Study on the Complexity Reduction of Observed Sequences Based on Different Sampling Methods: A Case of Wind Speed Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. A Description Method of Complexity—The Approximate Entropy
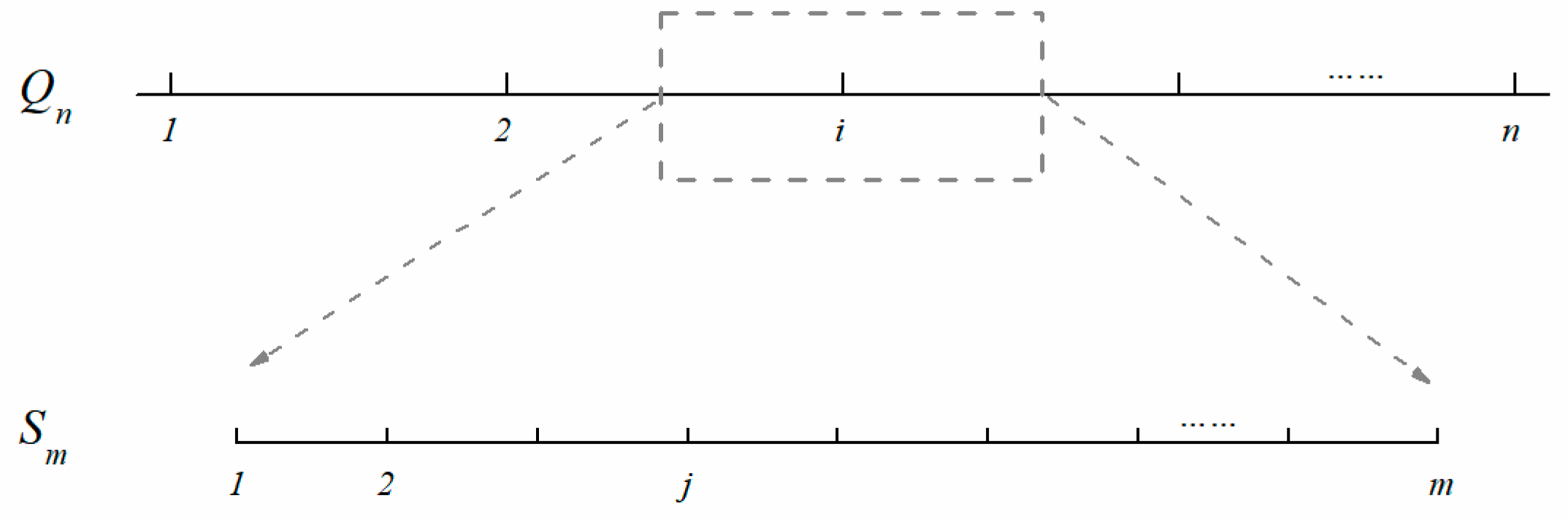
2.2. Sampling Methods
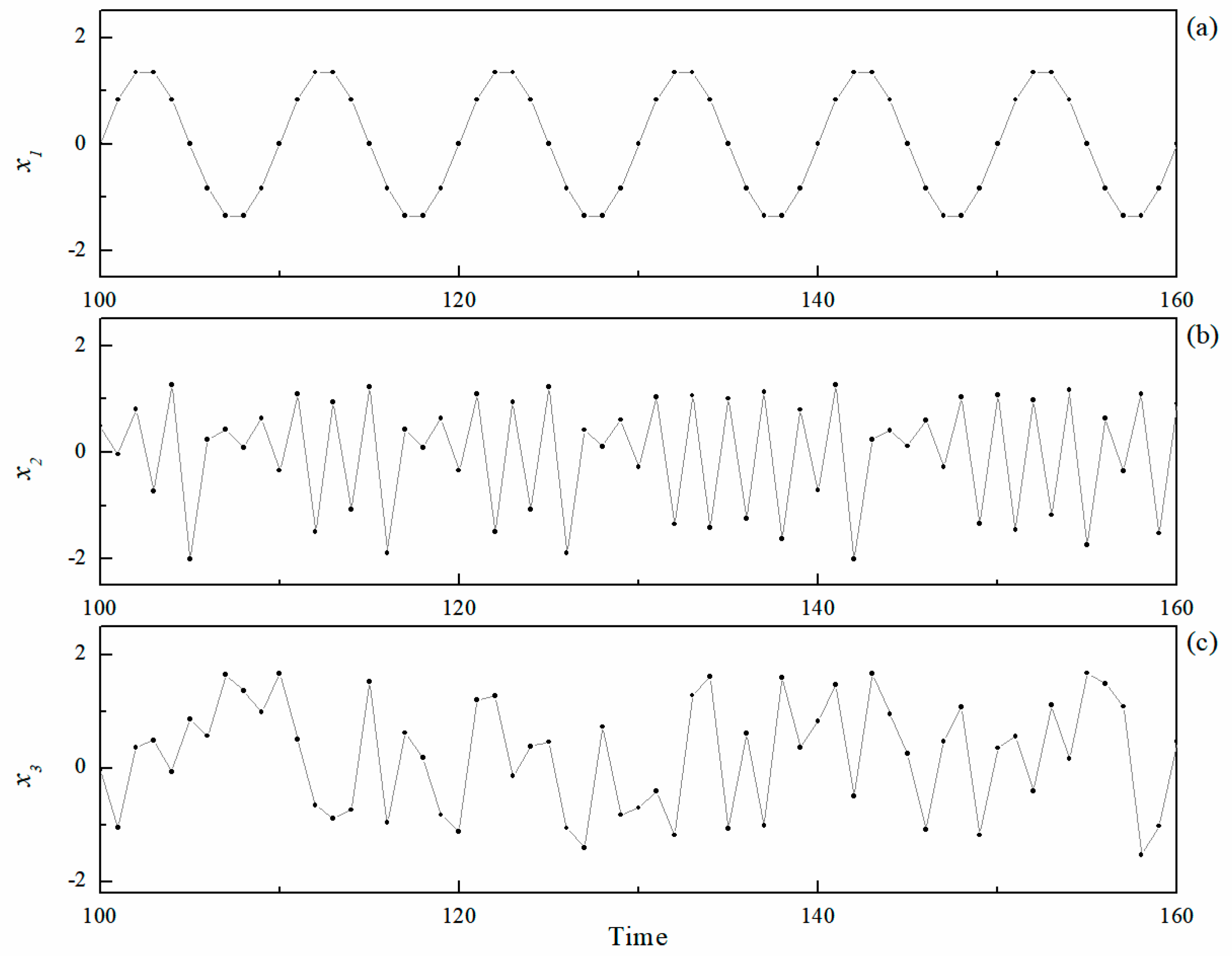
2.3. Ideal Time Series and the Observed Wind Speed
3. Results
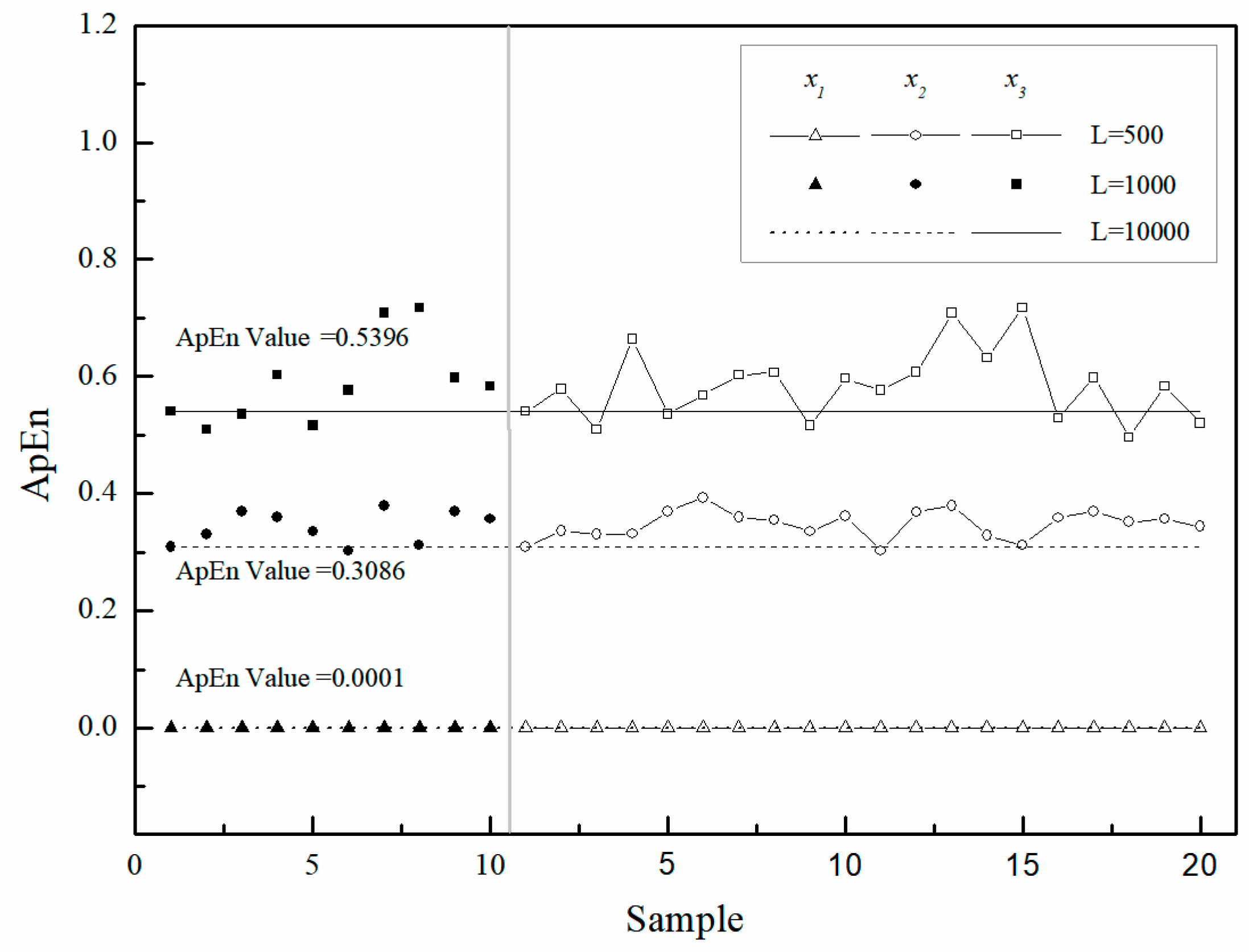
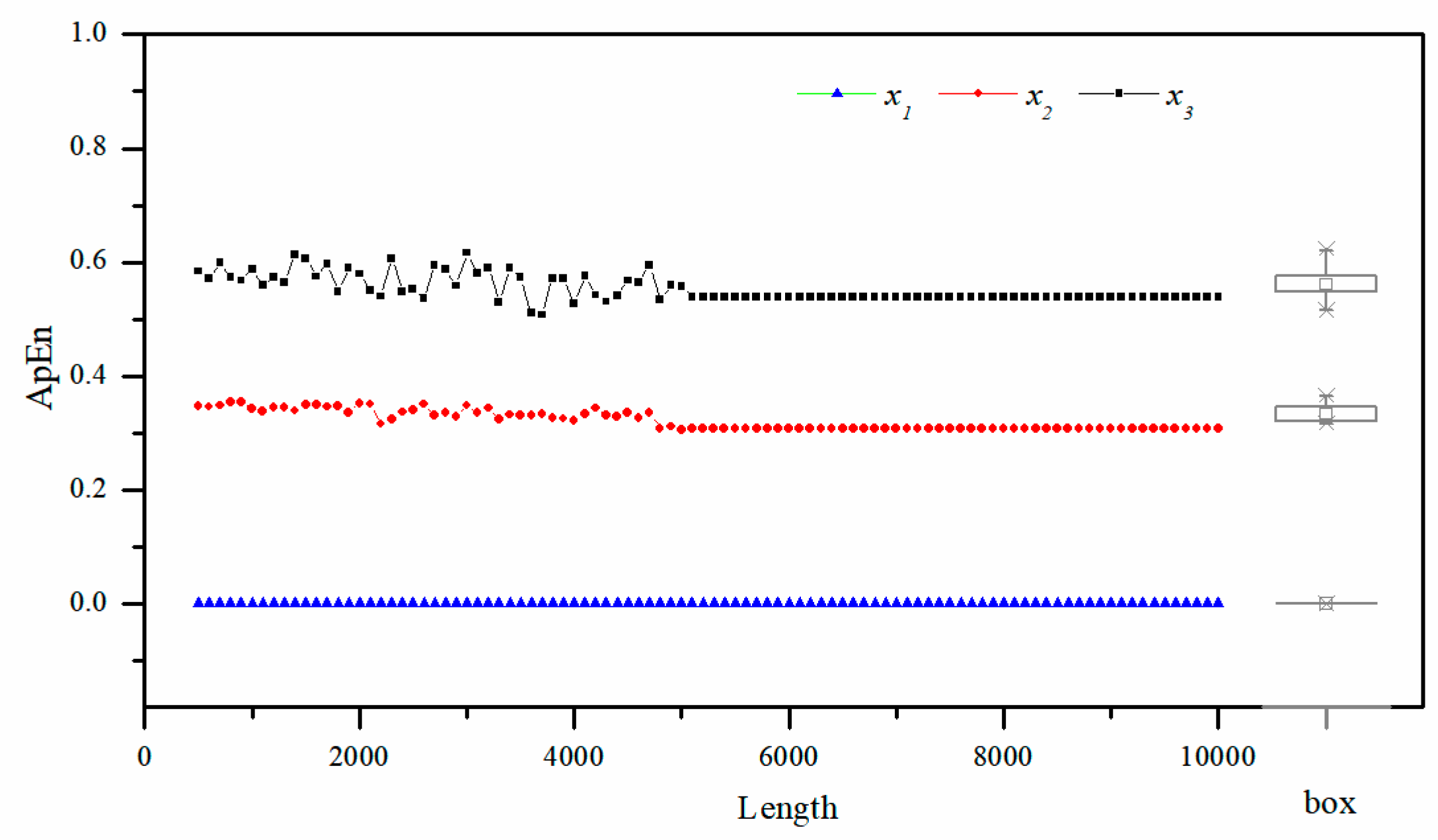
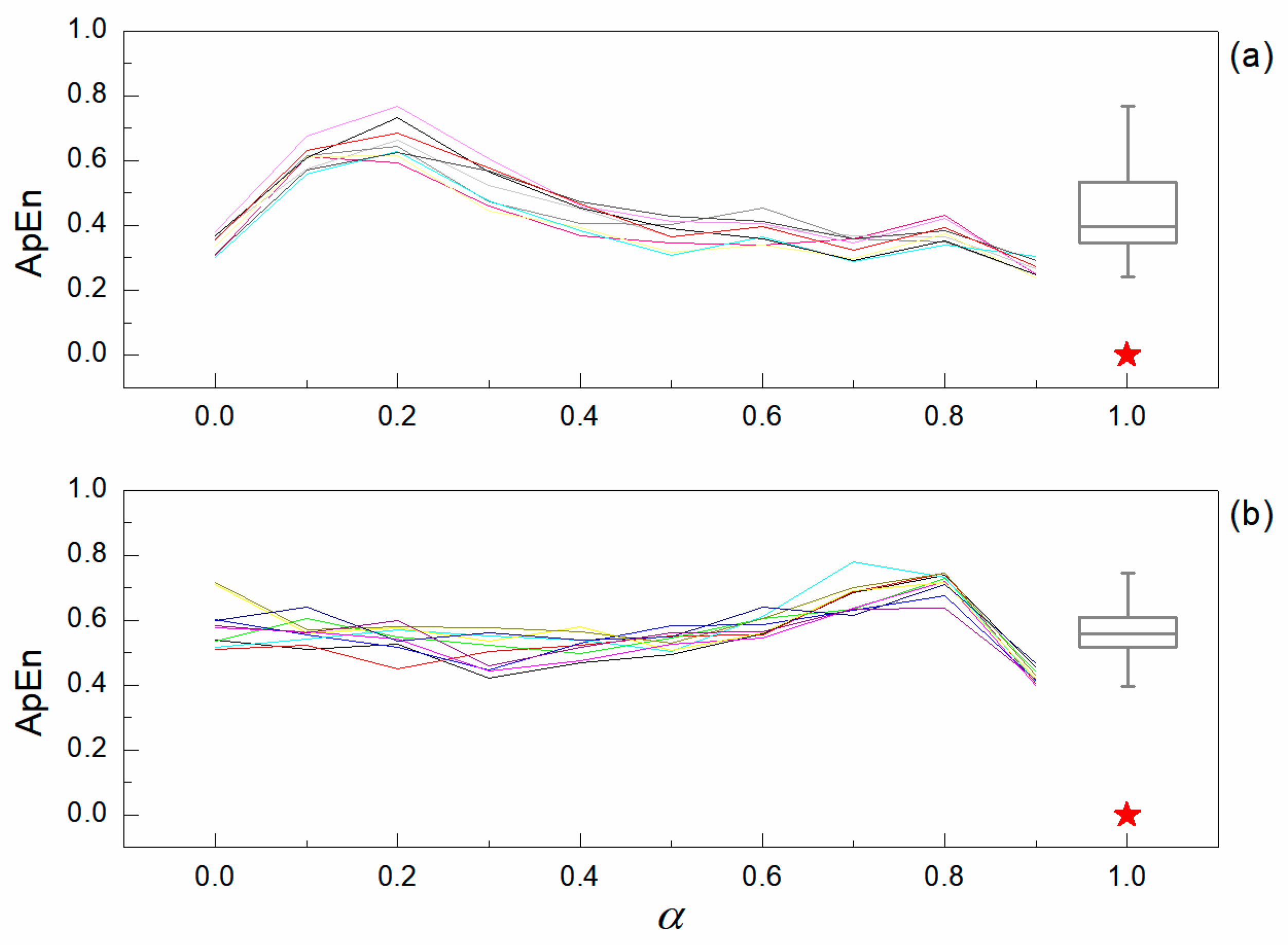
3.1. The Complexity of Ideal Time Series
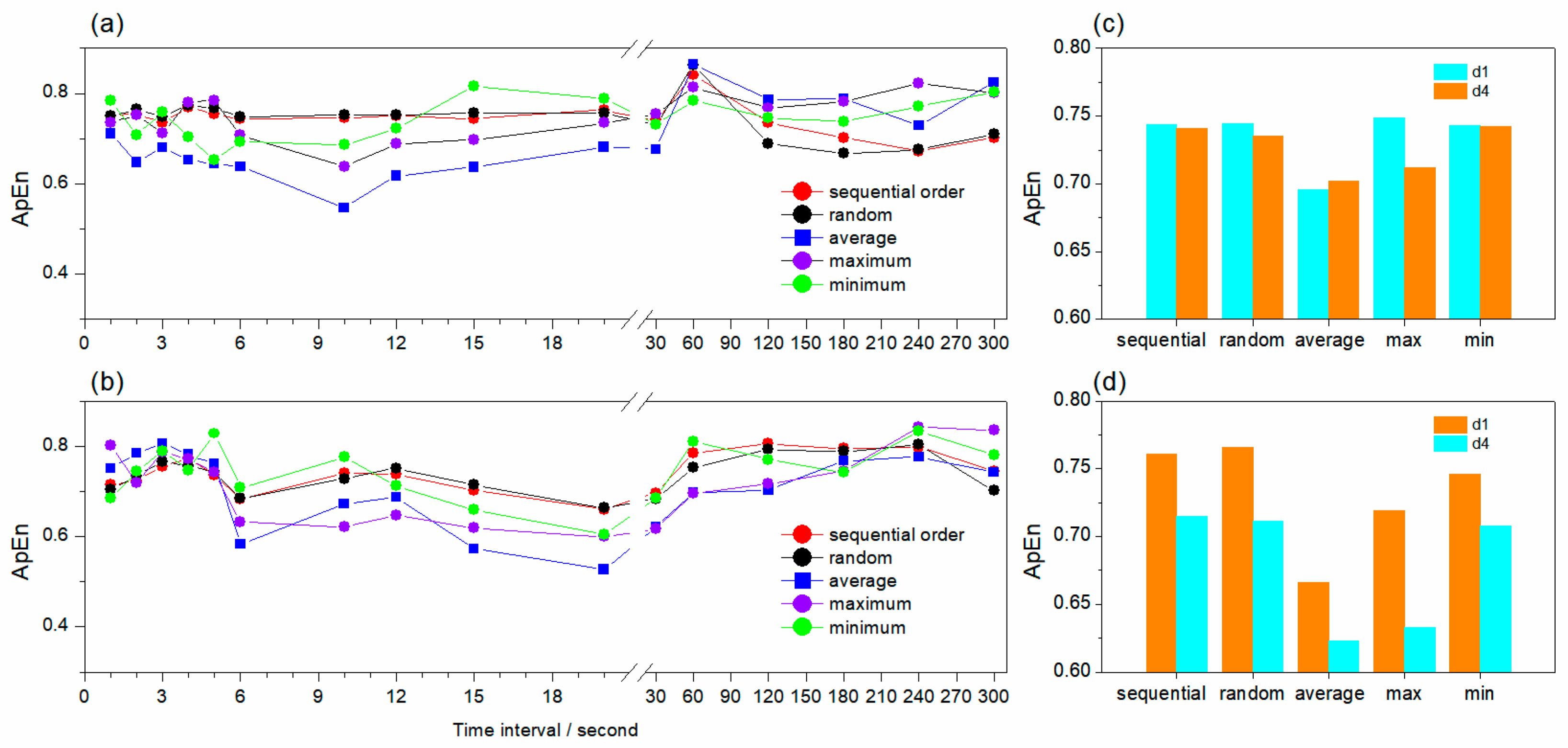
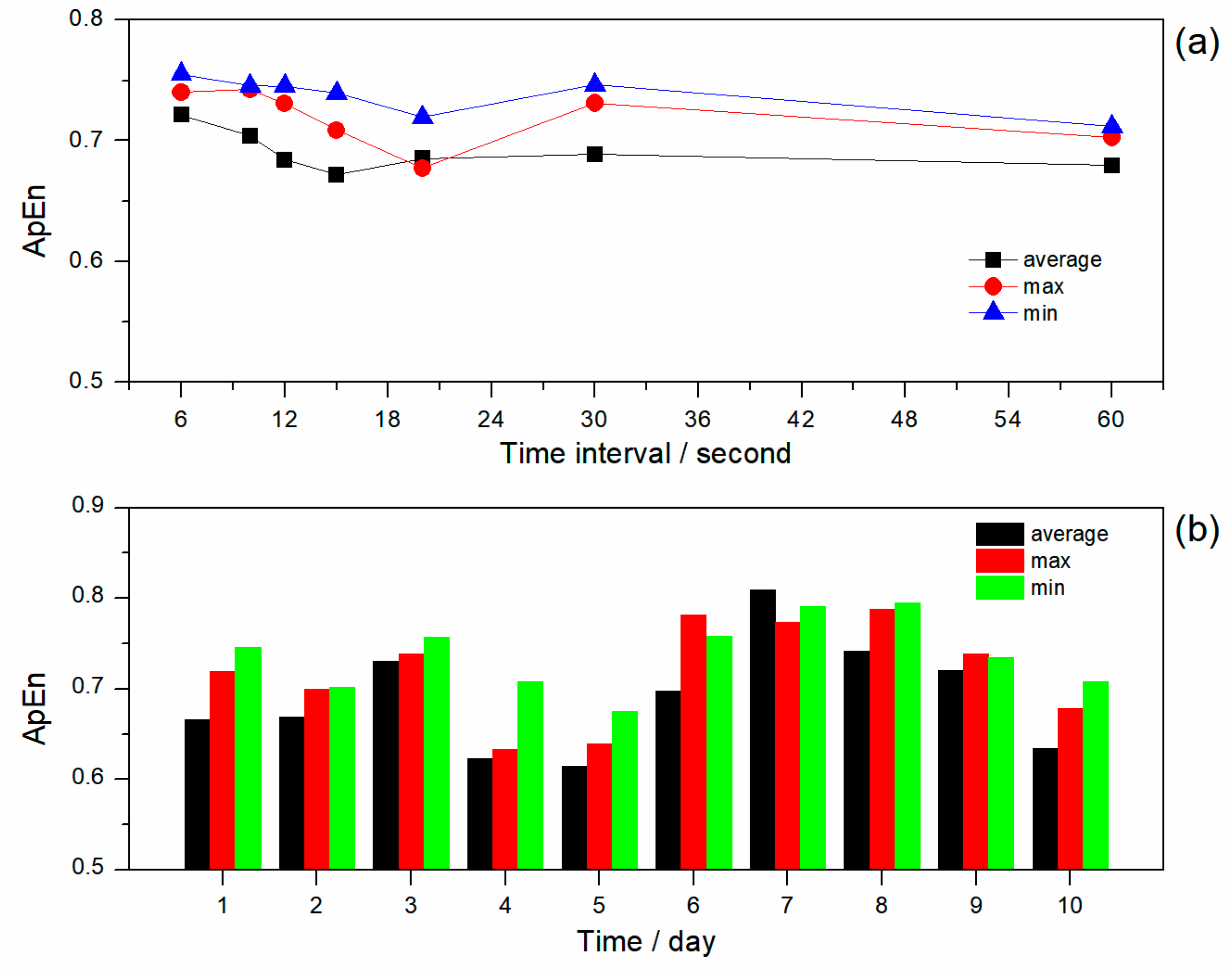
3.2. The Complexity of the Observed Wind Speed
4. Conclusion and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rind, D. Complexity and Climate. Science 1999, 284, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesvorny, D.; Morbidelli, A. Three-Body Mean Motion Resonances and the Chaotic Structure of the Asteroid Belt. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 3029–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodoc flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. The predictability of a flow which possesses many scales of motion. Tellus 1969, 21, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Feng, G.L.; Gao, X.Q.; Chou, J.F. Investigation on the time series of ice core and stalagmite based on the analysis of complexity. Acta Phys. Sin. 2005, 54, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Feng, G.L.; Dong, W.J. Investigation about the Lorenz model and logistic equation based on the complexity. Acta Phys. Sin. 2005, 54, 3940–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.F. Predictability of the atomosphere. Adv. At. Sci. 1989, 6, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.M.; He, W.P.; Zhang, W.; Feng, A.X.; Hou, W. Effects of noises on moving cut data-approximate entropy. Acta Phys. Sin. 2012, 61, 129202. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.M.; He, W.P.; Hou, W.; Zhang, D.Q. Effects of different trends on moving cut data-approximate entropy. Acta Phys. Sin. 2012, 61, 069201. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.M.; He, W.P.; Liu, Q.Q.; Wang, J.S.; Feng, G.L. The applicability of research on moving cut data-approximate entropy on abrupt climate change detection. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 124, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.P.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.G.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of characteristics of moving detrended fluctuation analysis with that of approximate entropy method in detecting abrupt dynamic change. Acta Phys. Sin. 2009, 58, 2862–2871. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.P.; He, T.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Q. A new method to detect abrupt change based on approximate entropy. Acta Phys. Sin. 2011, 60, 813–821. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. Lond. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weare, B.C.; Nasstrom, T.S. Examples of extended Empirical Orthogonal Function analyses. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1982, 110, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugene, M.R.; Phillip, A.A.; Chen, W.Y.; John, B.J. Biennial Variations in Surface Temperature over the United States as Revealed by Singular Decomposition. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1981, 109, 587–598. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zeng, J.; Ma, L.M.; Guan, L. Short-Term Dynamic Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Based on Wavelet Transform and Support Vector Machine. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ding, R.Q.; Li, J.P.; Wang, Z.G. Impacts of sampling interval and interpolation on the estimatimation of the predictability of chaotic systems. Mar. Forecast. 2015, 32, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, R.Q.; Li, J.P. The temporal-spatial distributions of weather predictability of different variables. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2009, 67, 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.D. Preliminary research of chaotic characteristics and prediction of short-term wind speed time series. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2020, 30, 2050176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeraj, D.B.; Zaher, M.Y.; Gorm, B.A. ForecastTB—An R Package as a Test-Bench for Time Series Forecasting—Application of Wind Speed and Solar Radiation Modeling. Energies 2020, 13, 2578. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.W.; Zhao, S. Wind speed prediction based on singular spectrum analysis and neuralnetwork structural learning. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 216, 112956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram., B.; Ajay, K.; Satyam, G. Deep Learning based Wind Speed Forecasting—A Review. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Noida, India, 10–11 January 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.X.; Gong, Z.Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.G. Spatiotemporal analysis of information entropy of the global temperature. Acta Phys. Sin. 2011, 60, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pincus, S.M.; Goldberger, A.L. Physiological time-series analysis, what does regularity quantify? Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.M.; Viscarello, R.R. Approximate entropy, a regularity measure for heart rate analysis. Obstet. Gynecol. 1992, 79, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Pawelzik, K.; Schuster, H.G. Generalized dimensions and entropies from a measured time series. Phys. Rev. A 1987, 35, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottwald, G.A.; Melbourne, I. A New Test for Chaos. Physics 2002, 460, 603–611. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, J.R. Statistical self -affinity, fractal dimension, and geological interpretation. Eng. Geol. 1987, 48, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.R.; Bhattachary, D. Hypothesis testing for long -term memory in hydrologic series. J. Hydrol. 1999, 216, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.C.; Feng, G.L.; Hou, W. A method for predicting the uncompleted climate transition. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2020, 27, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.C.; Hou, W.; Feng, G.L. Transition process of abrupt climate change based on global sea surface temperature over the past century. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2016, 23, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, J.F.; Zheng, Z.H.; Sun, S.P. The think about 10–30 d extended-range numerical weather prediction strategy—Facing the atmosphere chaos. Sci. Meteorol. Sin. 2010, 5, 569–573. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.Q.; Zhao, J.H.; Feng, G.L.; Chou, J.F. Dynamic-statistics combined forecast scheme based on the abrupt decadal change component of summer precipitation in East Asia. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Wind Direction (°) | Resolution | 0.1 |
| Range | 0~359 | |
| Wind Speed (m·s−1) | Resolution | 0.01 |
| Range | 0~65 | |
| Quartile | x1 | x2 | x3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | −1.35 | −2.03 | −1.72 |
| 25% | −0.83 | −0.67 | −0.88 |
| 50% | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.00 |
| 75% | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.86 |
| 100% | 1.35 | 1.27 | 1.73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huai, X.; Yan, P.; Li, L.; Cai, Z.; Xu, X.; Hu, X. Study on the Complexity Reduction of Observed Sequences Based on Different Sampling Methods: A Case of Wind Speed Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111746
Huai X, Yan P, Li L, Cai Z, Xu X, Hu X. Study on the Complexity Reduction of Observed Sequences Based on Different Sampling Methods: A Case of Wind Speed Data. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(11):1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111746
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuai, Xiaowei, Pengcheng Yan, Li Li, Zelin Cai, Xunjian Xu, and Xiaohui Hu. 2022. "Study on the Complexity Reduction of Observed Sequences Based on Different Sampling Methods: A Case of Wind Speed Data" Atmosphere 13, no. 11: 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111746
APA StyleHuai, X., Yan, P., Li, L., Cai, Z., Xu, X., & Hu, X. (2022). Study on the Complexity Reduction of Observed Sequences Based on Different Sampling Methods: A Case of Wind Speed Data. Atmosphere, 13(11), 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111746










