Abstract
Phytoplankton plays a key role in the stabilization of aquatic ecosystems. However, there is a lack of research on the structure of phytoplankton communities and their influencing factors in shallow lakes in Southeast Hubei. In this study, four typical lakes were selected in the summer of 2019, and the phytoplankton community structure and its drivers were investigated for each lake. The results showed that the number of phytoplankton species, dominant species, biomass, and abundance varied among lakes. A comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) assessment showed that Lake Xiandao was oligotrophic, Lake Baoan was light eutrophic, and Lake Wang and Lake Ci were moderate eutrophic. The Shannon–Wiener, Margalef, and Pielou indices showed that the phytoplankton communities of Lake Wang and Lake Ci are less stable, and the water bodies are more severely contaminated. In contrast, the communities of the Lake Baoan and Lake Xiandao are more stable and have superior water quality. A redundancy analysis (RDA) indicated that the primary variables influencing phytoplankton community structures were pH and water temperature (WT) (Lake Ci); permanganate index (CODMn) and pH (Lake Xiandao); WT and total nitrogen (TN) (Lake Wang); and WT and total phosphorus (TP) (Lake Baoan).
1. Introduction
As the primary producers in water bodies, phytoplankton are essential to the material cycle, energy transfer, and stability of aquatic ecosystems. In addition to photosynthesizing to supply aquatic environments with sufficient nutrients [1,2], phytoplankton are crucial for the production of organic matter. Because phytoplankton are highly sensitive to environmental changes [3], they may react quickly to significant changes in nutritional status or water quality [4,5,6], which can have a direct impact on the structure and operation of the entire aquatic ecosystem [7]. As a result, phytoplankton serve as both the foundation for the material cycle and the flow of energy throughout the aquatic environment and are a crucial indicator of the nutritional state of a water body [8].
Currently, studies on the structural changes of phytoplankton communities and the identification of their influencing factors are more mature and diversified in methodology. A large number of studies have shown that changes in phytoplankton community structure and population development are closely related to the nutrient status of the water body and external factors, such as water temperature, depth, dissolved oxygen, pH, Secchi depth (SD), and other environmental factors have different degrees of influence on the structure of the phytoplankton community [9,10,11,12]. Furthermore, the growth of phytoplankton populations is influenced by meteorological factors, such as temperature and light. Cyanobacterial blooms frequently occur when the effects of eutrophication are combined with ecological factors in the same water body [13]. Consequently, it is critical to determine how the phytoplankton community structure in lakes is related to the variables that influence it. Principal component analysis, cluster analysis, regression analysis, correlation analysis, and other statistical techniques have been employed in related studies. Multivariate statistics, such as canonical correspondence analyses and redundancy, are the most frequently used statistical techniques [7,14,15]. The trophic condition of a body of water is directly correlated with species variety in aquatic ecosystems. The species diversity index is a commonly used indicator of aquatic biodiversity. Water bodies with lower pollution levels tend to have higher community-diversity indices [16,17].
To understand which factors influence the phytoplankton community structure and water environment status in typical lakes in Southeast Hubei (China), we investigated and analyzed the abundance, biomass, and dominant species of phytoplankton in four lakes during the summer. We systematically analyzed the nutrient status of the water body and the phytoplankton community structure in each lake, using RDA to analyze the relationship between the phytoplankton and environmental factors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
The study was conducted in the four following water bodies. Lake Ci is situated amid the Yangtze River and is the largest urban lake in Huangshi City, with a watershed area of 62.19 km2 and a surface area of 10.5 km2. In 2019, Lake Ci achieved water-quality level IV (mainly applicable to general industrial water areas and recreational water areas not in direct contact with human beings) [18]. Lake Xiandao, situated near the northern base of Mufushan Mountain in Hubei Province, has an average depth of 25.7 m, a watershed area of 243.00 km2, a capacity of around 582 million m3, and excellent water quality [19,20]. Lake Wang covers an area of 40.2 km2 and is situated in Yangxin County on the south bank of the middle stages of the Yangtze River, where eutrophication and water pollution are severe issues [21]. Situated on the southern bank of the middle sections of the Yangtze River, Lake Baoan has a water area of 45.1 km2 and comparatively acceptable water quality [22].
2.2. Sampling Stations
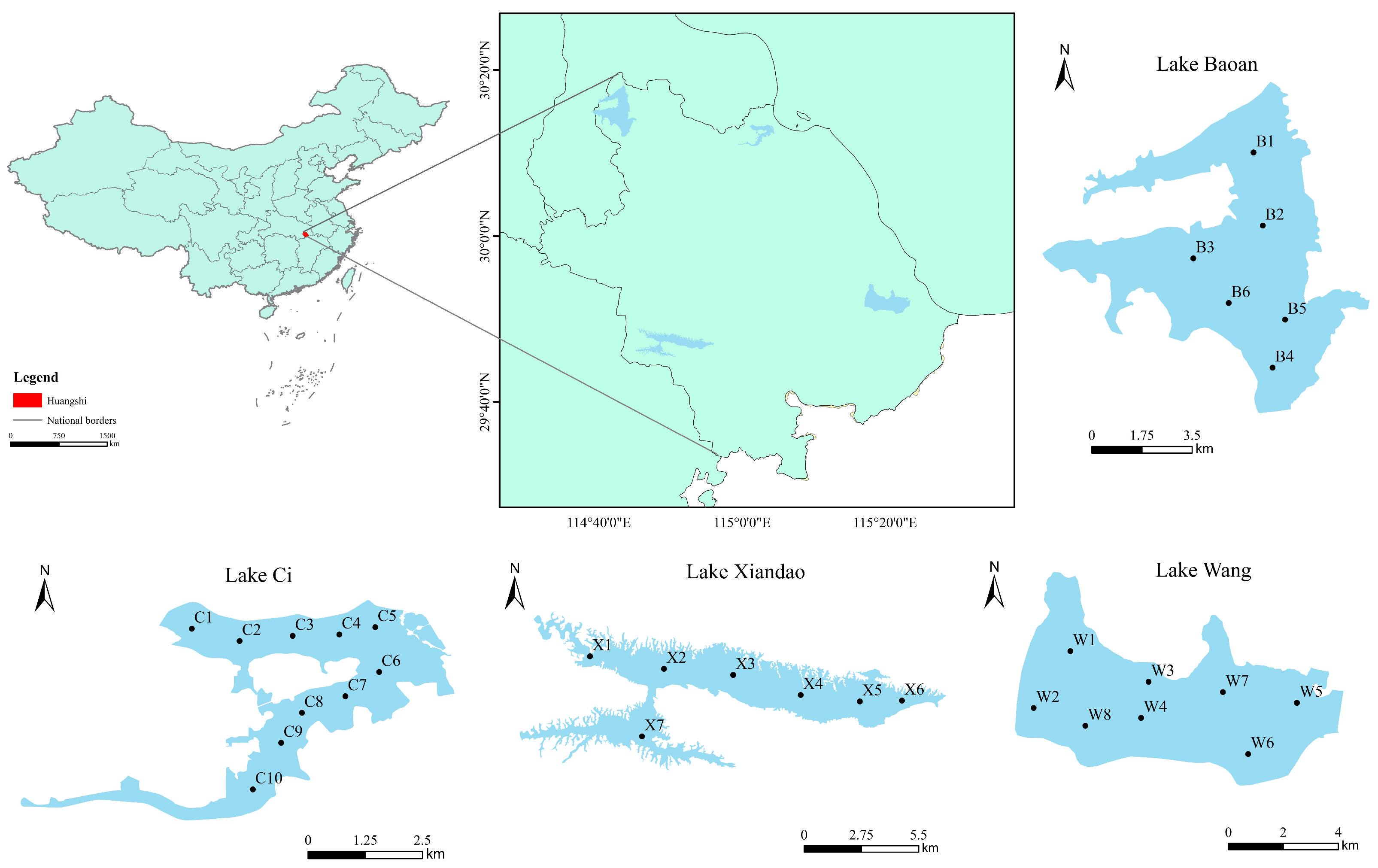
Based on the morphology and area characteristics of the lakes in the study area, 31 sampling points were established, comprising 10 in Lake Ci, 8 in Lake Wang, 7 in Lake Xiandao, and 6 in Lake Baoan (Figure 1).
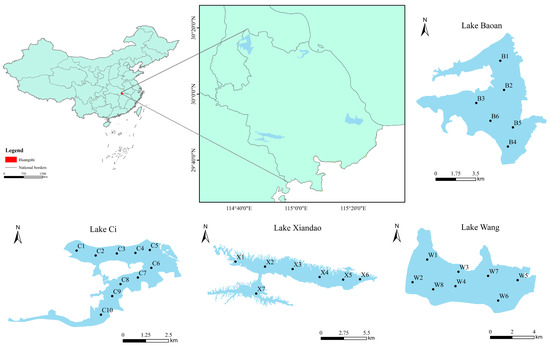
Figure 1.
Distribution of sampling points among four typical lakes in Southeast Hubei Province.
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Physical and Chemical Indicators
The Lake Ci, Lake Xiandao, Lake Wang, and Lake Baoan sampling dates are 17, 18, 19, and 20 July 2019, respectively. A portable multiparameter monitor (YSI EXO2, Yellow Springs, OH, USA) was used to evaluate four physical indicators on-site: water temperature (WT), dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, and conductivity (cond). Data were collected and the Secchi depth (SD) was assessed using black and white cycloramic discs. In parallel, samples (1 L each) were obtained using a water sampler at a depth of 0.5 m to measure several chemical indicators. Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry was used to determine ammonia–nitrogen (NH3-N), while potassium persulfate oxidation–ultraviolet and molybdenum–antimony anti-spectrophotometry were used to determine the total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP), respectively. The acid technique was used to measure the permanganate index (CODMn) [23].
2.3.2. Phytoplankton
For the qualitative samples, A 25# plankton net (mesh diameter 0.064 mm) was placed three meters off the coast at the surface of the water up to 0.5 m depth and dragged slowly in an “∞” shape at a speed of 20 cm/s to 30 cm/s for about 1~3 min. The filtered samples were placed in specimen bottles, to which was added 1.5% Lugol’s fixative for the subsequent qualitative analysis of phytoplankton. Samples were observed in the laboratory under a 10×40× (400 times) optical microscope for classification. For the quantitative samples, 1 L of water was collected using a plexiglass water collector, and 15 mL of Lugol’s solution was added to correct the water for phytoplankton sample analysis. The samples were returned to the laboratory and precipitated for 48 h. The supernatant was then pipetted using a 3–5 mm siphon tube to give a final sample volume of 30 mL [24]. After thorough shaking, 0.1 mL of the sample was aspirated into a phytoplankton counting frame to identify the phytoplankton species and count the number of cells using a 10×40× optical microscope. The eyepiece visual field method was used for counting, with each sample being counted two to three times, and 100 fields of view were observed each time. The error in each count was not greater than 15% to determine the average value, which was then converted to phytoplankton cell density per unit of volume. The cell volume method was used to estimate phytoplankton biomass [25].
2.3.3. Index Calculation
To describe the organization of the phytoplankton community, phytoplankton species diversity was examined using the Margalef richness index (D), Shannon–Weiner index (H′), Pielou evenness index (J), and phytoplankton dominance. Phytoplankton with a dominance value Y ≥ 0.02 were designated as the dominant species [26]. The formulas used for calculating each parameter are as follows:
where S is the total number of phytoplankton species; N is the total number of phytoplankton individuals; ni is the ith phytoplankton species; fi is the frequency of the ith species of phytoplankton at each sampling point, and the water-quality judgment standard [27] is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Water-quality determination criteria.
The comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) was calculated as [28]:
Here, Wj is the relative weight of the trophic state index of the jth parameter, and TLI (j) is the trophic state index of the jth parameter. The TLI was calculated using Chl-a, TP, TN, SD, and CODMn. The reference standards for each indicator are in Jin, Tu, 1990 [29].
2.4. Data Analysis
ArcGIS 10.2 was used to map the research region, Origin 2019 and GraphPad Prism 10.0 software were used for mapping, and Canoco 5.0 was used for redundancy analysis (RDA) and principal component analysis (PCA) of the data pertaining to the phytoplankton and environmental parameters, Prior to the analysis, the phytoplankton dominant species data of each lake were subjected to detrended correspondence analysis (DCA). When the maximum gradient length of the sorting axis was <3.0, RDA was chosen to constrain the sorting, and the forward introduction method and Monte Carlo replacement test were utilized to progressively screen out the environmental factors that had a significant impact on the phytoplankton dominant species of each lake to be analyzed. When the maximum gradient length of the sorting axis was >3.0, a principal component analysis (PCA) was applied. Microsoft Excel 2019, SPSS 24.0, and Prism 10.0 were used for data analysis and processing.
3. Results
3.1. Chemical and Physical Characteristics of Water Bodies
The main physical and chemical indices of the four typical lakes in Southeast Hubei are shown in Table 2. The WT and pH were significantly lower in Lake Xiandao than in Lake Ci and Lake Wang (p < 0.05), and the SD of Lake Xiandao was (564.00 258.09) cm throughout the year, which was about 13 times higher than that of the other three lakes. Cond and TP contents were significantly different within each lake (p < 0.05). The TN and NH3-N contents were significantly lower in Lake Xiandao compared with Lake Ci and Lake Wang (p < 0.05) but did not differ significantly from Lake Baoan (p > 0.05). The chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) content was significantly lower in Lake Xiandao and Lake Baoan than in Lake Ci and Lake Wang (p < 0.05). The TLI (Σ) values of Lake Xiandao, Lake Baoan, Lake Wang, and Lake Ci were 23.69 (oligotrophication), 57.19 (light eutrophication), 61.09 (moderate eutrophication), and 61.72 (moderate eutrophication), respectively.

Table 2.
Summer water characteristics of typical lakes in Southeast Hubei Province.
3.2. Phytoplankton Species Composition and Dominant Species
A total of 108 phytoplankton species from six phyla were identified in the four lakes. The species counts were 82 (six phyla) in Lake Ci, 37 (five phyla) in Lake Xiandao, 44 (six phyla) in Lake Wang, and 66 (six phyla) in Lake Baoan. Chlorophyta dominated the phytoplankton species in all lakes, followed by the phylum Cyanophyta, and the community composition showed a Chlorophyta–Cyanophyta–Bacillariophyta type (Table 3).

Table 3.
Phytoplankton species composition in typical lakes of Southeast Hubei Province.
Lake Ci contained five dominant species, all of which are members of the phylum Cyanophyta. Based on the theory that a species with a species dominance index of Y ≥ 0.02 is the dominant species, the following algae were used: Merismopedia tenuissima, Pseudoanabaena, Spirulina, Elegant planophyta, and Rhabdogloea. The predominant species in Lake Wang include Microcystis, Anabaena circinalis, Pseudoanabaena, and Oscillatoria princeps, all of which are members of the phylum Cyanobacteria. Nine dominant species were identified in Lake Xiandao, comprising two Cyanobacteria (Anabaena oscillarioides and Chroococcus), two Bacillariophyta (Cyclotella and Fragilaria), and five Chlorophyta (Chlorella, Scenedesmus bijuba, Coelastrum, Oocystis solitaria, and Quadrigula chodatii). The dominant phytoplankton species in Lake Baoan are all Cyanophyta, dominated by Cylindrospermopsis, Pseudoanabaena, Merismopedia tenuissima, Rhabdogloea, Lyngbya, Raphidiopsis, Elegant planophyta, and Anabaena (Table 4). In general, the phytoplankton species composition of each lake was dominated by Chlorophyta. The dominant phytoplankton species in Lake Ci, Lake Wang, and Lake Baoan were Cyanophyta, whereas those in Lake Xiandao were Chlorophyta.

Table 4.
Phytoplankton dominant species and dominance values.
3.3. Phytoplankton Biomass and Abundance
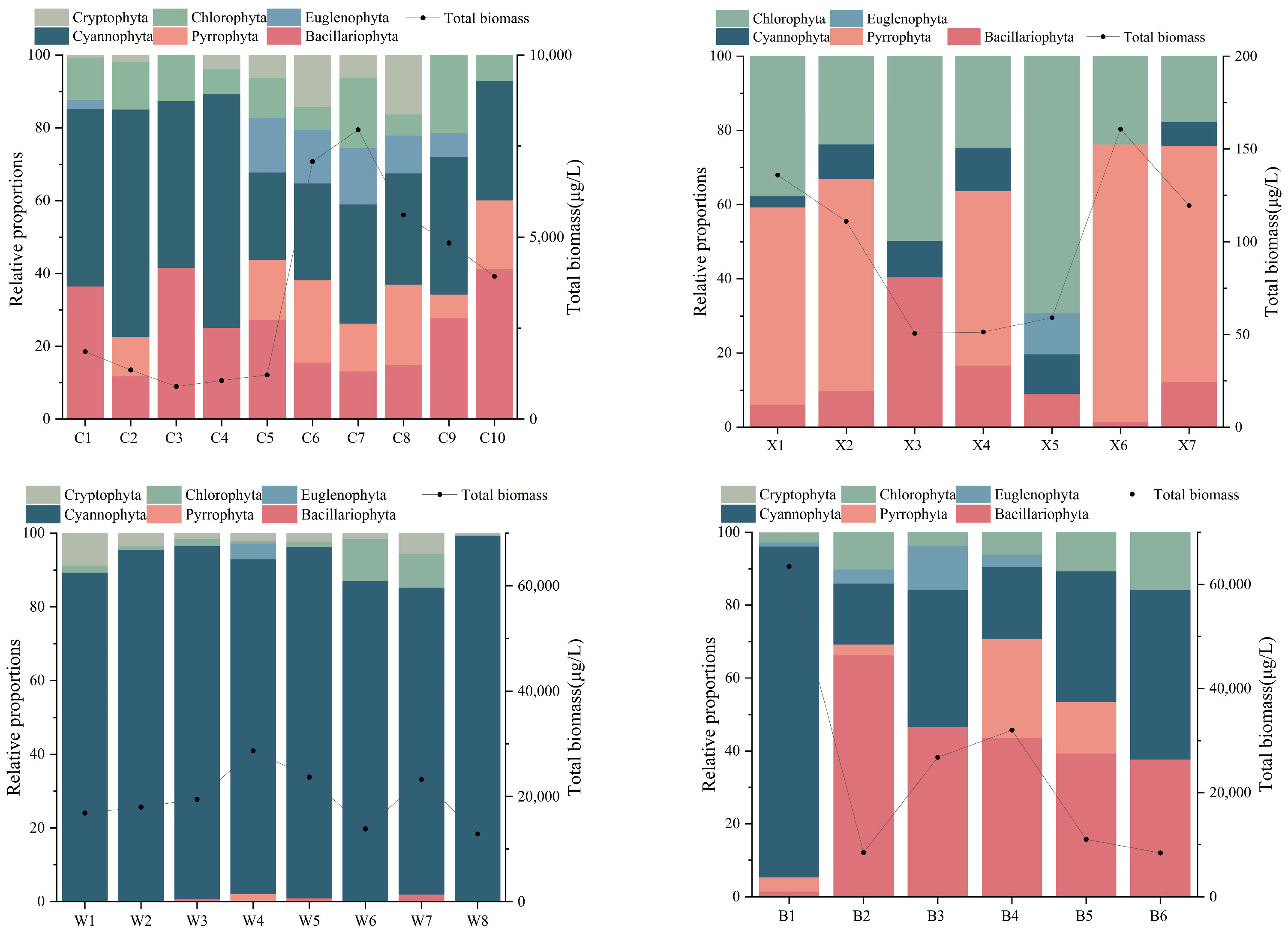
The summer phytoplankton biomass in Lake Xiandao ranged from 50.69 to 160.62 μg/L, with Pyrrophyta accounting for the majority (51.76%). Lake Ci ranged from 1957.25 to 8224.45 μg/L (average 4528.03 μg/L), with Cyanophyta biomass being the highest. Lake Wang ranged from 12,893.15 to 28,693.16 μg/L (average 19,583.92 μg/L), dominated by Cyanophyta (91.76%), and Lake Baoan ranged from 8,403.17 to 63,443.36 μg/L (Figure 2).
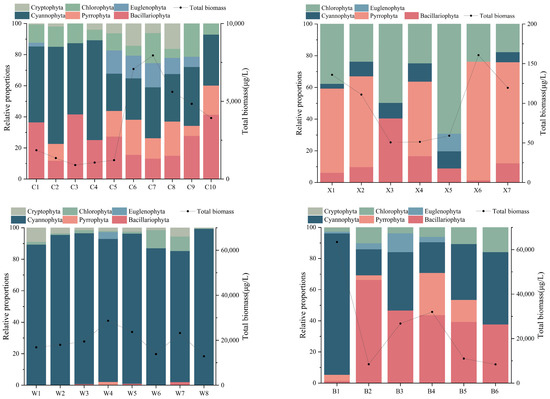
Figure 2.
Percentage biomass of phytoplankton taxa (horizontal axes are sampling stations of lakes; Pyrrophyta here means dinoflagellates).
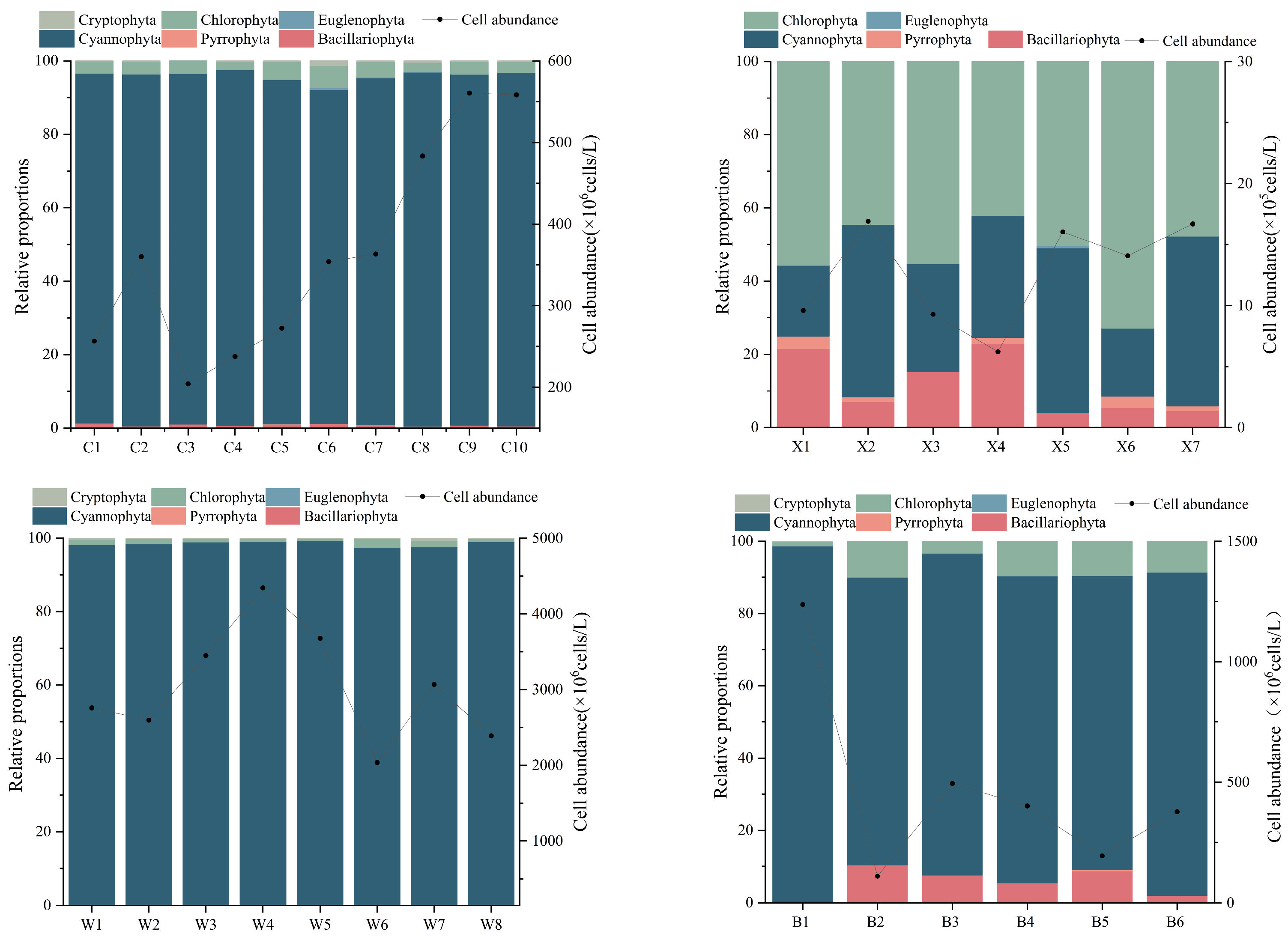
Chlorophyta were most abundant (52.83%) in Lake Xiandao, whereas Cyanophyta were most abundant in Lake Ci (95.17%), Lake Wang (98.49%), and Lake Baoan (91.64%). The phytoplankton abundance was 6.22 × 105 to 16.91 × 105 cells/L in Lake Xiandao, 203.65 × 106 to 434.27 × 106 cells/L in Lake Wang, 204.26 × 106 to 560.65 × 106 cells/L in Lake Ci, and 109.70 × 106 to 1237.46 × 106 cells/L in Lake Baoan. A one-way ANOVA showed that the spatial distribution of phytoplankton biomass was significantly lower in Lake Xiandao and Lake Ci than in Lake Wang and Lake Baoan (p < 0.05), and phytoplankton abundance was much lower in Lake Xiandao than in Lake Ci, Lake Wang, and Lake Baoan (Figure 3).
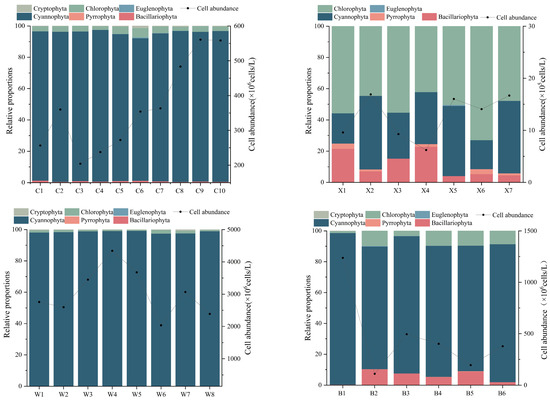
Figure 3.
Percentage abundance of phytoplankton taxa (horizontal axes are sampling stations of lakes; Pyrrophyta here means dinoflagellates).
3.4. Analysis of Phytoplankton Diversity and Water-Quality Categories
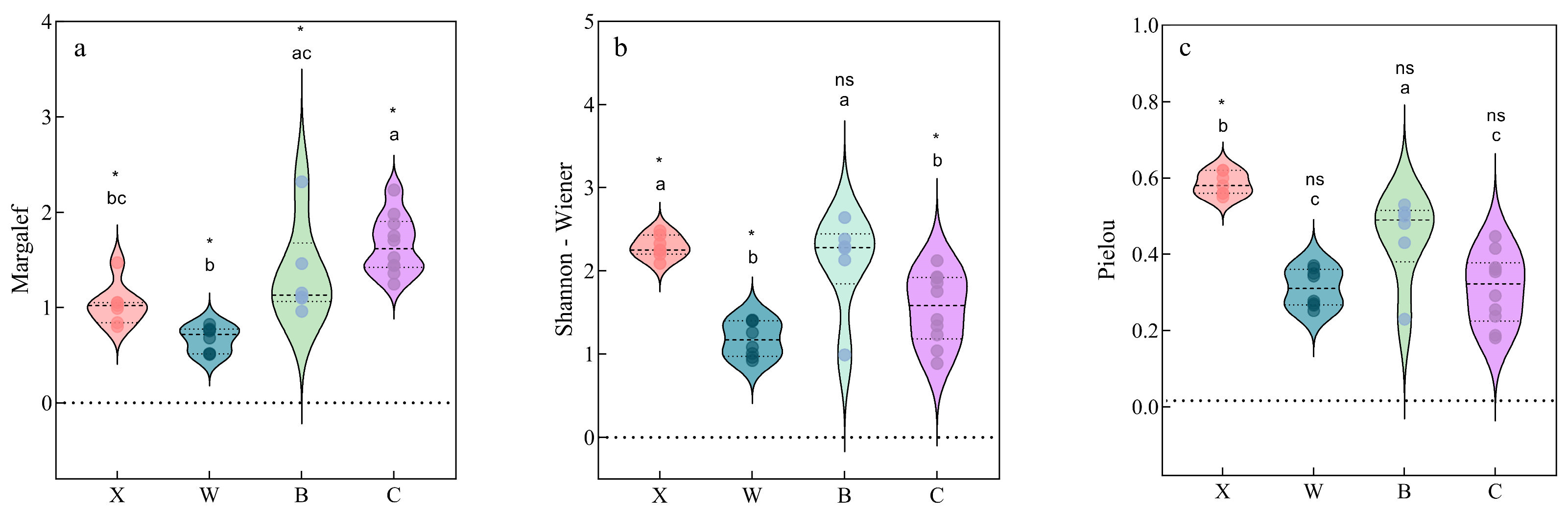
The four lakes showed some differences in biodiversity indices: Lake Xiandao and Lake Baoan had considerably higher Shannon–Wiener and Pielou indices than Lake Ci and Lake Wang (p < 0.05), but the Shannon–Wiener index for Lake Baoan was not significantly different from that of Lake Xiandao (p > 0.05).
For Lake Wang, Lake Xiandao, Lake Baoan, and Lake Ci, the corresponding Margalef index means and ranges were 0.67 (0.51–0.82), 1.03 (0.8–1.47), 1.35 (0.96–2.32), and 1.66 (1.24–2.23), respectively (Figure 4). The water bodies of Lake Wang and the other three lakes were classified as medium and severely contaminated, respectively, based on water-quality criteria. The Shannon–Wiener indices were 1.18 (0.92–1.41) for Lake Wang, 1.55 (0.89–2.12) for Lake Ci, 2.12 (0.99–2.64) for Lake Baoan, and 2.29 (2.09–2.48) for Lake Xiandao, and the water-quality criteria indicated that all four lakes experience medium levels of pollution. In summer, the Pielou indices were 0.31 (0.25–0.37) for Lake Wang, 0.31 (0.18–0.45) for Lake Ci, 0.44 (0.32–0.56) for Lake Baoan, and 0.58 (0.55–0.62) for Lake Xiandao, indicating that Lake Ci and Lake Wang were medium polluted and that Lake Baoan and Lake Xiandao were lightly polluted.
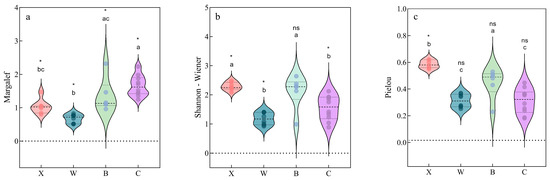
Figure 4.
Phytoplankton diversity index (the horizontal axis represents the four sampled lakes; letters a, b and c represent whether or not there is significant variability among lakes, and ns and * indicate whether there is a significant difference between the data for each lake and the standardized limits (the fraction of standardized limits for the Margalef (a), Shannon-Wiener (b), and Pielou (c) indices refers to 1, 1, and 0.3)).
3.5. Major Environmental Factors Affecting Phytoplankton Community Structure
The development of a phytoplankton community structure is affected by several physicochemical elements, including nutrients and water temperature. The DCA results showed that the maximum gradient length of the four lakes’ sorting axes was 1.21 (<3.0). Therefore, RDA was chosen for the constrained ranking.
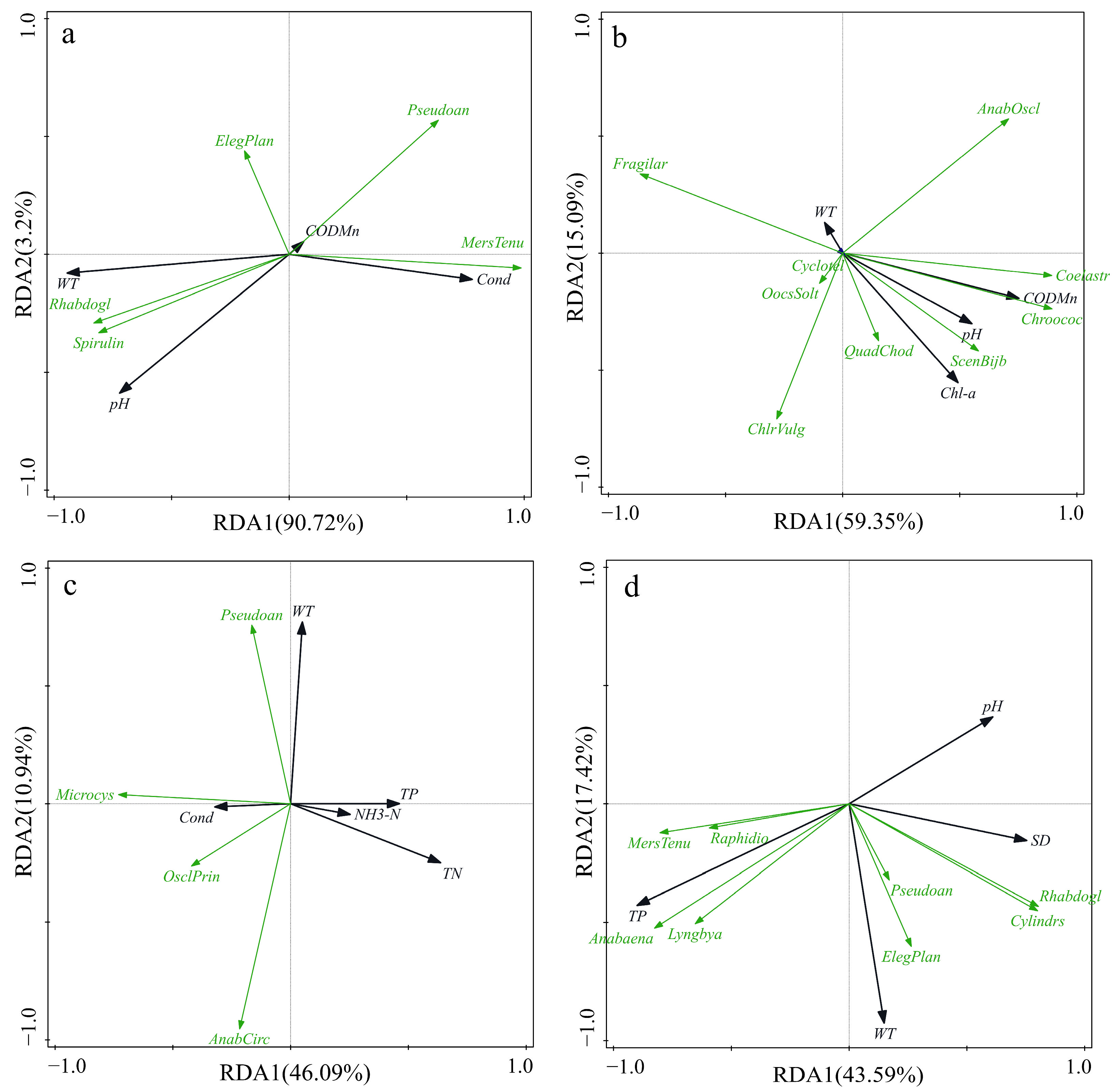
The RDA1 and RDA2 values were 0.9072 and 0.032 for Lake Ci, 0.5935 and 0.1509 for Lake Xiandao, 0.4609 and 0.1094 for Lake Wang, and 0.4359 and 0.1742 for Lake Baoan. The first and second axes of the corresponding environmental factors of each lake cumulatively explained 93.92% of the species variation for Lake Ci, 74.44% for Lake Xiandao, 57.03% for Lake Wang, and 61.01% for Lake Baoan, which indicated that the two sequencing axes could effectively reflect the interrelationships between phytoplankton and different environmental factors and that the results of the RDA were credible.
The phytoplankton community structure in each lake was affected by different environmental factors (Figure 5). The RDA ordination diagram of Lake Ci indicates a favorable correlation between pH and water temperature for the Cyanophyta Spirulina and Rhabdogloea and a negative correlation between WT and pH for Merismopedia tenuissima and Pseudoanabaena. Overall, summer water temperature and pH had the greatest effect on the phytoplankton community structure in Lake Ci. The RDA ordination diagram of Lake Xiandao had a pH and CODMn positively correlated with Chroococcus and Anabaena oscillarioides of the Cyanophyta, Cyclotella of the Bacillariophyta, chlorella, Scenedesmus bijuba, Coelastrum, Oocystis solitaria, and Quadrigula chodatii of the Chlorophyta, and negatively correlated with Fragilaria of the Bacillariophyta. Overall, in Lake Xiandao, pH and CODMn generally had the greatest effects on phytoplankton community structure. The RDA ordination diagram of Lake Wang showed a positive correlation between water temperature and Pseudoanabaena, a negative correlation between Microcystis, Anabaena circinalis, and Oscillatoria princeps, a positive correlation between cond and Microcystis, Anabaena circinalis, Pseudoanabaena, and Oscillatoria princeps, and a positive correlation between TN and Anabaena circinalis. The two factors that most affected summer phytoplankton in Lake Wang were TN and WT. According to the RDA ordination diagram for Lake Baoan, Elegant planophyta, Pseudoanabaena, Cylindrospermopsis, and Rhabdogloea were positively correlated with SD and WT, whereas Merismopedia tenuissima, Lyngbya, Raphidiopsis, and Anabaena were positively correlated with TP. Generally, WT and TP had the greatest impacts on phytoplankton in Lake Baoan.
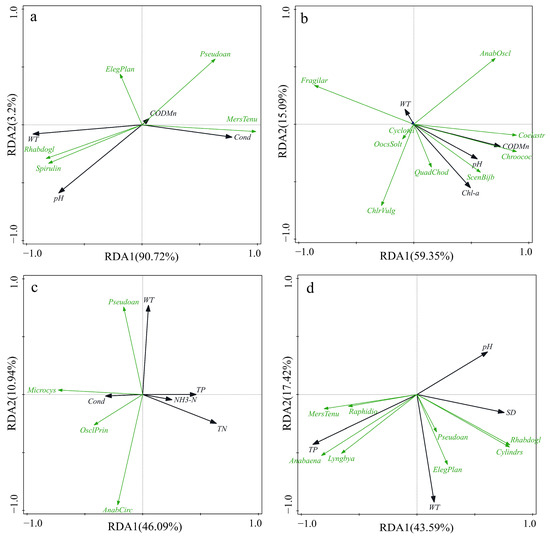
Figure 5.
RDA between phytoplankton and environmental factors. ((a): Lake Ci; (b): Lake Xiandao; (c): Lake Wang; (d): Lake Baoan; The black arrow color represents the physical and chemical indicators of the water body, and the green color represents the dominant phytoplankton species).
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization of Phytoplankton Community Structure
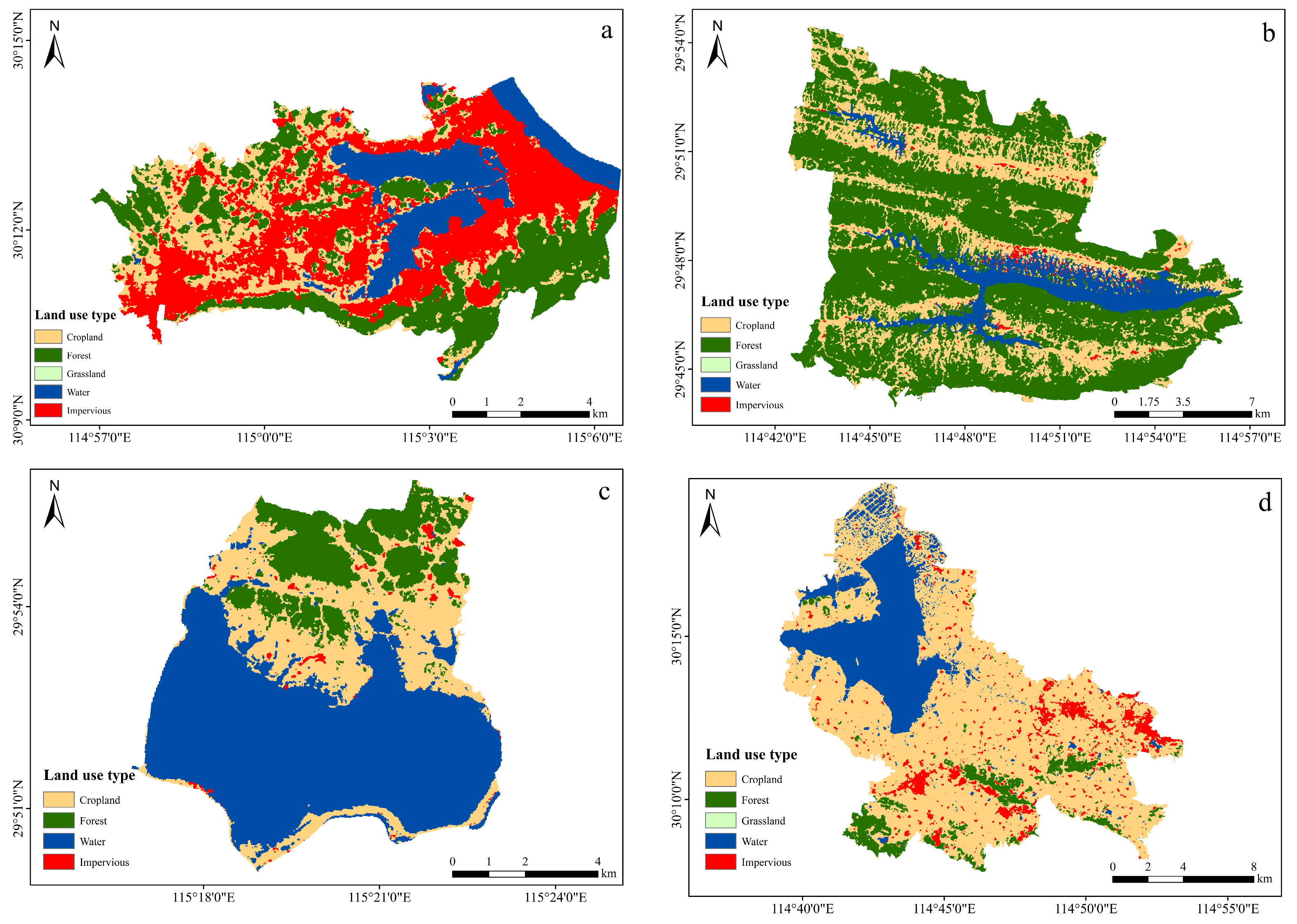
In the four typical lakes studied in southeast Hubei, summer phytoplankton communities were dominated by Chlorophyta, followed by Cyanophyta and Bacillariophyta. This finding is consistent with those of previous studies conducted on the Meiliangwan and East Lake Taihu, Lake Datong, and Lake Chaohu of Taihu Lake, which suggested that the four sampled lakes in the Southeast Hubei region had a generalized pattern [30,31,32]. The phytoplankton biomass of Lake Xiandao is dominated by Pyrrophyta, and the Cyanophyta biomass of Lake Ci, Lake Wang, and Lake Baoan is the largest. In Lake Ci, Lake Wang, and Lake Baoan, phytoplankton species and abundance were dominated by Cyanophyta, whereas in Lake Xiandao, Chlorophyta dominated. Mesotrophic lakes are typically dominated by Pyrrophyta, Bacillariophyta, and Cryptophyta [33]. Chlorophyta and Cyanophyta are heat- and pollution-resistant phytoplankton. Due to their ability to reproduce quickly at high temperatures and their strong ability to compete, cyanobacteria are frequently used as an indicator of eutrophication in water bodies [34]. The water temperature was high (averaging 28.58 to 31.68 °C) during the study period, which is conducive to the growth of heat-tolerant Cyanophyta and Chlorophyta. The study findings show that Lake Xiandao has greater Pyrrophyta biomass, which might be explained by the lake’s high DO level and relatively low temperature. Eutrophic indicator algae, or Cyanophyta, dominated the phytoplankton in Lake Ci, Lake Wang, and Lake Baoan. Different lakes had different dominant species and dominance indices, which were likely influenced by the type, connectivity, position, and land-use status of the watershed. Numerous studies have demonstrated the significant influence of land use on aquatic environments. The present study used remotely sensed images to classify land uses in the lake watersheds. The results indicated that the majority of land types in the watersheds of Lake Ci, Lake Wang, Lake Baoan, and Lake Xiandao were impervious surfaces (37.53%), water (56.64%), cropland (66.55%), and forest (62.69%), respectively (Figure 6).
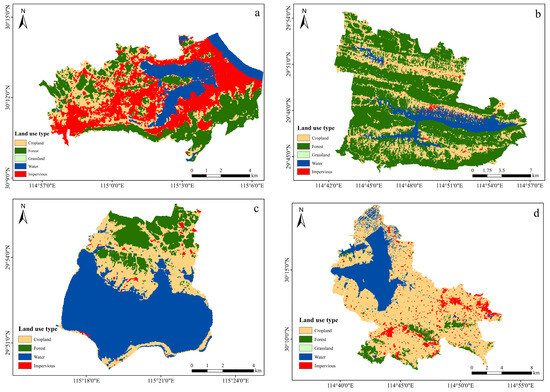
Figure 6.
Distribution of land use in typical lake watersheds in southeast Hubei. ((a): Lake Ci; (b): Lake Xiandao; (c): Lake Wang; (d): Lake Baoan).
Community-diversity indices are frequently used to assess the stability of biome structures. The more species and the number of each species in the community, the negative feedback mechanism is stronger, and its ecosystem tends to be more stable [35,36,37]. The Shannon–Wiener and Pielou indices should be less than 1.0 and 0.30, respectively, when there is little community diversity [12]. The Shannon–Wiener and Pielou indices of Lake Xiandao were significantly higher than 1 and 0.3 (p < 0.05), which may be attributed to the low level of anthropogenic disturbance at Lake Xiandao, where impervious surfaces and cropland accounted for 1.11% and 26.73% of the watershed area, respectively, combined with substantial vegetation cover (62.69%), the excellent environment favors the growth of various phytoplankton species, which are favorable for the growth of various phytoplankton species. On the other hand, Lake Ci and Lake Wang had lower Pielou indices, which showed no significant difference (p < 0.05) compared with the control value. Community diversity was poor, and the water quality was degraded due to high nutrient inputs into the water body as a result of endogenous and exogenous pollution. At the same time, water-body eutrophication indicator species cyanobacteria and green algae bloomed and gradually became dominant species [38].
The TLI and species diversity index indicated that Lake Baoan is a light eutrophic (light-medium pollution type) water body and that the phytoplankton species composition in summer is dominated by Chlorophyta, Cyanophyta, and Bacillariophyta. An investigation revealed ineffective control of domestic sewage, with some farms within the basin discharging wastewater directly into the lake, combined with a more serious problem of surface pollution resulting from a large area of intensive fish ponds and cultivated land [39]. For the medium eutrophication of lakes, Lake Ci, and Lake Wang’s phytoplankton community structure composition was the Cyanophyta–Chlorophyta type. The water body is essentially in the middle of the pollution type, and Lake Wang’s primary sources of pollution are agricultural production and domestic sewage discharge, as well as serious sub-lakes, fish ponds, and harbor canal pollution due to fishery breeding. Impervious surfaces were estimated to cover as much as 37.53% of the Lake Ci basin. The primary source of pollution is uncontrolled sewage discharge from urban areas, which contributes significantly to exogenous pollution. Additionally, some rivers that feed into the lake have poor water quality. Apart from Lake Xiandao, which has a healthier body of water, the combined effects of external pollution, internal bottom mud discharge pollution, and other factors generally led to water pollution in the other three lakes.
4.2. Relationship between Phytoplankton and Environmental Factors
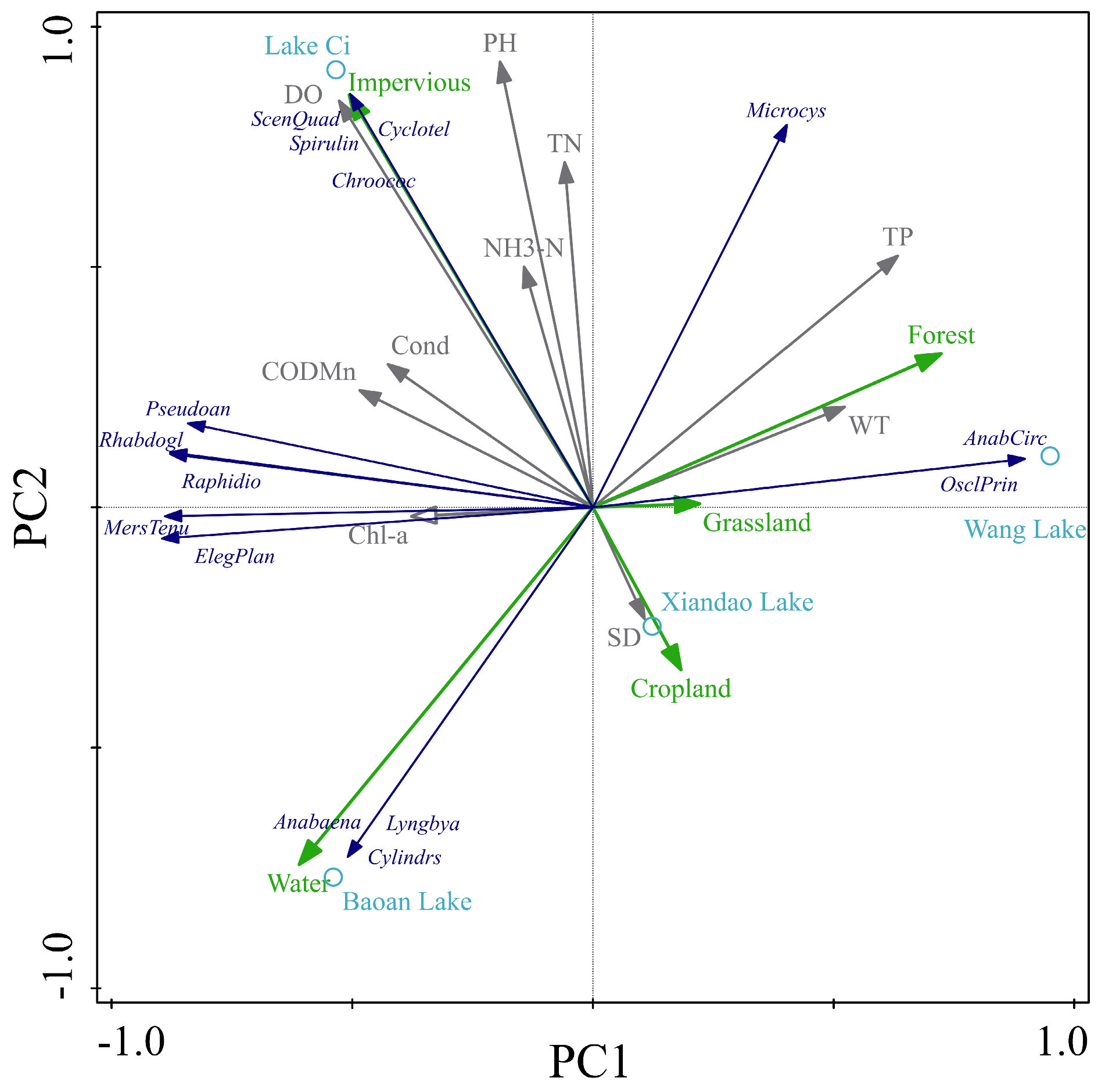
The makeup of the phytoplankton community and the succession of dominant species, growth, and reproduction in aquatic ecosystems are all strongly correlated with environmental conditions; TP, WT, pH, Cond, SD, CODMn, etc. are frequently thought to be the primary elements influencing the phytoplankton community structure [40,41,42]. According to the RDA of the study data, the phytoplankton community structures were mostly governed by WT and pH (Lake Ci), CODMn and pH (Lake Xiandao), WT and TN (Lake Wang), and by WT and TP (Lake Baoan). WT, pH, CODMn, TN, and TP were the primary vectors influencing the species composition of phytoplankton in various lakes, according to the RDA ordination diagram (Figure 5). In addition, we used PCA analysis to evaluate the influence of land use around the lakes on the phytoplankton community structure and the relationship with other environmental factors. The results of a PCA analysis showed that the composition of the phytoplankton community structure in Lake Xiandao and Lake Wang was mainly affected by the two land types of forested and impervious and that the forested was more strongly correlated with TP and WT. The phytoplankton community structure of Lake Baoan was more strongly correlated with water. The correlation between phytoplankton community structure and water was strong, and the water was positively correlated with Chl-a and SD and negatively correlated with TP. Impervious was the most important land-use type affecting the phytoplankton community structure of Lake Ci, and the correlation between impervious and environmental factors, such as pH, TN, NH3-N, DO, Cond, CODMn, was strong, which was similar to the previous research results (Figure 7) [43,44].
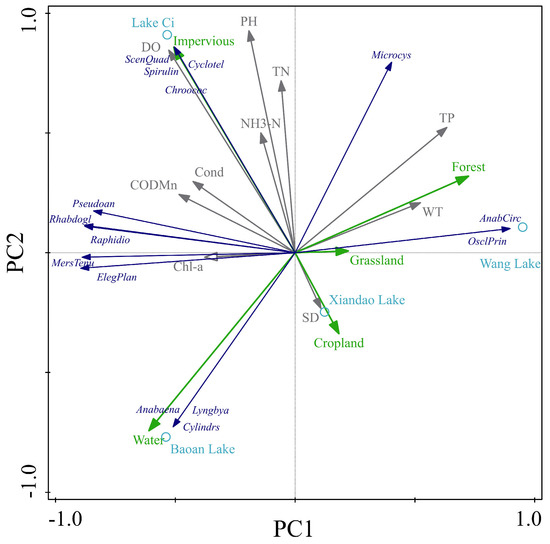
Figure 7.
RDA analysis of land-use types with phytoplankton community structure and environmental factors (Green arrows represent land use types, dark blue represents dominant phytoplankton species, gray represents water quality indicators, and light blue circles represent different lakes).
The primary environmental element influencing the composition and succession of phytoplankton communities is water temperature [45,46]. Temperature also affects phytoplankton metabolism by controlling the activity of enzymes involved in photosynthesis and respiration [47]. Thus, as the temperature increased, heat-tolerant phytoplankton, such as Cyanophyta and Chlorophyta, multiplied rapidly, while the growth of cold-tolerant Bacillariophyta was constrained. The dominant phytoplankton species in each lake are primarily Cyanophyta and Chlorophyta. The primary productivity of phytoplankton is strongly and positively correlated with water pH. A weakly alkaline environment encourages photosynthesis, whereas an acidic environment is detrimental to the survival of phytoplankton. pH is an essential factor in the normal growth and reproduction of phytoplankton [48]. The data indicated that all four lakes were just slightly alkaline (8.45–8.94), with Lake Ci having the highest pH, which was ideal for phytoplankton growth and reproduction. In addition to the physical factors mentioned above, nutrient salts are a dominant factor influencing the structure of phytoplankton communities, providing conditions for the growth and development of certain phytoplankton species, while possibly limiting that of others [49]. Research has shown a positive correlation between CODMn levels and the organic matter content of a water body. In turn, higher organic matter content can stimulate the growth and development of algae and aid in the establishment of a variety of phytoplankton communities [50].
Levels of total nitrogen and total phosphorus nutrients are key factors influencing the organization of phytoplankton communities in Lake Wang and Lake Baoan. The majority of nitrogen in Lake Wang is derived from wastewater discharge from industrial, agricultural, and fishery sources in Yangxin County. The most significant sources of pollution were the Liangjian River, Lake Saiqiao, and Halfbushan Farm, which is consistent with the results of our PCA analysis. The primary sources of total phosphorus content in the Lake Baoan watershed are agricultural pollutants, such as pesticides and fertilizers, as well as the direct discharge of wastewater from the water exchange of the watershed’s approximately 20,000 acres of intensive fishponds. Therefore, the structure of the phytoplankton community in Lake Baoan is mainly influenced by the water [51].
5. Conclusions
Anthropogenic disturbance often results in changes in the community structure of phytoplankton, disrupting the normal ecological pattern of water bodies. Consequently, the study of phytoplankton community structures and their influencing factors is of great importance for ecological restoration efforts. The following conclusions are drawn from the study. During the study period (summer 2019), a total of six phyla and 108 species of phytoplankton were detected in four lakes in the Southeast Hubei region, with six phyla and 82, 44, and 66 species in Lake Ci, Lake Wang, and Lake Baoan, respectively, and five phyla and 37 species in Lake Xiandao. The phytoplankton communities in each lake were dominated by chlorophytes, with the dominant species being mainly cyanophytes. The nutrient statuses of Lake Xiandao, Lake Baoan, Lake Ci, and Lake Wang were mesotrophic, light eutrophic, moderate eutrophic, and moderate eutrophic, respectively, and the water-quality statuses were light-medium pollution, light-medium pollution, medium pollution, and medium-severe pollution. Phytoplankton biomass followed the sequence of Lake Baoan > Lake Wang > Lake Ci > Lake Xiandao. The phytoplankton abundance was Lake Baoan > Lake Ci > Lake Wang > Lake Xiandao. A redundancy analysis showed that the main environmental factors affecting the phytoplankton community structures were pH and WT (Lake Ci), pH and CODMn (Lake Xiandao), TN and WT (Lake Wang), and TP and WT (Lake Baoan).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and X.Y.; methodology, M.L; software, M.L. and H.L.; validation, M.L., Z.H. and H.L.; formal analysis, M.L.; investigation, Y.C.; resources, X.W. and X.G.; data curation, M.L. and W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, X.W., G.L. and X.G.; supervision, H.L.; project administration, X.W., G.L., and X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Open Project Funding of Key Laboratory of Intelligent Health Perception and Ecological Restoration of Rivers and Lakes, Ministry of Education, Hubei University of Technology (HGKFYBP03), the Open Foundation of Resource-exhausted City Transformation and Development Research Center (Hubei Normal University) (KF2024Y07), the graduate innovative research project construction of Hubei Normal University (2023Z038), and the College Students’ Innovative Entrepreneurial Training Plan Program (202310513013, S202310513064).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, F.L.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Tao, S.; Li, B.G. Modeling the effects of ecological engineering on ecosystem health of a shallow eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chao). Ecol. Model. 1999, 117, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, M.; Sommer, U. Phytoplankton response to a changing climate. Hydrobiologia 2012, 698, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingole, S.B.; Naik, S.R.; Kadam, G. Study of phytoplankton of freshwater reservoir at majalgaon on sindphana river district beed (MS). Int. Res. J. 2010, 1, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Inyang, A.I.; Wang, Y.S. Phytoplankton diversity and community responses to physicochemical variables in mangrove zones of Guangzhou Province, China. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 650–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Jiang, T.; Cen, J.Y.; Ge, W.; Lu, S.H. Phytoplankton pigments and functional community structure in relation to environmental factors in the Pearl River Estuary. Oceanologia 2016, 58, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yang, E.J.; Park, J.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, S.H. Physical-biological coupling in the Amundsen Sea, Antarctica: Influence of physical factors on phytoplankton community structure and biomass. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 117, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, G.X.; Cheng, P.S. Phytoplankton community structure and water quality assessment in an ecological restoration area of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 18, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.A.; Feng, J.; Xie, S.L. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Assessment of Water Quality in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Fenhe River. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 915–923. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Deng, D.G.; Zhao, X.X.; Zhao, Z.Z. Temporal and spatial variations in phytoplankton: Correlations with environmental factors in Shengjin Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14144–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, G.Y.; Gotham, I.J. The effect of environmental factors on phytoplankton growth: Temperature and the interactions of temperature with nutrient limitation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firsova, A.; Galachyants, Y.; Bessudova, A.; Titova, A.; Sakirko, M.; Marchenkov, A.; Hilkhanova, D.; Nalimova, M.; Buzevich, V.; Mikhailov, I.; et al. Environmental factors affecting distribution and diversity of phytoplankton in the Irkutsk Reservoir ecosystem in June 2023. Diversity 2023, 15, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Deng, D.G.; Meng, X.L.; Zhang, X. Temporal and spatial variations of phytoplankton Community Structure in Lake Erhai, a Chinese plateau lake, with reference to environmental factors. Russ. J. Ecol. 2019, 50, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, C.; Reglero, P.; Hidalgo, M.; Sintes, E.; Sintes, E.; Santiago, R.; Martín, M.; Moyà, G.; Balbín, R. Phytoplankton community structure is driven by stratification in the oligotrophic Mediterranean Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarewicz, J.C.; Bertram, P.; Lewis, T.W. Changes in phytoplankton size-class abundance and species composition coinciding with changes in water chemistry and zooplankton community structure of Lake Michigan, 1983 to 1992. J. Great Lakes Res. 1998, 24, 637–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, C.X. Phytoplankton community structure in relation to environmental factors and ecological assessment of water quality in the upper reaches of the Genhe River in the Greater Hinggan Mountains. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17512–17519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, J.G.; Santhakumaran, P.; Kookal, S. Phytoplankton communities of eutrophic freshwater bodies (Kerala, India) in relation to the physicochemical water quality parameters. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 259–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.D.; Ma, X.C.; Jiang, B.H.; Ge, X.G.; Ren, W.X.; Qin, Y.; Tan, Y. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter in Cihu Lake of Huangshi City. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2020, 36, 1276–1284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.X.; Zhao, M.D. Investigation and evaluation of water trophication in Xiandao Lake. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2018, 38, 49–51. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.D.; Lin, G.Y.; Feng, N.; Yu, X.H.; Zhao, J.L.; Yang, Z.W.; Ren, W.X. Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Solids in lakes with Different Eultrophic Levels in Southeastern Hubei Province. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2022, 38, 437–445. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.B.; Wu, J.L.; Zeng, H.A.; Zhang, Y.D.; Jin, M. Distribution of n-alkanes from Lake Wanghu Sediments in Relation to Environmental Changes. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 3682–3688. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.M.; Qiao, R.T.; Liu, J.H.; Yu, Y.X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.J. Spatial and Temporal Distribution and Environmental Effects of Potamogeton Crispus Population in Bao’An Lake. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 1730–1740. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- The State Environmental Protection Administration The Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method Editorial Board. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Z. Methods for collecting and counting freshwater plankton. Bull. Biol. 1955, 6, 52–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.F.; Guo, F.F.; Li, J.Z.; Xiong, B.X. Community structures of phytoplankton and their relationships with environmental factors in the Jinshahe Reservoir, Hubei Province. J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 902–910. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, T.T.; Sun, Y.T.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Deng, D.G. Community structure characteristics of phytoplankton in small lakes of Huaibei excavating coal subsidence region. Freshw. Fish. 2020, 50, 51–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.P.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Q. Eutrophication Evaluation of Taihu Lake Based on Quantitative Remote Sensing Inversion. Geo. GIS 2007, 3, 33–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.T.; Lei, J.S.; Jia, H.Y.; Yang, C.G. Characteristics of Phytoplankton Community and Eutrophication Evaluation of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecol. Environ. Monit. Three Gorges 2020, 5, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.C.; Tu, Q.Y. Lake Eutrophication Survey Specification, 2nd ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, W.J.; Qian, C.Y.; Huang, X.F.; Sheng, J.; Li, C.T.; Deng, C.W.; Yu, M.J.; Yang, G.J. Study on seasonal variations of community structure of phytoplankton—Case study of Meiliang Bay and East Taihu Lake in Lake Taihu. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2022, 48, 81–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhu, C.; Tang, P.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.H. Correlation analysis of phytoplankton community and water quality in Chaohu factor. J. Biol. 2023, 40, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Xu, Q.; Qin, K.M.; Wang, N.Y.; Li, C.H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.S. Characteristics of community structure of phytoplankton in the Datong lake in summer and bioassessment of water quality in 2019. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 45, 126–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yao, X.H.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Shi, J.H.; Gao, H.W. Variations in the phytoplankton community due to dustadditions in eutrophication, LNLC and HNL Coceaniczones. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathleen, K.I. Allelopathic Influence on Blue-Green Bloom Sequence in a Eutrophic Lake. Science 1977, 196, 885–887. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.L.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, T.Y.; Yu, J.B.; Wang, H.Q.; Chen, K.J.; Liu, A.M.; Li, Z.J. Phytoplankton’s community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in an aquaculture lake, Datong Lake of China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q. Structure of Phytoplankton Community and Its Relationship with the Environmental Factors in Dali-Nor Lake. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kaparapu, J.; Geddada, M.N.R. Seasonal Distribution of Phytoplankton in Riwada Reservoir, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India. Not. Sci. Biol. 2013, 5, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.H.; Guo, Z.Q.; Wei, W.X.; Bi, J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Ji, X. Phytoplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Nanhai Lake. Diversity 2022, 14, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.X.; Wu, X.D.; Ge, X.G.; Lin, G.Y.; Feng, L.; Ma, W.Q.; Xu, D. Study on the Water Quality Characteristics of the Baoan Lake Basin in China under Different Land Use and Landscape Pattern Distributions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Wan, L.; Zhao, L.F. Effect of nutrient level on phytoplankton community structure in different water bodies. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, F.; Shi, K.; Johnes, P.J.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Ma, M.Z.; Lu, Y. Identifying the main drivers of change of phytoplankton community structure and gross primary productivity in a river-lake system. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.S.; Lv, X.C.; Geng, S.C.; Wang, G.F.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y. Canonical correspondence analysis of relationship between characteristics of phytoplankton community and environmental factors in Wolong Lake. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 621, 012107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namugize, J.N.; Jewitt, G.; Graham, M. Effects of land use and land cover changes on water quality in the uMngeni river catchment, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2018, 105, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.; Trolle, D.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Bjerring, R.; Olesen, J.; Jeppesen, E. Watershed land use effects on lake water quality in Denmark. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1187–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrantes, N.; Antunes, S.C.; Pereira, M.J.; Gonçalves, F. Seasonal succession of cladocerans and phytoplankton and their interaction in a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Vela, Portugal). Acta Oecologica 2005, 29, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.X.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.G. Controlling factors of spring–summer phytoplankton succession in Lake Taihu (Meiliang Bay, China). Hydrobiologia 2008, 607, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.S.; Ransangan, J. Effects of nutrients and zooplankton on the phytoplankton community structure in Marudu Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 194, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.G.; Xie, P.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, H.; Guo, L.G. Studies on temporal and spatial variations of phytoplankton in Lake Chaohu. J. Integr. Plant Bio. 2007, 49, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nydick, K.R.; Lafrancois, B.M.; Baron, J.S.; Johnson, B.M. Nitrogen regulation of algal biomass, productivity, and composition in shal-low mountain lakes, Snowy Range, Wyoming, USA. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Jiang, X.M.; Sun, X.; Miu, R.L.; Ai, X. Spatio-temporal patterns and influencing factors of phytoplankton communities in the main inflow rivers of Qinghai Lake. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2024, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, M.K.; Feng, L.; Wu, X.D.; Ge, X.G.; Lin, X.W.; Song, S.X.; Xu, R.; Sun, Z.H. Assessment of Water Eutrophication at Bao’an Lake in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Based on Multiple Methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).