Changes in Intensity and Variability of Tropical Cyclones over the Western North Pacific and Their Local Impacts under Different Types of El Niños
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Weather Stations
2.2. Classification of El Niño Events
2.3. Tropical Cyclone Data
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Kriging
2.4.2. Welch’s t-Test
2.4.3. Pettitt Test
3. Analysis Results
3.1. Characteristics of TCs under Different Types of El Niños
3.1.1. Magnitude of TCs
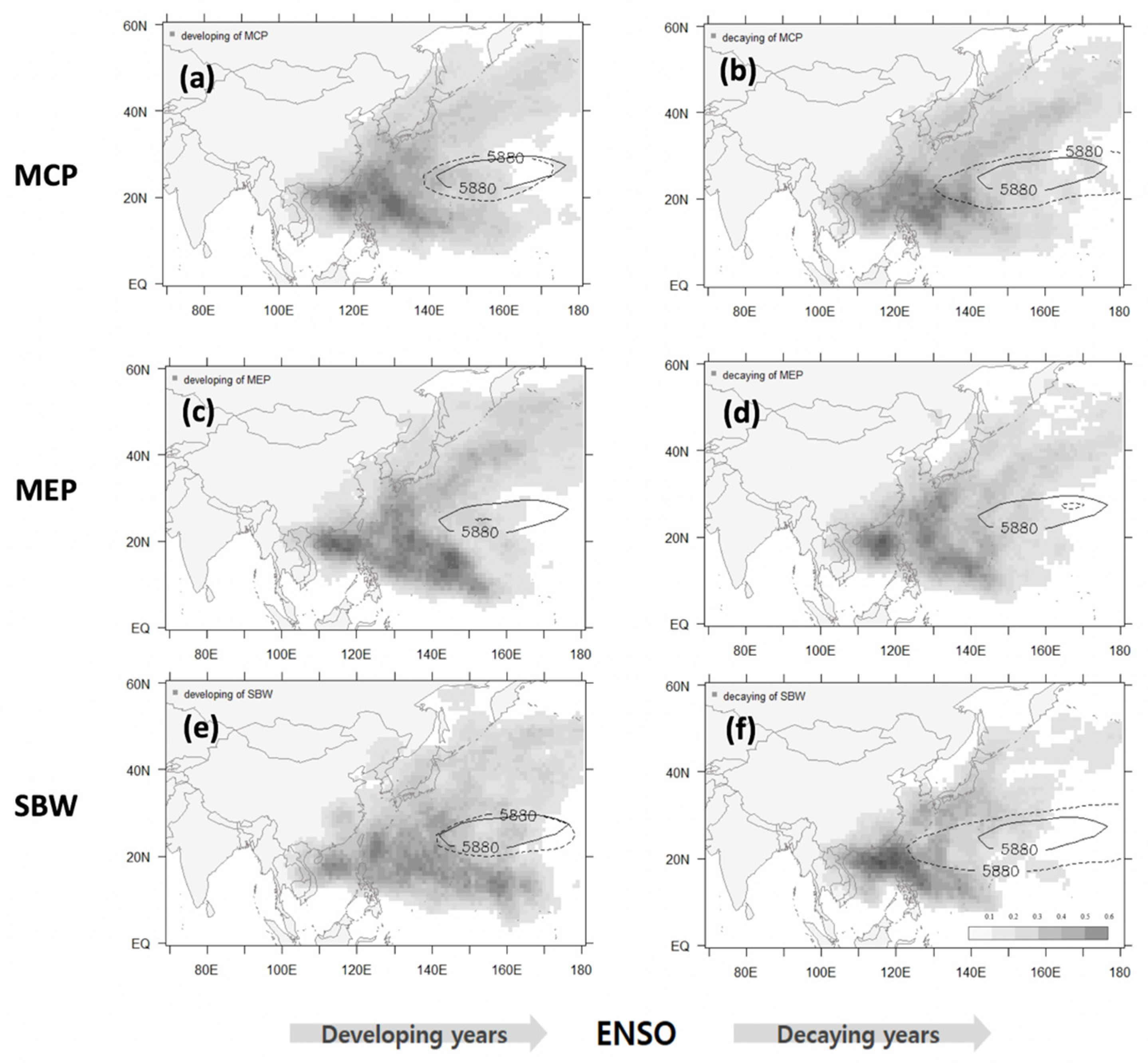
3.1.2. Genesis Positions and Tracks of TCs
3.2. TC-Induced Rainfall over China
Intensity of TC-Induced Rainfall
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, M. Tropical cyclone rainfall area controlled by relative sea surface temperature. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.-M.; Zhou, Y.P.; Wu, H.-T. Have tropical cyclones been feeding more extreme rainfall? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Bai, X.; Qi, D.; Xing, C. BMA probability quantitative precipitation forecasting of land-falling typhoons in south-east China. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 13, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, C. On the relationship between ENSO and tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific during the boreal summer. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deser, C.; Alexander, M.A.; Xie, S.-P.; Phillips, A.S. Sea surface temperature variability: Patterns and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuqiu, L.X.Y. El Niño and rainfall during the flood season (June-August) in China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1993, 51, 434–441. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Tank, A.K.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.W. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lai, Y.; Gu, X.; Shi, P.; Singh, V.P. Tropical cyclonic rainfall in China: Changing properties, seasonality, and causes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 4476–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekura, E.; Hall, T.M. A statistical model of tropical cyclone tracks in the western North Pacific with ENSO-dependent cyclogenesis. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 1725–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirata, H.; Kawamura, R. Scale interaction between typhoons and the North Pacific subtropical high and associated remote effects during the Baiu/Meiyu season. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5157–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Yi, L.; Li, T.; Chen, M.; Wan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, K. Dependence of the relationship between the tropical cyclone track and western Pacific subtropical high intensity on initial storm size: A numerical investigation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 11–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, Z.; Lu, W. Association of the poleward shift of East Asian subtropical upper-level jet with frequent tropical cyclone activities over the western North Pacific in summer. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5597–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, Z. Extreme Precipitation Experimentation over Eastern China Based on L-moment Estimation. Plateau Meteorol. 2007, 26, 012. [Google Scholar]
- Corporal-Lodangco, I.L.; Leslie, L.M.; Lamb, P.J. Impacts of ENSO on Philippine tropical cyclone activity. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1877–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Sobel, A.H. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone intensity and ENSO. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, A.J.; Soden, B.J.; Kirtman, B.P. The impact of natural and anthropogenic climate change on western North Pacific tropical cyclone tracks. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 1806–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, C.; Cao, M.; Wu, X.; Lu, S. Influence of ENSO Events on Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific. J. Ocean Univ. China 2019, 18, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.M. ENSO diversity from an atmospheric perspective. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2019, 5, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.; McPhaden, M.J.; Grimm, A.M.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Taschetto, A.S.; Garreaud, R.D.; Dewitte, B.; Poveda, G.; Ham, Y.-G.; Santoso, A. Climate impacts of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation on South America. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.-M.; Sun, W.; Cane, M.A.; Cai, W.; Yeh, S.-W.; Liu, J. Historical change of El Niño properties sheds light on future changes of extreme El Niño. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22512–22517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Ma, B.; Feng, J.; Lu, Y. Influence of the strongest central Pacific El Niño–Southern Oscillation events on the precipitation in eastern China. Int. J. Clim. 2019, 39, 3076–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, A.; Jia, S.; Yan, H.; Wang, S. El Nino-Southern Oscillation and water resources in headwaters region of the Yellow River: Links and potential for forecasting. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2010, 7, 8521–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Jain, S.; Yoon, S.-K. Warm season streamflow variability in the Korean Han River Basin: Links with atmospheric teleconnections. Int. J. Clim. 2012, 32, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Jain, S. Precipitation trends over the Korean peninsula: Typhoon-induced changes and a typology for characterizing climate-related risk. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 034033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Lin, X. Regional trends in recent precipitation indices in China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 90, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, A.; Evans, J.L. Introduction to Tropical Meteorology; Educational Material from the COMET Program; COMET MetEd: Boulder, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matheron, G. Principles of geostatistics. Econ. Geol. 1963, 58, 1246–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.D.; Zidek, J.V. Statistical Analysis of Environmental Space-Time Processes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cressie, N. The origins of kriging. Math. Geol. 1990, 22, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhomme, J.P. Kriging in the hydrosciences. Adv. Water Resour. 1978, 1, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Lin, A.; Liu, Q. The application of ordinary Kriging method in spatial interpolation. J. Jiangnan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2004, 3, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, B.L. The generalization of ‘Student’s’ problem when several different population variances are involved. Biometrika 1947, 34, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X. The Principle and Operation of Econometrics; ChongQing University Press: ChongQing, China, 2009; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K. Hydrologic Time Series Analysis: Theory and Practice; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pettitt, A.N. A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijngaard, J.B.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Können, G.P. Homogeneity of 20th century European daily temperature and precipitation series. Int. J. Clim. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 23, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadi, M.M.; Zghoul, A. A sudden change in rainfall characteristics in Amman, Jordan during the mid 1950s. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 2, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhorde, A.G.; Zarenistanak, M. Three-way approach to test data homogeneity: An analysis of temperature and precipitation series over southwestern Islamic Republic of Iran. J. Indian Geophys. Union 2013, 17, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Lohani, A.K.; Tiwari, H.L. Statistical analysis for change detection and trend assessment in climatological parameters. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.T.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Moon, Y.-I. Tropical cyclone activity in the northwestern Pacific associated with decaying Central Pacific El Ninos. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Moderate Central Pacific (MCP) | Moderate Eastern Pacific (MEP) | Strong Basin-Wide (SBW) |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Yoon, S.-K.; Kim, J.-S.; Xiong, L.; Lee, J.-H. Changes in Intensity and Variability of Tropical Cyclones over the Western North Pacific and Their Local Impacts under Different Types of El Niños. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010059
Liu Y, Yoon S-K, Kim J-S, Xiong L, Lee J-H. Changes in Intensity and Variability of Tropical Cyclones over the Western North Pacific and Their Local Impacts under Different Types of El Niños. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuhang, Sun-Kwon Yoon, Jong-Suk Kim, Lihua Xiong, and Joo-Heon Lee. 2021. "Changes in Intensity and Variability of Tropical Cyclones over the Western North Pacific and Their Local Impacts under Different Types of El Niños" Atmosphere 12, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010059
APA StyleLiu, Y., Yoon, S.-K., Kim, J.-S., Xiong, L., & Lee, J.-H. (2021). Changes in Intensity and Variability of Tropical Cyclones over the Western North Pacific and Their Local Impacts under Different Types of El Niños. Atmosphere, 12(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010059








