A Virome and Proteomic Analysis of Placental Microbiota in Pregnancies with and without Fetal Growth Restriction
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aim of Research/Hypothesis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Control and Study Group
3.2. Analysis of the Virus Proteome in the Study and Control Groups
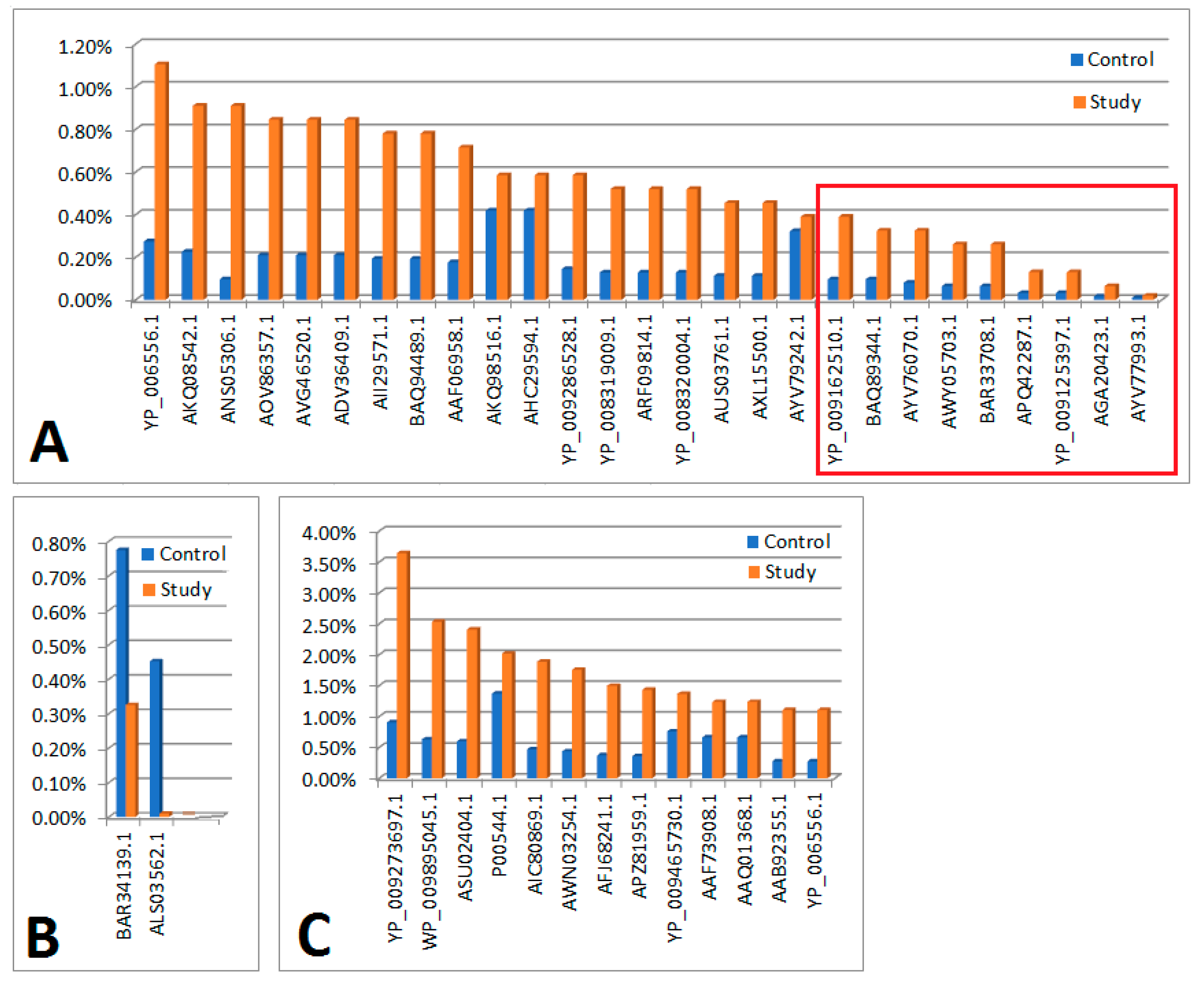
| Legend | |
| Figure 1A | In the order as in the figure |
| Significant differences in the control and test material in terms of protein content determined on the basis of em PAI | |
| YP_006556.1 | Ppp [Escherichia virus P1] |
| AKQ08542.1 | putative HNH endonuclease [Bacillus phage PBC2] |
| ANS05306.1 | hypothetical protein [uncultured Mediterranean phage] |
| AOV86357.1 | putative replication protein VP4 [uncultured virus] |
| AVG46520.1 | ankyrin repeat protein [Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus] |
| ADV36409.1 | tail fiber [Edwardsiella phage eiAU] |
| AII29571.1 | exonuclease [Propionibacterium phage PHL117M01] |
| BAQ94489.1 | minor capsid protein 10 [uncultured Mediterranean phage uvMED] |
| AAF06958.1 | replication initiation protein [Pepper golden mosaic virus-[CR]] |
| AKQ98516.1 | pol protein, partial [Human immunodeficiency virus 1] |
| AHC29594.1 | pol protein, partial [Human immunodeficiency virus 1] |
| YP_009286528.1 | head vertex protein II [Salmonella phage vB_SnwM_CGG4-1] |
| YP_008319009.1 | hypothetical protein pdul_cds_330 [Pandoravirus dulcis] |
| ARF09814.1 | DEAD/SNF2-like helicase [Indivirus ILV1] |
| YP_008320004.1 | hypothetical protein pdul_cds_1056 [Pandoravirus dulcis] |
| AUS03761.1 | terminase large subunit [Paenibacillus phage Tadhana] |
| AXL15500.1 | major capsid protein [Microviridae sp.] |
| AYV79242.1 | heat shock protein [Faunusvirus sp.] |
| Significant differences in the control and test material in terms of protein content determined on the basis of em PAI (maintaining significance after applying the Bonferoni correction) | |
| YP_009162510.1 | DEAD-like helicases superfamily D11 [Salmon gill poxvirus] |
| BAQ89344.1 | hypothetical protein [uncultured Mediterranean phage uvMED] |
| AYV76070.1 | hsp82-like protein [Terrestrivirus sp.] |
| AWY05703.1 | tape measure protein [Microbacterium phage Percival] |
| BAR33708.1 | internal virion protein D [uncultured Mediterranean phage uvMED] |
| APQ42287.1 | tape measure protein [Mycobacterium phage Rich] |
| YP_009125397.1 | tapemeasure [Mycobacterium phage Sparky] |
| AGA20423.1 | polyprotein [Deformed wing virus] |
| AYV77993.1 | hypothetical protein Edafosvirus3_71 [Edafosvirus sp.] |
| Figure 1B | |
| Significant or negligible differences in the control and test material in terms of protein content determined on the basis of em PAI | |
| BAR34139.1 | hypothetical protein [uncultured Mediterranean phage uvMED] |
| ALS03562.1 | VP4 [Gokushovirus WZ-2015a] |
| Figure 1C | |
| There were no significant differences in the control and test material in terms of protein content determined on the basis of em PAI | |
| YP_009273697.1 | hypothetical protein PAEP54_00150 [Pseudomonas phage YMC11/07/P54_PAE_BP] |
| WP_009895045.1 | MULTISPECIES: hypothetical protein [Clostridiales] |
| ASU02404.1 | hypothetical protein P1301_0041 [Bacteriophage T5-like chee130_1] |
| P00544.1 | RecName: Full=Tyrosine-protein kinase transforming protein Fgr |
| AIC80869.1 | Vpr [Simian immunodeficiency virus] |
| AWN03254.1 | HNH endonuclease [Microbacterium phage Camille] |
| AFJ68241.1 | non-structural protein 4 [Rotavirus A] |
| APZ81959.1 | hypothetical protein EFP01_032 [Enterococcus phage EFP01] |
| YP_009465730.1 | hypothetical protein DSLPV1_013 [Dishui lake phycodnavirus 1] |
| AAF73908.1 | polyprotein, partial [Bovine viral diarrhea virus-1 strain CP821] |
| AAQ01368.1 | glycoprotein, partial [Human metapneumovirus] |
| AAB92355.1 | nonstructural protein P125-2, partial [Bovine viral diarrhea virus 1] |

| Legend | |
| There were no significant differences in the control and test material in terms of protein content determined on the basis of em PAI | |
| Figure 2A | In the order as in the figure |
| ALF62340.1 | histone 4, partial [Cotesia sesamiae bracovirus] |
| AAV98010.1 | hypothetical protein ORF3006 [Cotesia plutellae polydnavirus] |
| AAQ11513.1 | fusion, partial [Avian avulavirus 1] |
| AGE15451.1 | p5 [Sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus] |
| AXQ68373.1 | hypothetical protein CcrBL10_gp169c [Caulobacter phage CcrBL10] |
| AYN57750.1 | hypothetical protein PBI_DRMANHATTAN_30 [Arthrobacter phage DrManhattan] |
| AMQ66724.1 | hypothetical protein [Bacillus phage Mgbh1] |
| AAX91636.1 | ORF097 [Staphylococcus virus 71] |
| AGH25217.1 | hypothetical protein kp_75 [Escherichia virus KP26] |
| AYV75487.1 | GTP-binding protein YPTC1 [Terrestrivirus sp.] |
| ARU13184.1 | Cro-like repressor [Streptococcus phage P0095] |
| YP_009345355.1 | ubiquitin [Noumeavirus] |
| AWY08214.1 | hypothetical protein [Klebsiella phage ZCKP1] |
| ASU01562.1 | hypothetical protein P24_0109 [Bacteriophage T5-like chee24] |
| YP_007674594.1 | hypothetical protein SWZG_00236 [Synechococcus phage S-SKS1] |
| NP_116536.1 | hypothetical protein BK5-Tp44 [Lactococcus phage BK5-T] |
| AVP40324.1 | hypothetical protein [Staphylococcus phage phiSA_BS1] |
| WP_057374675.1 | winged helix-turn-helix domain-containing protein [Propionibacterium freudenreichii] |
| YP_008319525.2 | Histone H2B domain [Pandoravirus dulcis] |
| O55654.1 | RecName: Full=Early E3B 10.4 kDa protein; Flags: Precursor |
| Figure 2B | |
| AEK32636.1 | hypothetical protein GEORGE_68 [Mycobacterium virus George] |
| YP_009254922.1 | hypothetical protein [Tokyovirus A1] |
| AYP28327.1 | hypothetical protein 3M_071 [Serratia phage vB_SmaA_3M] |
| AFK66023.1 | hypothetical protein OMVG_00018 [Ostreococcus lucimarinus virus OlV3] |
| ANS05579.1 | SET domain containing protein [uncultured Mediterranean phage] |
| AIY25871.1 | histone H4, partial [Cotesia sesamiae] |
| ALY07175.1 | hypothetical protein VmeM32_00189 [Vibrio phage vB_VmeM-32] |
| WP_002504512.1 | MULTISPECIES: hypothetical protein [Staphylococcus] |
| ARF08835.1 | ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 [Catovirus CTV1] |
| AAT05674.1 | envelope glycoprotein, partial [Human immunodeficiency virus 1] |
| ASN77904.1 | hypothetical protein [Grapevine virus H] |
| AKC02055.1 | hypothetical protein [Cyprinid herpes virus 2] |
| CBZ42254.1 | hypothetical protein [Campylobacter virus CP81] |
| BAQ85396.1 | Lysozyme family protein (zliS) [uncultured Mediterranean phage uvMED] |
| AIU36708.1 | ORF62 [Cydia pomonella granulovirus] |
| ADB11618.1 | M70R, partial [Myxoma virus] |
| NP_048429.1 | hypothetical protein [Paramecium bursaria Chlorella virus 1] |
| NP_203278.1 | LEF-7 [Epiphyas postvittana nucleopolyhedrovirus] |
| YP_001426186.1 | hypothetical protein FR483_n554L [Paramecium bursaria Chlorella virus FR483] |
| APG77349.1 | M protein [Xinzhou nematode virus 6] |
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The vocabulary of microbiome research: A proposal. Microbiome 2015, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulis, L.; Fester, R. Symbiosis as a Source of Evolutionary Innovation: Speciation and Morphogenesis; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; ISBN 978-0-262-51990-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, P.; Bressan, P. Humans as Superorganisms: How Microbes, Viruses, Imprinted Genes, and Other Selfish Entities Shape Our Behavior. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 10, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordenstein, S.R.; Theis, K.R. Host Biology in Light of the Microbiome: Ten Principles of Holobionts and Hologenomes. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002226. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, J.C.; Marchesi, J.R.; Mougel, C.; Selosse, M.-A. Host-microbiota interactions: From holobiont theory to analysis. Microbiome 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xie, L.; Li, Y.; Wei, C. More Than 9,000,000 Unique Genes in Human Gut Bacterial Community: Estimating Gene Numbers Inside a Human Body. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, S.L.; Bodewes, R.; Baumgärtner, W.; Koopmans, M.P.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Schürch, A.C. Assembly of viral genomes from metagenomes. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 118886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrby, E. Nobel prizes and the emerging virus concept. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, S.J.; Epstein, J.H.; Murray, K.A.; Navarrete-Macias, I.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.M.; Solovyov, A.; Ojeda-Flores, R.; Arrigo, N.C.; Islam, A.; Khan, S.A.; et al. A strategy to estimate unknown viral diversity in mammals. Mbio 2013, 4, e00598-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasso, G.; Mayer, S.V.; Winkelmann, E.R.; Chu, T.; Elliot, O.; Patino -Galindo, J.A.; Park, K.; Rabadan, R.; Honig, B.; Shapira, S.D. A Structure-Informed Atlas of Human-Virus Interactions. Cell 2019, 178, 1526–1541.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Łusiak-Szelachowska, M.; Weber-Dąbrowska, B.; Żaczek, M.; Borysowski, J.; Górski, A. The Presence of Bacteriophages in the Human Body: Good, Bad or Neutral? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moelling, K.; Broecker, F. Viruses and Evolution—Viruses First? A Personal Perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 435010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Caler, L.; Colombini -Hatch, S.; Glynn, S.; Srinivas, P. Research on the human virome: Where are we and what is next. Microbiome 2016, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Neil, J.A.; Cadwell, K. The Intestinal Virome and Immunity. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Adiliaghdam, F.; Jeffrey, K.L. Illuminating the human virome in health and disease. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bai, G.B.; Lin, S.C.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Chen, S.Y. The Human Viriome: Viral Metagenomics. Relations with human diseases and therapeutic applications. Viruses 2022, 14, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Lanteri, M.C.; Vahidnia, F.; Tan, S.; Stapleton, J.T.; Norris, P.J.; Heitman, J.; Deng, X.; Keating, S.M.; Brambilla, D.; Busch, M.P.; et al. Downregulation of cytokines and chemokines by GB virus C after transmission via blood transfusion in HIV-positive blood recipients. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, R.C.; Manges, A.R.; Finlay, B.B.; Prendergast, A.J. The Human Microbiome and Child Growth—First 1000 Days and Beyond. Trends Microbiol 2019, 27, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangeney, M.; Renard, M.; Schlecht-Louf, G.; Bouallaga, I.; Heidmann, O.; Letzelter, C.; Richaud, A.; Ducos, B.; Heidmann, T. Placental syncytins: Genetic disjunction between the fusogenic and immunosuppressive activity of retroviral envelope proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20534–20539. [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal, L.P. Viruses and the placenta: The essential virus first view. APMIS 2016, 124, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, M.; Frérot, A.; Novais, A.R.B.; Baud, O. Neonatal and Long-Term Consequences of Fetal Growth Restriction. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 14, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Megli, C.J.; Coyne, C.B. Infections at the maternal–fetal interface: An overview of pathogenesis and defense. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoffe, L.; Kuperman, A.A.; Isakov, O.; Haguel, D.; Polsky, A.L.; Farberov, L.; Pillar, N.; Gurevich, V.; Haviv, I.; Shomron, N. Assessing the involvement of the placental microbiome and virome in preeclampsia using non-coding RNA sequencing. J. Perinat. Med. 2021, 49, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupak, A.; Gęca, T.; Nawrot, R.; Goździcka-Józefiak, A.; Kwaśniewska, A.; Kwaśniewski, W. Comparative Analysis of the Placental Microbiome in Pregnancies with Late Fetal Growth Restriction versus Physiological Pregnancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordijn, S.J.; Beune, I.M.; Thilaganathan, B.; Papageorghiou, A.; Baschat, A.A.; Baker, P.N.; Silver, R.M.; Wynia, K.; Ganzevoort, W. Consensus definition of fetal growth restriction: A Delphi procedure. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.S.; Gudmundsson, S. Uterine and umbilical artery Doppler are comparable in predicting perinatal outcome of growth-restricted fetuses. BJOG 2009, 116, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diffley, J.F.; BStillman, B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science 1998, 246, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Nawrot, R.; Kalinowski, A.; Goździcka-Józefiak, A. Proteomic analysis of Chelidonium majas milky sap using two-dimensial gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. Phyochemistry 2007, 68, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama, Y.; Oda, Y.; Tabata, T.; Sato, T.; Nagasu, T.; Rappsilber, J.; Mann, M. Exponentially modified protein abundance index (emPAI) for estimation of absolute protein amount in proteomics by the number of sequenced peptides per protein. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Gęca, T.; Stupak, A.; Nawrot, R.; Goździcka-Józefiak, A.; Kwaśniewska, A.; Kwaśniewski, W. Placental proteome in late-onset of fetal growth restriction. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fox, G.E.; Stackebrandt, E.; Hespell, R.B.; Gibson, J.; Maniloff, J.; Dyer, T.A.; Wolfe, R.S.; Balch, W.E.; Tanner, R.S.; Magrum, L.J.; et al. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science 1980, 209, 457–463. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The human microbiome project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wylie, K.M.; Mihindukulasuriya, K.A.; Zhou, Y.; Sodergren, E.; Storch, G.A.; Weinstock, G.M. Metagenomic analysis of double-stranded DNA viruses in healthy adults. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tamburini, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, H.C.; Clemente, J.C. The microbiome in early life: Implications for health outcomes. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Medzhitov, R. Pattern recognition theory and the launch of modern innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4473–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausler, T. Bug killers. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 600–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ji, Y.; Su, J.; Xue, Y.; Xi, H.; Wang, Z.; Bi, L.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; et al. Therapeutic Efficacy of Phage PIZ SAE-01E2 against Abortion Caused by Salmonella enterica Serovar Abortusequi in Mice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01366-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Scola, B.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Jungang, L.; de Lamballerie, X.; Drancourt, M.; Birtles, R.; Claverie, J.M.; Raoult, D. A giant virus in amoebae. Science 2003, 299, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, L.M.; Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. Common origin of four diverse families of large eukaryotic DNA viruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11720–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; Verneau, J.; Raoult, D.; Levasseur, A.; La Scola, B. Deciphering viral presences: Two novel partial giant viruses detected in marine metagenome and in a mine drainage metagenome. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aherfi, S.; Colson, P.; La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. Giant Viruses of Amoebas: An Update. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, A.; Arantes, T.S.; Rodrigues, R.A.L.; Machado, T.B.; Dornas, F.P.; Landell, M.F.; Furst, C.; Borges, L.G.A.; Dutra, L.A.L.; Almeida, G.; et al. Ubiquitous giants: A plethora of giant viruses found in Brazil and Antarctica. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornas, F.P.; Assis, F.L.; Aherfi, S.; Arantes, T.; Abrahao, J.S.; Colson, P.; La Scola, B. A Brazilian Marseillevirus Is the Founding Member of a Lineage in Family Marseilleviridae. Viruses 2016, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, F.; Alteio, L.; Goudeau, D.; Ryan, E.M.; Yu, F.B.; Malmstrom, R.R.; Blanchard, J.; Woyke, T. Hidden diversity of soil giant viruses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backstrom, D.; Yutin, N.; Jorgensen, S.L.; Dharamshi, J.; Homa, F.; Zaremba-Niedwiedzka, K.; Spang, A.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V.; Ettema, T.J.G. Virus Genomes from Deep Sea Sediments Expand the Ocean Megavirome and Support Independent Origins of Viral Gigantism. MBio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Barai, A.; Sen, S.; Kondabagila, K. Amoebal Tubulin Cleavage Late during Infection Is a Characteristic Feature of Mimivirus but Not of Marseillevirus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02753-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greub, G.; Raoult, D. Microorganisms resistant to free-living amoebae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dupuy, M.; Berne, F.; Herbelin, P.; Binet, M.; Berthelot, N.; Rodier, M.H.; Soreau, S.; Héchard, Y. Sensitivity of free-living amoeba trophozoites and cysts to water disinfectants. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valster, R.M.; Wullings, B.A.; Bakker, G.; Smidt, H.; van der Kooij, D. Freeliving protozoa in two unchlorinated drinking water supplies, identified by phylogenic analysis of 18S rRNA gene sequences. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4736–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilbeck, P.M.; Evermann, J.F.; Crawford, T.B.; Ward, A.C.; Leathers, C.W.; Holland, C.J.; Mebus, C.A.; Logan, L.L.; Rurangirwa, F.R.; McGuire, T.C.; et al. Isolation of a previously undescribed rickettsia from an aborted bovine fetus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 814–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Goy, G.; Osterheld, M.C.; Croxatto, A.; Borel, N.; Vial, Y.; Pospischil, A.; Greub, G. Role of Waddlia chondrophila placental infection in miscarriage. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, S.P.; Kebbi Beghdadi, C.; Land, M.E.; Ouburg, S.; Morré, S.A.; Greub, G. Waddlia chondrophila and Chlamydia trachomatis antibodies in screening infertile women for tubal pathology. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goy, G.; Croxatto, A.; Posfay-Barbe, K.M.; Gervaix, A.; Greub, G. Development of a real-time PCR for the specific detection of Waddlia chondrophila in clinical samples. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 1483–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.; Collingro, A.; Walochnik, J.; Wagner, M.; Horn, M. Chlamydia-like bacteria in respiratory samples of community-acquired pneumonia patients. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 281, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammerdorffer, A.; Stojanov, M.; Greub, G.; Baud, D. Chlamydia trachomatis and chlamydia-like bacteria: New enemies of human pregnancies. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witney, A.A.; Aller, S.; Strang, B.L. Metagenomic profiling of placental tissue suggests DNA virus infection of the placenta is rare. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Goffau, M.C.; Lager, S.; Sovio, U.; Gaccioli, F.; Cook, E.; Peacock, S.J.; Parkhill, J.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Smith, G.C.S. Human placenta has no microbiome but can contain potential pathogens. Nature 2019, 572, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stupak, A.; Kwiatek, M.; Gęca, T.; Kwaśniewska, A.; Mlak, R.; Nawrot, R.; Goździcka-Józefiak, A.; Kwaśniewski, W. A Virome and Proteomic Analysis of Placental Microbiota in Pregnancies with and without Fetal Growth Restriction. Cells 2024, 13, 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13211753
Stupak A, Kwiatek M, Gęca T, Kwaśniewska A, Mlak R, Nawrot R, Goździcka-Józefiak A, Kwaśniewski W. A Virome and Proteomic Analysis of Placental Microbiota in Pregnancies with and without Fetal Growth Restriction. Cells. 2024; 13(21):1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13211753
Chicago/Turabian StyleStupak, Aleksandra, Maciej Kwiatek, Tomasz Gęca, Anna Kwaśniewska, Radosław Mlak, Robert Nawrot, Anna Goździcka-Józefiak, and Wojciech Kwaśniewski. 2024. "A Virome and Proteomic Analysis of Placental Microbiota in Pregnancies with and without Fetal Growth Restriction" Cells 13, no. 21: 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13211753
APA StyleStupak, A., Kwiatek, M., Gęca, T., Kwaśniewska, A., Mlak, R., Nawrot, R., Goździcka-Józefiak, A., & Kwaśniewski, W. (2024). A Virome and Proteomic Analysis of Placental Microbiota in Pregnancies with and without Fetal Growth Restriction. Cells, 13(21), 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13211753






