City-Scale Building Anthropogenic Heating during Heat Waves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
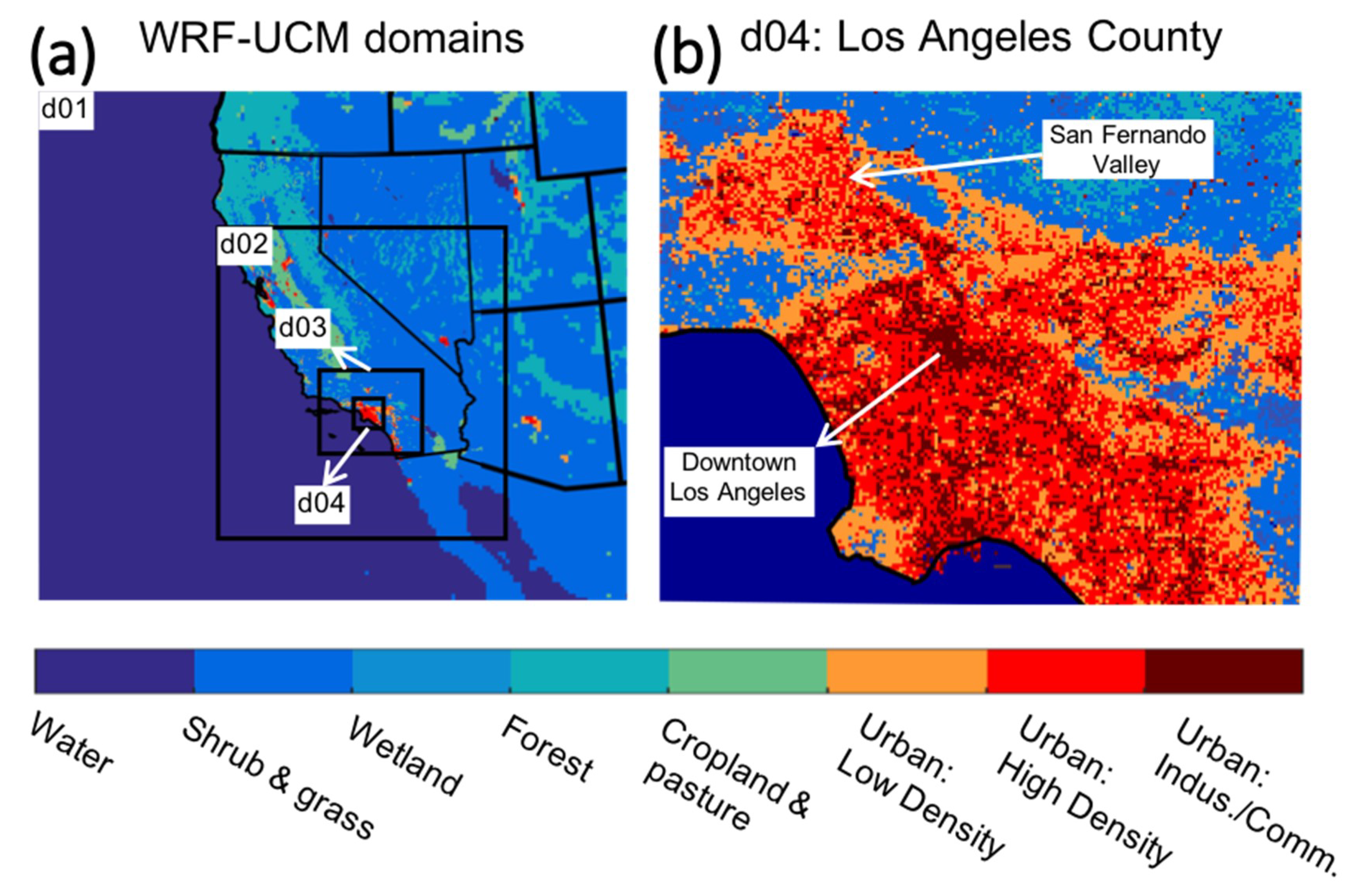
2.1. Area of Focus
2.2. Description of the WRF Model Set Up
2.3. Identification of the Heat Wave Event
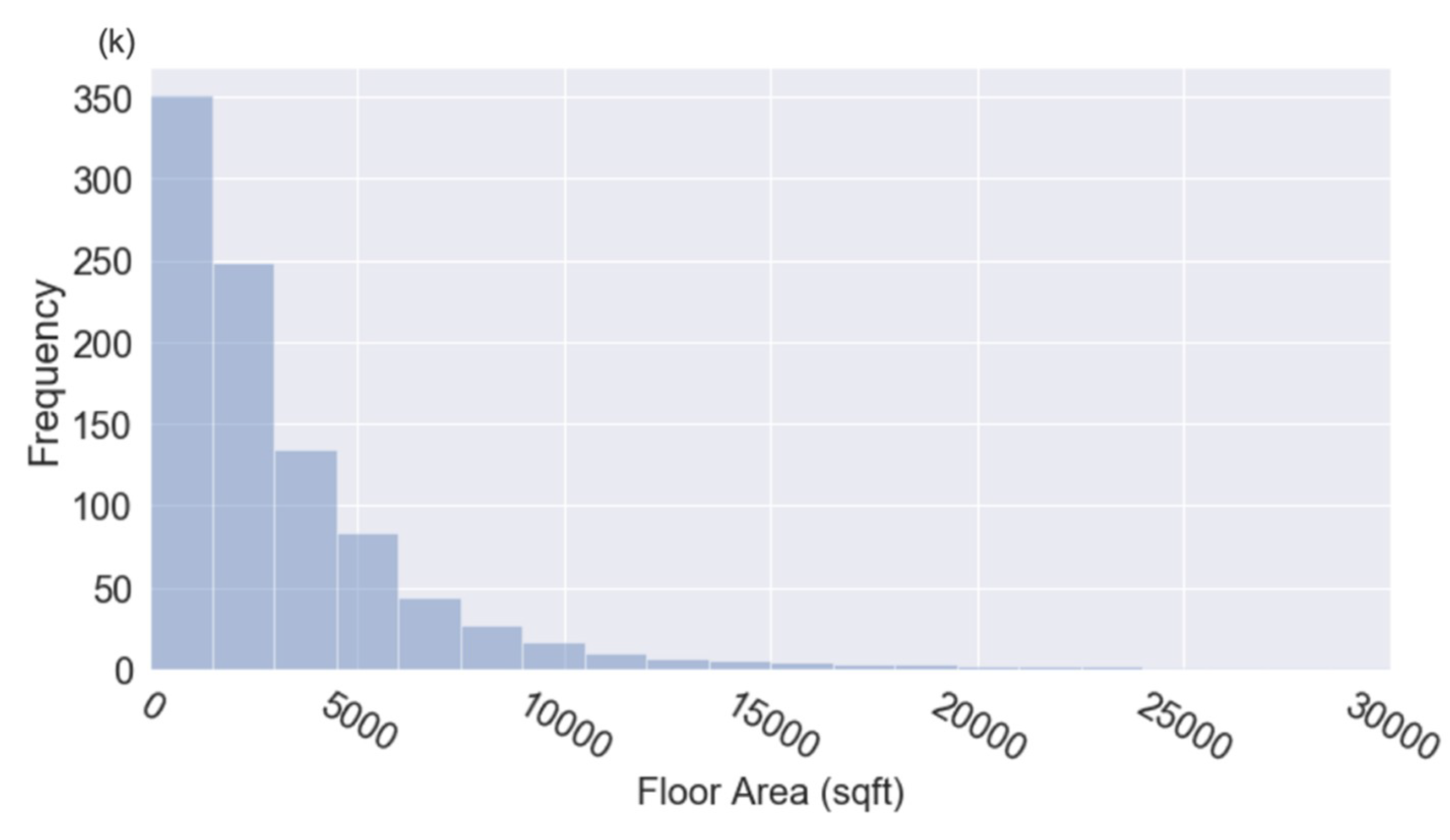
2.4. Urban Morphology Information
2.5. Building Waste Heat Simulation with EnergyPlus
2.6. Urban Building Heat Emission Profiles
3. Results
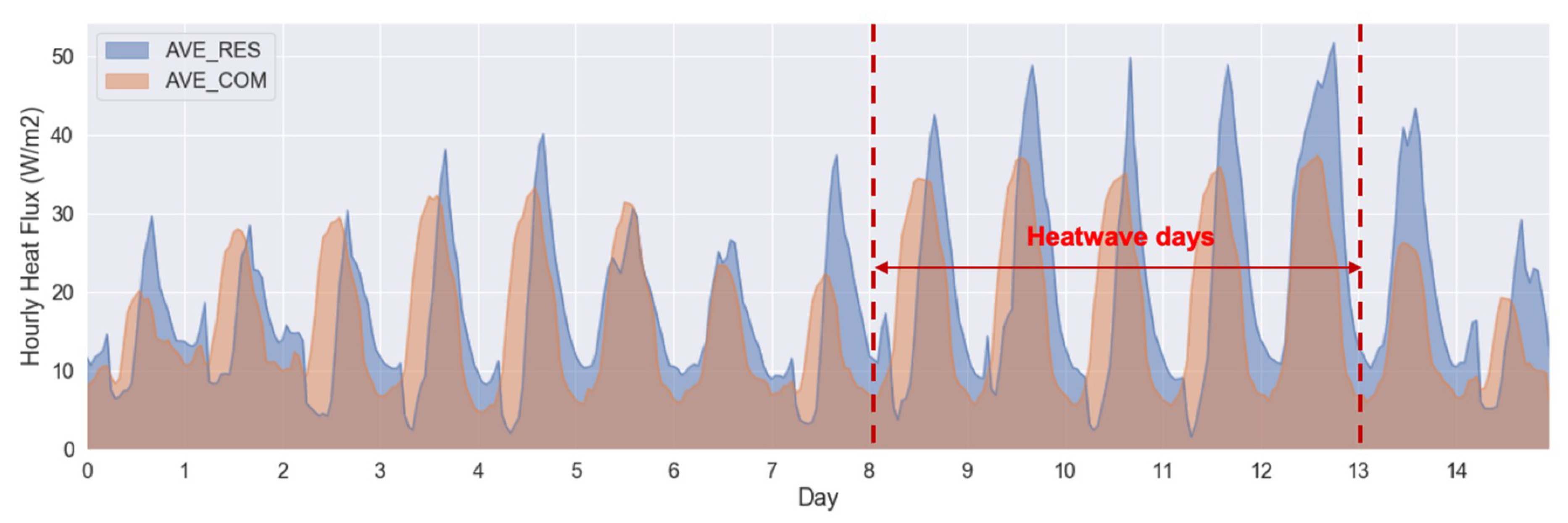
3.1. The Heat Wave and Its Energy Impact
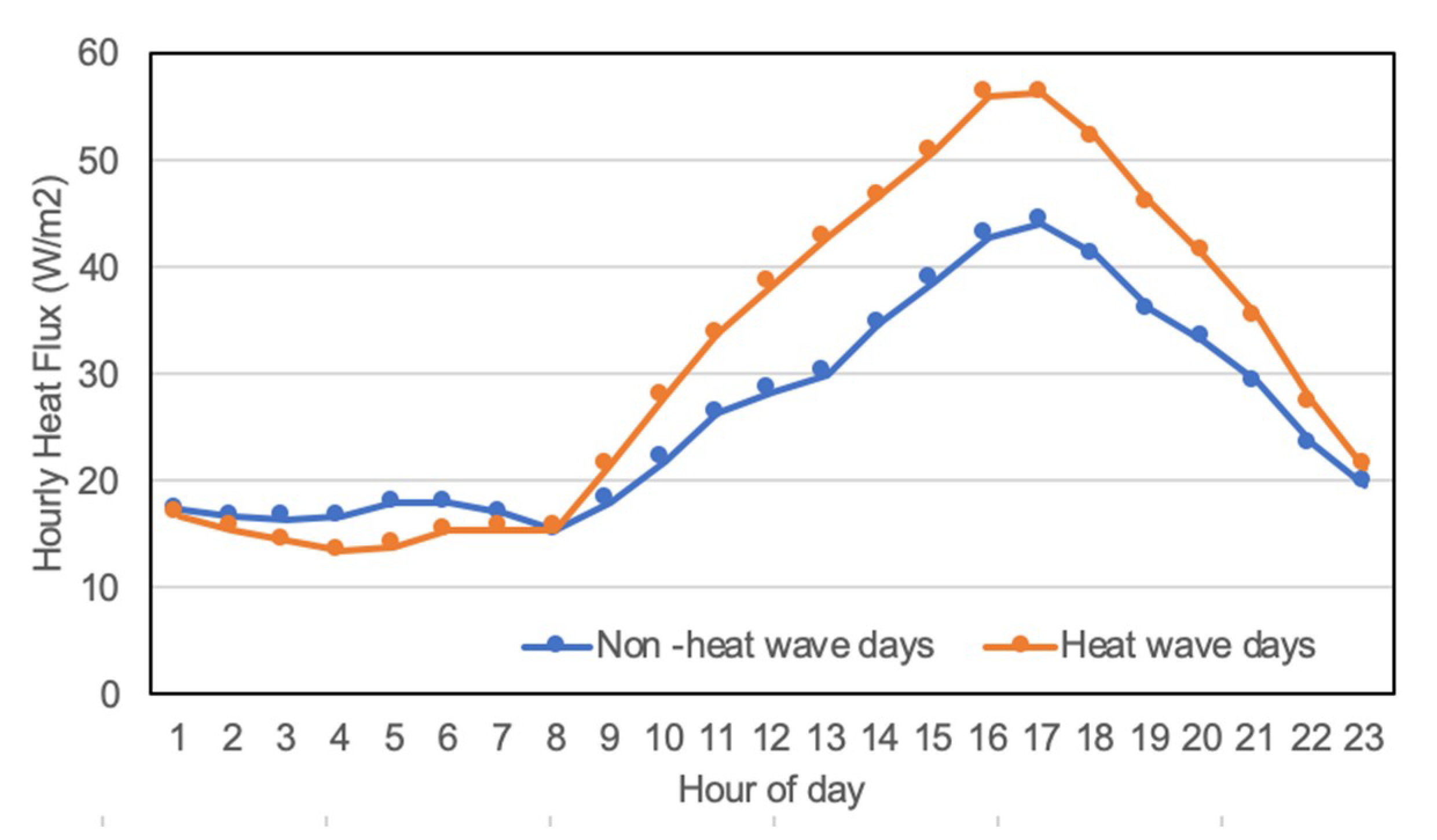
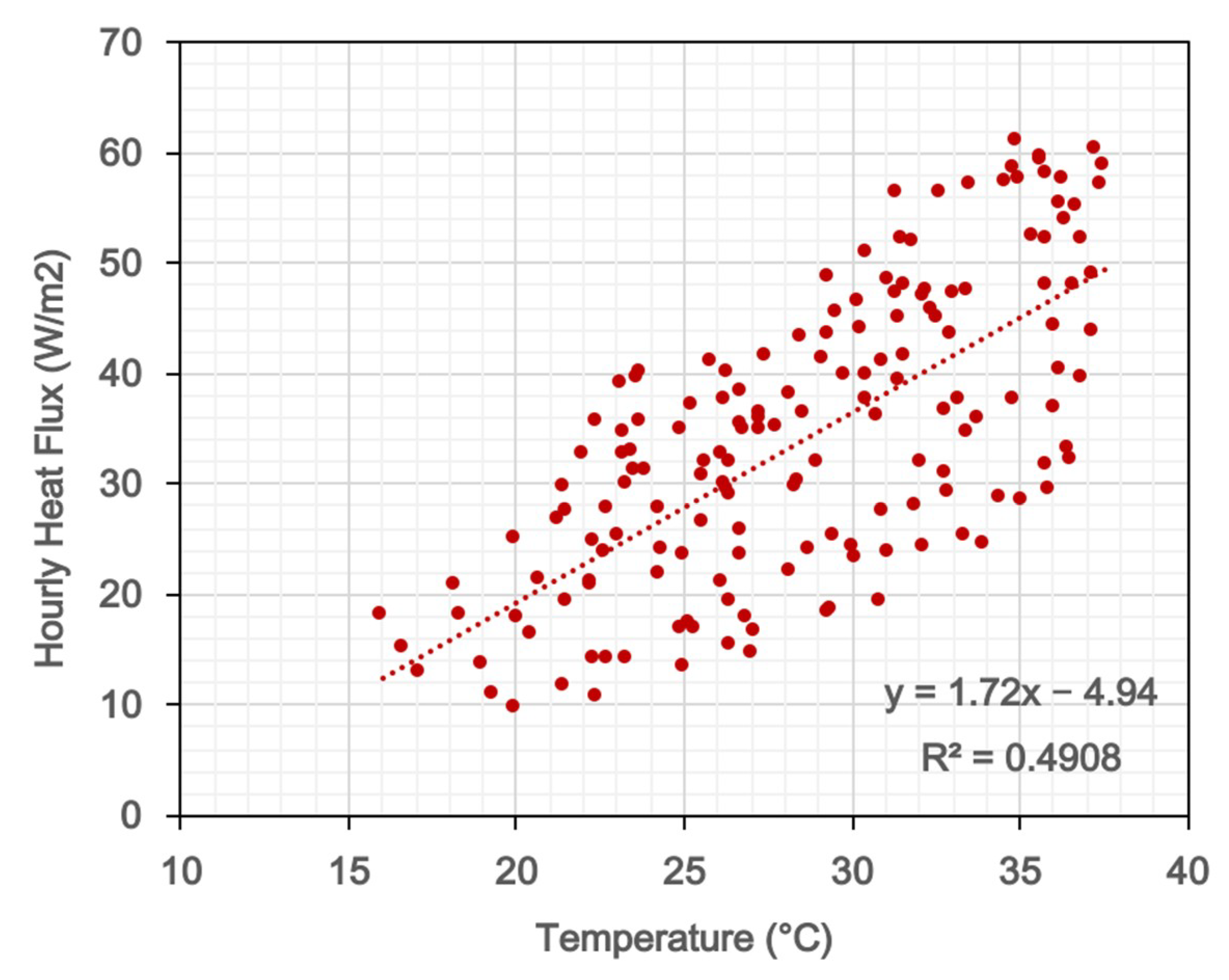
3.2. Temporal Variations of Anthropogenic Heat Intensity
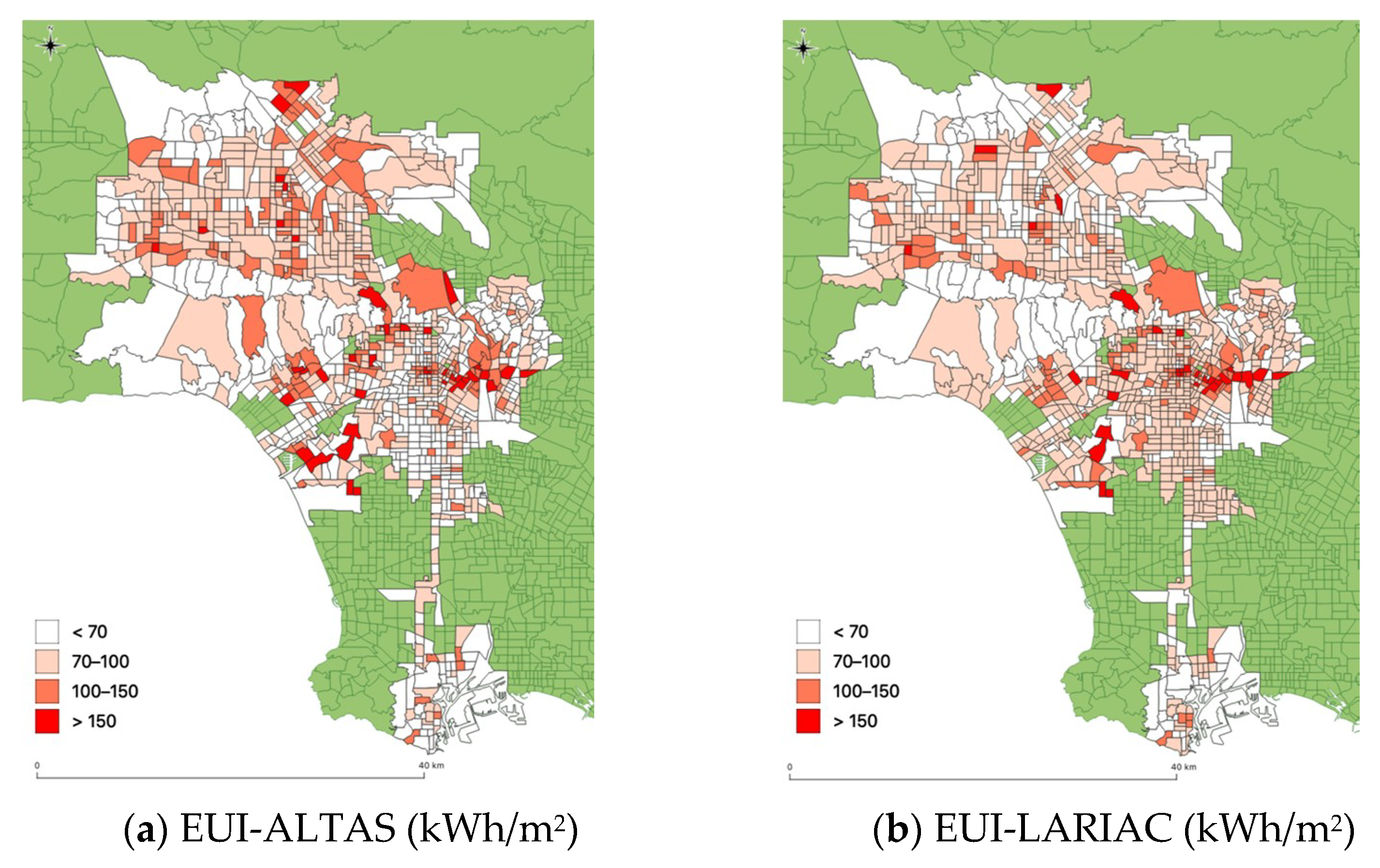
3.3. Spatial Variations of Anthropogenic Heat Intensity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. Global Climate Report—July 2019, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/global/201907 (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- July 2019 was Hottest Month on Record for the Planet|National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.noaa.gov/news/july-2019-was-hottest-month-on-record-for-planet (accessed on 3 August 2020).
- Sun, K.; Specian, M.; Hong, T. Nexus of thermal resilience and energy efficiency in buildings: A case study of a nursing home. Build. Environ. 2020, 177, 106842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E. Synergistic Interactions between Urban Heat Islands and Heat Waves: The Impact in Cities Is Larger than the Sum of Its Parts. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2013, 52, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemonsu, A.; Viguie, V.; Daniel, M.; Masson, V. Vulnerability to heat waves: Impact of urban expansion scenarios on urban heat island and heat stress in Paris (France). Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.-Y. Urbanization as a major driver of urban climate change. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Painel Intergovernamental sobre Mudanças Climáticas, Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change; Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzig, F.; Baiocchi, G.; Bierkandt, R.; Pichler, P.-P.; Seto, K.C. Global typology of urban energy use and potentials for an urbanization mitigation wedge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6283–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Yao, R.; Luo, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Quantitatively evaluating the effect of urbanization on heat waves in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 731, 138857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.J.; Georgescu, M.; Milne, J.M.; Hart, M.A. Development of a national anthropogenic heating database with an extrapolation for international cities. Atmospheric Environ. 2015, 118, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.M.; Zscheischler, J.; Wartenburger, R.; Dee, D.; Seneviratne, S.I. Concurrent 2018 Hot Extremes Across Northern Hemisphere Due to Human-Induced Climate Change. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.; Vasireddy, C. Correcting aggregate energy consumption data to account for variability in local weather. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. A distributed model for quantifying temporal-spatial patterns of anthropogenic heat based on energy consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Ferrando, M.; Luo, X.; Causone, F. Modeling and analysis of heat emissions from buildings to ambient air. Appl. Energy 2020, 277, 115566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.J.; Lu, L. A top–down methodology for developing diurnal and seasonal anthropogenic heating profiles for urban areas. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, J.; Brown, M.J.; McPherson, T.; Burian, S.; Chen, F.; Cionco, R.; Hanna, A.; Hultgren, T.; Sailor, D.; Taha, H.; et al. National Urban Database and Access Portal Tool. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Ni, G.; Sun, T. Impacts of Anthropogenic Heat on Summertime Rainfall in Beijing. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenstengel, S.I.; Hamilton, I.; Davies, M.; Belcher, S.E. Impact of anthropogenic heat emissions on London’s temperatures. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 140, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y.; Genchi, Y.; Kondo, H.; Kikegawa, Y.; Yoshikado, H.; Hirano, Y. Influence of Air-Conditioning Waste Heat on Air Temperature in Tokyo during Summer: Numerical Experiments Using an Urban Canopy Model Coupled with a Building Energy Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, T.; Shimodozono, K.; Hanaki, K. Impact of anthropogenic heat on urban climate in Tokyo. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3897–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, B.; Norford, L.; Pigeon, G.; Britter, R. A resistance-capacitance network model for the analysis of the interactions between the energy performance of buildings and the urban climate. Build. Environ. 2012, 54, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Benz, S.; Bayer, P.; Menberg, K.; Jung, S.; Blum, P. Spatial resolution of anthropogenic heat fluxes into urban aquifers. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 524–525, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.-M.; Wang, Y.-L.; Ma, Z.-G.; Liu, Y. Simulating the Regional Impacts of Urbanization and Anthropogenic Heat Release on Climate across China. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7187–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, F.; Grimmond, C.; Yogeswaran, N.; Kotthaus, S.; Allen, L. Impact of city changes and weather on anthropogenic heat flux in Europe 1995–2015. Urban Clim. 2013, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, A.; Keuler, K.; Schaller, E. Impacts of anthropogenic heat on regional climate patterns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Pitman, A.; Hart, M.; Evans, J.P.; Haghdadi, N.; MacGill, I. The impact of an urban canopy and anthropogenic heat fluxes on Sydney’s climate. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yang, X.; Leung, L.R.; Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J. Modeling the Impacts of Urbanization on Summer Thermal Comfort: The Role of Urban Land Use and Anthropogenic Heat. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6681–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.T.; Salamanca, F.; Georgescu, M.; Mahalov, A.; Milne, J.M.; Ruddell, B.L. A multi-method and multi-scale approach for estimating city-wide anthropogenic heat fluxes. Atmospheric Environ. 2014, 99, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S.C. Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: Los Angeles City, California, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/losangelescitycalifornia (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Zheng, Y.; Weng, Q. High spatial- and temporal-resolution anthropogenic heat discharge estimation in Los Angeles County, California. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusaka, H.; Kimura, F. Coupling a Single-Layer Urban Canopy Model with a Simple Atmospheric Model: Impact on Urban Heat Island Simulation for an Idealized Case. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 82, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.-H.; Baik, J.-J.; Lee, S.-H. A New Single-Layer Urban Canopy Model for Use in Mesoscale Atmospheric Models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 1773–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kusaka, H.; Bornstein, R.; Ching, J.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Loridan, T.; Manning, K.W.; Martilli, A.; Miao, S.; et al. The integrated WRF/urban modelling system: Development, evaluation, and applications to urban environmental problems. Int. J. Clim. 2011, 31, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Duda, M.G.; Fowler, L.D.; Park, S.-H.; Ringler, T.D. A Multiscale Nonhydrostatic Atmospheric Model Using Centroidal Voronoi Tesselations and C-Grid Staggering. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2012, 140, 3090–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.; Thompson, G.; Tatarskii, V. Impact of Cloud Microphysics on the Development of Trailing Stratiform Precipitation in a Simulated Squall Line: Comparison of One- and Two-Moment Schemes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two dimensional model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretherton, C.S.; Park, S. A New Moist Turbulence Parameterization in the Community Atmosphere Model. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3422–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Freitas, S.R. A scale and aerosol aware stochastic convective parameterization for weather and air quality modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 5233–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, A.S.; Obukhov, A.M. Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere, Contrib. Geophys. Inst. Acad. Sci. 1954, 24, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, J.A.; Xian, G.; Jin, S.; Dewitz, J.A.; Homer, C.G.; Yang, L.; Barnes, C.A.; Herold, N.D.; Wickham, J.D. Completion of the 2006 national land cover database for the conterminous united states. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2011, 77, 858–864. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, J.; Stehman, S.V.; Gass, L.; Dewitz, J.; Fry, J.A.; Wade, T.G. Accuracy assessment of NLCD 2006 land cover and impervious surface. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahmani, P.; Jones, A.D.; Patricola, C.M. Interacting implications of climate change, population dynamics, and urban heat mitigation for future exposure to heat extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 084051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; O’Neill, B.C.; McDaniel, L.; McGinnis, S.; Mearns, L.O.; Tebaldi, C. Future population exposure to US heat extremes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfin, G.; Jardine, A.; Merideth, R.; Black, M.; LeRoy, S. Assessment of Climate Change in the Southwest United States: A Report Prepared for the National Climate Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gershunov, A.; Cayan, D.R.; Iacobellis, S.F. The Great 2006 Heat Wave over California and Nevada: Signal of an Increasing Trend. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 6181–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Piette, M.A. CityBES: A web-based platform to support city-scale building energy efficiency. Urban Comput. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los Angeles County GIS Data Portal. Countywide Building Outlines—2014 (2014). Available online: https://geohub.lacity.org/datasets/57f5fc977d6a427a978003a6229ab5e7/ (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- DataLA: Information, Insights, and Analysis from the City of Angels: Los Angeles—Open Data Portal. City of Los Angeles. Available online: https://data.lacity.org/ (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Crawley, D.B.; Lawrie, L.K.; Pedersen, C.O.; Winkelmann, F.C. EnergyPlus: Energy simulation program. ASHRAE J. 2000, 42, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- ASHRAE. ANSI/ASHRAE/IES Standard 90.1-2010; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Vahmani, P.; Hong, T.; Jones, A. City-Scale Building Anthropogenic Heating during Heat Waves. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111206
Luo X, Vahmani P, Hong T, Jones A. City-Scale Building Anthropogenic Heating during Heat Waves. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(11):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111206
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xuan, Pouya Vahmani, Tianzhen Hong, and Andrew Jones. 2020. "City-Scale Building Anthropogenic Heating during Heat Waves" Atmosphere 11, no. 11: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111206
APA StyleLuo, X., Vahmani, P., Hong, T., & Jones, A. (2020). City-Scale Building Anthropogenic Heating during Heat Waves. Atmosphere, 11(11), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111206




