Bioavailability of Cd in Agricultural Soils Evaluated by DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model in Relation to Uptake by Rice and Tea Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
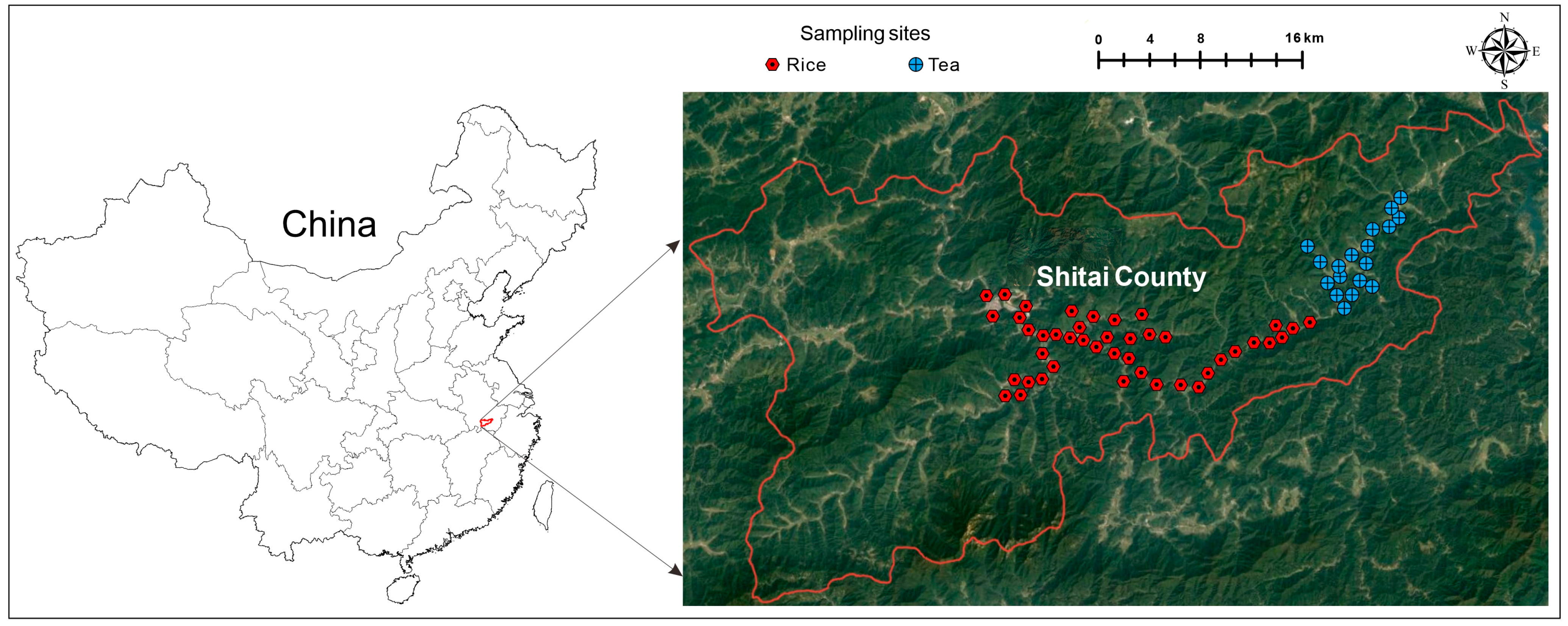
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentrations of Cadmium in Soils, Rice Grains and Tea Leaves
| Region | Anhui | Anhui | Jiangsu | Guizhou | Henan | Yunnan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop | rice | tea | rice | tea | rice | tea |
| n | 43 | 18 | 70 | 22 | 40 | 8 |
| pH | 6.33 | 5.39 | 6.10 | 4.30 | 5.90 | 4.48 |
| Total soil Cd | 0.737 | 0.417 | 0.970 | 0.330 | 0.124 | 0.079 |
| Crop Cd | 0.191 | 0.038 | 0.150 | 0.100 | 0.018 | 0.003 |
| BCF | 0.259 | 0.091 | 0.155 | 0.303 | 0.145 | 0.038 |
| Thresholds | 0.2 a | 1.0 b | 0.200 a | 1 b | 0.200 a | 1 b |
| Exceedance rate (%) | 32.5 | 0.0 | 30.6 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 0.0 |
| Reference | this study | this study | [8] | [38] | [33] | [39] |
3.2. Evaluation of Cd Bioavailability
3.3. Factors Controlling Cd Uptake by Rice and Tea
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.-J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil Contamination in China: Current Status and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Ji, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Theiss, F. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. Catena 2018, 175, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natasha; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Rashid, M.I. A critical review of selenium biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system with an inference to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 915–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupaie, E.H.; Eskicioglu, C. Health risk assessment of heavy metals through the consumption of food crops fertilized by biosolids: A probabilistic-based analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, T.; Bhagat, R. Trace elements in tea leaves, made tea and tea infusion: A review. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2234–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meharg, A.A.; Norton, G.; Deacon, C.; Williams, P.; Adomako, E.E.; Price, A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, F.-J.; McGrath, S.; et al. Variation in Rice Cadmium Related to Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5613–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, N.; Li, Y.W.; Cai, Q.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H. Cadmium in rice: Transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Saifullah Malhi, S.S.; Zia, M.H.; Naeem, A.; Bibi, S.; Farid, G. Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ji, J.; Shen, N.; Frost, R.L. Geological load and health risk of heavy metals uptake by tea from soil: What are the significant influencing factors? Catena 2021, 204, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, L.; Browne, P.; Yu, R. Effects of Soil Properties on the Transfer of Cadmium from Soil to Wheat in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China—A Typical Industry–Agriculture Transition Area. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2012, 148, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, D.; Hou, J.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Estimating cadmium availability to the hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola in a wide range of soil types using a piecewise function. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, A.; Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Fan, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Changes in surface soil organic/inorganic carbon concentrations and their driving forces in reclaimed coastal tidal flats. Geoderma 2019, 352, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, W.; Wei, N.; Liao, Q.; Huang, D.; Meng, X.; Song, Y. Influencing Factors of Elevated Levels of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils from Typical Karst Regions of China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, F.-J.; Davison, W. Distinguishing Diffusional and Plant Control of Cd and Ni Uptake by Hyperaccumulator and Nonhyperaccumulator Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6636–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhuo, X.; Guan, D.-X.; Song, Y.; Guo, C.; Ji, J. Evaluation of various approaches to predict cadmium bioavailability to rice grown in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 258, 113645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.N.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W.; Zhao, S.; Lu, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Q. Evaluation of in Situ DGT Measurements for Predicting the Concentration of Cd in Chinese Field-Cultivated Rice: Impact of Soil Cd:Zn Ratios. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8009–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almås, R.; Lombnæs, P.; Sogn, T.A.; Mulder, J. Speciation of Cd and Zn in contaminated soils assessed by DGT-DIFS, and WHAM/Model VI in relation to uptake by spinach and ryegrass. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.-X.; Zheng, J.-L.; Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W.; Ma, L.Q. A diffusive gradients in thin-films technique for the assessment of bisphenols desorption from soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World reference base for soil resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Z.; Yuan, L.; Hou, Y.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Liu, Y.; Pan, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, X. Spatial variations in soil selenium and residential dietary selenium intake in a selenium-rich county, Shitai, Anhui, China. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callesen, I.; Keck, H.; Andersen, T.J. Particle size distribution in soils and marine sediments by laser diffraction using Malvern Mastersizer 2000—Method uncertainty including the effect of hydrogen peroxide pretreatment. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of Holistic Approaches to Predicting the Concentrations of Metals in Field-Cultivated Rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7649–7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Hinojosa, R.P.; Föllmi, K.B.; Verrecchia, E.; Adatte, T.; Matera, V. Speciation and multivariable analyses of geogenic cadmium in soils at Le Gurnigel, Swiss Jura Mountains. Catena 2015, 125, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, J. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Chemosphere 2019, 245, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Cheng, H.; Ren, J.; Davison, W.; Zhang, H. Mechanistic Insights from DGT and Soil Solution Measurements on the Uptake of Ni and Cd by Radish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7305–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Xing, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Jia, M.; Hu, W.; Huang, B. Cadmium phytoavailability under greenhouse vegetable production system measured by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) and its implications for the soil threshold. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochaczewski, Ł.; Tych, W.; Davison, B.; Zhang, H. 2D DGT induced fluxes in sediments and soils (2D DIFS). Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Chopra, A.K.; Pathak, C. Accumulation of heavy metals in the vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated areas of Dehradun, India with reference to human health risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Shen, L.F.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, S.R. Uptake of toxic heavy metals by rice (Oryza sativa L.) cul-tivated in the agricultural soil near Zhengzhou City, People’s Republic of China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Luo, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; He, H.; Gong, Y.; Chen, M.; Wen, Y.; Ying, R. Geochemical Behaviors of Heavy Metal(loid)s in Soil Ferromanganese Nodules in Typical Karst Areas in Southwest China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrelli, D.; Caporale, A.G.; Adamo, P. Assessment of the Bioavailability and Speciation of Heavy Metal(loid)s and Hydrocarbons for Risk-Based Soil Remediation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB2762-2017; National Standards for Food Safety and Limits of Contaminants for Food. NHFPC and NMPA, National Health and Family Planning Commission and National Medical Products Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- NY 659-2003; Residue Limits for Chromium, Cadmium, Mercury, Arsenic and Fluoride in Tea. MARA, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.C.; Peng, Y.; Wen, X.; Ni, X. Distribution, accumulation, and potential risks of heavy metals in soil and tea leaves from geologically different plantations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Exposure and risk assessment for aluminum and heavy metals in Puerh tea. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Saint, C.; Kirkham, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lee, D.; Li, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; et al. Root Iron Plaque on Wetland Plants as a Dynamic Pool of Nutrients and Contaminants. Adv. Agron. 2016, 138, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.T.; Yao, A.J.; Cao, J.; Wu, Z.H.; Peng, Z.R.; Wang, S.Z.; Xiao, S.; Baker, A.J.M.; Qiu, L. Mitigation of Cd accumulation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) by Fe fertilization. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Cadmium Sorption and Desorption in Soils: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 489–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahervand, S.; Jalali, M. Sorption, desorption, and speciation of Cd, Ni, and Fe by four calcareous soils as affected by pH. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Xue, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Effect of the size of variable charge soil particles on cadmium accumulation and adsorption. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2810–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C.; Xiao, X.; He, Y. Factors influencing the effectiveness of liming on cadmium reduction in rice: A meta-analysis and decision tree analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 779, 146477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Adams, C.A.; Shi, Z.; Sun, Y. Combined effects of ZnO NPs and Cd on sweet sorghum as influenced by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.P.; Lv, X.Z.; Wang, G.Y. Effects of Se and Zn supplementation on the antagonism against Pb and Cd in vegetables. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Dai, H.; Cao, F.; Zhang, G.; Wu, F. Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Song, W. Cadmium transfer from contaminated soils to the human body through rice consumption in southern Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Niu, Y.; Fan, K.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zheng, S. Selenium-oxidizing Agrobacterium sp. T3F4 steadily colonizes in soil promoting selenium uptake by pak choi (Brassica campestris). Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 791, 148294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Measurements | Rice | Tea | Soil Properties | BCFrice | BCFtea | Soil Properties | BCFrice | BCFtea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGT and DIFS (CE) | 0.84 b | 0.79 b | pH | −0.42 b | −0.68 b | Zn | −0.49 b | 0.09 NS |
| Soil solution (Csolu) | 0.68 b | 0.71 b | SOC | −0.12 NS | 0.15 NS | Sand | −0.37 a | −0.57 a |
| DGT (CDGT) | 0.61 b | 0.66 a | CEC | −0.09 NS | −0.16 NS | Silt | 0.20 NS | −0.16 NS |
| MgCl2 extraction | 0.28 NS | 0.48 NS | Se | −0.41 b | −0.51 a | Clay | 0.39 a | 0.49 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, C.; Ji, W.; Huang, S.; Zhou, M.; Meng, X. Bioavailability of Cd in Agricultural Soils Evaluated by DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model in Relation to Uptake by Rice and Tea Plants. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092378
Wen Y, Wang Y, Tao C, Ji W, Huang S, Zhou M, Meng X. Bioavailability of Cd in Agricultural Soils Evaluated by DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model in Relation to Uptake by Rice and Tea Plants. Agronomy. 2023; 13(9):2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092378
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yubo, Yuanyuan Wang, Chunjun Tao, Wenbing Ji, Shunsheng Huang, Mo Zhou, and Xianqiang Meng. 2023. "Bioavailability of Cd in Agricultural Soils Evaluated by DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model in Relation to Uptake by Rice and Tea Plants" Agronomy 13, no. 9: 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092378
APA StyleWen, Y., Wang, Y., Tao, C., Ji, W., Huang, S., Zhou, M., & Meng, X. (2023). Bioavailability of Cd in Agricultural Soils Evaluated by DGT Measurements and the DIFS Model in Relation to Uptake by Rice and Tea Plants. Agronomy, 13(9), 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092378







