Skewed and Mixture of Gaussian Distributions for Ensemble Postprocessing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
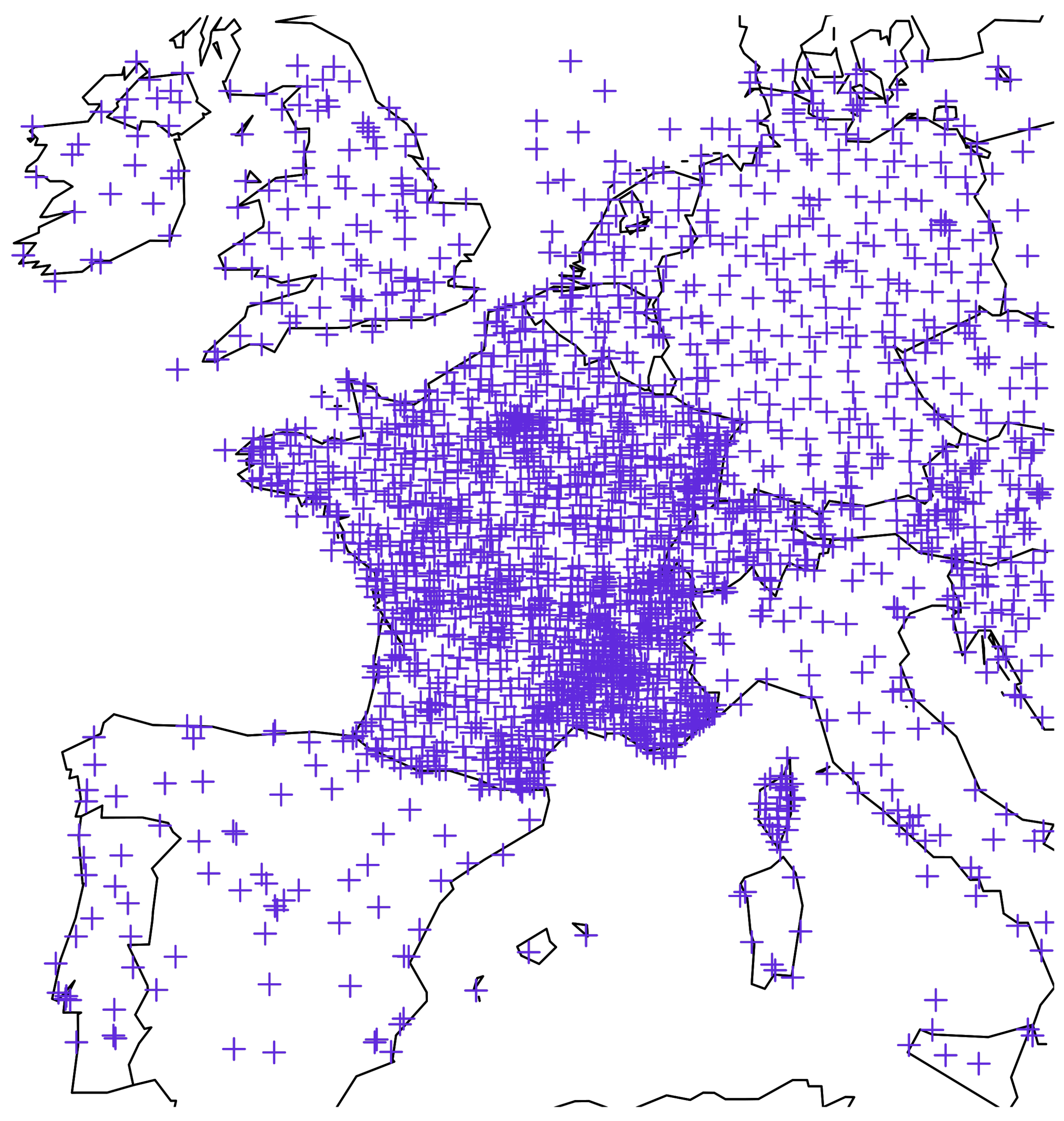
2. Data and Methods
2.1. European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Ensemble
2.2. Ensemble Model Output Statistics
2.2.1. Gaussian EMOS
2.2.2. The Skew Normal Distribution for EMOS
2.2.3. Mixture Distributions for EMOS
2.2.4. Training, Tuning, and Link Functions
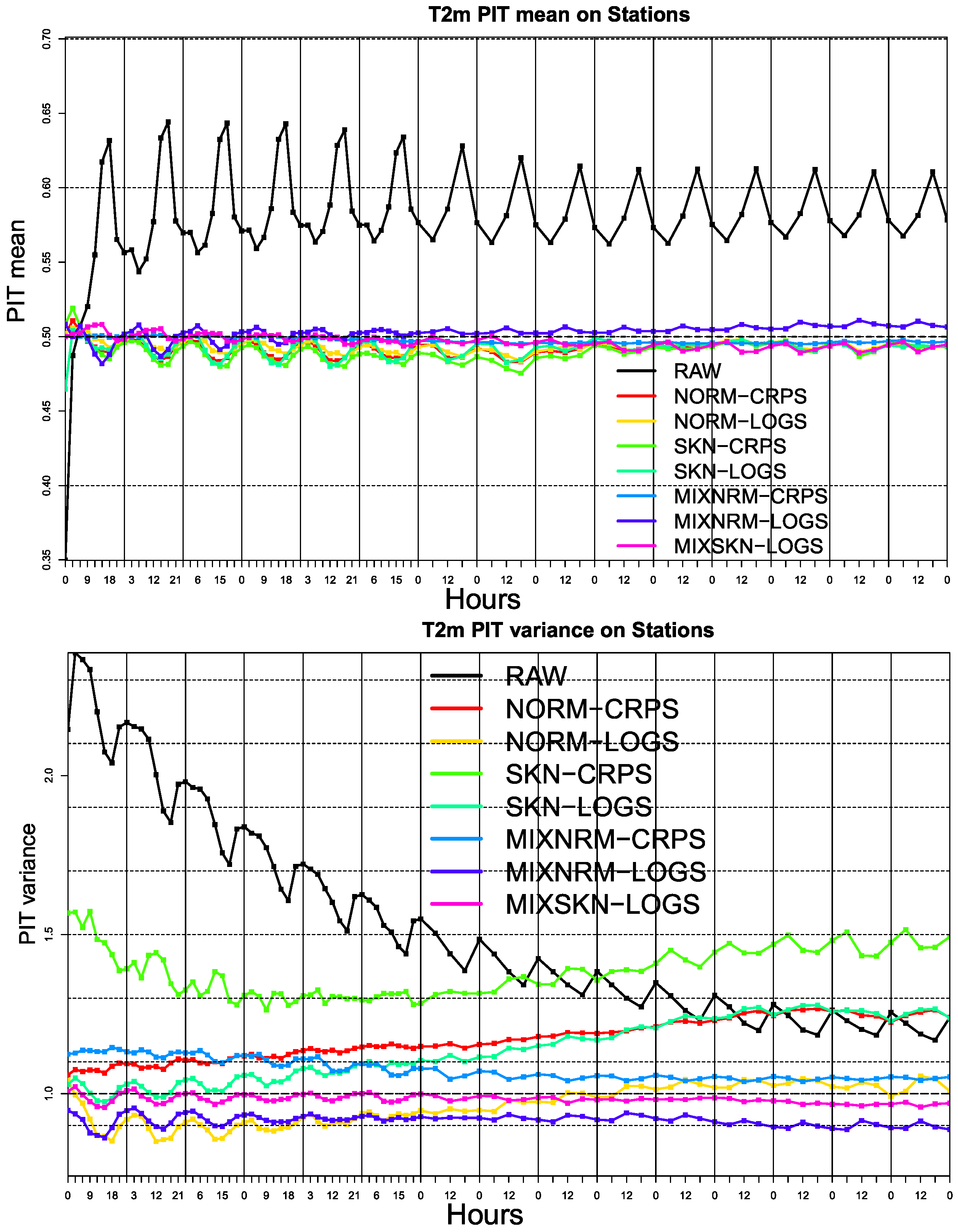
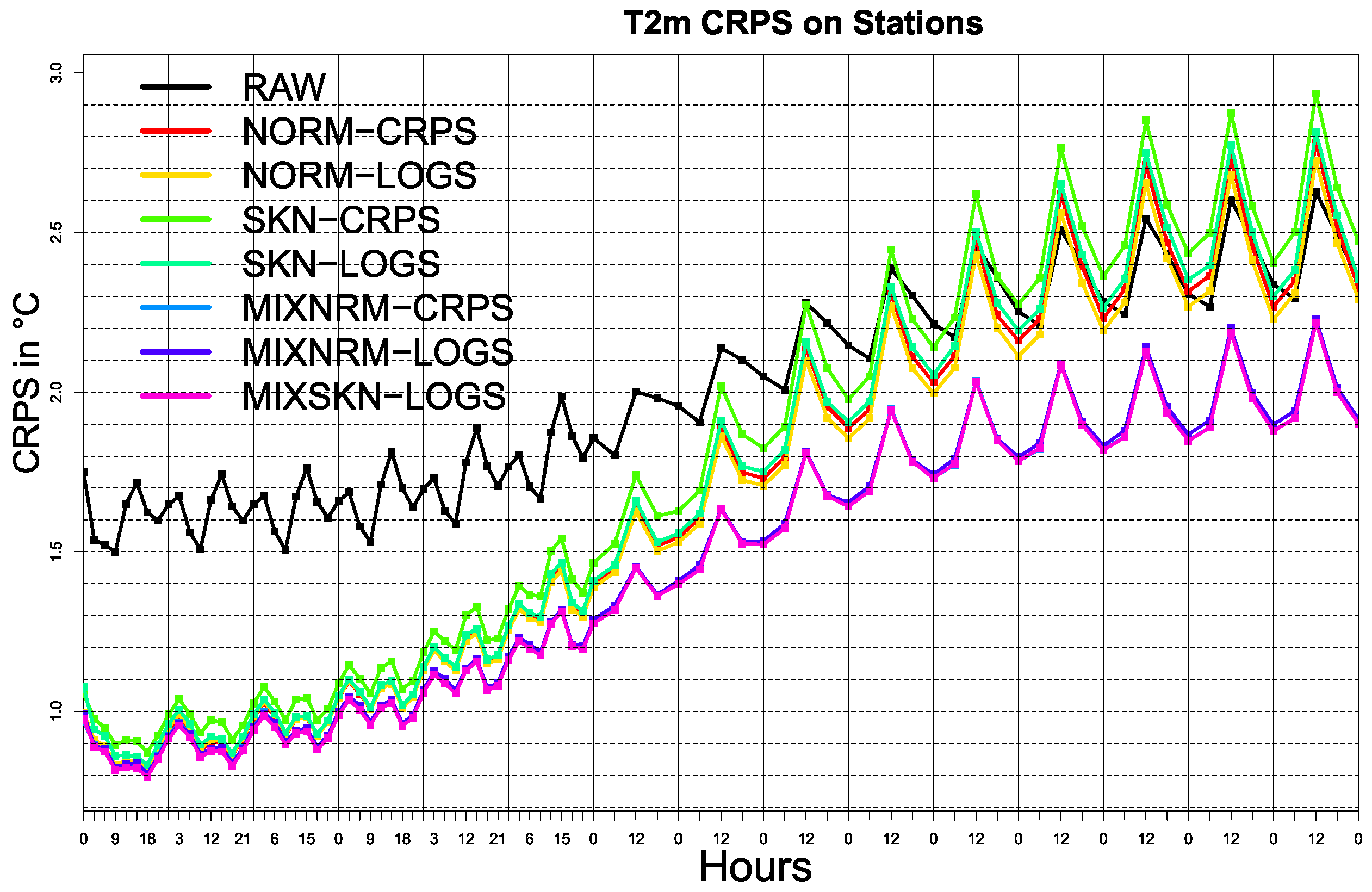
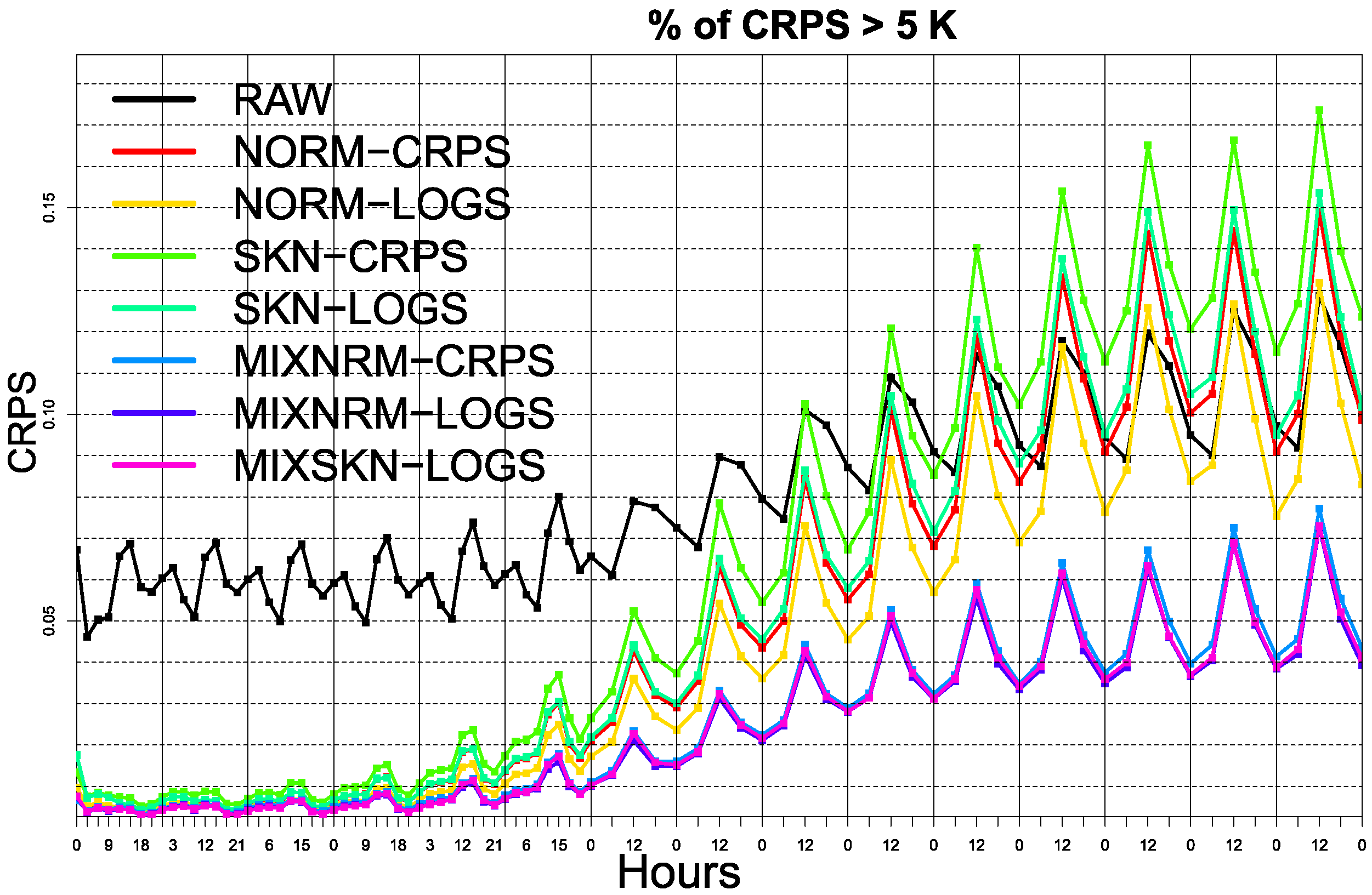
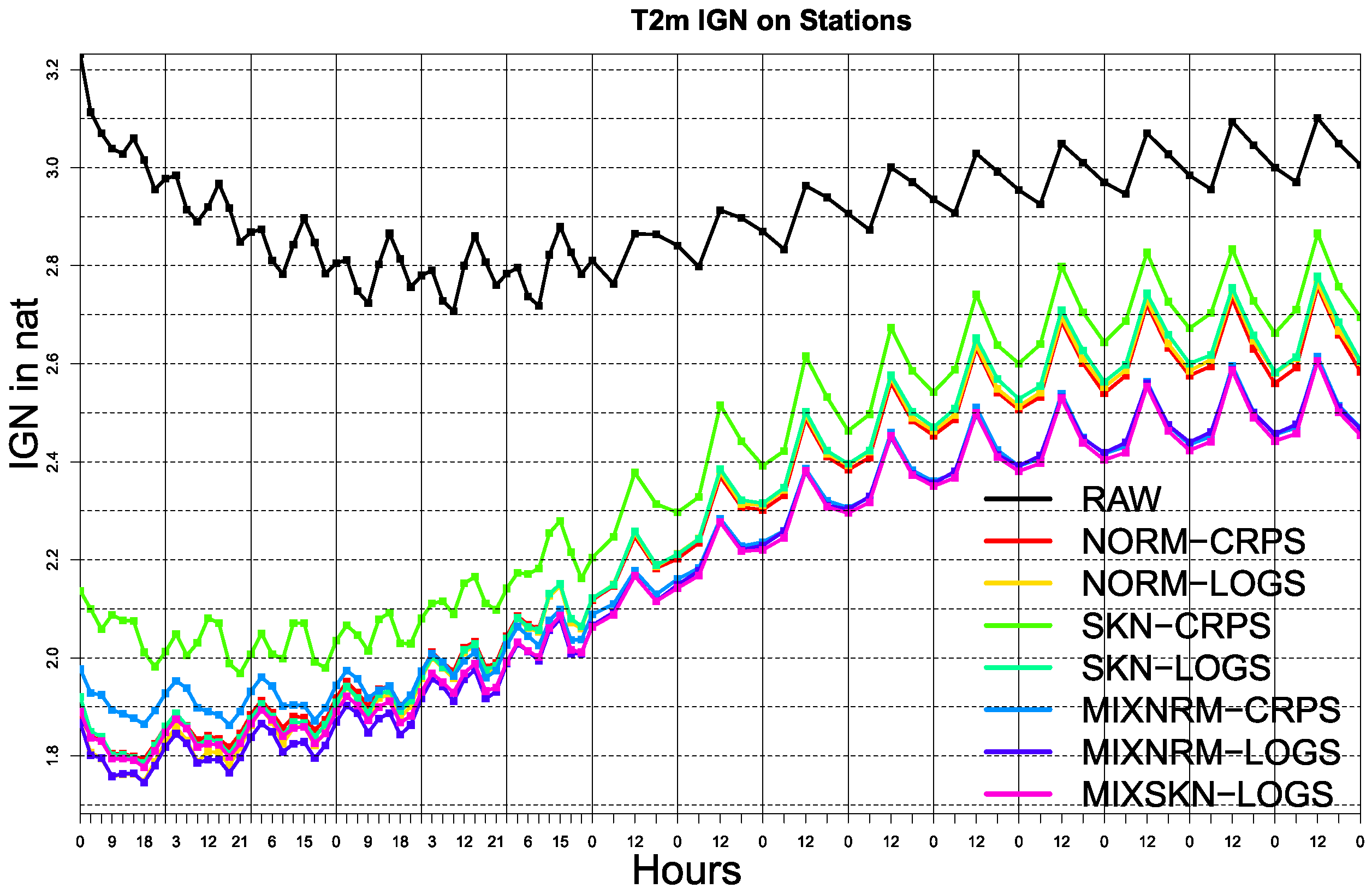
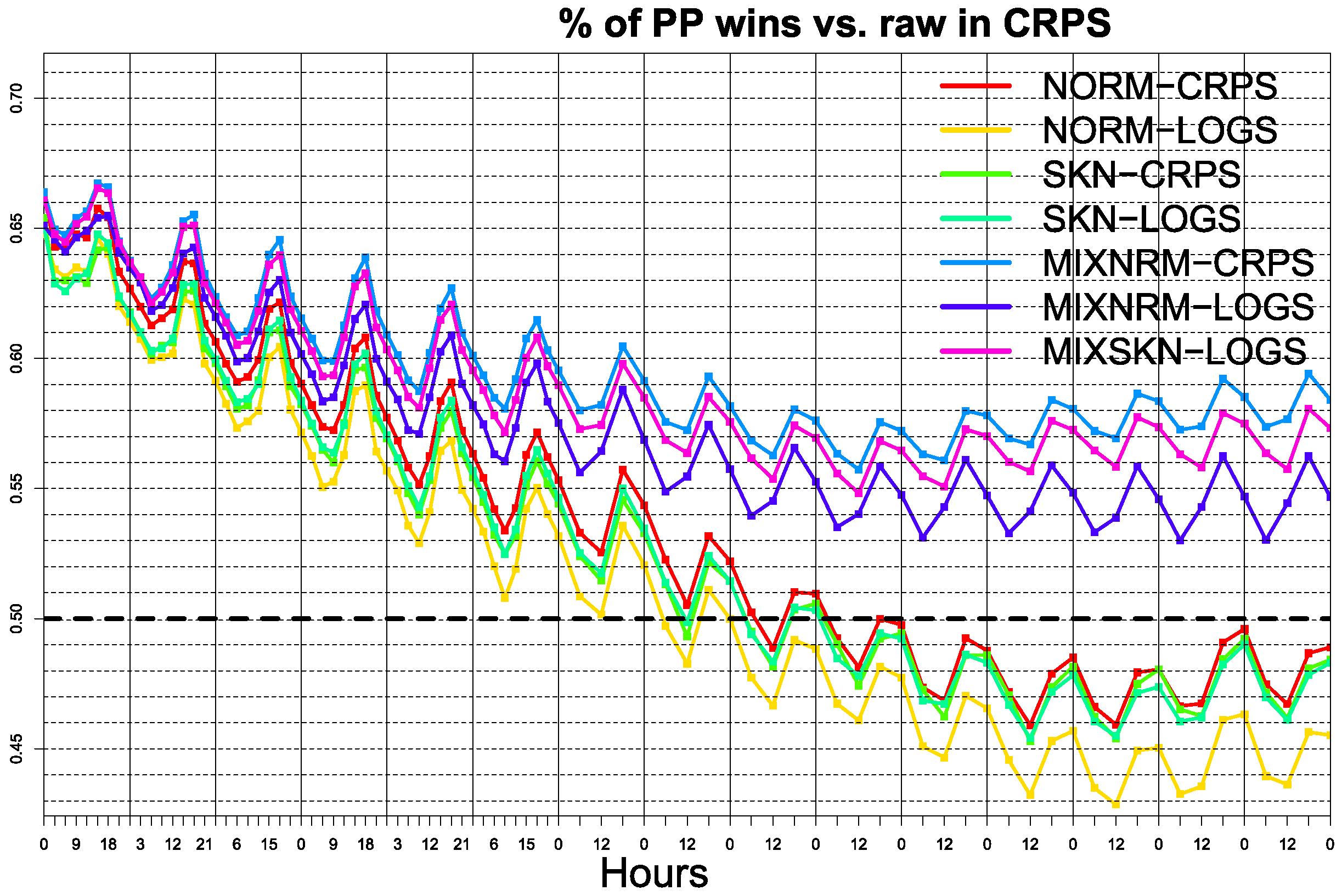
3. Results
Probabilistic Calibration
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leith, C. Theoretical skill of Monte Carlo forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 1974, 102, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, T. The economic value of ensemble forecasts as a tool for risk assessment: From days to decades. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 128, 747–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Katzfuss, M. Probabilistic forecasting. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2014, 1, 125–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannitsem, S.; Wilks, D.S.; Messner, J. Statistical Postprocessing of Ensemble Forecasts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vannitsem, S.; Bremnes, J.B.; Demaeyer, J.; Evans, G.R.; Flowerdew, J.; Hemri, S.; Lerch, S.; Roberts, N.; Theis, S.; Atencia, A.; et al. Statistical Postprocessing for Weather Forecasts: Review, Challenges, and Avenues in a Big Data World. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, E681–E699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, S.E.; Chapman, W.; Adams, S.V.; Kirkwood, C.; Hosking, J.S.; Robinson, N.H.; Lerch, S.; Subramanian, A.C. Towards implementing artificial intelligence post-processing in weather and climate: Proposed actions from the Oxford 2019 workshop. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillardat, M.; Mestre, O.; Zamo, M.; Naveau, P. Calibrated ensemble forecasts using quantile regression forests and ensemble model output statistics. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 2375–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasp, S.; Lerch, S. Neural networks for post-processing ensemble weather forecasts. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.09091. [Google Scholar]
- Scheuerer, M.; Switanek, M.B.; Worsnop, R.P.; Hamill, T.M. Using Artificial Neural Networks for Generating Probabilistic Subseasonal Precipitation Forecasts over California. Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 3489–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, S.; Whan, K.; Dirksen, S.; Schmeits, M. Statistical postprocessing of wind speed forecasts using convolutional neural networks. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönquist, P.; Yao, C.; Ben-Nun, T.; Dryden, N.; Dueben, P.; Li, S.; Hoefler, T. Deep learning for post-processing ensemble weather forecasts. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, R. Statistical postprocessing of ensemble forecasts for severe weather at Deutscher Wetterdienst. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2020, 27, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillardat, M.; Mestre, O. From research to applications—Examples of operational ensemble post-processing in France using machine learning. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2020, 27, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Raftery, A.E.; Westveld III, A.H.; Goldman, T. Calibrated probabilistic forecasting using ensemble model output statistics and minimum CRPS estimation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1098–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedorn, R.; Hamill, T.M.; Whitaker, J.S. Probabilistic forecast calibration using ECMWF and GFS ensemble reforecasts. Part I: Two-meter temperatures. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 2608–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, T.L.; Gneiting, T. Probabilistic forecasts of wind speed: Ensemble model output statistics by using heteroscedastic censored regression. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Stat. Soc.) 2010, 173, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, S.; Lerch, S. Log-normal distribution based Ensemble Model Output Statistics models for probabilistic wind-speed forecasting. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheuerer, M.; Hamill, T.M. Statistical postprocessing of ensemble precipitation forecasts by fitting censored, shifted gamma distributions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 4578–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friederichs, P.; Thorarinsdottir, T.L. Forecast verification for extreme value distributions with an application to probabilistic peak wind prediction. Environmetrics 2012, 23, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friederichs, P.; Göber, M.; Bentzien, S.; Lenz, A.; Krampitz, R. A probabilistic analysis of wind gusts using extreme value statistics. Meteorol. Z. 2009, 18, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.; Krüger, F.; Lerch, S. Evaluating Probabilistic Forecasts with scoringRules. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 90, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messner, J.W.; Mayr, G.J.; Zeileis, A. Nonhomogeneous Boosting for Predictor Selection in Ensemble Postprocessing. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junk, C.; Delle Monache, L.; Alessandrini, S. Analog-based ensemble model output statistics. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 2909–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, K.; Scheuerer, M.; Thorarinsdottir, T.L. Spatial postprocessing of ensemble forecasts for temperature using nonhomogeneous Gaussian regression. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1407.0058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabernig, M.; Mayr, G.J.; Messner, J.W.; Zeileis, A. Spatial Ensemble Post-Processing with Standardized Anomalies. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 143, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebetsberger, M.; Stauffer, R.; Mayr, G.J.; Zeileis, A. Skewed logistic distribution for statistical temperature post-processing in mountainous areas. Adv. Stat. Climatol. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2019, 5, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, S.; Lerch, S. Mixture EMOS model for calibrating ensemble forecasts of wind speed. Environmetrics 2016, 27, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baran, S.; Lerch, S. Combining predictive distributions for the statistical post-processing of ensemble forecasts. Int. J. Forecast. 2018, 34, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Möller, A.; Groß, J. Probabilistic temperature forecasting based on an ensemble autoregressive modification. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian model averaging to calibrate forecast ensembles. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mureau, R.; Molteni, F.; Palmer, T. Ensemble prediction using dynamically conditioned perturbations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T. Calibration of Medium-Range Weather Forecasts; European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roulston, M.S.; Smith, L.A. Evaluating probabilistic forecasts using information theory. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matheson, J.E.; Winkler, R.L. Scoring rules for continuous probability distributions. Manag. Sci. 1976, 22, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H. Decomposition of the continuous ranked probability score for ensemble prediction systems. Weather Forecast. 2000, 15, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Raftery, A.E. Strictly proper scoring rules, prediction, and estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2007, 102, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewsey, A. Problems of inference for Azzalini’s skewnormal distribution. J. Appl. Stat. 2000, 27, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Gneiting, T. Combining probability forecasts. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2010, 72, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gneiting, T.; Ranjan, R. Combining predictive distributions. Electron. J. Stat. 2013, 7, 1747–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamo, M.; Bel, L.; Mestre, O. Sequential aggregation of probabilistic forecasts—Application to wind speed ensemble forecasts. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 2021, 70, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimit, E.P.; Gneiting, T.; Berrocal, V.; Johnson, N.A. The Continuous Ranked Probability Score for Circular Variables and Its Application to Mesoscale Forecast Ensemble Verification; Technical Report; DTIC Document: Bedford, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, M.N.; Lerch, S.; Mayr, G.J.; Simon, T.; Stauffer, R.; Zeileis, A. Remember the past: A comparison of time-adaptive training schemes for non-homogeneous regression. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2020, 27, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebetsberger, M.; Messner, J.W.; Mayr, G.J.; Zeileis, A. Estimation methods for nonhomogeneous regression models: Minimum continuous ranked probability score versus maximum likelihood. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 4323–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, R.; Stoev, S. CRPS M-estimation for max-stable models. Extremes 2014, 17, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheuerer, M. Probabilistic quantitative precipitation forecasting using ensemble model output statistics. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebetsberger, M.; Messner, J.W.; Mayr, G.J.; Zeileis, A. Fine-tuning nonhomogeneous regression for probabilistic precipitation forecasts: Unanimous predictions, heavy tails, and link functions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 4693–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeCun, Y.A.; Bottou, L.; Orr, G.B.; Müller, K.R. Efficient backprop. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 9–48. [Google Scholar]
- Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Raftery, A.E. Probabilistic forecasts, calibration and sharpness. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2007, 69, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.L. A method for producing and evaluating probabilistic forecasts from ensemble model integrations. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talagrand, O.; Vautard, R.; Strauss, B. Evaluation of probabilistic prediction systems. In Proceedings of the ECMWF Workshop on Predictability, Reading, UK, 20–22 October 1997; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hamill, T.M.; Colucci, S.J. Verification of Eta-RSM short-range ensemble forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillardat, M.; Fougères, A.L.; Naveau, P.; Mestre, O. Forest-based and semiparametric methods for the postprocessing of rainfall ensemble forecasting. Weather Forecast. 2019, 34, 617–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C. Fair scores for ensemble forecasts. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamo, M.; Naveau, P. Estimation of the continuous ranked probability score with limited information and applications to ensemble weather forecasts. Math. Geosci. 2018, 50, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemri, S.; Scheuerer, M.; Pappenberger, F.; Bogner, K.; Haiden, T. Trends in the predictive performance of raw ensemble weather forecasts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 9197–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiden, T.; Janousek, M.; Bidlot, J.; Buizza, R.; Ferranti, L.; Prates, F.; Vitart, F. Evaluation of ECMWF Forecasts, Including the 2018 Upgrade; European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Weijs, S.V.; Van Nooijen, R.; Van De Giesen, N. Kullback–Leibler divergence as a forecast skill score with classic reliability–resolution–uncertainty decomposition. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tödter, J.; Ahrens, B. Generalization of the ignorance score: Continuous ranked version and its decomposition. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, S.; Ferro, C.A.; Stephenson, D.B.; Leutbecher, M. The ensemble-adjusted Ignorance Score for forecasts issued as normal distributions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, T. The ECMWF ensemble prediction system: Looking back (more than) 25 years and projecting forward 25 years. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagedorn, R.; Smith, L.A. Communicating the value of probabilistic forecasts with weather roulette. Meteorol. Appl. J. Forecast. Pract. Appl. Train. Tech. Model. 2009, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundel, V.J.; Fleischhut, N.; Herzog, S.M.; Göber, M.; Hagedorn, R. Promoting the use of probabilistic weather forecasts through a dialogue between scientists, developers and end-users. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 210–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, B.; El Ayari, M.; Lerch, S.; Baran, S. Post-processing numerical weather prediction ensembles for probabilistic solar irradiance forecasting. Sol. Energy 2021, 220, 1016–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, S.; Szokol, P.; Szabó, M. Truncated generalized extreme value distribution-based ensemble model output statistics model for calibration of wind speed ensemble forecasts. Environmetrics 2021, e2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutbecher, M.; Haiden, T. Understanding changes of the continuous ranked probability score using a homogeneous Gaussian approximation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinbank, R.; Kyouda, M.; Buchanan, P.; Froude, L.; Hamill, T.M.; Hewson, T.D.; Keller, J.H.; Matsueda, M.; Methven, J.; Pappenberger, F.; et al. The TIGGE project and its achievements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NORM-CRPS | NORM-LOGS | SKN-CRPS | SKN-LOGS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| quadratic | quadratic | quadratic | quadratic | |
| quadratic | quadratic | quadratic | quadratic | |
| quadratic | quadratic | |||
| quadratic | quadratic | |||
| MIXNRM-CRPS | MIXNRM-LOGS | MIXSKN-LOGS | ||
| identity | ||||
| identity | ||||
| - | ||||
| s | - | - | ||
| quadratic | ||||
| quadratic | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taillardat, M. Skewed and Mixture of Gaussian Distributions for Ensemble Postprocessing. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080966
Taillardat M. Skewed and Mixture of Gaussian Distributions for Ensemble Postprocessing. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(8):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080966
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaillardat, Maxime. 2021. "Skewed and Mixture of Gaussian Distributions for Ensemble Postprocessing" Atmosphere 12, no. 8: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080966
APA StyleTaillardat, M. (2021). Skewed and Mixture of Gaussian Distributions for Ensemble Postprocessing. Atmosphere, 12(8), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080966






