Abstract
Tumor microenvironment (TME) is composed of different cellular populations, such as stromal, immune, endothelial, and cancer stem cells. TME represents a key factor for tumor heterogeneity maintenance, tumor progression, and drug resistance. The transport of molecules via extracellular vesicles emerged as a key messenger in intercellular communication in the TME. Exosomes are small double-layered lipid extracellular vesicles that can carry a variety of molecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Exosomal miRNA released by cancer cells can mediate phenotypical changes in the cells of TME to promote tumor growth and therapy resistance, for example, fibroblast- and macrophages-induced differentiation. Cancer stem cells can transfer and enhance drug resistance in neighboring sensitive cancer cells by releasing exosomal miRNAs that target antiapoptotic and immune-suppressive pathways. Exosomes induce drug resistance by carrying ABC transporters, which export chemotherapeutic agents out of the recipient cells, thereby reducing the drug concentration to suboptimal levels. Exosome biogenesis inhibitors represent a promising adjunct therapeutic approach in cancer therapy to avoid the acquisition of a resistant phenotype. In conclusion, exosomal miRNAs play a crucial role in the TME to confer drug resistance and survivability to tumor cells, and we also highlight the need for further investigations in this promising field.
1. Introduction
Primary human tumors consist of a mixture of genetically and phenotypically distinct cellular subpopulations. The initial conversion of a non-malignant cell to a malignant one is driven by genetic, epigenetic, and phenotypic changes that lead to cellular overgrowth, suppression of death signals, induction of angiogenesis, and resistance to therapy. Genomic instability, such as changes in chromosome number and structure, is one of the causes of tumor heterogeneity and is critical to cancer initiation and progression [1]. The genetic diversity of cells during cancer initiation may be the result of accumulated mutations from exogenous sources, such as UV radiation and/or endogenous processes—for example, a mistake during DNA replication [2]. Aside from the linear nature of cancer initiation followed by tumor progression, tumorigenesis is a dynamic process and continues to evolve to maintain tumor heterogeneity.
Beyond genetic diversity, the tumor microenvironment (TME) is crucial for tumor heterogeneity as it shapes cancer and non-cancer cell phenotypes [3]. The TME comprises different cell types, such as leukocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells, within the tumor or in the tumor surroundings and is sustained by a vascular network and the extracellular matrix [4]. The interactions between tumor and non-tumor cells within the TME occur through direct cell-to-cell contact and secretion of soluble molecules, such as cytokines and chemokines [5]. Due to its heterogeneity and adaptability, the TME has been associated with the maintenance of the malignant behavior of cancer cells throughout different tumoral stages [6,7]. Additionally, the TME plays an important role in protecting cancer cells from drug therapy via crosstalk between cancer cells and surrounding cells.
Recently, the transport of biological mediators by extracellular vesicles (EVs) has received substantial attention and emerged as a key messenger in intercellular communication [8,9]. EVs are small, double-layered lipid vesicles released from the membranes of almost all cell types [10]. EVs carry lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, such as DNA, mRNA, miRNA, and other non-coding RNAs, that can affect multiple processes in recipient cells, including gene expression changes and activation of several signaling pathways [11]. Three different classes of EVs have been identified based on their biogenesis. Ectosomes originate from the plasma membrane (100–1000 nm in diameter), apoptotic bodies are generated from cells undergoing apoptosis (50–2000 nm in diameter), and exosomes originate from endocytosis into multivesicular bodies (30–100 nm in diameter) [5,10,12].
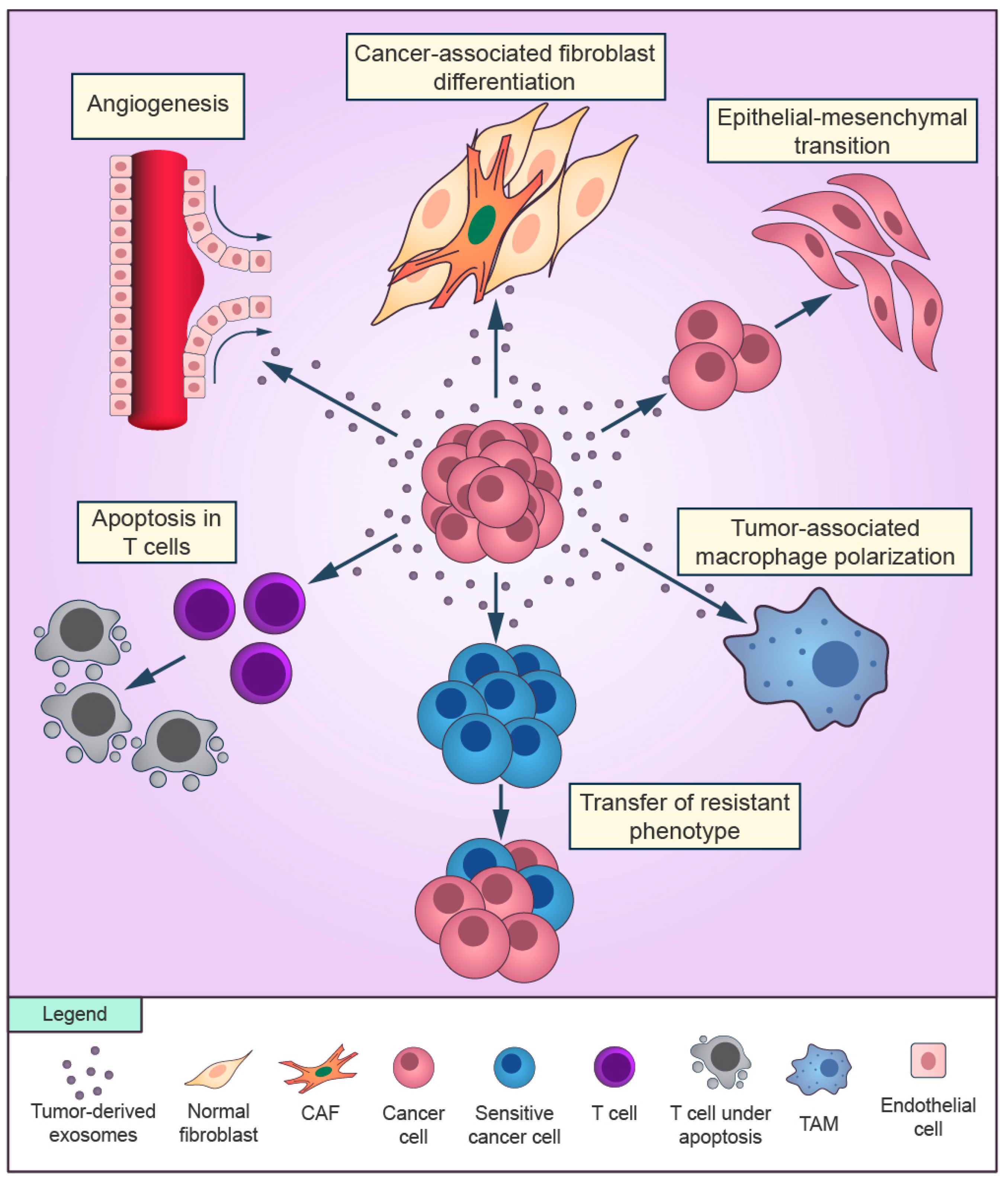
Currently, the aspects of tumor-derived exosomes in cancer progression and therapy resistance are the major focus of EV-associated pathology research [9]. Tumor-derived exosomes are involved in several hallmarks of cancer, including inflammatory responses, angiogenesis, evasion of apoptosis, cell proliferation, immune suppression, invasion, and metastasis [5,13,14] (Figure 1). Tumoral exosomes influence a plethora of cellular and molecular processes in the TME during acquired drug resistance in cancer cells, including the cell cycle, DNA repair, immune system surveillance, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [15]. Drug resistance induced by tumoral exosomes is mediated through different routes, such as direct drug export, transport of drug efflux pumps, and signaling of miRNAs [16,17].
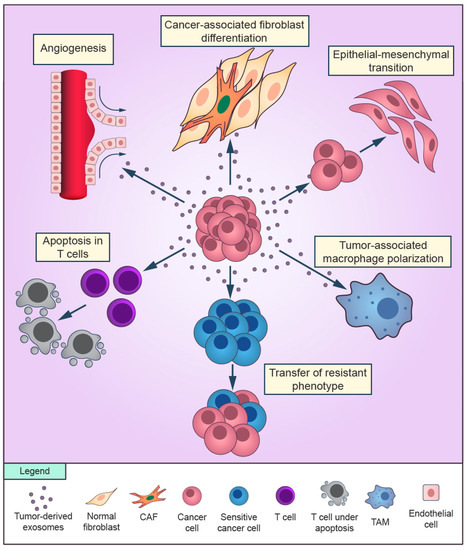
Figure 1.
Overview of the role of cancer-derived exosomes in the tumor microenvironment. Exosomes secreted by cancer cells can promote cancer-associated differentiation in adjacent fibroblasts and macrophages polarization towards a tumor-supportive phenotype. Cancer cells can release exosomes that induce the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in other cancer cells and transfer the resistant phenotype to sensitive cells in the surroundings. Cancer-derived exosomes are able to promote angiogenesis and to suppress the antitumor immune response of T cells.
Exosomal miRNAs released by cancer cells can directly induce drug resistance in the tumor surroundings from a drug-resistant cell to a sensitive counterpart, or cancer exosomes can interact and deliver miRNAs to TME cells that will modulate a drug resistance response in the area [18]. The exosomal miRNA horizontal transfer of a resistant phenotype to sensitive cancer cells has been reported in different types of tumors with a wide variety of anticancer drugs [12,19]. However, how exosomal miRNAs interact with the TME to confer drug resistance properties to cancer cells is not fully understood. Here, we discuss the recent developments in mechanisms mediated by tumoral exosomes, focusing on miRNA interactions and signaling in the TME that confer survivability and a therapy-resistant phenotype upon tumor cells.
2. TME as a Mediator of Drug Resistance
2.1. Drug Resistance Overview
Despite the development of effective drugs for cancer treatment and their initial positive responses, drug resistance is still a critical limiting factor for the achievement of cures in cancer patients [20]. Drug resistance can be classified as intrinsic or acquired. Intrinsic drug resistance can be attributed to pre-existing resistant cancer cells before treatment and associated with drug breakdown, alterations in drug transport, and reduced interaction between the drug and its molecular target [21]. Acquired drug resistance constitutes a group of cells that emerge resistant from a population that was previously drug-sensitive, resulting in tumor regrowth [22]. Genetic, epigenetic, transcriptomic, and proteomic changes in cancer cells cause tumor heterogeneity, which is directly associated with acquired drug resistance [23]. Many tumors become resistant due to a combination of intrinsic and acquired drug resistance factors [20]. Moreover, a drug-sensitive tumor that contains at least one resistant cell clone can acquire drug resistance by clonal expansion [21].
2.2. Drug Resistance Mediated by Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Exosomal miRNAs
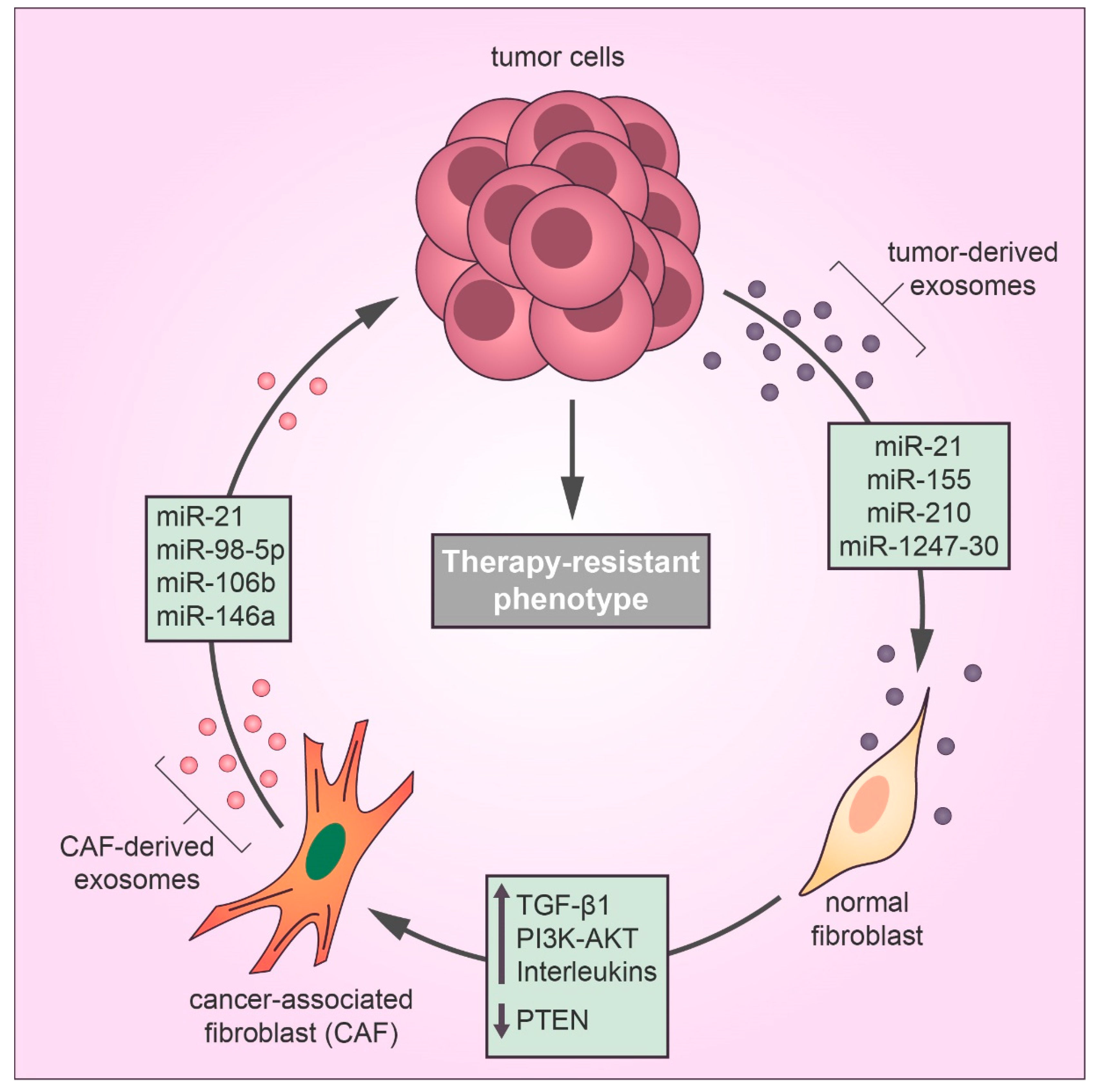
Well-established evidence supports the idea that the TME may alter the chemotherapy response in favor of a drug-resistant phenotype by different mechanisms [24]. In the TME, tumor-derived exosomes mediate communication between the tumor and stromal cells, contributing to therapy evasion and tumor growth [8]. Recently, tumor-derived exosomes have been reported to play a substantial role in the differentiation of TME fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), which promote tumor growth, pro-angiogenic, invasive, and drug-resistant phenotypes [25,26,27]. CAFs are the most abundant stromal cell type in the TME and feature the same characteristics of myofibroblasts found during the wound healing process [28]. According to Webber et al., the transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGFβ1) transported by cancer exosomes is required to activate the tumor-promoting stroma [29]. Recent studies have identified a relationship between cancer-derived exosomal miRNAs and CAF differentiation in many types of cancer [30] (Figure 2). MiR-21 is a key regulator of oncogenic processes, which promote cell survival and the formation and activation of CAFs by regulating TGFβ1 signaling [31]. Isolated exosomes derived from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) converted normal hepatic stellate cells to CAFs via miR-21 that downregulated the tumor suppressor gene PTEN and consequently upregulated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [32]. Similarly, exosomal miR-1247-30 from HCC cells induced CAF activation in the fibroblasts of a lung pre-metastatic niche, leading to the upregulation of pro-inflammatory genes, such as IL1B, IL6, and IL8, and therapy resistance to sorafenib treatment [33]. Sorafenib is a targeted therapy for advanced HCC with limited benefits for overall survival due to drug resistance, and the expression of inflammatory interleukins, such as IL-6, is directly associated with poor clinical prognosis and therapeutic inefficacy of sorafenib in HCC patients [34]. Also, a study using human melanoma exosomal miRNAs showed that miR-155 and miR-210 induced metabolic changes in human adult fibroblasts to increase aerobic glycolysis that promoted a pre-metastatic microenvironment [35]. Notably, miR-155 and miR-210 are referred to as oncogenic miRNAs that drive therapy resistance in several types of cancer [36,37,38].
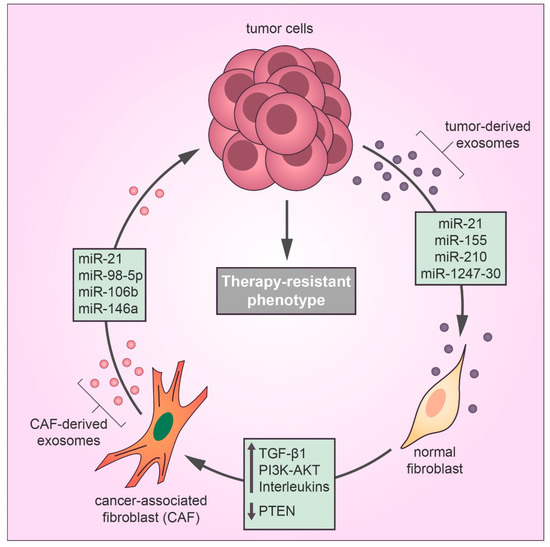
Figure 2.
Exosomes secreted by cancer cells transfer miRNAs to fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment that induce the cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) differentiation, thereby exosomal miRNAs derived from CAFs confer drug resistance in cancer cells by inducing metastasis and proliferation and inhibiting the antitumor effects of cytotoxic drugs, such as apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.
While cancer-derived exosomal miRNAs can promote CAF differentiation, exosomal miRNAs released by CAFs in the TME play an important role in therapy resistance. Next-generation sequencing technology has shown that the exosomal transfer of miR-21 from CAFs to ovarian cancer cells inhibited apoptosis and promoted resistance to paclitaxel treatment by downregulating the expression of apoptotic peptidase activating factor (APAF1) [39]. Cisplatin is a platinum-based drug that exerts anticancer effects by forming adducts in the DNA of cancer cells, which activate the DNA damage response and lead cancer cells to death by apoptosis [40]. However, a recent report showed that CAF-derived exosomal miR-98-5p increased ovarian cancer cell proliferation and promoted a cisplatin-resistant phenotype by downregulating CDKN1A, which is a vital regulator of cell cycle arrest [41]. Interestingly, cisplatin resistance can be induced by different CAF-derived exosomal miRNAs; for example, CAF-secreted exosomal miR-196a downregulated the expression of CDNK1B (another key gene in the transition between the G1 and S phases of the cell cycle) in head and neck cancer cells [42]. Moreover, miR-522 derived from CAF exosomes conferred cisplatin resistance to gastric cancer cells [43]. Gemcitabine, a front-line chemotherapeutic agent for pancreatic adenocarcinoma, is known to suppress DNA synthesis in cancer cells [44]. However, exosomal miR-106b from CAFs in the pancreatic TME was reported to promote gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cells by directly downregulating TP53INP1 expression [45]. Similarly, another study revealed that CAF-secreted exosomal miR-146a accelerated the gemcitabine-resistant phenotype in pancreatic cancer by targeting Snail pathways [46].
2.3. Tumor-Associated Macrophage Exosomal miRNAs Enhance Drug Resistance
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are the most abundant population of immune cells in the TME. Moreover, TAMs are extremely plastic cells that promote tumor angiogenesis, activate immunosuppression, and enhance tumor cell resistance to chemotherapy [47,48]. The size of the TAM population in the TME has been directly associated with poor prognosis in many types of cancer [49]. The chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL-2) is a chemoattractant protein for monocytes, which are secreted at high levels by cancer cells to recruit macrophages to infiltrate the tumor [50]. Recently, it was reported that colon cancer-derived exosomes carrying miR-1246 induced macrophages toward a TAM phenotype [51]. Similarly, other studies have shown that cancer-derived exosomes can carry miRNAs that promote the macrophage transition to TAMs in several types of cancers, including ovarian [52,53], bladder [54], head and neck [55], skin, and lung cancer [56]. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is directly associated with macrophage polarization, thereby promoting cancer migration, invasion, and drug resistance [57]. Several studies have reported that exosomes released by cancer cells modulate PI3K/AKT pathway-related genes in macrophages to promote TAM polarization [54,58,59,60].
However, in terms of drug resistance knowledge, how the exosomes released by TAMs contribute to drug resistance in tumor cells remains poorly understood. Few studies in the literature investigate the role of exosomal miRNAs derived from TAMs in drug resistance. For instance, TAMs are capable of conferring malignant phenotypes and enhancing drug resistance to epithelial ovarian cancer cells through the transfer of exosomes carrying miR-223 [61]. Another example of gemcitabine resistance was induced in pancreatic cancer cells by the delivery of miR365 through exosomes derived from TAMs [62]. Similar to CAFs, once activated, TAMs modulate the TME into an anti-inflammatory immunosuppression state by releasing exosomes carrying miRNAs in the extracellular milieu. For example, TAM-derived exosomal miR-21 leads gastric cancer cells to a cisplatin-resistant phenotype by suppressing cancer cell apoptosis and activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [59], which is similar to the previously mentioned mechanism of exosomal miR-21 released by HCC cells.
2.4. Transfer of Drug Resistance Mediated by Cancer Stem Cells Exosomes
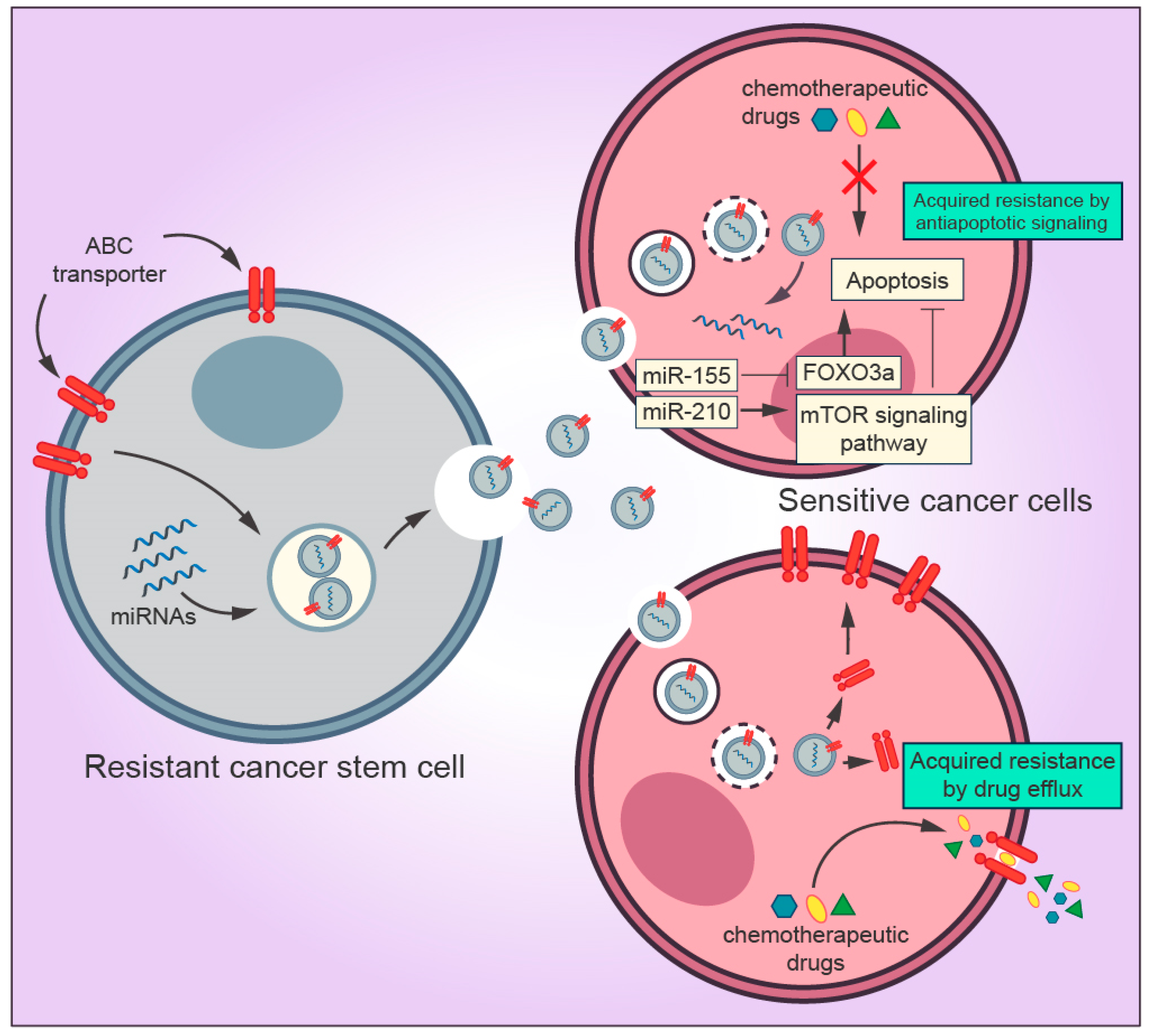
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are the self-renewing population in the TME that exert resistance to anticancer drugs and radiotherapy [63]. CSCs can be identified through the expression of several surface markers, including high expression of CD44 (CD44+) and low expression of CD24 (CD24-/low) [64]. There is a strong connection between CSCs and tumor proliferation, metastasis, and recurrence [65]. Among many researchers, the CSC population is considered to be the source from which primary tumors develop a metastatic and resistant phenotype [66,67,68]. Recent studies have demonstrated that exosomes derived from CSCs interact with other surrounding TME and cancer cells by releasing exosomes, thereby promoting cancer progression [69,70]. Several molecular mechanisms mediated by CSCs-derived exosomes in the TME have been described, such as activation of CAF and TAM phenotype differentiation, promotion of angionesis, and induction of EMT [70,71,72] (Figure 3). However, a narrow collection of literature is available regarding the roles of CSC-derived exosomes implicated in drug resistance. Although exosomal miRNAs from cancer cells and CSCs display different profiles, they contribute to the malignant phenotype in many types of tumors [73,74,75,76]. Interestingly, few studies investigating CSC-derived exosomes have shown that miRNAs from CSC-derived exosomes are capable of transferring drug resistance to sensitive cancer cells. For instance, a study conducted by Santos and colleagues showed that miR-155 transferred by CSC-derived exosomes enhanced the resistance of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin and paclitaxel treatment and induced the acquisition of EMT phenotype [77]. More recently, using in vitro and in vivo approaches, Yang et al. showed that gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic CSCs exosomes containing high levels of miR-210 horizontally transferred the resistant phenotype to gemcitabine-sensitive pancreatic cancer cells, thereby inhibiting apoptosis and promoting proliferation by targeting the mTOR signaling pathway [37].
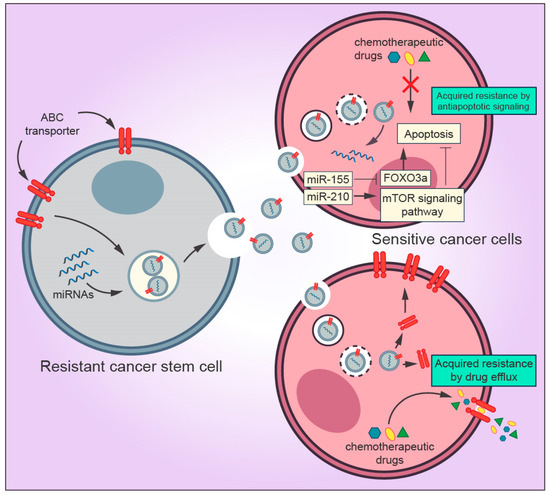
Figure 3.
Mechanisms by which exosomes derived from cancer stem cells (CSCs) regulate drug resistance in the tumor microenvironment. Exosomal miRNAs secreted by CSCs are transferred to sensitive cancer cells and inhibit the pro-apoptotic property of FOXO3a and activates the mTOR signaling pathway, which is directly associated with inhibition of apoptosis and tumor progression, thereby blocking the drug-induced apoptosis. Exosomes can promote drug resistance to sensitive cells by transferring ABC transporters (drug efflux pumps) that actively export drugs out of the cell.
The most prominent property of CSCs is their ability to resist conventional drug treatment regimens as mentioned earlier. Despite the horizontal transfer of miRNAs to neighboring cells mediated by exosomes, CSCs can also enhance multidrug resistance in many types of tumors due to the overexpression of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters [70,78]. Members of the ABC protein family, such as ABCB1 (also known as P-glycoprotein), ABCC1, and ABCG2, function as efflux transporters of a wide range of molecules, including anticancer drugs, to the extracellular milieu [79]. Several cytotoxic drugs, such as cisplatin, paclitaxel, and doxorubicin, are substrates to ABC transporters [80]. ABC transporters reduce the intracellular concentrations of chemotherapeutic drugs to suboptimal levels in CSCs, consequently leading the cells to survive under treatment conditions [78].
Recently, it was found that ABC drug efflux pumps are incorporated in the cargo of resistant cell exosomes and transferred to drug-sensitive cells [81]. Resistant cell exosomes transporting P-glycoprotein to neighboring cells is the most studied multidrug resistance mechanism mediated by ABC transporters in several types of cancer [8]. Docetaxel-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells promoted drug resistance by the exosomal delivery of P-glycoprotein to docetaxel-sensitive MCF-7 cells [82]. Likewise, using in vitro and preliminary clinical studies, Corcoran et al. observed that P-glycoprotein released by prostate cancer exosomes induced phenotypic changes toward cell proliferation and conferred a significant increase in docetaxel resistance to sensitive cells [83]. The drug resistance acquisition was also observed in ovarian cancer, in which A2780 human ovarian cancer cells became unresponsive to paclitaxel after the exosomal transfer of P-glycoprotein from paclitaxel-resistant A2780 cells [84]. Moreover, a recent study identified six different miRNAs associated with drug resistance (miR-204-5p, miR-139-5p, miR-29c-5p, miR-551b-3p, miR-29b-2-5p, and miR-204-3p) delivered by doxorubicin-resistant cancer exosomes. The authors reported that doxorubicin-resistant lung cancer and chronic myeloid leukemia cells transferred exosomal miRNAs responsible for P-glycoprotein regulation, thereby enhancing drug resistance in their sensitive counterparts [85].
2.5. EMT Mediated by Exosomal miRNAs
EMT is the process by which carcinoma cells lose their apical-basal polarity and cell junctions to acquire mesenchymal features, such as elongated morphology, resulting in cancer cells with high plasticity and increased motility [86,87]. Due to the highly invasive acquired phenotype, EMT cells are directly associated with cancer progression, metastasis, and drug resistance in different types of cancer [88]. Stromal cells, such as CAFs, play an important role in the TME to support EMT-driven drug resistance [89]. CAFs can regulate the EMT process via the paracrine release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby promoting acquired drug resistance in cancer cells undergoing EMT [90,91]. Additionally, EMT has a close connection to CSCs, including expression of the same surface markers CD44+ and CD24-/low [92] as well as activation of similar signaling pathways, such as Hedgehog, Wnt, and Notch [88]. As discussed previously, CSCs promote drug resistance due to excessive drug efflux mediated by ABC transporters; similarly, cells undergoing EMT have been reported to express high levels of ABC transporters, including P-glycoprotein [93,94].
In recent years, accumulating evidence has shown that cancer-derived exosomes can modulate the EMT process in the TME [16,95,96]. Xiao and colleagues provided strong evidence of cancer exosomes promoting EMT. In their study, melanoma-derived exosomes induced EMT in primary melanocytes by transferring miRNAs directly associated with EMT regulation, such as let-7a and miR-191 [97]. Exosomes released from drug-resistant endothelial cells triggered the EMT process and promoted doxorubicin resistance in nasopharyngeal cancer cells [98]. Emerging studies are revealing the influence of exosomal miRNAs in primary tumor cells by activating or stabilizing EMT. Recently, a multidrug-resistant HCC cell line (resistant to sorafenib, gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and 5-fluorouracil) delivered exosomal miR32-5p to HCC-sensitive cells, leading to activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and inducing multidrug resistance via angiogenesis and EMT [99]. Exosomal miR-155-5p released by paclitaxel-resistant gastric cancer MGC-803 cells induced the EMT malignant phenotype and enhanced paclitaxel resistance via the suppression of GATA3 and TP53INP1 in parental sensitive cells [100]. In another study, normal intestinal cells were transfected with miR-128-3p, and their exosomes were co-cultured with oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells. The results revealed that miR-128-3p suppressed EMT by upregulating E-cadherin levels and increasing the intracellular oxaliplatin concentration in colorectal cancer cells [101]. These findings provide a novel exosome-based treatment strategy.
2.6. Autophagy Induced by Cancer Exosomal miRNAs
Autophagy is a catabolic process responsible for the elimination of damaged or excessive macromolecules or organelles to maintain homeostasis and metabolic sufficiency [102]. Autophagy also plays a dual role in cancer by promoting tumor growth and increasing tumor resistance to therapy [103]. During cancer initiation, autophagy is frequently upregulated, thereby conferring a high energy supply and cell survival [104]. A high level of autophagy is directly associated with a hypoxic TME, which leads to oxidative stress, delays apoptotic cell death, and contributes to therapy resistance, a phenomenon called cytoprotective autophagy [105,106]. The crosstalk between cancer exosomes and autophagy has attracted substantial attention. According to some authors, this interaction is dynamic and directly associated with the tumor’s needs [107,108]. For example, under cellular stress, exosomes and autophagy can be upregulated in cancer cells to confer an adaptative response. On the other hand, cancer-derived exosomes can also promote the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and upregulate autophagy in recipient cells to promote the secretion of tumor growth factors [109]. Finally, under a drug treatment regimen, cancer cells release exosomes that upregulate cytoprotective autophagy in recipient cells, leading to a resistant phenotype [110].
Many other studies unrelated to cancer have shown that exosomal miRNAs can control autophagy in recipient cells by targeting specific autophagy-related signaling pathways [111,112]. Currently, there are a handful of studies investigating the role of exosomal miRNAs as autophagy mediators in therapy resistance. For instance, exosomal miR-425-3p derived from cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells decreased responsiveness to cisplatin via targeting the AKT1/mTOR signaling pathway, consequently leading to upregulation of autophagic activity [113]. Similar results were observed in a study by Ma et al., in which cisplatin-resistant NSCLC exosomal miR-425-3p facilitated autophagic activation and conferred cisplatin resistance in sensitive cells by also targeting the AKT1/mTOR signaling pathway [114]. Given these results, we can assume that miR-425-3p is a promising biomarker candidate for predicting the cisplatin response in NSCLC. More recently, cells from trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer patients showed a significantly lower expression of exosomal miR-567 in comparison with sensitive patients. Using in vitro and in vivo approaches, it was found that miR567 was downregulated in trastuzumab-resistant cells compared to sensitive cells. Moreover, miR-567 inhibited trastuzumab-induced autophagy and reverted the acquired drug resistance [115]. These results indicate that cancer cells can downregulate exosomal miRNAs that control anticancer mechanisms and drug sensitivity in neighboring cells.
3. Enhanced Drug Efficacy Mediated by Inhibitors of Exosome Biogenesis
As discussed above, exosomal miRNAs can modulate several different molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of neighboring cancer cells or TME-associated cells. This influence can either induce cancer growth, metastasis, and therapy resistance or inhibit the expression of tumor suppressors [116]. Tumor cells release more exosomes into the TME than non-tumoral cells, which means that the circulating level of exosomes in the TME is abundant [117,118]. According to Sharma, a reasonable strategy to overcome the drug resistance mediated by exosomes and exosomal miRNAs involves blocking exosome biogenesis [18]. Although exosome biogenesis is not completely understood [119], a few compounds have been identified as potential inhibitors of exosome generation. GW4869 is a pharmacological agent that showed promising results as an inhibitor of exosome biogenesis in different types of cancer, including prostate [120], colorectal [121], and pancreatic cancer [46]. Moreover, the inhibition of exosome biogenesis induced by GW4869 in combination with bortezomib showed a strong anti-tumor response in vivo [122]. For instance, an interesting study reported several other compounds as promising mediators of exosome biogenesis and secretion in prostate cancer cells, including farnesyl transferase inhibitors, such as tipifarnib and manumycin A, and azole antifungals, such as climbazole, ketoconazole, and neticonazole [123]. Also, a recent study showed that manumycin A is capable of inhibiting exosome biogenesis and secretion by targeting the inhibition of the Ras/Raf/ERK signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells [124]. Sulfisoxazole, an antibiotic drug, was recently identified as an inhibitor of exosome biogenesis in breast cancer cells. Additionally, sulfisoxazole in combination with docetaxel reduced the proliferation and metastasis in mouse models of cancer cells xenograft [125]. Moreover, a combination treatment of chloramidine with bisindolylmaleimide was reported to inhibit exosome biogenesis in resistant prostate and breast cancer cells. The synergistic effect of these compounds targeted specific extracellular vesicle biogenesis pathways and enhanced the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil, which leads cancer cells to apoptosis [126]. Likewise, indomethacin, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, was revealed to be an effective inhibitor of ABC transporter expression, consequently increasing the anticancer effects of pixantrone and doxorubicin in B-cell lymphoma cells in vitro [127]. As stated earlier, the transport of ABC transporters by exosomes is crucial to maintain the drug-resistant phenotype. Taken together, these studies highlight the inhibition of exosome biogenesis as a promising approach to improve drug efficacy and overcome therapy resistance as well as underscore the need for more investigation concerning the aspects of exosome biogenesis and exosome-mediated drug resistance.
4. Conclusions
Tumor heterogeneity comes from different interactions as well as intra- and extracellular alterations, resulting in a dynamic and reactive environment that promotes tumor growth and suppresses therapeutic approaches. Here, we presented a plethora of evidence that exosomes are key extracellular mediators of the communication between tumor cells and the TME during different cancer stages, including cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer-derived exosomes carry miRNAs that are crucial to promoting a switch in tumor heterogeneity to a resistant phenotype (Table 1). Moreover, cancer stem cells and non-cancer cells in the TME contribute to drug resistance by releasing exosomal miRNAs that have different effects on the target cells. Also, exosomal miRNAs can induce resistance to cytotoxic drugs as well as molecular target-specific drugs. For example, miR-155 has been reported to promote resistance to doxorubicin and paclitaxel treatment in multiple kinds of cancer. On the other hand, several distinct miRNAs induced gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Furthermore, some miRNAs seem to regulate therapy resistance in a tumor-specific manner; for example, different studies have demonstrated that miR-128-3p and miR-425-3p act as drug resistance mediators in colorectal and lung cancer, respectively. For this reason, exosomal miRNAs can be used as potential cancer biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis in a broad or tumor-specific way. Novel approaches to challenging the drug resistance barrier created by exosomes are emerging, such as the use of exosome biogenesis inhibitors in synergy with other therapeutic drugs. In summary, we conclude that the exosome investigation has emerged as a promising field in cancer research and provides tremendous insights into many aspects of cancer communication and acquired drug resistance. However, important questions remain, and further studies are needed to better understand the role and targets of miRNAs released by exosomes in acquired drug resistance. Future research on exosomal miRNAs and the TME in drug resistance will not only identify new exosomal miRNAs and their crucial functions during tumor progression but also pinpoint targets for the prevention, diagnosis, and development of new therapeutic strategies.

Table 1.
Function and effects of exosomal miRNAs involved in tumor drug resistance.
Author Contributions
F.A. conceived the idea. P.S. and F.A. designed, wrote, and edited the review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (2016/03322-7); Fundação de Apoio ao Ensino, Pesquisa e Assistência do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto da Universidade de São Paulo; CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – 420670/2018-1); and CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Nível Superior).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Janiszewska, M. The microcosmos of intratumor heterogeneity: The space-time of cancer evolution. Oncogene 2020, 39, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vessoni, A.T.; Filippi-Chiela, E.C.; Lenz, G.; Batista, L.F.Z. Tumor propagating cells: Drivers of tumor plasticity, heterogeneity, and recurrence. Oncogene 2020, 39, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Dai, Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Rai, A.; Chen, M.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Greening, D.W.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular vesicles in cancer - implications for future improvements in cancer care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Haass, N.K. Microenvironment-Driven Dynamic Heterogeneity and Phenotypic Plasticity as a Mechanism of Melanoma Therapy Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, M.R.; de Sauvage, F.J. Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature 2013, 501, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maacha, S.; Bhat, A.A.; Jimenez, L.; Raza, A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S.; Grivel, J.C. Extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication: Roles in the tumor microenvironment and anti-cancer drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.; Maresh, G.; Zhang, X.; Salomon, C.; Hooper, J.; Margolin, D.; Li, L. The Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles As Communication Vehicles within the Tumor Microenvironment and Beyond. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Lam, E.W.; Sun, Y. Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: Old stories, but new tales. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, D.H.; Hong, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.K. The role of exosomes and miRNAs in drug-resistance of cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, I.; Nabet, B.Y. Exosomes in the tumor microenvironment as mediators of cancer therapy resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangoda, L.; Boukouris, S.; Liem, M.; Kalra, H.; Mathivanan, S. Extracellular vesicles including exosomes are mediators of signal transduction: Are they protective or pathogenic? Proteomics 2015, 15, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudas, J.; Skvortsov, S.; Ganswindt, U.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I.I. Therapy resistance mediated by exosomes. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashouri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Aref, A.R.; Ahadi, A.M.; Molaei, F.; Alahari, S.K. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milman, N.; Ginini, L.; Gil, Z. Exosomes and their role in tumorigenesis and anticancer drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2019, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A. Chemoresistance in cancer cells: Exosomes as potential regulators of therapeutic tumor heterogeneity. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2017, 12, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.A.; Moeng, S.; Sim, S.; Kuh, H.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J.K. MicroRNA-Based Combinatorial Cancer Therapy: Effects of MicroRNAs on the Efficacy of Anti-Cancer Therapies. Cells 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasan, N.; Baselga, J.; Hyman, D.M. A view on drug resistance in cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, M.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Kyrodimos, E. The challenge of drug resistance in cancer treatment: A current overview. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2018, 35, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holohan, C.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Davudian, S.; Shirjang, S.; Baradaran, B. The Different Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance: A Brief Review. Adv. Pharm Bull. 2017, 7, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Wargo, J.A.; Ribas, A. Primary, Adaptive, and Acquired Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell 2017, 168, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringuette Goulet, C.; Bernard, G.; Tremblay, S.; Chabaud, S.; Bolduc, S.; Pouliot, F. Exosomes Induce Fibroblast Differentiation into Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts through TGFbeta Signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greening, D.W.; Gopal, S.K.; Mathias, R.A.; Liu, L.; Sheng, J.; Zhu, H.J.; Simpson, R.J. Emerging roles of exosomes during epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer progression. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeon, J.H.; Jeong, H.E.; Seo, H.; Cho, S.; Kim, K.; Na, D.; Chung, S.; Park, J.; Choi, N.; Kang, J.Y. Cancer-derived exosomes trigger endothelial to mesenchymal transition followed by the induction of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togo, S.; Polanska, U.M.; Horimoto, Y.; Orimo, A. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts are a promising therapeutic target. Cancers (Basel) 2013, 5, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, J.P.; Spary, L.K.; Sanders, A.J.; Chowdhury, R.; Jiang, W.G.; Steadman, R.; Wymant, J.; Jones, A.T.; Kynaston, H.; Mason, M.D.; et al. Differentiation of tumour-promoting stromal myofibroblasts by cancer exosomes. Oncogene 2015, 34, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Ning, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Shao, C.; Shu, Y.; Shen, H. Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Hou, X.; Larner, J.; Xiong, W.; Mi, J. MiR-21/Smad 7 signaling determines TGF-beta1-induced CAF formation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.C.; Su, Y.T.; Chi, C.C.; Kuo, Y.C.; Lee, K.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Lan, P.C.; Yang, M.H.; Chang, T.S.; Huang, Y.H. DNMT3b/OCT4 expression confers sorafenib resistance and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through IL-6/STAT3 regulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, S.; Yang, Y.; Allen, C.L.; Maguire, O.; Minderman, H.; Sen, A.; Ciesielski, M.J.; Collins, K.A.; Bush, P.J.; Singh, P.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming of stromal fibroblasts by melanoma exosome microRNA favours a pre-metastatic microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktar, R.; Van Roosbroeck, K. miR-155 in cancer drug resistance and as target for miRNA-based therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Exosomes derived from cancer stem cells of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells enhance drug resistance by delivering miR-210. Cell. Oncol. (Dordr) 2020, 43, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Sun, K.; Alahdal, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xia, T.; et al. Up-regulation of miR-210 induced by a hypoxic microenvironment promotes breast cancer stem cells metastasis, proliferation, and self-renewal by targeting E-cadherin. FASEB J. 1096, 32, 6965–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au Yeung, C.L.; Co, N.N.; Tsuruga, T.; Yeung, T.L.; Kwan, S.Y.; Leung, C.S.; Li, Y.; Lu, E.S.; Kwan, K.; Wong, K.K.; et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ha, C.; Dong, H.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-98-5p promotes cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by targeting CDKN1A. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Shi, J.; Lu, E.; Chen, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, T.; Liu, R.; Ning, T.; Yang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.; Ge, S.; Bai, M.; et al. CAF secreted miR-522 suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa Cavalcante, L.; Monteiro, G. Gemcitabine: Metabolism and molecular mechanisms of action, sensitivity and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Rong, Y.; Kuang, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, D.; Lou, W. Exosomal miRNA-106b from cancer-associated fibroblast promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 383, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, K.E.; Zeleniak, A.E.; Fishel, M.L.; Wu, J.; Littlepage, L.E.; Hill, R. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Du, W.; Gong, L.; Chang, H.; Zou, Z. Tumor-associated macrophages: An accomplice in solid tumor progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea-Maier, R.T.; Smit, J.W.A.; Netea, M.G. Metabolic changes in tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages: A mutual relationship. Cancer Lett. 2018, 413, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawa-Wejksza, K.; Kandefer-Szerszen, M. Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Target for Antitumor Therapy. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2018, 66, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Patel, L.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) as an example of translation of cancer molecular biology to the clinic. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2010, 95, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooks, T.; Pateras, I.S.; Jenkins, L.M.; Patel, K.M.; Robles, A.I.; Morris, J.; Forshew, T.; Appella, E.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Harris, C.C. Mutant p53 cancers reprogram macrophages to tumor supporting macrophages via exosomal miR-1246. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ying, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X. Exosomes derived from hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer deliver microRNA-940 to induce macrophage M2 polarization. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X. Exosomes derived from hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer cells deliver microRNAs to macrophages and elicit a tumor-promoted phenotype. Cancer Lett. 2018, 435, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Yin, H.B.; Li, X.Y.; Zhu, G.M.; He, W.Y.; Gou, X. Bladder cancer cellsecreted exosomal miR21 activates the PI3K/AKT pathway in macrophages to promote cancer progression. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Tai, S.K.; Yang, M.H. Snail-overexpressing Cancer Cells Promote M2-Like Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages by Delivering MiR-21-Abundant Exosomes. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Dutta, B.; Tse, S.W.; Gupta, N.; Tan, C.F.; Low, J.K.; Yeoh, K.W.; Kon, O.L.; Tam, J.P.; Sze, S.K. Hypoxia-induced tumor exosomes promote M2-like macrophage polarization of infiltrating myeloid cells and microRNA-mediated metabolic shift. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5158–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ji, H.; Niu, X.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Tumor-associated macrophages secrete CC-chemokine ligand 2 and induce tamoxifen resistance by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Huang, C.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Su, L.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-301a Mediates M2 Macrophage Polarization via PTEN/PI3Kgamma to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4586–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Chen, L.; Yuan, X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, G.; Ma, Y.; Shen, L. Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Si, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, S.; Wu, H.; Cui, S.; Qu, X.; Yu, X. Exosome-encapsulated miRNAs contribute to CXCL12/CXCR4-induced liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by enhancing M2 polarization of macrophages. Cancer Lett. 2020, 474, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, H.; Yin, X.; Yang, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Feng, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, Y. Macrophages derived exosomes deliver miR-223 to epithelial ovarian cancer cells to elicit a chemoresistant phenotype. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binenbaum, Y.; Fridman, E.; Yaari, Z.; Milman, N.; Schroeder, A.; Ben David, G.; Shlomi, T.; Gil, Z. Transfer of miRNA in Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Induces Drug Resistance in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5287–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liao, K.; Zhou, W. Exosomes Regulate the Transformation of Cancer Cells in Cancer Stem Cell Homeostasis. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 4837370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.T.; Ryu, C.J. Cancer stem cell surface markers on normal stem cells. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.C. Cancer stem cells: Role in tumor growth, recurrence, metastasis, and treatment resistance. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, S20–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colak, S.; Medema, J.P. Cancer stem cells--important players in tumor therapy resistance. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4779–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, H.; Ivaska, J. Every step of the way: Integrins in cancer progression and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, M. Exosome-Based Cancer Therapy: Implication for Targeting Cancer Stem Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannafon, B.N.; Ding, W.Q. Cancer stem cells and exosome signaling. Stem Cell Investig. 2015, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayob, A.Z.; Ramasamy, T.S. Cancer stem cells as key drivers of tumour progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Cui, X.; Lu, L.; Chen, G.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Exosomes from glioma cells induce a tumor-like phenotype in mesenchymal stem cells by activating glycolysis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindoso, R.S.; Collino, F.; Vieyra, A. Extracellular vesicles as regulators of tumor fate: Crosstalk among cancer stem cells, tumor cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Investig. 2017, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.A.; Andahur, E.I.; Valenzuela, R.; Castellon, E.A.; Fulla, J.A.; Ramos, C.G.; Trivino, J.C. Exosomes from bulk and stem cells from human prostate cancer have a differential microRNA content that contributes cooperatively over local and pre-metastatic niche. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3993–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.P.; Li, A.Q.; Jia, W.H.; Ye, S.; Van Eps, G.; Yu, J.M.; Yang, W.J. MicroRNA expression profiling in exosomes derived from gastric cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93839–93855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sai, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Wan, X.; Ouyang, M. microRNA-16-5p-containing exosomes derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion, while promoting apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating ITGA2. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 21380–21394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.C.; Lima, N.D.S.; Sarian, L.O.; Matheu, A.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Derchain, S.F.M. Exosome-mediated breast cancer chemoresistance via miR-155 transfer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begicevic, R.R.; Falasca, M. ABC Transporters in Cancer Stem Cells: Beyond Chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M. ABC transporters, drug resistance, and cancer stem cells. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2009, 14, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januchowski, R.; Sterzynska, K.; Zaorska, K.; Sosinska, P.; Klejewski, A.; Brazert, M.; Nowicki, M.; Zabel, M. Analysis of MDR genes expression and cross-resistance in eight drug resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. J. Ovarian Res. 2016, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soekmadji, C.; Nelson, C.C. The Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Drug Resistance in Cancers: Implications in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 454837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Chen, W.X.; Zhong, S.L.; Hu, Q.; Ma, T.F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Tang, J.H.; Zhao, J.H. Exosomes mediate drug resistance transfer in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and a probable mechanism is delivery of P-glycoprotein. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 10773–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, C.; Rani, S.; O’Brien, K.; O’Neill, A.; Prencipe, M.; Sheikh, R.; Webb, G.; McDermott, R.; Watson, W.; Crown, J.; et al. Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: Evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Zhu, Y.F.; Zhao, Q.N.; Yang, D.T.; Dong, Y.P.; Jiang, L.; Xing, W.X.; Li, X.Y.; Xing, H.; Shi, M.; et al. Microvesicles mediate transfer of P-glycoprotein to paclitaxel-sensitive A2780 human ovarian cancer cells, conferring paclitaxel-resistance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.; Matthiesen, R.; Lima, R.T.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Deep Sequencing Analysis Reveals Distinctive Non-Coding RNAs When Comparing Tumor Multidrug-Resistant Cells and Extracellular Vesicles with Drug-Sensitive Counterparts. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.A. Epithelial plasticity: A common theme in embryonic and cancer cells. Science 2013, 342, 1234850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavert, N.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the invasive potential of tumors. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Shim, J.S. Targeting Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer. Molecules 2016, 21, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Deng, C.X. Effect of Stromal Cells in Tumor Microenvironment on Metastasis Initiation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, N.J.; Sasser, A.K.; Axel, A.E.; Vesuna, F.; Raman, V.; Ramirez, N.; Oberyszyn, T.M.; Hall, B.M. Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiori, M.E.; Di Franco, S.; Villanova, L.; Bianca, P.; Stassi, G.; De Maria, R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts as abettors of tumor progression at the crossroads of EMT and therapy resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomono, T.; Machida, T.; Kamioka, H.; Shibasaki, Y.; Yano, K.; Ogihara, T. Entinostat reverses P-glycoprotein activation in snail-overexpressing adenocarcinoma HCC827 cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, K.; Tomono, T.; Ogihara, T. Advances in Studies of P-Glycoprotein and Its Expression Regulators. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigagli, E.; Cinci, L.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C. Transcriptomic Characterization, Chemosensitivity and Regulatory Effects of Exosomes in Spontaneous EMT/MET Transitions of Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2019, 16, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, H.; Helein, H.; Meyer, K.; Robertson, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, W.; Lloyd, R.V. Thyroid cancer stem-like cell exosomes: Regulation of EMT via transfer of lncRNAs. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Barry, S.; Kmetz, D.; Egger, M.; Pan, J.; Rai, S.N.; Qu, J.; McMasters, K.M.; Hao, H. Melanoma cell-derived exosomes promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary melanocytes through paracrine/autocrine signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2016, 376, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hu, C.; Chao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, J.; Xu, Z.; Lu, H.; Li, H.; Chen, H. Drug-resistant endothelial cells facilitate progression, EMT and chemoresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via exosomes. Cell Signal. 2019, 63, 109385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Qu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Qiu, R.; Yu, S.; Xu, X.; Li, G.; Gu, R.; Tan, C.; Zhu, W.; Shen, B. Paclitaxelresistant gastric cancer MGC803 cells promote epithelialtomesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxelsensitive cells via exosomal delivery of miR1555p. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, W.; et al. Exosome-transmitted miR-128-3p increase chemosensitivity of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy: Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 2011, 147, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, B.R.; Wang, Y.G. Role of autophagy in tumorigenesis, metastasis, targeted therapy and drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4643–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkerts, H.; Hilgendorf, S.; Vellenga, E.; Bremer, E.; Wiersma, V.R. The multifaceted role of autophagy in cancer and the microenvironment. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 517–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janji, B.; Berchem, G.; Chouaib, S. Targeting Autophagy in the Tumor Microenvironment: New Challenges and Opportunities for Regulating Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewirtz, D.A. Cytoprotective and nonprotective autophagy in cancer therapy. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Camfield, R.; Gorski, S.M. The interplay between exosomes and autophagy - partners in crime. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, A.S.; Bao, B.; Sarkar, F.H. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: A comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Warshall, C.; Bandyopadhyay, C.; Dutta, D.; Chandran, B. Interactions between exosomes from breast cancer cells and primary mammary epithelial cells leads to generation of reactive oxygen species which induce DNA damage response, stabilization of p53 and autophagy in epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Li, P.P.; Guo, J.P.; Li, L.L.; Guo, B.; Jiao, H.B.; Wu, J.H.; Chen, J.M. Exosomes derived from HBV-associated liver cancer promote chemoresistance by upregulating chaperone-mediated autophagy. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X.; Li, F.; Ma, Z.; Xu, M.; Lu, L. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Cao, S.; Yin, J.; Li, G. MicroRNA-30a ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting Beclin1-mediated autophagy. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3679–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuwen, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Fan, M.; Xu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Shu, Y. Prognostic Role of Circulating Exosomal miR-425-3p for the Response of NSCLC to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2019, 28, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yuwen, D.; Chen, J.; Zheng, B.; Gao, J.; Fan, M.; Xue, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Shu, Y.; et al. Exosomal Transfer Of Cisplatin-Induced miR-425-3p Confers Cisplatin Resistance In NSCLC Through Activating Autophagy. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 8121–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Hu, J.; Lu, P.; Cao, H.; Yu, C.; Li, X.; Qian, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Han, N.; et al. Exosome-transmitted miR-567 reverses trastuzumab resistance by inhibiting ATG5 in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasetti, M.; Lee, W.; Santarelli, L.; Neuzil, J. Exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer metabolism: Possible implications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Deng, C.X. Current Progresses of Exosomes as Cancer Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Brumbaugh, J.; Bonavida, B. Exosomes derived from cancerous and non-cancerous cells regulate the anti-tumor response in the tumor microenvironment. Genes Cancer 2018, 9, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Praharaj, P.P.; Peak, T.C.; Long, J.; Singh, R.; Rhim, J.S.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Deep, G. Hypoxia-induced exosome secretion promotes survival of African-American and Caucasian prostate cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Feng, Y. Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic Colorectal Cancer Cells Transfer Wnt4 to Normoxic Cells to Elicit a Prometastatic Phenotype. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faict, S.; Muller, J.; De Veirman, K.; De Bruyne, E.; Maes, K.; Vrancken, L.; Heusschen, R.; De Raeve, H.; Schots, R.; Vanderkerken, K.; et al. Exosomes play a role in multiple myeloma bone disease and tumor development by targeting osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Kim, H.; McGee, L.; Johnson, A.E.; Talwar, S.; Marugan, J.; Southall, N.; Hu, X.; Lal, M.; Mondal, D.; et al. High-throughput screening identified selective inhibitors of exosome biogenesis and secretion: A drug repurposing strategy for advanced cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Kim, H.; Lal, M.; McGee, L.; Johnson, A.; Moustafa, A.A.; Jones, J.C.; Mondal, D.; Ferrer, M.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B. Manumycin A suppresses exosome biogenesis and secretion via targeted inhibition of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling and hnRNP H1 in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 408, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, E.J.; Lee, C.H.; Moon, P.G.; Rangaswamy, G.G.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.C.; Jee, J.G.; Bae, J.S.; Kwon, T.K.; et al. Sulfisoxazole inhibits the secretion of small extracellular vesicles by targeting the endothelin receptor A. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Trindade, R.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. Chloramidine/Bisindolylmaleimide-I-Mediated Inhibition of Exosome and Microvesicle Release and Enhanced Efficacy of Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, R.; Aung, T.; Vogel, D.; Chapuy, B.; Wenzel, D.; Becker, S.; Sinzig, U.; Venkataramani, V.; von Mach, T.; Jacob, R.; et al. Nuclear Trapping through Inhibition of Exosomal Export by Indomethacin Increases Cytostatic Efficacy of Doxorubicin and Pixantrone. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H.; Yu, Q. Exosomal MicroRNA MiR-1246 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Drug Resistance by Targeting CCNG2 in Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, M.; Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, H. Cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-231 Cell-derived Exosomes Increase the Resistance of Recipient Cells in an Exosomal miR-423-5p-dependent Manner. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Shih, H.N.; Cheng, S.F.; Yang, C.K.; Chen, M.C.; Tu, C.C.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Liao, P.H.; Huang, C.Y. FOXC1 Regulation of miR-31-5p Confers Oxaliplatin Resistance by Targeting LATS2 in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingyue, S.; Xiao, W.; Juanmin, Z.; Wei, L.; Daoming, L.; Hong, X. TFAP2E methylation promotes 5fluorouracil resistance via exosomal miR106a5p and miR421 in gastric cancer MGC803 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Yan, W.; You, Y. Exosomal transfer of miR-1238 contributes to temozolomide-resistance in glioblastoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, A.; Wei, Z.; Yan, W.; Yin, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, R.; Shen, F.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-151a enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in drug-resistant glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2018, 436, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yu, S.; Zhou, L.; Shi, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Shen, B.; Liu, S.; Yan, D.; Feng, J. Cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cell-derived exosomes increase cisplatin resistance of recipient cells in exosomal miR-100-5p-dependent manner. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, C. Exosomal transfer of miR-214 mediates gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanlikilicer, P.; Bayraktar, R.; Denizli, M.; Rashed, M.H.; Ivan, C.; Aslan, B.; Mitra, R.; Karagoz, K.; Bayraktar, E.; Zhang, X.; et al. Exosomal miRNA confers chemo resistance via targeting Cav1/p-gp/M2-type macrophage axis in ovarian cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 38, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, G.K.; Khan, M.A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Zubair, H.; Patton, M.C.; Singh, S.; Khushman, M.; Singh, A.P. Exosomes confer chemoresistance to pancreatic cancer cells by promoting ROS detoxification and miR-155-mediated suppression of key gemcitabine-metabolising enzyme, DCK. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Hao, M.; Yeo, S.K.; Guan, J.L. FAK signaling in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes breast cancer cell migration and metastasis by exosomal miRNAs-mediated intercellular communication. Oncogene 2020, 39, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).