A Novel Method for Carbonate Quantification in Atmospheric Particulate Matter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
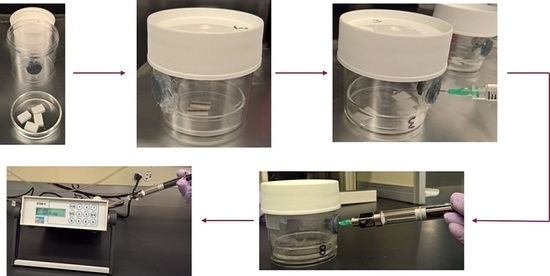
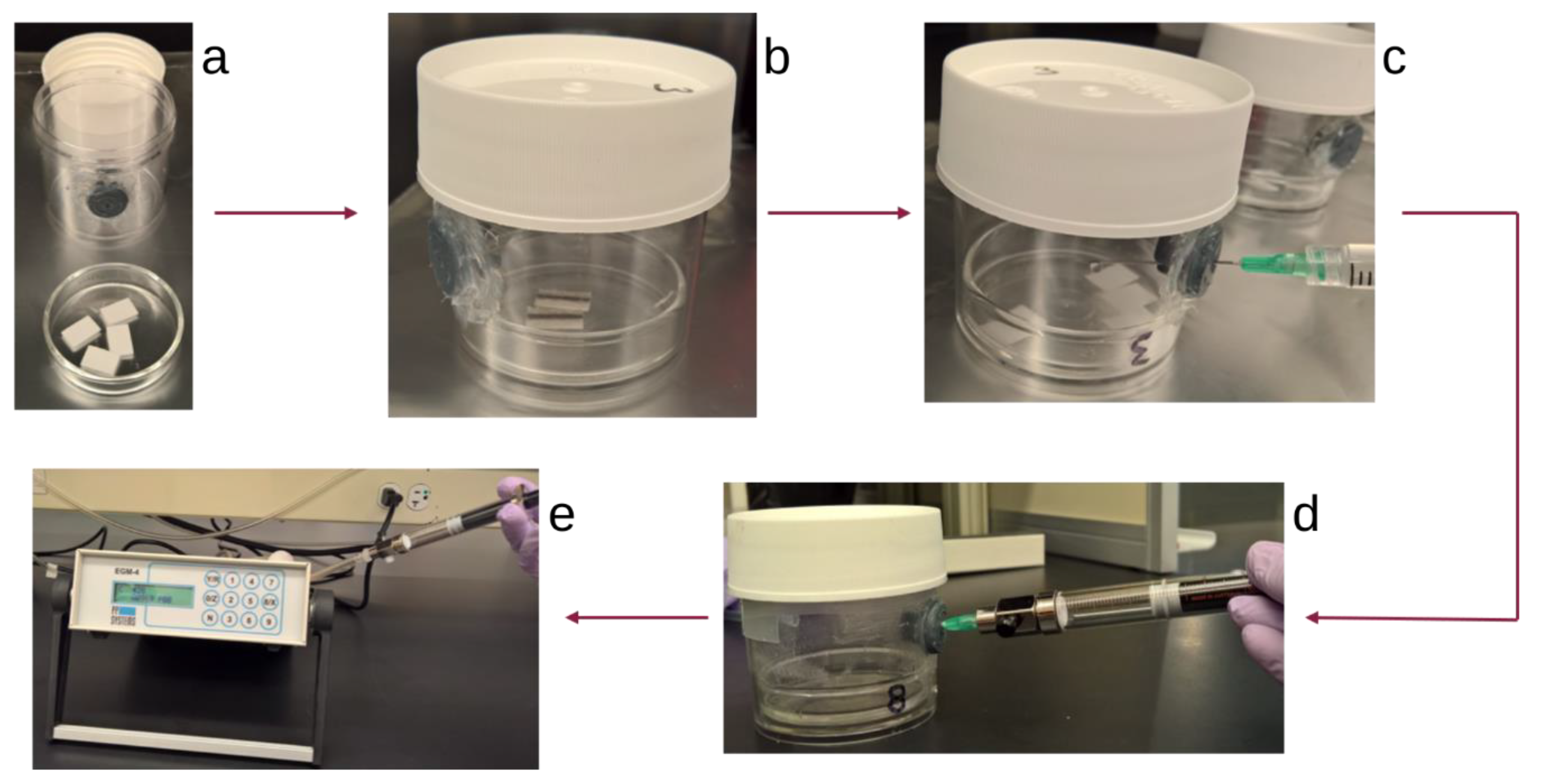
2.1. Principle and Experimental Setup
2.2. Optimization of Experimental Parameters
2.2.1. Incubation Jar Seal Test
2.2.2. Optimization of Incubation Time
2.3. Ambient Particulate Matter Sample Collection and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Incubation Jar Seal Tests
3.2. Optimization of Incubation Time
3.3. Application to Atmospheric Particulate Matter Samples
3.4. Implications for Generalized Application to Atmospheric Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramadan, Z.; Song, X.H.; Hopke, P.K. Identification of sources of Phoenix aerosol by positive matrix factorization. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1995, 50, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.W.; Norris, G.A.; Conner, T.L.; Henry, R.C. Source Apportionment of Phoenix PM2.5 Aerosol with the Unmix Receptor Model. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2003, 53, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.G.; Frankel, A.; Raffuse, S.M.; Roberts, P.T.; Hafner, H.R.; Anderson, D.J. Source apportionment of fine particulate matter in Phoenix, AZ, using positive matrix factorization. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N.; Clements, A.; Fraser, M.; Herckes, P. Chemical speciation of PM2.5 and PM10 in South Phoenix, AZ, USA. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, T.M. Annual cycle of size-resolved organic aerosol characterization in an urbanized desert environment. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, E.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Chemical characterization and source identification/apportionment of fine and coarse air particles in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardi, A.H.; Khaghani, A.; MacDonald, A.B.; Nguyen, P.; Karimi, N.; Heidary, P.; Karimi, N.; Saemian, P.; Sehatkashani, S.; Tajrishy, M.; et al. The Lake Urmia environmental disaster in Iran: A look at aerosol pollution. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2018, 633, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbaras, A.; Rimselyte, K.; Kvietkus, K.; Remeikis, V. δ13C values in size segregated atmospheric carbonaceous aerosols at a rural site in Lithuania. Lith. J. Phys. 2009, 49, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Veneroni, D. The stable carbon isotope composition of PM2.5 and PM10 in Mexico City Metropolitan Area air. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4491–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masalaite, A.; Remeikis, V.; Garbaras, A.; Dudoitis, V.; Ulevicius, V.; Ceburnis, D. Elucidating carbonaceous aerosol sources by the stable carbon δ13CTC ratio in size-segregated particles. Atmos. Res. 2015, 158–159, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Crow, D.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Merrifield, T. Comparison of IMPROVE and NIOSH Carbon Measurements. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. PM2.5 carbonate concentrations at regionally representative Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environment sites. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, ICC 6-1–ICC 6-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chow, J.C.; An, Z.S.; Ho, K.F.; Watson, J.G.; Fung, K.; Wang, Y.Q.; Shen, Z.X. Characterization of airborne carbonate over a site near Asian dust source regions during spring 2002 and its climatic and environmental significance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birch, M.E.; Cary, R.A. Elemental Carbon-Based Method for Monitoring Occupational Exposures to Particulate Diesel Exhaust. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 1996, 25, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachier, H.; Bremond, M.; Buat-Menard, P. Determination of atmospheric soot carbon with a simple thermal method. Tellus 1989, 41B, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herckes, P.; Engling, G.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Collett, J.L. Particle Size Distributions of Organic Aerosol Constituents during the 2002 Yosemite Aerosol Characterization Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4554–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunset Laboratory Inc., Retrieved. 2018. Available online: www.sunlab.com/ (accessed on 29 May 2018).
- Webb, T.L.; Kruger, J.E. Carbonates in Differential Thermal Analysis; MacKenzie, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970; pp. 303–341. [Google Scholar]
- Criado, J.M.; Ortega, A. A study of the influence of particle size on the thermal decomposition of CaCO3 by means of constant rate thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta 1992, 195, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, B.; (Sunset Laboratory Inc., Tigard, OR, USA). Personal communication, 2017.
- McCrea, J.M. On the Isotopic Chemistry of Carbonates and a Paleotemperature Scale. J. Chem. Phys. 1950, 18, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jie, D.; Shi, M.; Gao, P.; Shen, Z.; Uchida, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, K.; Kitagawa, H. Characteristics of 14C and 13C of carbonate aerosols in dust storm events in China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164–165, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y. Regional prediction of carbon isotopes in soil carbonates for Asian dust source tracer. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.G.; Karani, G.N. Characterization of the Carbonate Content of Atmospheric Aerosols. J. Atmos. Chem. 1992, 14, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, K. Element Use and Acquisition Strategies in Biological Soil Crusts. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, G.A. Soot Black Carbon Dynamics in Arid/Urban Ecosystems. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zappoli, S.; Andracchio, A.; Fuzzi, S.; Facchini, M.C.; Gelencsér, A.; Kiss, G.; Krivácsy, Z.; Molnár, Á.; Mészáros, E.; Hansson, H.-C.; et al. Inorganic, organic and macromolecular components of fine aerosol in different areas of Europe in relation to their water solubility. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R.; Brown, S.G.; Minor, H.A. EPA’s Pilot Study: Coarse PM Monitoring Program Results. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards. 2015. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttn/amtic/files/pm10pilot/PMc_ReportEPA454R-15-001.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2020).

| Incubation Conditions | 5−Minute Incubation | 10−Minute Incubation | 15−Minute Incubation | 2−Hour Incubation | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jar | Pres. (atm) | Temp. (K) | Amount of NaHCO3 (×10−7 mol) | Vol. (mL) | Bkgrd CO2 Conc. (ppmv) | HCl Added (mL) | CO2 Conc. (ppmv) | Moles CO2 Formed (×10−7 mol) | Rel. Error (%) | CO2 Conc. (ppmv) | Moles CO2 Formed (×10−7 mol) | Rel. Error (%) | CO2 Conc. (ppmv) | Moles CO2 Formed (×10−7 mol) | Rel. Error (%) | CO2 Conc. (ppmv) | Moles CO2 Formed (×10−7 mol) | Rel. Error (%) |
| A | 0.989 | 294.4 | 12.51 | 179.8 | 524 | 2.8 | 645 | 8.666 | −30.72 | 643 | 8.527 | −31.83 | 644 | 8.594 | −31.29 | 652 | 9.121 | −27.08 |
| B | 0.989 | 294.4 | 3.700 | 175.4 | 474 | 2.6 | 515 | 2.864 | −22.59 | 515 | 2.864 | −22.59 | 514 | 2.798 | −24.37 | 514 | 2.798 | −24.37 |
| C | 0.989 | 294.4 | 9.073 | 177.1 | 500 | 2.2 | 596 | 6.769 | −25.39 | 596 | 6.769 | −25.39 | 596 | 6.769 | −25.39 | 584 | 5.991 | −33.96 |
| D | 0.989 | 294.4 | 6.342 | 178.3 | 471 | 2.6 | 528 | 4.049 | −36.16 | 529 | 4.118 | −35.07 | 530 | 4.185 | −34.01 | 540 | 4.838 | −23.72 |
| E | 0.989 | 294.4 | 6.518 | 175.9 | 505 | 2.8 | 566 | 4.272 | −34.46 | 564 | 4.136 | −36.55 | 563 | 4.070 | −37.56 | 563 | 4.070 | −37.56 |
| F | 0.989 | 294.4 | 3.435 | 179.5 | 480 | 2.8 | 514 | 2.431 | −29.23 | 515 | 2.501 | −27.21 | 514 | 2.433 | −29.18 | 515 | 2.499 | −27.26 |
| G | 0.989 | 294.4 | 9.689 | 178.7 | 500 | 2.8 | 591 | 6.479 | −33.13 | 586 | 6.133 | −36.71 | 584 | 5.998 | −38.10 | 504 | 0.762 | −92.14 |
| H | 0.989 | 294.4 | 5.990 | 179.0 | 485 | 2.8 | 534 | 3.493 | −41.68 | 534 | 3.493 | −41.68 | 534 | 3.493 | −41.68 | 543 | 4.083 | −31.83 |
| I | 0.989 | 294.4 | 8.632 | 177.8 | 483 | 2.8 | 567 | 5.948 | −31.10 | 567 | 5.948 | −31.10 | 565 | 5.814 | −32.65 | 567 | 5.944 | −31.14 |
| J | 0.989 | 294.4 | 5.109 | 177.6 | 475 | 2.8 | 532 | 4.033 | −21.07 | 532 | 4.033 | −21.07 | 531 | 3.966 | −22.38 | 540 | 4.551 | −10.92 |
| K | 0.989 | 294.4 | 8.985 | 177.3 | 474 | 2.8 | 568 | 6.639 | −26.11 | 568 | 6.639 | −26.11 | 568 | 6.639 | −26.11 | 572 | 6.899 | −23.22 |
| Incubation Conditions | 20 Minute Incubation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jar | Ambient Pressure (atm) | Ambient Temp. (K) | Filter Area (cm2) | Container Volume (L) | Bkgrnd. CO2 (ppmv) | HCl Added (L) | CO2 Pressure (ppmv) | Moles CO2 Formed (×10−7 mol) | Carbonate Carbon Conc. (µgC/cm2) |
| C | 0.9905 | 294.5 | 4.5 | 0.1771 | 452 | 0.003 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| J | 0.9905 | 294.4 | 3.0 | 0.1776 | 449 | 0.003 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| K | 0.9905 | 294.4 | 3.0 | 0.1773 | 448 | 0.003 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| C | 0.9946 | 294.4 | 3.0 | 0.1771 | 520 | 0.003 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| J | 0.9946 | 294.4 | 3.0 | 0.1776 | 435 | 0.003 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| K | 0.9946 | 294.4 | 3.0 | 0.1773 | 434 | 0.003 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| Sample Description | Filter Area (cm2) | Carbonate Carbon Conc. (µgC/cm2) | Std. Dev. (µgC/cm2) | Number Of Replicates | Carbonate: Total Carbon (%) | Uncertainty (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM>2.5 | * | 4.4 | 0.3 | 6 | ** | ** |
| January PM>7.2 | 3 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 3 | 4.4 | 0.4 |
| January PM3-7.2 | 3 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 3 | 7.4 | 0.7 |
| January PM1.5-3 | 3 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 4 | 5.2 | 0.9 |
| January PM0.95-1.5 | 3 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 4 | 2.2 | 0.4 |
| January PM0.49-0.95 | 4.5 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 3 | 2.3 | 0.1 |
| January PM<0.49 | 6 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 3 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| April PM3-7.2 | 4.5 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 3 | 10 | 1 |
| April PM<0.49 | 6 | 3.7 | 0.2 | 3 | 5.5 | 0.4 |
| June PM<0.49 | 6 | 3.6 | 0.5 | 3 | 5.1 | 0.8 |
| October PM>7.2 | 4.5 | 3.01 | 0.06 | 3 | 5.7 | 0.3 |
| October PM3-7.2 | 4.5 | 3.0 | 0.1 | 3 | 7.1 | 0.5 |
| October PM<0.49 | 6 | 1.90 | 0.09 | 3 | 2.6 | 0.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Napolitano, D.C.; Hartnett, H.E.; Herckes, P. A Novel Method for Carbonate Quantification in Atmospheric Particulate Matter. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060661
Napolitano DC, Hartnett HE, Herckes P. A Novel Method for Carbonate Quantification in Atmospheric Particulate Matter. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(6):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060661
Chicago/Turabian StyleNapolitano, Denise C., Hilairy E. Hartnett, and Pierre Herckes. 2020. "A Novel Method for Carbonate Quantification in Atmospheric Particulate Matter" Atmosphere 11, no. 6: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060661
APA StyleNapolitano, D. C., Hartnett, H. E., & Herckes, P. (2020). A Novel Method for Carbonate Quantification in Atmospheric Particulate Matter. Atmosphere, 11(6), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060661