The Combination of Biochar and Phosphorus-Containing Materials Can Effectively Enhance the Remediation Capacity of Amaranth on Cadmium-Contaminated Soil and Improve the Structure of Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Tested Biochar Materials
2.1.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.1.3. Pot Experiment
2.1.4. Index Test Method
2.1.5. Data Processing and Analysis
- Bioconcentration factor (BCF) = Cd content in shoots/Cd content in soil;
- Transfer coefficient (TF) = shoot Cd content/root Cd content;
- Cadmium accumulation in aboveground part of plant = Cd content in aboveground part of plant × aboveground biomass of plant;
- Cadmium accumulation in plant roots = Cd content in plant roots × biomass in plant roots.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Properties and Available Cadmium
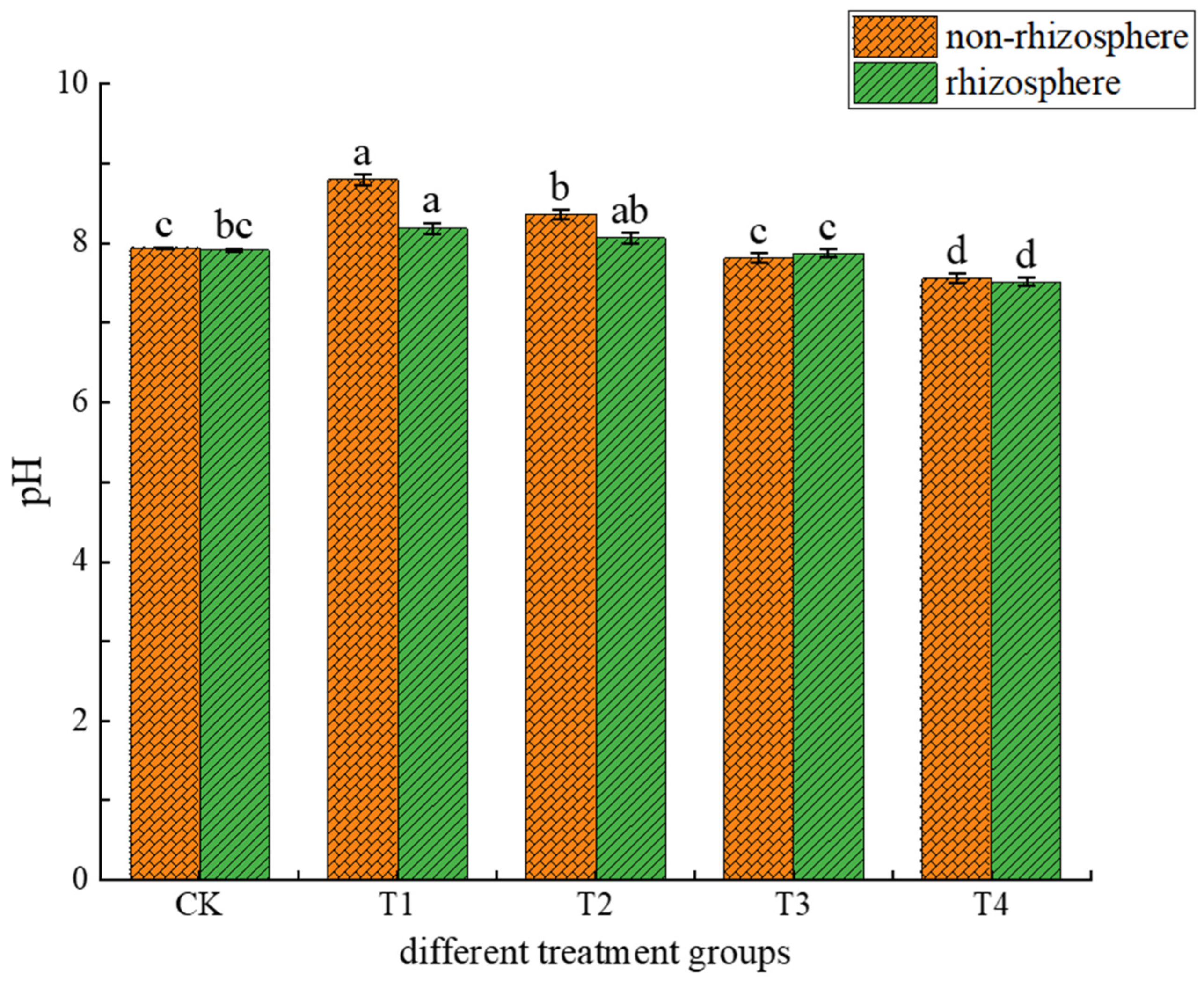
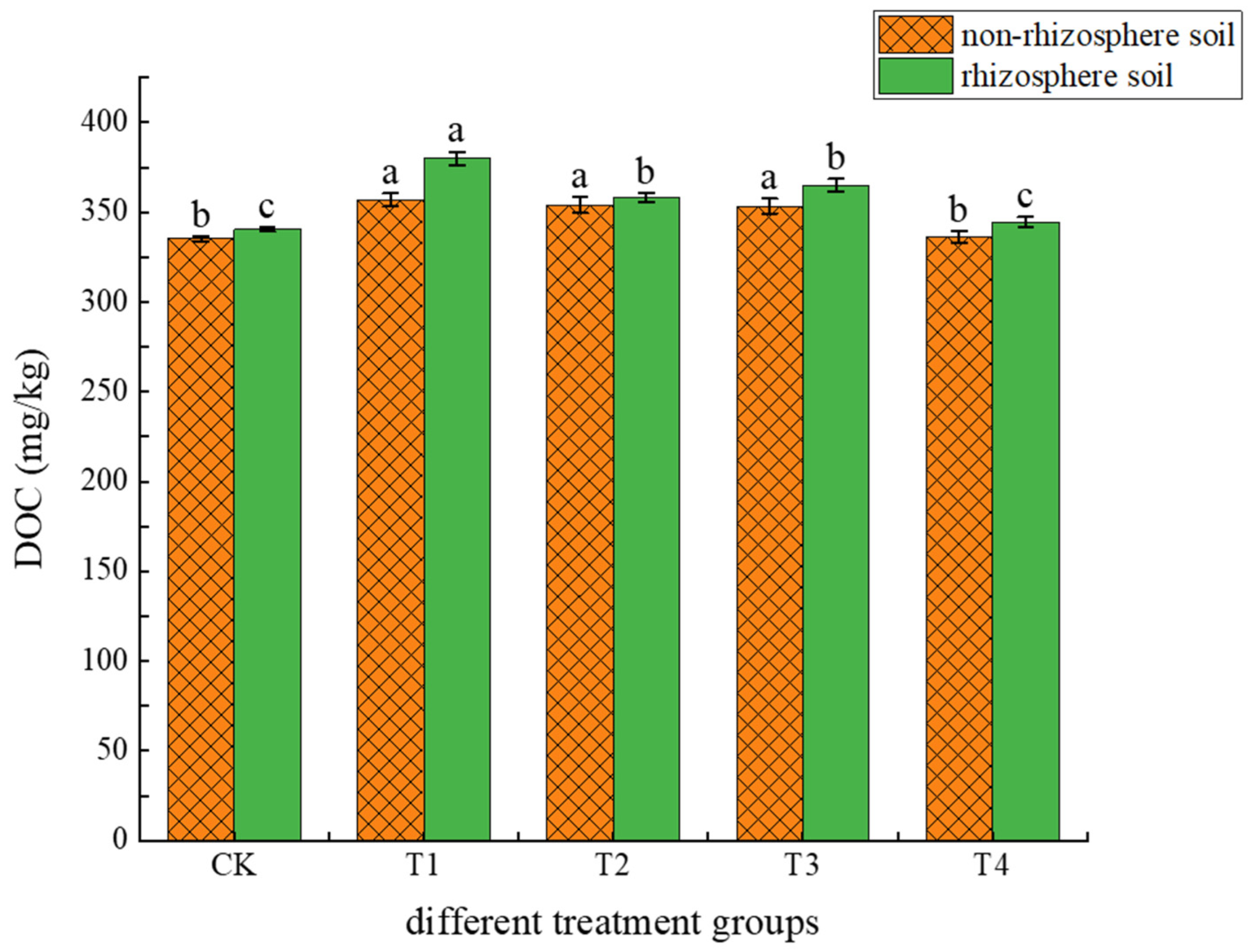
3.1.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil pH and DOC
3.1.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Cadmium Concentration in Soil Pore Water
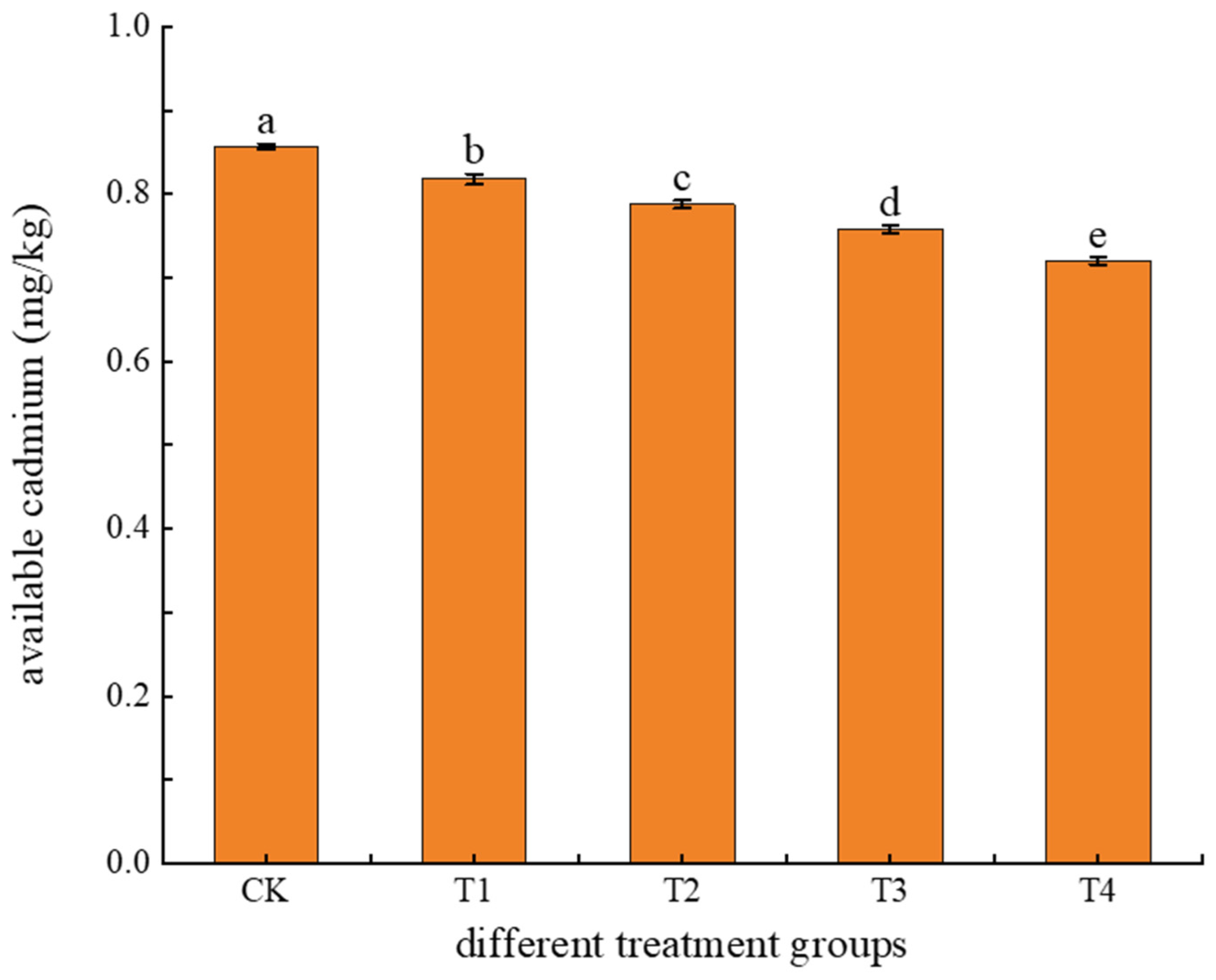
3.1.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Available Cadmium Content
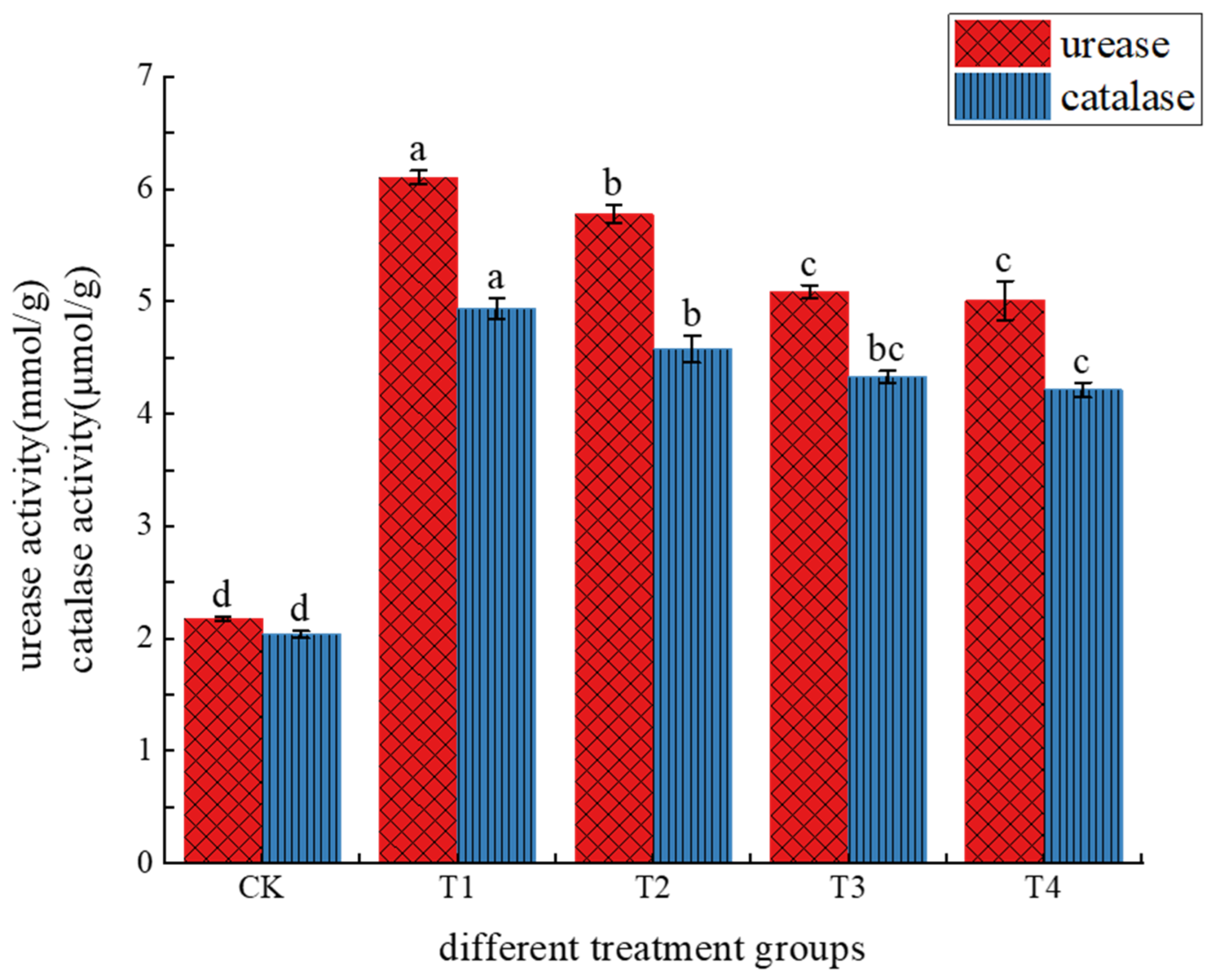
3.1.4. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Enzyme Activity
3.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Growth and Cadmium Accumulation of Amaranth
3.2.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Biomass of Amaranth in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil
3.2.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Absorption and Accumulation of Cadmium in Amaranth
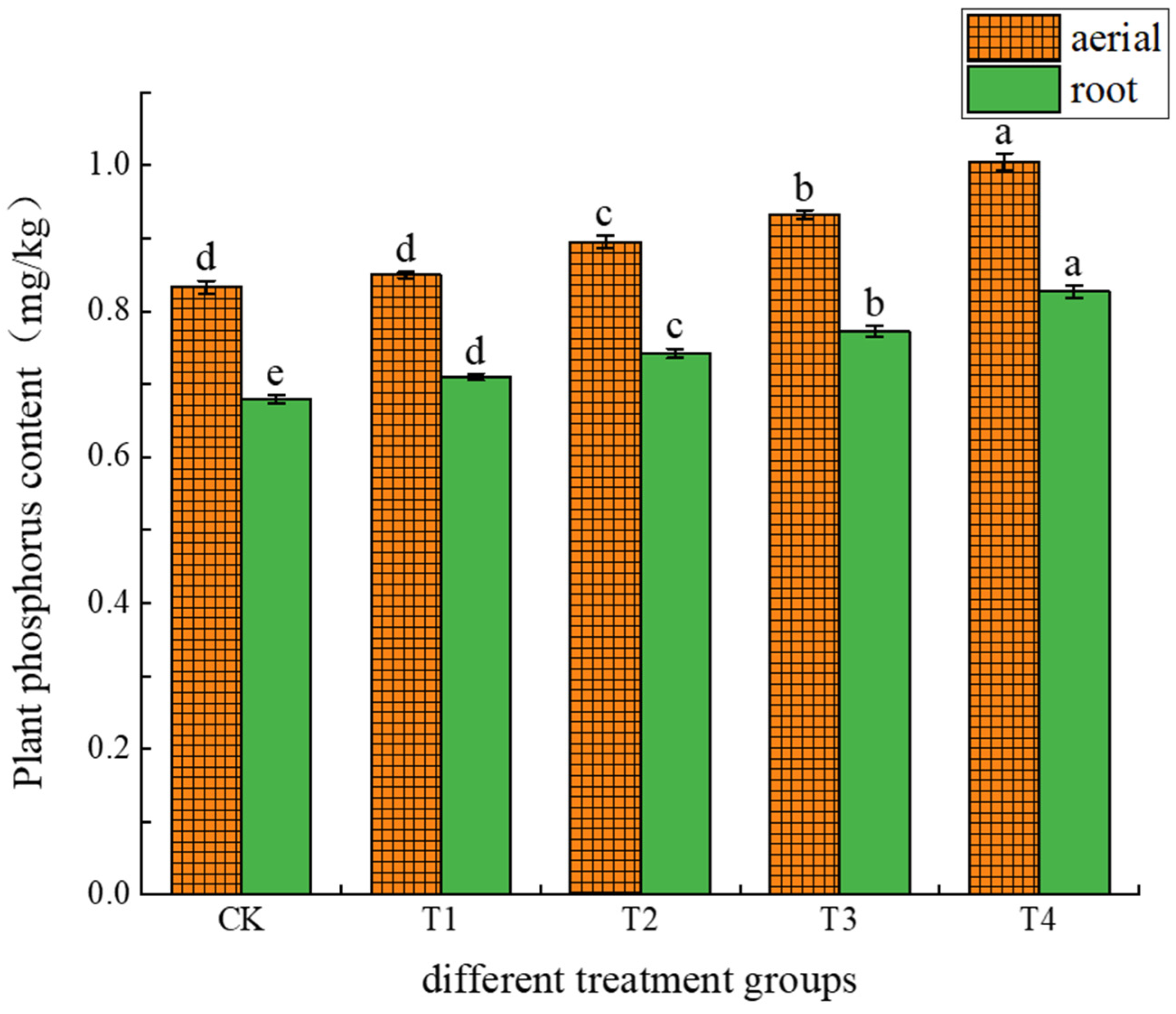
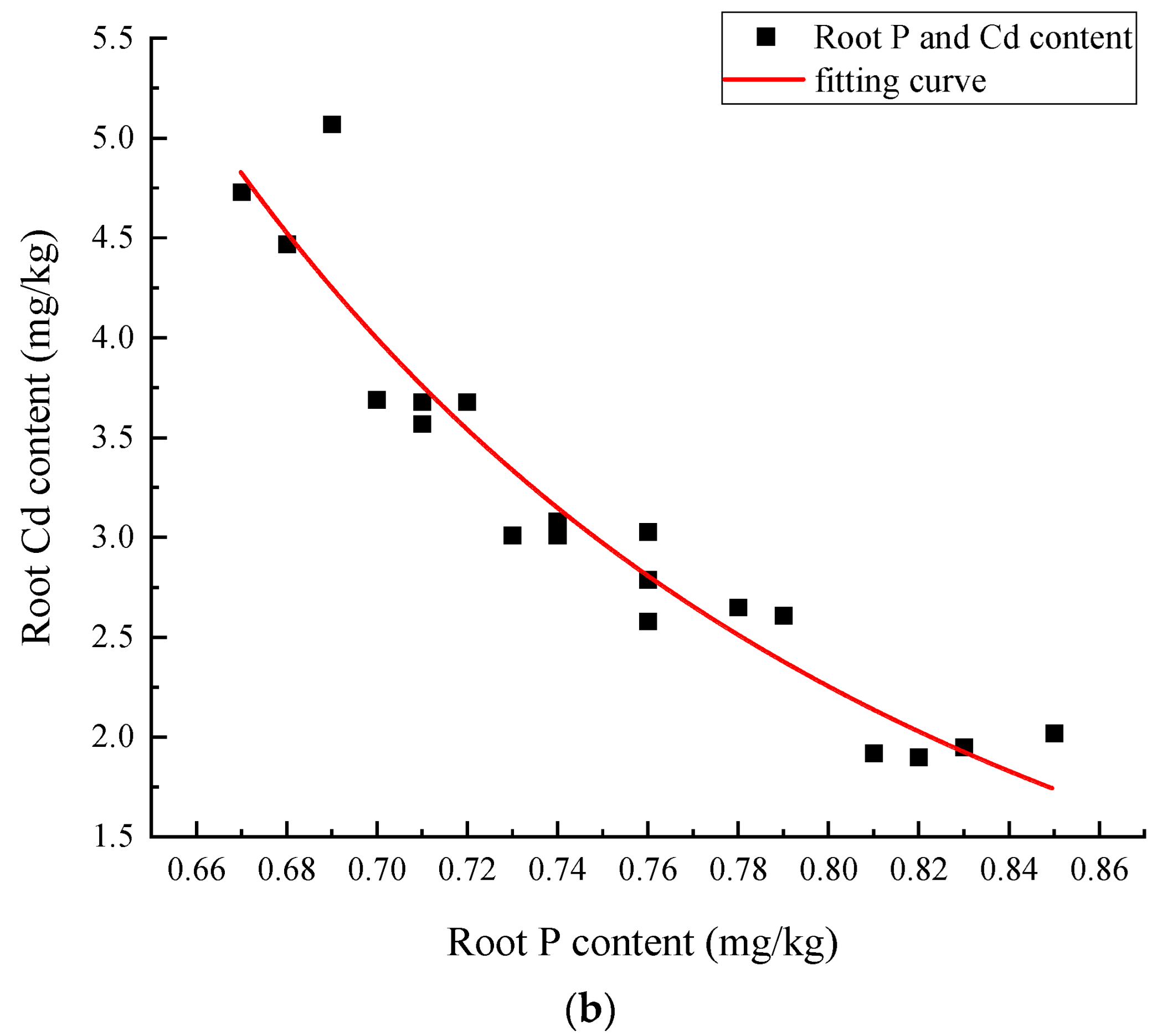
3.2.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Phosphorus Uptake and Accumulation in Amaranth
3.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Microbial Diversity and Community Structure
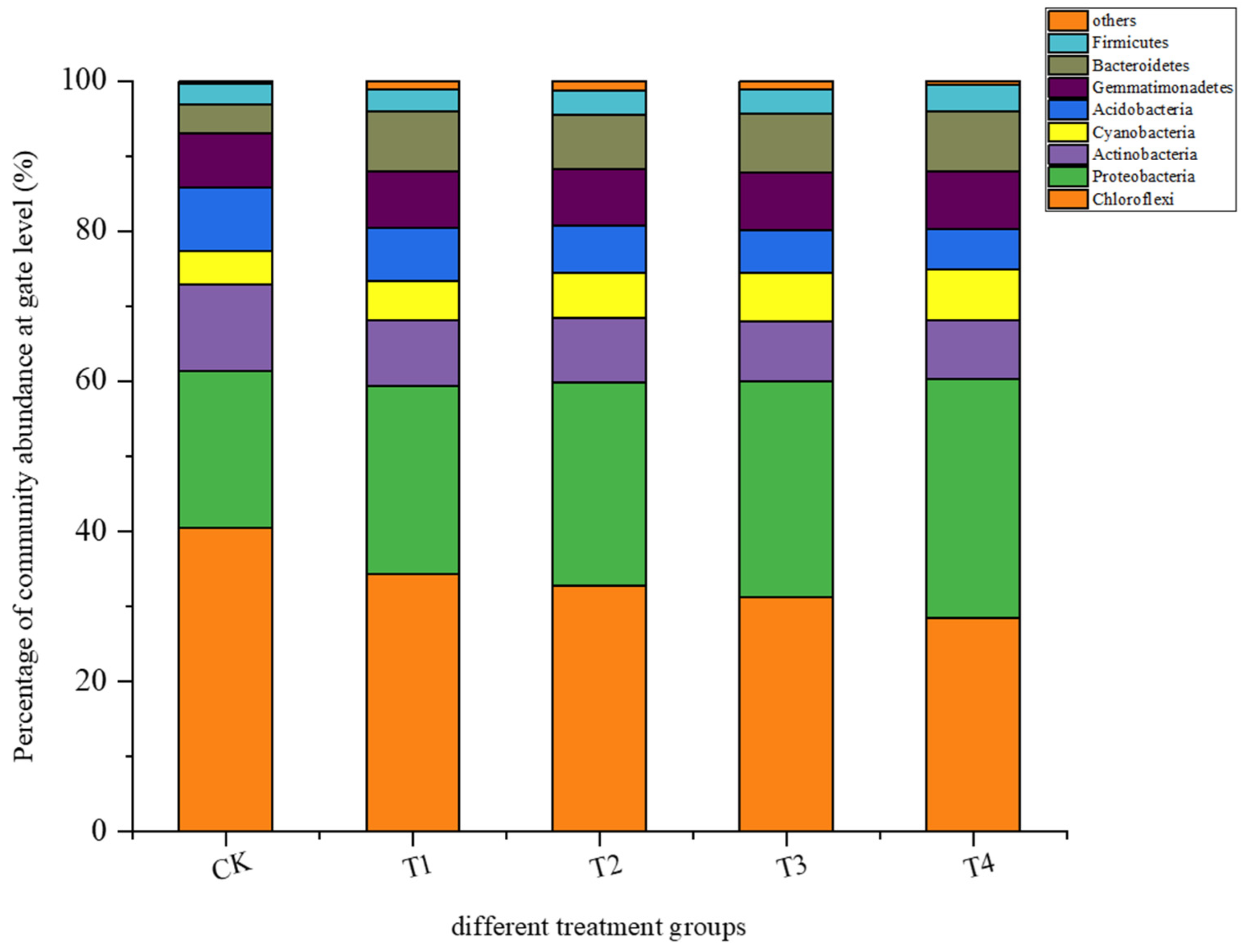
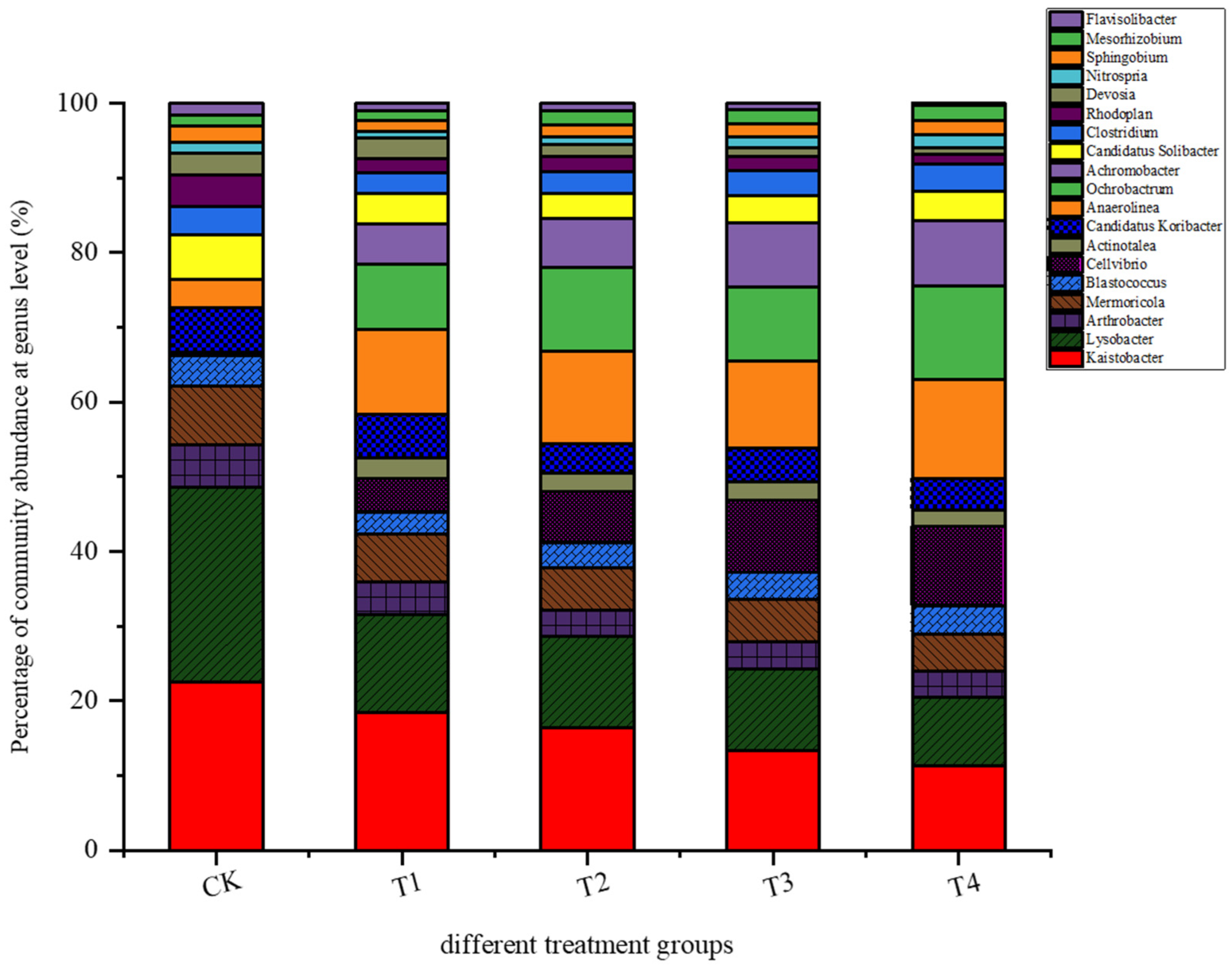
3.3.1. Microbial Community Structure in Rhizosphere Soil
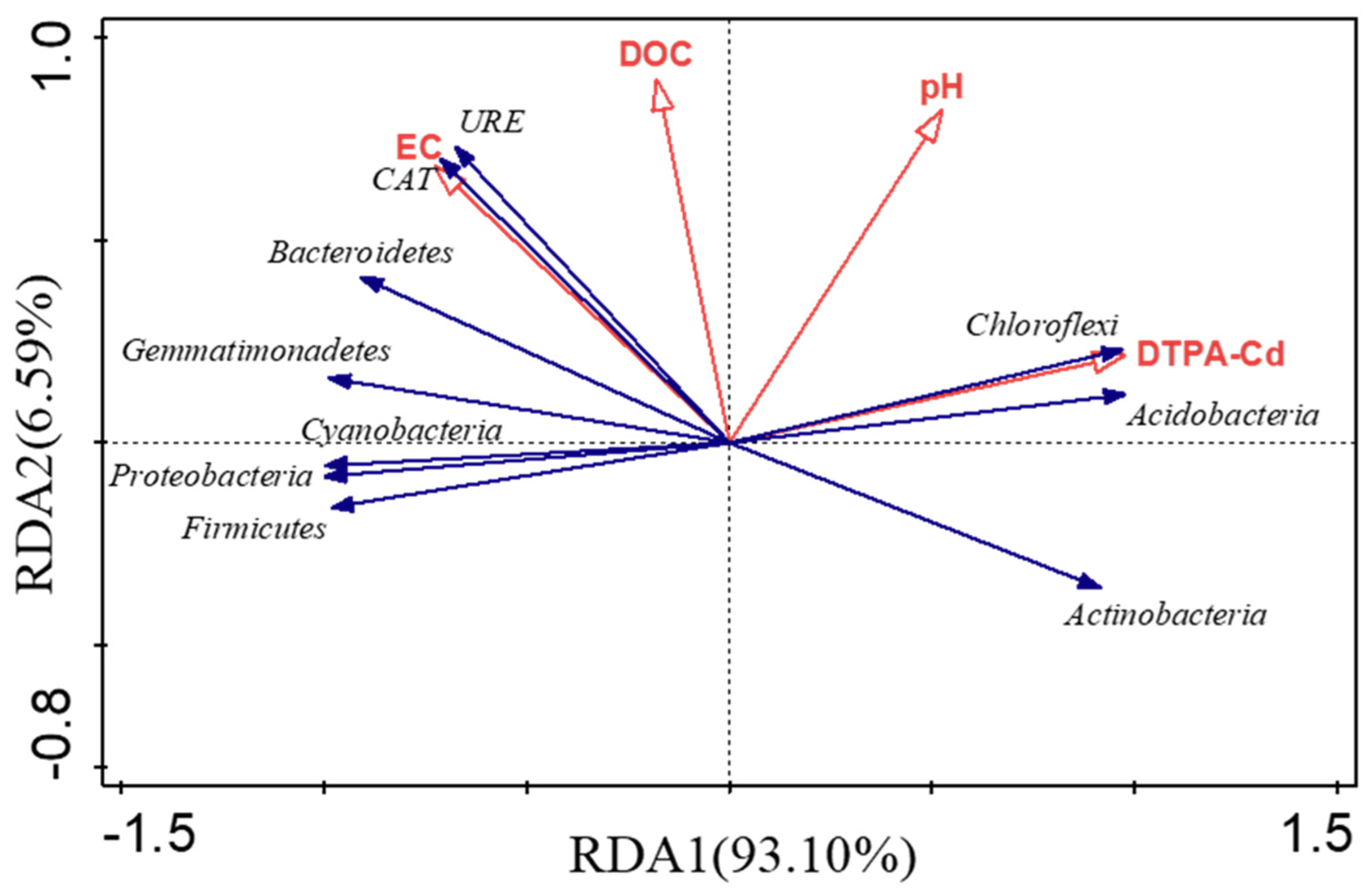
3.3.2. Analysis of Relationship
4. Discussion
4.1. Causes of Changes in Soil pH and DOC Content
4.2. Effects of Different Treatments on the Change in Cadmium Content in Soil Pore Water
4.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Available Cadmium Content
4.4. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Enzyme Activity
4.5. Effects of Different Treatments on the Growth of Amaranth in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil
4.6. Effects of Different Treatments on the Absorption and Accumulation of Cadmium and Phosphorus in Amaranth
4.7. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Microbial Community Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Lu, L.; Xiao, X.; Chen, B. Novel insights into effects of silicon-rich biochar (Sichar) amendment on cadmium uptake, translocation and accumulation in rice plants. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Sohail, M.I.; Cao, X.; Hussain, B.; Aziz, M.Z.; Usman, M.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X. An explanation of soil amendments to reduce cadmium phytoavailability and transfer to food chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Qiu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhong, L.; Fu, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Yang, D.; Xu, C.C. Lignin derived carbon materials: Current status and future trends. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Li, T.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J. Arsenic and cadmium in soils from a typical mining city in Huainan, China: Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and health risk assessment. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Huang, M. Effects of combined microbial fungicide and soybean straw biochar onnutrients and quality of Brassica napus in black soil of sand ginger. China Cucurbit 2024, 37, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, Y.; Wang, X.; Ji, M.; Sang, W.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Influence of temperature change on the immobilization of soil Pb and Zn by hydrochar: Roles of soil microbial modulation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, P.; Ye, H.; Chen, Z.; Guo, S.; Wang, L.; He, B.; Zeng, E. Impact of osmoregulation on the differences in Cd accumulation between two contrasting edible amaranth cultivars grown on Cd-polluted saline soils. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirahmadi, E.; Ghorbani, M.; Moudrý, J. Effects of zeolite on aggregation, nutrient availability, and growth characteristics of corn (Zea mays L.) in cadmium-contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, X.; Liu, F.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, P.; Ji, P. A two-year field study of using a new material for remediation of cadmium contaminated paddy soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Zhao, L.; Rui, X.; Hu, J.; Zhu, N. A review of pristine and modified biochar immobilizing typical heavy metals in soil: Applications and challenges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; Tian, Q.; Hou, R.; Wang, S. Combing phosphorus-modified hydrochar and zeolite prepared from coal gangue for highly effective immobilization of heavy metals in coal-mining contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Guo, C.; Lei, C.; Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Zheng, X.; Hu, Q. High-performance biochar derived from the residue of Chaga mushroom (Inonotus obliquus) for pollutants removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, H.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T. Efficient immobilization of toxic heavy metals in multi-contaminated agricultural soils by amino-functionalized hydrochar: Performance, plant responses and immobilization mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Dong, H.; Sarkar, B.; Song, H.; Li, J.; Bolan, N.; Quin, B.F.; Yang, X.; Li, F.; et al. Chitin and crawfish shell biochar composite decreased heavy metal bioavailability and shifted rhizosphere bacterial community in an arsenic/lead co-contaminated soil. Environ. Int. 2023, 176, 107989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Q.; Guo, X.; Zou, G.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Sun, Q. Hydrochar reduces oxytetracycline in soil and Chinese cabbage by altering soil properties, shifting microbial community structure and promoting microbial metabolism. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M.A. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovet, L.; Kammer, P.M.; Meylan-Bettex, M.; Guadagnuolo, R.; Matera, V. Cadmium accumulation capacities of Arabis alpina under environmental conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckeman, T.; Thomine, S. Mechanisms of cadmium accumulation in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2020, 39, 322–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Guo, N.; Chen, X. Intercropping with Brassica juncea L. enhances maize yield and promotes phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by changing rhizosphere properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C.; Shi, L.; Han, X.; Ran, H. Modelling mass balance of cadmium in paddy soils under long term control scenarios. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Zhang, X.; Qi, L.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Zhong, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer increases the uptake of soil heavy metal pollutants by plant community. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, B.K.; Akhtar, M.S.; Panwar, J. Rhizospheric Plant-Microbe Interactions: Key Factors to Soil Fertility and Plant Nutrition. In Plant Microbes Symbiosis: Applied Facets; Arora, N., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S. Soil Enzyme and Its Research Method; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R. Methods of Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S. Effects of Phosphorus on Cadmium Accumulation and Tolerance in Alfalfa and Its Mechanism; Yunnan Agricultural University: Kunming, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W. Reducing CH4 and CO2 emissions from waterlogged paddy soil with biochar. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Teng, W.; Mo, Y.T.; Yi, B.; Chen, W.L.; Pang, Y.P.; Wang, L. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilization on plant growth, element levels in plants and soil, and the relationships among nutrient concentrations, plant yield, and nutrient status in Erythropalum scandens (Blume). J. Plant Nutr. 2024, 47, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, L.A. Amino acids in the rhizosphere: From plants to microbes. Am. J. Bot. 2013, 100, 1692–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pei, J.; Fang, C.; Li, B.; Nie, M. Thermal adaptation of microbial respiration persists throughout long-term soil carbon decomposition. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 26, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Suriyagoda, L.D.; Lambers, H. Tightening the phosphorus cycle through phosphorus-efficient crop genotypes. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meharg, A.A.; Hartley Whitaker, J. Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and nonresistant plant species. New Phytol. 2002, 154, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Seo, B.; Owens, G.; Kim, K.R. Phytoavailability control based management for paddy soil contaminated with Cd and Pb: Implications for safer rice production. Geoderma 2016, 270, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, Y.; Demopoulos, G.P. Incorporation of arsenic into gypsum: Relevant to arsenic removal and immobilization process in hydrometallurgical industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ali, A.; Guan, W.; Xiao, R.; Wang, J.J.; Ma, S.; Guo, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Characterization of phosphorus engineered biochar and its impact on immobilization of Cd and Pb from smelting contaminated soils. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zheng, H.; Yin, S.; Zhang, X.; You, X.; Wu, H.; Suo, F.; Han, K.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Comparative study of pyrochar and hydrochar on peanut seedling growth in a coastal salt-affected soil of Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Li, T.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R. Influences of modified biochar on metal bioavailability, metal uptake by wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.) and the soil bacterial community. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Owens, V.N.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, S.M.; Park, H.C.; Kim, K.K.; Son, H.J.; Hong, C.O. Effect of phosphate addition on cadmium precipitation and adsorption in contaminated arable soil with a low concentration of cadmium. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Cao, K.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.X.; Wang, Z.J. Interaction and Mechanism Between Conditioning Agents and Two Elements in the Soil Enriched with Phosphorus and Cadmium. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2021, 42, 3028–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Rinklebe, J. Immobilization of zinc and cadmium by biochar-based sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron in a co-contaminated soil: Performance, mechanism, and microbial response. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 165968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Aizpurua, A.; Riga, P.; Amézaga, A.I. Soil enzyme activities as biological indicators of soil health. Rev. Environ. Health 2003, 18, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.A.; Scelza, R.; Acevedo, F.; Diez, M.C.; Gianfreda, L. Enzymes as useful tools for environmental purposes. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; McGrouther, K.; Huang, H.; Lu, K.; Guo, X.; He, L.; Lin, X.; Che, L.; Ye, Z.; et al. Effect of biochar on the extractability of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and enzyme activity in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, N.; Liang, X.F.; Qin, X.; Zhao, L.J.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.B. Remediation and persistent stability effects of sepiolite on cadmium-contaminated paddy soil. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kotroczo, Z.; Veres, Z.; Fekete, I.; Krakomperger, Z.; Tóth, J.A.; Lajtha, K.; Tóthmérész, B. Soil enzyme activity in response to long-term organic matter manipulation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, A.; Gurmesa, G.A.; Yang, F.; Long, C.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, X. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in secondary grasslands along a climatic gradient of subtropical China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawornchaisit, U.; Polprasert, C. Evaluation of phosphate fertilizers for the stabilization of cadmium in highly contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Ma, A.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, X.L.; Bai, Z.H.; Zhang, X.K.; Zhuang, G.Q. Assessing the effect of phosphate and silicate on Cd bioavailability in soil using an Escherichia coli cadAp: Luc-based whole-cell sensor. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, G.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liang, X.; Wang, L. Evaluation of the effectiveness of sepiolite, bentonite, and phosphate amendments on the stabilization remediation of cadmium-contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X. Biochar combined with phosphate fertilizer application reduces soil cadmium availability and cadmium uptake of maize in Cd-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 25925–25938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, T.; Liang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhao, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, G. Effectiveness of lime and peat applications on cadmium availability in a paddy soil under various moisture regimes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7757–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.S.; Choppala, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Sanderson, P.; Wang, H.; Currie, L.D.; Tsang, D.C.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, G. Potential value of phosphate compounds in enhancing immobilization and reducing bioavailability of mixed heavy metal contaminants in shooting range soil. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varalakshmi, L.R.; Ganeshamurthy, A.N. Effect of cadmium on plant biomass and cadmium accumulation in amaranthus (Amaranthus tricolor) cultivars. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 79, 861–864. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, R.; Wang, X.B.; Huo, W.M. Effects of different phosphate fertilizer varieties on cadmium accumulation in amaranth. China Soil Fertil. 2018, 1, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L. Effects of phosphorus amendments and plant growth on the mobility of Pb, Cu, and Zn in a multi-metal-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauddh, K.; Singh, R.P. Effects of organic and inorganic amendments on bio-accumulation and partitioning of Cd in Brassica juncea and Ricinus communis. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhai, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, H. Biochar derived from hydrolysis of sewage sludge influences soil properties and heavy metals distributed in the soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Shao, P.; Sun, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Z. Variation in bacterial community structure in rhizosphere and bulk soils of different halophytes in the yellow river delta. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 9, 816918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.Q.; Sha, C.Y.; Ye, C.M.; Huang, S.F. Effects of Manure and Organic Fertilizer Application on Soil Microbial Community Diversity in Paddy Fields. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4262–4272. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Lin, P.; Sun, H.; Hou, J.; Zuo, Q.; Huo, R. Response of CaCl2-extractable heavy metals, polychlorinated biphenyls, and microbial communities to biochar amendment in naturally contaminated soils. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Qu, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Pan, G. Consistent increase in abundance and diversity but variable change in community composition of bacteria in topsoil of rice paddy under short term biochar treatment across three sites from South China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 91, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.; Gupta, V.V.; Reith, F.; Bissett, A.; Mele, P.; Franco, C.M. Biogeography and emerging significance of Actinobacteria in Australia and Northern Antarctica soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.G.; Sun, W.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Long, S.X.; He, X.T.; Lin, Z.; Liang, J.L.; et al. Rhizobacteria communities reshaped by red mud based passivators is vital for reducing soil Cd accumulation in edible amaranth. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Lin, D.; Yao, Y.; Song, N.; Wang, F. Co-application of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer promotes rice performance, decreases cadmium availability, and shapes rhizosphere bacterial community in paddy soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, J.; Park, K. Long-term effects of imbalanced fertilization on the composition and diversity of soil bacterial community. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.G. Microbe Profile: Cellvibrio japonicus: Living the sweet life via biomass break-down. Microbiology 2024, 170, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ali, A.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, S. The performance and mechanism of simultaneous removal of calcium and heavy metals by Ochrobactrum sp. GMC12 with the chia seed (Salvia hispanica) gum as a synergist. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Effects of Cotton Straw Biochar on Soil Microbial Community Composition and Function. Master’s Thesis, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Hao, Z.; Wu, H.; Jiang, H.; Yang, M.; Wang, C. Co-occurrence patterns of the microbial community in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated riverine sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Vázquez, K.R.; García Cárdenas, E.; Barrera Ortiz, S.; Ortiz-Castro, R.; Ruiz-Herrera, L.F.; Ramos-Acosta, B.P.; Coria-Arellano, J.L.; Sáenz-Mata, J.; López-Bucio, J. The plant beneficial rhizobacterium Achromobacter sp. 5B1 influences root development through auxin signaling and redistribution. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1639–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Treatment | Cd Content (mg·kg−1) | Cd Accumulation (μg·pot−1) | Available Cadmium | Bioaccumulation Factor | Translocation Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot | Root | Shoot | Root | ||||
| CK | 2.02 ± 0.03 a | 4.75 ± 0.17 a | 2.81 ± 0.10 c | 6.02 ± 0.31 c | 0.85 ± 0.03 a | 2.13 | 0.42 |
| T1 | 1.68 ± 0.02 b | 3.65 ± 0.03 b | 3.66 ± 0.04 ab | 6.97 ± 0.16 ab | 0.81 ± 0.06 b | 1.77 | 0.46 |
| T2 | 1.57 ± 0.01 c | 3.03 ± 0.02 c | 3.89 ± 0.06 b | 6.60 ± 0.08 b | 0.78 ± 0.05 c | 1.65 | 0.51 |
| T3 | 1.34 ± 0.01 d | 2.65 ± 0.05 d | 3.91 ± 0.11 a | 7.26 ± 0.19 a | 0.75 ± 0.05 d | 1.42 | 0.51 |
| T4 | 1.07 ± 0.02 e | 1.94 ± 0.03 e | 3.90 ± 0.11 ab | 6.72 ± 0.11 ab | 0.72 ± 0.04 e | 1.12 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Z.; Hua, H.; Yin, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, W. The Combination of Biochar and Phosphorus-Containing Materials Can Effectively Enhance the Remediation Capacity of Amaranth on Cadmium-Contaminated Soil and Improve the Structure of Microbial Communities. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102300
Jiang Z, Hua H, Yin Z, Wu T, Zhou Y, Chen D, Li X, Zhao M, Wang W. The Combination of Biochar and Phosphorus-Containing Materials Can Effectively Enhance the Remediation Capacity of Amaranth on Cadmium-Contaminated Soil and Improve the Structure of Microbial Communities. Agronomy. 2024; 14(10):2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102300
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Zhiyang, Hongmei Hua, Zheng Yin, Tingsen Wu, Yuzhi Zhou, Daokun Chen, Xinbin Li, Mingze Zhao, and Wenshuo Wang. 2024. "The Combination of Biochar and Phosphorus-Containing Materials Can Effectively Enhance the Remediation Capacity of Amaranth on Cadmium-Contaminated Soil and Improve the Structure of Microbial Communities" Agronomy 14, no. 10: 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102300
APA StyleJiang, Z., Hua, H., Yin, Z., Wu, T., Zhou, Y., Chen, D., Li, X., Zhao, M., & Wang, W. (2024). The Combination of Biochar and Phosphorus-Containing Materials Can Effectively Enhance the Remediation Capacity of Amaranth on Cadmium-Contaminated Soil and Improve the Structure of Microbial Communities. Agronomy, 14(10), 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102300






