Evaluating the Forecast Skill of a Hydrometeorological Modelling System in Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Hydrometeorological System
2.1. Atmospheric Model Setup
2.2. Hydrological Model Setup
2.3. Hydraulic–Hydrodynamic Model Setup
3. Evaluation Methodology
- A: model forecast and measurement exceeded the threshold.
- B: model forecast exceeded the threshold but measurement did not.
- C: model forecast did not reach the threshold but measurement exceeded it.
- D: model forecast and measurement did not reach the threshold.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of Precipitation and River Water Level Forecast Skill for the 4-Year Period
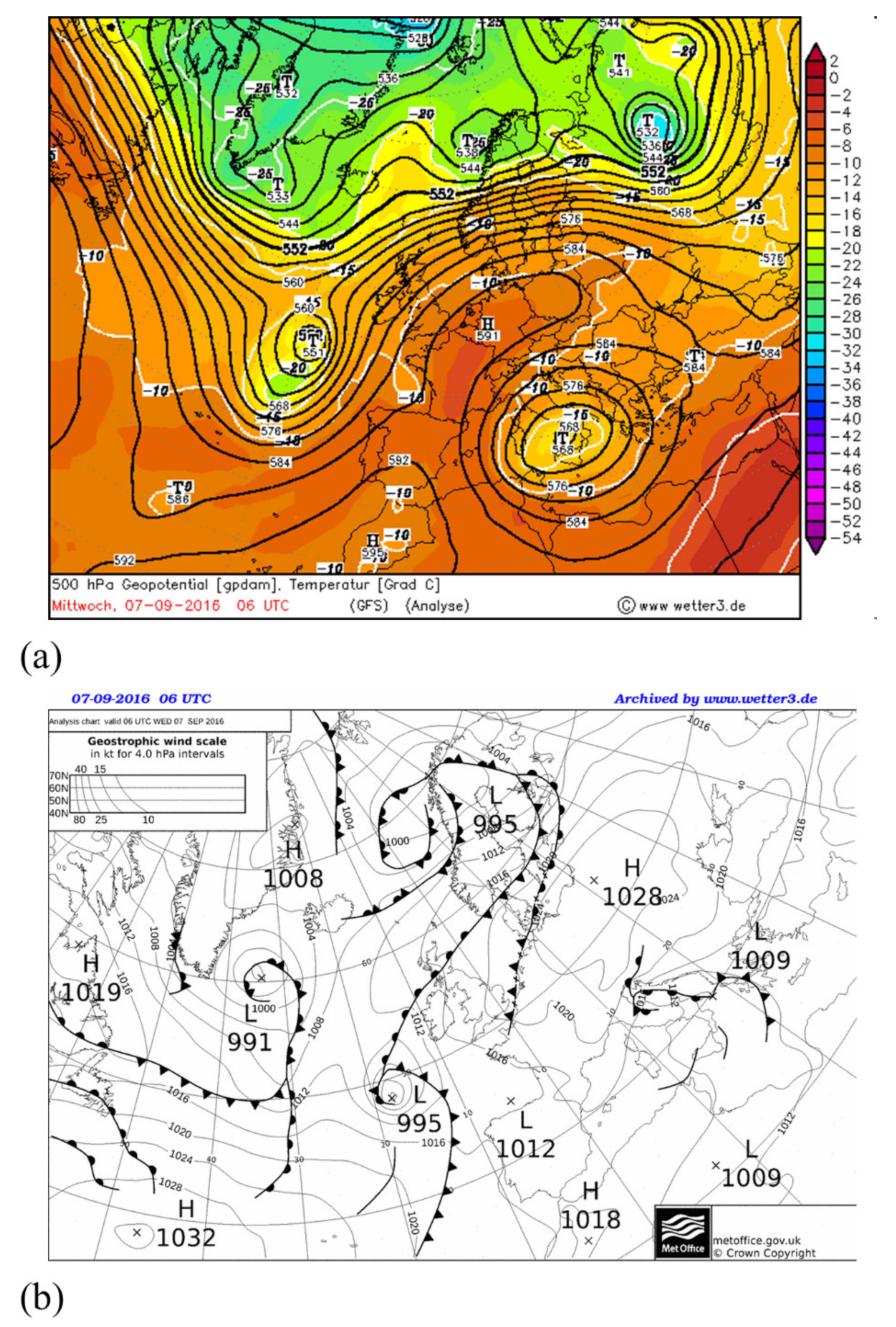
4.2. Evaluation of Flash Flood Forecast Skill: The Case of 7 September 2016, Evrotas River
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods. Nature 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghuijs, W.R.; Aalbers, E.E.; Larsen, J.R.; Trancoso, R.; Woods, R.A. Recent changes in extreme floods across multiple continents. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 114035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F. Ensemble flood forecasting: A review. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, D.R. Conceptual Framework for the National Flood Interoperability Experiment. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaros, C.; Galanaki, E.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Oikonomou, C.; Haralambous, H.; Giannaros, T.M. Pre-Operational Application of a WRF-Hydro-Based Fluvial Flood Forecasting System in the Southeast Mediterranean. Forecasting 2021, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerton, R.E.; Stephens, E.M.; Pappenberger, F.; Pagano, T.C.; Weerts, A.H.; Wood, A.W.; Salamon, P.; Brown, J.D.; Hjerdt, N.; Donnelly, C.; et al. Continental and global scale flood forecasting systems. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2016, 3, 391–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfieri, L.; Burek, P.; Dutra, E.; Krzeminski, B.; Muraro, D.; Thielen, J.; Pappenberger, F. GloFAS-global ensemble streamflow forecasting and flood early warning. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emerton, R.; Zsoter, E.; Arnal, L.; Cloke, H.L.; Muraro, D.; Prudhomme, C.; Stephens, E.M.; Salamon, P.; Pappenberger, F. Developing a global operational seasonal hydro-meteorological forecasting system: GloFAS-Seasonal v1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 3327–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viterbo, F.; Mahoney, K.; Read, L.; Salas, F.; Bates, B.; Elliott, J.; Cosgrove, B.; Dugger, A.; Gochis, D.; Cifelli, R. A multiscale, hydrometeorological forecast evaluation of national water model forecasts of the may 2018 Ellicott City, Maryland, Flood. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochis, D.; Yu, W.; Yates, D. WRF-Hydro Technical Description and User’s Guide The NCAR WRF-Hydro Technical Description and User’s Guide; NCAR: Boulder, CO, US, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholmes, J.C.; Thielen, J.; Ramos, M.H.; Gentilini, S. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences The European Flood Alert System EFAS-Part 2: Statistical Skill Assessment of Probabilistic and Deterministic Operational Forecasts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thielen, J.; Bartholmes, J.; Ramos, M.H.; De Roo, A. The European flood alert system–Part 1: Concept and development. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darras, T.; Borrell Estupina, V.; Kong-A-Siou, L.; Vayssade, B.; Johannet, A.; Pistre, S. Identification of spatial and temporal contributions of rainfalls to flash floods using neural network modelling: Case study on the Lez basin (southern France). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4397–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llasat, M.C.; Marcos, R.; Turco, M.; Gilabert, J.; Llasat-Botija, M. Trends in flash flood events versus convective precipitation in the Mediterranean region: The case of Catalonia. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avolio, E.; Cavalcanti, O.; Furnari, L.; Senatore, A.; Mendicino, G. Brief communication: Preliminary hydro-meteorological analysis of the flash flood of 20 August 2018 in Raganello Gorge, southern Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrucci, O.; Aceto, L.; Bianchi, C.; Bigot, V.; Brázdil, R.; Pereira, S.; Kahraman, A.; Kiliç, Ö.; Kotroni, V.; Llasat, M.C.; et al. Flood fatalities in Europe, 1980-2018: Variability, features, and lessons to learn. Water 2019, 11, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varlas, G.; Anagnostou, M.N.; Spyrou, C.; Papadopoulos, A.; Kalogiros, J.; Mentzafou, A.; Michaelides, S.; Baltas, E.; Karymbalis, E.; Katsafados, P. A multi-platform hydrometeorological analysis of the flash flood event of 15 November 2017 in Attica, Greece. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papaioannou, G.; Varlas, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Loukas, A.; Katsafados, P.; Dimitriou, E. Investigating sea-state effects on flash flood hydrograph and inundation forecasting. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Deligiannakis, G.; Andreadakis, E.; Katsetsiadou, K.N.; Spyrou, N.I.; Gogou, M.E. How different surrounding environments influence the characteristics of flash flood-mortality: The case of the 2017 extreme flood in Mandra, Greece. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, e12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Boufidis, N.; Grau, J.; Andreadakis, E.; Stamos, I. A systematic assessment of the effects of extreme flash floods on transportation infrastructure and circulation: The example of the 2017 Mandra flood. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 47, 101542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Andreadakis, E.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Spyrou, N.; Gogou, M.; Deligiannakis, G.; Katsetsiadou, N.; Antoniadis, Z.; Melaki, M.; Georgakopoulos, A.; et al. An integrated approach of ground and aerial observations in flash flood disaster investigations. The case of the 2017 Mandra flash flood in Greece. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 33, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrou, C.; Varlas, G.; Pappa, A.; Mentzafou, A.; Katsafados, P.; Papadopoulos, A.; Anagnostou, M.N.; Kalogiros, J. Implementation of a nowcasting hydrometeorological system for studying flash flood events: The Case of Mandra, Greece. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellos, V.; Papageorgaki, I.; Kourtis, I.; Vangelis, H.; Kalogiros, I.; Tsakiris, G. Reconstruction of a flash flood event using a 2D hydrodynamic model under spatial and temporal variability of storm. Nat. Hazards 2020, 101, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, G.; Varlas, G.; Terti, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Loukas, A.; Panagopoulos, Y.; Dimitriou, E. Flood inundation mapping at ungauged basins using coupled hydrometeorological-hydraulic modelling: The catastrophic case of the 2006 Flash Flood in Volos City, Greece. Water 2019, 11, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giannaros, C.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Oikonomou, C.; Haralambous, H.; Papagiannaki, K. Hydrometeorological and socio-economic impact assessment of stream flooding in southeast mediterranean: The case of rafina catchment (Attica, Greece). Water 2020, 12, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givati, A.; Gochis, D.; Rummler, T.; Kunstmann, H. Comparing One-Way and Two-Way Coupled Hydrometeorological Forecasting Systems for Flood Forecasting in the Mediterranean Region. Hydrology 2016, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.B.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.-Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3, NCAR Technical Note TN-475+STR; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- US Army Corps of Engineers HEC-RAS River Analysis System; User’s Manual Version 4.1; US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–790.
- Jiménez, P.A.; Dudhia, J.; González-Rouco, J.F.; Navarro, J.; Montávez, J.P.; García-Bustamante, E. A revised scheme for the WRF surface layer formulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukul Tewari, N.; Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.; Mitchell, K.; Ek, M.; Gayno, G.; Wegiel, J. Implementation and verification of the unified NOAH land surface model in the WRF model (Formerly Paper Number 17.5). In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 January 2004; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Freitas, S.R. A scale and aerosol aware stochastic convective parameterization for weather and air quality modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5233–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ek, M.B.; Mitchell, K.E.; Lin, Y.; Rogers, E.; Grunmann, P.; Koren, V.; Gayno, G.; Tarpley, J.D. Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction operational mesoscale Eta model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.Y.; Saghafian, B.; Ogden, F.L. Raster-based hydrologic modeling of spatially-varied surface runoff. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1995, 31, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, F.L. CASC2D Reference Manual; Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Connecticut: Storrs, CT, USA, 1997; 106p. [Google Scholar]
- Garbrecht, J.; Brunner, G. Hydrologic Channel-Flow Routing for Compound Sections. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1991, 117, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Guevara, E.; Reuter, H.; Nelson, A. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe: Version 4. CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90m Database. Available online: https://research.utwente.nl/en/publications/hole-filled-srtm-for-the-globe-version-4-data-grid (accessed on 12 July 2021).
- Lehner, B.; Verdin, K.; Jarvis, A. New global hydrography derived from spaceborne elevation data. Eos 2008, 89, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A. Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. GSA Bull. 1952, 63, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, C.; Bruggeman, A.; Zittis, G.; Sofokleous, I.; Arnault, J. Simulation of extreme rainfall and streamflow events in small Mediterranean watersheds with a one-way-coupled atmospheric-hydrologic modelling system. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2791–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Mendicino, G.; Gochis, D.J.; Yu, W.; Yates, D.N.; Kunstmann, H. Fully coupled atmosphere-hydrology simulations for the central Mediterranean: Impact of enhanced hydrological parameterization for short and long time scales. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 1693–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Furnari, L.; Mendicino, G. Impact of high-resolution sea surface temperature representation on the forecast of small Mediterranean catchments’ hydrological responses to heavy precipitation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yucel, I.; Onen, A.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Gochis, D.J. Calibration and evaluation of a flood forecasting system: Utility of numerical weather prediction model, data assimilation and satellite-based rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozkaya, A.; Akyurek, Z. WRF-Hydro Model Application in a Data-Scarce, Small and Topographically Steep Catchment in Samsun, Turkey. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 3781–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, G.W. HEC-RAS River Analysis System, 2D Modeling User’s Manual Version 5.0; US Army Corps of Engineers–Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–171.
- Muthusamy, M.; Casado, M.R.; Butler, D.; Leinster, P. Understanding the effects of Digital Elevation Model resolution in urban fluvial flood modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, O.; Elfeki, A.; Kamis, A.S.; Chaabani, A. Dam break analysis and flood disaster simulation in arid urban environment: The Um Al-Khair dam case study, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Nat. Hazards 2020, 100, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, M.; Sofia, G.; Koukoula, M.; Lazin, R.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Shen, X.; Anagnostou, E.N. Impact of compound flood event on coastal critical infrastructures considering current and future climate. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzică, A.; Mihu-Pintilie, A.; Stoleriu, C.C.; Cîmpianu, C.I.; Huţanu, E.; Pricop, C.I.; Grozavu, A. Using 2D HEC-RAS modeling and embankment dam break scenario for assessing the flood control capacity of a multireservoir system (Ne Romania). Water 2021, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psomiadis, E.; Tomanis, L.; Kavvadias, A.; Soulis, K.X.; Charizopoulos, N.; Michas, S. Potential dam breach analysis and flood wave risk assessment using HEC-RAS and remote sensing data: A multicriteria approach. Water 2021, 13, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, G.; Vasiliades, L.; Loukas, A.; Alamanos, A.; Efstratiadis, A.; Koukouvinos, A.; Tsoukalas, I.; Kossieris, P. A flood inundation modeling approach for urban and rural areas in lake and large-scale river basins. Water 2021, 13, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, G.; Efstratiadis, A.; Vasiliades, L.; Loukas, A.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Koukouvinos, A.; Tsoukalas, I.; Kossieris, P. An operational method for Flood Directive implementation in ungauged urban areas. Hydrology 2018, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunner, G.W.; Sanchez, A.; Molls, T.; Parr, D.A. HEC-RAS Verification and Validation Tests; US Army Corps of Engineers–Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–154.
- Brunner, G.W. CEIWR-HHT Benchmarking of the HEC-RAS Two-Dimensional Hydraulic Modeling Capabilities; US Army Corps of Engineers–Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2018.
- Papaioannou, G.; Loukas, A.; Vasiliades, L.; Aronica, G.T. Flood inundation mapping sensitivity to riverine spatial resolution and modelling approach. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Matgen, P.; Cutler, M.E.J.; Black, A.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Comparison of remotely sensed water stages from LiDAR, topographic contours and SRTM. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Yao, T. Evaluation of ASTER GDEM and SRTM and their suitability in hydraulic modelling of a glacial lake outburst flood in southeast Tibet. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E. Assessing the impact of topography and land cover data resolutions on two-dimensional HEC-RAS hydrodynamic model simulations for urban flood hazard analysis. Nat. Hazards 2020, 101, 995–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, N.J.; Brandt, S.A. Flood map boundary sensitivity due to combined effects of DEM resolution and roughness in relation to model performance. Geomatics Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 1613–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunner, G. HEC-RAS River Analysis System, Hydraulic Reference Manual, Version 4.1; US Army Corps of Engineers–Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–790.
- Warner, J.C.; Brunner, G.W.; Wolfe, B.C.; Piper, S.S. HEC-RAS. River Analysis System. Applications Guide. Version 4.0; US Army Corps of Engineers–Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2008.
- Water, S.S. Flood Risk Management Plans of Eastern Peloponnese River Basin District. Flood Risk Maps. ANNEX 8—Topographic Surveys of Technical Works—Sections; Ministry of Environment and Energy (SSW-MEE): Athens, Greece, 2018.
- Laconia Live The Skala’s Bridge “Disappeared”. 2016. Available online: https://laconialive.gr/εξαφανίστηκε-η-γέφυρα-της-σκάλας/ (accessed on 12 July 2021). (In Greek).
- Laconia’s Municipal Market Newspaper Municipality of Eurota “FLOOD 2016”. 2016. Available online: http://www.dimotikiagoratislakonias.gr/epikairotita/aftodioikisi/dimoi/item/1018-dimos-evrota-plimmyra-2016 (accessed on 12 July 2021). (In Greek).
- Papadopoulos, A.; Katsafados, P. Verification of operational weather forecasts from the POSEIDON system across the Eastern Mediterranean. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soukissian, T.; Papadopoulos, A. Effects of different wind data sources in offshore wind power assessment. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 100, p. 704. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Chronis, T.G.; Anagnostou, E.N. Improving convective precipitation forecasting through assimilation of regional lightning measurements in a mesoscale model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1961–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mentzafou, A.; Varlas, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Poulis, G.; Dimitriou, E. Assessment of Automatically Monitored Water Levels and Water Quality Indicators in Rivers with Different Hydromorphological Conditions and Pollution Levels in Greece. Hydrology 2021, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsafados, P.; Papadopoulos, A.; Mavromatidis, E.; Gikas, N. Quantitative Verification Statistics of WRF Predictions over the Mediterranean Region. Available online: http://www.erasmus.hua.gr/~meteoclima/images/stories/model/12WRF2011.extabs.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2021).
- Snook, N.; Kong, F.; Brewster, K.A.; Xue, M.; Thomas, K.W.; Supinie, T.A.; Perfater, S.; Albright, B. Evaluation of convection-permitting precipitation forecast products using WRF, NMMB, and FV3 for the 2016-17 NOAA hydrometeorology testbed flash flood and intense rainfall experiments. Weather Forecast. 2019, 34, 781–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsafados, P.; Papadopoulos, A.; Korres, G.; Varlas, G. A fully coupled atmosphere-ocean wave modeling system for the Mediterranean Sea: Interactions and sensitivity to the resolved scales and mechanisms. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsafados, P.; Varlas, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Spyrou, C.; Korres, G. Assessing the Implicit Rain Impact on Sea State During Hurricane Sandy (2012). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 12015–12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlas, G.; Katsafados, P.; Papadopoulos, A.; Korres, G. Implementation of a two-way coupled atmosphere-ocean wave modeling system for assessing air-sea interaction over the Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Res. 2018, 208, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlas, G.; Spyrou, C.; Papadopoulos, A.; Korres, G.; Katsafados, P. One-year assessment of the CHAOS two-way coupled atmosphere-ocean wave modelling system over the Mediterranean and Black Seas. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2020, 21, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlas, G.; Vervatis, V.; Spyrou, C.; Papadopoulou, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Katsafados, P. Investigating the impact of atmosphere–wave–ocean interactions on a Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone. Ocean Model. 2020, 153, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlas, G.; Marinou, E.; Gialitaki, A.; Siomos, N.; Tsarpalis, K.; Kalivitis, N.; Solomos, S.; Tsekeri, A.; Spyrou, C.; Tsichla, M.; et al. Assessing sea-state effects on sea-salt aerosol modeling in the lower atmosphere using lidar and in-situ measurements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Stream Order | Manning | CBW (m) | CSS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.65 | 2 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 5 | 0.6 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 10 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.18 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 30 | 0.05 |
| 6 | 0.03 | 50 | 0.05 |
| WMO ID | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Altitude (m) | WMO ID | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16622 | 40.52 | 22.97 | 4 | 16706 | 38.33 | 26.13 | 4 |
| 16624 | 40.98 | 24.6 | 5 | 16715 | 38.1 | 23.78 | 235 |
| 16627 | 40.85 | 25.92 | 3 | 16718 | 38.07 | 23.55 | 31 |
| 16641 | 39.62 | 19.92 | 4 | 16723 | 37.7 | 26.92 | 7 |
| 16642 | 39.7 | 20.82 | 483 | 16726 | 37.07 | 22.02 | 8 |
| 16643 | 38.62 | 20.77 | 4 | 16741 | 37.92 | 23.92 | 72 |
| 16648 | 39.63 | 22.42 | 74 | 16742 | 36.78 | 27.07 | 129 |
| 16650 | 39.92 | 25.23 | 4 | 16746 | 35.48 | 24.12 | 151 |
| 16667 | 39.07 | 26.6 | 5 | 16749 | 36.4 | 28.08 | 11 |
| 16682 | 37.92 | 21.28 | 14 | 16754 | 35.33 | 25.18 | 39 |
| 16684 | 38.97 | 24.48 | 28 | 16760 | 35.18 | 25.32 | 336 |
| 16685 | 38.12 | 20.5 | 22 | 16765 | 35.52 | 27.25 | 20 |
| Event Forecast | Event Observed | |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |
| Yes | A | B |
| No | C | D |
| Hour (UTC) | Streamflow (m3 s−1) | Hour (UTC) | Streamflow (m3 s−1) | Hour (UTC) | Streamflow (m3 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 0.5 | 08 | 704.66 | 16 | 250.74 |
| 01 | 0.56 | 09 | 704.96 | 17 | 223.49 |
| 02 | 0.59 | 10 | 596.65 | 18 | 196.72 |
| 03 | 0.67 | 11 | 555.4 | 19 | 170.8 |
| 04 | 1.4 | 12 | 485.63 | 20 | 147.72 |
| 05 | 1.69 | 13 | 401.06 | 21 | 128.14 |
| 06 | 2.33 | 14 | 339.46 | 22 | 111.81 |
| 07 | 2.34 | 15 | 288.38 | 23 | 98.46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varlas, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Papaioannou, G.; Dimitriou, E. Evaluating the Forecast Skill of a Hydrometeorological Modelling System in Greece. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070902
Varlas G, Papadopoulos A, Papaioannou G, Dimitriou E. Evaluating the Forecast Skill of a Hydrometeorological Modelling System in Greece. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(7):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070902
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarlas, George, Anastasios Papadopoulos, George Papaioannou, and Elias Dimitriou. 2021. "Evaluating the Forecast Skill of a Hydrometeorological Modelling System in Greece" Atmosphere 12, no. 7: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070902
APA StyleVarlas, G., Papadopoulos, A., Papaioannou, G., & Dimitriou, E. (2021). Evaluating the Forecast Skill of a Hydrometeorological Modelling System in Greece. Atmosphere, 12(7), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070902









