The Impact of Applying Different Fertilizers on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ammonia Volatilization from Northeast Spring Corn
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Site
2.2. Field Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Greenhouse Gas Flux
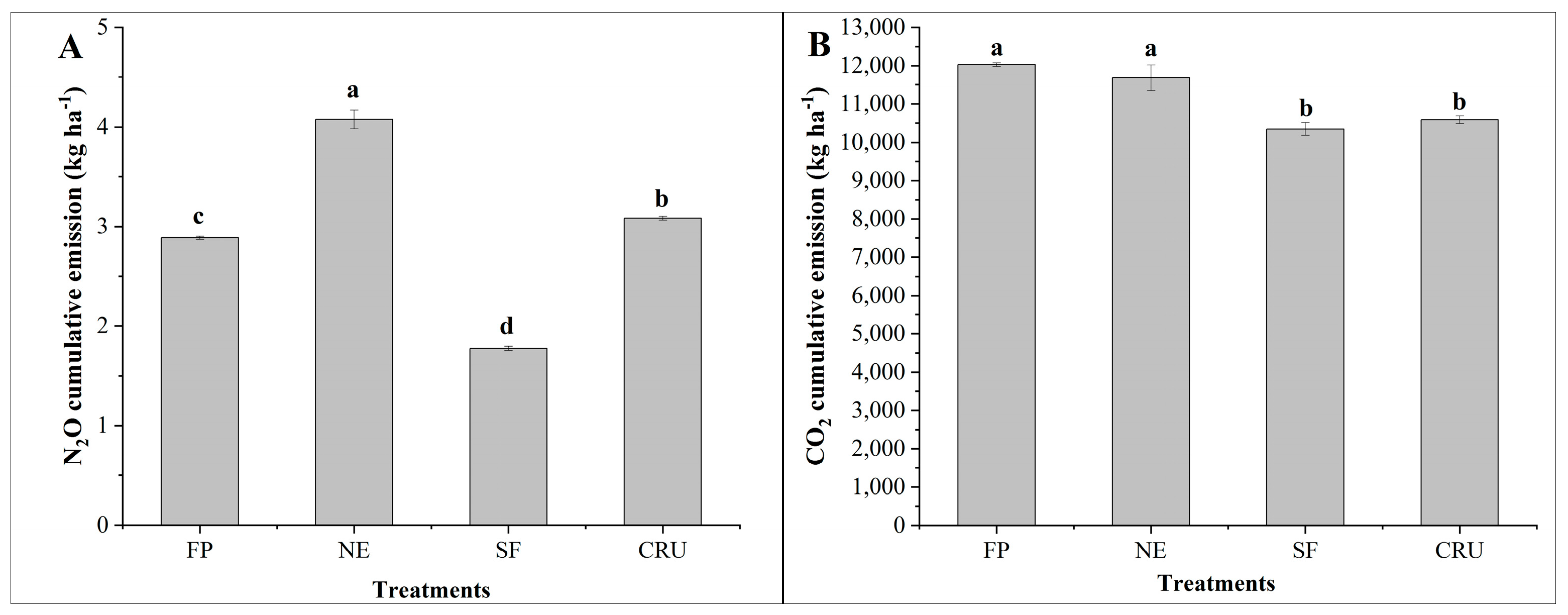
3.2. Greenhouse Gas Accumulation
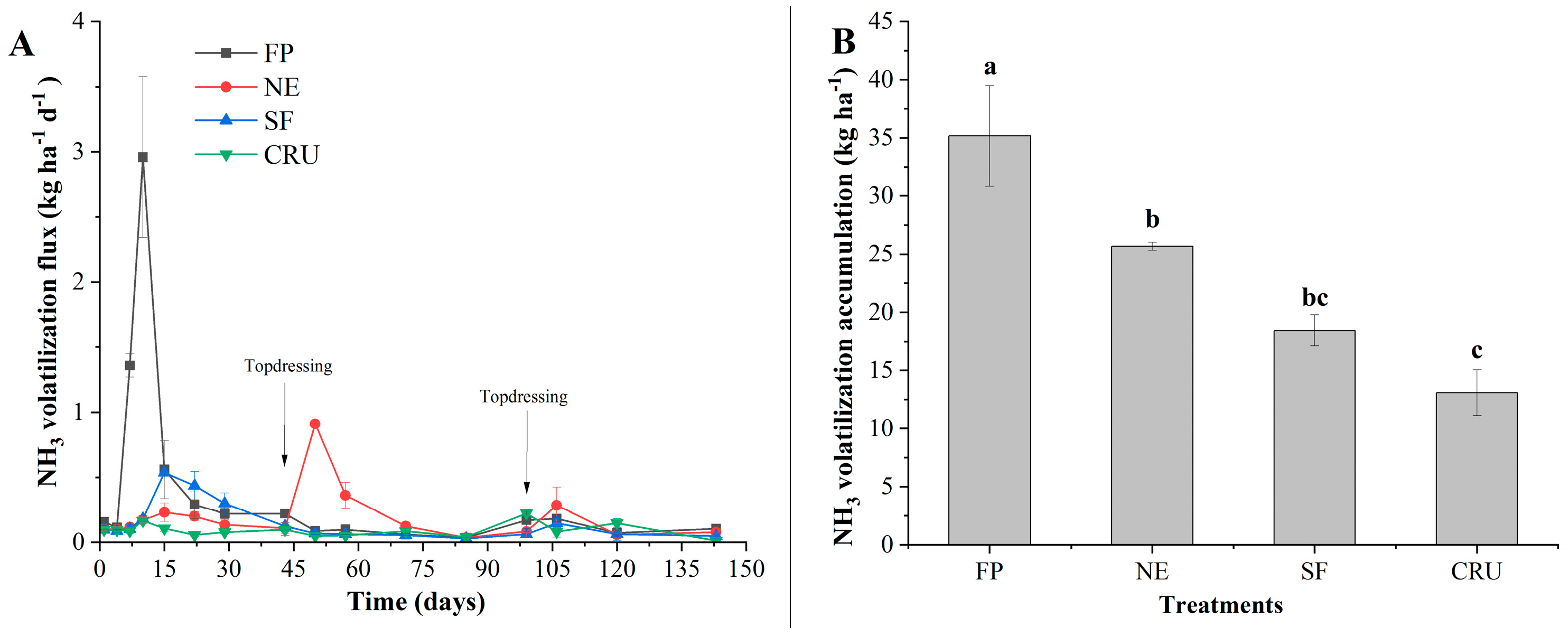
3.3. Ammonia Volatilization Flux and Accumulation
3.4. Global Warming Potential, Corn Yieldp, and Greenhouse Gas Emission Intensity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidson, E.A. The contribution of manure and fertilizer nitrogen to atmospheric nitrous oxide since 1860. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.; von Braun, J. Climate Change Impacts on Global Food Security. Science 2013, 341, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, L.; Bai, W.; Feng, C.; Song, Y.; Gong, P.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L. Effects of Corn Stalks and Urea on N2O Production from Corn Field Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Bai, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Rong, M.; Wang, Z. Strip-Till Farming: Combining Controlled-Release Blended Fertilizer to Enhance Rainfed Maize Yield While Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wei, P.; Hao, F. Farmland-atmosphere feedbacks amplify decreases in diffuse nitrogen pollution in a freeze-thaw agricultural area under climate warming conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Zhai, L.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, Q.; Bashir, M.A.; et al. Long-term manure application increased greenhouse gas emissions but had no effect on ammonia volatilization in a Northern China upland field. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dodla, S.K.; Myers, G. Application effects of coated urea and urease and nitrification inhibitors on ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from a subtropical cotton field of the Mississippi delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.P.; Tobin, J.T.; Forrestal, P.J.; Danaher, M.; Nkwonta, C.G.; Richards, K.; Cummins, E.; Hogan, S.A.; O’Callaghan, T.F. Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors—As Mitigation Tools for Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Sustainable Dairy Systems: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.L.; Sermarini, R.A.; Filho, C.R.d.S.A.; Bendassolli, J.A.; Boschiero, B.N.; Trivelin, P.C.O. 15N-Fertilizer Recovery in Maize as an Additional Strategy for Understanding Nitrogen Fertilization Management with Blends of Controlled-Release and Conventional Urea. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, R.K.; Bijarniya, D.; Kakraliya, S.K.; Sapkota, T.B.; Kakraliya, M.; Jat, M.L. Precision Nutrient Rates and Placement in Conservation Maize-Wheat System: Effects on Crop Productivity, Profitability, Nutrient-Use Efficiency, and Environmental Footprints. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanick, B.; Kumar, M.; Naik, B.M.; Kumar, M.; Singh, S.K.; Maitra, S.; Naik, B.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T. Long-Term Conservation Tillage and Precision Nutrient Management in Maize-Wheat Cropping System: Effect on Soil Properties, Crop Production, and Economics. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Yin, G.; Gu, J.; Ma, N. Estimation of Spring Maize Evapotranspiration in Semi-Arid Regions of Northeast China Using Machine Learning: An Improved SVR Model Based on PSO and RF Algorithms. Water 2023, 15, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; He, P.; Xu, X.P.; Ding, W.C.; Ullah, S.; Wang, Y.L.; Jia, L.L.; Cui, R.Z.; Wang, H.T.; Zhou, W. Nutrient Expert Improves Nitrogen Efficiency and Environmental Benefits for Winter Wheat in China. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, B.; Waqas, M.A.; Cai, W.; Guo, C.; Zhou, S.; Su, R.; Qin, X.; et al. Combination of modified nitrogen fertilizers and water saving irrigation can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase rice yield. Geoderma 2018, 315, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Bai, E.; Cui, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, X. The strategy of microbial utilization of the deposited N in a temperate forest soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 56, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Fan, D.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, J.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizers reduces ammonia volatilization and increases nitrogen utilization efficiency in no-tillage paddy fields in central China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ren, T.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Zou, J.; Hussain, S.; Cong, R.; Wu, L.; Lu, J.; Li, X. Producing more grain yield of rice with less ammonia volatilization and greenhouse gases emission using slow/controlled-release urea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 2569–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizimana, F.; Timilsina, A.; Dong, W.; Uwamungu, J.Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Pandey, B.; Qin, S.; Hu, C. Effects of long-term nitrogen fertilization on N2O, N2 and their yield-scaled emissions in a temperate semi-arid agro-ecosystem. J. Soil. Sediment. 2021, 21, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, R.; Kumar, D.; Sepat, S.; Ghosh, A.; Banerjee, K.; Shivay, Y.S.; Gawdiya, S.; Harish, M.N.; Bhatia, A.; Kumawat, A.; et al. Precision nutrient management influences the productivity, nutrients use efficiency, N2O fluxes and soil enzymatic activity in zero-till wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Field Crops Res. 2024, 317, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitthisuwannakul, K.; Boonpavanitchakul, K.; Wirunmongkol, T.; Muthitamongkol, P.; Kangwansupamonkon, W. A tunable controlled-release urea fertilizer coated with a biodegradable polyurethane-nanoclay composite layer. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2022, 20, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Burger, M.; Doane, T.A.; Horwath, W.R. Ammonia oxidation pathways and nitrifier denitrification are significant sources of N2O and NO under low oxygen availability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruser, R.; Schulz, R. The effect of nitrification inhibitors on the nitrous oxide (N2O) release from agricultural soils-a review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xue, L.; Liu, J.; Xia, L.; Jia, P.; Feng, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhao, X. Biochar application reduced carbon footprint of maize production in the saline-alkali soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 368, 109001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, C.; Lamprecht, R.E.; Marushchak, M.E.; Lind, S.E.; Novakovskiy, A.; Aurela, M.; Martikainen, P.J.; Biasi, C. Warming of subarctic tundra increases emissions of all three important greenhouse gases—Carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 23, 3121–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Jeffery, S.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Guardia, G.; Vallejo, A. Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.M.a.; Yusop, M.K.; Othman, R.; Wahid, S.A. Field Evaluation of Newly-Developed Controlled Release Fertilizer on Rice Production and Nitrogen Uptake. Sains Malays. 2017, 46, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasda, G.; Hähndel, R.; Zerulla, W. Effect of fertilizers with the new nitrification inhibitor DMPP (3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate) on yield and quality of agricultural and horticultural crops. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venterea, R.T.; Bijesh, M.; Dolan, M.S. Fertilizer source and tillage effects on yield-scaled nitrous oxide emissions in a corn cropping system. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Base Fertilizer | First Topdressing | Second Topdressing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N Kg ha−1 | P2O5 kg ha−1 | K2O kg ha−1 | N kg ha−1 | P2O5 kg ha−1 | K2O kg ha−1 | N kg ha−1 | P2O5 kg ha−1 | K2O kg ha−1 | |
| FP | 156 | 60 | 72 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NE | 83 | 120 | 69 | 69 | 0 | 61 | 48 | 0 | 0 |
| SF | 200 | 120 | 130 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CRU | 200 | 120 | 130 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Treatments | N2O Cumulative Emissions kg ha−1 | CO2 Cumulative Emissions kg ha−1 | GWP kg CO2-eq ha−1 | Corn Yield kg ha−1 | GHGI kg kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP | 2.89 ± 0.02c | 12,031 ± 44a | 12,891 ± 41a | 12,182 ± 492b | 1.06 ± 0.04a |
| NE | 4.07 ± 0.09a | 11,685 ± 339a | 12,899 ± 333a | 12,498 ± 749ab | 1.04 ± 0.06a |
| SF | 1.78 ± 0.02d | 10,351 ± 163b | 10,881 ± 157c | 14,113 ± 351a | 0.77 ± 0.01c |
| CRU | 3.08 ± 0.02b | 10,589 ± 100b | 11,508 ± 100b | 12,594 ± 172ab | 0.91 ± 0.01b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Han, M.; Gong, P.; Xue, Y.; Song, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L. The Impact of Applying Different Fertilizers on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ammonia Volatilization from Northeast Spring Corn. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122798
Wu K, Wang L, Zhang L, Han M, Gong P, Xue Y, Song Y, Wu Z, Zhang L. The Impact of Applying Different Fertilizers on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ammonia Volatilization from Northeast Spring Corn. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122798
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kaikuo, Longfei Wang, Lei Zhang, Mei Han, Ping Gong, Yan Xue, Yuchao Song, Zhijie Wu, and Lili Zhang. 2024. "The Impact of Applying Different Fertilizers on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ammonia Volatilization from Northeast Spring Corn" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122798
APA StyleWu, K., Wang, L., Zhang, L., Han, M., Gong, P., Xue, Y., Song, Y., Wu, Z., & Zhang, L. (2024). The Impact of Applying Different Fertilizers on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ammonia Volatilization from Northeast Spring Corn. Agronomy, 14(12), 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122798





