Breeding Novel Rice Hybrids for Aerobic Ecology: A Way Out from Global Warming and Water Crisis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Planting Materials
Experimental Locations
2.2. Layout and Experimental Design
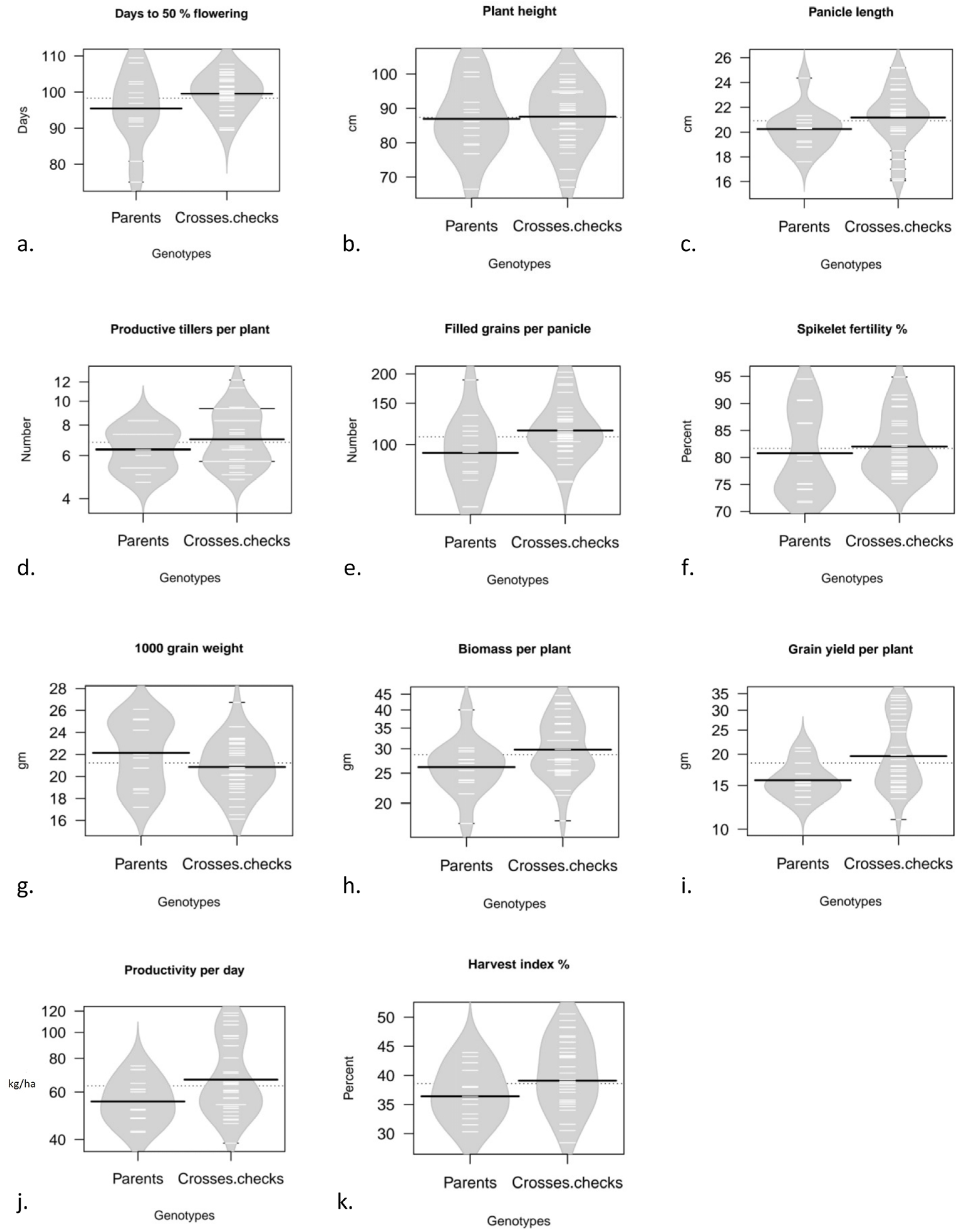
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Visualization and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Degenkolbe, T.; Thi, P.; Kopka, J.; Zuther, E.; Hincha, D.K.; Köhl, K. Identification of Drought Tolerance Markers in a Diverse Population of Rice Cultivars by Expression and Metabolite Profiling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illukpitiya, P.; Samonte, S.O.P.B.; Wilson, L.T. Aerobic Rice: Production Inputs and Breeding Selection Criteria. Tex. Rice 2009, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tuong, T.P.; Bouman, B.A.M. Rice production in water-scare environments. In Water Productivity in Agriculture: Limits and Opportunities for Improvement; Kijne, J.W., Barker, R., Molden, D.J., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.; Olesen, J.E. Synergies between the Mitigation of, and Adaptation to, Climate Change in Agriculture. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 148, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlin, G.N.; Lafitte, H.R.; Tao, D.; Laza, M.; Amante, M.; Courtois, B. Developing Rice Cultivars for High-Fertility Upland Systems in the Asian Tropics. Field Crops Res. 2006, 97, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeba, A.; Vivekanandan, P.; Veerabadran, V. Identification of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Genotypes for Aerobic Condition under Different Water Regimes. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2005, 65, 287–289. [Google Scholar]
- Amudha, K.; Thiyagarajan, K.; Sakthivel, N. Aerobic Rice: A Review. Agric. Rev. 2009, 30, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R. Aerobic rice systems. Adv. Agron. 2011, 111, 207–247. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, R.V.; Rudresh, N.S.; Shivamurthy, M.; Hittalmani, S. Performance and Adoption of New Aerobic Rice Variety MAS 946-1 (Sharada) in Southern Karnataka. Karnataka J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 25, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Chinnusamy, V. Aerobic rice: A success story. Ind. Farm. 2007, 57, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kampstra, P. Beanplot: A Boxplot Alternative for Visual Comparison of Distributions. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempthorne, O. An Introduction to Genetic Studies; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.H.; Reddy, C.R.; Dayton, A.D. Heterosis, Inbreeding Depression, and Heritability Estimates in a Systematic Series of Grain Sorghum Genotypes. Crop Sci. 1972, 12, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhart, S.A.; Russell, W.A. Stability Parameters for Comparing Varieties. Crop Sci. 1966, 6, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breese, E.L. The Measurement and Significance of Genotype-Environment Interactions in Grasses. Heredity 1969, 24, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, K.; Wilkinson, G. The Analysis of Adaptation in a Plant-Breeding Programme. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1963, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidaiah, P.; Ramesha, M.S.; Kumar, S.S. Line x tester Analysis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Madras Agric. J. 2010, 97, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Parimala, C. Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agricultural University, Hyderabad, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Saidaiah, P.; Ramesha, M.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Suresh, J. Combining Ability Analysis for Yield and Yield Component Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Res. ANGRAU 2011, 39, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, B.; Lal, G.M. Combining Ability Analysis for Yield and Yield Components in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2015, 6, 360–365. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.; Kulsum, M.U.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahmat, N.M.F. Combining Ability Analysis for Identifying Elite Parents for Heterotic Rice Hybrids. Acad. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 3, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, G.; Sujatha, M.; Senguttuvel, P.; Subramanyam, D. Combining Ability Analysis for Grain Yield and its Component Traits in Aerobic Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 7, 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Thakare, A.K.; Mehta, A.M.; Patel, J.S.; Takle, S.R. Combining Ability Analysis for Yield and Grain Quality Traits in Rice Hybrids. J. Rice Res. 2010, 3, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Padmavathi, P.V.; Satyanarayana, P.V.; Ahmed, M.L.; Rani, A.; Rao, V.S. Combining Ability Studies for Yield and Yield Components in Hybrid Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2012, 3, 836–842. [Google Scholar]
- Ghara, A.G.; Nematzadeh, G.; Morteza Oladi, N.B.; Bagheri, A. Heritability and Heterosis of Agronomic Traits in Rice Lines. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2014, 3, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, M.A. Combining Ability Studies in Rice Hybrids Involving New CMS Lines in Bangladesh. Agric. Sci. Dig. 2016, 29, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, C. Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Master’s Thesis, Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agricultural University, Hyderabad, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, D.K.; Pandey, M.P. Gene Action and Heterosis for Yield and Associated Traits in Indica and Tropical Japonica Crosses of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Involving Wide Compatibility Gene(s). Int. J. Plant Breed. Genet. 2012, 6, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghera, G.S.; Hussain, W. Gene Action and Combining Ability Studies Using CMS System for Developments of Hybrid Rice under Temperate Conditions. Am. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 1, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.N.; Jaiswal, H.K. Combining Ability Analysis for Yield and Earliness in Hybrid Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Crop Sci. 2015, 7, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, W.; Sanghera, G.S. Exploitation of Heterosis in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Using CMS System under Temperate Conditions. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2012, 3, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, R.; Chandra Babu, R.; Gomez, S.M.; Shanmugasundaram, P. Genetic Analysis of Yield Traits in Rice under Irrigated and Water Stress Environments. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2013, 73, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, S.; Pandey, D.P.; Singh, D.K. Gene Action and Combining Ability Studies in Rice. ORYZA-Int. J. Rice 2014, 51, 162–164. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, G.K.; Satyanarayana, P.V.; Rao, C.P.; Rao, V.S. Combining Ability for Yield Components and Quality Traits in Hybrid Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Andhra Agric. J. 2010, 57, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Jarwar, A.D.; Cruz, S.J.G.; Jarwar, M. Gene Action of Some Agronomic, Yield and Quality Characters in Aromatic Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Varieties and Their F1 Hybrids under Lowland and Upland Environments. Pak. J. Agric. Agric. Eng. Vet. Sci. 2014, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, M.A. Study of Nature and Magnitude of Gene Action in Hybrid Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) through Experiment of Line X Tester Mating Design. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2016, 2, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, M.; Shanthi, P.; Selvi, B.; Ravi, V.; Raveendran, M.; Vijayalakshmi, C. Combining Ability Studies for Yield and Yield Contributing Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Green Farming 2016, 7, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Dharwal, G.; Verma, O.P.; Verma, G.P. Combining Ability Analysis for Grain Yield and Other Associated Traits in Rice. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2017, 5, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Netam, H.K. Studies on Grain Yield Components in NPT Lines of Rice to Develop Super Rice Hybrid. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 589–590. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, K.; Jaiswal, H.K.; Waza, S.A. Combining Ability and Heterosis for Yield, Its Component Traits and Some Grain Quality Parameters in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2014, 6, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.M.; Patel, V.J.; Chaudhari, M.H.; Desai, N.M. Heterosisand Heterobeltiosis for Grain Yield and Yield Attributing Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Bioinfolet 2015, 12, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Srijan, A. Studies on Combining Ability and Blast Resistance in Hybrid Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Master’s Thesis, Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agricultural University, Hyderabad, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Srijan, A.; Kumar, S.S.; Raju, C.D.; Jagadeeshwar, R. Heterosis Studies in Rice for the Identification of Better Hybrids for Telangana, India. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2016, 8, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srijan, A.; Kumar, S.S.; Raju, C.D. Studieson Gene Action and Combining Ability in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Ecol. 2016, 34, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar]
- Madhukar, P. Stability Analysis of Pre-Release and Released Rice Hybrids for Grain Yield and Quality Characters. Master’s Thesis, Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agricultural University, Hyderabad, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saidaiah, P.; Kumar, S.S.; Ramesha, M.S. Stability Analysis of Rice Hybrids and Parents. Indian Agric. 2010, 54, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Sreedhar, S.; Reddy, T.D.; Ramesha, M.S. Genotype X Environment Interaction and Stability for Yield and Its Components in Hybrid Rice Cultivars. (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Plant Breed. Genet. 2011, 5, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banumathy, S.; Sheeba, N.; Shanthi, P.; Manimaran, R.; Agila, R. Assessment of Yield Stability of Rice Genotypes through Stability Analysis. J. Rice Res. 2016, 9, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Waghmode, B.D.; Mehta, H.D. Genotype X Environment Interaction and Stability Analysis in Hybrid Rice. Crop Improv. 2011, 38, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
| (a) | ||
| S. No. | Parental Lines | Source |
|---|---|---|
| CMS Lines | ||
| L01 | IR-79156B | IRRI, Philippines |
| L02 | APMS-6B | RARS, Maruteru (ANGRAU) |
| L03 | IR-68897B | IRRI, Philippines |
| Restorer lines | ||
| T01 | ATR-177 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T02 | ATR-186 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T03 | ATR-216 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T04 | ATR-372 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T05 | ATR-374 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T06 | ATR-375 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T07 | KS-22 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T08 | KS-24 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T09 | AR-19–18 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| T10 | HRSV-7 | IIRR, Hyderabad |
| Checks | ||
| 1 | CR Dhan-201 | NRRI, Cuttak (varietal check) |
| 2 | GK 5022 | Early duration, hybrid check |
| (b) | ||
| Measurement | Unit | Description |
| Days to 50% flowering | DFF (Number) | The total number of days taken from the date of sowing to extrusion of the panicle tip above the sheath of the flag leaf in 50% of plants in a plot. |
| Plant height | PH (cm) | It was measured at maturity from the base of the plant to the tip of the main panicle and expressed in cm. |
| Panicle length | PL (Number) | It was measured as the length of the panicle from the base to the tip in cm. |
| Number of productive tillers per plant | PT (Number) | The number of tillers in a plant that bears panicles was recorded as the number of productive tillers per plant at maturity. |
| Number of filled grains per panicle | FG (Number) | The number of filled grains per panicle was counted and recorded. |
| Spikelet fertility | SF (%) | The spikelet fertility percent was calculated as the ratio of filled grains per panicle to the total number of grains in a panicle and was expressed as a percentage. |
| 1000 grain weight | TGW (g) | Thousand-filled grains were randomly counted, and the weight was recorded in grams with the help of electronic balance. |
| Biomass | BM (g) | Biomass (above ground), which refers to the total yield of plant material without economic yield, was recorded in grams. |
| Grain yield per plant | GY (g) | At maturity, single plants were harvested, threshed, cleaned, and dried to 12% moisture content, and the weight was recorded in grams. |
| Productivity per day | PDP (kg/ha) | It is the ratio of grain yield in kilograms of a parent /hybrid per hectare to the number of days to its maturity and expressed in kilograms per hectare. |
| Harvest index | HI (%) | Harvest index measured crop yield as the ratio of economical yield, i.e., grain yield per plant, to biological yield (grain plus biomass yield per plant). |
| Character | Source of Variation and (df) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replication-2 | Genotypes-44 | Error-88 | |||||||
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E1 | E2 | E3 | |
| DFF | 0.31 | 3.02 | 0.71 | 114.33 ** | 132.41 ** | 211.84 ** | 3.48 | 3.00 | 3.75 |
| PH | 1.53 | 1.74 | 4.18 | 246.27 ** | 271.49 ** | 281.06 ** | 1.76 | 2.24 | 2.83 |
| PL | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 12.87 ** | 14.98 ** | 14.48 ** | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.13 |
| PT | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.35 ** | 10.47 ** | 9.61 ** | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| FG | 0.22 | 2.78 | 7.47 | 3824.77 ** | 3788.74 ** | 3702.19 ** | 4.11 | 3.52 | 3.85 |
| SF | 0.68 | 1.88 | 3.82 | 148.20 ** | 115.15 ** | 108.74 ** | 3.13 | 3.10 | 2.80 |
| TGW | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 20.75 ** | 20.85 ** | 20.96 ** | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| BM | 0.54 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 129.46 ** | 129.63 ** | 122.16 ** | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.38 |
| GY | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 127.90 ** | 131.00 ** | 113.38 ** | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.13 |
| PPD | 3.50 | 0.62 | 4.42 | 1533.70 ** | 1451.80 ** | 1168.95 ** | 1.39 | 1.59 | 1.92 |
| HI | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 105.19 ** | 110.60 ** | 127.48 ** | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.31 |
| Character | Location | σ2gca | σ2sca | σ2gca/σ2sca | Gene Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFF | Rajendranagar | 2.02 | 18.03 | 0.11 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 2.33 | 18.92 | 0.12 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 4.52 | 30.32 | 0.15 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 2.60 | 20.86 | 0.12 | Non-additive | |
| PH | Rajendranagar | 17.69 | 43.15 | 0.41 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 18.73 | 47.75 | 0.39 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 17.19 | 46.83 | 0.37 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 17.78 | 45.96 | 0.39 | Non-additive | |
| PL | Rajendranagar | 0.57 | 5.47 | 0.10 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 0.70 | 6.36 | 0.11 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 0.71 | 6.43 | 0.11 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 0.66 | 6.10 | 0.11 | Non-additive | |
| PT | Rajendranagar | 1.69 | 1.89 | 0.90 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 2.07 | 2.37 | 0.87 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 1.96 | 2.21 | 0.89 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 1.90 | 2.14 | 0.89 | Non-additive | |
| FG | Rajendranagar | 262.92 | 621.79 | 0.42 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 262.34 | 604.36 | 0.43 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 246.11 | 601.61 | 0.41 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 257.04 | 608.69 | 0.42 | Non-additive | |
| SF | Rajendranagar | 9.62 | 19.14 | 0.50 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 14.76 | 14.82 | 0.99 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 12.71 | 19.63 | 0.65 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 12.30 | 17.93 | 0.69 | Non-additive | |
| TGW | Rajendranagar | 0.77 | 4.55 | 0.17 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 0.96 | 5.44 | 0.18 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 0.71 | 5.47 | 0.13 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 0.79 | 5.01 | 0.16 | Non-additive | |
| BM | Rajendranagar | 8.85 | 39.04 | 0.23 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 8.50 | 39.06 | 0.22 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 7.98 | 36.59 | 0.22 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 8.42 | 38.22 | 0.22 | Non-additive | |
| GY | Rajendranagar | 12.25 | 36.44 | 0.34 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 13.26 | 37.13 | 0.36 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 10.76 | 31.37 | 0.34 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 12.05 | 34.84 | 0.35 | Non-additive | |
| PDP | Rajendranagar | 144.64 | 437.87 | 0.33 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 139.36 | 405.95 | 0.34 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 104.81 | 307.45 | 0.34 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 128.66 | 379.45 | 0.34 | Non-additive | |
| HI | Rajendranagar | 6.01 | 30.00 | 0.20 | Non-additive |
| Warangal | 6.85 | 29.63 | 0.23 | Non-additive | |
| Kampasagar | 11.65 | 35.89 | 0.32 | Non-additive | |
| Pooled | 7.28 | 27.08 | 0.27 | Non-additive |
| S. No. | Character | Contribution | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line (%) | Tester (%) | Lines × Tester (%) | ||
| 1 | DFF | 38.29% | 59.48% | 2.24% |
| 2 | PH | 58.14% | 35.18% | 6.68% |
| 3 | PL | 28.32% | 67.40% | 4.28% |
| 4 | PT | 30.07% | 33.55% | 36.37% |
| 5 | FG | 62.79% | 31.78% | 5.42% |
| 6 | SF | 19.47% | 42.96% | 37.57% |
| 7 | TGW | 42.21% | 54.77% | 3.02% |
| 8 | BM | 38.75% | 53.00% | 8.25% |
| 9 | GY | 42.26% | 44.78% | 12.97% |
| 10 | PDP | 44.44% | 43.93% | 11.63% |
| 11 | HI | 46.65% | 45.90% | 7.44% |
| S. No. | Crosses | Heterosis | Heterobeltiosis | Standard Heterosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR Dhan 201 | GK 5022 | ||||
| DFF | |||||
| H27 | IR-68897A × KS-22 | −2.25 ** | −12.50 ** | −0.25 | −6.83 ** |
| PH | |||||
| H30 | IR-68897A × HRSV-7 | −8.00 ** | −15.41 ** | −31.36 ** | −18.27 ** |
| H21 | IR-68897A × ATR-177 | −8.39 ** | −18.05 ** | −29.32 ** | −15.83 ** |
| H10 | IR-79156A × HRSV-7 | −7.47 ** | −8.96 ** | −26.14 ** | −12.05 ** |
| H07 | IR-79156A × KS-22 | −8.77 ** | −16.22 ** | −21.36 ** | −6.36 ** |
| PL | |||||
| H27 | IR-68897A × KS-22 | 24.66 ** | 18.41 ** | 13.37 ** | 16.71 ** |
| H08 | IR-79156A × KS-24 | 25.88 ** | 21.46 ** | 13.18 ** | 16.51 ** |
| H28 | IR-68897A × KS-24 | 22.01 ** | 17.41 ** | 9.40 ** | 12.62 ** |
| H15 | APMS-6A × ATR-374 | 17.28 ** | 17.00 ** | 7.14 ** | 10.29 ** |
| H01 | IR-79156A × ATR-177 | 27.17 ** | 21.68 ** | 5.42 ** | 8.52 ** |
| PT | |||||
| H18 | APMS-6A × KS-24 | 98.20 ** | 66.68 ** | 115.66 ** | 86.39 ** |
| H15 | APMS-6A × ATR-374 | 78.91 ** | 54.53 ** | 99.94 ** | 72.81 ** |
| H04 | IR-79156A × ATR-372 | 61.87 ** | 49.10 ** | 66.63 ** | 44.02 ** |
| H20 | APMS-6A × HRSV-7 | 27.29 ** | 27.29 ** | 64.69 ** | 42.34 ** |
| FG | |||||
| H20 | APMS-6A × HRSV-7 | 90.74 ** | 78.31 ** | 54.55 ** | 107.59 ** |
| H04 | IR-79156A × ATR-372 | 84.54 ** | 45.49 ** | 46.96 ** | 97.40 ** |
| SF | |||||
| H04 | IR-79156A × ATR-372 | 11.21 ** | 1.17 | 6.15 ** | −3.52 ** |
| TGW | |||||
| H11 | APMS-6A × ATR-177 | 26.25 ** | 6.30 ** | 38.48 ** | 13.91 ** |
| H07 | IR-79156A × KS-22 | 12.30 ** | −2.68 * | 27.07 ** | 4.52 ** |
| BM | |||||
| H15 | APMS-6A × ATR-374 | 51.41 ** | 50.56 ** | 80.91 ** | 23.15 ** |
| H14 | APMS-6A × ATR-372 | 53.78 ** | 43.80 ** | 70.84 ** | 16.30 ** |
| GY | |||||
| H20 | APMS-6A × HRSV-7 | 94.17 ** | 62.44 ** | 109.43 ** | 12.86 ** |
| H18 | APMS-6A × KS-24 | 99.93 ** | 59.17 ** | 105.21 ** | 10.59 ** |
| H04 | IR-79156A × ATR-372 | 131.13 ** | 119.25 ** | 99.21 ** | 7.36 ** |
| PPD | |||||
| H20 | APMS-6A × HRSV-7 | 90.08 ** | 62.54 ** | 95.44 ** | 10.69 ** |
| H04 | IR-79156A × ATR-372 | 131.21 ** | 122.76 ** | 91.11 ** | 8.24 ** |
| H18 | APMS-6A × KS-24 | 91.29 ** | 51.66 ** | 82.36 ** | 3.28 ** |
| HI | |||||
| H20 | APMS-6A × HRSV-7 | 28.79 ** | 20.01 ** | 29.91 ** | 10.54 ** |
| H22 | IR-68897A × ATR-186 | 25.23 ** | 20.99 ** | 26.98 ** | 8.05 ** |
| H24 | IR-68897A × ATR-372 | 30.56 ** | 26.77 ** | 24.04 ** | 5.54 ** |
| H18 | APMS-6A × KS-24 | 27.70 ** | 14.38 ** | 23.81 ** | 5.35 ** |
| Character | Locations | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rajendranagar | Warangal | Kampasagar | |
| DFF | −5.281 | −0.400 | 5.681 |
| PH | −4.040 | 0.138 | 3.901 |
| PL | −0.561 | 0.669 | −0.107 |
| PT | −0.286 | 0.602 | −0.316 |
| FG | −3.126 | −0.978 | 4.104 |
| SF | −1.221 | 0.218 | 1.003 |
| TGW | −0.19 | 0.094 | 0.096 |
| BM | −0.839 | −0.309 | 1.148 |
| GY | −0.873 | −0.105 | 0.978 |
| PPD | −0.320 | −0.159 | 0.479 |
| HI | −0.408 | 0.170 | 0.239 |
| Characters | X > X, bi = 1, S2di = 0 | bi > 1, S2di = 0 | bi < 1, S2di = 0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Stability | Suitable for Favorable Environments | Specifically Adapted to Poor Environments | ||
| DFF | P | L03 and T03 | T01 and T02 | - |
| C | H04, H05, H10, H27 and H30 | H17 and H18 | - | |
| PH | P | L01, L03, T06 and T10 | T04 | - |
| C | H07, H10, H13, H21, H22 and H30 | H14 and H15 | ||
| FG | P | T04 and T09 | L02 and T03 | - |
| C | H03, H04, H14, H16, H17, H18 and H20 | H05, H10, H19 and H21 | ||
| SF | P | - | - | - |
| C | - | H05, H20, H23, H27 and H30 | ||
| BM | P | T09 | - | - |
| C | H04, H15, H16 and H18 | H14 and H03 | ||
| GY | P | T02 | T05 | - |
| C | H04 and H20 | - | - | |
| PPD | P | L02 and T02 | - | - |
| C | - | H03 | H04, H15, H16 and H20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srijan, A.; Senguttuvel, P.; Dangi, K.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Sundaram, R.M.; Chary, D.S. Breeding Novel Rice Hybrids for Aerobic Ecology: A Way Out from Global Warming and Water Crisis. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092353
Srijan A, Senguttuvel P, Dangi KS, Kumar SS, Sundaram RM, Chary DS. Breeding Novel Rice Hybrids for Aerobic Ecology: A Way Out from Global Warming and Water Crisis. Agronomy. 2023; 13(9):2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092353
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrijan, Ambati, Ponnuvel Senguttuvel, Kuldeep Singh Dangi, Sagi Sudheer Kumar, Raman Meenakshi Sundaram, and Darshanoju Srinivasa Chary. 2023. "Breeding Novel Rice Hybrids for Aerobic Ecology: A Way Out from Global Warming and Water Crisis" Agronomy 13, no. 9: 2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092353
APA StyleSrijan, A., Senguttuvel, P., Dangi, K. S., Kumar, S. S., Sundaram, R. M., & Chary, D. S. (2023). Breeding Novel Rice Hybrids for Aerobic Ecology: A Way Out from Global Warming and Water Crisis. Agronomy, 13(9), 2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092353






