A Two-Year Study on Yield and Yield Components of Maize-White Bean Intercropping Systems under Different Sowing Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Location
2.2. Soil Characteristics
2.3. Climatic Characteristics of Study Area
2.4. Experimental Layout
2.5. Data Acquisition Related to Crop Growth, Yield and Its Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
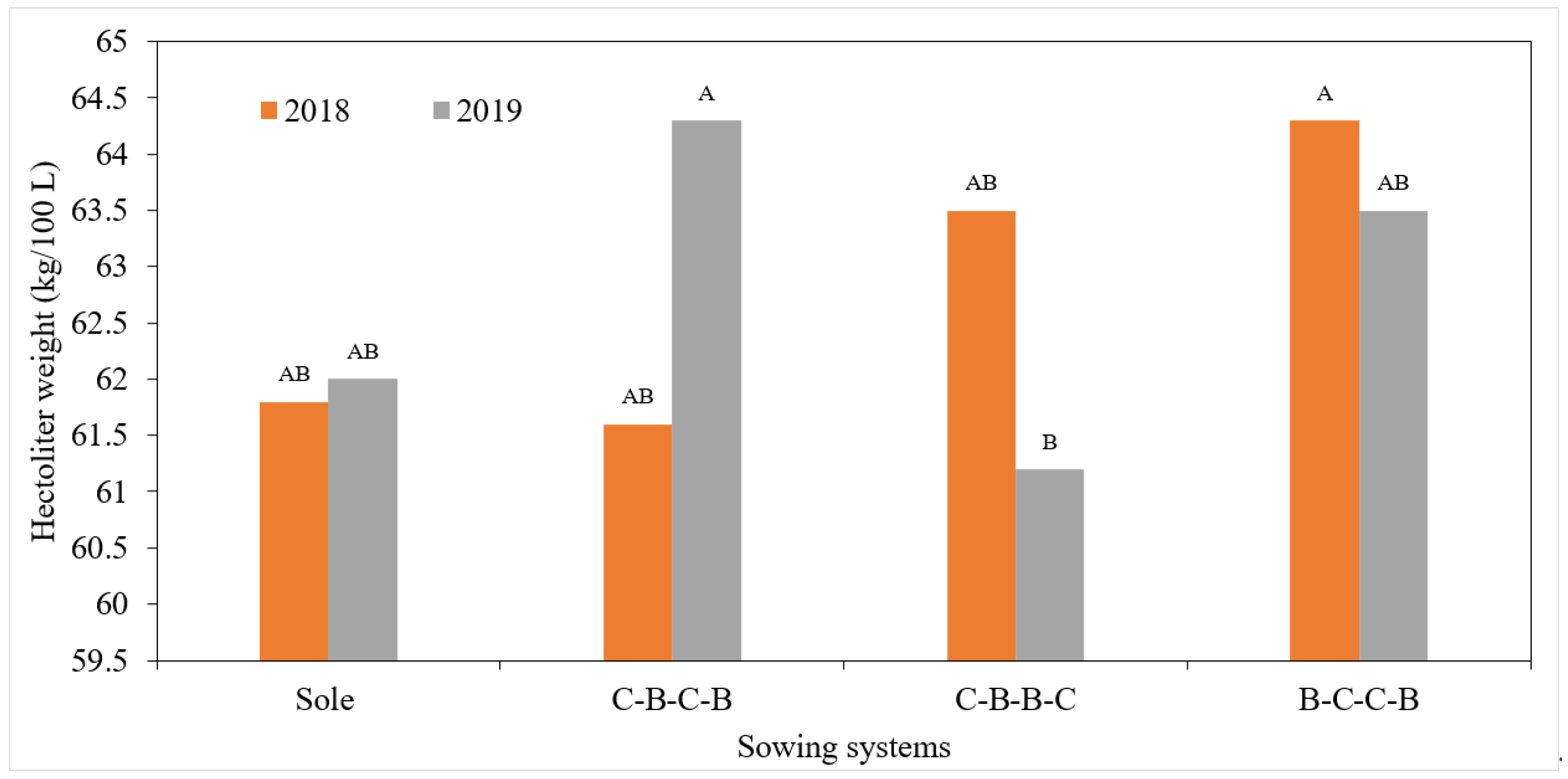
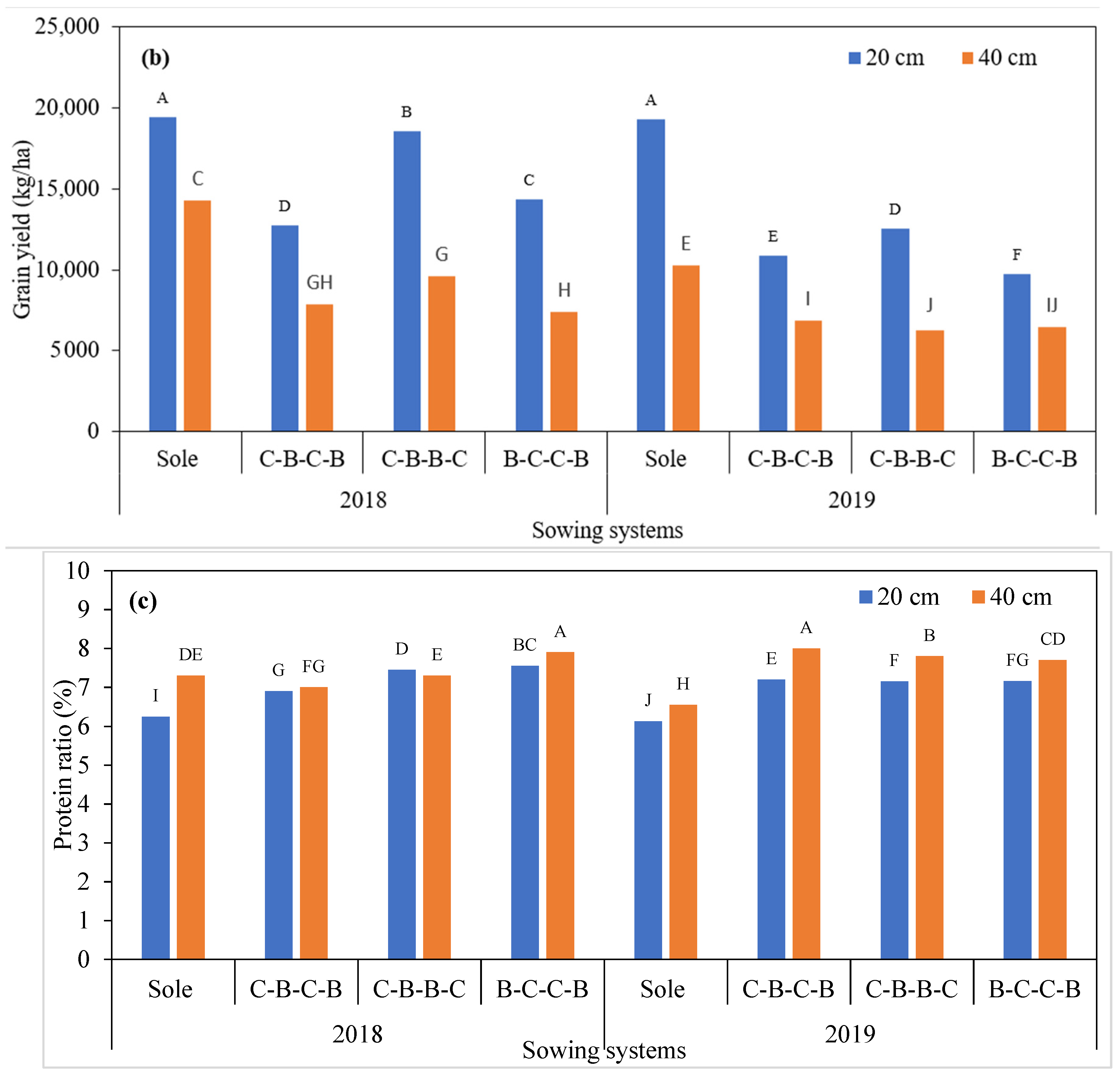
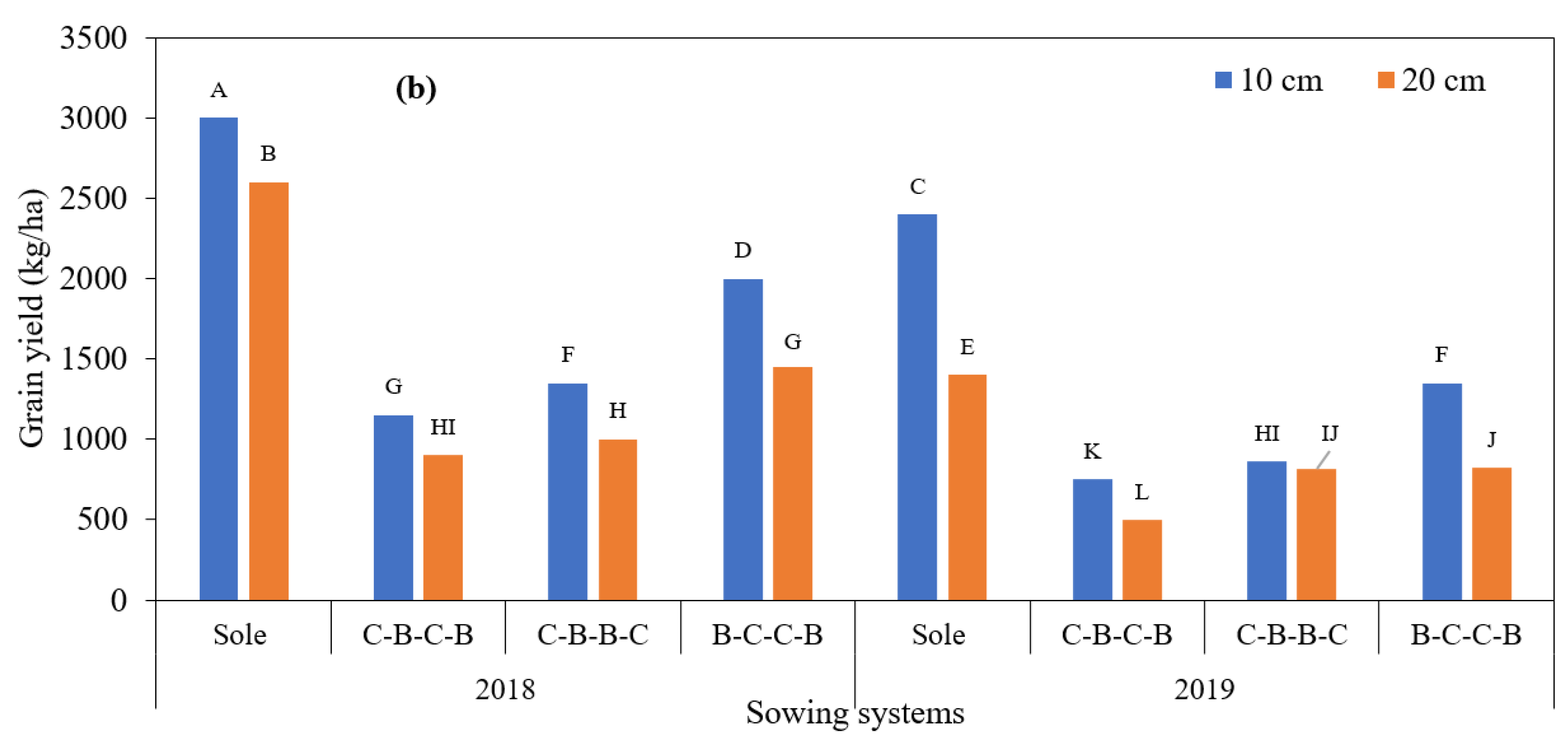
3.1. Yield Characteristics of Maize
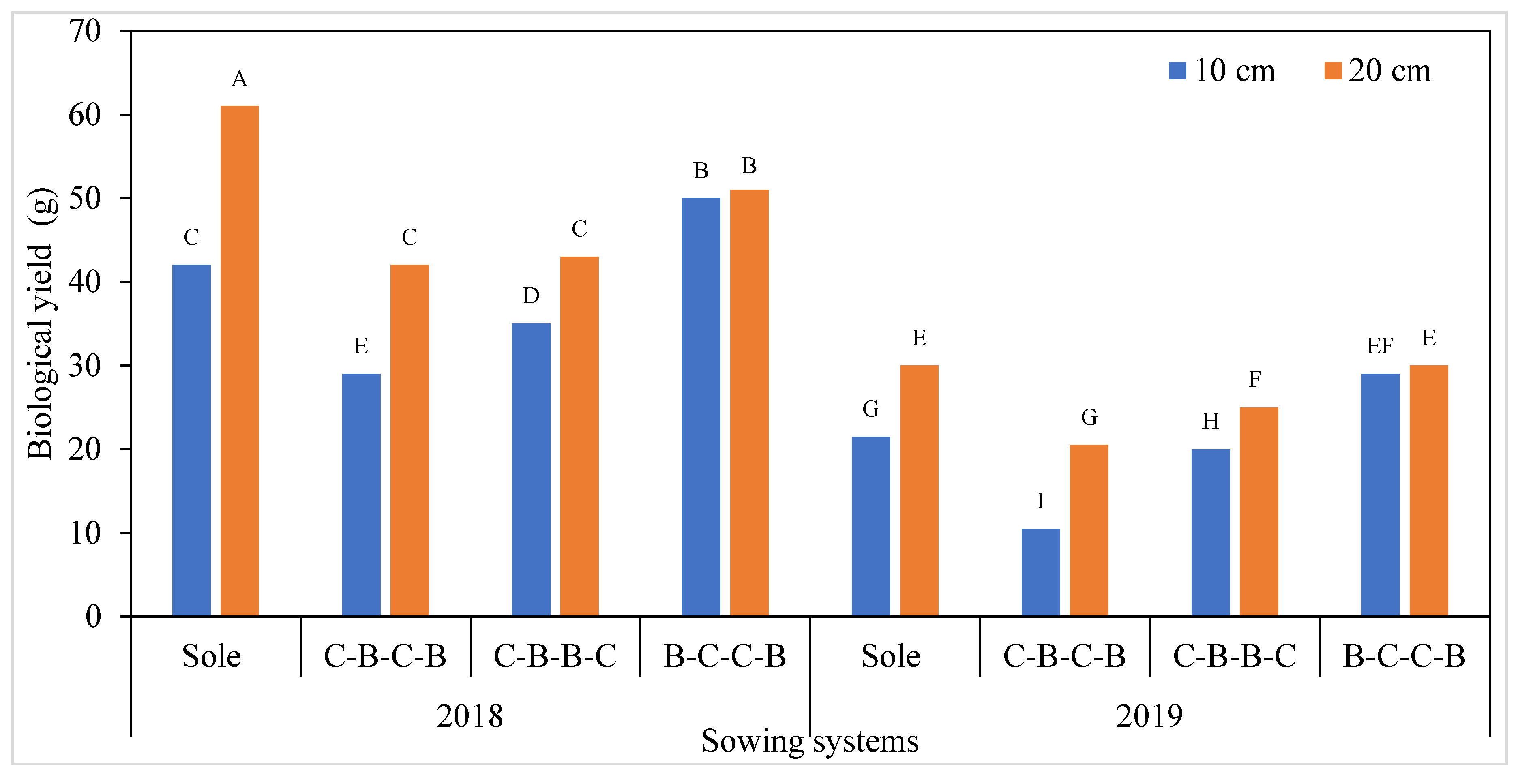
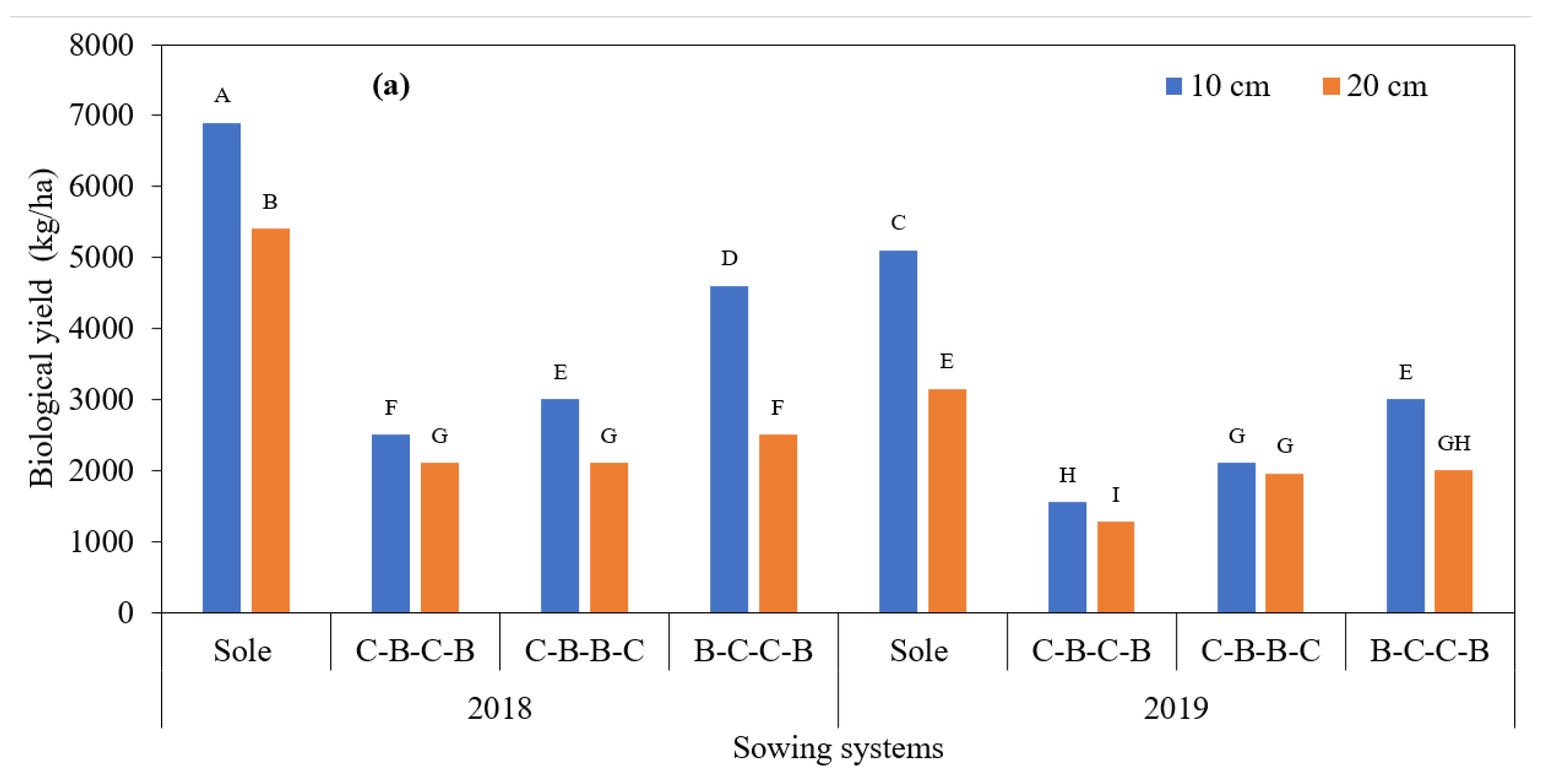
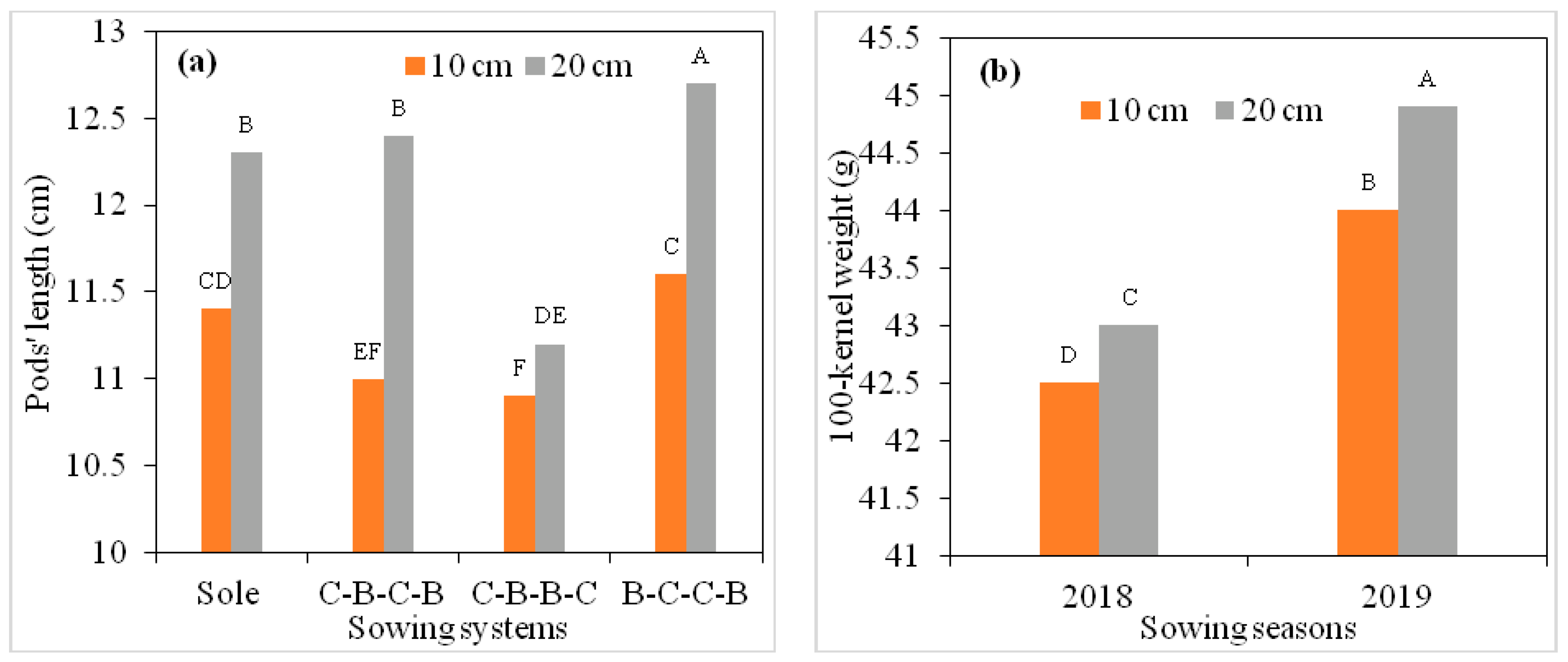
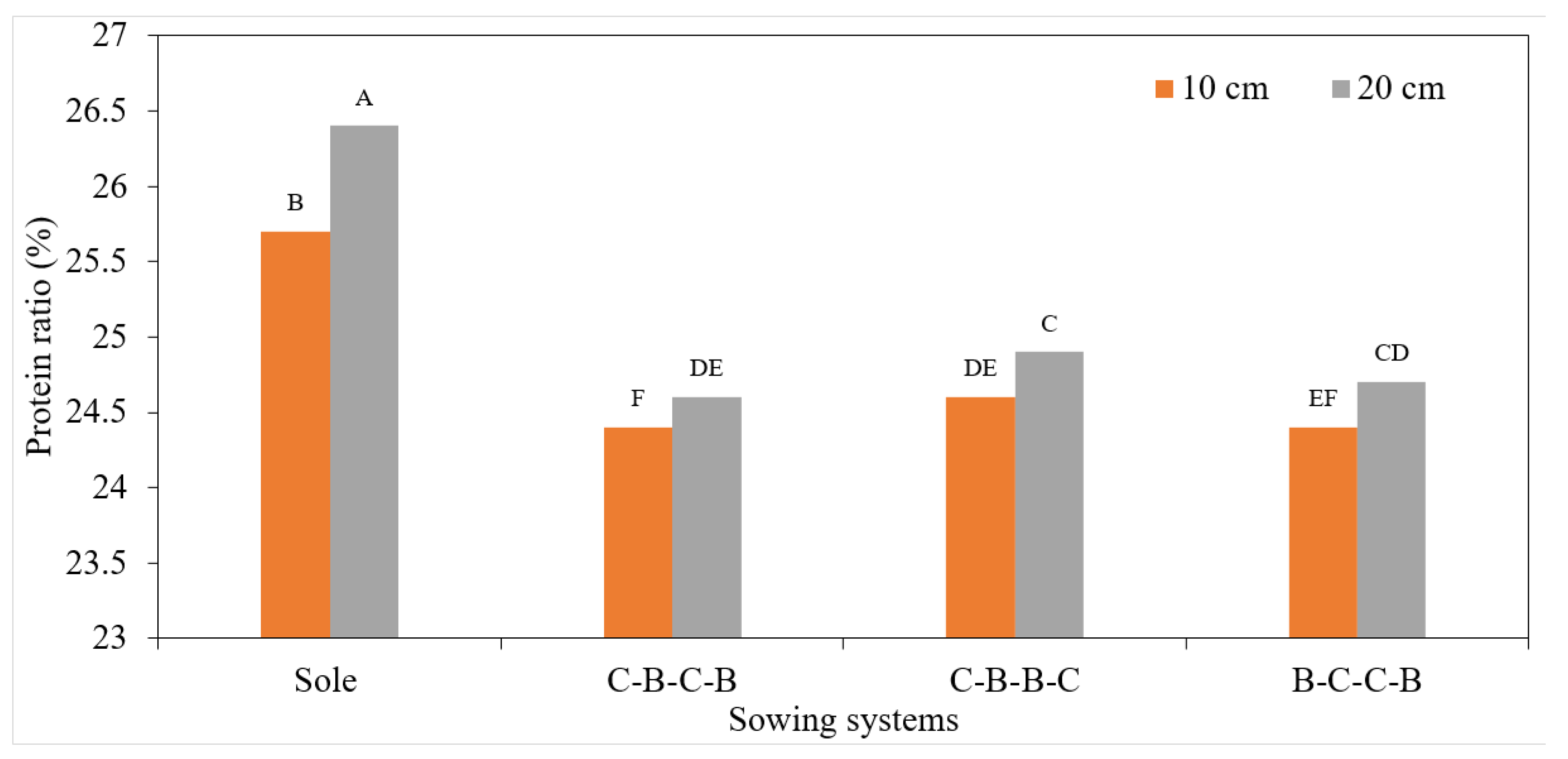
3.2. Yield Characteristics of White Bean
3.3. Land Equivalent Ratio (LER) of Maize-White Bean Intercropping Sowing Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maitra, S.; Hossain, A.; Brestic, M.; Skalicky, M.; Ondrisik, P.; Gitari, H.; Brahmachari, K.; Shankar, T.; Bhadra, P.; Palai, J.B.; et al. Intercropping—A low input agricultural strategy for food and environmental security. Agronomy 2021, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waha, K.; Dietrich, J.P.; Portmann, F.T.; Siebert, S.; Thornton, P.K.; Bondeau, A.; Herrero, M. Multiple cropping systems of the world and the potential for increasing cropping intensity. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2020, 64, 102131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agegnehu, G.; Ghizaw, A.; Sinebo, W. Yield performance and land-use efficiency of Barley and Faba White Bean mixed cropping in Ethiopian highlands. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 25, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Zhou, L.; Bao, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F. Diversity Enhances Agricultural Productivity via Rhizosphere Phosphorus Facilitation on Phosphorus-Deficient Soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11192–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenbath, B.R. Intercropping for the management of pests and diseases. Field Crops Res. 1993, 34, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Fan, J.X.; Yang, S.; Hu, L.; Leung, H.; et al. Genetic diversity and disease control in Rice. Nature 2000, 406, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusinamhodzi, L.; Corbeels, M.; Nyamangara, J.; Giller, K.E. Field crops research maize-grain legume intercropping is an attractive option for ecological intensification that reduces climatic risk for smallholder farmers in central Mozambique. Field Crops. Res. 2012, 136, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liu, Q.; Heerink, N.; Stomph, T.; Li, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Economic performance and sustainability of a novel sowing system on the North China Plain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A.; Nicholls, C.I. An agroecological basis for designing diversified cropping systems in the tropics. J. Crop Improv. 2004, 11, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, H.M.; Schochow, M.; Ulber, B.; Kuhne, S.; Rahmann, G. Mixed cropping systems for biological control of weeds and pests in organic oilseed crops. Asp. Appl. Biol. 2006, 79, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Knörzer, H.; Graeff-hönninger, S.; Guo, B.; Wang, P. Climate Change, Intercropping, Pest Control and Beneficial Microorganisms; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Dordas, C.A.; Damalas, C.A.; Vlachostergios, D.N. Annual intercrops: An alternative pathway for sustainable agriculture. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 396–410. [Google Scholar]
- Stanisławska-Glubiak, E.; Korzeniowska, J. Effect of excessive zinc content in soil on the phosphorus content in wheat plants. Electron. J. Pol. Agric. Univ. 2005, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F. Crop mixtures and the mechanisms of overyielding. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, L. Using competitive and facilitative interactions in intercropping systems enhances crop productivity and nutrient-use efficiency. Ann. Oper. Res. 2003, 248, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeer, J.H. The Ecology of Intercropping; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Jensen, E.S. Evaluating pea and barley cultivars for complementarity in intercropping at different levels of soil n availability. Field. Crop. Res. 2001, 72, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Hector, A. Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature 2001, 412, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Barré, P.; Trindade, H.; Virto, I. Different efficiencies of grain legumes in crop rotations to improve soil aggregation and organic carbon in the short-term in a sandy cambisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogindo, H.O.; Walker, S. Comparison of measured changes in seasonal soil water content by rainfed maize-white bean intercrop and component cropping systems in a semi-arid region of Southern Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth 2005, 30, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubo, M.; Walker, S.; Ogindo, H.O. A simulation model of cereal-legume intercropping systems for semi-arid regions: Ii. model application. Field. Crop. Res. 2005, 93, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, J.R.; Maende, C.; Wyseure, G.C.L. Modelling the intercropping of maize and white beans in Kenya. Comput. Electron. Agric. 1994, 11, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, K.D.; Ma, B.L. Maize Crop Production: Growth, Fertilization and Yield; Nova Publisher: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilalis, D.; Papastylianou, P.; Konstantas, A.; Patsiali, S.; Karkanis, A.; Efthimiadou, A. Weed-suppressive effects of maize-legume intercropping in organic farming. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2010, 56, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutungi, C.; Muthoni, F.; Bekunda, M.; Gaspar, A.; Kabula, E.; Abass, A. Physical quality of maize grain harvested and stored by smallholder farmers in the northern highlands of Tanzania: Effects of harvesting and pre-storage handling practices in two marginally contrasting agro-locations. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 84, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, G.M.; Oad, F.C.; Tunio, S.; Chachar, Q.; Gandahi, A.W.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Waseem, S.; Hassan, U.L.; Ali, A. Growth and yield attributes of wheat at different seed rates. Sarhad J. Agric. 2011, 27, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, P.L. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. J. Farm Econ. 1946, 28, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Inorganic forms of Nitrogen. In Handbook of Soil Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 767–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broka, S.; Giertz, Å.; Christensen, G.; Rasmussen, D.; Morgounov, A.; Fileccia, T.; Rubaiza, R. Kazakhstan: Agricultural Sector Risk Assessment; Report Number 103076-KZ; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moosavi, S.G. The effect of water deficit stress and nitrogen fertilizer levels on morphology traits, yield and leaf area index in maize. Pakistan J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Rasul, G.; Chaudhry, Q.Z.; Mahmood, A.; Hyder, K.W. Effect of temperature rise on crop growth & productivity. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2002, 8, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Çakir, R. Effect of water stress at different development stages on vegetative and reproductive growth of maize. Field. Crop. Res. 2004, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajah, J.; Nmadu, J.N. Socio-economic factors influencing the output of small-scale maize farmers in Abuja, Nigeria. Kasetsart J. Soc. Sci. 2012, 33, 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Undp, K. Building the Climate Resilience of Grain Farming in Northern Kazakhstan; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A. Effect of plant population density on yield and yield components of eight Egyptian maize hybrids. Bull. Fac. Agric. Univ. Cairo 2000, 51, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A. Evaluation of maize hybrids for grain yield in D.I. Khan. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 1999, 2, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.R.; Prakash, O.M.; Kharwara, P.C.; Bhalla, S.K. Effect of nitrogen and plant spacing on growth, yield and economics of baby maize (Zea Mays). Indian J. Agron. 1997, 42, 479–483. [Google Scholar]
- Masood, T.; Gul, R.; Munsif, F.; Jalal, F.; Hussain, Z.; Noreen, N.; Khan, H.H. Effect of different phosphorus levels on the yield and yield components of maize. Sarhad J. Agric. 2011, 27, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, M.S.I.; Ahmad, A.H.; Javeed, H.M.R.; Latif, T. Growth and yield behaviour of two maize hybrids (Zea Mays L.) towards different plant spacing. Cercet. Agron. Mold. 2013, 44, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharazmshahi, H.A.; Zahedi, H.; Alipour, A. Effects of sowing date on yield and yield components in sweet maize (Zea Mays L.) hybrids. Maydica 2015, 60, 835–840. [Google Scholar]
- Licht, M.A. Influence of Maize Seeding Rate, Soil Attributes, and Topographic Characteristics on Grain Yield, Yield Components, and Grain Composition. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, A.; Alhossini, M.; Khorasani, S. Effect of planting date and plant densities on yield and yield components of sweet maize (Zea Mays L. Var Saccharata). Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2016, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi-afshar, H.R.; Madani, H.; Shirzadi, M.H.; Najafi, I. Archive of SID study of effects of cultivar, weeds and plant density on yield and yield components of sweet maize under Iranian warm environment. Arch. SID 2009, 3, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, P.S. Response of sweet maize hybrid to varying plant densities and nitrogen levels. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 6158–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, A.D.B.; Uribelarreà, M.; Ainsworth, E.A.; Naidu, S.L.; Rogers, A.; Ort, D.R.; Long, S.P. Photosynthesis, productivity, and yield of maize are not affected by open-air elevation of CO2 concentration in the absence of drought. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Singh, R.; Avasthe, R.K.; Yadav, G.S.; Das, A.; Singh, V.K.; Mohapatra, K.P.; Rathore, S.S.; Chandra, P.; Kumar, A. Impact of land configuration and organic nutrient management on productivity, quality and soil properties under baby maize in eastern Himalayas. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.K. Diversification in utilization of maize and production diversification in utilization of maize and production. Perspect. Maize Prod. Value Chain-A Compend. 2017, 5, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Singode, A.; Mukri, G.; Sah, R.P.; Tiwana, U.S.; Kumar, B. Evaluation of normal and specialty maize for fodder yield and quality traits. Range Manag. Agrofor. 2016, 37, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Xie, R.Z.; Zhang, W.F.; Wang, K.R.; Hou, P.; Ming, B.; Gou, L.; Li, S. Research progress on reduced lodging of high-yield and -density maize. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyambo, P.; Chiduza, C.; Araya, T. Carbon input and maize productivity as influenced by tillage, crop rotation, residue management and biochar in a semiarid region in South Africa. Agronomy 2020, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.R.; Willey, R.W. Effects of pigeonpea plant population and row arrangement in sorghum/pigeonpea intercropping. Field. Crop. Res. 1983, 7, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoneke, C. Effect of maize planting density on the performance of maize/soy white bean intercropping system in a guinea savannah agroecosystem. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 2, 667–677. [Google Scholar]
- Sarlak, S. Effect of plant density and mixing ratio on crop yield in sweet maize/mung white bean intercropping. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 11, 2128–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rai, A.; Sharma, V.; Heitholt, J. Dry white bean [phaseolus vulgaris l.] growth and yield response to variable irrigation in the arid to semi-arid climate. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, R.J.; Roberts, E.H.; Ellis, R.H.; Lawn, R.J. Towards the reliable prediction of time to flowering in six annual crops in the development of simple models for fluctuating field environments. Exp. Agric. 1991, 27, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, S.A.; Vieira, J.H.; dos Santos Farias, D.B.; da Silva, G.H.; Aleman, C.C. Impact of irrigation frequency and planting density on white bean’s morpho-physiological and productive traits. Water 2020, 12, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Aftab, S.; Hussain, S.; Cheema, H.N.; Liu, W.; Yang, F.; Yang, W. Nutrient accumulation and distribution assessment in response to potassium application under maize-soywhite bean intercropping system. Agronomy 2020, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craine, J.M.; Dybzinski, R. Mechanisms of plant competition for nutrients, water and light. Funct. Ecol. 2013, 27, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafroudi, A.T.; Moghaddam, A.F.; Hasanzade, A.; Yazdifar, S.; Rahmanzade, S. Row spacing and inter row spacing effects on some agro-physiological traits of two common white bean (Phaseolous vulgaris L.) cultivars. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 4543–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathna, M.S.; McElroy, M.S.; Chapagain, T.; Papadopoulos, Y.A.; Raizada, M.N. Belowground nitrogen transfer from legumes to non-legumes under managed herbaceous cropping systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz Tiryaki, G.; Cil, A.; Tiryaki, I. Revealing seed coat colour variation and their possible association with seed yield parameters in common vetch (Vicia sativa L.). Int. J. Agron. 2016, 2016, 1804108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassary, E.K.; Baijukya, F.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Assessing the productivity of common white bean in intercrop with maize across agro-ecological zones of smallholder farms in the northern highlands of Tanzania. Agriculture 2020, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkuijl, H.; Mwangi, W.; Moshi, A.J.; Chilagane, A.; Kaswende, J.S. Adoption of Maize Production Technologies in Eastern Tanzania Adoption of Maize Production Technologies in 1998; International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), The United Republic of Tanzania, The Southern Africa Centre for Cooperation in Agricultural Research (SACCAR): Texcoco, Mexico, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tanveer, M.; Anjum, S.A.; Zahid, H.; Rehman, A.; Sajjad, A. Growth and development of maize (Zea mays L.). J. Agric. Res. 2014, 52, 511–523. [Google Scholar]






| Year | Depth (cm) | pH | Lime (%CaCO3) | Salinity (%) | Organic Matter (%) | P2O5−1 (kg/ha) | K2O−1 (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 0–30 | 7.71 | 2.69 | 0.07 | 1.82 | 85.21 | 1133.0 |
| 2019 | 0–30 | 7.66 | 2.14 | 0.08 | 1.51 | 109.11 | 1952.3 |
| Month | Precipitation (mm) | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | Mean * | 2018 | 2019 | Mean * | 2018 | 2019 | Mean * | |
| May | 58.2 | 19.4 | 40.5 | 11.48 | 15.1 | 15.71 | 54.5 | 36.7 | 45.67 |
| June | 84.1 | 70.2 | 58.89 | 19.43 | 18.13 | 20.99 | 54.7 | 66.0 | 50.31 |
| July | 64.7 | 57.2 | 78 | 22.35 | 23.48 | 21.9 | 60.3 | 55.0 | 54.58 |
| August | 130.9 | 40.7 | 48.94 | 19.58 | 21.29 | 21.07 | 64.7 | 49.4 | 50.28 |
| September | 31.3 | 52.6 | 26.0 | 14.5 | 13.2 | 14.29 | 57.3 | 56.6 | 50.31 |
| Selected Crops | Treatments | Crop Rotation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maize (SY Miami) White bean (Göynük-98) | T1 | S-C | Sole maize |
| T2 | S-B | Sole white bean | |
| T3 | C-B-C-B | Maize-white bean-maize-white bean | |
| T4 | C-B-B-C | Maize-white bean-white bean-maize | |
| T5 | B-C-C-B | White bean-maize-maize-white bean | |
| Sowing Systems | Row Spacing (cm) | Number of Plants Per m2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | White Bean | Maize | White Bean | |
| Sole maize | 20 | – | 7 | – |
| Sole white bean | – | 10 | – | 28 |
| Sole maize | 40 | – | 4 | |
| Sole white bean | – | 20 | 14 | |
| C-B-C-B | 20 | 10 | 7 | 14 |
| C-B-C-B | 40 | 20 | 4 | 7 |
| C-B-B-C | 20 | 10 | 7 | 14 |
| C-B-B-C | 40 | 20 | 4 | 7 |
| B-C-C-B | 20 | 10 | 7 | 14 |
| B-C-C-B | 40 | 20 | 4 | 7 |
| Genotypes | N.S.P. | S.W. (g) | S.U. (cm) | N.O.S. | N.S.S. | S.W.S. (g) | H.W. (kg/100 L) | T.K.W. (g) | G.Y. (kg/ha) | P.R. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 1.17 B | 357.10 A | 20.88 A | 16.95 A | 676.45 A | 292.12 A | 62.83 | 430.50 A | 1242.92 A | 7.24 A |
| 2019 | 1.21 A | 262.79 B | 18.41 B | 16.17 B | 601.49 B | 241.34 B | 62.70 | 400.45 B | 989.92 B | 7.14 B |
| Mean | 1.19 | 309.94 | 19.64 | 16.56 | 638.97 | 266.73 | 62.76 | 415.47 | 1116.42 | 7.19 |
| 20 cm | 1.13 B | 293.36 B | 19.12 B | 16.36 | 610.46 B | 250.14 B | 62.58 | 408.04 B | 1412.17 A | 6.99 B |
| 40 cm | 1.25 A | 326.54 A | 20.17 A | 16.76 | 667.48 A | 283.32 A | 62.95 | 422.91 A | 820.67 B | 7.39 A |
| Mean | 1.19 | 309.94 | 19.64 | 16.56 | 638.97 | 266.73 | 62.76 | 415.47 | 1116.42 | 7.19 |
| Sole maize | 1.04 C | 272.28 D | 18.47 D | 16.68 | 605.98 C | 229.62 D | 61.83 B | 378.16 D | 1572.25 A | 6.61 D |
| C-B-C-B | 1.21 B | 320.75 B | 19.95 B | 16.90 | 650.61 B | 281.13 B | 63.00 EU | 432.75 B | 924.92 C | 7.28 C |
| C-B-B-C | 1.28 A | 354.38 A | 21.31 A | 16.58 | 685.91 A | 303.75 A | 62.33 EU | 441.33 A | 1065.67 B | 7.37 B |
| B-C-C-B | 1.21 B | 292.39 C | 18.85 C | 16.09 | 613.38 C | 252.43 C | 63.91 A | 409.66 C | 902.83 C | 7.51 A |
| Mean | 1.19 | 309.94 | 19.64 | 16.56 | 638.97 | 266.73 | 62.76 | 415.47 | 1116.42 | 7.19 |
| Years | * | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Row spacing | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Sowing systems | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | ** |
| Year × row spacing | ** | * | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Year × sowing systems | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Row spacing × sowing system | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Year × row spacing × sowing system | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Genotypes | B.Y.P. (g) | N.P.P. | N.S.P. | N.S. Pod | S.Y.P. (g) | P.L. (cm) | H.I. (%) | T.K.W. (g) | B.Y. (kg/ha) | G.Y. (kg/ha) | P.R. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 45.54 a | 18.58 a | 46.40 a | 3.01 a | 19.86 a | 11.61 | 43.72 | 427.9 b | 3691.67 a | 1598.12 a | 24.39 b |
| 2019 | 24.82 b | 12.10 b | 30.54 b | 2.59 b | 13.58 b | 11.72 | 43.78 | 444.2 a | 2592.08 b | 1121.29 b | 25.55 a |
| mean | 35.18 | 15.34 | 38.47 | 2.80 | 16.72 | 11.66 | 43.75 | 436.0 | 3141.87 | 1359.70 | 24.97 |
| 10 cm | 39.22 a | 14.49 b | 34.30 b | 2.61 b | 14.79 b | 11.20 b | 43.55 | 432.6 b | 3638.75 a | 1570.79 a | 24.77 b |
| 20 cm | 31.15 b | 16.20 a | 42.63 a | 2.99 a | 18.65 a | 12.13 a | 43.96 | 439.4 a | 2645.00 b | 1148.62 b | 25.18 a |
| mean | 35.18 | 15.34 | 38.47 | 2.80 | 16.72 | 11.66 | 43.75 | 436.0 | 3141.87 | 1359.70 | 24.97 |
| Sole white bean | 39.85 a | 14.83 c | 42.35 b | 3.09 a | 19.20 a | 11.82 b | 43.55 | 459.2 a | 5147.50 a | 2226.75 a | 25.99 a |
| C-B-C-B | 28.05 c | 13.98 d | 31.57 d | 2.65 b | 13.49 c | 11.64 c | 43.82 | 431.5 b | 1989.17 d | 857.83 d | 24.47 c |
| C-B-B-C | 32.07 b | 16.52 a | 35.40 c | 2.45 c | 14.93 b | 11.03 d | 43.95 | 429.8 b | 2385.00 c | 1037.00 c | 24.77 b |
| B-C-C-B | 40.75 a | 16.05 b | 44.55 a | 3.00 a | 19.25 a | 12.18 a | 43.69 | 423.6 c | 3045.83 b | 1317.25 b | 24.66 b |
| mean | 35.18 | 15.34 | 38.47 | 2.80 | 16.72 | 11.66 | 43.75 | 436.0 | 3141.87 | 1359.70 | 24.97 |
| Years | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Row spacing | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Sowing systems | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Year × row spacing | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | * | ** | ** | * |
| Year × sowing systems | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Row spacing × sowing system | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | * | ** | ** | * |
| Year × row spacing × sowing system | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ns | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns |
| Row Spacing | Sowing Systems | LERmaize | LERwhite bean | LER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10–20 cm | C-B-C-B | 0.68 | 0.63 | 1.31 |
| C-B-B-C | 0.78 * | 0.76 * | 1.54 | |
| B-C-C-B | 0.82 ** | 0.97 ** | 1.79 | |
| 20–40 cm | C-B-C-B | 0.79 * | 0.73 * | 1.52 |
| C-B-B-C | 0.91 ** | 0.89 ** | 1.80 | |
| B-C-C-B | 0.95 ** | 0.99 ** | 1.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhanbota, A.; Noor, R.S.; Khan, A.I.; Wang, G.; Waqas, M.M.; Shah, A.N.; Ullah, S. A Two-Year Study on Yield and Yield Components of Maize-White Bean Intercropping Systems under Different Sowing Techniques. Agronomy 2022, 12, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020240
Zhanbota A, Noor RS, Khan AI, Wang G, Waqas MM, Shah AN, Ullah S. A Two-Year Study on Yield and Yield Components of Maize-White Bean Intercropping Systems under Different Sowing Techniques. Agronomy. 2022; 12(2):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020240
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhanbota, Aidyn, Rana Shahzad Noor, Azeem Iqbal Khan, Gangyi Wang, Muhammad Mohsin Waqas, Adnan Noor Shah, and Sami Ullah. 2022. "A Two-Year Study on Yield and Yield Components of Maize-White Bean Intercropping Systems under Different Sowing Techniques" Agronomy 12, no. 2: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020240
APA StyleZhanbota, A., Noor, R. S., Khan, A. I., Wang, G., Waqas, M. M., Shah, A. N., & Ullah, S. (2022). A Two-Year Study on Yield and Yield Components of Maize-White Bean Intercropping Systems under Different Sowing Techniques. Agronomy, 12(2), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020240







