Development and Experimental Validation of Machine Learning-Based Disulfidptosis-Related Ferroptosis Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.4. Screening DRFGs in IBD
2.5. Screening of Candidate Diagnostic Biomarkers by Machine Learning
2.6. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curves
2.7. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.8. Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA)
2.9. GO and KEGG Analysis
2.10. Correlation Assessment of Genes
2.11. Immune Cell Infiltration (ICI) Assessment and Identification of Co-Characteristic Genes
2.12. Unsupervised Cluster Analysis
2.13. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.14. Experimental Animals and DSS-Induced Colitis
2.15. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
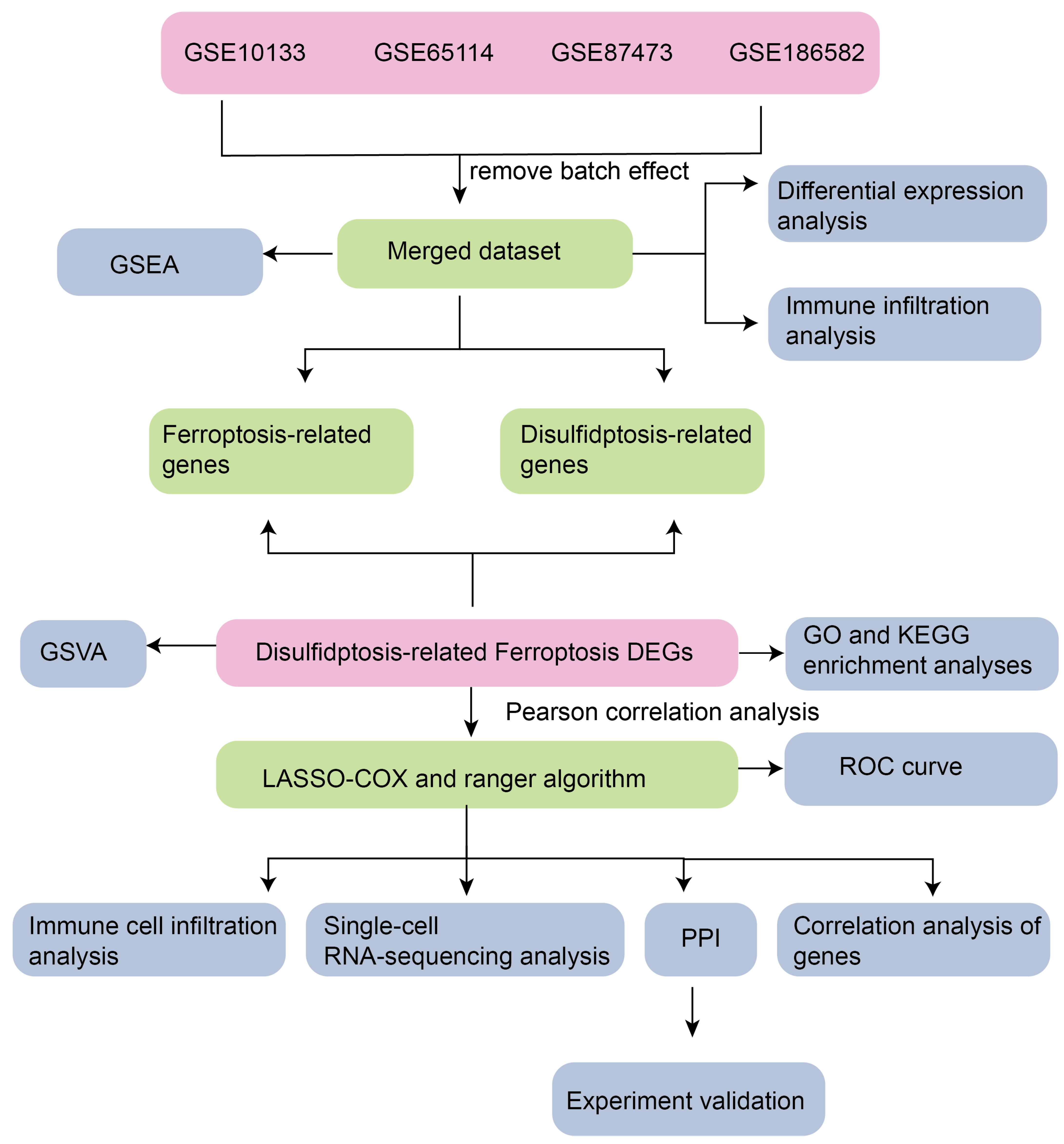
3.1. Technology Roadmap
3.2. Batch Removal for Dataset Integration
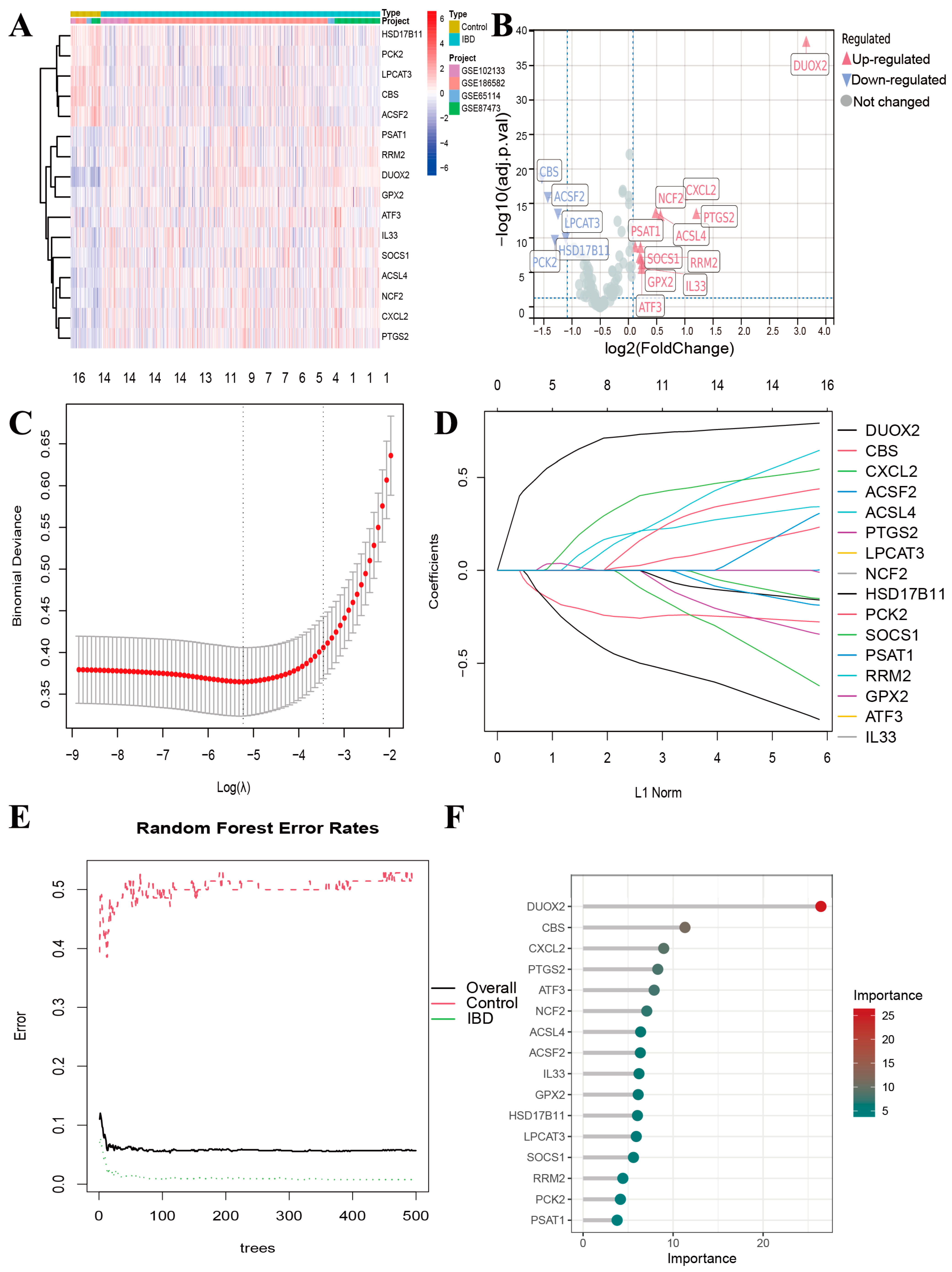
3.3. Screening of DRFGs in IBD
3.4. Gene Expression of DRFGs
3.5. Gene Ontology (GO)-Based Functional Annotation Profiling and KEGG Pathway Ontology Mapping
3.6. Correlation Analysis and the Functional Similarity Analysis of DRFGs
3.7. Enrichment Analysis of Functions and Pathways
3.8. Functional Pathway Enrichment Analysis in the Merged Dataset
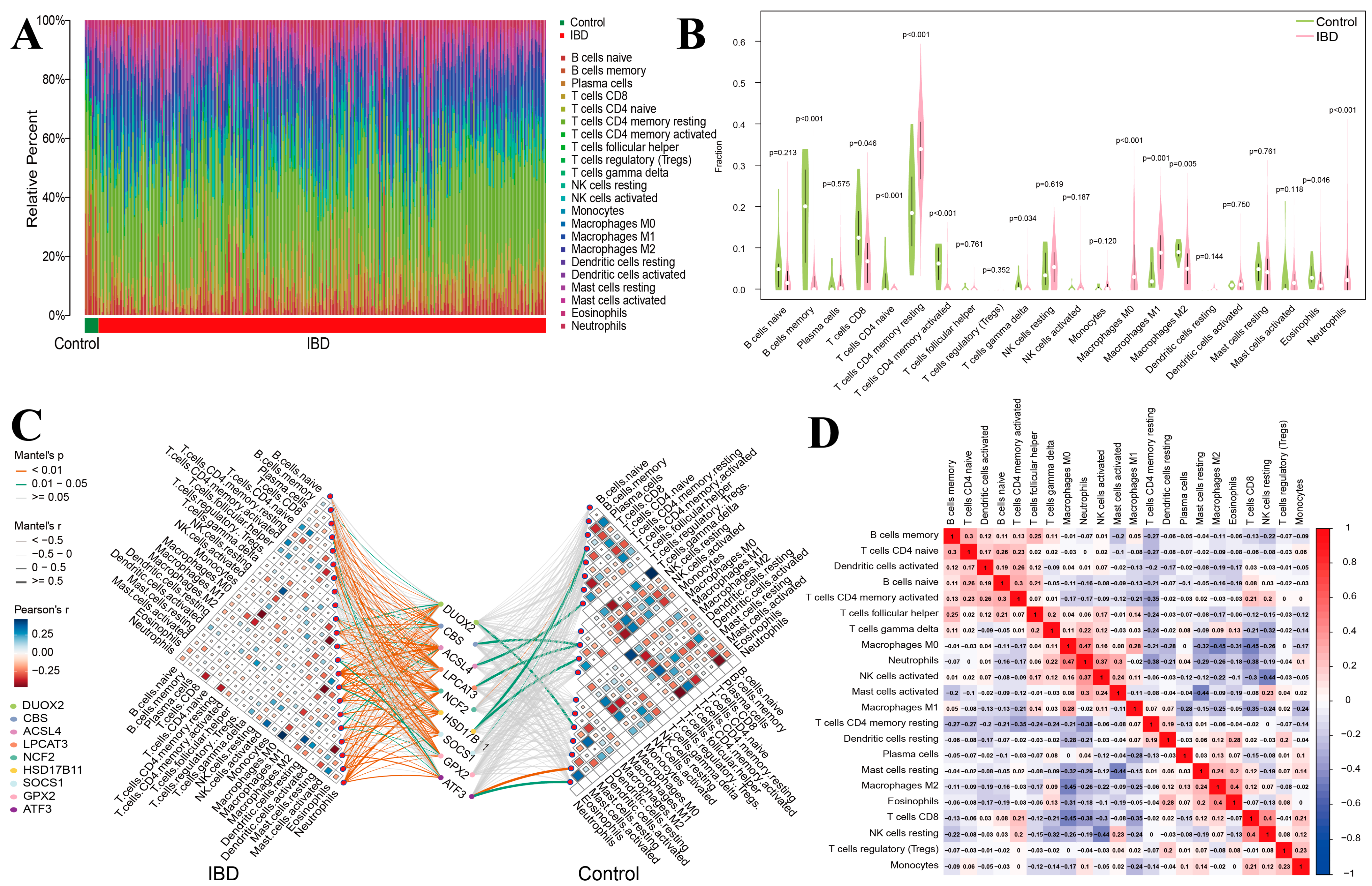
3.9. Analysis of Immune Cell Infiltration Patterns in IBD
3.10. Immune Subtypes and Hub Gene Correlation
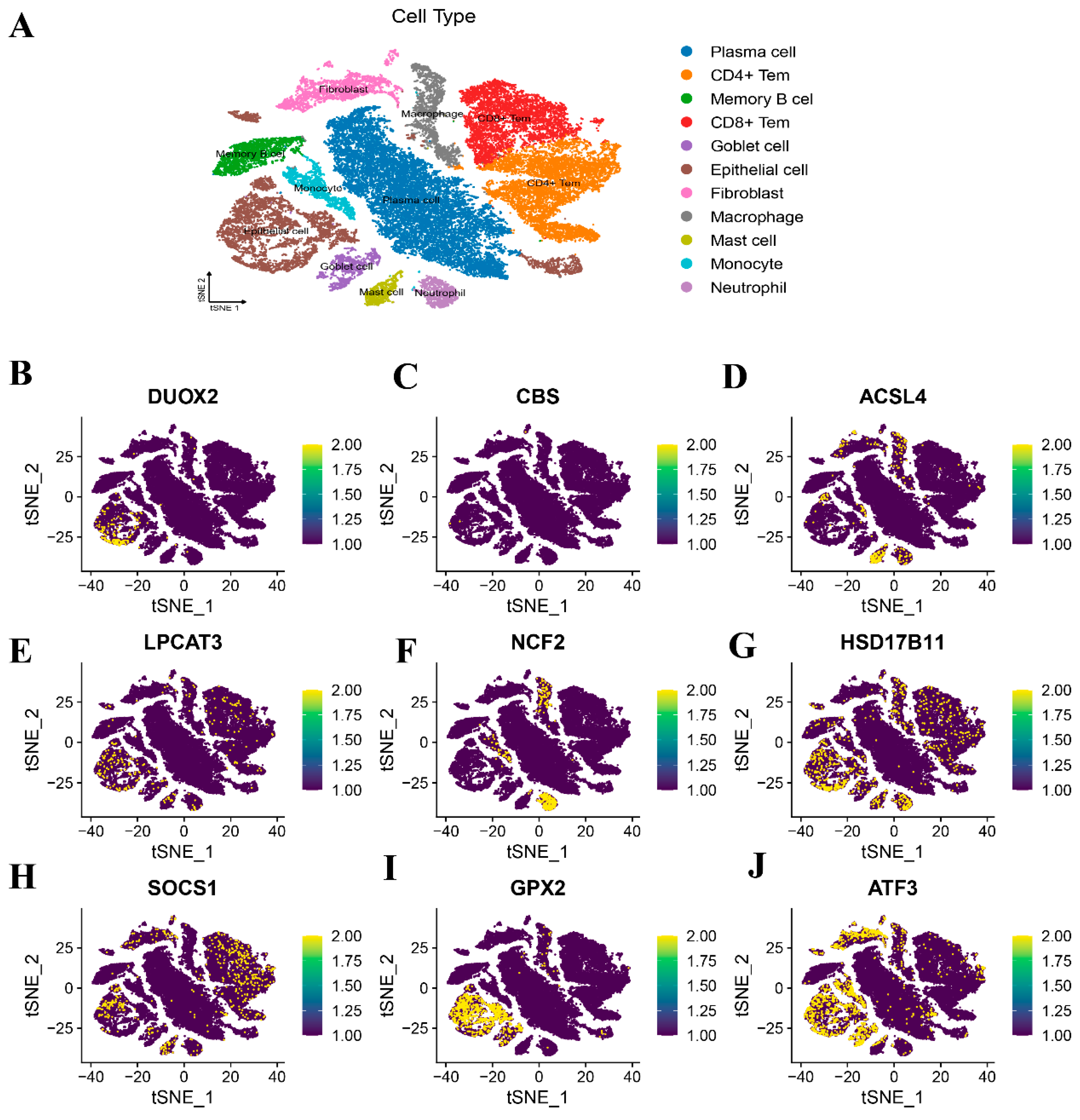
3.11. Spatial Mapping Profiling via Single-Cell Transcriptomic Datasets
3.12. Validation of DRFGs in Mouse Colonic Tissues of DSS-Mediated Colitis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torres, J.; Mehandru, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.F. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, M.; Allin, K.H.; Petralia, F.; Colombel, J.F.; Jess, T. Multiomics to elucidate inflammatory bowel disease risk factors and pathways. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Saikam, V.; Skrada, K.A.; Merlin, D.; Iyer, S.S. Inflammatory bowel disease biomarkers. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1856–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel diseases: A review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Bernstein, C.N.; Iliopoulos, D.; Macpherson, A.; Neurath, M.F.; Ali, R.A.R.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fiocchi, C. Environmental triggers in IBD: A review of progress and evidence. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Spencer, E.A.; Colombel, J.F.; Ungaro, R.C. Approach to the Management of Recently Diagnosed Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: A User’s Guide for Adult and Pediatric Gastroenterologists. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Colic, M.; Olszewski, K.; Horbath, A.; Chen, X.; Lei, G.; et al. Actin cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates disulfidptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, T.; Ji, K.; Cao, S.; Ai, J.; Pan, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jing, L.; Sun, J.H. Development and experimental validation of a machine learning-based disulfidptosis-related ferroptosis score for hepatocellular carcinoma. Apoptosis 2024, 29, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Ai, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. Membrane Damage during Ferroptosis Is Caused by Oxidation of Phospholipids Catalyzed by the Oxidoreductases POR and CYB5R1. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 355–369.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Zhong, L.S.; Huang, C.; Guo, Y.Y.; Jin, F.J.; Hu, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.B.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Y.F. β-Caryophyllene Acts as a Ferroptosis Inhibitor to Ameliorate Experimental Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H. Emerging Pathological Engagement of Ferroptosis in Gut Diseases. Oxid Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 4246255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Yuan, X.; Du, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Bao, J.; Ning, Y.; Peng, L. FerrDb V2: Update of the manually curated database of ferroptosis regulators and ferroptosis-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D571–D582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Pan, Y. Cuproptosis related genes associated with Jab1 shapes tumor microenvironment and pharmacological profile in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 989286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhen, H.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Cao, B. Identification of hub genes and potential molecular mechanisms related to radiotherapy sensitivity in rectal cancer based on multiple datasets. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hua, L.; Hou, C.; Jia, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Jia, E. Verification of ferroptosis and pyroptosis and identification of PTGS2 as the hub gene in human coronary artery atherosclerosis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; He, R.; Dai, Y.; Lu, X.; Deng, L.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lu, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification of TGF-β signaling-related molecular patterns, construction of a prognostic model, and prediction of immunotherapy response in gastric cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1069204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, L.; Xie, F.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Shen, X. Dehydrocostus Lactone Suppresses Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Targeting the IKKα/β-NF-κB and Keap1-Nrf2 Signalling Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 817596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitz, S.M. The epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Clues to pathogenesis? Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 1103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.C.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blander, J.M. Death in the intestinal epithelium-basic biology and implications for inflammatory bowel disease. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2720–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Zhou, J. The Induction Mechanism of Ferroptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Colorectal Cancer, and Intestinal Injury. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittner, L.; Wagener, L.; Wiese, J.J.; Stolzer, I.; Krug, S.M.; Naschberger, E.; Jackstadt, R.; Beyaert, R.; Atreya, R.; Kühl, A.A.; et al. Proteolytic Activity of the Paracaspase MALT1 Is Involved in Epithelial Restitution and Mucosal Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Guo, J.A.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.H.; Xia, W.Y.; Wang, D.X.; Xie, L.S.; Wang, J.M.; Wu, Q.F. Disulfidptosis and Its Hub Gene Slc3a2 Involved in Ulcerative Colitis Pathogenesis, Disease Progression, and Patient Responses to Biologic Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Y.; Dixon, S.J. Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2195–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Shen, Y. Inhibition of LncRNA-NEAT1 alleviates intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) dysfunction in ulcerative colitis by maintaining the homeostasis of the glucose metabolism through the miR-410-3p-LDHA axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8961–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, P.D.; Rhenius, S.T.; Hunter, J.O. Xanthine oxidase activity is not increased in the colonic mucosa of ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, C.S. The ubiquitin-proteasome system links NADPH metabolism to ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 1088–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogboo, B.C.; Grabovyy, U.V.; Maini, A.; Scouten, S.; van der Vliet, A.; Mattevi, A.; Heppner, D.E. Architecture of the NADPH oxidase family of enzymes. Redox Biol. 2022, 52, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillón-Betancur, J.C.; López-Agudelo, V.A.; Sommer, N.; Cleeves, S.; Bernardes, J.P.; Weber-Stiehl, S.; Rosenstiel, P.; Sommer, F. Epithelial Dual Oxidase 2 Shapes the Mucosal Microbiome and Contributes to Inflammatory Susceptibility. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Ingold, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Sun, C.; Kong, J. Vitamin D Attenuates Ulcerative Colitis by Inhibiting ACSL4-Mediated Ferroptosis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groemping, Y.; Rittinger, K. Activation and assembly of the NADPH oxidase: A structural perspective. Biochem. J. 2005, 386 Pt 3, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denson, L.A.; Sun, C.; Kong, J. Clinical and Genomic Correlates of Neutrophil Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Pediatric Patients With Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Kugathasan, S.; Annese, V.; Bradfield, J.P.; Russell, R.K.; Sleiman, P.M.; Imielinski, M.; Glessner, J.; Hou, C.; et al. Diverse genome-wide association studies associate the IL12/IL23 pathway with Crohn Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jostins, L.; Ripke, S.; Weersma, R.K.; Duerr, R.H.; McGovern, D.P.; Hui, K.Y.; Lee, J.C.; Schumm, L.P.; Sharma, Y.; Anderson, C.A.; et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2012, 491, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.; Siegel, D. NQO1 in protection against oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, F.; Besselt, K.; Deubel, S.; Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Kipp, A.P. GPx2 Induction Is Mediated Through STAT Transcription Factors During Acute Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Gao, H.; Yang, J. Development and Validation of a Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature for Overall Survival Prediction in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 684259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zuo, S.; Zhu, J.; Yue, T.; Bu, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y. Decreased Expression of Cystathionine β-Synthase Exacerbates Intestinal Barrier Injury in Ulcerative Colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.J.; Chen, W.L.; Yi, J.; Li, W.; Liu, J.Y.; Fu, W.Q.; Ren, L.W.; Li, S.; Ge, B.B.; Yang, Y.H.; et al. Apolipoprotein C1 promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis by reducing KEAP1/NRF2 and CBS-regulated ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, S. Ferroptosis Signaling Pathways: Alzheimer’s Disease. Horm. Metab. Res. 2023, 55, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Wang, T.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; Shen, H.; Chen, G. LPCAT3 exacerbates early brain injury and ferroptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Brain Res. 2024, 1832, 148864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, K.; Deng, L.; Qing, Q.; Li, J.; Zhi, F.; Li, M. Tollip Orchestrates Macrophage Polarization to Alleviate Intestinal Mucosal Inflammation. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 1151–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Di, Q.; Liu, H.; Quan, J.; Ling, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, Z.; Song, W.; et al. MEF2C promotes M1 macrophage polarization and Th1 responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Trigo, A.; Corraliza, A.M.; Veny, M.; Dotti, I.; Melón-Ardanaz, E.; Rill, A.; Crowell, H.L.; Corbí, Á.; Gudiño, V.; Esteller, M.; et al. Macrophage and neutrophil heterogeneity at single-cell spatial resolution in human inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.; Durant, L.; Hoyles, L.; McCartney, A.L.; Man, R.; Segal, J.; Costello, S.P.; Hendy, P.; Reddi, D.; Bouri, S.; et al. Deficient Resident Memory T Cell and CD8 T Cell Response to Commensals in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, C.; Arijs, I.; Staelens, D.; Breynaert, C.; Cleynen, I.; Covens, K.; Ferrante, M.; Van Assche, G.; Vermeire, S.; de Hertogh, G.; et al. Interleukin-15 receptor α expression in inflammatory bowel disease patients before and after normalization of inflammation with infliximab. Immunology 2013, 138, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Genes | Sequences |
|---|---|
| DUOX2 | F: CCT GCT CTC CTT GGT CCC TGT C |
| R: AGT TCC CTG GCT ACG GTC TCA AG | |
| ACSL4 | F: CAA TAG AGC AGA GTA CCC TGA G |
| R: TAG AAC CAC TGG TGT ACA TGA C | |
| NCF2 | F: GAA GAT ACC TCT CCA GAA TCC G |
| R: TTC TTA GAC ACC ATG TTC CGA A | |
| GPX2 | F: GTC ACT CTG AGG AAC AAC TAC C |
| R: TTC TGA CAG TTC TCC TGA TGT C | |
| CBS | F: GAA GCC TGG AGA CAC TAT CAT T |
| R: CAT CAC GAT AAT GCA GCG ATA G | |
| LPCAT3 | F: CAT GAA AGT GTG GCT CTT TGA A |
| R: GTT TGA AGA TGT AAC GGG CTA C | |
| GAPDH | F: GGT TGT CTC CTG CGA CTTCA |
| R: TGG TCC AGG GTT TCT TAC TCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Sang, M.; Xu, Q.; Mao, L. Development and Experimental Validation of Machine Learning-Based Disulfidptosis-Related Ferroptosis Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Genes 2025, 16, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050496
Liu Y, Shao J, Zhang J, Sang M, Xu Q, Mao L. Development and Experimental Validation of Machine Learning-Based Disulfidptosis-Related Ferroptosis Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Genes. 2025; 16(5):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050496
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yongchao, Jing Shao, Jie Zhang, Mengmeng Sang, Qiuyun Xu, and Liming Mao. 2025. "Development and Experimental Validation of Machine Learning-Based Disulfidptosis-Related Ferroptosis Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Disease" Genes 16, no. 5: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050496
APA StyleLiu, Y., Shao, J., Zhang, J., Sang, M., Xu, Q., & Mao, L. (2025). Development and Experimental Validation of Machine Learning-Based Disulfidptosis-Related Ferroptosis Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Genes, 16(5), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050496






