Abstract
Due to its broad yield-increasing effect and low cost, humic acid urea (HAU) has become one of the leading modified fertilizers worldwide. The fertisphere is the primary space where urea (U) granules participate in the soil nitrogen cycle, forming a nutrient concentration gradient centered on the point of fertilization. The closer the circle layers to the urea granule in the fertisphere, the higher the nitrogen concentration. However, HAU in this microregion remains poorly understood. The differences in the transformation process from the inside to outside circle layers of the U and HAU fertispheres were simulated and studied using soil incubation experiments under 20, 10, 2, 1, and 0.2 g kg−1 nitrogen inputs. The 20 and 10 g kg−1 inputs represent the layers closest to the urea granule. Within the first seven days, HAU treatment showed higher concentrations of soil ammonia-N content than U treatment within the two layers closest to the fertilizer core, while exhibiting lower concentrations under the farthest two layers. Under 2 g kg−1 nitrogen input, the nitrate nitrogen under the HAU treatment was significantly higher than that in the U treatment, indicating a higher nitrification rate. During the 42-day incubation period, soil mineral nitrogen content under the HAU treatment was higher than that for the U treatment in the two closest circles. On the 42nd day, the residual urea-N under the HAU treatment was significantly higher than that for the U treatment when the nitrogen input was higher than 1 g kg−1. The effect of higher fertilizer preservation and supply capacity of HAU in Fluvo-aquic soil was achieved by changing the urease activity and nitrification rate in fertisphere ranges closer to the fertilizer core. An improved understanding of the high-efficiency mechanism of HAU in the fertisphere process will contribute to the development of new-generation high-efficiency urea products.
1. Introduction
Urea (U) is the most consumed N fertilizer and is widely used to meet N nutrient requirements in agricultural production [1,2,3]. However, the nutrient use efficiency of common urea is approximately 50–70%, and the average urea utilization rate in China is only 30–40% [4,5,6]. When efficiency is low, farmers apply more urea to ensure crop production. This, in turn, causes even lower use efficiency and leads to unnecessary waste of urea. More importantly, the application of excessive urea to farmlands poses public environmental risks, as unused N nutrients can cause eutrophication of surface water, a decline in groundwater quality, and greenhouse gas emissions [7]. The world population continues to increase, and the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals are under pressure. However, to achieve global food security and environmental benefits, achieving 100% use efficiency of urea is a shared goal among agricultural scientists. In addition to perfecting fertilization techniques, developing more efficient urea products in combination with synergists is a more direct approach to improving the use efficiency of urea. In the fertilizer market, green high-efficiency urea products that have been industrialized are divided into four main categories: slow-release urea [8], stabilized urea (e.g., nitrification and urease inhibitors) [9], urea-aldehyde fertilizers, and value-added urea [10,11]. Although the development of value-added urea is recent, it has become the largest application of green, high-efficiency urea products worldwide.
Humic acid urea (HAU) is a typical value-added urea product, and its effects have been widely approved by farmers and scientists. A series of field experiments have demonstrated that HAU significantly increases crop yields by 5.58–33.08%, including the yield of winter wheat [12,13], summer maize [14,15], and potatoes [16]. HAU enhanced N use efficiency by 3.70–12.00 percentage points compared to that of common U [11,15], and this is accompanied by a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, including ammonia volatilization [17] and nitrous oxide [18,19]. Concurrently, HAU reduced N pollution via runoff and leaching and decreased groundwater pollution. HAU is produced by several significant firms in China due to its high profitability margins and positive performance [10]. The core essence or effect mechanism of value-added urea is that it can comprehensively regulate the “fertilizer–crop–soil” system to achieve a general increment in crop productivity and product value, unlike other fertilizers that are single-regulated fertilizers to increase crop production.
Previous studies by our team demonstrated that the high-efficiency mechanism of HAU is in agreement with that of value-added urea, which can be divided into three aspects. As a biostimulant, humic acid (HA) stimulates the growth and development of crop roots by altering the permeability of the cell plasma membrane [16,20]. After conducting several split-root and hydroponic experiments, we observed that both humic acid and the reaction products of humic acid and urea positively affected root proliferation [21,22]. The root system is the main nitrogen-absorbing organ of crops, and HAU can increase root biomass, total root activity, total root length, root diameter, root surface area, and root volume [16]. These parameters indicate an enhanced capacity for N acquisition after HAU application. Additionally, humic acid possesses a high adsorption capacity because it contains a large number of functional groups, which absorb a large amount of ammonium nitrogen [23]. Humic acid can reduce the conversion rate of urea-N, as urea-N can bond to the amino, carboxyl, and hydroxyl groups of HA [24]. Third, HAU can improve the soil environment and achieve increased efficiency. In alkaline soil, HAU can slightly reduce soil pH and reduce the volatilization loss of ammonium nitrogen released by urea [25]. Using soil incubation experiments, humic acids were observed to buffer the effects of common U on soil ammonia oxidizers and potential nitrification through inhibition of the change in structure and composition of the microbial community and inhibition of AOB population size to reduce the hydrolysis rate from urea to ammonium in soils [26].
However, the process of HAU transformation in the fertispheres remains unclear. After application to the soil, urea is rapidly dissolved, transformed, and diffused, ultimately causing the properties of the surrounding soil to change from those of the unaffected soil. Similar to the rhizosphere soil, the surrounding soil can be referred to as fertisphere soil. The fertisphere is the primary space where urea granules participate in the soil nitrogen cycle [27]. Previous research demonstrated that the lateral migration distance of common urea at 90 days was approximately 5–7 cm, whereas vertical migration was primarily centered in the soil layer range of 6–18 cm [28]. Additionally, the nitrate nitrogen in the soil increases over time and with decreasing soil water content, while the ammonium nitrogen migration distance increases with both increasing soil water content and time [29]. Both water-soluble and quick-acting nitrogen contents decreased with increasing migration distance in fertisphere microdomains [30]. In previous studies, fertisphere microdomains have been investigated using in situ soil sectioning [30] and by applying an optical sensor system to laboratory microcosm chambers [31], but using those methods, it is difficult to obtain accurate sampling. In addition, fertisphere microdomains can be simulated using different nitrogen fertilizer concentrations [32,33]. In our field experiments, HAU showed a good yield-increase effect on crops planted in Fluvo-aquic soil. Fluvo-aquic soil is an important agricultural soil in China, widely distributed in the Huang-Huai-hai Plain, which is also the main grain- and oil-producing area in China, accounting for a quarter of the total grain and oil production in the country [34].
In this study, a simulated fertisphere research study using Fluvo-aquic soil was conducted using a series of soil incubation experiments under different nitrogen input levels. First, we studied the N transformation characteristics of HAU by measuring key parameters in soil, including ammonium N, nitrate N, mineral N, and residue urea-N. Second, the parameter differences between U and HAU were compared for each circular layer and incubation time. Third, the high-efficiency mechanism of HAU in the fertisphere microdomain was clarified by analyzing these variations along with additional soil properties. The results of this study will serve the widespread applications of HAU in fertilizer markets worldwide.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Description
The soil samples used for the incubation experiments were gathered at a depth of 0–20 cm from the long-term positioning test field in the Lingxian Experimental Base of Dezhou Saline-alkali Soil Improvement Experimental Station, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Dezhou, Shandong Province, China (37°20′ N, 116°38′ E, 22.36 m a.s.l.). The collected soil was air-dried in the laboratory and then passed through a 2-mm mesh sieve to prepare for subsequent simulation experiments. The tested soil type was Fluvo-aquic soil according to the FAO Soil Classification System (1988, Rome, Italy). The soil consisted of 13.88% clay (<2 μm), 49.17% silt (2–20 μm), and 36.95% sand (0.02–2 mm) and was classified as light loam. The basic soil properties were a pH of 8.38, soil organic matter of 14.80 g kg−1, total nitrogen of 1.17 g kg−1, Olsen P of 20.88 g kg−1, available K of 168.99 g kg−1, nitrate nitrogen content of 57.36 g kg−1, and ammonium nitrogen content of 26.33 g kg−1.
The two tested urea fertilizers used in the experiment were common urea (45.08% N), purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and HAU. The HAU was prepared by adding a 5.0% (w w−1) dosage of HA to common urea via a chemical reaction; common urea was first heated at 120 °C with a laboratory electric furnace under stirring, and then HA was added and stirred for 30 s, as described by Jing et al. [21]. HA was derived from weathered coal (Huolinhe, Tongliao, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Northeast China), and its extraction and purification processes were conducted as described by Gao et al. [11].
2.2. Experimental Design
Differences in the transformation processes from the inside to outside circle layers of the U (common urea) and HAU fertispheres were simulated and studied using soil incubation experiments under 20, 10, 2, 1, and 0.2 g kg−1 nitrogen input levels (Figure 1). The fertisphere is formed around the point of fertilizer application after fertilizer is applied to the soil, especially when it is applied intensively (strip-applied, hole-applied, band-applied, etc.), where nutrient concentrations are abnormally high, and there is a clear specificity in the nitrogen transformation of the fertilizer. The upper limit level was based on the works of Cheng et al. [32] and Chen et al. [33]; ammonium nitrogen content in the soil after band application or point injection of fertilizer can easily exceed 3000 mg kg−1 [35], and ammonium nitrogen contents of up to 2000 mg kg−1 have been measured in soil within the 8.5 cm radius [36]. The lower limit level was based on the normal usage in field applications. The gradient level for each fertilizer was set at 21 replicates. Each replicate used a 200 mL plastic container with a circular cylinder, and each container contained 100 g of dried soil. The fertilizers were thoroughly mixed with the dried soil before being packed into containers. The control (CK) had no nitrogen input, and the humic acid dosage of the humic acid (HA) treatment was equal to the content of humic acid in the HAU treatment, with five dosage levels of 2.31, 1.15, 0.23, 0.12, and 0.02 g kg−1.
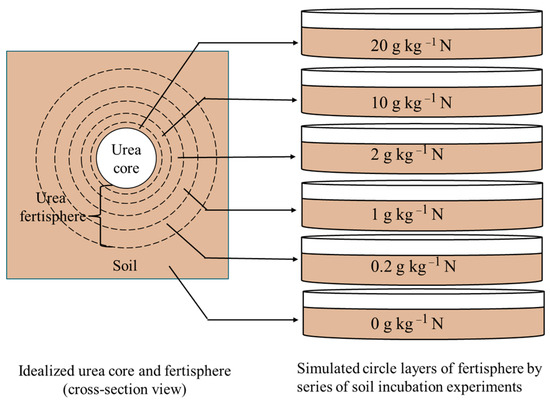
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the simulated experiment.
All the containers were placed in a growth chamber in the dark for incubation at 25 °C, and the container was covered with a plastic film with ten holes to allow gas exchange while minimizing moisture loss. The soil moisture content was adjusted to 60% of the maximum soil water-holding capacity using the weighing method and maintained at this soil moisture content throughout the simulation experiment. We weighed the plastic container every three days and compensated for any losses with sterile distilled water.
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination
Experimental soil samples were taken at 1, 3, 5, 7, 14, 28, and 42 days, with three replicates taken at each time point. A portion of fresh soil was taken for the determination of urea nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen content, and ammonium nitrogen content. The rest of the soil was air-dried and passed through a 1-mm sieve to determine other indicators.
Soil particle size distribution analysis was performed using the pipette method. Soil organic matter was determined using the potassium dichromate oxidation–sulfuric acid digestion method. Soil total nitrogen content was determined using the Kjeldahl method. Soil nitrate nitrogen content and ammonium nitrogen contents were determined by using an automated flow injection analyzer (AutoAnalyzer 3, Hamburg, Germany) after the soil sample was extracted with 1 mol L−1 potassium chloride solution at a ratio of 1:5 (soil:KCl solution), followed by filtration through a filter membrane. The urea-N content of the soil was determined by using the o-pthalaldehyde method [37]. The soil pH value was determined using a combined glass electrode in a 1:2.5 (w/v) ratio of soil and distilled water. The urease activity was determined using the sodium phenol–sodium hypochlorite colorimetric method [38].
The nitrification rate and urea residual rate during the incubation were calculated using the following equations:
where is the number of days from d0 to dt; the subscripts d0 and dt represent incubation time at 0 and t, respectively.
where t is the number of days, T represents the urea-N content of the U and HAU treatments, ck represents the urea-N content of the CK treatment, and represents the urea input amount of the U and HAU treatments.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 22.0 (Chicago, IL, USA). A one-way analysis of variance with a Duncan post hoc test was used to establish the differences. Significant differences (p < 0.05) are indicated by different lowercase letters. The tables were made using Excel 2019 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA), and the figures were plotted with Origin 2023b software (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Soil Urea-N Content and Urea Residual Rate
The two fertilizers decomposed during the incubation period, and the soil urea-N contents in the HAU treatment were higher than those in the U treatment under the same nitrogen input (or under the same simulated circular layers of the fertisphere) (Figure 2). The soil urea-N content under the humic acid treatments was 0.16–0.31 g kg−1, consistent with that of the CK treatment. At a nitrogen input of 0.2 g kg−1, the urea-N content was 53.97% and 12.74% higher in the HAU treatment than in the U treatment on days 7 and 14, respectively, and no urea-N was detected in either treatment on day 28. At other equal nitrogen inputs, no significant difference was observed between HAU and U during the first 7 days. On day 28 of incubation, the difference between HAU and U at the same nitrogen input level was significant (p < 0.05). On the 42nd day of incubation, the urea-N content in the HAU20, HAU10, HAU2, and HAU1 treatments was higher than that in the U20, U10, U2, and U1 treatments by 48.42, 28.41, 101.92, and 14.38%, respectively. The difference in the urea residue rate between the two fertilizers was almost the same as the difference in soil urea-N content (Figure 3). Under the same nitrogen inputs, the urea residue rate of HAU was higher than that of U, averaging 2.71 percentage points higher at the end of incubation. Overall, these results demonstrated that urea decomposition in the soil was slowed by HAU.
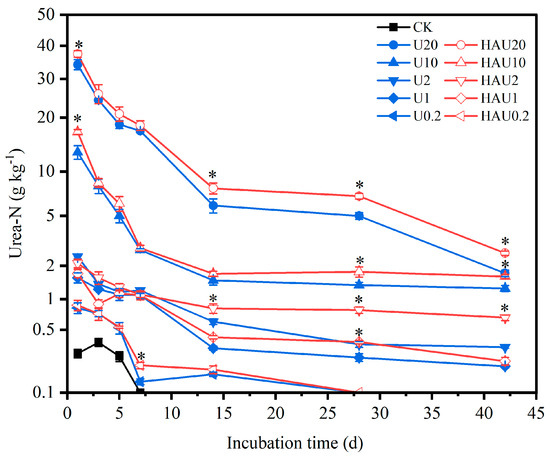
Figure 2.
Dynamics of soil urea−N content in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during incubation days. Note: Error bars represent standard deviations, n = 3. * Values above the lines denote statistically significant differences between U and HAU under the same nitrogen concentration according to Duncan’s test at p = 0.05.
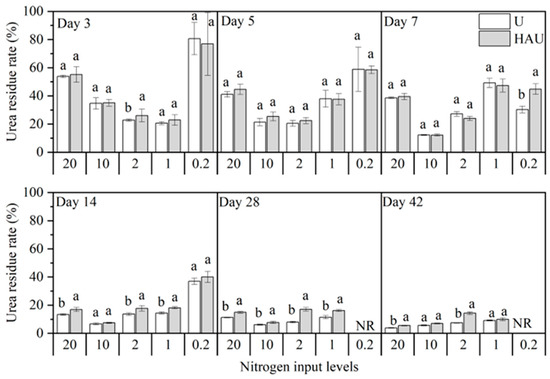
Figure 3.
Dynamics of urea residual rate in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during incubation days. Note: Error bars represent standard deviations, n = 3. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the U and HAU treatments at the same nitrogen concentration based on Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05).
3.2. Soil Nitrate Nitrogen Content and Ammonium Nitrogen Content
The two fertilizers exhibited a similar trend in nitrate nitrogen content under the same nitrogen input during incubation (Figure 4). The soil nitrate nitrogen content under the humic acid treatments was 44.56–139.39 mg kg−1, consistent with that of the CK treatment. The nitrate nitrogen contents of the U and HAU treatments did not change significantly throughout the incubation period when nitrogen was applied at 20 and 10 g kg−1. Under 2 g kg−1 nitrogen input, the nitrate nitrogen content was significantly different between the HAU and U treatments in the first 14 days, and the nitrate nitrogen content of the HAU treatment increased rapidly from day 28, and it was significantly higher than that of the U treatment by 3.42-fold at day 42. This increase in nitrate nitrogen content was observed when the nitrogen input was 1 and 0.2 g kg−1. On the 28th day, there was a significant (p < 0.05) difference between HAU and U at the nitrogen input levels of 1 and 0.2 g kg−1. The nitrate nitrogen content of the HAU0.2 treatment was significantly higher than that of the U0.2 treatment by 13.01% (p < 0.05), and the nitrate nitrogen content of the U1 treatment was significantly higher than that of the HAU1 treatment by 43.81% (p < 0.05).
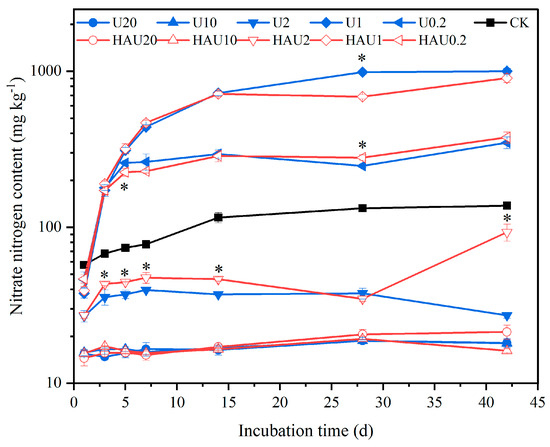
Figure 4.
Dynamics of soil nitrate nitrogen content in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during incubation days. Note: Error bars represent standard deviations, n = 3. * Values above the lines denote statistically significant differences between U and HAU under the same nitrogen concentration according to Duncan’s test at p = 0.05.
The two fertilizers exhibited similar trends in regard to ammonium nitrogen content under the same nitrogen input during incubation (Figure 5). The soil ammonium nitrogen content under the humic acid treatments was 3.49–22.42 mg kg−1, consistent with that of the CK treatment. When the nitrogen input was 20, 10, 2, and 1 g kg−1, the ammonium nitrogen content of the two fertilizers first increased and subsequently declined with incubation time. When the nitrogen input was 0.2 g kg−1, the ammonium nitrogen concentration of the two fertilizers gradually decreased with incubation time. During the first 7 days, the ammonium nitrogen content of the HAU treatment was significantly higher than that of the U treatment when the nitrogen input was 20 and 10 g kg−1 (p < 0.05), whereas the ammonium nitrogen concentration of the HAU treatment was lower than that of the U treatment when the nitrogen input was 0.2 g kg−1.
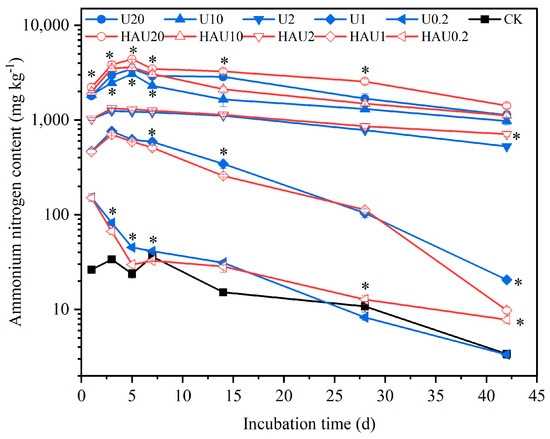
Figure 5.
Dynamics of soil ammonium nitrogen content in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during incubation days. Note: Error bars represent standard deviations, n = 3. * Values above the lines denote statistically significant differences between U and HAU under the same nitrogen concentration according to Duncan’s test at p = 0.05.
3.3. Soil Mineral Nitrogen Content and Nitrification Rate
The mineral nitrogen content of the two fertilizers showed a similar trend under the same nitrogen input during incubation (Figure 6). The soil mineral nitrogen content under the humic acid treatments was 50.28–164.67 mg kg−1, consistent with that of the CK treatment. The soil mineral nitrogen content of the two fertilizers tended to increase and then decrease with incubation time when the nitrogen input was 20, 10, and 2 g kg−1, whereas the mineral nitrogen content gradually increased with incubation time when the nitrogen input was 1 and 0.2 g kg−1. On the 42nd day of incubation, the mineral nitrogen content in the HAU treatments was significantly higher than that in the U treatment under nitrogen inputs of 20, 10, and 2 g kg−1, and the values were 25.07%, 14.21%, and 44.66% higher than that in the U treatment (p < 0.05), respectively. The nitrification rates of the two fertilizers first increased and then decreased with increasing nitrogen input levels (Table 1). Nitrification rates were low and negligible when the nitrogen application was 10 and 20 g kg−1. When the nitrogen application was 2 g kg−1, the nitrification rate in the HAU treatment was significantly higher than that in the U treatment (p < 0.05). As shown in Table 1, the nitrification rate was the highest at 1 g kg−1 N application, and the nitrification rate in U was 10.24% higher than that in HAU. This revealed that HAU could increase mineral nitrogen content during the entire 42-day incubation period when the nitrogen input was 20 and 10 g k−1, and it could promote nitrification when the nitrogen input was 2 g kg−1.
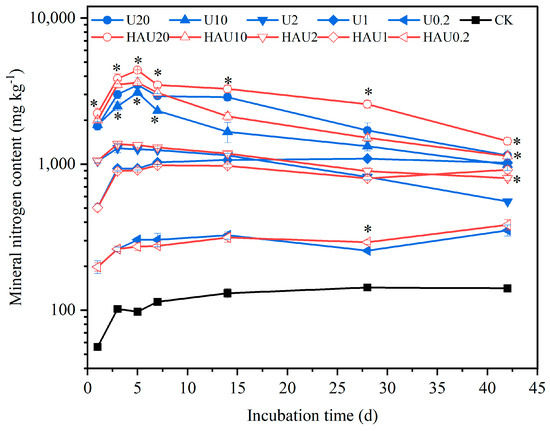
Figure 6.
Dynamics of soil mineral nitrogen content in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during incubation days. Note: Error bars represent standard deviations, n = 3. * Values above the lines denote statistically significant differences between U and HAU under the same nitrogen concentration according to Duncan’s test at p = 0.05.

Table 1.
Nitrification rate in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during the incubation period (mg kg−1 d−1).
3.4. Soil pH Value
The value of soil pH increased rapidly with increasing N input and was lower in the HAU treatment than it was in the U treatment (Figure 7). Under the nitrogen input of 20, 10, and 2 g kg−1, soil pH was considerably higher in the HAU and U treatments than in the CK treatment during the incubation period in Figure 7a–c; the soil pH in the U and HAU treatments averagely increased by 0.79 and 0.75 units compared to that in the CK treatment, respectively. In the circles farthest from the fertilizer core (when the nitrogen input was 1 and 0.2 g kg−1), the soil pH in the U and HAU treatments was lower than that in the CK treatment (Figure 7d,e). However, the soil pH of HAU treatment was slightly lower than that of U treatment under the same nitrogen input level. For example, on the 42nd day, the soil pH in the HAU20 treatment was significantly lower than that in the U20 treatment by 0.08 units. The soil pH values in humic acid treatments were 7.70–8.12, consistent with those in the CK treatment.
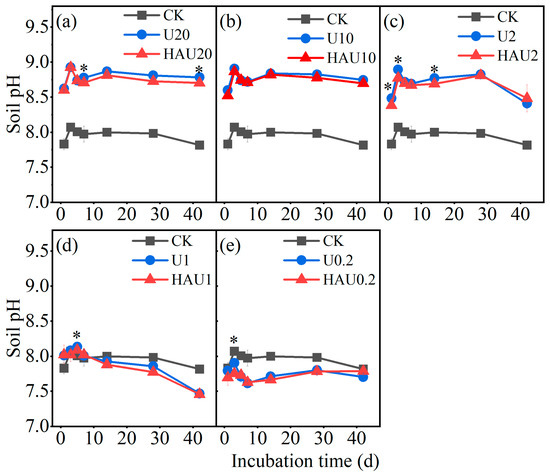
Figure 7.
Dynamics of soil pH values in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during incubation days. The (a–e) denote soil pH values for U and HAU treatments with nitrogen input was 20, 10, 2, 1, and 0.2 g kg−1, respectively. Note: Error bars represent standard deviations, n = 3. * Values above the lines denote statistically significant differences between U and HAU under the same nitrogen concentration according to Duncan’s test at p = 0.05.
3.5. Soil Urease Activity
The urease activity of the two fertilizers showed a similar trend in the same simulated circle layers of the fertisphere during the incubation period (Figure 8). Urease activity under humic acid treatments was 3.34–4.86 mg g−1 d−1, consistent with that of the CK treatment. The two fertilizers promoted urease activity when the nitrogen input was 20 and 10 g kg−1 and exhibited a tendency to increase and then decrease with incubation time. On the 42nd day, the urease activity of the HAU treatment was significantly lower than that of the U treatment by 17.78%, 21.09%, and 14.57% when the nitrogen input was 20, 10, and 2 g kg−1, respectively (p < 0.05). When the nitrogen input was 1 g kg−1, the urease activity of the U and HAU treatments decreased and then increased with incubation time. Compared to the CK treatment, the U1 and HAU1 treatments considerably reduced urease activity.
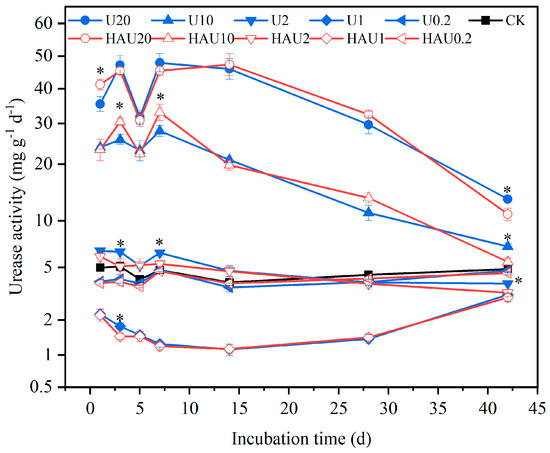
Figure 8.
Dynamics of urease activity in simulated circle layers of the fertisphere of U and HAU during incubation days. Note: Error bars represent standard deviations, n = 3. * Values above the lines denote statistically significant differences between U and HAU under the same nitrogen concentration according to Duncan’s test at p = 0.05.
4. Discussion
Overall, HAU retained the basic characteristics of common urea in the soil fertisphere. All tested parameters of all circle layers at any sampling time had similar changing trends for both fertilizers in this study. Before the incubation experiments, we assumed that the urea residue rates of the two fertilizers in Fluvo-aquic soils would gradually decrease with increasing distance from the fertilizer core. The urea residue rate conformed to our hypothesis in the four circle layers closer to the fertilizer core on the 3rd day, but the urea residue rate in soils exhibited the opposite trend on the 42nd day. Additionally, the urea residue rate exhibited an irregular change on other incubation days. Nitrogen input levels were not designed according to the principle of equal ratios or equal differences. Other parameters suggested that urea decomposition was promoted or inhibited under different nitrogen input levels and that the concentration of urea decomposition products may also affect urea decomposition. Therefore, the results did not vary linearly in our study. The urea decomposition in Fluvo-aquic soil was slowed down by HAU during the incubation period, particularly in the two circles closest to the fertilizer core. Our previous field soil column experiments [11] and the work of others [39,40] also confirmed that urea residue under HAU treatment was higher than that under common urea treatment, thus indicating the higher fertilizer preservation and supply capacity of HAU. Additionally, the increased mineral nitrogen content in the two circles closest to the fertilizer core showed that HAU exhibited a higher supply capacity of available nitrogen for the earlier stage of crops.
Higher fertilizer preservation and supply capacity of HAU were realized by changing urease activity in the fertisphere ranges closer to the fertilizer core. Only a large amount of urea input stimulated the activity of soil urease during the initial incubation period. To the best of our knowledge, the higher urease activities for HAU have not been reported in the space closest to the fertilizer core. Lignite, which is used as a raw material for HA, can inhibit soil urease activity when applied to soil [41,42]. Shen et al. [39] also reported that urease activity in soil containing HAU was substantially lower than that in soil supplemented with urea, ultimately resulting in higher urea residues in the soil. Additionally, HA forms a larger complex with the urease functional group, and this inhibits urease activity [43]. At the same time, HA interacts with urease for a certain period, and the functional groups of HA interact with the hydrophobic groups in urease, thus reducing soil urease activity [44]. These results could explain why HAU inhibited urease activity under the circle layers farthest from the fertilizer core. The promotional effect of HAU on the urease activity deserved further investigation.
The ammonium nitrogen concentration of the HAU treatment was higher than that of U in the two circle layers closest to the fertilizer core, and this could be due to humic acid containing a large number of carboxyl groups, which can adsorb more ammonium nitrogen [24,45]. In addition, humic acid possesses abundant hydrophilic functional groups that can quickly adsorb nitrogen fertilizer, hydrolyze it into ammonium ions, and convert it into humic acid ammonium salt with a lower dissociation degree [46,47]. The production of large amounts of ammonium nitrogen led to a rapid increase in soil pH in the two circle layers closest to the fertilizer core. Additionally, the soil pH dropped as one moved farther away from the fertilizer application core, as the ammonium nitrogen content in the soil was reduced. The decrease in soil ammonium nitrogen concentration could be due to nitrification and ammonia volatilization [32]; however, the nitrification of U and HAU was negligible during the incubation period when it was closer to the fertilizer application core. This finding was consistent with those of Deppe et al. [48] and Merl et al. [31]. This may be due to the toxic effects of high concentrations of ammonium nitrogen on soil nitrifying microorganisms [33] that inhibit the activity of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms, thereby inhibiting nitrification [32]. The high NH4+ concentration and pH around the fertilizer core will be maintained for a long time, which will inhibit nitrification, and inhibiting nitrification can reduce nitrous oxide production in agricultural systems.
HAU has become a more green and efficient nitrogen fertilizer for improving crop yield and nitrogen use efficiency. Compared with other fertilizers, HAU is more efficient, more convenient, and cheaper. Although the nitrogen applied in the design of this experiment is high, it does exist in the fertisphere when fertilizer is applied in the field in strips or point injections. The nitrogen concentration near the fertilization point may be much higher than 20 g N kg−1. Previously, simple soil incubation experiments with a normal amount of urea input reflected only the average performance of fertilizer characteristics. This study revealed the soil regulation by HAU from the fertisphere core to the boundary, and this compensates for some weak links in the comprehensive regulation of the “fertilizer–soil–plant” system by HAU. The diffusion of urea in the soil is a dynamic and continuous process, and urea continues to spread from the fertisphere core into an ever-expanding fertisphere. This is accompanied by the simultaneous transformation of nitrogen. This study simulated the concentration of urea in each circular layer after a short period of rapid diffusion. Moreover, the fertisphere boundary is similar to the model simulated in this study from the horizontal direction, whereas in the vertical direction, the boundary is not spherical and could be closer to a cone. Fertisphere cones have also been studied by our team, and the results will be published in the near future.
This study characterizes the nitrogen transformation of humic acid urea in fertisphere microdomains, providing a theoretical basis for the development and application of HAU. It provides the theoretical basis for increasing the yield of crops by applying HAU and for maintaining yields while decreasing the application of HAU in the field. Future research needs to be conducted in several areas: Microbial characteristics related to further carbon and nitrogen cycling should be studied and analyzed to gain an understanding of the physicochemical mechanisms and microbial mechanisms of the initial fertilizer–soil interface process of HAU. In addition, a wide range of soil types should be investigated to determine the general characteristics of the HAU fertisphere that could be further analyzed to clarify its high-efficiency mechanism.
5. Conclusions
First, the basic characteristics of urea in Fluvo-aquic soil were preserved by HAU. They exhibited a similar variation trend for all key parameters in all circle layers of the fertisphere with incubation time. Secondly, the differences provide insights into the reasons for the high-efficiency mechanism of HAU applied to field crops. In Fluvo-aquic soil, different circle layers with different distances from the fertilizer core had different performances.
In the circular layers closer to the fertilizer core, compared to U treatment, HAU increased urease activity and promoted the transformation of urea-N to ammonium nitrogen in the preincubation period and inhibited the nitrification, while in the late incubation period, HAU inhibited urease activity and slowed down urea decomposition. As a result, HAU had a high capacity to supply nitrogen, which was reflected more in the continuous diffusion of fertilizer cores, which helped to meet the demand for nitrogen in the early stages of the crop. At the end of incubation, the residual urea-N under the HAU treatment was significantly higher than that under the U treatment when the circle layers were closer to the fertilizer core. This resulted in HAU having a higher fertilizer preservation. Overall, the effects of higher fertilizer preservation and supply capacity of HAU were all reflected in the inner fertisphere of Fluvo-aquic soil. A deeper understanding of the high-efficiency mechanism of HAU in the fertisphere formation process will promote the development of a new generation of highly efficient urea production. In the future, microbial characteristics will be further clarified to gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms in the fertisphere soil process of HAU and establish a theoretical foundation for its application and the development of a new generation of highly efficient urea production.
Author Contributions
M.L.: formal analysis, data curation, software, visualization, writing—original draft preparation; M.X.: conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation; L.Y.: writing—review and editing; S.Z.: methodology, software, data curation; Y.L.: supervision, validation. B.Z.: funding acquisition, project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China during the 14th Five-Year Plan period (2023YFD1700201), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Grant No. 32202611), China Agriculture Research System (Grant No. CARS–03), and Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-profit Scientific Institution (1610132023017).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for support from Key Field Scientific Observation and Experiment Station of Agricultural Resources and Ecological Environment in Dezhou, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs/Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Giroto, A.S.; do Valle, S.F.; Guimarães, G.G.F.; Wuyts, N.; Ohrem, B.; Jablonowski, N.D.; Ribeiro, C.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Zinc Loading in Urea-Formaldehyde Nanocomposites Increases Nitrogen and Zinc Micronutrient Fertilization Efficiencies in Poor Sand Substrate. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Lu, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.C. Applying and Optimizing Water-Soluble, Slow-Release Nitrogen Fertilizers for Water-Saving Agriculture. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11342–11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.; Pacholski, A.; Kage, H. Ammonia Volatilization after Application of Urea to Winter Wheat over 3 Years Affected by Novel Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 197, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhao, X.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Optimal Nitrogen Rate Strategy for Sustainable Rice Production in China. Nature 2023, 615, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing Nitrogen for Sustainable Development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conant, R.T.; Berdanier, A.B.; Grace, P.R. Patterns and Trends in Nitrogen Use and Nitrogen Recovery Efficiency in World Agriculture. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A.P.; Grutzmacher, P.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Ribeirinho, V.S.; Andrade, C.A.d. Biochar-Based Nitrogen Fertilizers: Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Use Efficiency, and Maize Yield in Tropical Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.-R.; Hosny, A.; Saad-Allah, K. Reducing Nitrogen Leaching While Enhancing Growth, Yield Performance and Physiological Traits of Rice by the Application of Controlled-Release Urea Fertilizer. Paddy Water Environ. 2021, 19, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Afshar, R.; Lin, R.; Mohammed, Y.A.; Chen, C. Agronomic Effects of Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors on Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrogen Utilization in a Dryland Farming System: Field and Laboratory Investigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4130–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yuan, L. Innovation and industrial development of green efficiency fertilizers in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhao, B. Humic Acids Incorporated into Urea at Different Proportions Increased Winter Wheat Yield and Optimized Fertilizer-Nitrogen Fate. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktem, A.G.; Oktem, A. Effect of Humic Acid Application Methods on Yield and Some Yield Characteristics of Corn Plant (Zea mays L. indentata). J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 2020, 23, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Ming, Y.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Jiao, S.; Shi, L.; et al. The Application of Humic Acid Urea Improves Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Crop Yield by Reducing the Nitrogen Loss Compared with Urea. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Guo, W.; Xu, L.; Shi, L. Beneficial Effect of Humic Acid Urea on Improving Physiological Characteristics and Yield of Maize (Zea mays L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2022, 44, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Şenbayram, M.; Akram, N.A.; Ashraf, M.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Sulfur-Enriched Leonardite and Humic Acid Soil Amendments Enhance Tolerance to Drought and Phosphorus Deficiency Stress in Maize (Zea mays L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kou, M.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Li, H.; Wei, M. Responses of Root Physiological Characteristics and Yield of Sweet Potato to Humic Acid Urea Fertilizer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Wong, V.N.L.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Patti, A.F. Nitrogen Dynamics in Soil Fertilized with Slow Release Brown Coal-Urea Fertilizers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Wong, V.N.L.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Patti, A.F. A Slow Release Brown Coal-Urea Fertiliser Reduced Gaseous N Loss from Soil and Increased Silver Beet Yield and N Uptake. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Saline-Alkali Soil Applied with Vermicompost and Humic Acid Fertilizer Improved Macroaggregate Microstructure to Enhance Salt Leaching and Inhibit Nitrogen Losses. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.T.; Patti, A.F.; Little, K.R.; Brown, A.L.; Jackson, W.R.; Cavagnaro, T.R. A Meta-Analysis and Review of Plant-Growth Response to Humic Substances. Adv. Agron. 2014, 124, 37–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, B. Humic Acid Complex Formation with Urea Alters Its Structure and Enhances Biomass Production in Hydroponic Maize. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 3636–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L. Production of Border Cells and Colonization of Maize Root Tips by Herbaspirillum seropedicae are Modulated by Humic Acid. Plant Soil 2017, 417, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Aminuddin, H.; Husni, M.H.A. Reducing Ammonia Loss from Urea and Improving Soil-Exchangeable Ammonium Retention through Mixing Triple Superphosphate, Humic Acid and Zeolite. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 22, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.; Yan, Q. Characterization of Humic Acids from Original Coal and Its Oxidization Production. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Lan, Y.; Cheng, K.; Yang, F. Synthesis of Artificial Humic Acid-Urea Complex Improves Nitrogen Utilization. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Córdova-Kreylos, A.L.; Yang, J.; Yuan, H.; Scow, K.M. Humic Acids Buffer the Effects of Urea on Soil Ammonia Oxidizers and Potential Nitrification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Progress on Migration and Transformation of Nitrogen Fertilizer in Soil and the Biological Effects. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 28, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lu, D.; Zu, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Effects of Different Fertilization Methods and Nitrogen Fertilizers on Nitrogen Diffusion and Migration in Lime Concretion Black Soil. Soils 2018, 50, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, H.; Chen, X.; Lu, D.; Wang, H. Primary Study on Nutrient Migration Under Hole Fertilization in Soils. Soils 2020, 52, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; You, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Luo, Y. Effect of Nitrogen Reduction on Migration of Nutrients in Fertisphere of Fluvo-aquic Soil. Soils 2023, 55, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merl, T.; Sedlacek, C.J.; Pjevac, P.; Fuchslueger, L.; Sandén, T.; Spiegel, H.; Koren, K.; Giguere, A.T. Visualizing Small-Scale Subsurface NH3 and pH Dynamics Surrounding Nitrogen Fertilizer Granules and Impacts on Nitrification Activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 189, 109273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, D.; Wang, H. Long-Acting Mechanisms of Concentrated Urea Application—High Urea Concentrations Are Biological Inhibitors. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Zou, P.; Bao, L. Restricted Nitrous Oxide Emissions by Ammonia Oxidizers in Two Agricultural Soils Following Excessive Urea Fertilization. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, D.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Ai, C.; Zhou, W. Maize Biochar Addition Rate Influences Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Community Composition in a Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfab, H.; Palmer, I.; Buegger, F.; Fiedler, S.; Müller, T.; Ruser, R. Influence of a Nitrification Inhibitor and of Placed N-Fertilization on N2O Fluxes from a Vegetable Cropped Loamy Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 150, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppe, M.; Well, R.; Kücke, M.; Fuß, R.; Giesemann, A.; Flessa, H. Impact of CULTAN Fertilization with Ammonium Sulfate on Field Emissions of Nitrous Oxide. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 219, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neithercut, W.D.; el Nujumi, A.M.; McColl, K.E. Measurement of Urea and Ammonium Concentrations in Gastric Juice. J. Clin. Pathol. 1993, 46, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liu, X. The Effect of Soil Salt Content and Ionic Composition on Nitrification in a Fluvisol of the Yellow River Delta. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lin, H.; Gao, W.; Li, M. The Effects of Humic Acid Urea and Polyaspartic Acid Urea on Reducing Nitrogen Loss Compared with Urea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4425–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsakov, K.; Stepanov, A.; Pozdnyakov, L.; Yakimenko, O. Humate-Coated Urea as a Tool to Decrease Nitrogen Losses in Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, A.; Laanbroek, H.J. Continuous Culture Enrichments of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria at Low Ammonium Concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 37, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Wong, V.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Patti, A.F. Hybrid Brown Coal-Urea Fertiliser Reduces Nitrogen Loss Compared to Urea Alone. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, D.-J. Inhibition of Urease Activity by Humic Acid Extracted from Sludge Fermentation Liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tan, W.; Koopal, L.K.; Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Norde, W. Influence of Soil Humic and Fulvic Acid on the Activity and Stability of Lysozyme and Urease. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5050–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Miao, Z.; Gao, M.; Wan, K. Structural Analysis of Lignite-Derived Humic Acid and Its Microscopic Interactions with Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampong, K.; Thilakaranthna, M.S.; Gorim, L.Y. Understanding the Role of Humic Acids on Crop Performance and Soil Health. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 848621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Xi, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, X. Climate-Zone-Dependent Effect Mechanism of Humic Acid and Fulvic Acid Extracted from River Sediments on Aggregation Behavior of Graphene Oxide. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppe, M.; Well, R.; Giesemann, A.; Spott, O.; Flessa, H. Soil N2O Fluxes and Related Processes in Laboratory Incubations Simulating Ammonium Fertilizer Depots. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).