Abstract
This study focused on the phytolith characteristics of leaves and culm sheaths from nine bamboo species across three genera (Bambusa Schreb., Gigantochloa Nees, and Dendrocalamus Kurz ex Munro) in the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden. By analyzing phytolith content, concentration, particle size distribution, morphometric parameters of elongated saddle-type phytoliths, and phytolith–assemblage composition, we aimed to elucidate the distribution patterns and morphological features of phytoliths in clumping bamboos, thereby providing morphological evidence for genus-level classification within the Bambusoideae. The results demonstrated the following. (1) Leaves exhibited significantly higher phytolith content and concentration than did culm sheaths across all genera, with Dendrocalamus being the sole exception, showing no significant intrageneric differences. (2) Distinct particle size distribution patterns were observed—leaves consistently peaked at 10–20 μm, whereas culm sheaths displayed triple peaks at 10–20 μm, 20–30 μm, and 900–1000 μm. (3) Morphometric analysis revealed that culm sheaths contained larger elongated saddle-type phytoliths (length, width, and area) compared to leaves across all genera. (4) Among the 37 identified phytolith morphotypes, culm sheaths exhibited greater diversity, with 35 types (dominated by rondel and elongate), while leaves contained 31 types primarily characterized by saddle and stomatal phytoliths, with elongated saddles being the most abundant. Collectively, our findings demonstrate significant morphological disparities between foliar and culm sheath phytoliths in sympodial bamboos (Bambusa), with culm sheath phytoliths exhibiting greater taxonomic potential for generic-level classification within the subfamily Bambusoideae.
1. Introduction
Phytoliths are carbon-encapsulated silica structures formed within plant cell lumina or intercellular spaces through the deposition of amorphous silicic acid [Si(OH)4], which is absorbed by roots and transported via vascular bundles during plant growth. These microscopic silica bodies are present in nearly all vascular plants and particularly abundant in Bambusoideae species [1,2] Renowned for their exceptional physicochemical stability, phytoliths exhibit unique advantages, such as in- situ deposition, long-term preservation, and ubiquitous distribution [3], making them indispensable tools across diverse disciplines, including botany, paleoecology, geology [4,5,6,7], plant taxonomy, paleovegetation reconstruction, soil silicon cycling, and agricultural archaeology [8,9].
Early studies primarily focused on phytoliths in agricultural crops to facilitate species identification, elucidate cultivation evolution, and investigate their roles in enhancing mechanical support, pest resistance, and lodging tolerance [10,11,12]. Recent advances have revealed that bamboo phytoliths surpass those of other higher vascular plants in both content and morphological diversity [13]. Bamboo phytoliths also contribute to growth by absorbing and storing essential minerals and nutrients. Notably, leaves and culm sheaths exhibit the richest phytolith morphotypes [14]. Comparative analyses of these organ-specific phytolith characteristics provide critical insights into bamboo growth dynamics, sustainable management, and taxonomic classification, establishing a robust morphological foundation for Bambusoideae systematics.
Studies on Pleioblastus amarus (Keng) P.C. Keng, Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro, and Bambusa oldhamii Munro have demonstrated organ-specific phytolith distribution patterns: leaves > branches > culms [15,16,17]. While most research emphasizes foliar phytoliths, emerging evidence indicates that culm sheaths also harbor abundant phytoliths with diagnostic value for taxonomic identification [14]. However, comprehensive analyses of phytolith distribution patterns, size characteristics, and morphological features across different clumping bamboo genera—and their potential for generic-level classification in Bambusoideae—remain unexplored.
Building on Tao Xinyue’s research on phytolith morphology and assemblages in Bambusoideae leaves, which demonstrated that specific phytolith morphotypes, their combinations, and saddle-shaped phytolith parameters can be used to classify bamboos at the genus level [18,19], this study focuses on leaves and culm sheaths of nine clumping bamboo species from three genera (Bambusa, Gigantochloa, and Dendrocalamus) at the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden. The species include Bambusa longispiculata Gamble ex Brandis, B. intermedia (Hsueh and Yi) T.P. Yi, B. dolichoclada Hayata, Dendrocalamus sinicus L.C. Chia and J.L. Sun, D. barbatus J.R. Xue and D.Z. Li, D. bambusoides J.R. Xue and D.Z. Li, Gigantochloa atroviolacea Widjaja, G. verticillata (Willd.) Munro, and G. albociliata (Munro) Kurz. Leaves and culm sheaths were collected from one-year-old bamboos grown under uniform climatic and soil conditions. Phytoliths were extracted using an improved wet oxidation method [20], followed by systematic analysis of their content, concentration, particle size distribution, and morphological characteristics through microscopic observation and particle size analysis. This research investigates variation patterns in phytolith content, concentration, size, and morphology between leaves and culm sheaths across genera while evaluating their combined potential for enhancing taxonomic precision at the generic level within Bambusoideae.
2. Research Area and Methods
2.1. Research Area
Located in Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture of Yunnan Province, China, the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden consists of eastern and western sections, with its 6.9-hectare Bamboo Garden (21°52′–21°57′ N, 101°14′–101°18′ E) situated in the western area housing approximately 250 bamboo species. At an average elevation of 600 m in the northern tropical margin, the garden experiences a typical southern Yunnan tropical monsoon climate characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons—the rainy season extends from May to October and the dry season occurs from November to April—with an annual mean temperature of 21.3 °C and average precipitation of 1557 mm [21].
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Sampling
During the sampling period from October 2022 to June 2023, representative bamboo species were collected from the botanical garden, including B. longispiculata, B. intermedia, B. dolichoclada, D. sinicus, D. barbatus, D. bambusoides, G. atroviolacea, G. verticillata, and G. albociliata. Sampling focused on one-year-old healthy plants with well-developed growth. For culm sheaths, we carefully selected intact specimens (including both sheath blades and sheath auricles) that had formed abscission layers at their bases but not yet detached, considering different species’ shedding patterns (delayed shedding or persistent sheaths). From each species, culm sheaths were collected from at least three different culms. Mature leaves were sampled from sun-exposed surfaces, with mixed samples taken from upper, middle, and lower canopy positions. Detailed collection records were maintained, including scientific names (Latin and Chinese), collection numbers, dates, collectors’ names, locations with GPS coordinates (latitude/longitude), and elevation data for each specimen.
2.2.2. Phytolith Extraction
Phytoliths were extracted from leaves and culm sheaths using an improved wet oxidation method [20]. The samples were first oven-dried (Wujiang Lilong Electric Heating Equipment Co., Ltd., Wujiang, China) at 60 °C, and 0.3 g aliquots were sequentially treated with 5 mL each of concentrated hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and perchloric acid (Shandong Xinchang Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shaoxing, China) for overnight defoaming, followed by microwave digestion. The digested samples were then transferred to centrifuge tubes, brought to constant volume, and centrifuged (Wujiang Lilong Electric Heating Equipment Co., Ltd., Wujiang, China) at 3500 rpm for five cycles (5 min each) until neutral pH was achieved. The white precipitates collected at the bottom of the tubes represented the extracted phytoliths.
For morphological analysis, the phytoliths were mounted on slides in neutral resin(Tianjin Bohong Resin Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), and over 100 images per sample were captured at 40× magnification (Ningbo Shunyu Instrument Co., Ltd.; Yuyao, China). Phytoliths were classified and described according to the International Code for Phytolith Nomenclature (ICPN 1.0 [8] and 2.0 [22]) [23,24]. Quantitative analyses included the following.
① Phytolith content (g/kg) = [(mass of dried phytoliths + tube) − (mass of empty tube)]/sample weight × 1000;
② Phytolith concentration (particles/g) = (microscopic particle count × 10,315)/(spore count × 0.3 g).
Morphometric parameters (length, width, and area) of elongated saddle phytoliths were measured with ImageJ-Win64, while particle size distribution was determined using a Mastersizer instrument with Malvernsizer 3000+ Lab, with triplicate measurements performed for each sample [25].
2.2.3. Data Processing
This study statistically analyzed mean values from three representative species per genus (Bambusa, Gigantochloa, and Dendrocalamus) with SPSS 25. Intergeneric comparisons between leaves and culm sheaths were conducted through one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc tests, while intrageneric comparisons employed ANOVA and independent t-tests. The collective characteristics of sympodial bamboos were assessed via t-tests on tri-generic means. All graphical representations were generated using Adobe Photoshop 2021 for image processing and Origin 2021 for data visualization [25].
3. Results
3.1. Phytolith Content Analysis
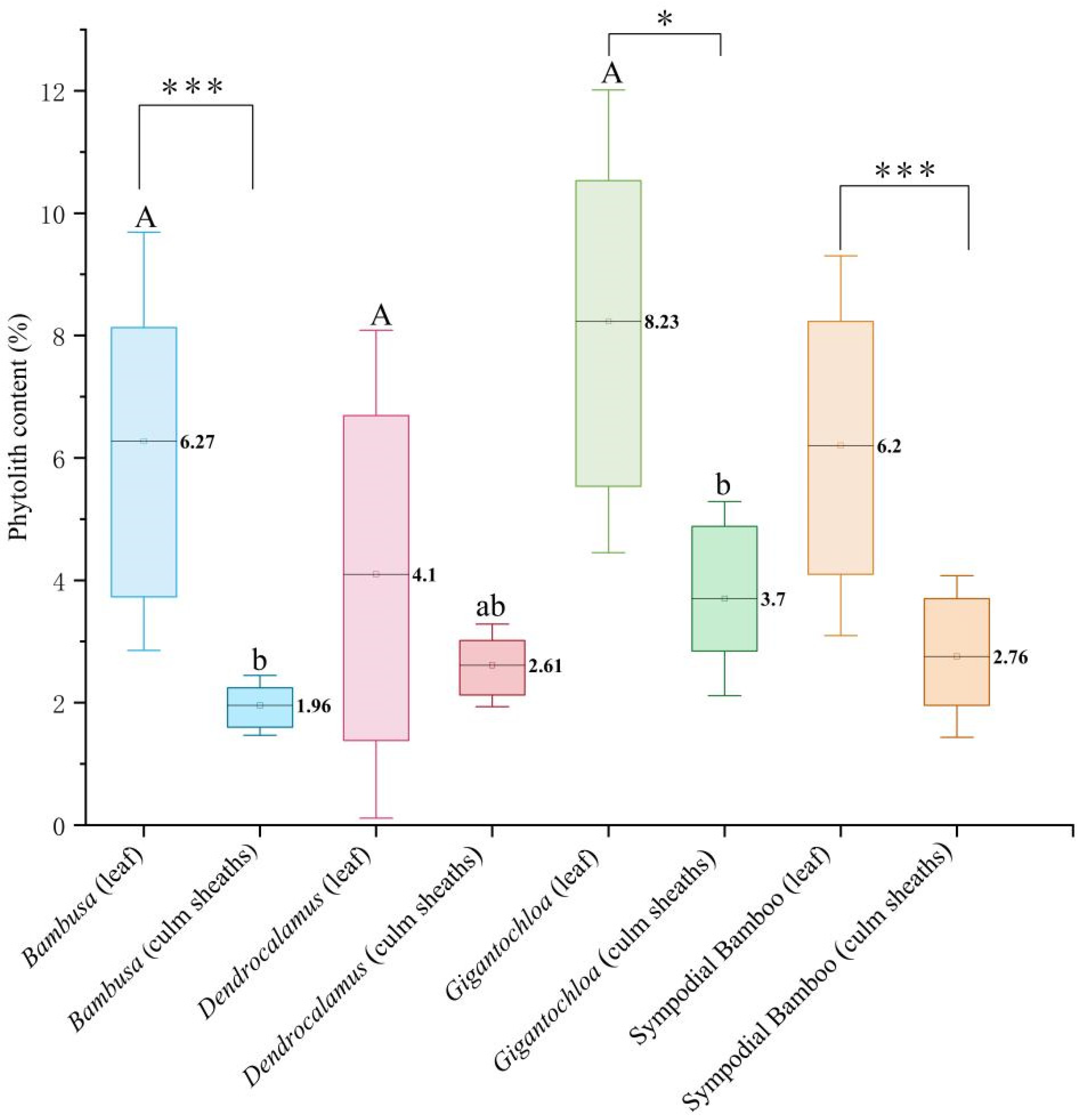
The results from Figure 1 demonstrate highly significant differences (p < 0.01) in phytolith content between leaves and culm sheaths across all studied clumping bamboos. At the intrageneric level, significant variations (p < 0.05) were observed between leaves and culm sheaths in both Bambusa and Gigantochloa, while Dendrocalamus showed no statistically significant difference. Intergeneric comparisons revealed that significant differences existed specifically in culm sheaths but not in leaves. Notably, Gigantochloa exhibited the highest phytolith content among all genera, with leaves containing 8.23% and culm sheaths 3.7% phytoliths by weight. The phytolith content displayed distinct genus-specific patterns; for culm sheaths, the content decreased in the order Gigantochloa > Dendrocalamus > Bambusa, whereas for leaves, the order was Gigantochloa > Bambusa > Dendrocalamus.
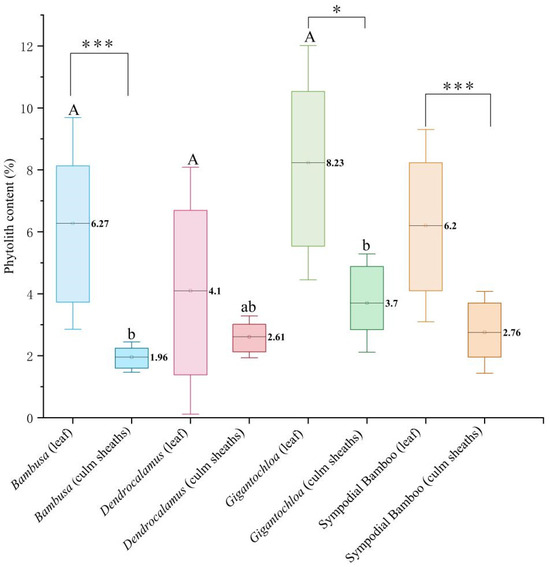
Figure 1.
Comparison of phytolith content in leaves and culm sheaths among the three genera. Uppercase letters indicate significance between leaves of different genera; lowercase letters denote significance between culm sheaths of different genera; * represents significance between leaves and culm sheaths within the same genus. Note: The symbols indicate statistical significance levels, with (*) representing p < 0.05 and (***) representing p < 0.001.
3.2. Phytolith Concentration Analysis
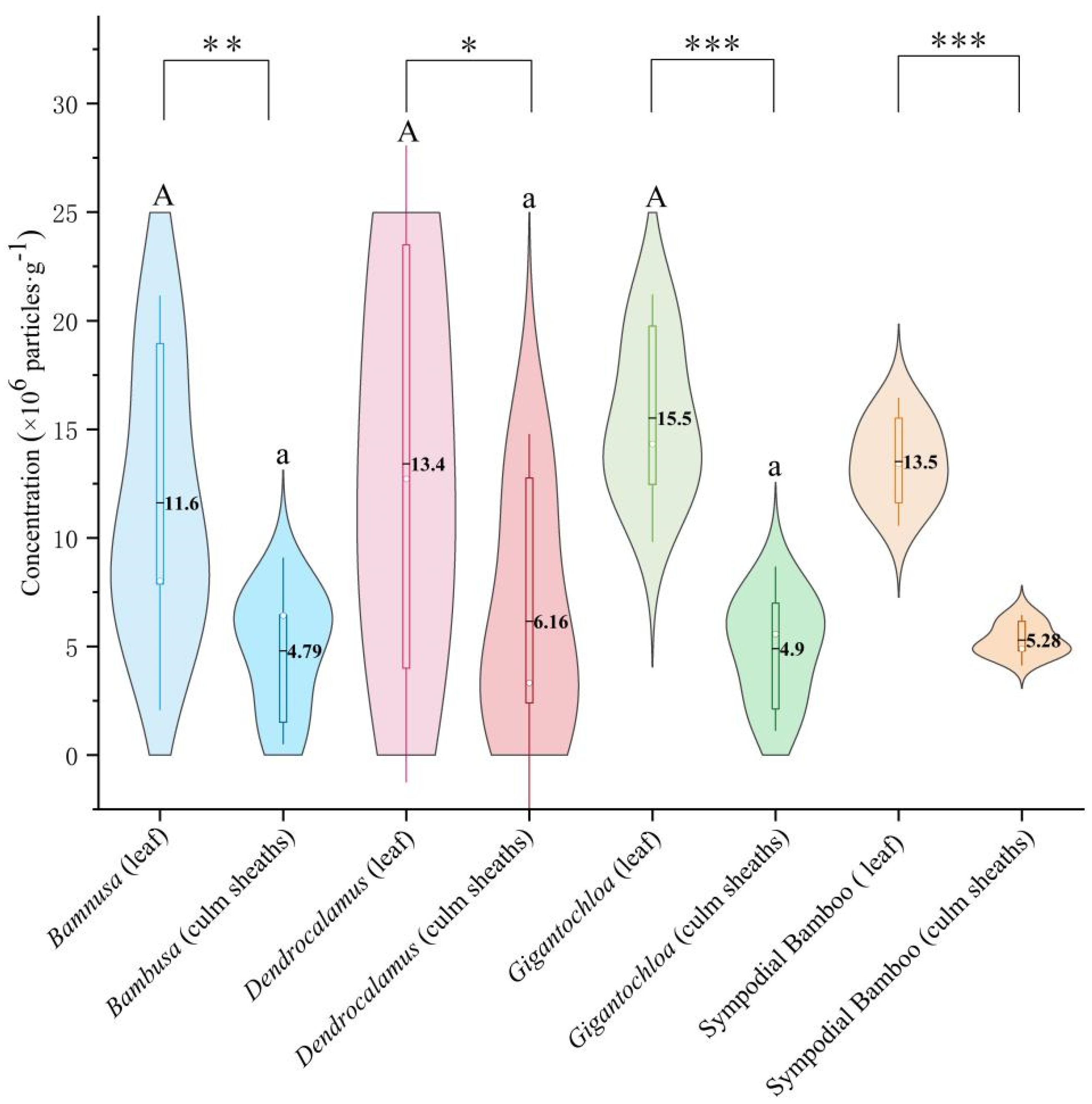
Comparative analysis of the three genera revealed that phytolith concentrations in leaves were significantly higher than in culm sheaths (p < 0.01) across all clumping bamboos. Significant differences (p < 0.05) were consistently observed between leaves and culm sheaths within each genus. However, no significant variations were detected when comparing leaves or culm sheaths separately among different genera (Figure 2).
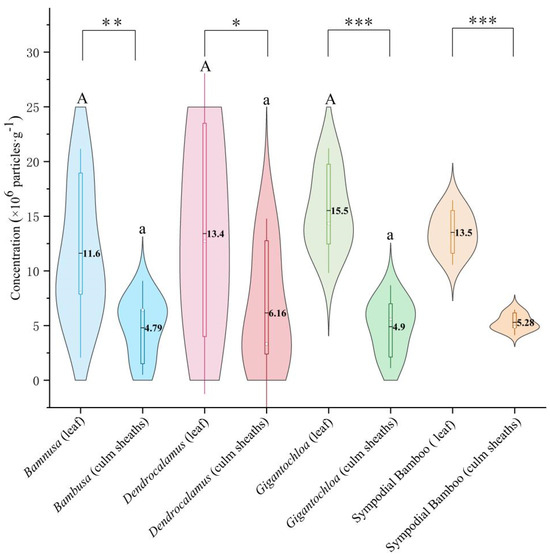
Figure 2.
Phytolith concentration. Uppercase letters indicate significance between leaves of different genera; lowercase letters denote significance between culm sheaths of different genera; * represents significance between leaves and culm sheaths within the same genus. Note: Asterisks mark significance thresholds, with (*) for p < 0.05, (**) for 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05, and (***) for p < 0.001.
Notably, Gigantochloa exhibited the highest phytolith concentration in leaves (15.5%), followed by Dendrocalamus (13.4%) and Bambusa (11.6%). This pattern persisted in culm sheaths, with Gigantochloa maintaining significantly higher concentrations than the other two genera.
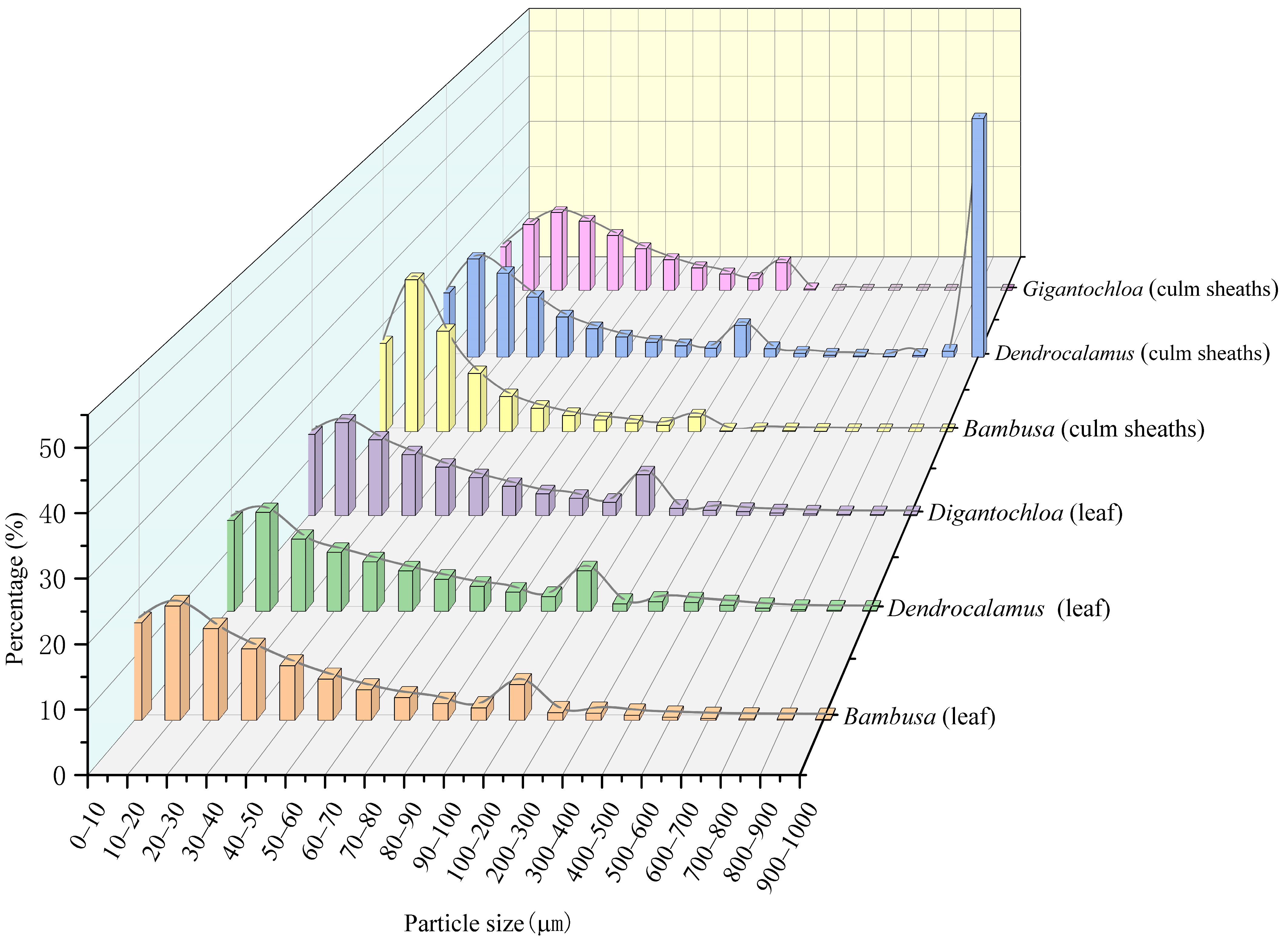
3.3. Comparison of Phytolith Particle Size
Figure 3 demonstrates distinct phytolith particle size distribution patterns for leaves and culm sheaths in the studied bamboos. While leaves consistently showed a single peak at 10–20 μm, culm sheaths exhibited multiple peaks at 10–20 μm, 20–30 μm, and 900–1000 μm. Analysis of sub-100 μm particles (divided into 10 μm intervals) revealed that all three genera shared nearly identical distribution patterns in leaves, with the 10–20 μm range exceeding 25% and intervals (0–10 μm, 20–30 μm) maintaining over 20%. In culm sheaths, particle distributions varied more significantly among genera, with all three showing over 40% in the 10–20 μm range (Bambusa exceeding 50%), while Dendrocalamus uniquely dominated the 900–1000 μm range at 50%, a particle size class fraction nearly absent in the other two genera. Secondary peaks appeared at 0–10 μm and 20–30 μm (both >20%), followed by 30–40 μm (>15%). Notably, all three genera maintained over 10% particle frequency in the 100–200 μm range for leaves, demonstrating conserved distribution patterns at larger sizes despite their genus-specific variation in culm sheaths.
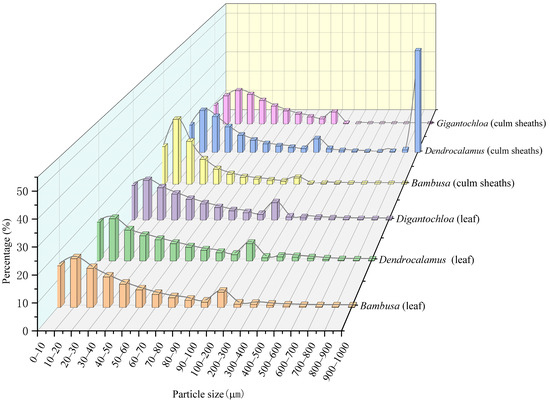
Figure 3.
Phytolith particle size.
3.4. Comparison of Long Saddle-Shaped Phytolith Morphological Parameters
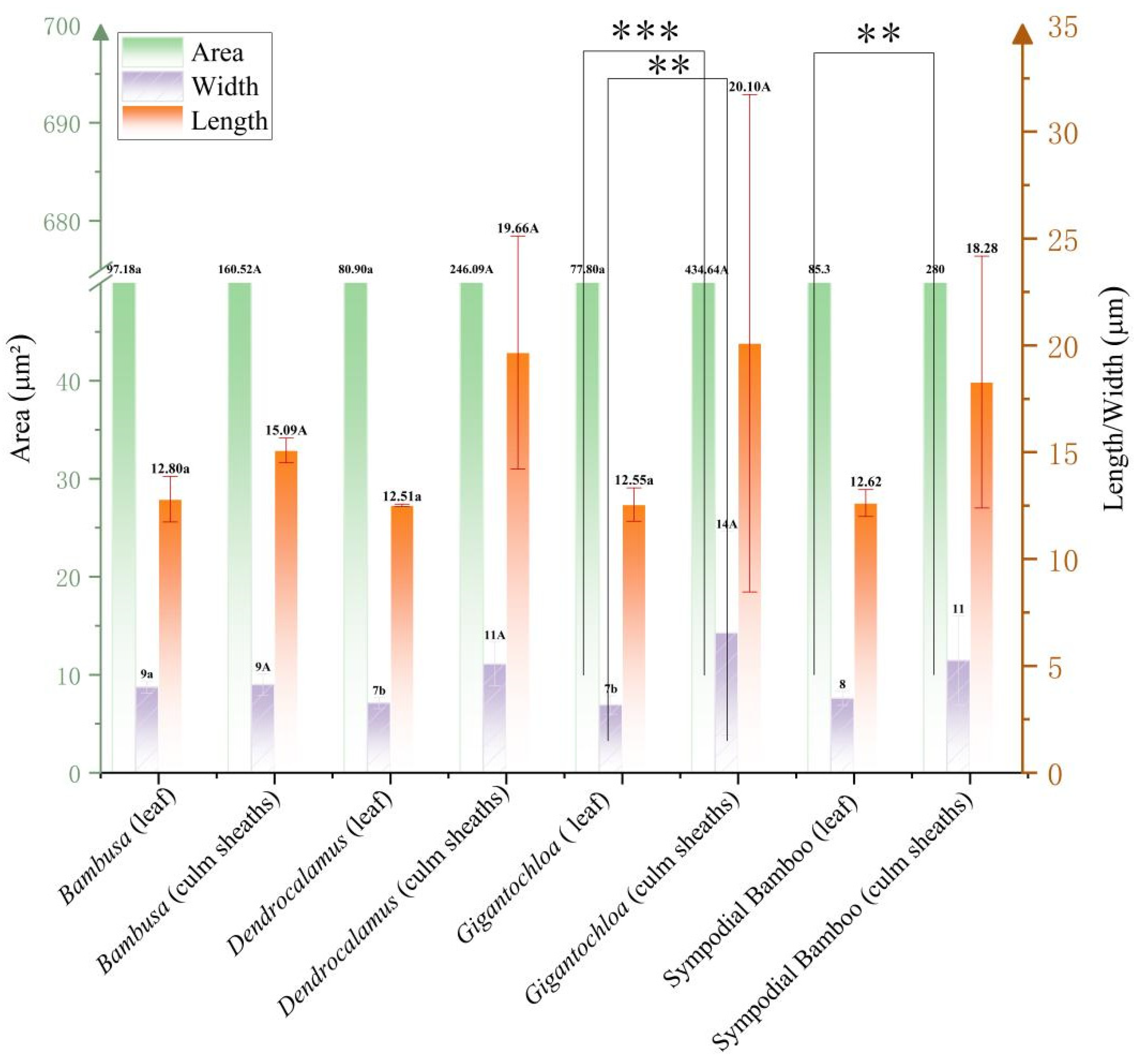
The morphometric analysis of saddle-shaped phytoliths revealed dimensional characteristics between leaves and culm sheaths across the three genera (Bambusa, Gigantochloa, and Dendrocalamus). In leaves, phytolith length narrowly ranged from 12.51 to 12.80 μm, displaying the hierarchical order Bambusa > Gigantochloa > Dendrocalamus, while area measurements showed limited variation (77.80–97.18 μm2, range = 19.38 μm2), with the comparative sequence Bambusa > Dendrocalamus > Gigantochloa. Culm sheath phytoliths exhibited substantially greater dimensional variability, with length (15.09–20.10 μm, range = 5.01 μm), width (9–14 μm, range = 5 μm), and area values (160.52–434.64 μm2, range = 274.12 μm2) all consistently following the ranking Gigantochloa > Dendrocalamus > Bambusa. Notably, Gigantochloa consistently ranked highest across all of these parameters (length = 20.10 μm, width = 14 μm, area = 434.64 μm2) compared to Bambusa. Statistical evaluation of these morphological parameters identified significant intergeneric differences exclusively in area measurements when comparing leaves and culm sheaths, with leaf width representing the sole parameter exhibiting significant variation in intergeneric leaf comparisons. At the intrageneric level, only Gigantochloa exhibited statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) in both area and width parameters. The comprehensive analysis revealed that Gigantochloa culm sheaths showed significantly higher values in phytolith area, length, and width than did Dendrocalamus and Bambusa, while an inverse size distribution pattern was observed in leaf tissues, with Bambusa > Dendrocalamus > Gigantochloa (Figure 4).
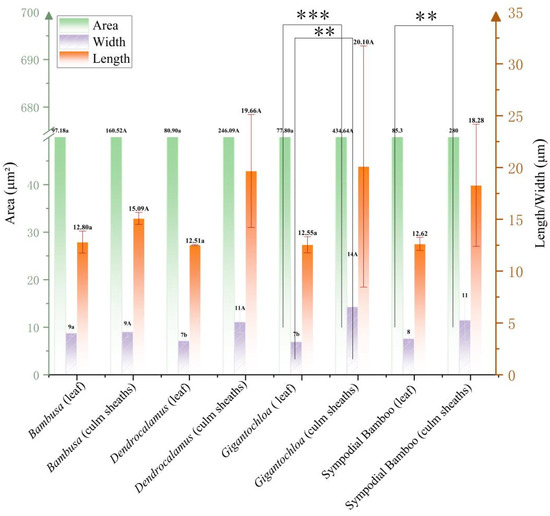
Figure 4.
Morphometric parameters of elongated saddle phytoliths. Uppercase letters indicate significance between leaves of different genera; lowercase letters denote significance between culm sheaths of different genera; Asterisk represents significance between leaves and culm sheaths within the same genus. Note: Asterisks mark significance thresholds, with (**) for 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05, and (***) for p < 0.001.
3.5. Phytolith Morphology and Combinations
This study systematically identified and analyzed phytolith morphotypes in leaves and culm sheaths from three clumping bamboo genera (Bambusa, Dendrocalamus, and Gigantochloa) according to the International Code for Phytolith Nomenclature (ICPN 1.0 [8] and 2.0 [22]) standards [23,24]. A comprehensive analysis revealed 37 distinct phytolith morphotypes (Figure 5) demonstrating significant variation in their distribution between leaves and culm sheaths. Quantitative analysis showed that saddle phytoliths predominated in leaves, while ruffle-top rondel and elongated phytoliths were more abundant in culm sheaths (Table 1).
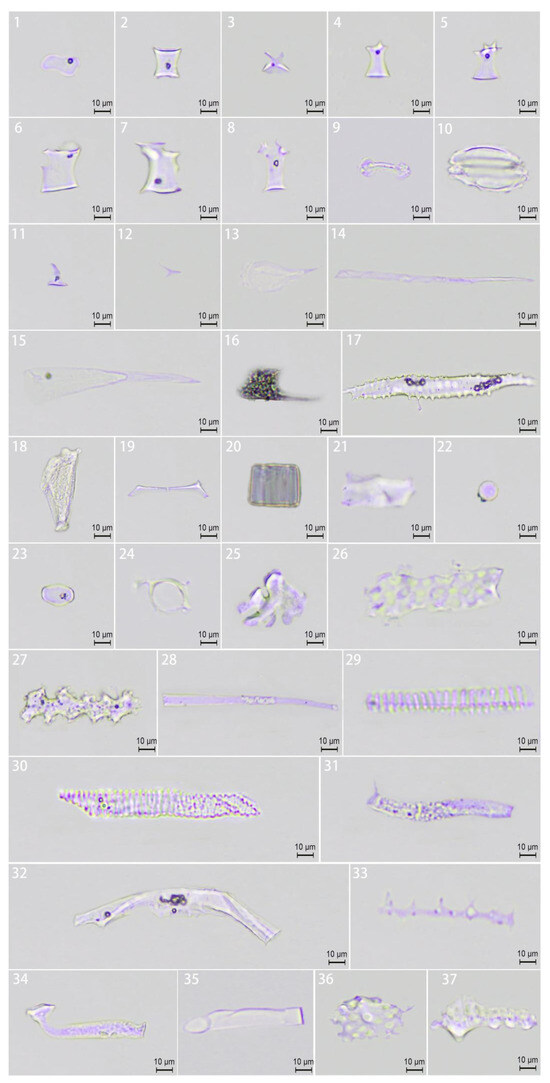
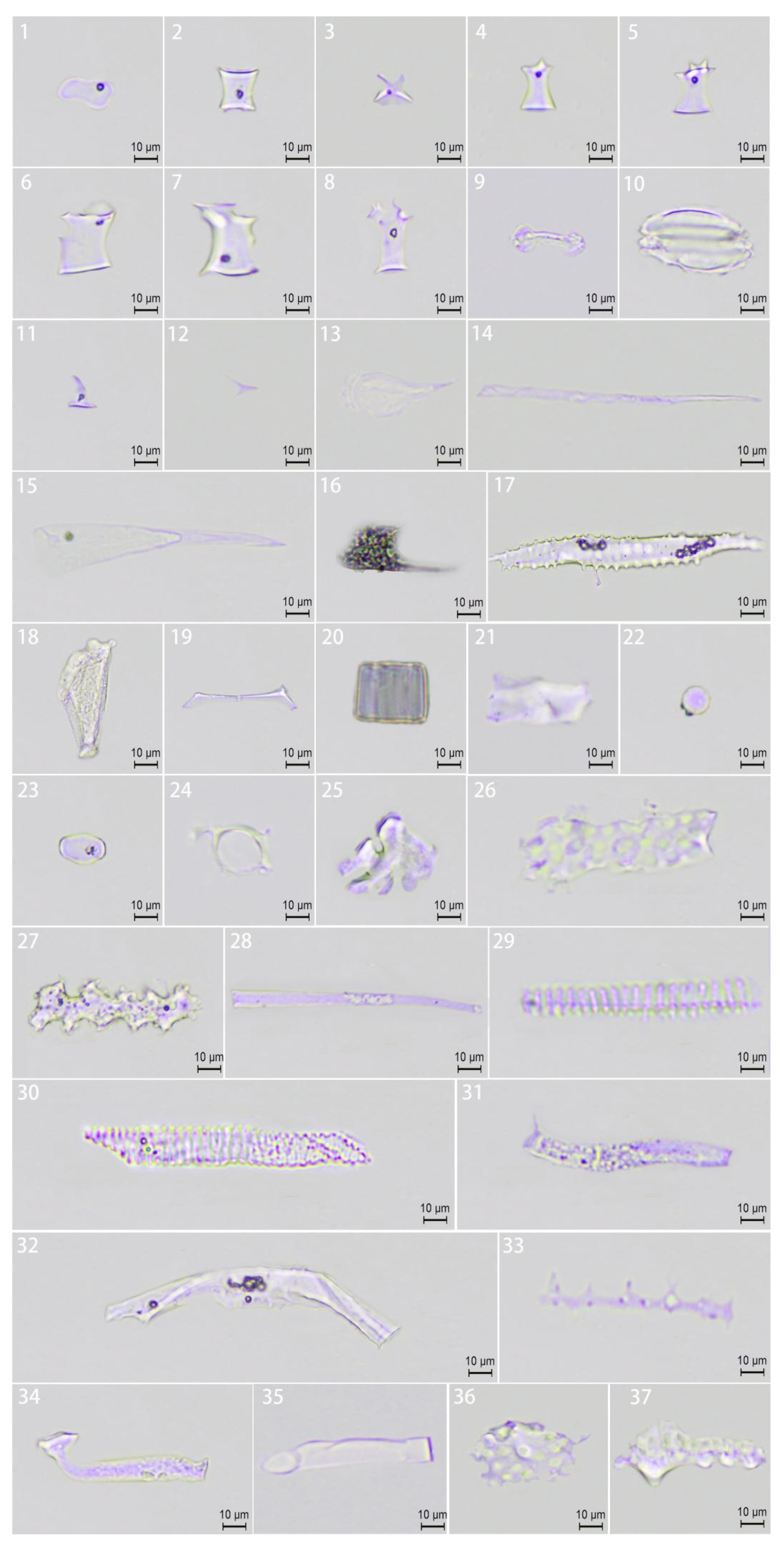
Figure 5.
Phytolith morphology. (1) Saddle; (2) ruffle-top rondel; (3) two-spiked rondel; (4) three-spiked rondel; (5) four-spiked rondel; (6–8) irregular rondel; (9) bilobate; (10) silica stoma; (11) acute dumbbell; (12) short acute; (13) spheroidal acute; (14) acute extended; (15) acute extended laminar; (16) acute extended elbow; (17) acute extended baculate; (18) flabellate; (19) brachiate; (20) blocky; (21) tabular; (22) circular; (23) oblong; (24) homogeneous; (25) nodulate; (26) elongated scrobicuate; (27) elongated dendritic; (28) elongated hollow; (29) elongated helical; (30) elongated annulate; (31) elongated granulate; (32) elongated maculose; (33) elongated baculate; (34) elongated elbow; (35) elongated bulbous; (36) scrobiculate; (37) tuberculate.

Table 1.
Phytolith morphotype proportions.
Five morphotypes—saddle, ruffle-top rondel, two-spiked rondel, short acute, and elongated bulbous phytoliths—were common across all three genera. Notably, blocky, acute extended, baculate, and tuberculate phytoliths were absent in leaves, and D. sinicus exhibited the highest proportion (32.6%) of elongated scrobiculate phytoliths. The remarkable diversity of phytolith morphologies observed in this study provides valuable diagnostic characteristics for precise taxonomic classification within Bambusoideae.
Analysis of the Proportion of Major Phytolith Morphological Classes
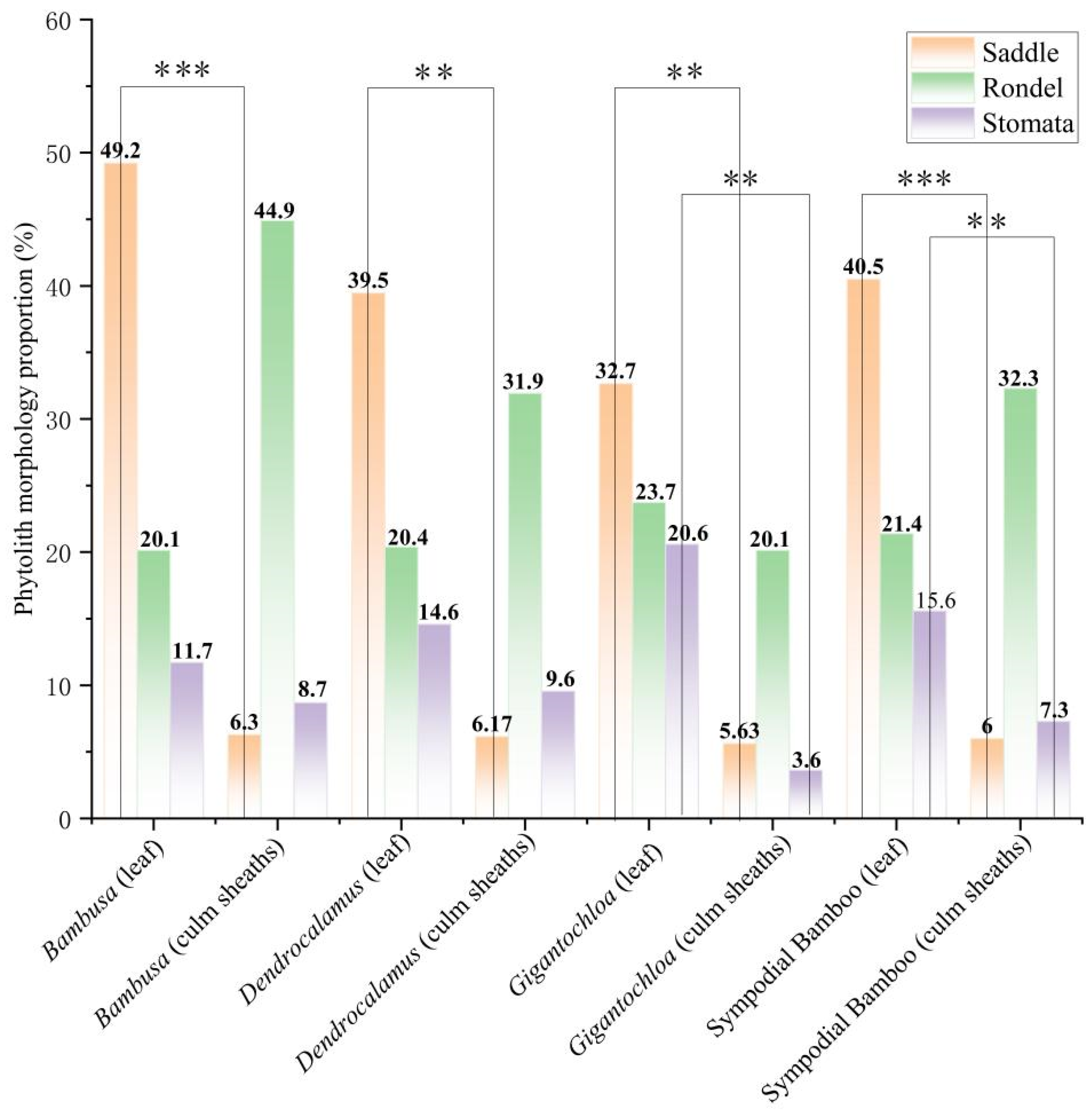
The comparative analysis of key phytolith morphotypes revealed distinct distribution patterns between leaves and culm sheaths across the three bamboo genera (Figure 6). Saddle phytolith proportions showed highly significant differences (p < 0.01) between leaves and culm sheaths in all genera, while silica stoma phytoliths exhibited significant variation (p < 0.05) only in Gigantochloa. Rondel phytolith distributions showed no statistically significant differences.
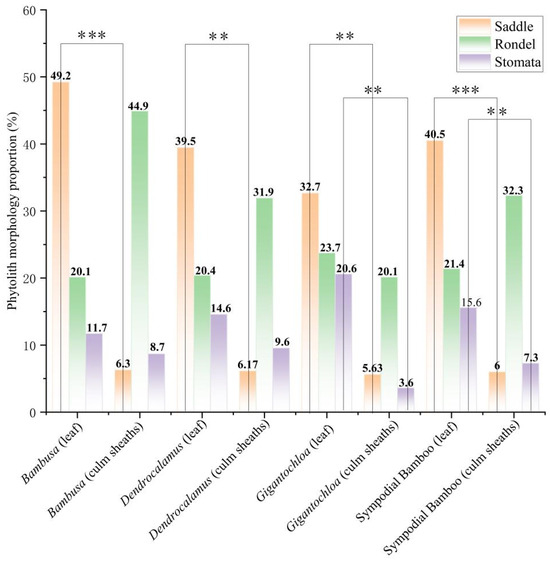
Figure 6.
Proportions of major phytolith morphotypes. Asterisk indicates significance between the leaf and sheath of the culm. Note: The asterisks denote statistical significance levels: (**) indicates p values between 0.01 and 0.05, while (***) represents p < 0.001.
Notably, saddle and silica stoma phytoliths were consistently more abundant in leaves than in culm sheaths across all three genera. In contrast, rondel phytoliths were more prevalent in culm sheaths than in leaves for both Bambusa and Dendrocalamus. Quantitative analysis revealed maximum proportions of 49.2% for saddle phytoliths and 44.9% for rondel phytoliths in Bambusa, while Gigantochloa showed the highest proportion (20.6%) of silica stoma phytoliths. These findings collectively demonstrate that (1) saddle and silica stoma phytoliths show significant leaf-predominant distributions, (2) rondel phytoliths exhibit non-significant but consistent sheath-predominant patterns in two genera, and (3) each genus displays characteristic phytolith proportion maxima that may serve as taxonomic indicators.
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in Phytolith Content and Concentration Between Leaves and Culm Sheaths of Clumping Bamboos
Phytoliths play a protective role in plant growth and are present in the vast majority of plant species, accounting for approximately 0.1% to 10% of plant dry weight. However, their content varies significantly among different species and even between organs of the same plant [22]. Liu Junxia’s research [26] demonstrated uneven phytolith distribution in various organs of Dendrocalamus giganteus Wall. ex Munro, with leaves exhibiting significantly higher phytolith content compared to other organs. Similarly, Xu Rui et al. [14] demonstrated through their study on Ferrocalamus strictus J.R. Xue and P.C. Keng that phytolith content in plant leaves is significantly higher than in stems and roots. Their findings revealed distinct variations of phytolith concentration among different plant organs, with notable differences even within the same species during the same growth period. Our study conclusively demonstrates that leaf phytolith concentrations in clumping bamboos are markedly and significantly greater (p < 0.01) than those in culm sheaths. Additionally, studies on Phragmites have shown that phytolith concentrations peak in August through September, suggesting alignment with plant silicon demand dynamics [27]. In our study, leaves exhibited higher phytolith concentrations than culm sheaths, attributed to their role as primary nutrient organs capable of continuous silicon uptake during development. These results corroborate previous findings, reinforcing the organ-specific patterns of phytolith deposition and their relationship to physiological functionality.
Work by Zhu Fangwei et al. [28] revealed that variation in phytolith content and morphology in Dendrocalamus giganteus Wall. ex Munro is closely linked to its growth and phenology. Phytolith accumulation continuously increased from the branch extension and leaf expansion stage to the shoot emergence stage, followed by a decline during dormancy. This pattern aligns with our sampling strategy targeting the shoot emergence period to maximize phytolith yields.
Similarly, Xie Dongbo et al. [29] demonstrated in Dendrocalamus brandisii (Munro) Kurz. that shifts in the relative abundance of phytolith morphotypes (e.g., square and fan-shaped forms) correlate with leaf physiological processes, including transpiration, respiration, and photosynthesis. They observed that mature leaves with heightened transpiration rates exhibited increased proportions of square and fan-shaped phytoliths. Our findings in a tropical region characterized by intense leaf physiological activity (transpiration, respiration, and photosynthesis) corroborate these patterns, showing both high phytolith diversity and abundance. The consistency between these studies highlights the potential of phytolith characteristics as indicators of plant–environment interactions under varying climatic conditions.
4.2. Morphological Characteristics and Functional Relationships of Phytoliths in Leaves and Culm Sheaths of Clumping Bamboos
We observed 37 phytolith morphotypes in the leaves and culm sheaths of three clumping bamboo genera, with 31 types in leaves and 35 types in culm sheaths, reflecting significant organ-specific diversity [22]. Our study found that leaves are predominantly characterized by elongated saddle and stomatal phytoliths, while culm sheaths are dominated by truncated cone and rod-shaped phytoliths. These differences likely reflect distinct physiological functions and ecological adaptations of bamboo organs, consistent with Li.C. et al.’s findings on phytolith assemblages in surface soils and vegetation in northeastern China [30] Observed morphological variation between organs further elucidates developmental and functional specialization, aligning with Xu et al.’s research on Ferrocalamus strictus phytoliths [14]. For instance, leaves exhibit greater morphological consistency, whereas culm sheaths display greater diversity, potentially linked to their multifunctional roles in protecting juvenile culms and regulating water exchange [23,31,32].
Liu Jie’s phylogenetic studies revealed systematic patterns in diagnostic phytolith morphotypes among bamboo lineages [33], supporting the presence of phylogenetic signals in Bambusoideae phytoliths. Our study identified several distinctive morphotypes, including tuberculate, elbow-shaped, and homogeneous phytoliths, which warrant further analysis to explore their phylogenetic regularity. Future research should expand to include mixed-growth amphimorph and running leptomorph bamboos to compare phytolith morphotypes in leaves and culm sheaths across species with different rhizome types. Such efforts may enrich the taxonomic utility of phytoliths for broad and precise classification within Bambusoideae.
4.3. Ecological Significance and Taxonomic Application of Elongated Saddle Phytoliths in Leaves and Culm Sheaths of Clumping Bamboos
Reports by Wang and Lu [13] and Rapp and Mulholland [34] on Poaceae phytoliths identified elongated saddle phytoliths as the representative short-cell phytoliths in Bambusoideae. In our study, morphometric analyses of elongated saddle phytoliths (length, width, and area) revealed that culm sheaths in clumping bamboos exhibited significantly greater dimensions than those in leaves, indicating their potential mechanical support role prior to full culm maturation, particularly in resisting wind, pests, and mechanical damage [35,36,37]. While no significant intergeneric differences were observed in the area or length of elongated saddle phytoliths between leaves and culm sheaths, leaf width showed significant variation, indicating pronounced functional differentiation between organs linked to ecological adaptation strategies [38]. The higher proportion of elongated saddle phytoliths in leaves compared to culm sheaths reflects their greater silicon uptake capacity as photosynthetic organs, enhancing mechanical strength and stress resistance [35,36,37]. Intergeneric phytolith variation among clumping bamboos likely represents adaptive responses to ecological pressures. Future studies should integrate habitat characteristics (e.g., soil silicon content, climatic conditions) to explore silicon accumulation dynamics and employ molecular approaches to elucidate genetic regulation of phytolith formation [39], thus advancing our understanding of bamboo’s adaptive evolution.
Elongated saddle phytoliths exhibit taxonomic potential at tribal and generic levels due to variation in length, width, surface wrinkles, and granular ornamentation [34]. Liu Lidan et al. demonstrated that temperature and precipitation significantly influence short-cell phytolith size (including saddle and rondel types), although their width–length ratios remain stable [40], supporting their utility in Poaceae classification and helping to validate the scientific rigor of using elongated saddle phytoliths for clumping bamboo taxonomy. Our results show that leaves, with higher proportions of elongated saddle phytoliths, provide greater accuracy for generic-level classification in Bambusoideae, while culm sheaths offer richer morphological diversity. Combined analysis of both organs enhances taxonomic precision. Notably, we identified “irregular saddle-shaped” phytolith variants, which require systematic categorization to align them with diagnostic morphotype methodologies and more fully exploit their classificatory value.
5. Conclusions
Our findings revealed that sympodial bamboo leaves exhibit significantly greater phytolith content, concentration, and long saddle-shaped phytolith area than do culm sheaths, with statistically significant differences between the two organs. The particle size frequency distribution curves of phytoliths differ markedly; leaf phytoliths show a dominant peak at 10–20 μm, while culm sheath phytoliths display peaks at 10–20 μm, 20–30 μm, and 900–1000 μm. Among genera, only Gigantochloa exhibits significant differences in saddle phytolith area and width. Proportional analysis (Table 1) demonstrates distinct phytolith morphotype assemblages that differ substantially between leaves and culm sheaths across genera, with a total of 37 major phytolith morphotypes identified (31 in leaves and 35 in culm sheaths). Leaves are dominated by saddle, ruffle-top rondel, and silica stoma types, while culm sheaths show higher proportions of truncated cones. Notably, saddle and stomatal phytoliths differ significantly between organs (higher in leaves), whereas truncated cones show no significant difference but are more abundant in culm sheaths. Leaves are more suitable for genus-level classification within Bambusoideae by using saddle phytoliths, while culm sheaths, with richer phytolith diversity, provide complementary taxonomic utility. Comprehensive analysis reveals significant morphological divergence between leaf and culm sheath phytoliths in Bambusa species, with culm sheath phytoliths demonstrating superior taxonomic utility for generic-level classification within the subfamily Bambusoideae. This study expands the phytolith morphological spectrum of bamboos and establishes a theoretical framework for advancing bamboo systematics.
Author Contributions
C.W. and R.X. were the experimental designers of this study. T.Z. collated the data and wrote the first draft of the paper. M.D., G.L., K.G., T.F. and X.W. participated in the experiments. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32160415 and 31460169.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to every scientific researcher who supports and helps us in our work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chang, S. Phytolith-occluded organic carbon in intensively managed Lei bamboo (Phyllostachys praecox) stands and implications for carbon sequestration. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Analysis Method of Soil Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, D.R. Phytolith Analysis: An Archaeological and Geological Perspective; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Meunier, J.D.; Grauby, O.; Labille, J.; Alexandre, A.; Barboni, D. Dissolution does not affect grass phytolith assemblages. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2023, 610, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperno, D.R. Phytolith taphonomy and distributions in archeological sediments from Panama. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1985, 12, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Jie, D.; Gao, G.; Gao, T.; Xu, S.; Lian, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Niu, H.; et al. Characteristics of burned phytolith from representative plants in Northeast China and implications for paleo-fire reconstruction. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2022, 300, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Xie, B. Phytoliths from woody plants: A review. Diversity 2022, 14, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madella, M.; Alexandre, A.; Ball, T. International code for phytolith nomenclature 1.0. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Han, J. Phytoliths in modern plants from Amazonia and the Neotropics: A reference collection for paleoecological and archaeological reconstructions. Exp. App. Under Fossil. Organi. Lessons. Liv. 2014, 41, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J. Biomineralization of Nanosilicon and the Cytological Role of Silicon in Rice; Gansu Agricultural University: Lanzhou, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Studies on the Physiological Function of Silicon and the Deposition Mechanism in Rice; China Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.Y.; Chen, X.F.; Liu, X.D.; Guo, H.B. Scanning electron microscopy observation of silicon cells on the leaf surface of different rice varieties. Acta Microsc. Sin. 2016, 35, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lü, H. Research and Application of Plant Siliceous Bodies; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Zhu, F.; Wang, S.; Dai, C.; Zheng, X.; Xie, D.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; et al. Characteristics of silicon and phytolith distribution in bamboo (Ferrocalamus strictus): Variations between different organs and ages. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2023, 311, 104817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Jiang, P.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, P.; He, S. A study of phytolith-occluded carbon stock in monopodial bamboo in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Qi, L.H.; Hu, X.; Ding, X.; Cheng, C.J.; Lei, G. A study of phytolith carbon of bamboo plants in China. World For. Res. 2019, 32, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S. Phytolith Carbon Sequestration of Two Important Clumping Bamboos and Their Relationship with Soil Available Silicon; Zhejiang A&F University: Hangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, X. Classification Significance of Phytolith Morphology and Microelement Composition in Bamboo Leaves; Guilin University of Technology: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wen, M.; Li, R.; Vachula, R.S.; Pang, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, N. Phytolith sizes and assemblages differentiate genera and ecotypes of woody bamboos in subtropical Southwest China. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2020, 272, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H. Phytolith Study and It’s Application; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J. Investigation on the Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden; Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden): Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- International Committee for Phytolith Taxonomy (ICPT). International code for phytolith nomenclature (ICPN)2.0. Ann. Bot. 2019, 124, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madella, M.; Jones, M.K.; Echlin, P. Plant water availability and analytical microscopy of phytoliths: Implications for ancient irrigation in arid zones. Quatern Int. 2009, 193, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Qiu, J.; Luo, B.; Deng, Y. Developmental changes and morphology of phytolith in Bambusa emeiensis. J. Northwest A F Univ. 2018, 46, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Zheng, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Duan, S. Phytolith morphological differences of bamboo culm leaf in Phyllostachys edulis and two variants. J. West China For. Sci. 2024, 53, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, G.; Song, Z.; Gao, P.; Li, Z. The distribution characteristics of silicon in different ecotypes of bamboo. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ. 2015, 32, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-D.; Jie, D.-M.; Liu, H.-Y.; Guo, M.-E.; Li, N.-N. Change Characters of Phragmites australis phytolith in northeast China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 37, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Niu, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhan, H. Phytolith content and morphological changes in Dendrocalamus giganteus during different phenological stages. J. Southwest For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 42, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Duan, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhan, H. Characteristics of phytolith content and morphological variations in Dendrocalamus brandisii leaves across developmental stages. J. Southwest For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 45, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.C.; Fan, J.; Gao, C.G. Advances in Modern Phytolith Research. Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, H. Morphological Characteristics of Phytoliths in 10 Clumping Bamboo Species and the Effects of Exogenous Silicon on Bamboo Seedling Cold Resistance. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.K.; Lu, Z.; Wang, S.G.; Long, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.H. Comparison of anatomical structure of six bamboo species cotyedon organs. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2023, 47, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. The Application of Phytolith Morphology for Taxonomy and Identification of Bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae); Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Kunming, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rapp, G.; Mulholland, S.C. Phytolith Systematics: Emerging Issues; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, M.; Goro, M. The morphology and distribution of silica bodies in the leaves of Zingiberaceae. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 463–472. [Google Scholar]
- Samuels, G.; Gauthier, G. Silicon and its role in plant physiology and anatomy: A review. Ann. Bot. 2012, 90, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, J.; Troughton, J. The distribution of silicified cells in the leaves and stems of Eucalyptus species. Austral. J. Bot. 1968, 16, 231–248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Feng, G. An introduction to the research and application of phytolith morphometrics. Quat. Res. 2019, 39, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.A.; Leishman, M.R. Silica deposition in plants: A review. Funct. Plant Biol. 2011, 38, 332–352. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jie, D.; Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; Gao, G.; Li, N.; Guo, J.; Qiao, Z. An orthogonal experimental study of phytolith size of Phragmites communis in northeast China. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sin. 2016, 33, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).