Assessment of GPM-Era Satellite Products’ (IMERG and GSMaP) Ability to Detect Precipitation Extremes over Mountainous Country Nepal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Manual Rain Gauge Data
2.2.2. IMERG Product
2.2.3. GSMaP Product
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Pre-Processing of Datasets
2.3.2. Statistical Evaluation Metrics
2.3.3. Extreme Precipitation Indices
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variability
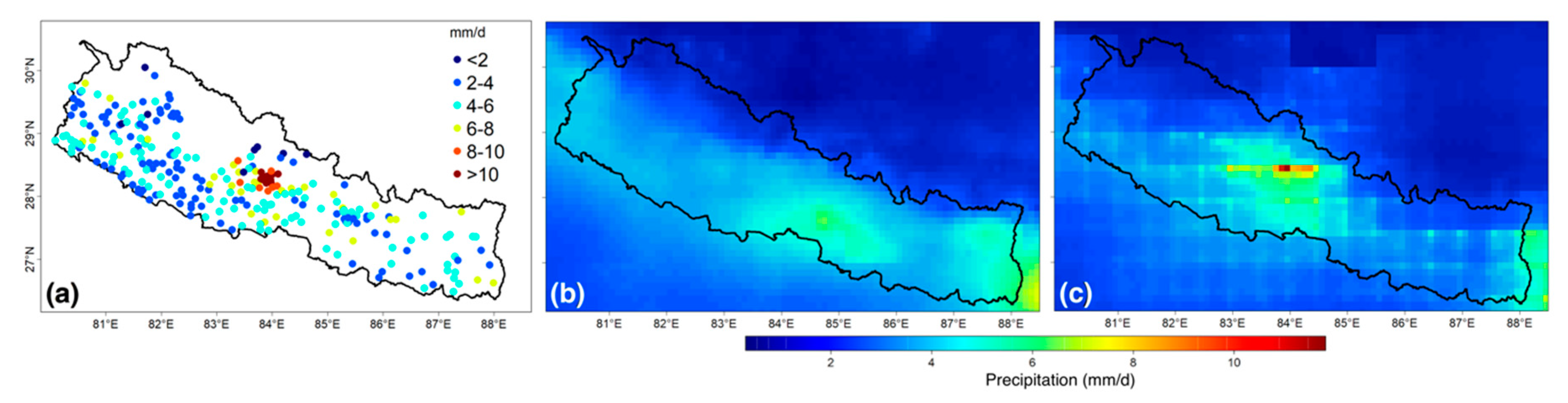
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution of Mean Annual Precipitation in Nepal
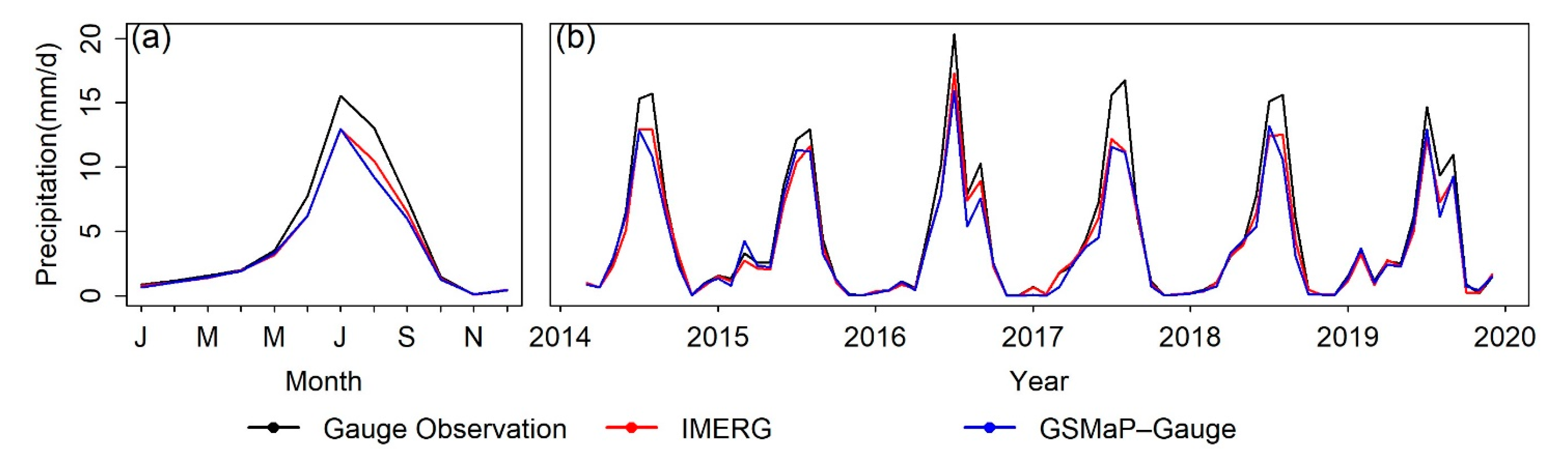
3.1.2. Monthly Precipitation Distribution
3.2. Performance Based on Daily Time Scale
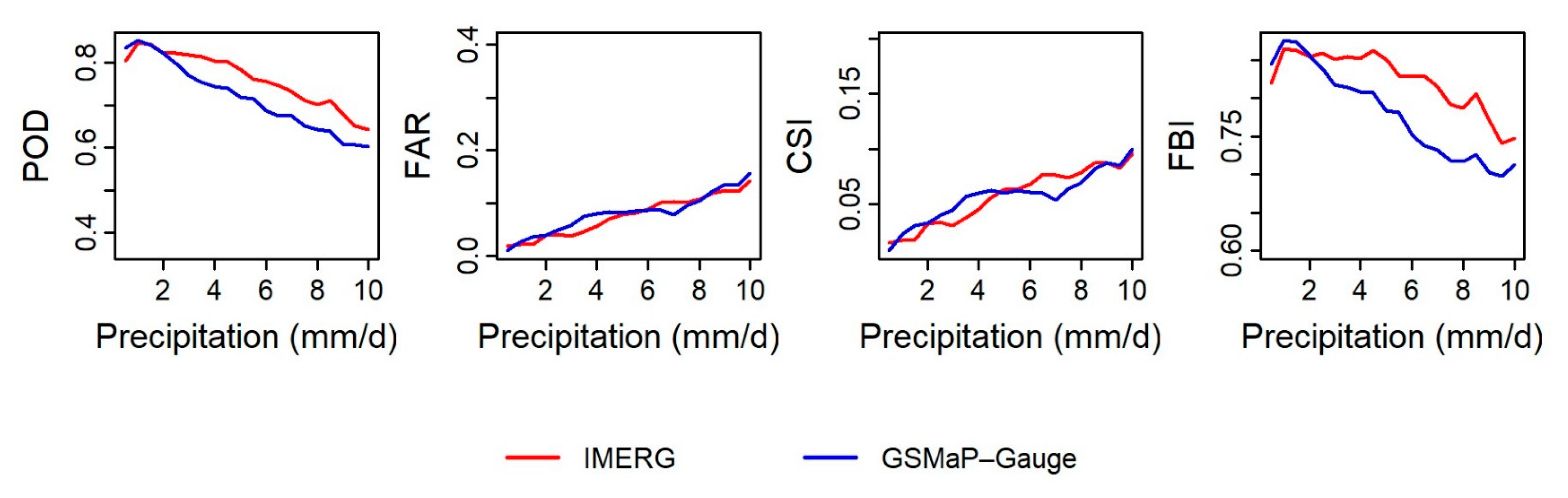
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution of Statistical Scores
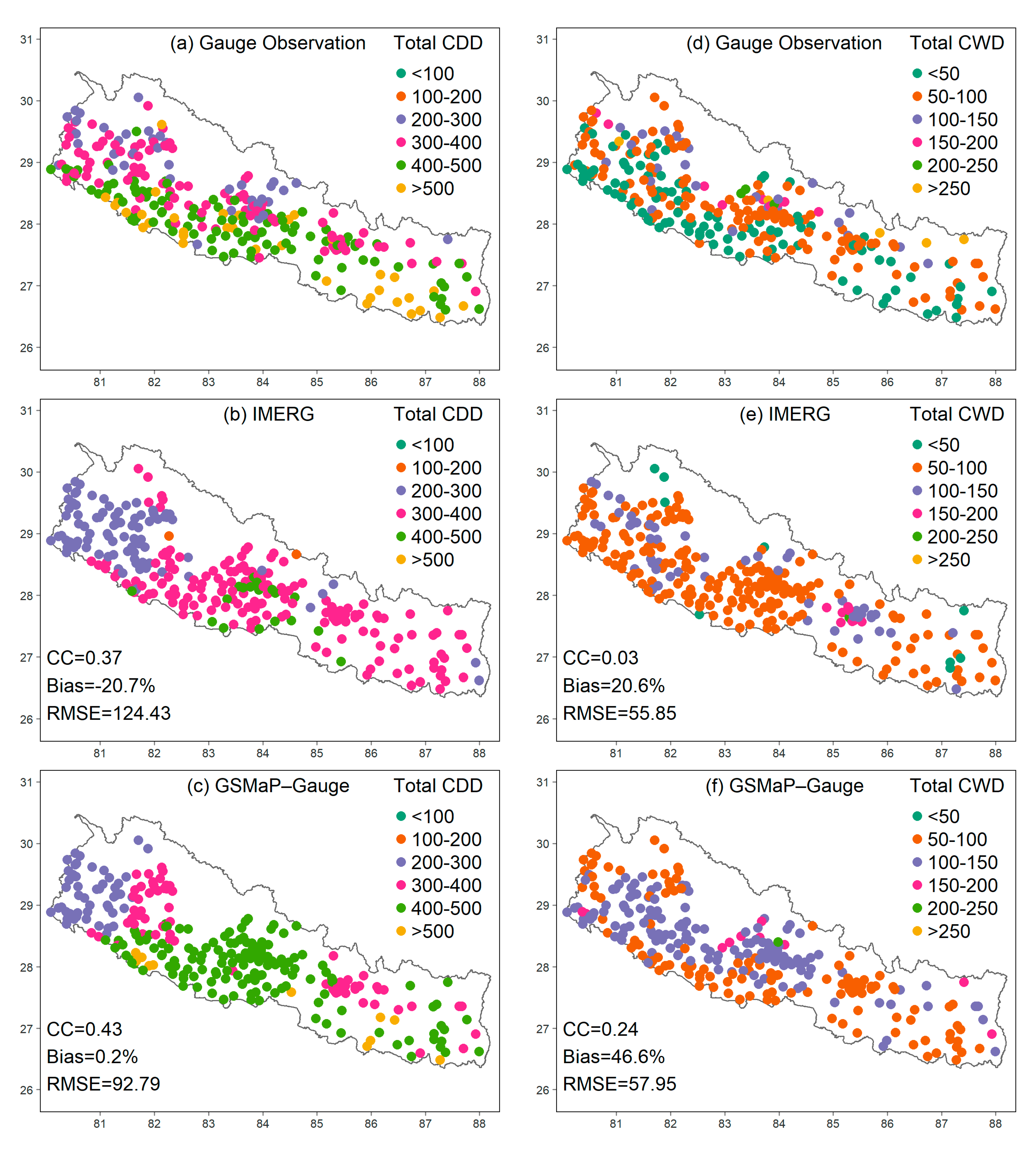
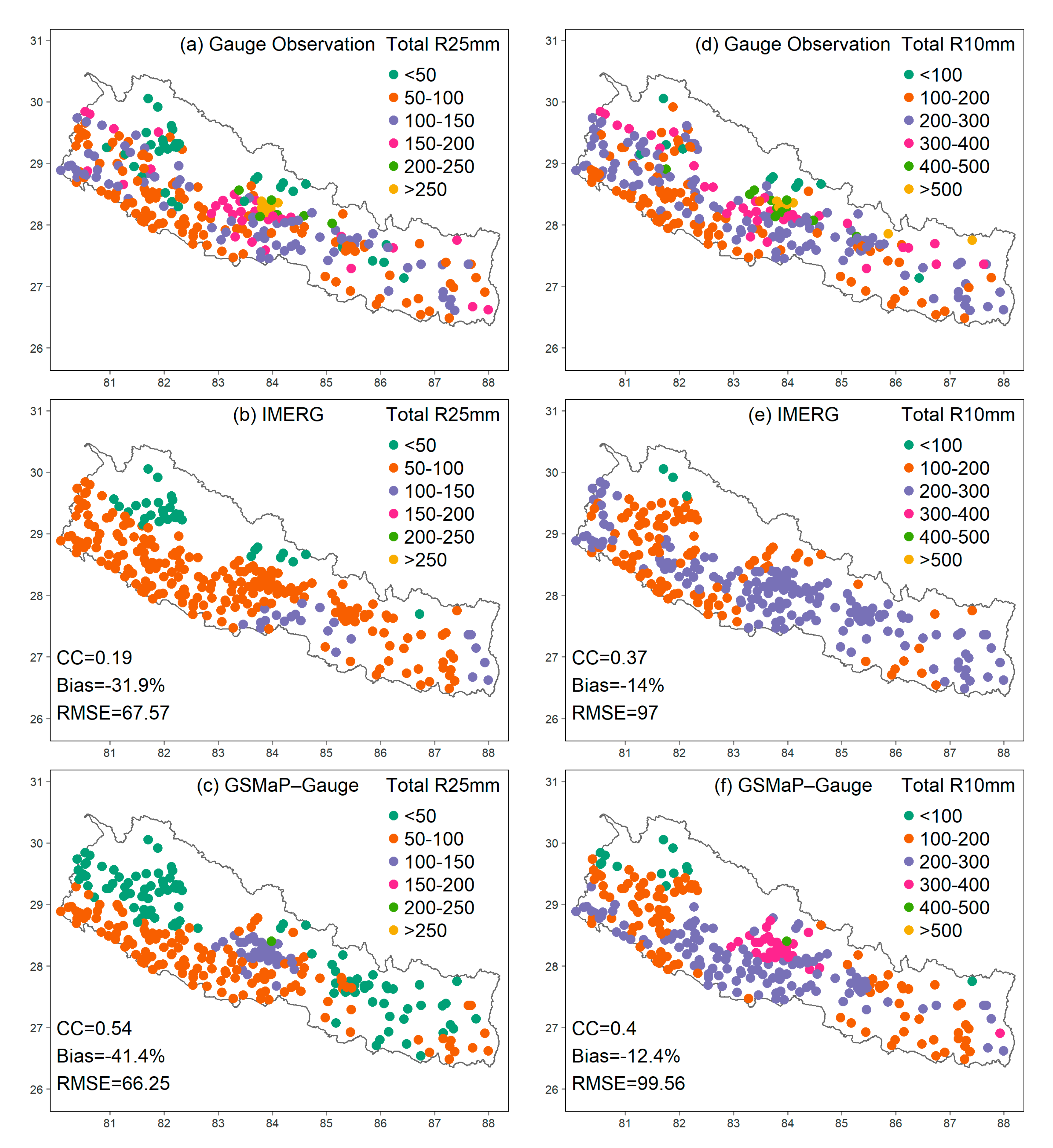
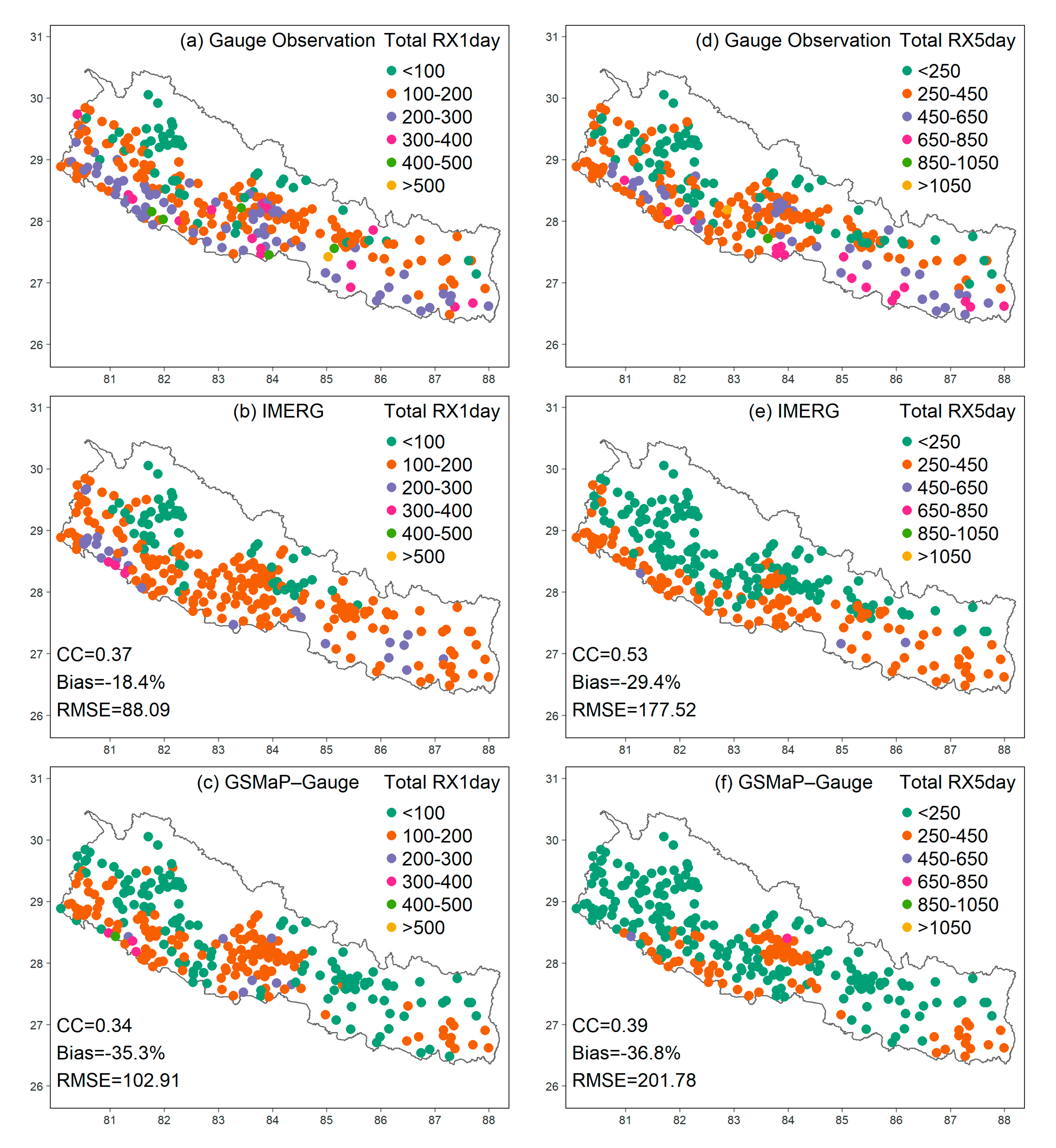
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution of Extreme Precipitation Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karki, R. Rainfall Pattern over Kathmandu Valley during Summer Monsoon Season and Its Long-Term Change; 2008; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Du, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Evaluating extreme precipitation estimations based on the GPM IMERG products over the Yangtze River Basin, China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Chandrasekar, V. Cross-validation of observations between the GPM dual-frequency precipitation radar and ground based dual-polarization radars. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangang, F.; Supari, S.; Chung, J.X.; Cruz, F.; Salimun, E.; Ngai, S.T.; Juneng, L.; Santisirisomboon, J.; Santisirisomboon, J.; Ngo-Duc, T. Future changes in annual precipitation extremes over Southeast Asia under global warming of 2 C. APN Sci. Bull. 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Besselaar, E.; Klein Tank, A.; Buishand, T. Trends in European precipitation extremes over 1951–2010. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendon, E.J.; Stratton, R.A.; Tucker, S.; Marsham, J.H.; Berthou, S.; Rowell, D.P.; Senior, C.A. Enhanced future changes in wet and dry extremes over Africa at convection-permitting scale. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Schickhoff, U.; Scholten, T.; Böhner, J. Rising precipitation extremes across Nepal. Climate 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, U.; Rajeevan, M. Trends in Precipitation Extremes over India; National Climate Centre, India Meteorological Department: Mausam Bhavan, Lodhi Road, New Delhi, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S. Trends in extreme rainfall events of Bangladesh. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 104, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Tsiang, M.; Rajaratnam, B.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Precipitation extremes over the continental United States in a transient, high-resolution, ensemble climate model experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7063–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talchabhadel, R.; Karki, R.; Thapa, B.R.; Maharjan, M.; Parajuli, B. Spatio-temporal variability of extreme precipitation in Nepal. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4296–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, B.; Wang, S.Y.S.; Meyer, J.; Marahatta, S.; Nepal, B.; Chikamoto, Y.; Gillies, R. The east–west division of changing precipitation in Nepal. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 3348–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Anagnostou, E.N. Estimating extreme precipitation using multiple satellite-based precipitation products. In Extreme Hydroclimatic Events and Multivariate Hazards in a Changing Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2019; pp. 163–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, C.; Huffman, G. Global precipitation measurement. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Todd, M.; Hulme, M.; Jones, P. Precipitation measurements and trends in the twentieth century. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 21, 1889–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansakar, S.R.; Hannah, D.M.; Gerrard, J.; Rees, G. Spatial pattern in the precipitation regime of Nepal. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.M.; Biggs, E.M. Assessing the accuracy and applied use of satellite-derived precipitation estimates over Nepal. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Khadka, N.; Hamal, K.; Shrestha, D.; Talchabhadel, R.; Chen, Y. How accurately can satellite products (TMPA and IMERG) detect precipitation patterns, extremities, and drought across the Nepalese Himalaya? Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Neilson, R.P.; Phillips, D.L. A statistical-topographic model for mapping climatological precipitation over mountainous terrain. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, E.; Steinacker, R.; Saghafian, B. Assessment of GPM-IMERG and Other Precipitation Products against Gauge Data under Different Topographic and Climatic Conditions in Iran: Preliminary Results. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, E.Z.X.; Jaafar, W.Z.W.; Lai, S.H.; Othman, F.; Elshafie, A.; Islam, T.; Srivastava, P.; Hadi, H.S.O. Evaluation of bias-adjusted satellite precipitation estimations for extreme flood events in Langat river basin, Malaysia. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 51, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Xia, J.; Zou, L. Evaluation of Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products and Their Ability in Capturing the Characteristics of Extreme Climate Events over the Yangtze River Basin, China. Water 2020, 12, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Maidment, R.; Tadesse, T.; Gadain, H.; Ceccato, P. Validation of the CHIRPS satellite rainfall estimates over eastern Africa. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed imagery using an artificial neural network cloud classification system. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1834–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yarosh, Y.; Love, T.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A. A REAL-TIME DAILY PRECIPITATION ANALYSIS OVER SOUTH ASIA. In Proceedings of the Preprints of the 16th Conference of Hydrology, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) technical documentation. Tech. Doc. NASA GSFC 2015, 612, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Ushio, T.; Okamoto, K.i.; Iguchi, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iwanami, K.; Aonashi, K.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Kubota, T.; Inoue, T. The global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP) project. In Aqua (AMSR-E) 2003; National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sapiano, M.; Arkin, P. An intercomparison and validation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates with 3-hourly gauge data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Anagnostou, E.; Berne, A.; Borga, M.; Boudevillain, B.; Buytaert, W.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, H.; Delrieu, G.; Hsu, Y.C. Evaluation of GPM-era Global Satellite Precipitation Products over Multiple Complex Terrain Regions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunilkumar, K.; Yatagai, A.; Masuda, M. Preliminary evaluation of GPM-IMERG rainfall estimates over three distinct climate zones with APHRODITE. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.; Ropelewski, C. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Yilmaz, K.K. Evaluation of multiple satellite-based precipitation products over complex topography. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Hossain, F. Understanding the dependence of satellite rainfall uncertainty on topography and climate for hydrologic model simulation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, G.W.; Krajewski, W.F. Satellite estimation of precipitation over land. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1996, 41, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D. A global map of uncertainties in satellite-based precipitation measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 24407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Barella-Ortiz, A. A nonparametric statistical technique for combining global precipitation datasets: Development and hydrological evaluation over the Iberian Peninsula. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1371–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Yang, F.; Biswas, N.K.; Rahat, S.H.; Neelam, T.J. Machine learning-based error modeling to improve GPM IMERG precipitation product over the brahmaputra river basin. Forecasting 2020, 2, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Anagnostou, E.; Kalogiros, J.; Anagnostou, M.N. Modeling Level 2 Passive Microwave Precipitation Retrieval Error Over Complex Terrain Using a Nonparametric Statistical Technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Guo, S.; Gu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.-Y. Blending multi-satellite, atmospheric reanalysis and gauge precipitation products to facilitate hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2020, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wei, M.; Tang, G.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation and correction of the TRMM 3B43V7 and GPM 3IMERGM satellite precipitation products by use of ground-based data over Xinjiang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. Evaluation and hydrological utility of the latest GPM IMERG V5 and GSMaP V7 precipitation products over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.K.; Hogue, T.S.; Hsu, K.-l.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V.; Wagener, T. Intercomparison of rain gauge, radar, and satellite-based precipitation estimates with emphasis on hydrologic forecasting. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Hou, A.; Smith, E.; Bringi, V.; Rutledge, S.; Gorgucci, E.; Petersen, W.; Jackson, G.S. Potential role of dual-polarization radar in the validation of satellite precipitation measurements: Rationale and opportunities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1127–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Khairul, I.M.; Mastrantonas, N.; Rasmy, M.; Koike, T.; Takeuchi, K. Inter-Comparison of Gauge-Corrected Global Satellite Rainfall Estimates and Their Applicability for Effective Water Resource Management in a Transboundary River Basin: The Case of the Meghna River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Comparison of Integrated Multisatellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) and TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Monthly Precipitation Products: Initial Results. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Niu, X.; Hu, X.; Khadka, N. Evaluation of GPM-Era Satellite Precipitation Products on the Southern Slopes of the Central Himalayas Against Rain Gauge Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yuan, F.; Shi, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Ren, L.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Statistical Evaluation of the Latest GPM-Era IMERG and GSMaP Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yellow River Source Region. Water 2020, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Mitra, A.K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Liu, Z.; Norouzi, H.; Pai, D. A preliminary assessment of GPM-based multi-satellite precipitation estimates over a monsoon dominated region. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Clark, M.P.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Ma, Z.; Hong, Y. Have satellite precipitation products improved over last two decades? A comprehensive comparison of GPM IMERG with nine satellite and reanalysis datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Hong, Y.E.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Petersen, W.A.; Xue, X.; Schwaller, M.R. To what extent is the day 1 GPM IMERG satellite precipitation estimate improved as compared to TRMM TMPA-RT? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsotas, N.; Anagnostou, E.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Kallos, G. Investigating satellite precipitation uncertainty over complex terrain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5346–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.K.; Kumar, T.L.; Rao, K.K.; Barbosa, H.; Rao, V.B. A new perspective in understanding rainfall from satellites over a complex topographic region of India. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, X. Evaluation of IMERG and TRMM 3B43 monthly precipitation products over mainland China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yong, B. Quasi-Global Evaluation of IMERG and GSMaP Precipitation Products over Land Using Gauge Observations. Water 2020, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Talchabhadel, R.; Aalto, J.; Baidya, S.K. New climatic classification of Nepal. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayava, J.L. Rainfall in Nepal. Himal. Rev. 1980, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Hamal, K.; Khadka, N.; Joshi, B.B. Dominant pattern of year-to-year variability of summer precipitation in Nepal during 1987–2015. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 142, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamal, K.; Sharma, S.; Baniya, B.; Khadka, N.; Zhou, X. Inter-annual variability of Winter Precipitation coupled with ocean-atmospheric patterns over Nepal during 1987-2015. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.; Ghimire, S.K.; Chen, X.; Thakuri, S.; Hamal, K.; Shrestha, D.; Sharma, S. Dynamics of Maximum Snow Cover Area and Snow Line Altitude Across Nepal (2003-2018) Using Improved MODIS Data. J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talchabhadel, R.; Karki, R.; Parajuli, B. Intercomparison of precipitation measured between automatic and manual precipitation gauge in Nepal. Measurement 2017, 106, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, F. User Manual; RClimDex 1.0; Climate Research Branch Environment: Downsview, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Chan, R. Introduction to RClimDex; Climate Research Division Environment Canada: Downsview, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, A.; Kakar, R.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K. Global precipitation map using satellite-borne microwave radiometers by the GSMaP project: Production and validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Ushio, T.; Iguchi, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iwanami, K. The global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP) project. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2005. IGARSS′05, Seoul, Korea, 29 July 2005; pp. 3414–3416. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Kachi, M.; Arai, Y.; Tashima, T.; Masaki, T.; Kawamoto, N. Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) products in the GPM era. In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.K.; Shige, S.; Yu, C.-K.; Cheng, L.-W. Further improvement of the heavy orographic rainfall retrievals in the GSMaP algorithm for microwave radiometers. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Sasashige, K.; Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Okamoto, K.i.; Aonashi, K.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Kachi, M. A Kalman filter approach to the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) from combined passive microwave and infrared radiometric data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2009, 87, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Performance of three reanalysis precipitation datasets over the qinling-daba mountains, eastern fringe of tibetan plateau, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidas, H. Validation of satellite rainfall products over Greece. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, S.R.; Palash, W.; Shrestha, M.S.; Khadgi, V.R.; Duo, C.; Das, P.J.; Dorji, C. Systematic evaluation of satellite-based rainfall products over the Brahmaputra Basin for hydrological applications. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Liu, X. Evaluation of five satellite-based precipitation products in two gauge-scarce basins on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Tank, A.K.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.W. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Luo, P.; Hu, M.; Alias, N.E.; Nover, D. Changes of precipitation amounts and extremes over Japan between 1901 and 2012 and their connection to climate indices. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2273–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sharma, S.; Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Niu, X.; Hu, X.; Khadka, N. Spatial performance of multiple reanalysis precipitation datasets on the southern slope of central Himalaya. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. IMERG V06: Changes to the Morphing Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019, 36, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.L.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Gourley, J.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Hydrologic evaluation of Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis standard precipitation products in basins beyond its inclined latitude band: A case study in Laohahe basin, China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; Takara, K.; Kubota, T.; Bajracharya, S. Verification of GSMaP rainfall estimates over the central Himalayas. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 (Hydraul. Eng.) 2011, 67, I_37–I_42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Song, F.; Udmale, P.; Jin, J.; Thapa, B.R.; Ishidaira, H. Error analysis and evaluation of the latest GSMap and IMERG precipitation products over Eastern China. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Kummerow, C.D. Precipitation-top heights of heavy orographic rainfall in the Asian monsoon region. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 3009–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; García-Ortega, E.; Merino, A.; Sánchez, J.L. Extreme Events of Precipitation over Complex Terrain Derived from Satellite Data for Climate Applications: An Evaluation of the Southern Slopes of the Pyrenees. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Hamouda, M.A.; Mahmoud, M.T.; Mohamed, M.M. Performance of GPM-IMERG precipitation products under diverse topographical features and multiple-intensity rainfall in an arid region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Ishidaira, H. Assessment of the latest GPM-Era high-resolution satellite precipitation products by comparison with observation gauge data over the Chinese mainland. Water 2016, 8, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Datasets | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Coverage | Time Span | Study Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge | Point | Daily | 279 stations | 13 March 2014 to 31 December 2019 | |
| IMERG-V06 | 0.1° × 0.1° | Half-hourly | 60° N–60° S | June 2000 to present | |
| GSMaP-Gauge (V7) | 0.1° × 0.1° | Hourly | 60° N–60° S | 1 March 2014 to present |
| Statistical Index | Equations | Perfect Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson correlation coefficient (CC) | 1 | |
| Relative bias (RB) | 0 | |
| Root mean square error (RMSE) | 0 | |
| Kling Gupta efficiency (KGE) | 1 | |
| Probability of detection | 1 | |
| False alarm ratio | 0 | |
| Critical success index | 1 | |
| Frequency bias index | 1 |
| Class | Index ID | Index Name | Index Definition | Index Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute Indices | RX1day | Max 1-day precipitation amount | Annual maximum 1-day precipitation | mm |
| RX5day | Max 5-day precipitation amount | Annual maximum consecutive 5-day precipitation | mm | |
| Threshold Indices | R10 | Number of heavy precipitation days | Annual count of days when precipitation is ≥10 mm | Days |
| R25 | Number of extreme precipitation days | Annual count of days when precipitation is ≥25 mm | Days | |
| Duration Indices | CDD | Consecutive dry days | Maximum number of consecutive dry days (precipitation <1 mm) | Days |
| CWD | Consecutive wet days | Maximum number of consecutive wet days (precipitation ≥1 mm) | Days |
| SRE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge-Observed | No-rain | Rain | |
| No-rain | Q1 | Q2 | |
| Rain | Q3 | Q4 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nepal, B.; Shrestha, D.; Sharma, S.; Shrestha, M.S.; Aryal, D.; Shrestha, N. Assessment of GPM-Era Satellite Products’ (IMERG and GSMaP) Ability to Detect Precipitation Extremes over Mountainous Country Nepal. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020254
Nepal B, Shrestha D, Sharma S, Shrestha MS, Aryal D, Shrestha N. Assessment of GPM-Era Satellite Products’ (IMERG and GSMaP) Ability to Detect Precipitation Extremes over Mountainous Country Nepal. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020254
Chicago/Turabian StyleNepal, Bikash, Dibas Shrestha, Shankar Sharma, Mandira Singh Shrestha, Deepak Aryal, and Nitesh Shrestha. 2021. "Assessment of GPM-Era Satellite Products’ (IMERG and GSMaP) Ability to Detect Precipitation Extremes over Mountainous Country Nepal" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020254
APA StyleNepal, B., Shrestha, D., Sharma, S., Shrestha, M. S., Aryal, D., & Shrestha, N. (2021). Assessment of GPM-Era Satellite Products’ (IMERG and GSMaP) Ability to Detect Precipitation Extremes over Mountainous Country Nepal. Atmosphere, 12(2), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020254








