Abstract
Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) is widely distributed in temperate zones across the world. Since its introduction to USA in the late 19th century, this species has been hybridized with up to 15 different diploid Prunus species. This high level of introgression has resulted in a wide range of traits and agronomic behaviors among currently grown cultivars. In this work, 161 Japanese plum-type accessions were genotyped using a set of eight Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) markers to assess the current genetic diversity and population structure. A total of 104 alleles were detected, with an average of 13 alleles per locus. The overall Polymorphic Informative Content (PIC) value of SSR markers was 0.75, which indicates that these SSR markers are highly polymorphic. The Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic (UPGMA) dendrogram and the seven groups inferred by Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components (DAPC) revealed a strong correlation of the population structure to the parentage background of the accessions, supported by a moderate but highly significant genetic differentiation. The results reported herein provide useful information for breeders and for the preservation of germplasm resources.
1. Introduction
Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) belongs to the Prunus genus in the Rosaceae family [1], which includes around 430 species [2]. This crop was originated approximately in 300 B.C. in the Yangtze River basin in China, where wild populations can be currently found [3,4]. Japanese plum was introduced to Japan from China more than 2000 years ago [5]. In the late 19th century, it was introduced to California (USA) from Japan, so it was called “Japanese plum” [2,6]. Now, this crop is widely distributed in temperate zones across the world [4].
In California, Luther Burbank started Japanese plum modern breeding by intercrossing P. salicina with Prunus simonii Carr. and other native American diploid plums in order to improve its adaptation to local conditions [7]. A number of cultivars were released from these hybridizations, such as “Beauty”, “Burbank”, “Duarte”, “Eldorado”, “Formosa”, “Santa Rosa”, and “Wickson”, some of which are currently available and widely grown [2,5,6]. In these hybrids, P. salicina contributed to the improvement of fruit traits of size, flavor, color, and storability; P. simonii contributed to firm flesh and strong flavor; and the native American species such as Prunus americana Marsh. or Prunus besseyi Bailey contributed to disease resistance, tough skin, and aromatic quality [8]. In the southern United States, some of these cultivars were hybridized with the local Prunus angustifolia Marsh., obtaining cultivars such as “Bruce” and “Six Weeks”. Later, breeding programs in the Southern Hemisphere used Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. as the parent to create early and cold-hardy hybrids, such as “Methley” in South Africa or “Wilson” in Australia [9].
At present, an important renewal of plant material is underway due to the introduction of a number of new Japanese plum-type cultivars from different breeding programs across the world. These efforts share goals such as productivity, fruit size and quality, extension of the harvest season, and adaptation to growing areas [6,10]. As result of breeding activity, the Community Plant Variety Office of the European Union (CPVO) registered 149 new Japanese plum cultivars from 1995 to 2020 [11]. The term “Japanese plum” now includes a heterogeneous group of interspecific hybrids [6] and few cultivars currently grown are pure P. salicina. The high variability generated by the interspecific crosses of P. salicina with up to 15 other Prunus species is reflected in the different behavior observed in the modern commercial cultivars [12,13,14,15,16].
The use of molecular markers for studies of diversity and population genetics on fruit tree species is steadily increasing [6] because they can be linked to specific alleles [17]. Genetic diversity can be analyzed using a wide array of molecular markers, such as Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs), Randomly Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPDs), Amplification Fragment Length Polymorphisms (AFLPs), Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) [6], and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) [18,19]. During the past 20 years, SSR markers have emerged as a powerful tool for this type of study because they are highly informative, polymorphic, and codominant, and present transferability among close species [20,21].
Initial work with SSR markers in pome and stone fruits was carried out on the identification and the establishment of genetic relationships of apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) genotypes [22,23,24,25]. The first SSR markers in Prunus species were developed in peach [Prunus persica (L) Batsch], verifying their transferability to other Prunus species [26]. Currently, most SSR markers available derive from cherry [27,28,29,30] and peach [26,31,32,33], although a small number have been developed in apricot [34] and Japanese plum [35]. They have been used to analyze the genetic diversity and to improve the management of plant genetic resources in almond [36,37,38,39], apricot [40,41], European plum [42,43], peach [44], and sweet cherry [45,46,47].
The significant variability observed in Japanese plum cultivars led to early diversity studies to estimate genetic relationships using isoenzymes [48], RAPDs [49,50], and SSR developed in Japanese plum [35] and other Prunus species [46,51,52,53,54,55]. However, the genetic diversity of the cultivars currently grown globally is unknown, because the previous studies were mainly focused on traditional cultivars. This study aims to determine: (i) the current genetic diversity, (ii) genetic relationships among cultivars, and (iii) population structure of a set of 161 Japanese plum-type accessions released from breeding programs from Israel, South Africa, Spain, and the United States.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
A total of 161 Japanese plum-type accessions, comprising traditional and modern commercial cultivars, advanced selections, and six reference genotypes of P. salicina, P. cerasifera and P. simonii from 27 breeding programs were evaluated. The plant material was obtained from different germplasm collections: the Centro de Investigaciones Científicas y Tecnológicas de Extremadura (CICYTEX-La Orden) located in Badajoz (42 accessions); the Centro de Investigación y Tecnología Agroalimentaria de Aragón (CITA) located in Zaragoza (74 accessions); the Asociación de Fruticultores de la Comarca de Caspe (AFRUCCAS) located in Caspe, Zaragoza (2 accessions); and the Viveros Mariano Soria located in La Almunia de Doña Godina, Zaragoza (43 accessions) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Japanese plum-type accessions analyzed in this study.
2.2. DNA Extraction and SSR Analysis
Young leaf samples were collected in spring and preserved in silica gel [56]. The dried leaves were ground on a TissueLysser (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) prior to the DNA extraction. Genomic DNA was extracted following the protocol described by Hormaza [40] and using a Speedtools Plant DNA Extraction Kit (Biotools, Madrid, Spain) according to the manufacturer’s instructions [13,57,58]. Quantity and quality of DNA was assessed using a microvolume spectrophotometer NanoDrop 1000 (ThermoScientific, Delaware, USA) and diluted at 10 ng/μL prior to PCR amplification [13].
A total of 13 SSR markers developed in Japanese plum, peach, and sweet cherry were used (Table 2). The DNA fragments were amplified using six sets of multiplex PCR reactions (M01 to M06). Each multiplex reaction was designed by combining the expected molecular size (pb) of the fragments amplified by each SSR primer pair and four fluorescent dyes (PET, 6-FAM, VIC, NED). Multiplex PCRs M01-M04 were performed in a final volume of 12.5 µL, and M05 and M06 in a final volume of 11.5 µL. A Qiagen Multiplex PCR Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) was used for all reactions according to the manufacturer’s instructions, with different concentrations for each SSR marker (Table 2) and 10 ng of genomic DNA. The temperature profile used in M01 to M04 had an initial step of 15 min at 95 °C, 35 cycles of 45 s at 95 °C, 45 s at 57 °C, and 2 min at 72 °C, and a final step of 30 min at 72 °C [31]. M05 and M06 were performed using the same conditions with modifications at the annealing temperature of 46 and 62 °C, respectively [35]. All PCR reactions were carried out using a SimplyAmp Thermal Cycler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). PCR products were separated by capillary electrophoresis using a genetic analyzer ABI3730 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The amplified fragments were sized and scored with a size standard GeneScan 500LIZ (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) [57] on “Fragman” v. 1.0.9 [59], an R package [60] for fragment analysis and revised with the software PeakScanner v. 1.0 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The genetic profiles were organized in a table in csv format for the subsequent analysis.

Table 2.
Multiplex (Mp) design, SSR loci, linkage group (LG), fluorescent dyes, primer concentration (PC), PCR details, and characteristics of the 13 SSR markers analyzed in this study.
2.3. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Genetic Relationships among Accessions
The analysis of genetic diversity and genetic relationships were performed using R software v. 3.6.0 (R Development Core and Team, 2020). For the genetic diversity and population structure analysis, the data of alleles generated by the SSR markers were converted to an object of the class genind using the “df2genind” function of the “adegenet” package v. 2.1.2 [62].
Number of alleles per locus (NA), private alleles (PA), Polymorphism Information Content (PIC), allelic richness (AR), observed heterozygosity (Ho), expected heterozygosity (He), and the F-statistics (FIS and FST) were determined on the whole population and on each predetermined group using the packages: “adegenet” v. 2.1.2 [62]; “hierfstat” v. 0.5-7 [63]; “pegas” v. 0.13 [64]; and “PopGenReport” v. 3.0.4 [65]. The correlation matrix of the pairwise FST values was plotted with the package “corrplot” v. 0.90 [66].
A R script was developed to detect synonymies and homonymies in the data. Synonymies were identified by comparison of the allele data using the “duplicated” function to detect identical genetic profiles considered as synonymies. All accession names were also compared by the “duplicated” function to detect homonymies.
The genetic relationships among accessions were determined using an Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic averages (UPGMA) cluster analysis according to Nei and Li [67]. The “poppr” package v. 2.8.5 was used to generate an UPGMA dendrogram with a “bootstrap” supported by 1000 replicates [68]. The genetic structure was also analyzed using the “adegenet” package v. 2.1.2. [61] by a Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components (DAPC). The optimal number of groups (K) in the whole population was inferred using the “find.clusters” function according to the lowest Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) value. A cross-validation function, “xvalDapc” [61], was used to determine the correct number of Principal Components (PCs) to be retained. An Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) was conducted using the “poppr” package v. 2.8.5 to calculate the variance components among the inferred groups and among the accessions [68].
3. Results
3.1. SSR Genotyping
Eight of the 13 SSR primers pairs (62%) showed good amplification and were selected to evaluate the genetic diversity and population structure. The remaining five (CPPCT-029, UDP96-008, UDP98-406, UDP98-409, and UDP98-412) were excluded from the analysis due to null or poor amplification (Table 2). A total of 104 alleles were amplified using eight SSR primers across 161 Japanese plum-type accessions (155 commercial cultivars and selections, and six reference cultivars). The number of alleles per locus (NA) ranged from nine (CPPCT033) to 16 (BPPCT007), with an average value of 13 and an allele size range of 93–208 pb. Polymorphism Information Content (PIC) values ranged between 0.56 (CPPCT033) and 0.84 (CPSCT005), with an average of 0.75 per locus. The lowest observed heterozygosity (Ho) was 0.45 for BPPCT039 and the highest was 0.85 for pchgms2 with a mean of 0.65 for all accessions. The values of expected heterozygosity (He) ranged from 0.51 (CPPCT033) to 0.80 (CPSCT005), with an average of 0.68. The F statistics showed moderate population differentiations for each locus. FIS varied from −0.13 (pchgms2) to 0.22 (BPPCT025) with a mean of 0.05, whereas FST ranged between 0.06 (CPSCT005 and UDP96005) to 0.30 for BPPCT039 with an average of 0.12 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Number of alleles and allele size range in base pairs amplified by eight polymorphic SSR in Japanese plum-type accessions. Number of alleles (NA), Polymorphism Information Content (PIC), Observed heterozygosity (Ho), Expected heterozygosity (He), Inbreeding coefficient (FIS), and Wright’s Fixation index (FST).
3.2. Genetic Relationships among Accessions
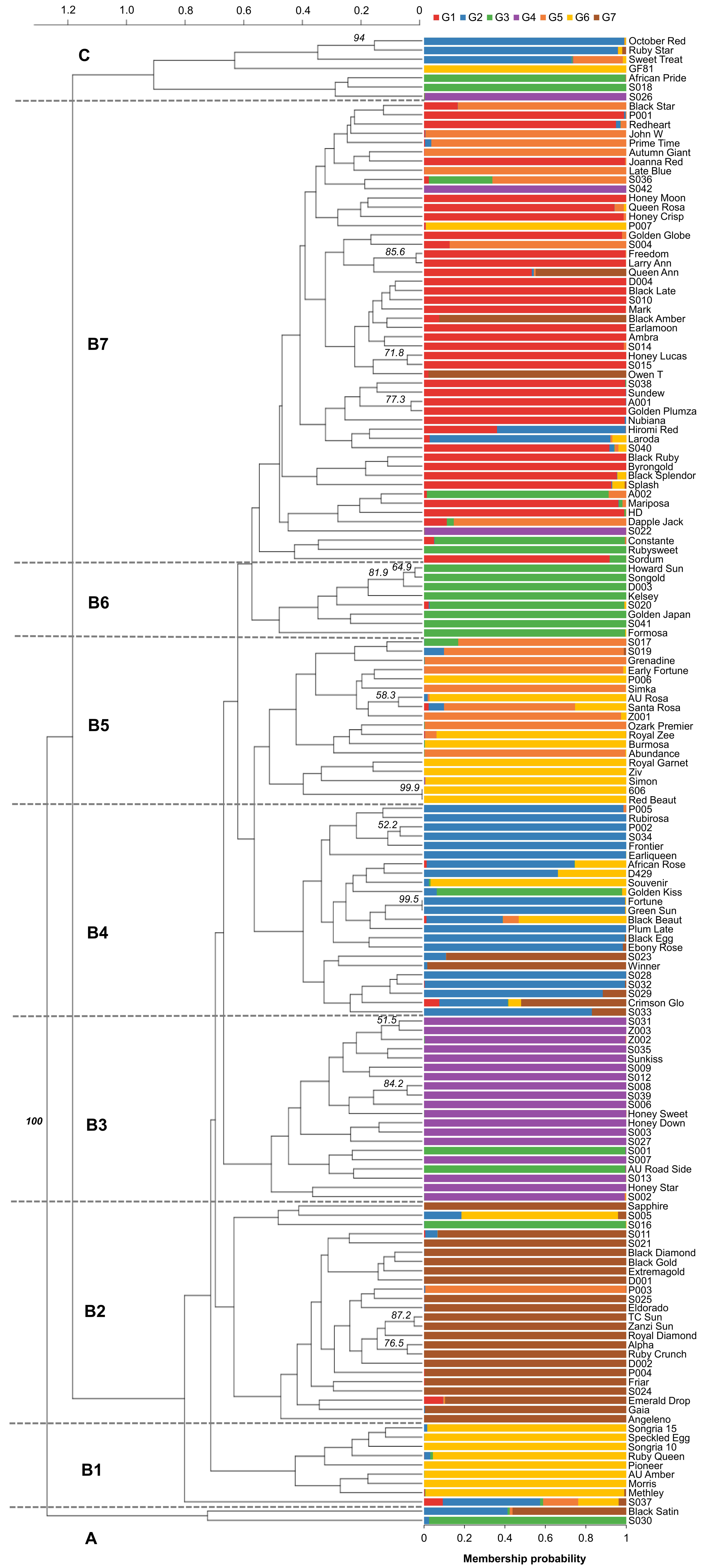
The UPGMA dendrogram grouped the accessions into two major clusters supported by a strong bootstrap value (100) (Figure 1), allowing the identification of 159 genotypes and two pairs of synonymies (“Red Beaut” and “606”, “Fortune” and “Green Sun”). The clustering of the accessions by their SSR profile was consistent with the available parentage information (Supplementary Materials, Table S1), but weak correspondence with the program breeding or geographical origin was found. According to the dendrogram, “Black Satin” and the accession “S030” clustered separately, forming the smallest cluster (A). Cluster B was the largest cluster, comprising 152 accessions distributed in seven subclusters. The subcluster B1 comprised nine accessions, some of them derived from the same pedigree as “Methley”, “Morris”, and “AU Amber”, and the remaining accessions shared a common and known South African origin, with the exception of “Speckled Egg”. The subcluster B2 comprised a set of Californian cultivars of “Eldorado” (cultivar released by Luther Burbank), “Friar”, “Angeleno”, “Black Diamond”, “Royal Diamond”, and 19 other accessions, including “Alpha” (Prunus maritima). The subcluster B3 comprised 20 accessions, most of which were commercial cultivars and early selections from South Africa, such as “Sunkiss”, “Honey Sweet”, “Honey Down”, and “Honey Star”. The subcluster B4 comprised 22 accessions, including some commercial cultivars: “African Rose”, “Black Beaut”, “Crimson Glo”, “Earliqueen”, “Golden Kiss”, and “Souvenir”. The subcluster B5 was formed by two reference genotypes [“Abundance” (P. salicina) and “Simon” (P. simonii)] and 15 other accessions, including “Burmosa” and its descendants, “Red Beaut” and “606”. The subcluster B6 comprised eight accessions, including the reference genotypes of P. salicina “Kelsey” and “Formosa”, in addition to the traditional cultivars “Golden Japan” and “Songold”. The subcluster B7 encompassed 49 accessions and the reference genotype “Mariposa” (P. salicina). Finally, the cluster C comprised seven accessions, including two accessions from USA (“October Red” and “Sweet Treat”), four accessions from South Africa (“African Pride”, “Ruby Star”, “S018”, and “S026”), and the rootstock cultivar “GF81”.
Figure 1.
Genetic relationships and genetic structure from 161 Japanese plum-type accessions by DAPC. The genetic relationships are represented by a UPGMA dendrogram created from 1000 bootstrap replications. Bootstrap values >50% are placed on the branches. The stacked bar charts represent different assigned groups with the following color codes: G1 = red, G2 = blue, G3 = green, G4 = purple, G5 = orange, G6 = yellow, and G7 = brown. The x-axis provides the probability of each accession belonging to the assigned group.
3.3. Analysis Genetic Structure
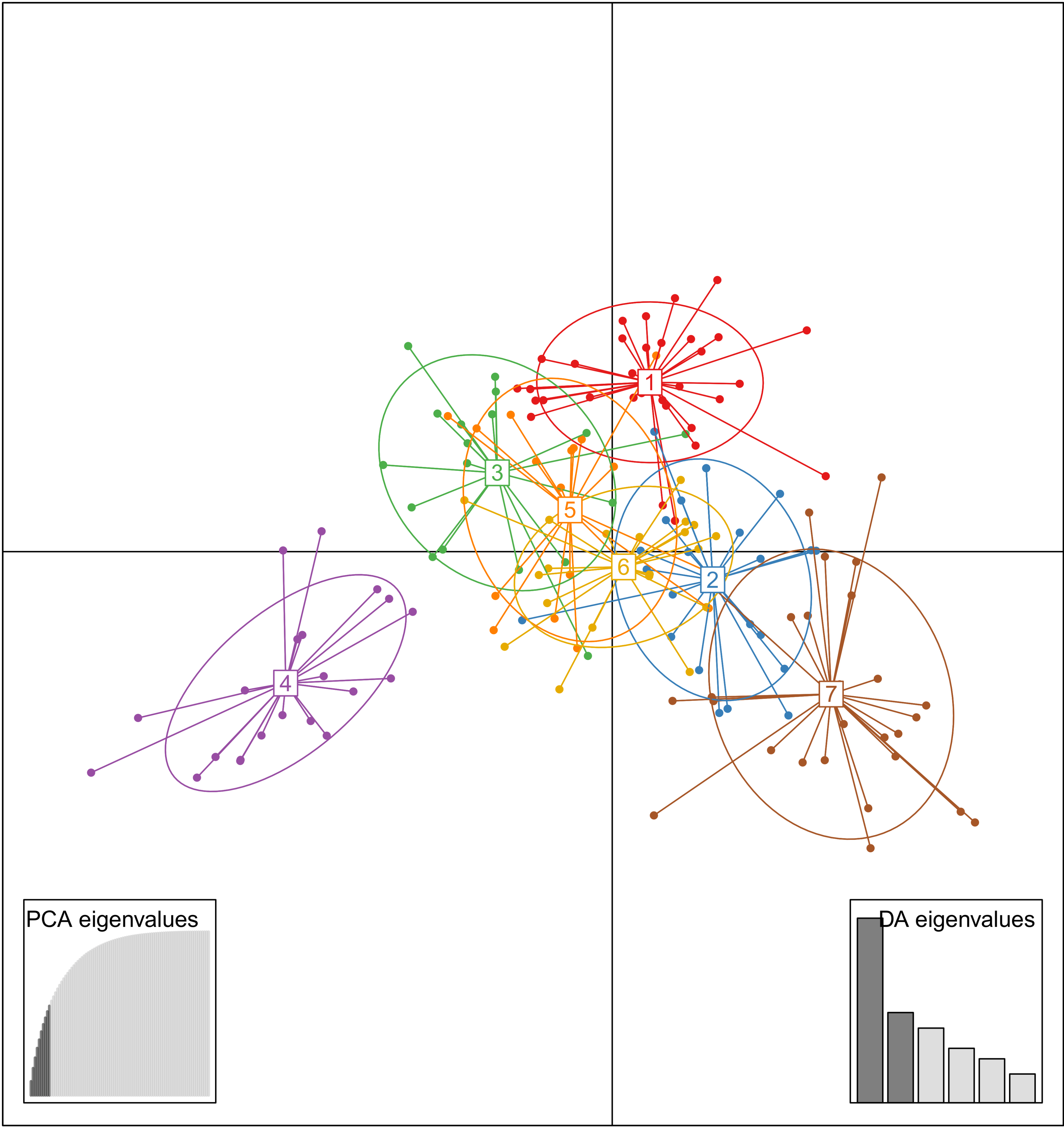
The genetic structure analyzed by DAPC showed a K = 7 value as the optimal clustering, according to the lowest BIC value. The optimal number of PCs to be retained for the subsequent analysis was 10 (Supplementary Materials, Figure S1). This scenario showed groups 1 to 3 and 5 to 7 (G1–G3 to G5–G7) overlapped, and group 4 (G4) clearly differentiated from them across the first two linear discriminant functions (LD1 and LD2) (Figure 2). The reports of the allele frequencies (loadings) in the dataset allowed determination of the contribution of alleles to the distribution of accessions in the DAPC scatterplot (Supplementary Materials, Figure S2).
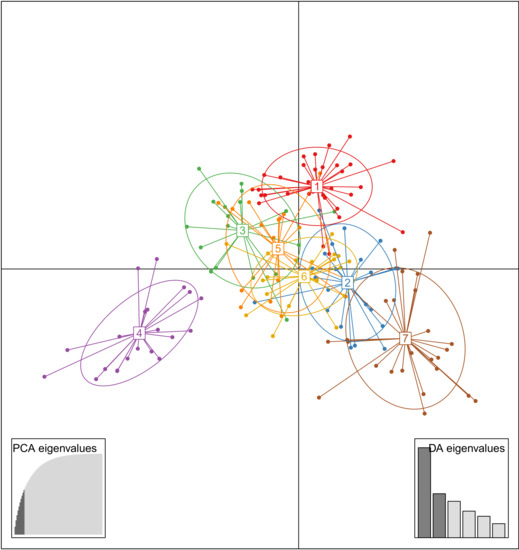
Figure 2.
Scatterplot of DAPC of population structure of 161 Japanese plum-type accessions, showing the first two principal linear discriminants of the DAPC according to the optimal K value (K = 7). Each colored circle represents a group: G1 = red, G2 = blue, G3 = green, G4 = purple, G5 = orange, G6 = yellow, and G7 = brown. Each dot represents an accession. The insets represent the eigenvalues of the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Discriminant Analysis (DA).
The DAPC analysis allowed allocation of most of the accessions to their original group according to a membership probability up to 0.9, indicating clear-cut groups. However, some accessions showed lower membership probabilities, ranging from 0.3 to 0.7, which indicate some admixtures in the structured population (Figure 1). Group G1 comprised a set of 32 accessions (19.9%), including the P. salicina reference “Mariposa” and other commercial cultivars of “Black Splendor”, “Queen Rosa”, and “Queen Ann”. Group G2 comprised 23 accessions (14.3%), mostly cultivars from California (“Hiromi Red”, “Earliqueen”, “Frontier”, and “Green Sun”, among others) and South Africa (“African Rose”, “Ruby Star”, and some advanced selections). Group G3 (n = 18, 11.2%) included the two P. salicina genotype-references “Kelsey” and “Formosa”. Group G4 comprised 21 accessions (13%), most of modern cultivars (“Honey Down”, “Honey Star”, “Honey Sweet”, and “Sunkiss”), and some advanced selections from South Africa. A group of 18 accessions (11.2%) formed the group G5, including “Abundance” (P. salicina) and traditional cultivars of “John W”, “Santa Rosa” and “Simka”. The group G6 comprised 22 accessions (13.7%), including the genotype-reference “Simon” (P. simonii) and some accessions with P. cerasifera in their pedigree (“Methley”, “Morris”, and the rootstock “GF81′). Finally, group G7 was formed by 27 accessions (16.8%) and encompassed a high diversity of origins of the traditional cultivars “Angeleno”, “Black Diamond”, “Eldorado”, “Friar”, “TC Sun”, and “Zanzi Sun”.
3.4. Genetic Diversity among Groups
Significance variance differences (p < 0.01) were found within the accessions and the AMOVA showed that 81.8% of the total variance observed in the K = 7 scenario was also due to differences within accessions, 14.2% was due to differences among groups, and the remaining 4.0% was due to differences among accessions within groups (Table 4).

Table 4.
Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) for 161 Japanese plum-type accessions clustered in seven groups.
The statistics of genetic diversity were calculated and summarized per group (K = 7) (Table 5). The number of alleles (NA) per locus ranged from 6.25 (G4) to 7.63 (G2). The total number of alleles varied from 50 (G4) to 61 (G2). The allelic richness (AR) ranged from 6.01 (G4) to 7.25 (G3). The highest number of private alleles (PA), those present in only one group, was 10 (G2), and only one was observed in G5. Among the groups, the lowest Ho was determined in G1 (0.59), and the highest was observed in G3 and G7 (0.69). The lowest He was recorded in G1 (0.63), and the highest in G3 (0.73). All groups had Inbreeding Coefficient values (FIS) close to zero, ranging from −0.01 (G7) to 0.15 (G6), showing no excess of homo- or hetero-zygotes.

Table 5.
Statistics of genetic variation for 161 Japanese plum-type accessions clustered in seven groups. Number of accessions (n), Number of alleles (NA), Number of private alleles (PA), Allelic richness (AR), Observed heterozygosity (Ho), Expected heterozygosity (He), Inbreeding coefficient (FIS).
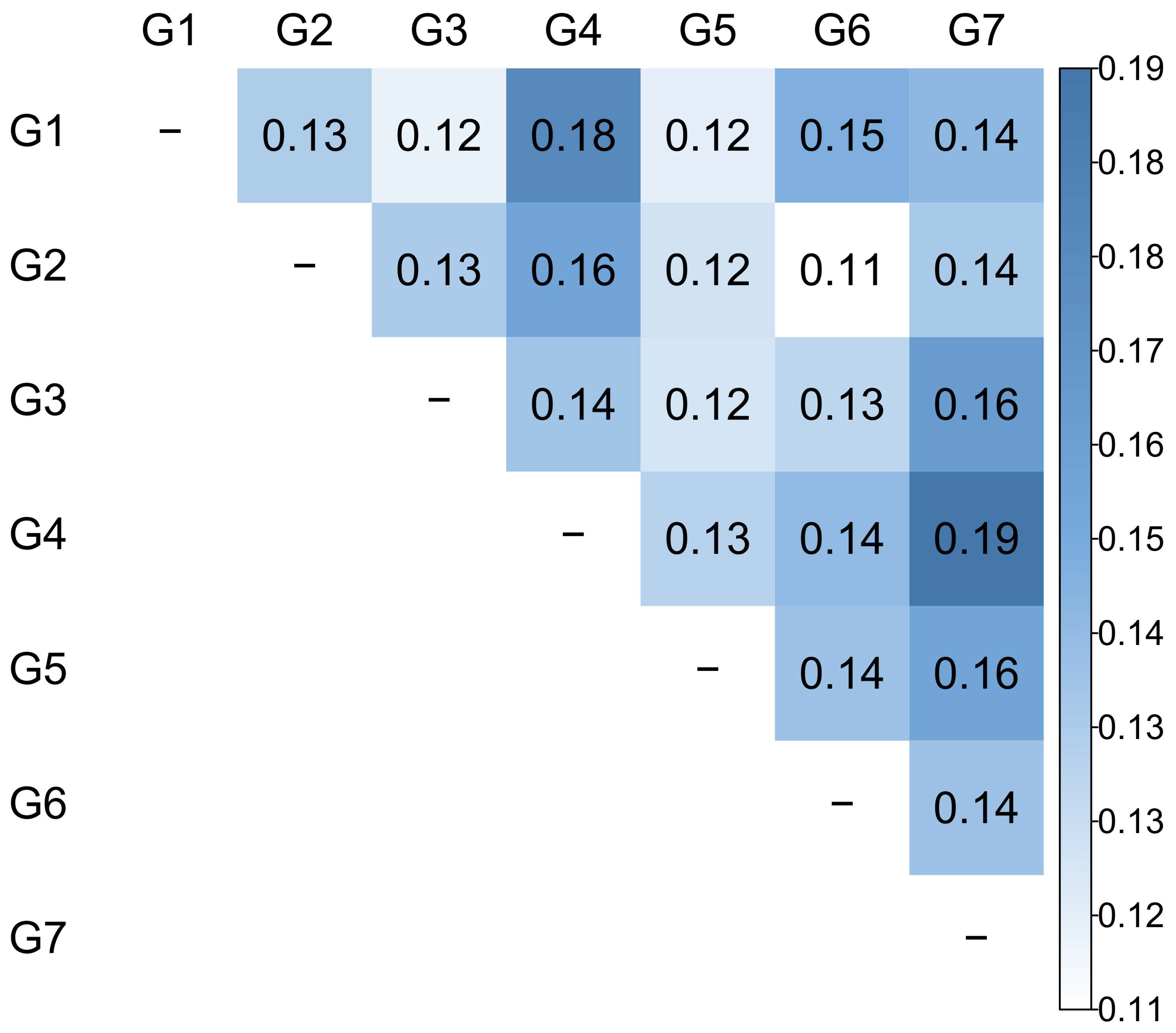
To validate the genetic differentiation among the seven groups, the FST values based on Nei’s genetic distance among groups were determined (Figure 3). The overall pairwise FST values of 0.14 suggested a moderate differentiation between groups and varied from 0.11 (between G2 and G6) to 0.19 (between G4 and G7). Most of the groups with paired G4 exhibited higher FST values than the other pairs. All of these comparisons had non-zero lower and upper 99% confidence intervals (Supplementary Materials, Table S2).
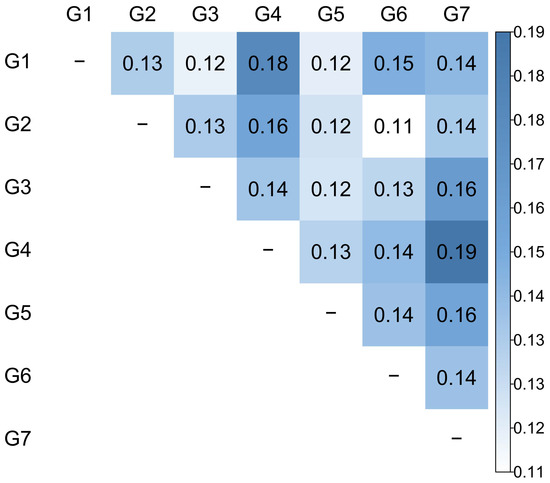
Figure 3.
Weighted pairwise FST values estimated from the seven inferred groups (K = 7).
4. Discussion
The analysis of the genetic relationships and the genetic diversity in the germplasm analyzed, including 155 accessions and six Japanese plum-type reference-genotypes, by SSR markers, showed the correct amplification in eight of the 13 SSR markers used in this study, which were previously developed in Japanese plum [35], peach [26,30,31,61], and sweet cherry [26]. Although extrapolation of the results generated by this approach is complex due to the differences in the number of accessions and SSR markers used in the different studies [69], this approach has proven to be highly useful for cultivar identification because SSR are multi-allelic, codominant markers and most of them are transferable within Prunus species [31].
A total of 104 alleles were amplified by the set of SSR markers, emphasizing their high degree of polymorphism. Similar results were found in a previous study analyzing 47 accessions of Japanese plum using eight SSR markers (NA TOTAL = 104, average of NA PER LOCUS = 13) [51]. The PIC values for all loci found in this study were higher than 0.5, and therefore they were considered highly informative [70].
The observed heterozygosity found in this study was higher than that determined in previous reports in apricot (Ho = 0.51, 48 accessions, 31 SSR markers [40]), sweet cherry (Ho = 0.49, 76 accessions, 24 SSR markers [47]), and peach (Ho = 0.47, 50 accessions, 26 SSR markers [33]; Ho = 0.45, 28 accessions, 10 SSR markers [30]). This higher heterozygosity can be explained by the high number of accessions used in this study, and also by the high degree of introgression of the analyzed accessions, which mostly derived from interspecific crosses between the original species of P. salicina with up to 15 other Prunus species [12].
Genotypes were considered to be duplicated (synonymies) when they were paired on all alleles of the whole set of SSR markers. Two pairs of duplicates were found based on the SSR profile. “Red Beaut” showed 100% of similarity with “606” as expected, because “606” is a selection of cv. “Red Beaut” [15]. The other pair of duplicates was “Fortune” with “Green Sun”, although both cultivars are well known and have different phenotypic characteristics [9]. Further research with samples of the same cultivars from other collections or additional SSR markers would be needed to distinguish them.
The UPGMA dendrogram arrangement indicated a stronger correlation with the parentage background (progenitors) of the accessions than their geographical or breeding program origin. The reference genotypes were allocated across the dendrogram, showing an introgression degree correlation. Two clusters (A and C) displayed a highly degree of admixture. The other cluster (B) was larger and divided into seven subclusters (B1 to B7). In subcluster B1, “Methley”, “Morris”, and “AU Amber” were allocated together, confirming their parentage with P. cerasifera [9]. In subcluster B2, several cultivars were closely related according to their pedigree, such as “Black Diamond” (“Angeleno” × OP), “Angeleno” (“Eldorado” × “Queen Ann”) [55], and “Eldorado” (hybrid P. salicina × P. simonii, [71]). The presence of “Royal Diamond” in this subcluster indicates its possible parentage with “Angeleno”, as has been previously suggested [9]. The closeness between “Alpha”, a cultivar selected from wild trees of P. maritima Kerr. [72], and “Ruby Crunch” suggests possible common ancestry. The subcluster B3 was formed mostly by cultivars and selections from South Africa, where plum breeding represents a slightly different gene pool by the use of local cultivars as parents [9]. In B4, several cultivars with common genetic background were grouped: “African Rose”, “Souvenir”, and “Golden Kiss” from South Africa [13,73]; “Crimson Glo” and “Fortune” and their ancestors “Laroda” and “Queen Ann” [9]; “Rubirosa” and “Black Beaut” [74]. The subcluster B5 contained “Red Beaut” and its selection “606” [15] and comprised the reference genotypes “Mariposa” (P. salicina) and “Simon” (P. simonii), and their descendants “Santa Rosa” and its mutant “AU Rosa” [75]. “Red Beaut” and “Santa Rosa” were also grouped in the same subcluster in a previous report [76]. The closeness observed between “Burmosa” and “Red Beaut”, in B5, and “Formosa”, in B6, may be related to the use of “Formosa” as the parent of “Burmosa”, which is the parent of “Red Beaut” [9]. Subcluster B6 comprises “Kelsey” (P. salicina) and its descendent “Songold”, and “Howard Sun” and “Golden Japan”, both cultivars with yellow flesh fruits, like “Songold” [6]. Subcluster B7 comprises a group of cultivars with common genetic background: “Laroda”, “Black Amber”, “Black Splendor” (“Black Amber” × OP), and “Queen Rosa”, descendants of “Santa Rosa” [9]; and “Mariposa”, “Rubysweet” (“Mariposa” × “Methley”) [8], and “Byrongold”, which are closely related to “Rubysweet” due to both having P. cerasifera in their parentage [9,49].
According to the DAPC clustering, the 161 accessions were distributed in seven groups, in which the main source of the total genetic variation was attributed to variance within accessions. The percentage variation among groups was low, resulting in high similarity among these groups. Six groups were clustered together and difficult to differentiate, which may be due to the use of the same cultivars as the parents in different breeding programs, which could lead to a gene flow across the groups. Most genetic variation within groups rather than among groups has been also found in apricot accessions [41]. In almond, He values higher than Ho values, consistent with the results reported herein, have been attributed to the human selection and the exhausting breeding activity [37]. The highest values of PA were found in G2, indicating that the cultivars in this group may have potential for use for breeding purposes to avoid bottleneck effects, and to be conserved in germplasm banks to maintain diversity [77,78,79]. In this study, moderate genetic diversity (He) was found in all groups and FIS values ranged close to zero, indicating no excess of homo- or –hetero-zygotes. Similarly, FST values indicated a moderate degree of genetic differentiation [80], supporting the genetic structure obtained herein. The distribution of all accessions across the inferred seven groups corresponded with the genetic relationships observed in the UPGMA dendrogram, revealing a high correlation with the parentage background.
Further research is required to determine the optimal number of SSR markers needed for the analysis of genetic diversity and genetic structure. Although the addition of a new marker should not significantly affect the structure inferred by a sufficiently informative set of SSR [81], the optimal number of markers required to consistently infer the genetic structure in this and other fruit tree species remains unknown.
5. Conclusions
The SSR markers used herein were highly informative and revealed high genetic diversity within accessions. The entire population was structured in seven groups and confirmed the genetic relationships observed in the UPGMA dendrogram. Although a higher number of accessions were analyzed herein, the genetic diversity was similar to that of previous studies [46,51,53,54,55]. This may be due to the high number of modern cultivars and advanced selections of breeding programs analyzed, which reveal a bottleneck effect caused by the breeding system practices. The establishment of genetic relationships in Japanese plum-type accessions is highly complex due to their interspecific origin, but can be supported by the knowledge of the parentage lines in commercial cultivars. However, the genealogy of some of the ancestors widely used in most breeding programs is not available [5]. The use of chloroplast markers (cpDNA), and the application of next-generation sequencing technologies (NGS) and high-density SNP-based genotyping [19,76], may lead to additional insight into the degree of diversity among Japanese plum hybrids and the reconstruction of the genealogy of each cultivar.
The conservation of the native Prunus germplasm used in early plum breeding may help to maintain and improve the genetic diversity in Japanese plum-type cultivars. Unfortunately, only a few selections of this material are currently available for breeders [8]. The knowledge of the genetic diversity among Japanese plum-type accessions can enable more informed decisions by breeders for the selection of parents, to maintain biodiversity through germplasm conservation, and to find genotype–phenotype association patterns to be applied by producers and genetic research.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy11091748/s1, Figure S1: Clustering and DAPC Cross-validation. (a) Inference of the optimal number of clusters in the 161 Japanese plum-type accessions and (b) DAPC cross-validation for the optimal number of Principal Components (PCs) retained for the analysis in the seven predefined groups. Figure S2: Loading plots for the alleles contributions to the (a) Linear Discriminant Function 1 (LD1) and (b) Linear Discriminant Function 2 (LD2) of the DAPC when K = 7. Each plot computes the most informative and contributing alleles to the discriminant analysis. Table S1. Genealogical information of the analyzed accessions in which it is available. Table S2. Lower limit (below the diagonal) and upper limit (above the diagonal) of the 99% confidence interval based on 1000 bootstrap replicates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E.G., A.P. and J.R.; Data curation, B.I.G., S.H. and P.I.; Methodology, B.I.G. and P.I.; Writing—original draft, B.I.G., M.E.G., A.P. and J.R.; Writing—review & editing, B.I.G., M.E.G., S.H., P.I., A.P. and J.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Tecnología Agraria y Alimentaria (RTA2017-00003-00); Agencia Estatal de Investigación (PID2020-115473RR-I00/AEI 436/10.13039/501100011033); Gobierno de Aragón—European Social Fund, European Union (Grupo Consolidado A12_17R), and Junta de Extremadura—Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER), Plan Regional de Investigación (IB16181), Grupo de Investigación (AGA001, GR18196). B.I. Guerrero was supported by a fellowship of Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología of México (CONACYT, 471839).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Rehder, A. Manual of Cultivated Trees and Shrubs Hardy in North America: Exclusive of the Subtropical and Warmer Temperate Regions, 2nd ed.; MacMillan: New York, NY, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Faust, M.; Surányi, D. Origin and dissemination of plums. In Origin and Dissemination of Prunus Crops: Peach, Cherry, Apricot, Plum and Almond; Janick, J., Ed.; Horticultural Reviews: Gent-Oostakker, Belgium, 2011; pp. 139–186. ISBN 978-90-6605-436-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, M. The origin of fruits. 2: Plums. Fruit Japan 1987, 42, 49–53. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Okie, W.R.; Weinberger, J.H. Plums. In Fruit Breeding. Volume 1: Tree and Tropical Fruits; Janick, J., Moore, J.N., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 559–608. [Google Scholar]
- Milošević, T.; Milošević, N. Plum (Prunus spp.) breeding. In Advances in Plant Breeding Strategies: Fruits; Al-Khayri, J., Jain, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 165–215. ISBN 9783319919447. [Google Scholar]
- Topp, B.L.; Russell, D.M.; Neumüller, M.; Dalbó, M.A.; Liu, W. Plum. In Fruit Breeding; Badenes, M.L., Byrne, D.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 571–621. ISBN 978-1-4419-0763-9. [Google Scholar]
- Burbank, L. Luther Burbank: His Methods and Discoveries and Their Practical Application; Luther Burbank Press: New York, NY, USA, 1914; ISBN 3192400897. [Google Scholar]
- Okie, W.R. Introgression of Prunus species in plum. N. Y. Fruit Q. 2006, 14, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Okie, W.R.; Ramming, D.W. Plum breeding worldwide. Horttechnology 1999, 9, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batlle, I.; Iglesias, I.; Cantin, C.M.; Badenes, M.L.; Ríos, G.; Ruiz, D.; Dicenta, F.; Egea, J.; López-Corrales, M.; Guerra, M.E.; et al. Frutales de hueso y pepita. In Influencia del Cambio Climático en la Mejora Genética de Plantas; García-Brunton, J., Tornero, O., Cos-Terrer, J., Ruíz-García, L., Sanchez, E., Eds.; Sociedad Española de Ciencias Hortícolas: Murcia, Spain, 2018; pp. 79–132. ISBN 978-84-948233-8-1. [Google Scholar]
- Community Plant Variety Office. CPVO Annual Statistics. Available online: https://cpvo.europa.eu/ (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Guerra, M.E.; Rodrigo, J. Japanese plum pollination: A review. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 197, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.; Guerrero, B.I.; Casadomet, C.; Rodrigo, J. Self-(in)compatibility, S-RNase allele identification, and selection of pollinizers in new Japanese plum-type cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 109022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.; Wunsch, A.; López-Corrales, M.; Rodrigo, J. Flower emasculation as the cause for lack of fruit set in Japanese plum crosses. J. Amer. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 135, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.; Rodrigo, J.; López-Corrales, M.; Wünsch, A. S-RNase genotyping and incompatibility group assignment by PCR and pollination experiments in Japanese plum. Plant Breed. 2009, 128, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.; Wünsch, A.; López-Corrales, M.; Rodrigo, J. Lack of fruit set caused by ovule degeneration in Japanese plum. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2011, 136, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira-Lorenzo, S.; Ramos-Cabrer, A.M.; Fischer, M. Breeding apple (Malus × domestica Borkh). In Breeding Plantation Tree Crops: Temperate Species; Mohan, S., Priyadarshan, P.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 33–82. ISBN 978-0-387-71202-4. [Google Scholar]
- Campoy, J.A.; Lerigoleur-Balsemin, E.; Christmann, H.; Beauvieux, R.; Girollet, N.; Quero-García, J.; Dirlewanger, E.; Barreneche, T. Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium, population structure and construction of a core collection of Prunus avium L. landraces and bred cultivars. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mas-Gómez, J.; Cantín, C.M.; Moreno, M.; Prudencio, Á.S.; Gómez-Abajo, M.; Bianco, L.; Troggio, M.; Martínez-Gómez, P.; Rubio, M.; Martínez-García, P.J. Exploring genome-wide diversity in the national peach (Prunus persica) germplasm collection at CITA (Zaragoza, Spain). Agronomy 2021, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.S. SSR genotyping. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1245, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucia, M.; Vieira, C.; Santini, L.; Diniz, A.L.; Munhoz, C.D.F. Microsatellite markers: What they mean and why they are so useful. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilford, P.; Prakash, S.; Zhu, J.M.; Rikkerink, E.; Gardiner, S.; Bassett, H.; Forster, R. Microsatellites in Malus × domestica (apple): Abundance, polymorphism and cultivar identification. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 94, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokanson, S.C.; Szewc-McFadden, A.K.; Lamboy, W.F.; McFerson, J.R. Microsatellite (SSR) markers reveal genetic identities, genetic diversity and relationships in a Malus × domestica Borkh. core subset collection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Lorenzo, S.; Ramos-Cabrer, A.M.; Díaz-Hernández, M.B. Evaluation of genetic identity and variation of local apple cultivars (Malus × domestica Borkh.) from Spain using microsatellite markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2007, 54, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabe, P.R.; Baumgarten, A.; Onan, K.; Luby, J.J.; Bedford, D.S. Using microsatellite analysis to verify breeding records: A study of “Honeycrisp” and other cold-hardy apple cultivars. HortScience 2005, 40, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipriani, G.; Lot, G.; Huang, W.G.; Marrazzo, M.T.; Peterlunger, E.; Testolin, R. AC/GT and AG/CT microsatellite repeats in peach [Prunus persica (L) Batsch]: Isolation, characterisation and cross-species amplification in Prunus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 99, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantini, C.; Iezzoni, A.F.; Lamboy, W.F.; Boritzki, M.; Struss, D. DNA fingerprinting of tetraploid cherry germplasm using simple sequence repeats. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2001, 126, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, S.L.; Iezzoni, A.F. Polymorphic DNA markers in black cherry (Prunus serotina) are identified using sequences from sweet cherry, peach, and sour cherry. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 125, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Struss, D.; Ahmad, R.; Southwick, S.M.; Boritzki, M. Analysis of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars using SSR and AFLP markers. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2003, 128, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sosinski, B.; Gannavarapu, M.; Hager, L.D.; Beck, L.E.; KIng, J.J.; Ryder, C.D.; Rajapakse, S.; Baird, W.V.; Ballard, R.E.; Abbot, A.G. Characterization of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirlewanger, E.; Cosson, P.; Tavaud, M.; Aranzana, M.; Poizat, C.; Zanetto, A.; Arús, P.; Laigret, F. Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Wu, D.; Xu, C.; Chen, K. Development of high quality EST-SSR markers without stutter bands in peach and their application in cultivar discrimination and hybrid authentication. HortScience 2017, 52, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Testolin, R.; Marrazzo, T.; Cipriani, G.; Quarta, R.; Verde, I.; Dettori, M.T.; Pancaldi, M.; Sansavini, S. Microsatellite DNA in peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) and its use in fingerprinting and testing the genetic origin of cultivars. Genome 2000, 43, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, R.; Lain, O.; Marrazzo, M.T.; Cipriano, G.; Testolin, R. New set of microsatellite loci isolated in apricot. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnejja, M.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Howad, W.; Badenes, M.L.; Arús, P. Simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers of Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) are highly polymorphic and transferable to peach and almond. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, R.; Ballester, J.; Dicenta, F.; Arús, P.; Martínez-Gómez, P. Comparison of SSR polymorphisms using automated capillary sequencers, and polyacrylamide and agarose gel electrophoresis: Implications for the assessment of genetic diversity and relatedness in almond. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 108, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, J.; Kodad, O.; Galiba, G.M.; Skola, I.; Ercisli, S.; Ledbetter, C.A.; Hegedűs, A. Genetic variability is preserved among strongly differentiated and geographically diverse almond germplasm: An assessment by simple sequence repeat markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2019, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aranzana, M.; Pineda, A.; Cosson, P.; Dirlewanger, E.; Ascasibar, J.; Cipriani, G.; Ryder, C.D.; Testolin, R.; Abbot, A.; King, G.J.; et al. A set of simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers covering the Prunus genome. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnejja, M.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Audergon, J.M.; Arús, P. Prunus microsatellite marker transferability across Rosaceous crops. Tree Genet. Genomes 2010, 6, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormaza, J.I. Molecular characterization and similarity relationships among apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) genotypes using simple sequence repeats. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguiba, H.; Scotti, I.; Sauvage, C.; Zhebentyayeva, T.; Ledbetter, C.; Krška, B.; Remay, A.; D’Onofrio, C.; Iketani, H.; Christen, D.; et al. Genetic structure of a worldwide germplasm collection of Prunus armeniaca L. reveals three major diffusion routes for varieties coming from the species’ center of origin. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrestarazu, J.; Errea, P.; Miranda, C.; Santesteban, L.G.; Pina, A. Genetic diversity of Spanish Prunus domestica L. germplasm reveals a complex genetic structure underlying. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195591. [Google Scholar]
- Gharbi, O.; Wünsch, A.; Rodrigo, J. Characterization of accessions of “Reine Claude Verte” plum using Prunus SRR and phenotypic traits. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 169, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitther, V.; Zhang, D.; Dhekney, S.A.; Harris, D.L.; Yadav, A.K.; Okie, W.R. Cultivar identification, pedigree verification, diversity analysis among peach cultivars simple sequence repeat markers. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2012, 137, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wünsch, A. Cross-transferable polymorphic SSR loci in Prunus species. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 120, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öz, M.H.; Vurgun, H.; Bakir, M.; Büyük, I.; Yüksel, C.; Ünlü, H.M.; Çukadar, K.; Karadoǧan, B.; Köse, Ö.; Ergül, A. Molecular analysis of East Anatolian traditional plum and cherry accessions using SSR markers. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 5310–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünsch, A.; Hormaza, J.I. Molecular characterisation of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genotypes using peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] SSR sequences. Heredity 2002, 89, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byrne, D.H.; Littleton, T.G. Electrophoretic characterization of diploid plums of the southeastern United States. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1988, 113, 918–924. [Google Scholar]
- Boonprakob, U.; Byrne, D.H.; Graham, C.J.; Smith, B.R. Genetic relationships among cultivated diploid plums and their progenitors as determined by RAPD markers. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2001, 126, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.S.; Fang, J.G.; Cong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of genetic diversity of Japanese plum cultivars based on RAPD, ISSR and SSR markers. Acta Hortic. 2007, 763, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klabunde, G.H.F.; Dalbó, M.A.; Nodari, R.O. DNA fingerprinting of Japanese plum (Prunus salicina) cultivars based on microsatellite markers. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyawo, T.A. Fingerprinting and Molecular Characterisation of ARC’s Apricot and Plum Collection. Master’s Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, B.; Díaz, C.; Moya, M.; Gebauer, M.; García-González, R. Genetic characterization of Japanese plum cultivars (Prunus salicina) using SSR and ISSR molecular markers. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2012, 39, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, D.; Baraket, G.; Perez, V.; Ben Mustapha, S.; Salhi-Hannachi, A.; Hormaza, J.I. Analysis of self-incompatibility and genetic diversity in diploid and hexaploid plum genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Potter, D.; Southwick, S.M. Identification and characterization of plum and pluot cultivars by microsatellite markers. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 79, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, V.; Larrañaga, N.; Abdallah, D.; Wünsch, A.; Hormaza, J.I. Genetic diversity of local peach (Prunus persica) accessions from La Palma Island (Canary Islands, Spain). Agronomy 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerra, M.E.; López-Corrales, M.; Wünsch, A. Improved S-genotyping and new incompatibility groups in Japanese plum. Euphytica 2012, 186, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, B.I.; Guerra, M.E.; Rodrigo, J. Establishing pollination requirements in Japanese plum by phenological monitoring, hand pollinations, fluorescence microscopy and molecular genotyping. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias-Pazaran, G.; Diaz-Garcia, L.; Schlautman, B.; Salazar, W.; Zalapa, J. Fragman: An R package for fragment analysis. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2020. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Aranzana, M.J.; García-Mas, J.; Carbó, J.; Arús, P. Development and variability analysis of microsatellite markers in peach. Plant Breed. 2002, 121, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T. Adegenet: A R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goudet, J. Hierfstat, a package for R to compute and test hierarchical F-statistics. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paradis, E. Pegas: An R package for population genetics with an integrated-modular approach. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamack, A.; Gruber, B. PopGenReport: Simplifying basic population genetic analyses in R. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix, Version 0.90. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Nei, M.; Li, W.H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamvar, Z.N.; Tabima, J.F.; Grünwald, N.J. Poppr: An R package for genetic analysis of populations with clonal, partially clonal, and/or sexual reproduction. PeerJ 2014, 2, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wünsch, A.; Hormaza, J.I. Cultivar identification and genetic fingerprinting of temperate fruit tree species using DNA markers. Euphytica 2002, 125, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R. Construction of a linkage map using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howard, W.L. Luther Burbank’s Plant Contributions; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick, U.P. The Plums of New York; J.B. Lyon Company, State Printers: Albany, NY, USA, 1911. [Google Scholar]
- Agricultural Research Council. Product Catalogue. Available online: https://www.arc.agric.za/arc-infruitec-nietvoorbij/Pages/Product-Catalogue.aspx (accessed on 26 June 2021).
- Okie, W.R. Register of new fruit and nut varieties. HortScience 2019, 39, 1509–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.M.; Priyadarshan, P.M. Breeding Plantation Tree Crops: Temperate Species, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780387712031. [Google Scholar]
- García-Gómez, B.; Razi, M.; Salazar, J.A.; Prudencio, A.S.; Ruiz, D.; Dondini, L.; Martínez-Gómez, P. Comparative analysis of SSR markers developed in exon, intron, and intergenic regions and distributed in regions controlling fruit quality traits in Prunus species: Genetic diversity and association studies. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 36, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T. Counting alleles with rarefaction: Private alleles and hierarchical sampling designs. Conserv. Genet. 2004, 5, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Lee, J.R.; Sebastin, R.; Shin, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, G.T.; Hyun, D.Y. Genetic diversity assessed by genotyping by sequencing (GBS) in watermelon germplasm. Genes 2019, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.J.; Lee, J.R.; Sebastin, R.; Cho, G.T.; Hyun, D.Y. Molecular genetic diversity and population structure of ginseng germplasm in RDA-geneBank: Implications for breeding and conservation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, S. Evolution and the genetics of populations. In Variability within and among Natural Populations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Urrestarazu, J.; Royo, J.B.; Santesteban, L.G.; Miranda, C. Evaluating the influence of the microsatellite marker set on the genetic structure inferred in Pyrus communis L. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).