Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Maize Landraces from Central China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Genotyping by SLAF-Seq and Quality Control
2.3. SNP Characteristics
2.4. Linkage Disequilibrium (LD)
2.5. Population Structure Analysis
2.6. Genetic Distance
2.7. Multidimensional Scaling (MDS)
2.8. Population Distance
3. Results
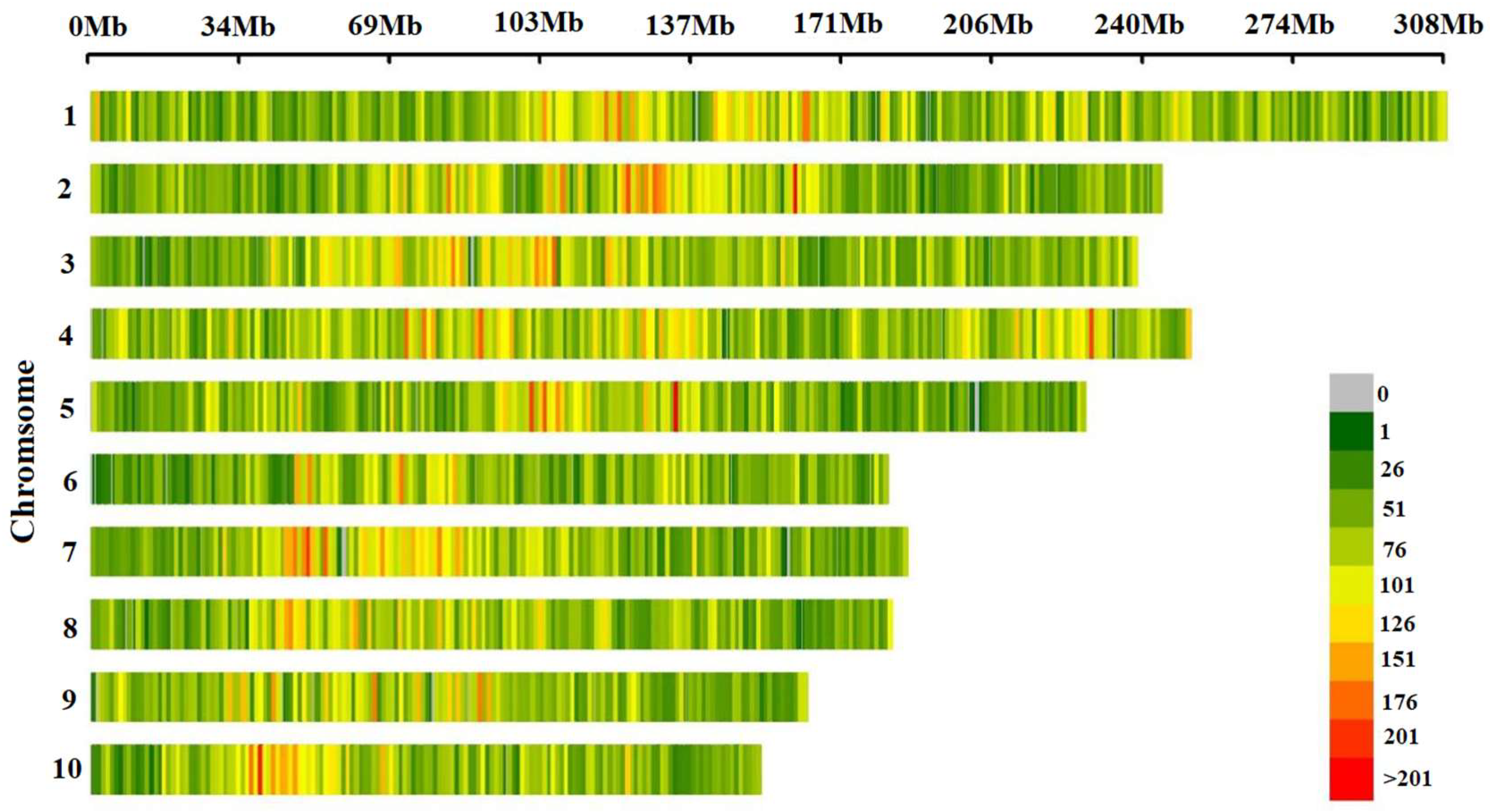
3.1. Distribution and Statistical Analysis of SNPs Markers on Chromosomes
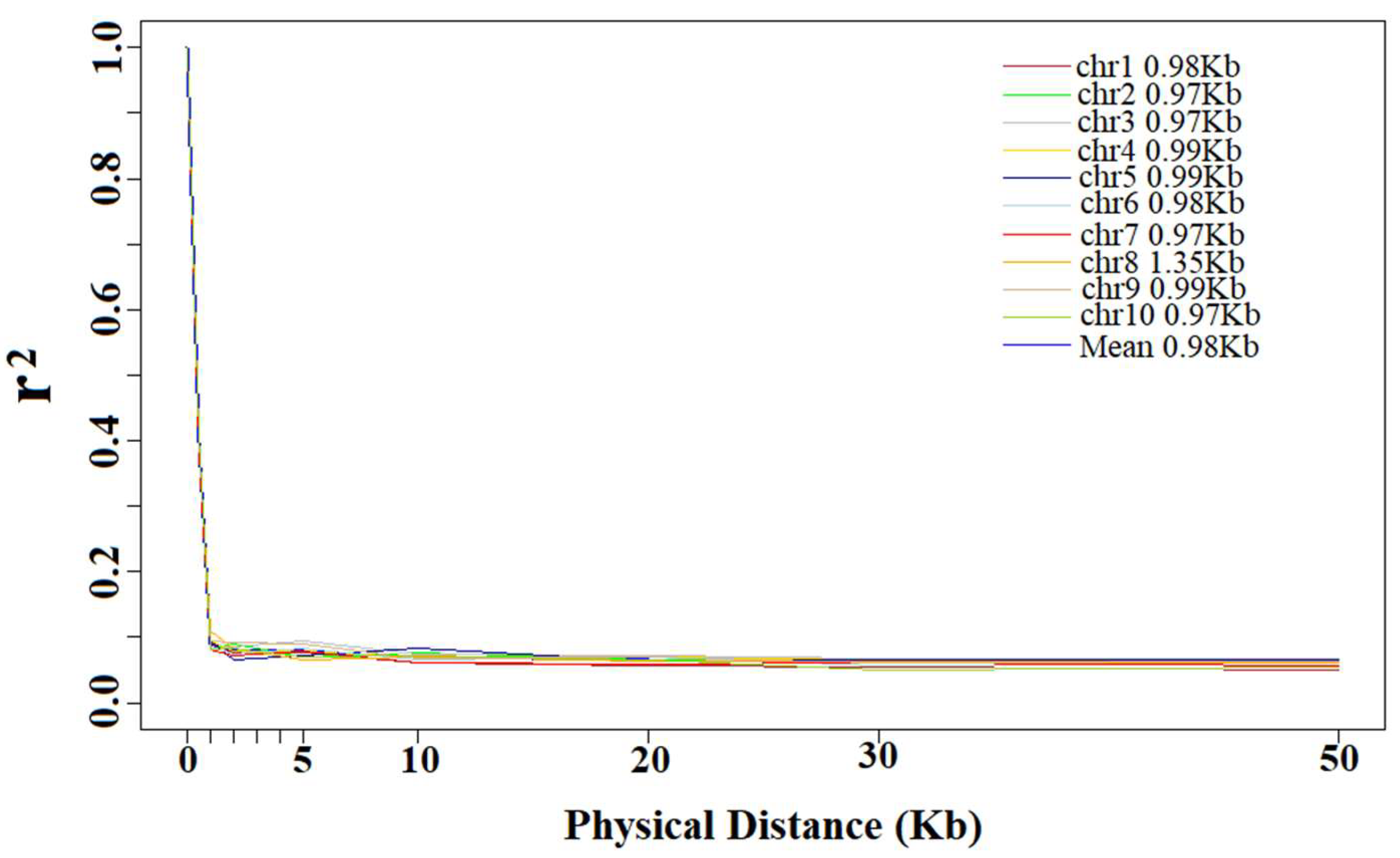
3.2. Linkage Disequilibrium Decay Distance
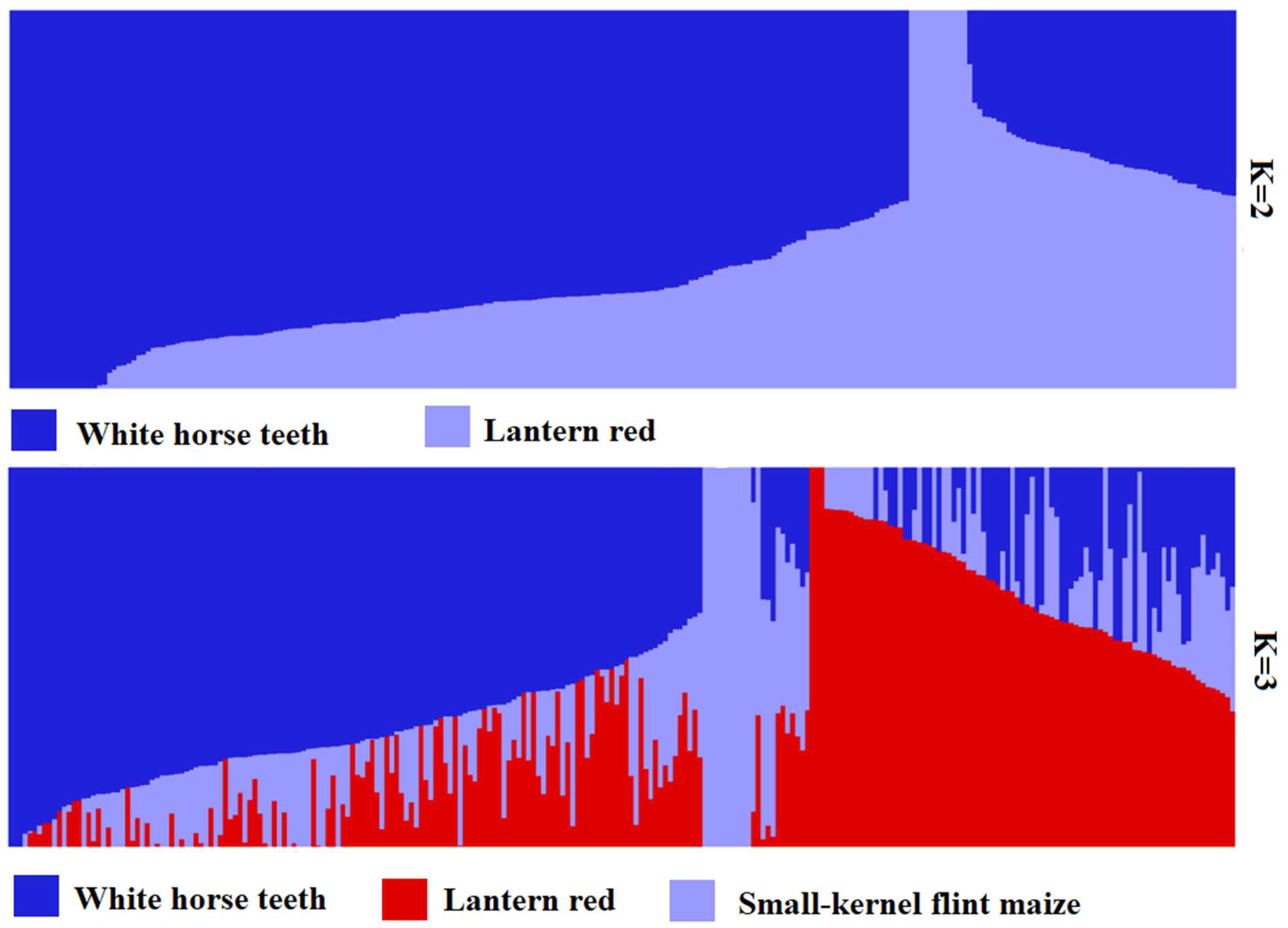
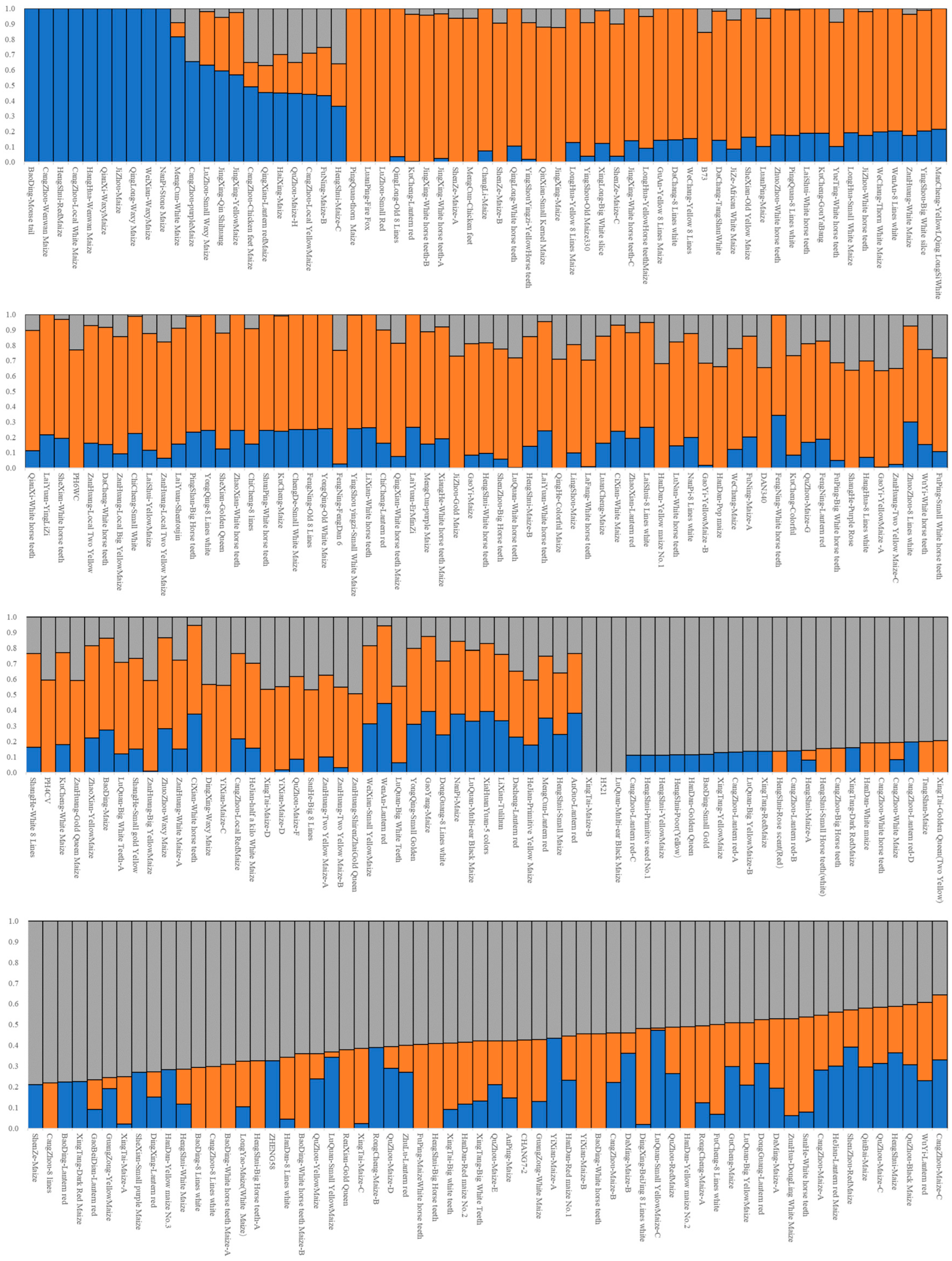
3.3. Structure Analysis
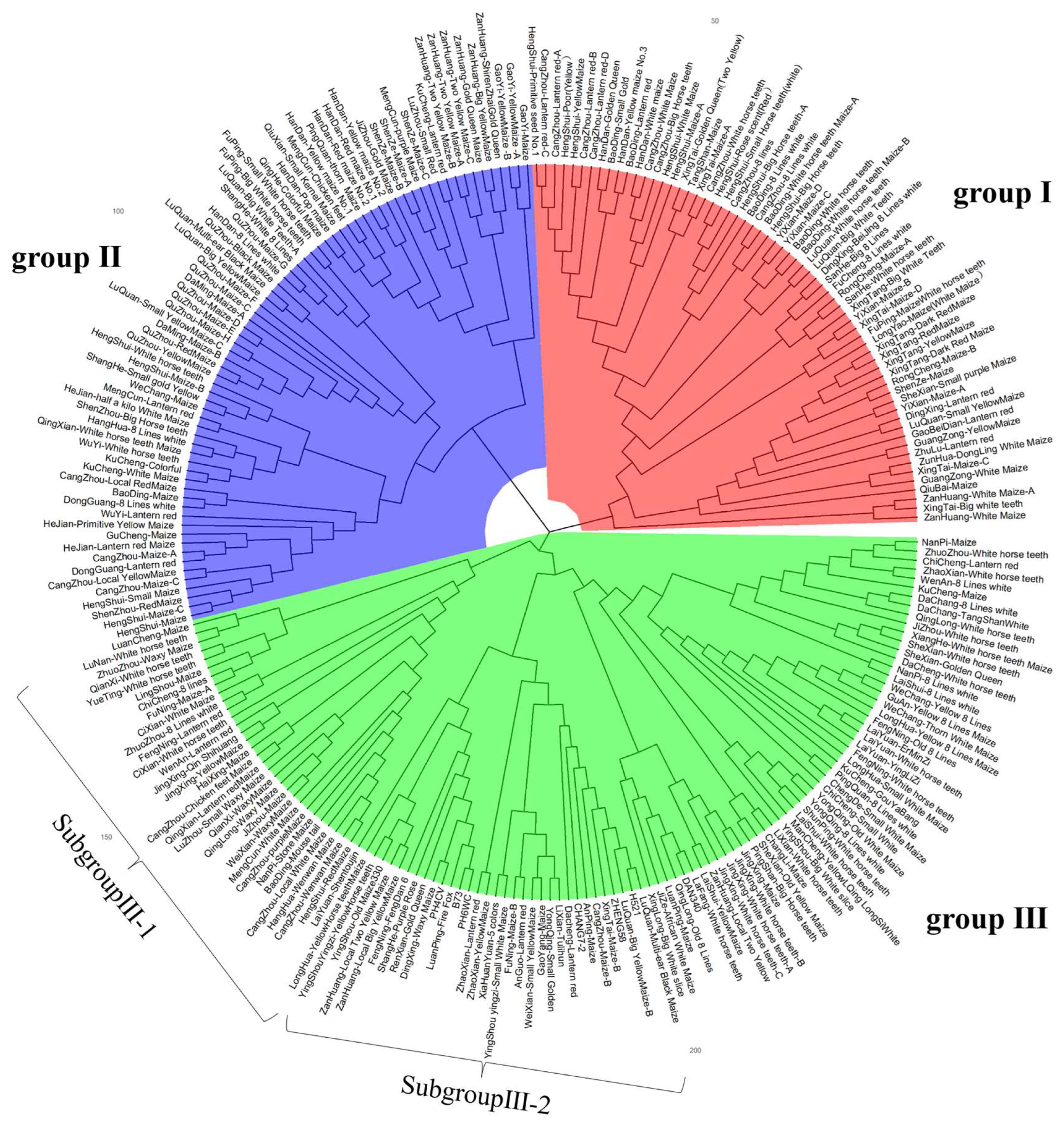
3.4. Cluster Analysis
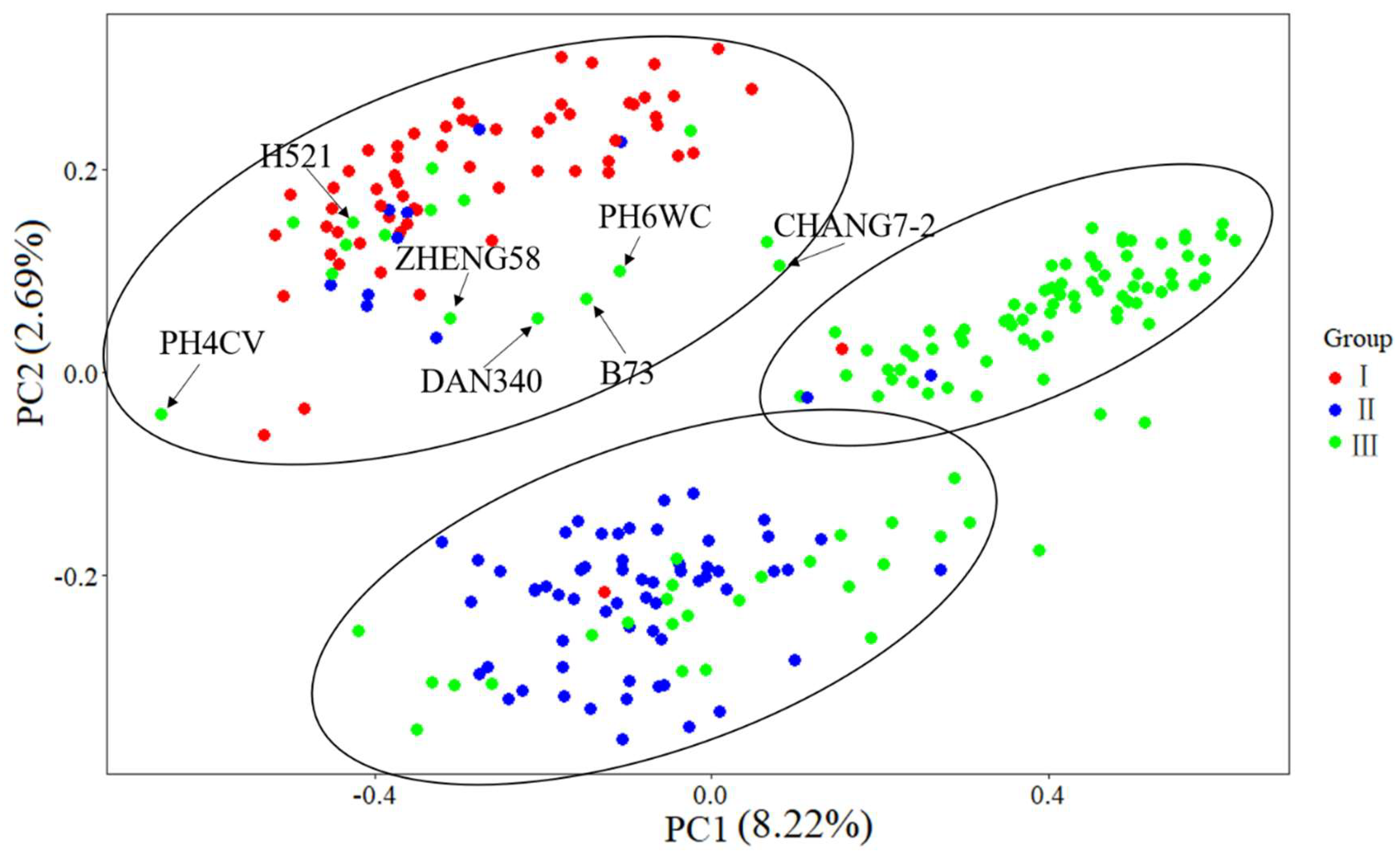
3.5. MDS
4. Discussion
4.1. Heterotic Groups Inferred in Landrace Germplasm in China Central Belt
4.2. Linkage Disequilibrium Decay Distance
4.3. Genetic Divergence of Three Groups
4.4. Use of Maize Landraces in Breeding Programs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. FAOSTAT, Production. 2014. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Zhang, R.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Yan, J.; Li, H.; Yang, X. Patterns of genomic variation in Chinese maize inbred lines and implications for genetic improvement. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Thornton, P. The potential impacts of climate change on maize production in Africa and Latin America in 2055. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2003, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, Y.; Semagn, K.; Crossa, J.; Mugo, S.; Atlin, G.N.; Tarekegne, A.; Meisel, B.; Sehabiagur, P.; Vivek, B.S.; Alvarado, G.; et al. Improving Maize Grain Yield under Drought Stress and Non-stress Environments in Sub-Saharan Africa using Marker-Assisted Recurrent Selection. Crop Sci. 2016, 56, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Lan, H.; Ren, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Jaqueth, J.; Li, B.; et al. Characterizing the population structure and genetic diversity of maize breeding germplasm in Southwest China using genome-wide SNP markers. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.S. Production, breeding and process of maize in China. In Handbook of Maize: Its Biology; Jeff, L.B., Sarah, C.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 563–576. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, T. Germplasm base of maize breeding in China and formation of foundation parents. Maize Sci. 2010, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Troyer, A.F. Adaptedness and Heterosis in Corn and Mule Hybrids. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, G.H. Beginnings of the heterosis concept. In Heterosis; Gowan, J.W., Ed.; Iowa State College Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1952; pp. 14–49. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, W.R. Handbook of hybrid corn. J. Hered. 1963, 54, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallauer, A.R.; Miranda, J.B. Quantitative Genetics in Maize Breeding; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Sprague, G.F. Heterosis in maize: Theory and practice. In Heterosis; Frankel, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; pp. 47–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hallauer, A.R.; Russell, W.A.; Lamkey, K.R. Corn breeding. In Corn and Corn Improvement, 3rd ed.; Sprague, G.F., Dudley, J.W., Eds.; Crop Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Tracy, W.F.; Chandler, M.A. The Historical and Biological Basis of the Concept of Heterotic Patterns in Corn Belt Dent Maize. In Plant Breeding: The Arnel R. Hallauer International Symposium (Lamkey/Plant); Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2006; pp. 219–233. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Development and germplasm base of maize hybrids in China. Maydica 1998, 43, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science. Elite Germplasm of Maize—Index to Research and Utility; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Bai, D.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Tan, X.; Shi, Y.; Song, Y.; Carlone, M.; et al. Changes in Yield and Yield Components of Single-Cross Maize Hybrids Released in China between 1964 and 2001. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Cao, G.; Li, N.; Wang, A.; Wei, F.; Li, T.; Yi, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Genetic variation and population structure in China summer maize germplasm. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Xu, W.W.; Chen, D.Y.; Li, F.Z.; Shi, J.G.; Liu, X.; Ning, J.L. The breeding and application of the elite maize inbred line Dan340. J. Maize Sci. 2002, 10, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Melchinger, A.E.; Gumber, R.K. Overview of heterosis and heterotic groups in agronomic crops. In Concepts and Breeding of Heterosis in Crop Plants; Larnkey, K.R., Staub, J.E., Eds.; CSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1998; pp. 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Chen, J.; Petroli, C.D.; Pacheco, A.; Zhang, X.; San Vicente, F.; Hearne, S.J.; Dhliwayo, T. The genetic structure of CIMMYT and U.S. inbreds and its implications for tropical maize breeding. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 1666–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.T.; Can, J.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, X.H.; Jing, X.Q.; Zhang, F.J.; Li, J.S. Analysis of maize heterotic groups and patterns during past decade in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2004, 37, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.H.; Yu, Y.T.; Zhao, J.R.; Shi, Y.; Song, Y.C.; Wang, T.Y.; Li, Y. Population structure and linkage disequilibrium of a mini core set of maize inbred lines in China. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.X.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, M.S.; Li, X.H.; Hao, Z.F.; Bai, L.; Zhang, D.G.; Liang, Y.H. Inferring genome ancestry and estimating molecular relatedness among 187 Chinese maize inbred lines. J. Genet. Genom. 2007, 34, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; San Vicente, F.; Huang, K.; Dhliwayo, T.; Costich, D.E.; Semagn, K.; Sudha, N.; Olsen, M.; Prasanna, B.M.; Zhang, X.; et al. Molecular characterization of CIMMYT maize inbred lines with genotyping-by-sequencing SNPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Hong, W.; Jiang, C.; Guan, N.; Ma, C.; Zeng, H.; et al. SLAF-seq: An Efficient Method of Large-Scale de Novo SNP Discovery and Genotyping Using High-Throughput Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. The genetical structure of populations. Ann. Eugen. 1951, 15, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koichiro, T.; Glen, S.; Sudhir, K. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Lam, T.T.Y.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y. Two methods for mapping and visualizing associated data on phylogeny using ggtree. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 3041–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.H.D. The estimation of Wright’s fixation index from genotypic frequencies. Genetica 1970, 41, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; Depristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.B. Phenotypic and molecular diversity of maize landraces: Characterization and utilization. Indian J. Genet. 2010, 70, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T. Establishment of a core collection for maize germplasm preserved in Chinese National Genebank using geographic distribution and characterization data. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2004, 51, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebourg, C.; Gouesnard, B.; Charcosset, A. Large scale molecular analysis of traditional European maize populations—Relationships with morphological variation. Heredity 2001, 86, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Shah, T.; Warburton, M.L.; Buckler, E.S.; McMullen, M.D.; Crouch, J. Genetic Characterization and Linkage Disequilibrium Estimation of a Global Maize Collection Using SNP Markers. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean-Rodríguez, F.D.; Costich, D.E.; Camacho-Villa, T.C.; Mario, E.P.; Matteo, D.A. Genetic diversity and selection signatures in maize landraces compared across 50 years of in situ and ex situ conservation. Heredity 2021, 126, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, B.S.; Prasanna, B.M. Maize. In Breeding Field Crops; Chopra, V.L., Ed.; Oxford & IBH: New Delhi, India, 2001; pp. 147–189. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, B.S.; Vasal, S.K.; Prasanna, B.M. Maize. In Evolution and Adaptation of Cereal Crops; Chopra, V.L., Shyam, P., Eds.; Oxford & IBH: New Delhi, India, 2002; pp. 99–133. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, L.; Arnason, J.T.; Nozzolillo, C.; Hamilton, R.H. Resistance of maize to the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis, as related to the geographical origin of maize. Can. J. Bot. 1990, 68, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIMMYT. Development of New Stress Resistant Maize Genetic Resources (UNDP Project GLO/90/003); CIMMYT Maize Programme Special Report; CIMMYT: Mexico City, Mexico, 1997. [Google Scholar]

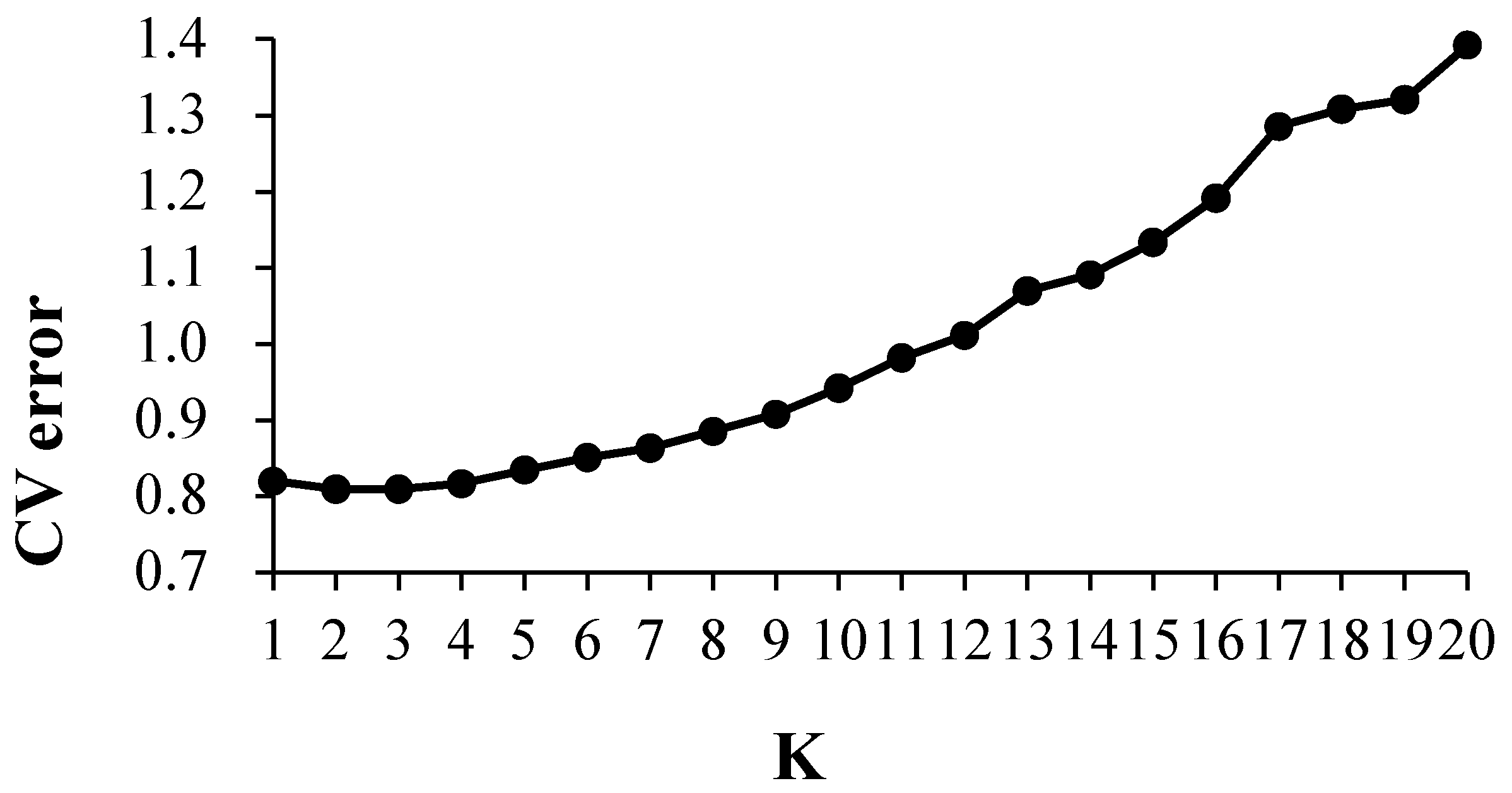
| Name | B73 | PH6WC | PH4CV | ZHENG58 | CHANG7-2 | DAN340 | H521 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterosis groups | BSSS | BSSS | NSSS | M-Reid | Tang SiPing Tou | LvDa Red Cob | Domestic synthetic species |
| Group | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | - | 0.053 | 0.045 |
| II | 0.053 | - | 0.035 |
| III | 0.045 | 0.035 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, R.; Li, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Song, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wei, J.; et al. Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Maize Landraces from Central China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061278
Guo R, Li T, Zhang Q, Wang J, Guo J, Wang L, Song L, Yan Y, Zhang D, Wei J, et al. Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Maize Landraces from Central China. Agronomy. 2024; 14(6):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061278
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Rui, Tingting Li, Quanguo Zhang, Jianghao Wang, Jinjie Guo, Liwei Wang, Liang Song, Yuanyuan Yan, Dongmin Zhang, Jianfeng Wei, and et al. 2024. "Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Maize Landraces from Central China" Agronomy 14, no. 6: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061278
APA StyleGuo, R., Li, T., Zhang, Q., Wang, J., Guo, J., Wang, L., Song, L., Yan, Y., Zhang, D., Wei, J., Li, X., & Song, W. (2024). Genetic and Molecular Characterization of Maize Landraces from Central China. Agronomy, 14(6), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061278




