Abstract
House mouse (Mus musculus) is a cosmopolitan pest in agricultural facilities, commodity stores and rural and urban environments. It is regularly controlled by anticoagulant-based baits. Since the number of registered active ingredients is limited, the producers are trying to develop new formulations with increased tamper-resistance, attractiveness and palatability. Reliable and economical methods for laboratory screening/testing are needed. Therefore, this work compared simple no-choice with more economically demanding choice feeding tests for laboratory evaluation of efficacy of rodenticide anticoagulant-based preparations in wild populations of house mouse. We analyzed mice survival and bait intake of the various rodenticide commercial preparations differing in a toxic active substance (warfarin, bromadiolone, brodifacoum, difethialone) and nontoxic food lure components. In most cases, we found insignificant differences in survival of house mice treated with eight test baits within the no-choice and choice feeding tests. We rejected the tested hypothesis that there would be significant differences in all tested preparations for two different testing approaches.
1. Introduction
Populations of worldwide distributed synanthropic rodents, such as house mice (Mus musculus), brown rats (Rattus norvegicus) and black rats (Rattus rattus), are associated with huge damages on stored agricultural commodities caused by feeding and gnawing [1] and also by contamination by large numbers of feces [2]. These rodent pests are controlled with various formulations of rodenticide preparations and formulations that include baits, foams, dusts, smokes and fumigants [3]. Although toxic baits are the predominant formulation, other physical formulations may be appropriate supplements or alternatives for specific situations. Some of these minority formulations and their applications are described in more detail in a recent paper by Aulicky et al. [4]. Certain rodenticides—released as fumes from pyrotechnic fume-generators or as gas-fumigants—are allowed to be applied to burrows outside buildings in some countries. Fumigants, such as phosphine, are the most commonly released rodenticide gases by reaction with air moisture from tablets (phosphides) after their application to burrows. Foams and dusts, in turn, serve or have served as contact rodenticides for situations where synanthropic rodents avoid the applied rodenticide baits [5]. A contact rodenticide formulation in the form of a foam (Racumin Foam—Bayer, Germany), with coumatetralyl as the active ingredient, is currently registered in a number of European Union (EU) countries and elsewhere. Although this product is used in practice, no freely available peer-reviewed scientific study on its efficacy has been published to our knowledge. However, baits are currently the most frequently used tool for control of rodent population both in agricultural and urban environments. Rodenticide baits consist of a nontoxic food base, flavor, attractants, additional additives (such as bittering, moisture-resistant, coloring and preservative agents) and toxic active substance. Food composition plays a key aspect for bait efficacy as it ensures its palatability. Baits may be based on acute [6] or anticoagulant active ingredients [7]. Anticoagulants belong to the chronic rodenticides with the delayed mode of action. They stop the blood coagulation process in the liver via interruption of the vitamin K cycle, which results in a fatal hemorrhage after several days (typically 4–10). This delay prevents rodents from connecting the signs of toxicity with the consumed food, which favors anticoagulants over the acute rodenticides. Although mode of action in terms of mortality is not instant, they may inhibit food acceptance quite rapidly [8].
Historically many types of formulations and active ingredients of pesticides have been developed [3,9]. This process has not stopped until today even in rodenticides due to optimization of baits for various environments (e.g., waterproof formulations), rodent behavioral adaptations and new EU regulation (e.g., leading to lower concentration of active substances [10]). Since the number of the registered active ingredients is limited, the producers are also trying to develop new formulations with increased tamper-resistance, attractiveness and palatability. Almost any modification in recipe could change the palatability for rodents, and thus, validation of efficacy each new or modified bait product on wild/laboratory animals is required by the EU legislative framework (European Biocidal Products Regulation EU 528/2012; BPR). For innovative rodent bait research and development, the reliable and economically affordable methods for laboratory screening and testing have always been needed. However, in the EU, the development and testing of new formulations is economically, legislatively and methodically demanding. First, all experimental procedures with vertebrate animals must be conducted in authorized facility and according to the approved procedures. Second, there is an increasing effort to minimize numbers and also suffering of animals used for scientific purposes (Directive 2010/63/EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes). In addition, laboratory trials with rodenticides should be preferably performed on wild, not laboratory animals as laboratory rodents differ in behavior relevant to rodent control [11]. All these aspects led recently to the decreased number of facilities competent to conduct such validation trials and their absence in some countries.
As all biocides according to the BPR, rodenticide products must meet the requirements for registration and/or authorization before their introduction to the European market. Besides other issues, these requirements also cover methodical approaches for evaluating efficacy of rodenticide preparations for different standards of field of use. The procedures are based on standard protocols, e.g., [12], on efficacy evaluation of rodenticides in laboratory and field trials. For authorization purposes, choice feeding tests are currently preferred for efficacy evaluation of rodenticide products [11]. No-choice feeding tests are the alternative to molecular methods for evaluation of susceptibility of rodent populations to various anticoagulant active substances [13,14]. On one hand, no-choice tests are easier to conduct than the choice tests and thus may seem to be a more economical option for large-scale prescreening testing of new rodenticide formulations or repellents [15]. On the other hand, there may be significant concern about rodent behavioral reaction resulting in bait acceptance bias. Although there are generally a number of publicly available studies on both types of rodenticide bait tests conducted on wild rodent strains, e.g., [16,17,18,19,20], there are fewer directly side-by-side comparisons of choice and no-choice tests of modern formulations of anticoagulant rodenticides; most of them examined only a single or couple of baits [21,22,23,24]. Moreover, particular studies differ in their methodology (e.g., the duration of introduction of the bait, type of animal housing, concentration of the active substance), which makes the results hard to fully compare.
Therefore, the present work was aimed at comparison of two standard methods for efficacy evaluation of rodenticide preparations in wild populations of house mouse (Mus musculus). In laboratory conditions, we analyzed survival and bait intake after introduction of various anticoagulant-based rodenticide preparations differing both in their recipe of nontoxic food components and toxic active substance. The tested hypothesis was that there would be significant differences in tested preparations for two different testing approaches (i.e., no-choice and choice feeding tests).
2. Materials and Methods
The tested wild house mice were a mix of populations originated from the agriculture buildings in Prague area (central Bohemia, Czech Republic) and Zamberk (east Bohemia, Czech Republic). Animals were housed in standard plastic cages (30 × 15 × 15 cm) in breeding pairs and same-sex sibling groups after weaning. Animals were kept under standard laboratory condition (temperature 19–22 °C, 12:12 light cycle). Water and food (standard diet for laboratory mice: Ssniff, Germany) were provided ad libitum.
Experimental animals were adult (3–6 months old), captive-bred mice of the first generation. At the beginning of each experiment, mice were individually housed in the experimental wire-mesh cages (26 × 17 × 17 cm). We tested in total 111 males (mean body weight = 18.2 g, range 13.7–26.0 g) and 111 females (mean body weight = 15.8 g, range 10.4–23.5 g). Mice were randomly assigned to the control (n = 16 males, 15 females) and experimental group (n = 95 males, 96 females; one male died from unknown reasons before the experiment). We tested eight types of bait, for each bait were used 12 individuals for the no-choice test (6 males and 6 females) and 12 individuals for the choice test (6 males and 6 females; in the Lanirat G (meat–bone flour) group only 5 males were tested). Experimental animals were fed solely a rodenticide bait (no-choice feeding test), a rodenticide bait and standard diet (choice feeding test) or solely a standard diet (control group). Food and water was provided ad libitum. Mice were checked daily, and remaining food was weighted (including spillage and crumbled food) and replenished. This procedure was repeated daily, and the times of death of the experimental animals were recorded. The experiment was terminated by the death of the last experimental individual of the tested group or by day 21 of the experiment. The surviving individuals were transferred back to the breeding stock and considered as anticoagulant-resistant individuals (in the case of sufficient bait consumption).
We tested four different anticoagulant active substances administered in eight commercial rodenticide baits: Baraki G (two added flavors: sugar and fish flour; DDD servis, Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic), Lanirat G (three added flavors: sugar, fish flour and meat–bone flour; DDD servis, Ltd., Czech Republic), Hubex B (no added flavor; Hubex, Ltd., Benesov, Czech Republic), Kumatox G (no added flavor; Druchema, Czech Republic), Norat ATG (no added flavor; PelGar, Ltd., Prague, Czech Republic). For the further details regarding active ingredients and its concentrations in the tested baits see Table 1. The experimental design included the available baits representing three categories of anticoagulant active substances classification: first generation (warfarin), less potent second generation (bromadiolone) and most potent second generation (brodifacoum, difethialone).

Table 1.
Overview and characterization of rodenticide baits included in the house mouse choice and no-choice feeding trials.
Differences in times to death among the examined baits were analyzed separately for the no-choice and choice feeding test using ANOVA. Because differences were not observed between sexes, data for males and females were pooled for further analysis. The Tukey test was applied for post hoc comparisons. To compare the effect of feeding tests on survival, the times to death were further compared between the no-choice and choice feeding test for each bait separately by a two-sample t-test.
The same procedures were used for evaluation of bait consumption. Individual consumption of food per experiment was expressed as the amount of the consumed food per day and per gram of individual body weight.
All calculations were performed using Statistica 14.0.0.15 (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA; 2020).
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy and Time to Death
All control individuals survived the experiment and all experimental mice in no-choice feeding tests died during the experiment (100% mortality for all tested baits). There were two experimental mice in choice feeding tests that survived the experiment (a female fed Kumatox G, a male fed Norat ATG bait). The achieved mortality for those baits was 91.7%; for the remaining ones was 100%.
The times to death in the no-choice feeding test (mean = 7.0; range 3–21 days) were not affected by factors sex (F(1,80) = 0.18, p > 0.05), type of bait (F(7,80) = 1.47, p > 0.05) nor sex*type of bait interaction (F(7,80) = 1.08, p > 0.05).
The times to death in the choice feeding test (mean = 7.6, range 3–15 days) differed significantly among the examined baits (F(7,77) = 3.48, p = 0.003). The factors sex (F(1,77) = 0.77, p > 0.05) and sex*type of bait interaction (F(7,79) = 0.73, p > 0.05) remained insignificant. Tukey post hoc test revealed significantly higher time to death in Lanirat G (sugar) than in following four baits: Baraki G (fish flour), Hubex B, Lanirat G (fish flour) and Norat ATG (p = 0.007, 0.019, 0.007 and 0.014, respectively); Table 2, Figure 1.

Table 2.
Times to death achieved in no-choice and choice laboratory feeding tests with house mice. Data are presented as means ± SD; significance at the level p < 0.05.
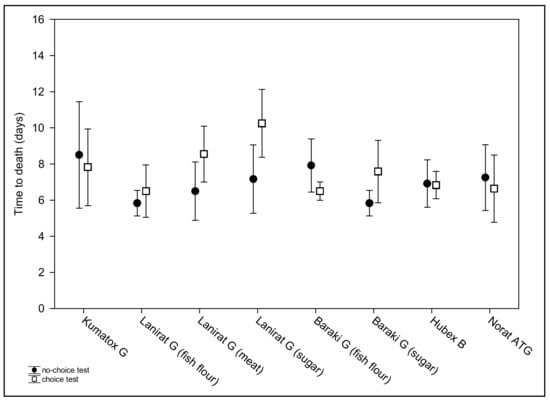
Figure 1.
Average times to death of the tested house mice following consumption of baits either in no-choice (filled circles) or choice (empty squares) feeding trials. Data are presented as means and 95% CI.
To compare the effect of feeding tests on survival, the times to death were compared between the no-choice and choice feeding test for each type of bait. The times to death between the feeding tests differed significantly only in the case of bait Lanirat G (sugar): t = 2.54, p = 0.02 (higher time to death in the choice test) but approached significance in Baraki G (fish flour): t = −2.00, p = 0.057 (higher time to death in the no-choice test); Baraki G (sugar): t = 2.07, p = 0.051; and Lanirat G (meat–bone flour): t = 2.02, p = 0.056; with higher time to death in the choice test in both baits; Table 2, Figure 1.
3.2. Bait Intake
To compare bait intake among individuals, the amount of the consumed bait was expressed per day and per gram of individual body weight (bw). In the no-choice feeding test, consumption was not affected by the studied factors: sex (F(1,80) = 1.21, p > 0.05), type of bait (F(7,80) = 1.54, p > 0.05) nor sex*type of bait interaction (F(7,80) = 0.72, p > 0.05). Mice consumed similar amounts of all tested rodenticide baits, mean 122.7 ± 39.9 g/g of bw.
In the choice feeding test, consumption was not affected by factors sex (F(1,77) = 0.45, p > 0.05) nor sex*type of bait interaction (F(7,77) = 1.27, p > 0.05), but mice consumed significantly different amounts of tested baits (F(7,77) = 4.05, p < 0.001). Mice fed the bait Lanirat G (fish flour) consumed a significantly higher amount of this bait than those fed the baits Baraki G (fish flour) (p < 0.001), Lanirat G (meat–bone flour) (p < 0.05) or Norat ATG (p = 0.003); all other comparisons remained nonsignificant (for means see Table 3).

Table 3.
Bait and active ingredient dosage intake by house mice in the no-choice and choice feeding tests. Data on active ingredients have to be considered with regard to the nominal concentration in the baits (see under Table 1). Data are presented as means ± SD; significance at the level p < 0.05.
Mean values of corresponding dosages of ingested active substances expressed per day and body weight are shown in Table 3. As there were three various concentration of active substances (see Table 1), the data were not statistically compared.
Further, the bait consumption was evaluated between the no-choice and choice feeding test for each type of bait. Bait intake differed significantly between the feeding tests in the case of baits Baraki G (fish flour): t = −2.44, p < 0.05; Kumatox G: t = −2.14, p < 0.05; Lanirat G (meat–bone flour): t = −2.17, p < 0.05; Lanirat G (sugar): t = −2.21, p < 0.05; and Norat ATG: t = −2.92, p < 0.01. The intake of the remaining three baits did not differ between the no-choice and choice feeding test; for all means, see Table 3.
In choice feeding tests, the tested baits were preferred over the standard diet (i.e., proportions of bait exceed 50% of total consumption) in all preparations: Kumatox G—59%, Lanirat G (fish flour)—89%, Lanirat G (meat–bone flour)—86%, Lanirat G (sugar)—85%, Baraki G (fish flour)—74%, Baraki G (sugar)—79%, Hubex B—74%, Norat ATG—53%.
4. Discussion
Efficacy evaluation trials belong to the mandatory data input for the purpose of registration and/or authorization of each rodenticide product before its introduction to the EU market. There are two basic methodical approaches for evaluating bait efficacy of anticoagulant rodenticide baits with experimental animals/rodents. While the no-choice feeding tests are used for evaluating the susceptibility to active substances, the choice feeding tests serve for evaluation of bait palatability.
This methodical study brings the side-by-side evaluation of the no-choice and choice tests in vast array of baits. In most cases, we detected insignificant differences in survival of house mice fed eight different baits within the no-choice and choice feeding tests (Table 2), which shows that various rodenticide baits display nearly identical outcomes in the susceptible mice. Our comprehensive study provided testing of anticoagulant rodenticide baits with various active substances, bait formulae and flavors.
Both no-choice and choice rodent feeding tests have been used during the development of the new active substances in the past, e.g., [21]. Our approach provided the first side-by-side comparisons of both tests for testing multiple rodenticide active ingredients and flavors/formulations. It also suggested a possibly new application of these tests in the present. It was similar with the idea previously described by Pitt et al. [23] in their work that examined a wide range of rodenticide active substances in three rodent species including house mice. They initially used the choice tests to determine the palatability of nine baits based on both acute and anticoagulant active substances. In the case of low mortality of the tested individuals, a no-choice test was consequently applied to distinguish between low palatability of the bait and rodenticide resistance to the active substance. However, as the no-choice tests were applied in only two of nine baits, this work did not provide side-by-side evaluation of all initially examined baits.
In spite of uniformed results and behavioral/feeding reaction in most of the tested baits there were some individuals that exhibited prolonged times to death (in both no-choice and choice feeding tests) and two mice which survived the experiment (in the choice feeding test). A tendency to prolong survival associated with sufficient bait consumption was detected for warfarin-based bait (Kumatox G), and one of the tested house mouse individuals survived the experiment; in spite of that it consumed a large amount of the bait. These findings indicated decreased susceptibility or even resistance to warfarin in some of the tested individuals. However, it was not surprising, since resistance for the first generation anticoagulant was reported to be widespread in several EU countries [7]. The second surviving individual of house mice was recorded for the choice test with Norat ATG bait (brodifacoum-based bait); nevertheless, this individual did not accept the bait (consumed only a little amount of the bait per 21 experimental days).
We can generally conclude that mice willingly consumed large amount of the bait in the no-choice tests (i.e., the amount similar to what was obtained for the choice tests). Our results indicate that they may be useful for quick comparative screenings of commercial baits on house mice. If new formulations were being tested, choice tests would be more likely to show if there were palatability issues or active ingredient issues. It further should be stressed that the implications from our no-choice tests should not be extrapolated beyond what was tested in our species, strain and laboratory conditions. Various house mouse field strains may show behavioral differences [25,26] or feeding preferences, or presence of alternative foods may lead to decreased mortality [24]. We cannot exclude that the various degree of resistance may also affect the outcome of the experimental testing regarding efficacy, e.g., [23]. Another rodent species (e.g., brown and black rats) may have different behavioral reaction to a particular bait and/or sensitivity to the identical active ingredient than house mice. Mice were, for example, reported by some studies to be more tolerant to anticoagulants than rats [27,28]. Additionally, feeding behavior and level of neophobia differ among the three commensal rodents, when both brown and black rats are known for their naturally neophobic behavior as they avoid a new food [29,30,31].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.F., R.A. and V.S.; Methodology, M.F. and R.A.; Formal Analysis, M.F.; Data Curation, M.F. and R.A.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.F. and V.S.; Writing—Review and Editing, M.F., R.A. and V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic (grant number MZe RO0418) and the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports (HR Award project: Strengthening strategic management of science and research in the CRI, p.r.i. (project registration no.: CZ.02.2.69/0.0/0.0/18_054/0014700)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This study was carried out in strict accordance with the Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes and Czech national legislation (Act No. 246/1992 Coll., on the protection of animals against cruelty, as amended). The experimental protocols were approved by the local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic (permits number 15430/2008-17210, 3886/2009-17210, 76668/2011-MZE).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Z. Brázdová for the help with maintaining animals in the breeding facility and helping with the experiments. We thank the reviewers for insightful comments that helped to improve the previous version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Buckle, A.; Smith, R. Rodent Pests and Their Control, 2nd ed.; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Frankova, M.; Kaftanova, B.; Aulicky, R.; Rodl, P.; Frynta, D.; Stejskal, V. Temporal production of coloured faeces in wild roof rats (Rattus rattus) following consumption of fluorescent non-toxic bait and a comparison with wild R. norvegicus and Mus musculus. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 81, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckle, A.; Eason, C. Control methods: Chemical. In Rodent Pests and Their Control, 2nd ed.; Buckle, A., Smith, R., Eds.; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2015; pp. 123–154. [Google Scholar]
- Aulicky, R.; Tkadlec, E.; Suchomel, J.; Frankova, M.; Heroldova, M.; Stejskal, V. Management of the common vole in the Czech lands: Historical and current perspectives. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy, R.J.; Shepherd, D.S.; Inglis, I.R. Bait avoidance and effectiveness of anticoagulant rodenticides against warfarin- and difenacoum-resistant populations of Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus). Crop Prot. 1992, 11, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; Brown, P.R.; Van de Weyer, N.; Robinson, F.; Hinds, L.A. Effects of background food on alternative grain uptake and zinc phosphide efficacy in wild house mice. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, C.F.; McGilloway, D.A.; Buckle, A.P. Anticoagulant rodenticides and resistance development in rodent pest species—A comprehensive review. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2020, 88, 101688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankova, M.; Stejskal, V.; Aulicky, R. Suppression of food intake by house mouse (Mus musculus) following ingestion of brodifacoum-based rodenticide bait. Crop Prot. 2017, 100, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, V.; Vendl, T.; Aulicky, R.; Athanassiou, C. Synthetic and natural insecticides: Gas, liquid, gel and solid formulations for stored-product and food-industry pest control. Insects 2021, 12, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankova, M.; Stejskal, V.; Aulicky, R. Efficacy of rodenticide baits with decreased concentrations of brodifacoum: Validation of the impact of the new EU anticoagulant regulation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ECHA. Guidance on the Biocidal Products Regulation: Volume II Efficacy—Assessment and Evaluation (Parts B + C), Version 4.0. 2021. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/2324906/bpr_guidance_assessment_evaluation_part_vol_ii_part_bc_si.pdf/82523dd9-f251-d69e-338d-c3d1ac6b4db7?t=1639124056526 (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- EPPO Standards PP1/144 (2); Efficacy Evaluation of Rodenticides. Field Tests against Synanthropic Rodents (Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, R. rattus). European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO): Paris, France, 1998.
- Pelz, H.J.; Prescott, C.V. Resistance to anticoagulant rodenticides. In Rodent Pests and Their Control, 2nd ed.; Buckle, A., Smith, R., Eds.; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2015; pp. 187–208. [Google Scholar]
- Blažić, T.; Jokić, G.; Götz, M.; Esther, A.; Vukša, M.; Đedović, S. Brodifacoum as a first choice rodenticide for controlling bromadiolone-resistant Mus musculus. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2018, 79, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.G.; Curtis, P.D.; Dunn, J.A.; Austic, R.E.; Richmond, M.E. Field evaluation of capsaicin as a rodent aversion agent for poultry feed. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukeinen, D.E.; Rampaud, M. A review of brodifacoum efficacy in the US and worldwide. In Proceedings of the 12th Vertebrate Pest Conference, 12th Vertebrate Pest Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–6 March 1986; Salmon, T.P., Ed.; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1986; pp. 16–50. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, C.E.; Booth, L.H. Palatability of rodent baits to wild house mice. Sci. Conserv. 2001, 184, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Morriss, G.C.; O’Connor, A.A.; Fisher, P. Factors influencing palatability and efficacy of toxic baits in ship rats, Norway rats and house mice. Sci. Conserv. 2008, 282, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Guidobono, J.S.; Leon, V.; Gomez Villafane, I.E.; Busch, M. Bromadiolone susceptibility in wild and laboratory Mus musculus L. (house mice) in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, G.W.; Moulton, R.S. Improving invasive house mice control and eradication strategies via more effective rodenticides. In Proceedings of the 26th Vertebrate Pest Conference, 26th Vertebrate Pest Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–6 March 2014; Timm, R.M., O’Brien, J.M., Eds.; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, F.P.; Bradfield, A. Trials of the anticoagulants rodenticide WBA 8119 against confined colonies of warfarin-resistant house mice (Mus musculus L.). J. Hyg. 1976, 77, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuthbert, R.J.; Visser, P.; Louw, H.; Ryan, P.G. Palatability and efficacy of rodent baits for eradicating house mice (Mus musculus) from Gough Island, Tristan da Cunha. Wildl. Res. 2011, 38, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, W.C.; Driscoll, L.C.; Sugihara, R.T. Efficacy of rodenticide baits for the control of three invasive rodent species in Hawaii. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kappes, P.J.; Siers, S.R.; Leinbach, I.L.; Sugihara, R.T.; Jolley, W.J.; Plissner, J.H.; Flint, E.N.; Goodale, K.L.; Howald, G.R. Relative palatability and efficacy of brodifacoum-25D conservation rodenticide pellets for mouse eradication on Midway Atoll. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 1375–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, P.; Singleton, G.R.; Price, W.J. Can social behaviour influence food preference of wild mice, Mus domesticus, in confined field populations? Aust. J. Zool. 1996, 44, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.E.; Sibly, R.M.; Meehan, A.P. Cereal aversion in behaviourally resistant house mice in Birmingham, UK. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2000, 66, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P. Review of House Mouse (Mus musculus) Susceptibility to Anticoagulant Poisons; DOC Science Internal Series; Department of Conservation: Wellington, New Zealand, 2005; Volume 198, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Buckle, A.; Prescott, C. The Current Status of Anticoagulant Resistance in Rats and Mice in the UK; Report from the Rodenticide Resistance Action Group of the United Kingdom to the Health and Safety Executive, Rodenticide Resistance Action Group: Reading, UK, 2012; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, L.K.P.; Clark, N.M. Bait avoidance and habitat use by the roof rat, Rattus rattus, in a piggery. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2005, 55, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlinska, K.; Stryjek, R.; Pisula, W. Food neophobia in wild and laboratory rats (multi-strain comparison). Behav. Processes 2015, 113, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modlinska, K.; Stryjek, R. Food neophobia in wild rats (Rattus norvegicus) inhabiting a changeable environment—A field study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).

