holbach, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, B.; Norra, S.; Bi, Y.; Schramm, K.-W.; Tiehm, A. Dechlorination and organohalide-respiring bacteria dynamics in sediment samples of the Yangtze Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7046–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Seasonal and diurnal variations of atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate, peroxypropionyl nitrate, and carbon tetrachloride in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, M.; Shendi, M.R.A.; Ghaffari, H.R.; Aval, H.E.; Ahmadi, E.; Taban, E.; Gholizadeh, A.; Aval, M.Y.; Mohammadi, A.; Azari, A. Investigation of outdoor BTEX: Concentration, variations, sources, spatial distribution, and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Gschwend, P.M.; Imboden, D.M. Environmental Organic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buchmann, B.; Stemmler, K.; Reimann, S. Regional emissions of anthropogenic halocarbons derived from continuous measurements of ambient air in Switzerland. CHIMIA 2003, 57, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, P.M.; Liang, Y.; Johnson, R.L.; Mattes, T.E. Cryogenic soil coring reveals coexistence of aerobic and anaerobic vinyl chloride degrading bacteria in a chlorinated ethene contaminated aquifer. Water Res. 2019, 157, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lohner, S.T.; Becker, D.; Mangold, K.-M.; Tiehm, A. Sequential reductive and oxidative biodegradation of chloroethenes stimulated in a coupled bioelectro-process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6491–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, M.; Frascari, D.; Zannoni, D.; Fedi, S. Microbial degradation of chloroform. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1395–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballschmiter, K. Transport and fate of organic compounds in the global environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1992, 31, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Huang, D.; Gu, D.; Lu, S.; Chang, C.; Wang, J. Estimate of anthropogenic halocarbon emission based on measured ratio relative to CO in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5011–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, H.; Jing, S.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, L.; Song, W.; Kan, H. VOC characteristics and inhalation health risks in newly renovated residences in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, S.J. A National Survey of Methyl Tert-Butyl Ether and Other Volatile Organic Compounds in Drinking-Water Sources: Results of the Randon [ie Random] Survey; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Chan, C.C.; Mundle, S.O.; Eckert, T.; Liang, X.; Tang, S.; Lacrampe-Couloume, G.; Edwards, E.A.; Sherwood Lollar, B. Large carbon isotope fractionation during biodegradation of chloroform by Dehalobacter cultures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10154–10160. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, P.P.; Yu, H. Photomutagenicity of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the US EPA priority pollutant list. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. 2004, 557, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalil, M.; Moore, R.; Harper, D.; Lobert, J.; Erickson, D.; Koropalov, V.; Sturges, W.; Keene, W. Natural emissions of chlorine-containing gases: Reactive Chlorine Emissions Inventory. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 8333–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Rasmussen, R. Atmospheric chloroform. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, W.; Frank, H. Concentrations of airborne C1-and C2-halocarbons in forest areas in West Germany: Results of three campaigns in 1986, 1987 and 1988. Atmos. Environ. A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidorov, V.; Prilepsky, E.; Povarov, V. Photochemically and optically active components of minerals and gas emissions of mining plants. J. Ecol. Chem. 1993, 1, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, B.; Wang, J.-Z.; Guan, Y.-F.; Zeng, E.Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in upstream riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, China: An assessment of regional input sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 167, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Hu, P.; Tan, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Spatial-temporal distributions, sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface water and suspended particular matter from the upper reach of Huaihe River, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gaya, B.; Martínez-Varela, A.; Vila-Costa, M.; Casal, P.; Cerro-Gálvez, E.; Berrojalbiz, N.; Lundin, D.; Vidal, M.; Mompeán, C.; Bode, A. Biodegradation as an important sink of aromatic hydrocarbons in the oceans. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belpaire, C.; Goemans, G. Eels: Contaminant cocktails pinpointing environmental contamination. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salahova, S.; Topchiyeva, S.A.; Alakbarov, I.K.; Ramazanov, M. Influences of chemical pollutants to the biota of the Caspian Sea. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 60, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-W.; Chen, L.-H.; Yet-Pole, I.; Lai, C.-Y. Microbial communities and biodegradation in lab-scale BTEX-contaminated groundwater remediation using an oxygen-releasing reactive barrier. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjani, S.J. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, H.; Lim, J.M.; Lee, S.W.; Jang, J.S.; Park, Y.J.; Seralathan, K.K.; Oh, B.T. Enhanced visible light photocatalysis with E-waste-based V2O5/zinc–ferrite: BTEX degradation and mechanism. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2842–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Eberlein, L.; Langford, C.H. Pathways of phenol and benzene photooxidation using TiO2 supported on a zeolite. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2002, 148, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, A.; Iordache, M.; Sandru, C.; Voica, C.; Stegarus, D.; Zgavarogea, R.; Ionete, R.E.; Cotorcea, S.; Miriciorp, M.G. A Fugacity Based Model for the Assessment of Pollutant Dynamic Evolution of VOCS and BTEX in the Olt River Basin (Romania). Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, B., Jr. Delineating and quantifying ground water discharge zones using streambed temperatures. Groundwater 2004, 42, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, P.A.; Mackay, R.; Rivett, M.O. Quantifying urban river–aquifer fluid exchange processes: A multi-scale problem. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2007, 91, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, P.A.; Rivett, M.O. Assessing the impact of VOC-contaminated groundwater on surface water at the city scale. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2007, 91, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaSage, D.M.; Fryar, A.E.; Mukherjee, A.; Sturchio, N.C.; Heraty, L.J. Groundwater-derived contaminant fluxes along a channelized Coastal Plain stream. J. Hydrol. 2008, 360, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbun, R. Transport, behavior, and fate of volatile organic compounds in streams. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 30, 129–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Fryar, A.E.; LaSage, D.M. Using tracer tests to assess natural attenuation of contaminants along a channelized Coastal Plain stream. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2005, 11, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamonts, K. Structure and Pollutant-Degrading Activity of the Microbial Community in Eutrophic River Sediments Impacted by Discharging Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbonpolluted Groundwater. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Catholic University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, T.K.; Hamonts, K.; Dijk, J.A.; Kalka, H.; Stichler, W.; Springael, D.; Dejonghe, W.; Meckenstock, R.U. Assessment of the intrinsic bioremediation capacity of an eutrophic river sediment polluted by discharging chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons: A compound-specific isotope approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5263–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, N.; Cuadras, A.; Rovira, E.; Borrull, F.; Marcé, R.M. Chronic risk assessment of exposure to volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere near the largest Mediterranean industrial site. Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sui, Q.; Lyu, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Zhao, W.; Wang, B.; Xu, D.; Kong, M.; Zhang, Y. Tracking emission sources of PAHs in a region with pollution-intensive industries, Taihu Basin: From potential pollution sources to surface water. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, S.; Mingazzini, M.; Vigano, L.; Cesareo, D.; Tosato, M. Approaches to modeling toxic responses of aquatic organisms to aromatic hydrocarbons. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1988, 16, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, R.; Pattard, M.; Pernak, K.-D.; Winter, A. Results of the harmful effects of water pollutants to Daphnia magna in the 21 day reproduction test. Water Res. 1989, 23, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, S.; Tosato, M.L.; Norberg-King, T.J.; Hammermeister, D.E.; Hoglund, M.D. Lethal and sublethal toxicity of benzene derivatives to the fathead minnow, using a short-term test. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1992, 11, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, M.; Takagi, M.; Walterfang, M.; Lubman, D.I. Toluene misuse and long-term harms: A systematic review of the neuropsychological and neuroimaging literature. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classification | Retention Time (min) | Quantification Ion (m/z) | MDL (µg/L) | LOQ (µg/L) | Recovery (%) | Precision (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,1-Dichloroethylene (1,1-DCE) | 8.27 | 60.7 | 0.006 | 0.020 | 94 1, 105 2 | 4.2 1, 2.8 2 |
| 1,1,1-Trichloroethane (1,1,1-TCA) | 13.01 | 96.8 | 0.011 | 0.036 | 108, 89 | 6.7, 2.9 |
| Bromoform | 22.93 | 172.6 | 0.010 | 0.031 | 105, 92 | 5.9, 1.1 |
| Chloroform | 12.68 | 82.7 | 0.012 | 0.038 | 118, 96 | 6.4, 1.3 |
| Naphthalene | 30.93 | 127.8 | 0.007 | 0.024 | 106, 104 | 4.5, 1.9 |
| Styrene | 22.36 | 103.9 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 100, 99 | 3.1, 1.4 |
| Tetrachloroethylene (PCE) | 18.90 | 165.7 | 0.010 | 0.030 | 97, 94 | 6.3, 2.3 |
| Toluene | 17.75 | 90.9 | 0.009 | 0.030 | 105, 98 | 5.7, 1.4 |
| Trichloroethylene (TCE) | 15.05 | 94.8 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 101, 101 | 3.2, 1.9 |
| Vinyl chloride | 5.21 | 62.0 | 0.009 | 0.029 | 100, 90 | 5.8, 2.4 |
| m,p-Xylene | 21.36 | 90.9 | 0.007 | 0.021 | 103, 98 | 4.0, 0.9 |
| o-Xylene | 22.32 | 90.9 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 102, 97 | 3.1, 1.4 |
| Classification | Species | Effect | Parameter | Conc. (mg/L) | Test Duration (Days) | Ref. | AF | PNEC * (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bromoform | Cyprinus carpio | Mortality | LC50 | 52 | NR 1 | [34] | 100 | 520 |
| Chloroform | Daphnia magna | Mortality | NOEC | 1.8 | 21 | [35] | 50 | 36 |
| Naphthalene | Oncorhynchus mykiss | Mortality | LC50 | 0.11 | 27 | [36] | 1000 | 0.110 |
| Styrene | Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata | Population | NOEC | 0.063 | 4 | [37] | 1000 | 0.063 |
| PCE | Pimephales promelas | Growth | NOEC | 0.5 | 32 | [38] | 50 | 10 |
| Toluene | Oncorhynchus mykiss | Mortality | LC10 | 0.0029 | 27 | [39] | 50 | 0.058 |
| TCE | Ceriodaphnia dubia | Reproduction | NOEL | 7.26 | 7 | [40] | 50 | 145 |
| Xylenes | Lepomis macrochirus | Mortality | LC50 | 10.4 | 1 | [41] | 1000 | 10.4 |
| Classification | Mean Conc. ± Std (µg L−1) | Min Conc. (µg L−1) | Max Conc. (µg L−1) | Total Conc. (µg L−1) | Frequency Detected (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,1-DCE | NA | NA | NA | NA 1 | NA |
| 1,1,1-TCA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Bromoform | 0.0036 ± 0.0076 | 0.0000 | 0.0210 | 0.1310 | 19.4 |
| Chloroform | 0.0596 ± 0.1312 | 0.0000 | 0.5940 | 2.1450 | 47.2 |
| Naphthalene | 0.0004 ± 0.0025 | 0.0000 | 0.0150 | 0.0150 | 2.8 |
| Styrene | 0.0033 ± 0.0095 | 0.0000 | 0.0340 | 0.1180 | 11.1 |
| PCE | 0.0049 ± 0.0203 | 0.0000 | 0.115 | 0.1780 | 8.3 |
| Toluene | 0.0054 ± 0.0139 | 0.0000 | 0.0670 | 0.1960 | 19.4 |
| TCE | 0.0253 ± 0.0781 | 0.0000 | 0.4150 | 0.9110 | 27.8 |
| Vinyl chloride | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Xylenes | 0.0027 ± 0.0072 | 0.0000 | 0.0300 | 0.1940 | 15.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Im, J.-K.; Cho, Y.-C.; Noh, H.-R.; Yu, S.-J. Geographical Distribution and Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Tributaries of the Han River Watershed. Agronomy 2021, 11, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050956
Im J-K, Cho Y-C, Noh H-R, Yu S-J. Geographical Distribution and Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Tributaries of the Han River Watershed. Agronomy. 2021; 11(5):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050956
Chicago/Turabian StyleIm, Jong-Kwon, Yong-Chul Cho, Hye-Ran Noh, and Soon-Ju Yu. 2021. "Geographical Distribution and Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Tributaries of the Han River Watershed" Agronomy 11, no. 5: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050956
APA StyleIm, J. -K., Cho, Y. -C., Noh, H. -R., & Yu, S. -J. (2021). Geographical Distribution and Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Tributaries of the Han River Watershed. Agronomy, 11(5), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050956






