Effect of Agroforestry Systems on Soil NPK and C Improvements in Karst Graben Basin of Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
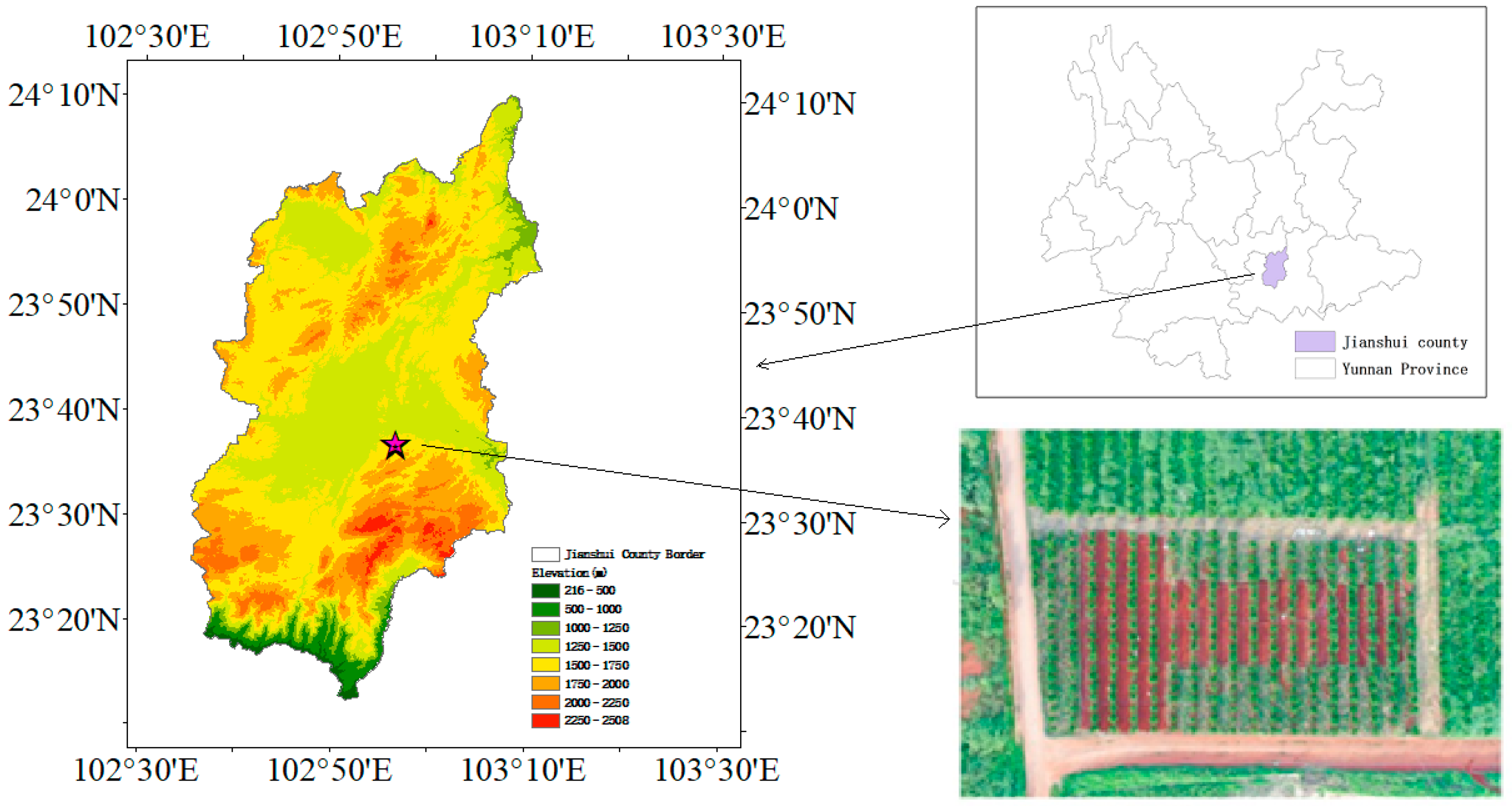
2.1. Site Description
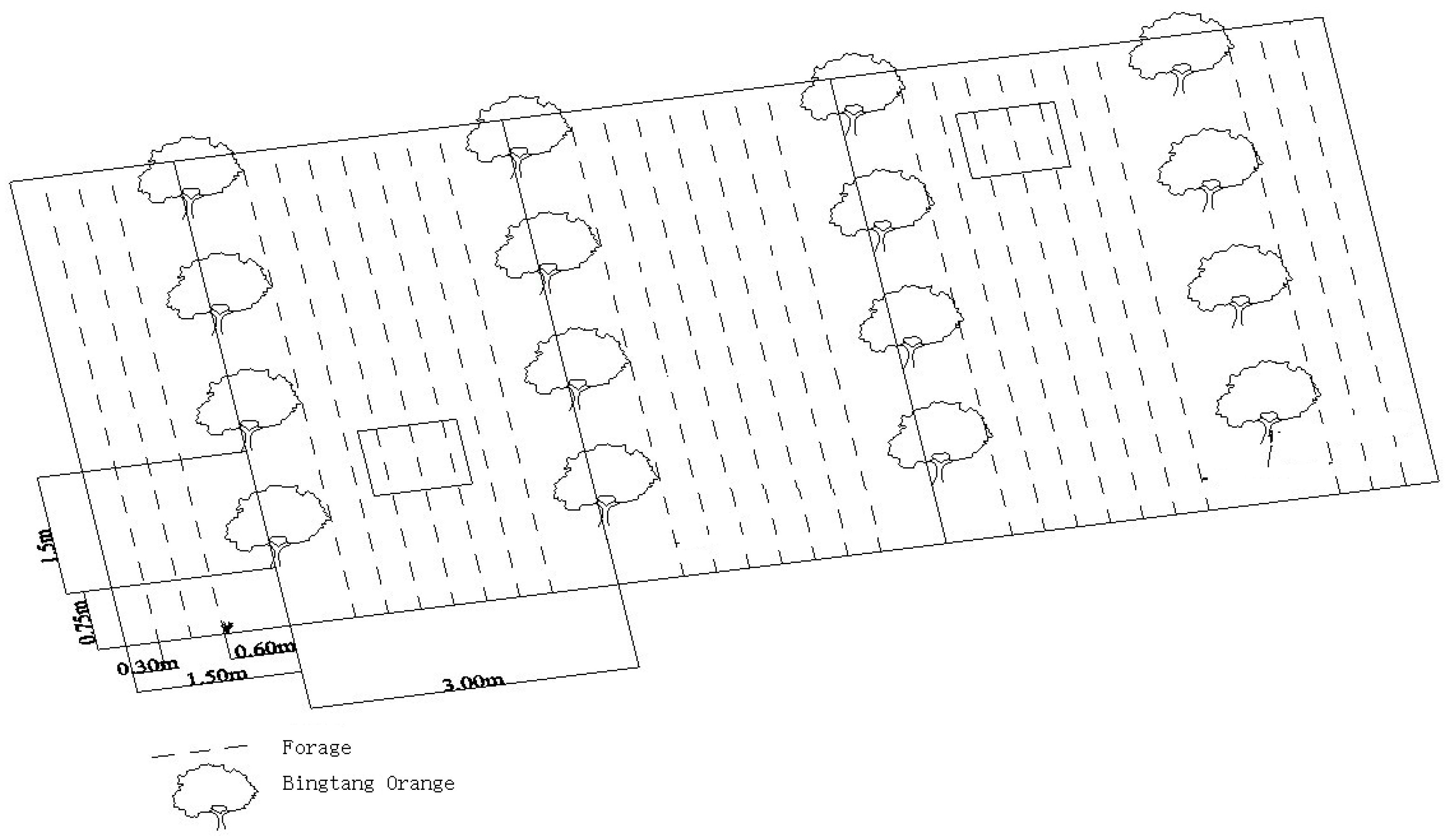
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
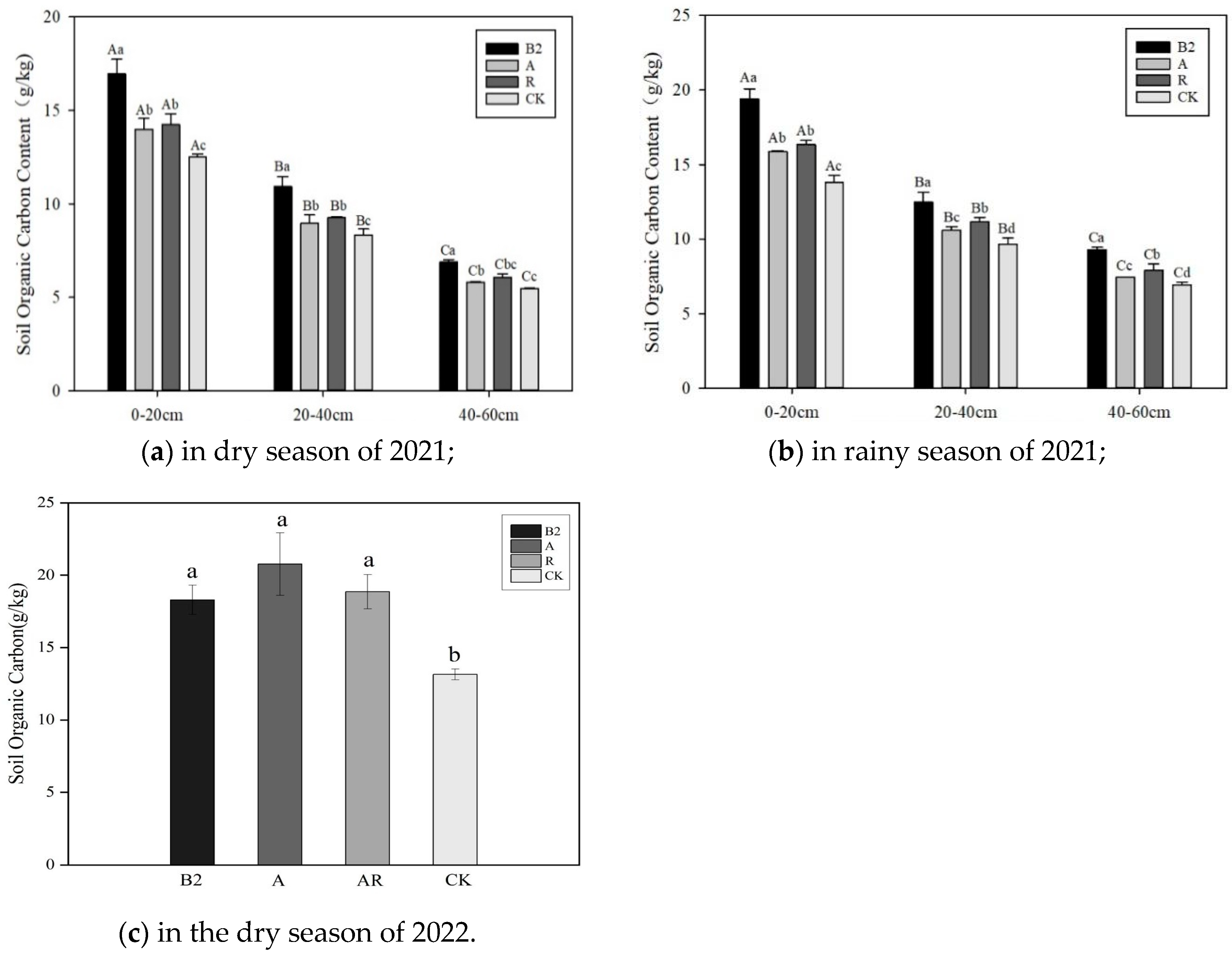
3.1. Soil SOC Characteristics
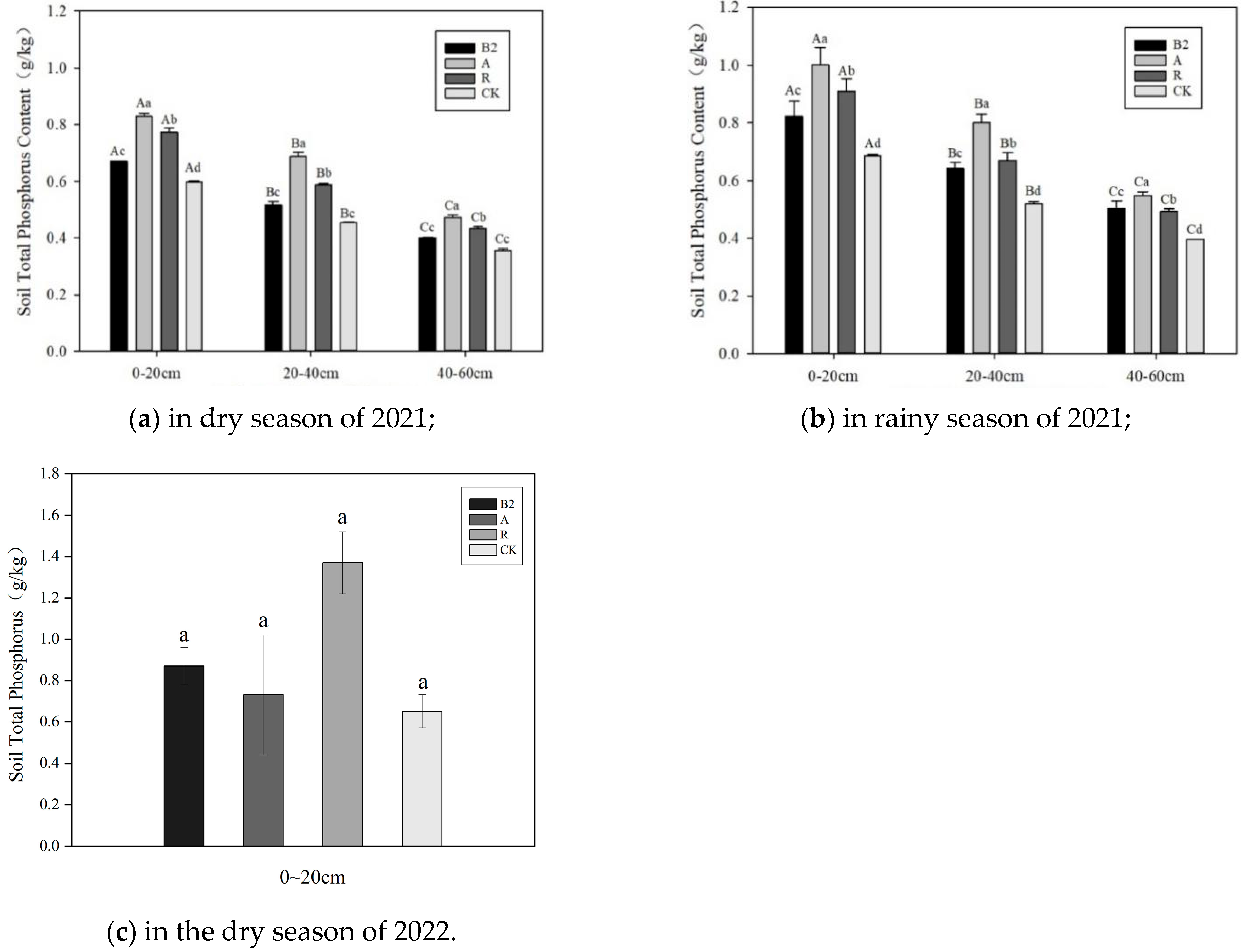
3.2. Characteristics of Total N, Total P, and Total K in Soil
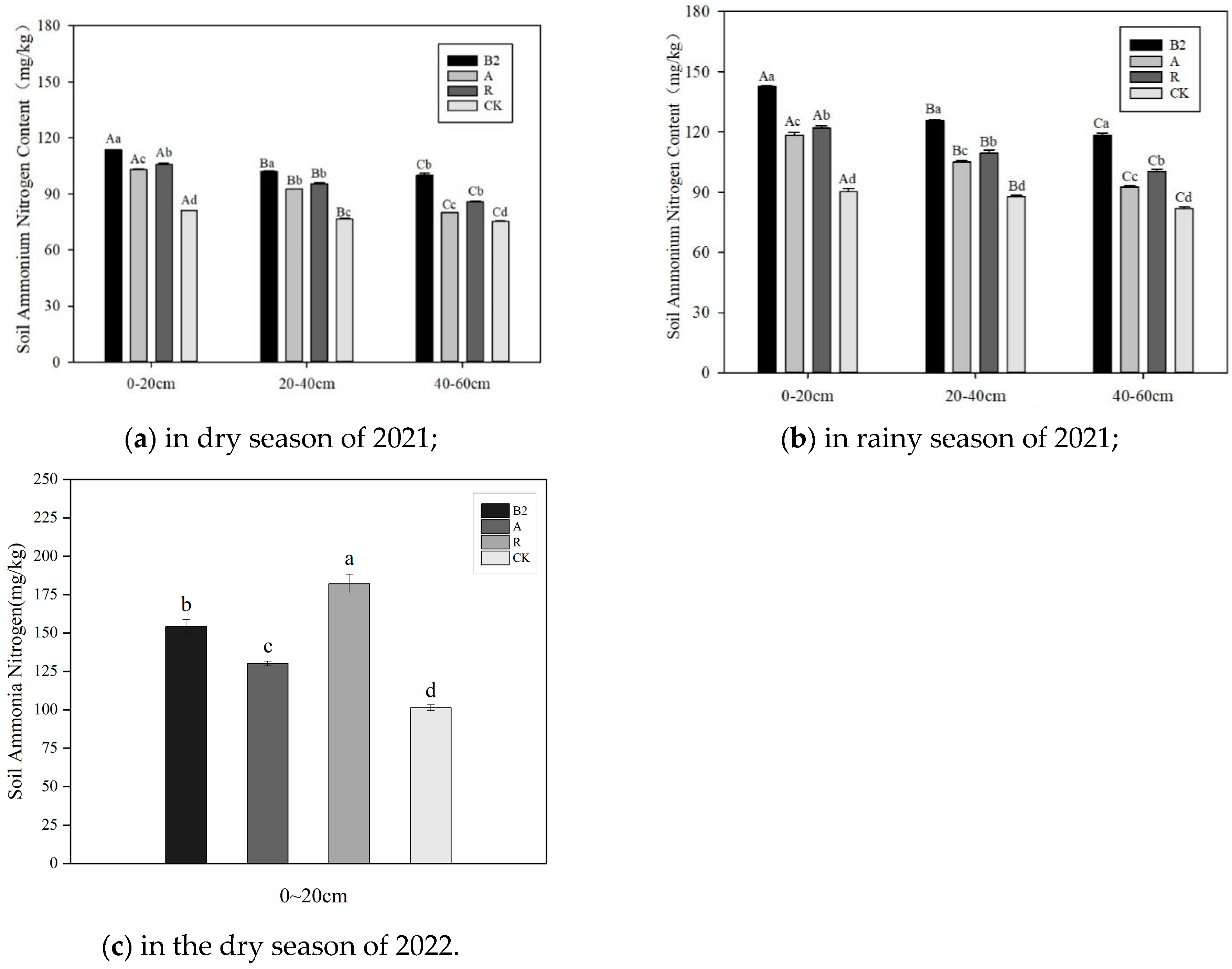
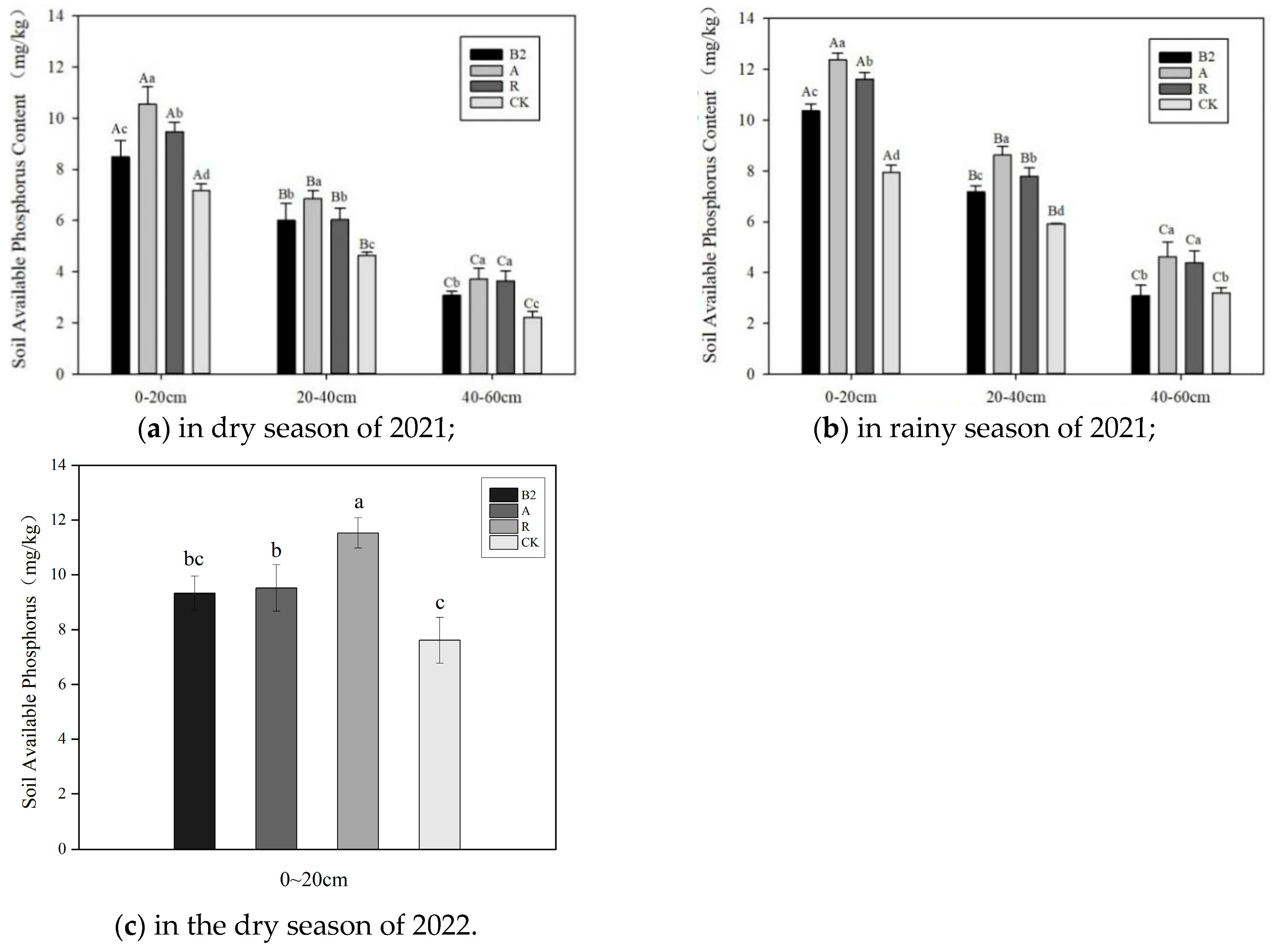
3.3. Characteristics of Available Nutrients in the Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Forest–Grass Composite Patterns on SOC
4.2. Influence of Forest-Grass Composite Patterns on Total Nutrients in Soil
4.3. Influence of Forest-Grass Composite Patterns on Rapidly Available Nutrients in the Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Fu, Z.; Wang, K. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil properties along an elevation gradient in the karst region of southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 320, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, A.; Yang, H.; Werner, E. Impact of rocky desertification control on soil bacterial community in karst graben basin, Southwestern China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, F.; Tang, Y. Variations in soil organic carbon contents and isotopic compositions under different land uses in a typical karst area in southwest china. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Ci, E.; Tang, X.; Liu, S.; Ding, Z.; Ma, M. The increased soil aggregate stability and aggregate-associated carbon by farmland use change in a karst region of southwest China. CATENA 2023, 231, 107284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Amirahmadi, E.; Konvalina, P.; Moudrý, J.; Kopecký, M.; Hoang, T.N. Carbon pool dynamic and soil microbial respiration affected by land use alteration: A case study in humid subtropical area. Land 2023, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, K.D. Linking Land Quality, Agricultural Productivity, and Food Security; USDA-ERS Agricultural Economic Report; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Lin, Z.M.; Hou, Q.Z.; Luo, G.Y.; Dong, C.H.; Mai, R.Z.; Chen, S.G. Study on screening the forages for suitable planting under the camellia oleifera and eucalyptus plantations. For. Environ. Sci. 2018, 34, 85–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- King, K.F.S. The History of Agroforestry; World Agroforestry Centre: Nairobi, Kenya, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Rocheleau, D.; Weber, F.; Fieldjuma, A. Agroforestry in Dryland Africa; International Council for Research in Agroforestry: Nairobi, Kenya, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, P.K.R.; Altieri, M.A.; Hecht, S.B. Agroforestry: An approach to sustainable land use in the tropics. In Agroecology and Small Farm Development; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Ren, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y. Forest and grass composite patterns improve the soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali land of the yellow river delta, China. Geoderma 2019, 349, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Liu, T.; Wei, W.; Zhang, S.; Tuerti, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, W. Juvenile plumcot tree can improve fruit quality and economic benefits by intercropping with alfalfa in semi-arid areas. Agric. Syst. 2023, 205, 103590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, T.; Wei, W.; Shen, L.; Wang, X.; Tuertia, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, W. In arid regions, forage mulching between fruit trees rows enhances fruit tree light and lowers soil salinity. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, S.; Chavan, S.B.; Chichaghare, A.R.; Uthappa, A.R.; Kumar, M.; Kakade, V.; Pradhan, A.; Jinger, D.; Rawale, G.; Yadav, D.K.; et al. Agroforestry Systems for Soil Health Improvement and Maintenance. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; Ma, Y.; Ge, H.X.; Ge, X.; Fu, S. Pecan agroforestry systems improve soil quality by stimulating enzyme activity. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, L.R.; Salazar, J.C.S.; Casanoves, F.; Bieng, M.A.N. Cacao agroforestry systems improve soil fertility: Comparison of soil properties between forest, cacao agroforestry systems, and pasture in the Colombian Amazon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 314, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Kassahun, G.; Yimer, F.; Brüggemann, N.; Glaser, B. Agroforestry practices and on-site charcoal production enhance soil fertility and climate change mitigation in northwestern Ethiopia. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, N.; Schickhoff, U.; Fischer, E. Transition to agroforestry significantly improves soil quality: A case study in the central mid-hills of Nepal. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 205, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahangdale, C.P.; Kosta, L.D.; Rajawat, B.S. Impact of bamboo based agroforestry system on organic matter built-up and nutritional status of soil. J. Trop. For. 2014, 30, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Waswa, B. Soil Organic Matter Status under Different Agroforestry Management Practices in Three Selected Sites in Kenya; Kenyatta University Library: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Xiong, K.; Chi, Y.; Song, S. Effects of crop and grass intercropping on the soil environment in the karst area. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, R.; Kühnel, A.; Lu, J.; Dettmann, H.; Wang, W.; Wiesmeier, M. Soil carbon sequestration by agroforestry systems in China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 315, 107437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, A.; Jacobson, M.G. Soil carbon sequestration in agroforestry systems: A meta-analysis. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Nair, P.; Nair, V.D.; Viswanath, S.; Bhattacharjee, A. Depth-wise distribution of soil-carbon stock in aggregate-sized fractions under shaded-perennial agroforestry systems in the western ghats of Karnataka, India. Agrofor. Syst. 2020, 94, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.E.; Benitez, E.; Garcia, P.A.; Robles, A.B. Cover crop under different managements vs. frequent tillage in almond orchards in semiarid conditions: Effects on soil quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Leggett, Z.H.; Sucre, E.B.; Bradford, M.A. Biofuel intercropping effects on soil carbon and microbial activity. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, J.; Ahmed, T.; Hasnat, M.Z.; Karim, D. Screening of tomato varieties for fruit tree based agroforestry system. Int. J. Agric. Res. Innov. Technol. 2015, 4, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Guaitoli, F.; Santoro, A.; Cerdà, A. Managing soil nitrate with cover crops and buffer strips in Sicilian vineyards. Solid Earth 2013, 4, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenwerth, K.; Belina, K.M. Cover crops and cultivation: Impacts on soil N dynamics and microbiological function in a Mediterranean vineyard agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; Kong, T.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zheng, S.; Gao, X. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients and Intercropping Effect in Sandy Land Apple-peanut Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 43–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Hao, M.; Zhang, M. Changes in aggregate-associated organic carbon and nitrogen after 27 years of fertilization in a dryland alfalfa grassland on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Arid Land 2015, 7, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querné, A.; Battie-laclau, P.; Dufour, L.; Wery, J.; Dupraz, C. Effects of walnut trees on biological nitrogen fixation and yield of intercropped alfalfa in a Mediterranean agroforestry system. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 84, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.; Makaju, S.; Ibrahim, R.; Missaoui, A. Current progress in nitrogen fixing plants and microbiome research. Plants 2020, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zamanan, S.M.; El-Nakhlawy, F.S.; Elfeil, A. Effect of nitrogen, shading and intercropping on alfalfa-ziziphus agroforestry system under arid land conditions. J. Arid. Agric. 2016, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Porder, S.; Houlton, B.Z.; Chadwick, O.A. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergio, S.; Valeria, U.; Gaetano, A.; Salvatore, F.A.; Dario, G.; Paolo, R.; Giuseppe, D.M. Mediterranean forage legumes grown alone or in mixture with annual ryegrass: Biomass production, N2 fixation, and indices of intercrop efficiency. Plant Soil 2016, 402, 395–407. [Google Scholar]
- Clermont-Dauphin, C.; Suvannang, N.; Pongwichian, P.; Cheylan, V.; Hammecker, C.; Harmand, J. Dinitrogen fixation by the legume cover crop Pueraria phaseoloides and transfer of fixed N to Hevea brasiliensis—Impact on tree growth and vulnerability to drought. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 217, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Masoni, A.; Ercoli, L.; Arduini, I. Above- and below-ground competition between barley, wheat, lupin and vetch in a cereal and legume intercropping system. Grass Forage Sci. 2010, 64, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, X.; Hayashi, J.; Li, H. Advanced design of the ultrahigh-channel-count fiber Bragg grating based on the double sampling method. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 8382–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinael, R.; Chevallier, T.; Cambou, A.; Béral, C.; Barthès, B.G.; Dupraz, C.; Durand, C.; Kouakoua, E.; Chenu, C. Increased soil organic carbon stocks under agroforestry: A survey of six different sites in France. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Sun, W.; Chang, J.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Fang, J. Terrestrial carbon sinks in China and around the world and their contribution to carbon neutrality. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 861–895. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Torn, M.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.; et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumpel, C.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Deep soil organic matter—A key but poorly understood component of terrestrial C cycle. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Luo, C.-L.; Zhang, X.-F.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, F.-M.; Xiong, L.-B.; Kavagi, L.; Nguluu, S.N. Ridge-furrow plastic-mulching with balanced fertilization in rainfed maize (Zea mays L.): An adaptive management in east African plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 236, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Wen-Xia, D.; Tu, C.; Washburn, S.; Cheng, L.; Hu, S. Soil carbon, nitrogen and microbial dynamics of pasturelands: Impacts of grazing intensity and planting systems. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 408–416. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, T.; Mu, Y.; Jin, J.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, Z.; Nian, H. Impact of intercropping on the coupling between soil microbial community structure, activity, and nutrient-use efficiencies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasani, J. Yield comparison of mono-cropping and intercropping of legumes and grass with different rates of seed under rainfed conditions. Iran. J. Range Desert Res. 2013, 20, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- McNally, S.R.; Laughlin, D.C.; Rutledge, S.; Dodd, M.B.; Six, J.; Schipper, L.A. Root carbon inputs under moderately diverse sward and conventional ryegrass-clover pasture: Implications for soil carbon sequestration. Plant Soil 2015, 392, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, H.; Meng, C.; Jiang, P.; Fu, W. Effects of intercropping grasses on soil organic carbon and microbial community functional diversity under Chinese hickory (Carya cathayensis Sarg.) stands. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottinger, S.L.; Miniat, C.F.; Wurzburger, N. Nitrogen and light regulate symbiotic nitrogen fixation by a temperate forest tree. Oecologia 2023, 201, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, P.G.; Grimoldi, A.; Lattanzi, F.; Omacini, M. Emerging benefits of the coexistence of two microbial symbionts in pastures: Epichloid endophytes and rhizobia in a grass-legume system. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium of Forage Breeding, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 19–21 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.; Fang, L.; Wang, M.; Jiang, M.; Shen, G. Intercropping of gramineous pasture ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and leguminous forage alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) increases the resistance of plants to heavy metals. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 7803408. [Google Scholar]
- Radersma, S.; Grierson, P.F. Phosphorus mobilization in agroforestry: Organic anions, phosphatase activity and phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 2004, 259, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.L.; Alexandre, F.; Hedley, P.E.; Morris, J.A.; Derek, S.; Susanne, B. Early response mechanisms of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) to phosphorus deficiency. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.W.; Chen, Y.Q.; Egrinya, E.A.; Sui, P.; Huang, J.X. Impacts of maize intercropping with ryegrass and alfalfa on environment in fields with nitrogen fertilizer over-dose. Environ. Sci. 2012, 10, 896–901. [Google Scholar]
- Peiter, E.; Senbayram, M.; Zorb, C. Potassium in agriculture-status and perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 656–669. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, L.; Cai, Q. Linkages of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry and their relationships to forest growth in subtropical plantations. Plant Soil 2015, 392, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulc, R.M.; Albrecht, K.A.; Casler, M.D. Ryegrass companion crops for alfalfa establishment: I. Forage yield and alfalfa suppression. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E.; Barea, J.M.; McNeill, A.M.; Prigent-Combaret, C. Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhong, R.; Jiang, J.; He, L.; Huang, Z.; Shi, G.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Xiong, F.; Han, Z.; et al. Cassava/peanut intercropping improves soil quality via rhizospheric microbes increased available nitrogen contents. BMC Biotechnol. 2020, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrini, B.; Herrmann, A.M.; Nannipieri, P.; Schmidt, M.; Abiven, S. Ryegrass-derived pyrogenic organic matter changes organic carbon and nitrogen mineralization in a temperate forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, N.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Meena, V.S. Nutrient solubilizing microbes (NSMs): Its role in sustainable crop production. Agric. Important Microbes Sustain. Agric. 2017, 2, 25–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Luo, Z.; Niu, Y.; Coulter, J.A.; Zhang, R.; Li, L. Forage yield, water use efficiency, and soil fertility response to alfalfa growing age in the semiarid loess plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.; Zhang, L.Y.; Yang, H.S. Effect of different planting years on the yield of alfalfa and content of N,P,K in soil. Pratacultural Sci. 2009, 12, 82–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.R.; Condron, L.M.; Davis, M.R.; Sherlock, R.R. Phosphorus dynamics in the rhizosphere of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and radiata pine (Pinus radiata D. Don.). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Department of Systems Ecology, Research Center for Eco Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium recycling in an agroforestry ecosystem of Huanghuaihai Plain: With Paulownia elongata intercropped wheat and maize as an example. J. Environ. Sci. 1998, 2, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, C.; Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Cartes, P.; Gianfreda, L.; Mora, M.L. Phosphorus and nitrogen fertilization effect on phosphorus uptake and phosphatase activity in ryegrass and tall fescue grown in a Chilean Andisol. Soil Sci. 2011, 176, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soil Depth | Moisture Content % | pH | Soil Bulk Density g·m−3 | Soil Organic Carbon g·kg−1 | Total N g·kg−1 | Total P g·kg−1 | Total K g·kg−1 | Ammonium Nitrogen mg·kg−1 | Nitrate Nitrogen mg·kg−1 | Rapidly Available Phosphorus mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 28.04 ± 0.85 | 5.22 ± 0.16 | 1.14 ± 0.05 | 13.54 ± 0.51 | 1.04 ± 0.12 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 3.94 ± 0.25 | 70.97 ± 3.21 | 5.94 ± 0.33 | 7.12 ± 1.02 |
| 20–40 cm | 31.88 ± 1.24 | 5.70 ± 0.12 | 1.23 ± 0.03 | 7.47 ± 0.43 | 0.75 ± 0.05 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 3.55 ± 0.34 | 61.79 ± 1.65 | 3.28 ± 0.40 | 3.63 ± 0.68 |
| 40–60 cm | 36.85 ± 1.02 | 5.90 ± 0.18 | 1.27 ± 0.02 | 4.68 ± 0.45 | 0.47 ± 0.04 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 3.39 ± 0.21 | 53.34 ± 1.89 | 0.85 ± 0.30 | 1.40 ± 0.32 |
| Planting Pattern | Treatment | Forest–Grass Spacing (cm) | Time of Sowing | Seeding Rate (kg·m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bingtang orange–alfalfa single sowing | B2 | 60 | September, 2020 | 0.0018 |
| Bingtang orange–ryegrass × alfalfa mixed sowing | A | 60 | September, 2020 | 0.0018 |
| Bingtang orange–ryegrass × alfalfa intercropping | R | 60 | September, 2020 | 0.0018 |
| Bingtang orange pure forest | CK | - | - | - |
| B | CK | A | R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| the dry season in 2001 | 13.18 ± 0.68 Aa | 12.96 ± 0.55 Cab | 11.84 ± 0.71 Bb | 11.76 ± 0.41 Bb |
| rainy season in 2001 | 12.88 ± 0.97 Aab | 13.85 ± 0.17 Ba | 12.44 ± 0.48 Bb | 12.23 ± 0.12 Bb |
| dry season 2022 | 10.40 ± 0.54 Bd | 22.66 ± 0.75 Ab | 27.33 ± 0.84 Aa | 19.24 ± 0.36 Ac |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, L.; Yang, J.; Zheng, C.; Guo, J.; Zhou, J.; Han, Y.; Rebi, A. Effect of Agroforestry Systems on Soil NPK and C Improvements in Karst Graben Basin of Southwest China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061179
Wan L, Yang J, Zheng C, Guo J, Zhou J, Han Y, Rebi A. Effect of Agroforestry Systems on Soil NPK and C Improvements in Karst Graben Basin of Southwest China. Agronomy. 2024; 14(6):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061179
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Long, Jiaqi Yang, Chenghao Zheng, Jianbin Guo, Jinxing Zhou, Yuguo Han, and Ansa Rebi. 2024. "Effect of Agroforestry Systems on Soil NPK and C Improvements in Karst Graben Basin of Southwest China" Agronomy 14, no. 6: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061179
APA StyleWan, L., Yang, J., Zheng, C., Guo, J., Zhou, J., Han, Y., & Rebi, A. (2024). Effect of Agroforestry Systems on Soil NPK and C Improvements in Karst Graben Basin of Southwest China. Agronomy, 14(6), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061179






