Asian Long-Range Transport in Relation to Atmospheric Rivers in Northern California
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. AR Events and Synoptic Conditions in 2017
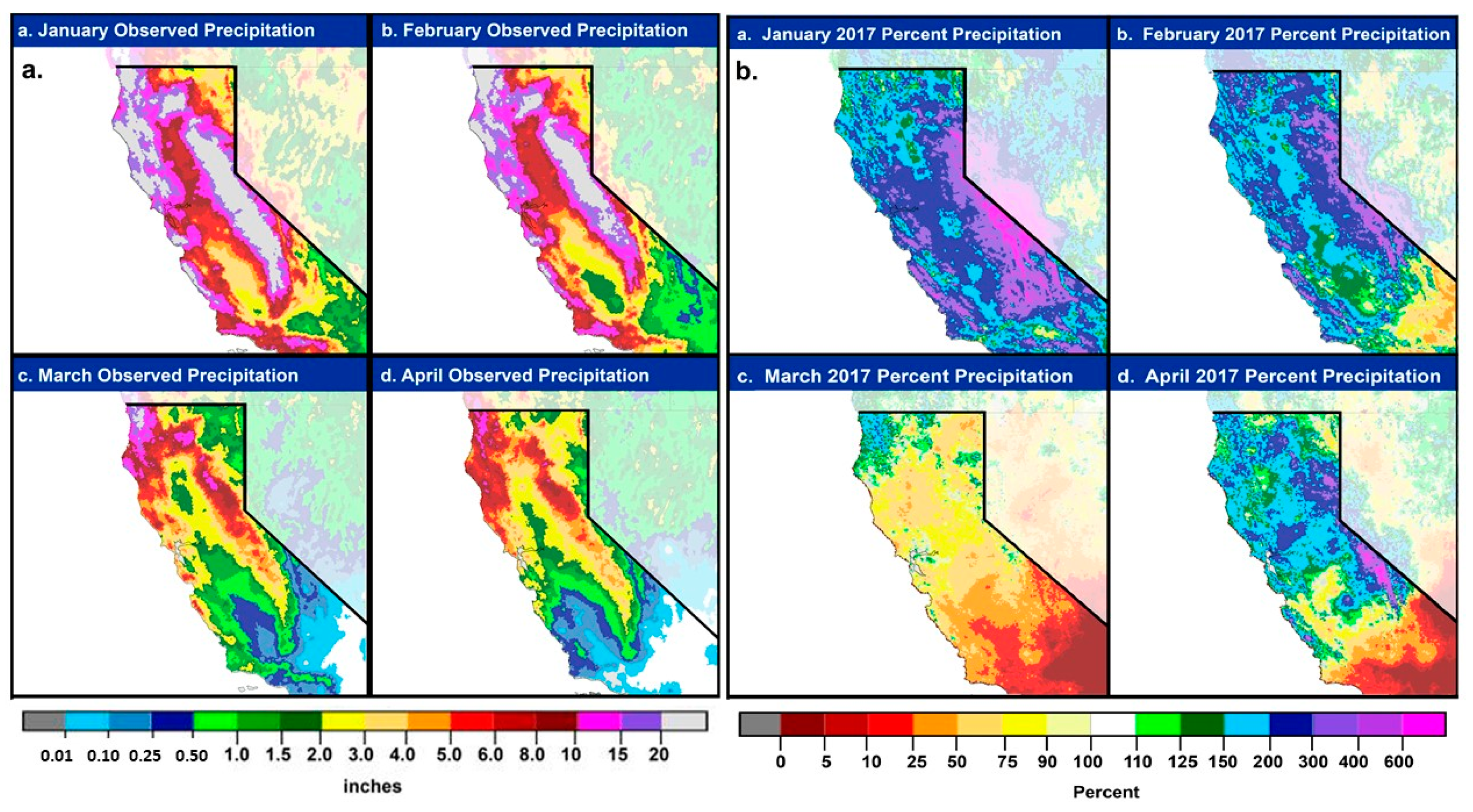
2.1. January 2017
2.2. February 2017
2.3. Synoptic Conditions and the Observed Characteristics of ARs
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Satellite Data
3.2. Observation Site Data
3.3. Precipitation Data
3.4. Back Trajectory Model Simulation
4. Results
4.1. Dust Measurements
4.2. 2006–2016 Climatological Analysis in Comparison to 2017
4.3. HYSPLIT Back Trajectory Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Governor’s Drought Declaration. Available online: http://www.water.ca.gov/waterconditions/declaration.cfm (accessed on 30 April 2017).
- Climate Station Predition Summary. Available online: http://www.cnrfc.noaa.gov/awipsProducts/RNOWRKCLI.php (accessed on 27 April 2017).
- Dettinger, M. Climate Change, Atmospheric Rivers, and Floods in California—A Multimodel Analysis of Storm Frequency and Magnitude Changes. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 47, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiserloh, A.J.; Chiao, S. Modeling studies of landfalling atmospheric rivers and orographic precipitation over northern California. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2015, 127, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Wick, G.A.; Lundquist, J.D.; Dettinger, M.D. Meteorological Characteristics and Overland Precipitation Impacts of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America Based on Eight Years of SSM/I Satellite Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Prather, K.A. Calwater Field Studies Designed to Quantify the Roles of Atmospheric River and Aerosols in Modulating U.S. West Coast Precipitation in a Changing Climate. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 1209–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, J.J.; Steenburgh, W.J.; Ralph, F.M. Climatological Characteristics of Atmospheric Rivers and Their Inland Penetration over the Western United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Ghan, S.J.; Lin, Y.; Hu, J.; Pan, B.; Levy, M.; Jiang, J.H.; Molina, M.J.; et al. Assessing the effects of anthropogenic aerosols on Pacific storm track using a multiscale global climate model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6894–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, A.; Wang, T.; Fu, C. Transport characteristics and origins of carbon monoxide and ozone in Hong Kong, South China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9475–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamean, J.M.; Suski, K.J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Cazorla, A.; DeMott, P.J.; Sullivan, R.C.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Minnis, P.; Comstock, J.M.; et al. Dust and Biological Aerosols from the Sahara and Asia Influence Precipitation in the Western U.S. Science 2013, 339, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Q.; Jaeglé, L.; Jaffe, D.A.; Weiss-Penzias, P.; Heckman, A.; Snow, J.A. Long-range transport of Asian pollution to the northeast Pacific: Seasonal variations and transport pathways of carbon monoxide. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jang, C.; Phillips, S.; Wang, B. Modeling intercontinental air pollution transport over the trans-pacific region in 2001 using the community multiscale air quality modeling system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Fan, J.; Wu, D.L.; Molina, M.J. Intensification of Pacific storm track linked to Asian pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5295–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creamean, J.M.; Axson, J.L.; Bondy, A.L.; Craig, R.L.; May, N.W.; Shen, H.; Weber, M.H.; Pratt, K.A.; Ault, A.P. Atmospheres and elevation in the California Sierra Nevada. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 7296–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Fan, J.; Leung, L.R.; DeMott, P.J.; Comstock, J.M.; Singh, B.; Rosenfeld, D.; Tomlinson, J.M.; White, A.; Prather, K.A.; et al. Aerosol impacts on California winter clouds and precipitation during calwater 2011: Local pollution versus long-range transported dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ault, A.P.; Williams, C.R.; White, A.B.; Neiman, P.J.; Creamean, J.M.; Gaston, C.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Prather, K.A. Detection of Asian dust in California orographic precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Dave, P.; Venkataraman, C.; Crawford, I.; Rasch, P.J. Contrasting influences of aerosols on cloud properties during deficient and abundant monsoon years. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heald, C.L.; Jacob, D.J.; Park, R.J.; Alexander, B.; Fairlie, T.D.; Yantosca, R.M.; Chu, D.A. Transpacific transport of Asian anthropogenic aerosols and its impact on surface air quality in the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Weather Service: AHPS Precipitation Analysis 2018. Available online: https://water.weather.gov/precip/index.php?location_type=wfo&location_name=mtr (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- Santa Clara Valley Water District, 2017: 2017 Flooding REPORT FINAL. Available online: https://www.valleywater.org/sites/default/files/2017 Flood Report.pdf (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes, 2017: CW3E AR Update. Available online: http://cw3e.ucsd.edu/author/cw3e-web/page/12/ (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- White, A.B.; Moore, B.J.; Gottas, D.J.; Neiman, P.J. Winter Storm Conditions Leading to Excessive Runoff above California’s Oroville Dam during January and February 2017. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorncroft, C.D.; Hoskins, B.J.; McIntyre, M.E. Two paradigms of baroclinic-wave life-cycle behaviour. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 17–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.; Hilburn, K.A.; Smith, D.K. Remote Sensing Systems DMSP SSMIS Daily Environmental Suite on 0.25 Deg Grid; Version 7; Northern Pacific; Remote Sensing Systems: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2012; Available online: http://www.remss.com/missions/ssmi (accessed on 13 August 2017).
- Interagency Monitoring Protected Visual Environment (IMPROVE) Program. Available online: http://vista.cira.colostate.edu/Improve/improve-program/ (accessed on 6 June 2017).
- Creamean, J.M.; Lee, C.; Hill, T.C.; Ault, A.P.; DeMott, P.J.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Prather, K.A. Chemical properties of insoluble precipitation residue particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 76, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanCuren, R.A.; Cliff, S.S.; Perry, K.D.; Jimenez-Cruz, M. Asian continental aerosol persistence above the marine boundary layer over the eastern North Pacific: Continuous aerosol measurements from Intercontinental Transport and Chemical Transformation 2002 (ITCT 2 K2). J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Rutz, J.J.; Cordeira, J.M.; Dettinger, M.; Anderson, M.; Reynolds, D.; Schick, L.J.; Smallcomb, C. A Scale to Characterize the Strength and Impacts of Atmospheric Rivers. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Coasts | Inland | Mountains | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rdwd | ptrey | pinn | fres | lavo | bliss | kais | ||||||||||||||
| Y | frq | str | Y | frq | str | Y | frq | str | Y | frq | str | Y | frq | str | Y | frq | str | Y | frq | str |
| 6 | 5 | w | 6 | 6 1 | wm | 6 | 1 1 | wm | 6 | 1 1 | wm | 6 | 3 | w | 6 | 0 | --- | 6 | 0 | --- |
| 7 | 1 | w | 7 | 3 | w | 7 | 2 | w | 7 | 0 | --- | 7 | 0 | --- | 7 | 0 | --- | 7 | 0 | --- |
| 8 | 1 | w | 8 | 2 | w | 8 | 1 | w | 8 | 1 | --- | 8 | 0 | --- | 8 | 1 | w | 8 | 0 | --- |
| 9 | 4 | w | 9 | 3 1 | wm | 9 | 3 | w | 9 | 0 | --- | 9 | 3 | w | 9 | 1 | w | 9 | 0 | --- |
| 10 | 3 1 | wm | 10 | 5 | w | 10 | 1 | w | 10 | 1 | w | 10 | 3 | w | 10 | 1 | w | 10 | 0 | --- |
| 11 | 4 | w | 11 | 8 | w | 11 | 3 | w | 11 | 2 | w | 11 | 3 | w | 11 | 1 | w | 11 | 0 | --- |
| 12 | 5 1 | wm | 12 | 7 | w | 12 | 1 | w | 12 | 2 | w | 12 | 3 | w | 12 | 0 | --- | 12 | 0 | --- |
| 13 | 1 | w | 13 | 0 | w | 13 | 1 | w | 13 | 0 | --- | 13 | 0 | --- | 13 | 0 | --- | 13 | 0 | --- |
| 14 | 1 1 | wm | 14 | 6 | w | 14 | 2 | w | 14 | 3 | w | 14 | 3 | w | 14 | 0 | --- | 14 | 0 | --- |
| 15 | 3 1 | wm | 15 | 2 | w | 15 | 2 | w | 15 | 0 | --- | 15 | 2 | w | 15 | 0 | --- | 15 | 0 | --- |
| 16 | 4 | w | 16 | 8 | w | 16 | 2 | w | 16 | 1 | w | 16 | 2 | w | 16 | 0 | --- | 16 | 0 | --- |
| 17 | 4 1 | wm | 17 | 11 | w | 17 | 6 | w | 17 | 3 | w | 17 | 6 | w | 17 | 5 | w | 17 | 4 | w |
| 2007–2016 Correlations | ||||||||
| Dust (Asian) | Dust (Non-Asian) | Black Carbon | Sulfate | |||||
| R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | |
| RDWD | −0.15 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.48 | −0.23 | 5.21 | −0.12 | 0.02 |
| PTREY | −0.07 | 0.15 | −0.07 | 0.19 | −0.11 | 0.02 | −0.02 | 0.76 |
| PINN | −0.07 | 0.14 | −0.08 | 0.10 ** | −0.18 | 0.00 | −0.08 | 0.09 ** |
| FRES | −0.03 | 0.61 | −0.01 | 0.91 | 0.02 | 0.76 | −0.03 | 0.54 |
| LAVO | −0.06 | 0.22 | −0.08 | 0.09 ** | −0.12 | 0.01 | −0.08 | 0.10 ** |
| BLISS | −0.07 | 0.14 | −0.07 | 0.14 | −0.11 | 0.02 | −0.09 | 0.06 ** |
| KAIS | −0.09 | 0.06 ** | −0.06 | 0.20 | −0.14 | 0.01 | −0.12 | 0.02 |
| 2017 Correlations | ||||||||
| Dust (Asian) | Dust (Non-Asian) | Black Carbon | Sulfate | |||||
| R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | |
| RDWD | −0.44 | 0.00 | −0.17 | 0.47 | −0.64 | 7.38 | −0.43 | 0.01 |
| PTREY | −0.15 | 0.37 | −0.18 | 0.26 | −0.30 | 0.06 ** | −0.27 | 0.09 ** |
| PINN | −0.08 | 0.60 | −0.33 | 0.04 | −0.44 | 0.00 | −0.37 | 0.02 |
| FRES | 0.25 | 0.12 | −0.46 | 0.00 | −0.39 | 0.01 | −0.39 | 0.01 |
| LAVO | −0.23 | 0.15 | −0.36 | 0.02 | −0.47 | 0.00 | −0.39 | 0.01 |
| BLISS | −0.18 | 0.26 | −0.31 | 0.04 | −0.36 | 0.02 | −0.28 | 0.08 ** |
| KAIS | −0.14 | 0.38 | −0.19 | 0.24 | −0.20 | 0.23 | −0.20 | 0.23 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.N.; Chiao, S.; Ryoo, J.-M. Asian Long-Range Transport in Relation to Atmospheric Rivers in Northern California. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060313
Liu CN, Chiao S, Ryoo J-M. Asian Long-Range Transport in Relation to Atmospheric Rivers in Northern California. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(6):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060313
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Catherine N., Sen Chiao, and Ju-Mee Ryoo. 2019. "Asian Long-Range Transport in Relation to Atmospheric Rivers in Northern California" Atmosphere 10, no. 6: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060313
APA StyleLiu, C. N., Chiao, S., & Ryoo, J. -M. (2019). Asian Long-Range Transport in Relation to Atmospheric Rivers in Northern California. Atmosphere, 10(6), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060313





