Abstract
Long-range transport (LRT) can carry air pollutants to downwind areas. However, studies about the impacts of LRT on bacterial communities are few. This study investigated the influence of Asian dust storms (ADS) and frontal pollution (FP) on bacterial communities in ambient air using next-generation sequencing (NGS) and Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (T-RFLP). Air samples were collected at Cape Fugui (CF) and National Taiwan University (NTU) in northern Taiwan before (or background days), during, and after LRTs from November 2013 to March 2015. The richness, H index, and evenness increased during FPs and then decreased after FPs. During and after ADS and FP, the prevalence of the phylum Proteobacteria decreased, but that of Firmicutes increased. The dominant class of Proteobacteria changed from Alphaproteobacteria on background days to Betaproteobacteria during LRTs. At the genus level, the high abundance of Ralstonia and Bacillus during FP and Clostridium during ADS were detected at both locations. Additionally, Ralstonia was dominant at CF during ADS. In conclusion, FP and ADS both changed the bacterial community. The indicator genus was Clostridium and Ralstonia for ADS as well as Bacillus and Ralstonia for FP. Given the potential health threats posed by the bioaerosols transported, people should avoid outdoor activities during LRTs.
1. Introduction
Taiwan is located off the southeastern coast of mainland China, and the East Asian winter monsoon strongly affects its climate in winter [1]. The Siberian High, an important component of the East Asian winter monsoon, dominates the weather pattern of East Asia [2,3]. The main track of this anticyclone extends from the source regions (near Mongolia) [4] southeastward, passes the lower part of the Yellow River, and then moves eastward through the Yellow Sea, southern Korea, and then to Japan [5]. When the winter progresses, the major track could shift southeastward through East China Sea and reach Taiwan due to the northeasterly winds. Frontal passages can transport dust and air pollutants from desert sources or industrial emissions from China to Taiwan. Asian dust storms (ADSs) and frontal pollution cases (FPs) are the two major types of long-range transport (LRT) in the northeast monsoon season. ADSs are associated with desert sources, which contain mineral sands but not essentially air pollutants. Oppositely, FPs transport air pollutants from industrial areas, and mineral sands are not necessarily involved.
Microbes can be transported along with air pollutants. Previous studies have suggested that LRT events carry microbes to downwind areas [6]. In the atmosphere, bacteria are typically embedded in organic or coarse particles, which protect the bacteria from exposure to environmental stresses such as ultraviolet radiation or from drying out and provide the nutrients needed for the bacteria to survive [7,8]. Bacteria can thus remain in the air and be transferred over long distances on current winds. When bacteria are transported to a downwind area, the bacterial community in that area is likely to be changed. Studies have found that the bacterial community on dusty days was different from that on non-dusty days [9,10]. In addition, some bacteria produce endospores that are highly resistant to harsh environments [11]. Consequently, endospore-forming bacteria such as Bacillus are frequently isolated in viable conditions during dust storm events [12,13,14,15]. However, the studies for the impacts of LRTs on bacterial community are still few, especially for FP cases.
The bacteria transported during LRTs may then affect human health and the environment in downwind areas. Polymenakou et al. [16] indicated that approximately 24% of the clones sequenced in their study might potentially be human, animal, or plant pathogens. Human exposure to airborne bacteria is unavoidable because on average, a person inhales an estimated 8 m3 of air every day [17]. Relatively large airborne particles are trapped in the upper respiratory tract, whereas particles smaller than 5 μm can be transported to the lungs [18]. Many studies have suggested that ADSs are associated with respiratory diseases, such as asthma, pneumonia, and tracheitis. A study in Japan demonstrated that ADSs worsened asthma in children and increased the hospitalization rate [19]. Chien et al. [20] reported an increase in clinical visits due to respiratory disease among children in Taiwan during ADSs. A study in Hong Kong also revealed a significant increase in emergency admissions due to respiratory problems during ADSs [21]. Lee and Lee [22] further reported a 22% increase in asthma treatments during an ADS in Korea, with a six-day lag. In addition to the impact on human health, the presence of pathogens in air exerts considerable effects on ecology, climate, and agriculture [23,24,25]. Therefore, the understanding of the changes in the bacterial community during LRTs is in favor of assessing the reason for the increase in health impacts during LRTs and the potential effects on environments and human health.
The frequency of DSs has increased in the last 20 years due to desertification caused by climate change and human activities [26,27,28,29]. Moreover, the incidence of the FP cases is approximately once a week in Taiwan [30]. This highlights the importance of evaluating the impacts of LRTs on bacterial communities. Because the influence of LRTs on bioaerosols can last for at least two days [6], the comparison of the effects before, during, and after LRTs is essential. Therefore, this study assessed and compared the bacterial community structures in the ambient air in northern Taiwan before, during, and after ADS and FP events.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study included two sampling sites, Cape Fugui (CF, rural area) and National Taiwan University (NTU, urban area), in northern Taiwan (Figure 1). The air mass crossing the East Sea from China arrives at CF, the northernmost point of Taiwan. NTU is located in the Taipei metropolis, which is crowded and has heavy traffic. The distance between CF and NTU is approximately 60 km. The sampling during September 2013–April 2015 was conducted when the forecast of Taiwan Central Weather Bureau (Taiwan CWB, Taipei, Taiwan) reported that the LRT might arrive Taiwan in the following few days. However, during September 2014–April 2015, the sampling was only performed at the NTU station because the CF station was under repair. In the second week of each month, daily sampling was also conducted for three continuous days in the absence of LRT.
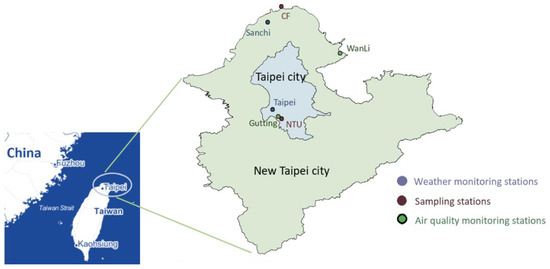
Figure 1.
Distribution of sampling locations, weather monitoring stations, and air quality motioning stations.
During our sampling period, daily data of meteorological factors and air pollution levels were collected, which were used to determine when to end each LRT sampling and to identify the occurrence and type of LRTs. These data were also used to define the days before (1–2 days), during (the days significantly affected by LRT), and after (1–2 days) an LRT event. Finally, the bacterial community in air samples was compared among the days before, during, and after an LRT event to evaluate the impact of LRTs on the bacterial community structure. If samples of the before LRT period were unavailable, samples collected from background days were used as the reference in these LRTs.
2.2. LRT Forecast and Sampling
The dust-related information posted on the websites of the Taiwan Environmental Pollution Agency (EPA), Japan Meteorological Agency, and Taiwan CWB were evaluated daily to assess the occurrence of an LRT event. The sampling was started when three criteria were met and continued until 2 days after the LRT event. The details of the three criteria were reported in our previous study [6]. Briefly, we estimated whether there was a high-pressure system (>1030 hPa) in northern China and a low pressure system near the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan based on the Current Weather Chart of the Taiwan CWB. Within the next few days, according to the 7-Day Forecast Chart of the Taiwan CWB, Aeolian Dust Information of the Japan Meteorological Agency, and Taiwan CWB’s announcement, respectively, the air masses would move from China to Taiwan, desert sands would be likely to be transported to Taiwan, and a cold wave will arrive Taiwan.
Air samples were collected in duplicate using air pumps (SPP-25GA, HIBOW, Osaka, Japan) and cassettes containing sterilized Nuclepore Teflon filters (37 mm, 0.2 µm, Critical Process Filtration Inc., Nashua, NH, USA) at 25–33 L/min for 24 h. The sampling at CF and NTU was conducted at 1.2 m and 15 m above the ground surface, respectively. After the sample collection, duplicate filters were placed in a 15-mL centrifuge tube containing 4 mL of sterile deionized water and stored at 4 °C. Samples were shipped to our laboratory at 4 °C and then stored at −80 °C until bacterial DNA extraction. A field blank and trip blank were also prepared for each sampling.
2.3. Identification of LRT
After sampling, we identified the occurrence and type of LRTs based on the changes in weather conditions and air pollution levels [6]. The criteria for the identification of FP cases were as follows: (1) an anticyclonic high-pressure system moved from Siberia to Taiwan; (2) temperature decreased, the wind speed increased, and the prevailing wind most often blew from the northeast and east-northeast; (3) the levels of gaseous pollutants, such as NOX, O3, CO, and SO2, increased, and O3 lost the diurnal pattern; (4) the concentrations of particulate matter ≤2.5 μm (PM2.5) and ≤10 μm (PM10) significantly increased and PM2.5/PM10 ratios did not decrease; and (5) air masses passed over the industrial areas of the eastern Chinese coast according to the HYSPLIT model 48-h backward trajectory (Supplementary Material, Figure S1).
For ADS identification, six criteria should be met, including the first three criteria for FP cases and three additional criteria: (1) based on the HYSPLIT model 48-h backward trajectory, the air mass came from China’s deserts or Mongolian deserts (Supplementary Material, Figure S2), (2) the concentration of PM10 was >120 μg/m3, and the PM2.5/PM10 ratio was approximately equal to or less than 0.5 [31], and (3) the satellite images of MTSAT-1R displayed dust emissions in the arid area of China.
2.4. Weather and Air Pollution
Hourly data concerning air pollution (SO2, O3, NOX, CO, PM2.5, and PM10) and weather conditions (temperature, wind speed, and wind direction) were obtained from Taiwan EPA and Taiwan CWB, respectively. The data collected from Wan-Li and Guting air monitoring stations were used to represent the air pollution of CF and NTU, respectively. The weather conditions of CF and NTU were extracted from the measures of Sanzhi and Taipei stations, respectively. To understand the sources of air masses during each LRT event, a 48-h backward trajectory analysis was performed using the HYSPLIT model (http://www.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 10 May 2022)) at altitudes of 500, 1000, and 1500 m. This study included six FPs and one ADS (Table 1).

Table 1.
Long-range transport (LRT) events from September 2013 to April 2015.
2.5. Bacterial Community Analyses
2.5.1. Sample Pretreatment and Genomic DNA Extraction
Before genomic DNA (gDNA) extraction, transferring the centrifuge tubes containing filters from −20 °C to 4 °C until perfectly thawed was necessary. Bacterial cells were pre-treated using the following steps: (1) the centrifuge tubes were vortexed for 30 s, (2) the filters were pressed using pipette tips, (3) a 30-s vortex was conducted again, and (4) a 200-rpm centrifugation was performed at 4 °C for 1 min. Thereafter, a 250-μL cell suspension was used for bacterial gDNA extraction with the TANBead Gram Bacteria DNA Kit coupled with Smart LabAssist series-32 (Taiwan Advance Nanotech Inc., Taoyuan, Taiwan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Only one modification was made: the centrifugation speed of the first extraction step was changed to 2214× g. The extracted gDNA was stored at −20 °C until further analyses of bacterial community compositions.
2.5.2. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
To compare the bacterial community compositions between ADS and FP, samples of an ADS in October 2013 and FP1 in November 2013 were analyzed through MiSeq sequencing. NGS was performed by the Center for Genomic Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan. Before NGS analysis, bacterial DNA in each sample was quantified by using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Given the low gDNA concentrations in our samples, all gDNA extracted from samples of the same LRT period were pooled in one tube. Therefore, for each LRT event, there were three gDNA samples (i.e., background days; during and after LRTs) for the NGS analysis.
Prior to sequencing, two rounds of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) were performed to amplify the specific region V3–V5 of 16S rRNA genes. The forward and reverse primers of the first PCR amplification were 5′-ACTGAGACACGGTCCAGAC-3′ and 3′-GCGTTGCATCGAATTAAACCA-5′, respectively. In the second round of PCR, the primers used were 5′-Fusion-Barcoded-Fusion-CCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′ (forward) and 3′-Fusion-Barcoded-Fusion-CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGT-5′ (reverse). The DreamTaq DNA polymerase kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used for PCR reactions according to the supplier’s instructions. The PCR amplicons were then purified using Agencourt AMPure XP PCR purification kit (Beckman Coulter Inc., Beverly, MA, USA). The fragment size of the purified amplicon was assessed using Caliper LabChip, and the concentration was quantified using a Qubit fluorometer (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and qPCR. Equal amounts of PCR amplicons for each sample were loaded into the MiSeq sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). To minimize the effects of sequencing errors, the low-quality sequences in raw sequence reads were removed from the libraries by passing them through filters.
2.5.3. Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (T-RFLP)
To further investigate the impact of FPs on bacterial community diversity, we also collected FP samples from September 2014 to April 2015, which were analyzed using PCR-based T-RFLP [32]. A 5′ fluorescently labeled primer was used to amplify a region of genes encoding 16S rRNA. The PCR products with a fluorescence label at the 5′ end were digested and cut into smaller fragments with restriction enzymes, and the fluorescently labeled terminal restriction fragments were separated by size in an automatic DNA sequencer. This study conducted the nested-PCR reaction for 16S rRNA amplification because of the low concentrations of bacterial DNA in air samples. The entire experiment was operated in the dark to avoid decay of the fluorescently labeled samples.
Nested PCR
The bacterial 16S rRNA genes of the extracted gDNA were first amplified using the forward primer 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′) and reverse primer 1492R (5′-TACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) [33,34,35]. A 21-µL PCR mixture contained 1 µL of extracted gDNA, 0.2 µM of each primer (Protech, Kaohsiung, Taiwan), 0.2 nM of dNTP, 0.02 U of ExTaq, and 5× buffer (Takara, Japan). The PCR program consisted of initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 1-min denaturation at 94 °C, annealing for 1 min at 52 °C, and extension at 72 °C for 1.5 min. The final extension step was performed at 72 °C for 10 min. Each sample was amplified in 10 tubes. In each PCR run, a no template control (NTC) and a positive control (i.e., Escherichia coli DNA) were also analyzed. The PCR analysis was run on a GeneAmp PCR System 2700 (Applied Biosystems, Sparta, NJ, USA).
For nested PCR, the primer set was composed of fluorescently labeled forward primer 338F (5′-6-FAM-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGC-3′; Integrated DNA Technologies, Singapore) and reverse primer 927R (5′-CCGTCAATTCCTTTAAGTTT-3′) [36]. This nested PCR primer set generated approximately 600-bp amplicons. The preparation process of the reaction mixture and reaction program for nested PCR were the same as those described above, except that 1 µL of PCR product was used instead of the extracted gDNA.
Restriction Digestion
To purify the nested PCR products and make them suitable for enzyme reaction and sequencing, purification with a QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) was conducted to remove excess enzymes, primers, deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (dNTP), and salts. The purification steps were conducted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After purification, 30 µL of nested PCR products was eluted for further analyses. To confirm the fragment size (about 600 bp) of nested PCR products, electrophoresis was performed in 1.5% (w/v) agarose gels.
The purified nested PCR products were quantified using the NanoDrop 2000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific) at 260 nm. Subsequently, approximately 400 ng of the purified nested PCR product was added to a 12-µL mixture containing 40 U of the restriction endonuclease enzyme MspI and 1× CutSmart buffer (both New England Biolabs Ltd., Hitchin, UK), which was then incubated at 37 °C for 14 h. Finally, heating at 75 °C for 15 min was conducted to end the enzyme reaction.
Terminal Fragment Length Analysis
The enzyme-digested samples (2 µL) were mixed with 7 µL of highly deionized formamide (Applied Biosystems) and 1 µL of internal size standard (GeneScanTM-500 LIZTM; Applied Biosystems), which were denatured at 95 °C for 5 min to remove the ghost peaks and then transferred to a 96-well plate for terminal fragment length analysis. The terminal fragment length analysis was performed on an ABI 3130 automatic DNA sequencer with GeneMapper Version 4.0 (both Applied Biosystems). The injection voltage was 2.1 kV, and the injection time was 12 s.
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. NGS
The sequence reads were classified into libraries according their respective barcodes. Among all libraries, a total of 10,272,139 sequences were observed using MiSeq sequencing. After quality control (passing through filters), 10,073,593 sequences were obtained (Table S1). When the primer, barcode, and fusion sequences were excluded, the mean length of 16S RNA reads in each library was approximately 500 bp, with a read quality score >30. The qualified sequences were then aligned based on the Greengenes version 13.5 16S rRNA database [37], and subsequently, a taxonomic classification was established. Bacterial taxa identified at the kingdom level accounted for 99.89–100% of sequences from all the libraries. The cluster files were also constructed as a metagenomics workflow with QIIME [38]. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were picked based on a 97% similarity threshold within the qualified sequence reads (Table S1). A biological observation matrix table was also constructed, containing the core data used in the downstream analysis of OTUs or taxa.
Based on the taxonomy, we estimated the bacterial community structure macroscopically at the phylum level by using a bar chart of the relative abundance of sequences [39]. We then analyzed the bacterial community structure in more detail at the class level using a pie chart [34]. Finally, a heat map, which was designed using the sequence frequencies of the top 10 genus taxa accounting for 78.36–92.93% of all sequences, was used to understand the community structure at the genus taxonomic level [40]. The hierarchical analysis estimated the degree of similarity in the bacterial community among samples collected in different locations and periods.
2.6.2. T-RFLP
For the T-RFLP, data on the terminal reaction fragments (T-RFs) with fragment sizes of 50–600 bp and a peak height of over 50 relative fluorescent intensity were included. The proportion of each T-RF in the samples was calculated, and samples with values below 0.1% were excluded from subsequent analysis. Subsequently, three diversity indices were estimated as follows [41]. Richness (S) was defined as the number of species (T-RFs) in the samples, with a high value representing greater richness. The Shannon–Weiner index (H) was calculated using the formula: −Σ(Pi · ln(Pi)), where Pi is the peak area divided by the sum of the peak area in the samples and a high value represents greater richness for the number of species and that the species are more evenly distributed in a community. Evenness was calculated as H/lnS, with a high value representing the more evenly distributed species in a community.
3. Results
3.1. Compositions of Bacterial Community: FP Case
3.1.1. Phylum Taxon
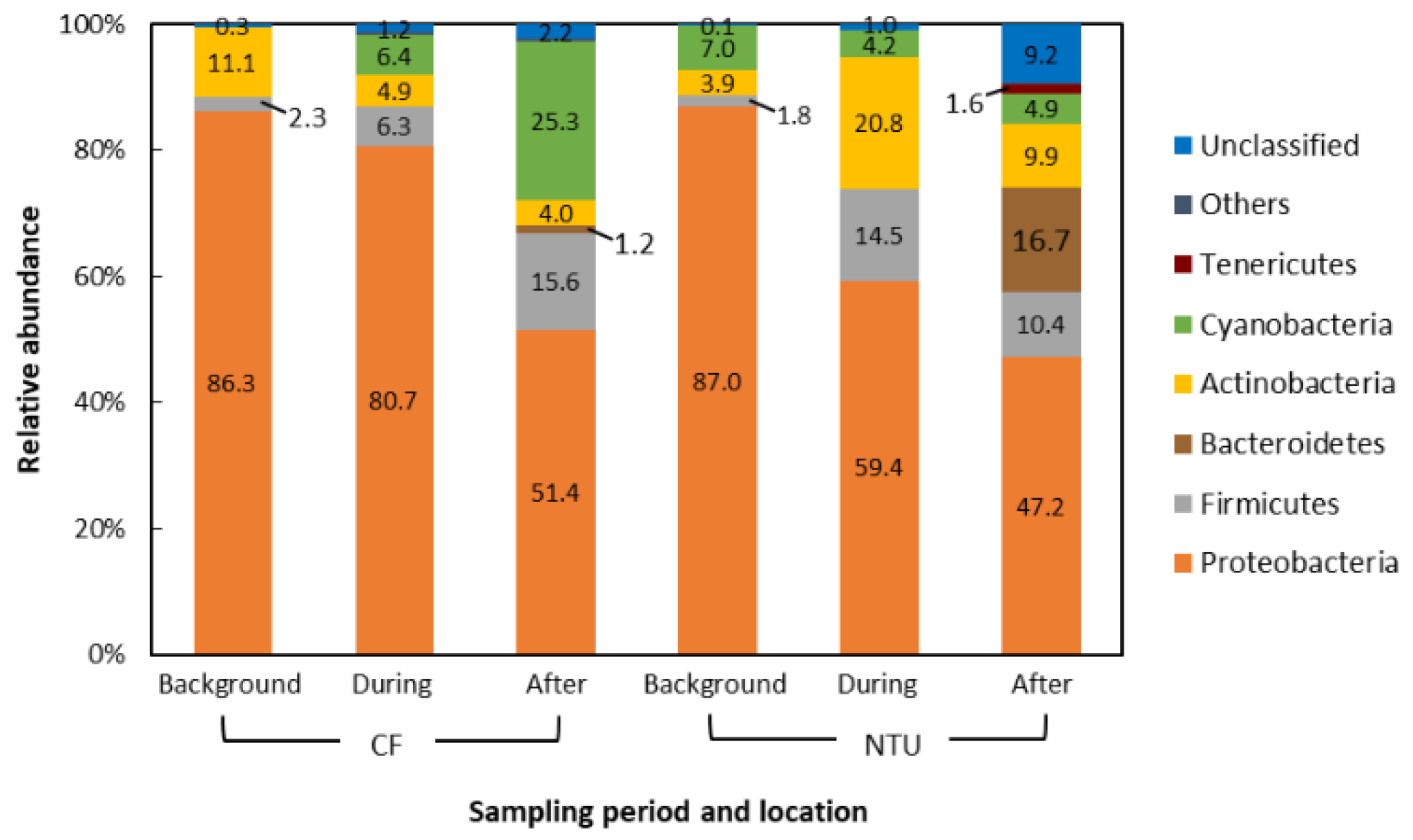
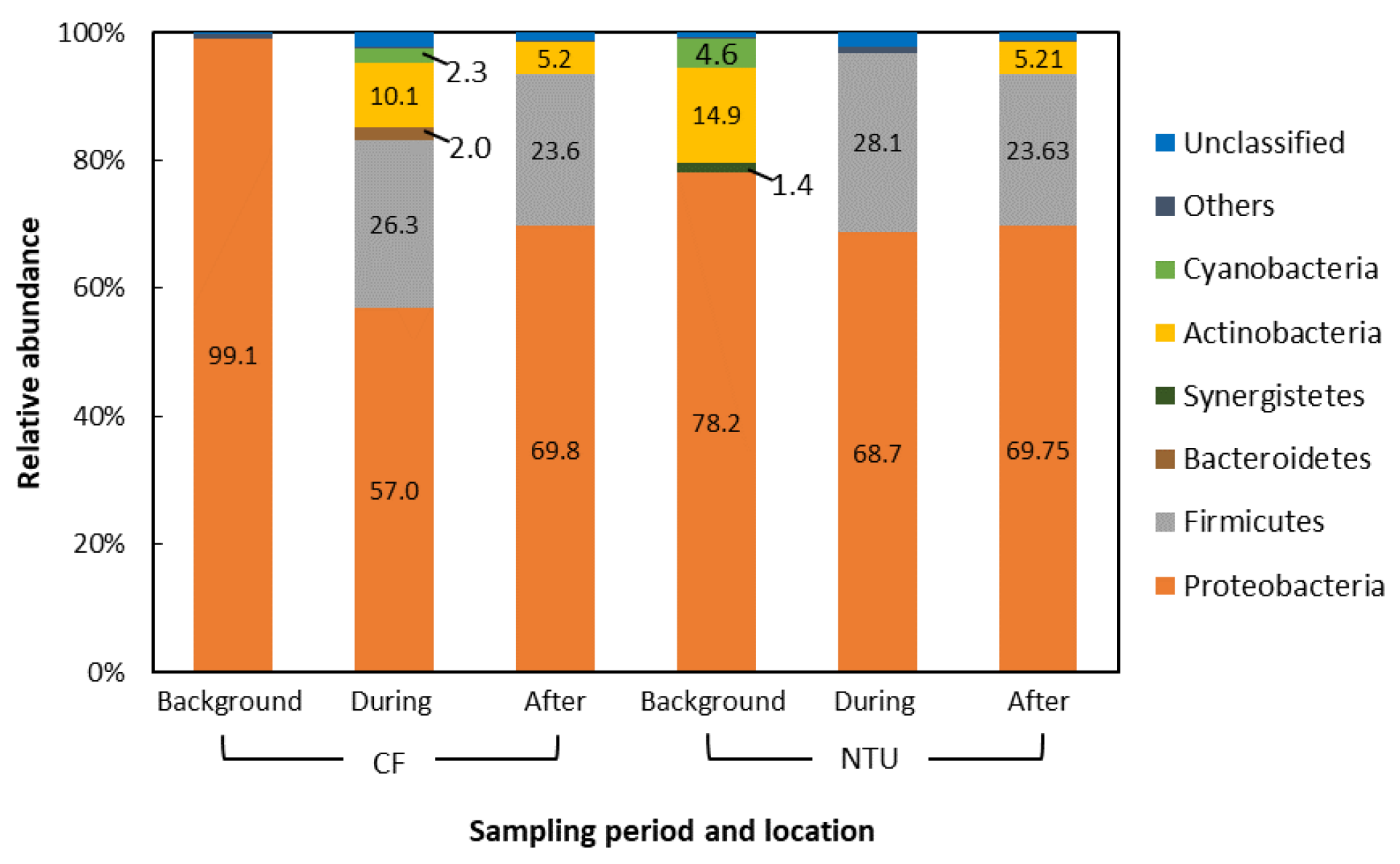
The dominant phyla in the air samples of background days as well as during and after the FP1 case accounted for 90.7–99.6% of all sequences. Generally, the dominant phyla taxa and changes in phyla taxa were similar between CF and NTU samples. However, the relative abundance differed (Figure 2). Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum regardless of sampling periods and locations. However, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria decreased from >80% to less than 60% at CF after FP1 as well as at NTU during and after FP1 (51.4%, 59.4%, and 47.2%, respectively). At both CF and NTU, the sequence abundance of Firmicutes increased during and after FP1 compared with that on background days. At CF, Cyanobacteria abundance increased during and after FP1 but Actinobacteria abundance decreased. However, samples of NTU revealed opposite results, i.e., during and after FP1, Cyanobacteria abundance decreased slightly but Actinobacteria abundance increased. The abundance of Bacteroidetes, Tenericutes, and unclassified bacteria also increased after FP1, especially at NTU.
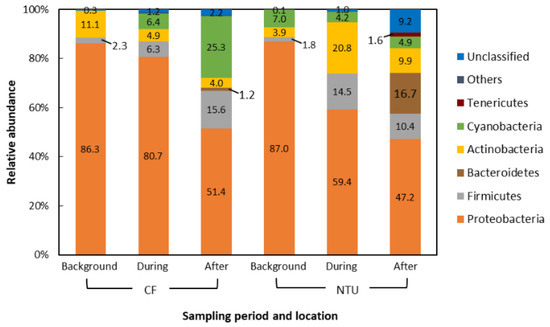
Figure 2.
Compositions of the bacterial community at phylum taxon for FP1 (frontal pollution case 1). The phyla with the relative abundance of less than 1% were not listed.
3.1.2. Class Taxon
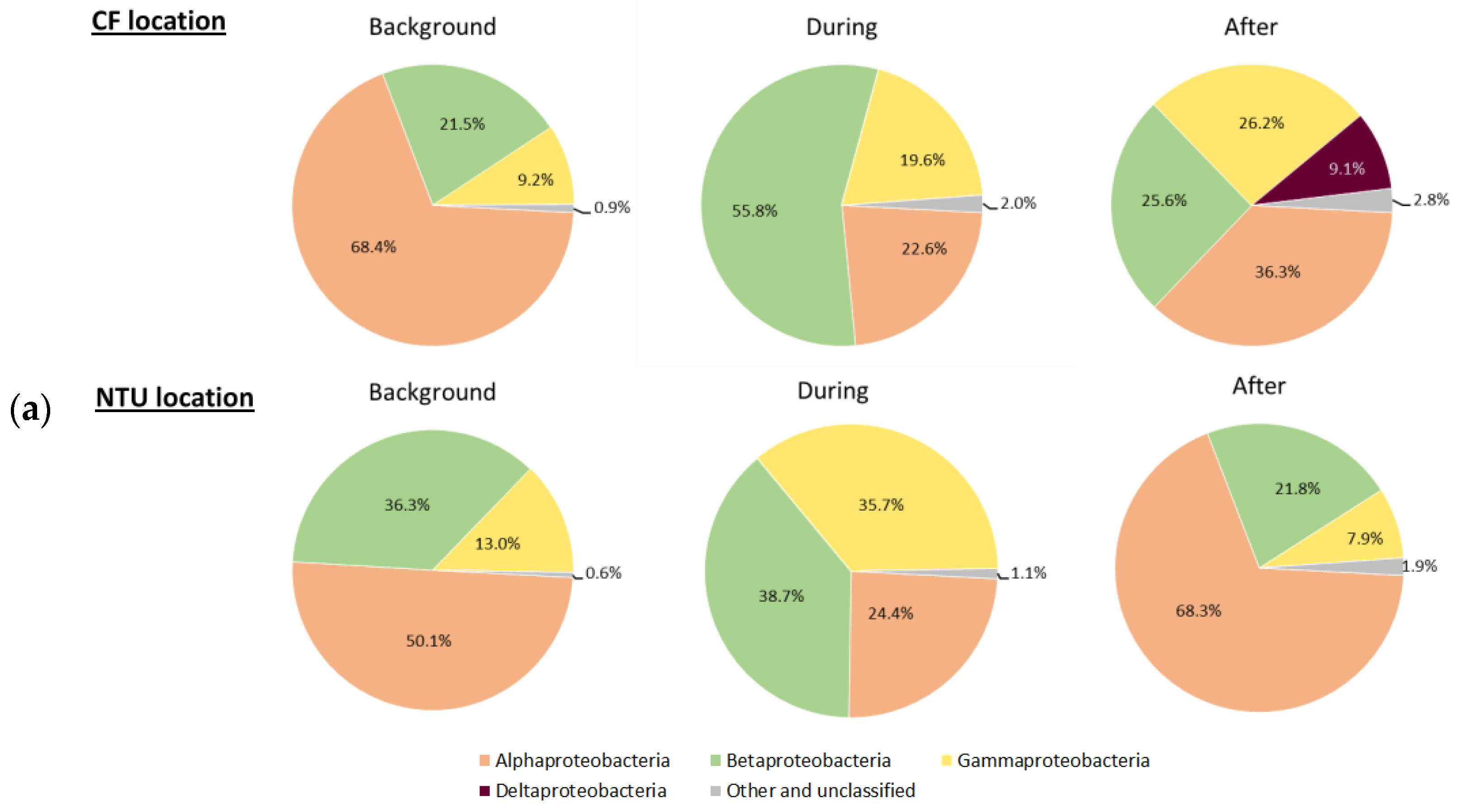
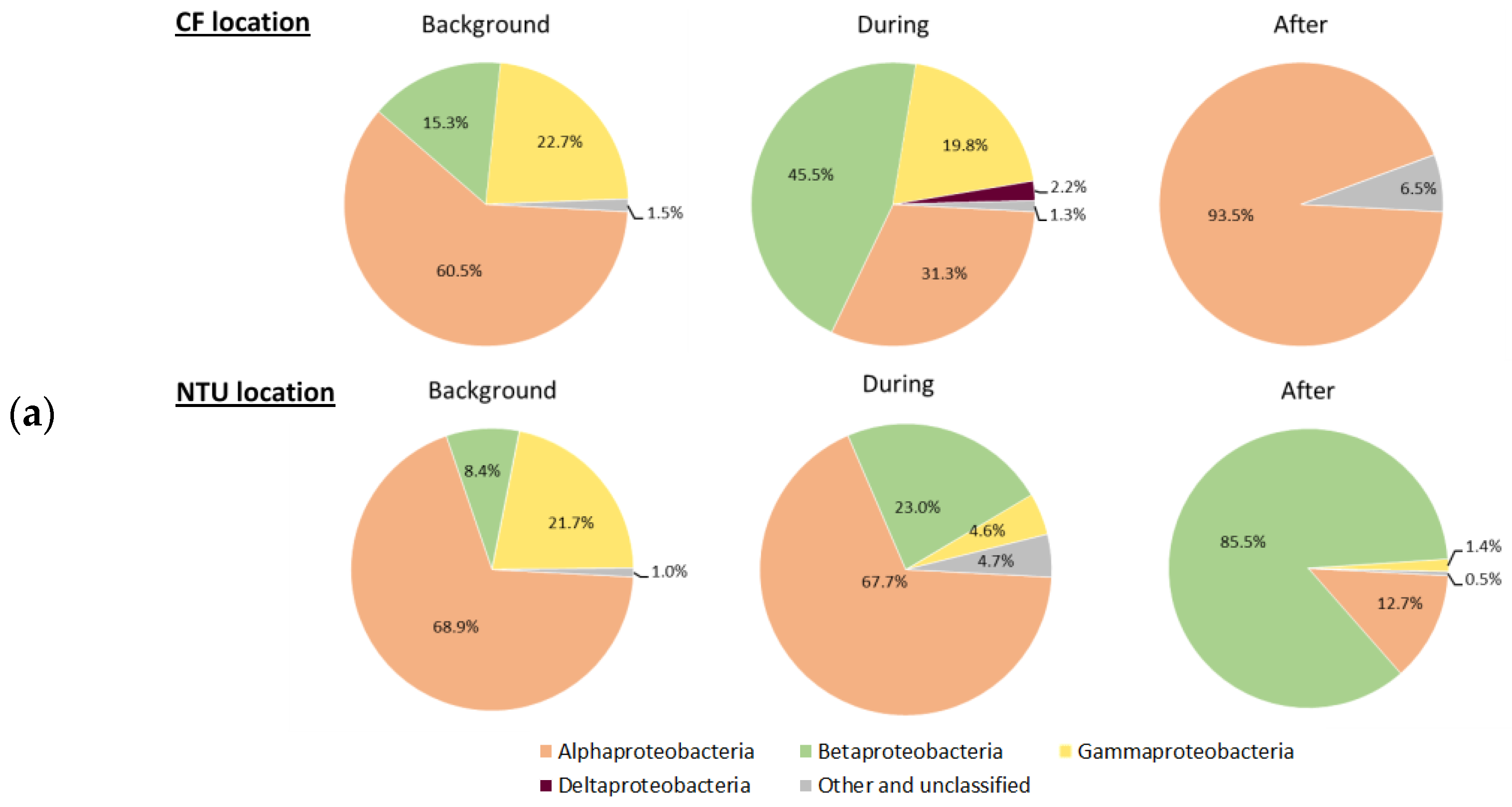
Three main phyla, Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Cyanobacteria, which accounted for 62.5–93.4% of all sequences, were further analyzed for the communities at class taxon. For Proteobacteria-related classes, Alphaproteobacteria was predominant at both locations on background days (Figure 3a). However, at CF during FP1, the relative abundance of Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria increased, whereas that of Alphaproteobacteria decreased. After FP1, Alphaproteobacteria became dominant again, Deltaproteobacteria appeared, and the prevalence of Betaproteobacteria decreased. At NTU, the sequence frequency of Gammaproteobacteria increased but that of Alphaproteobacteria decreased during FP1. After FP1, the proportion of Alphaproteobacteria increased again and those of Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria decreased. Notably, the sequence frequency of the other and unclassified classes slightly increased during and after FP1 regardless of the sampling locations.
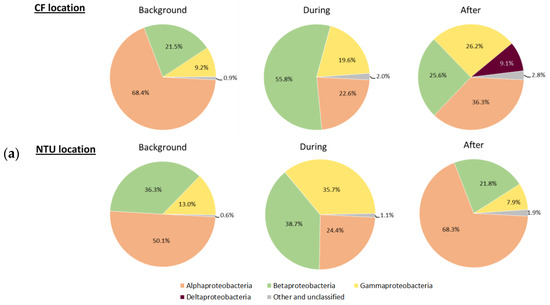
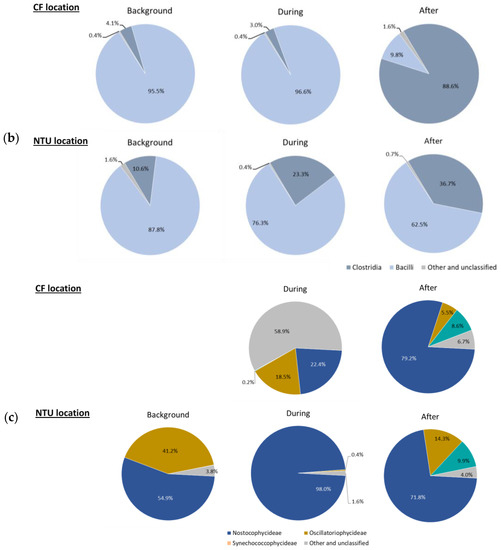
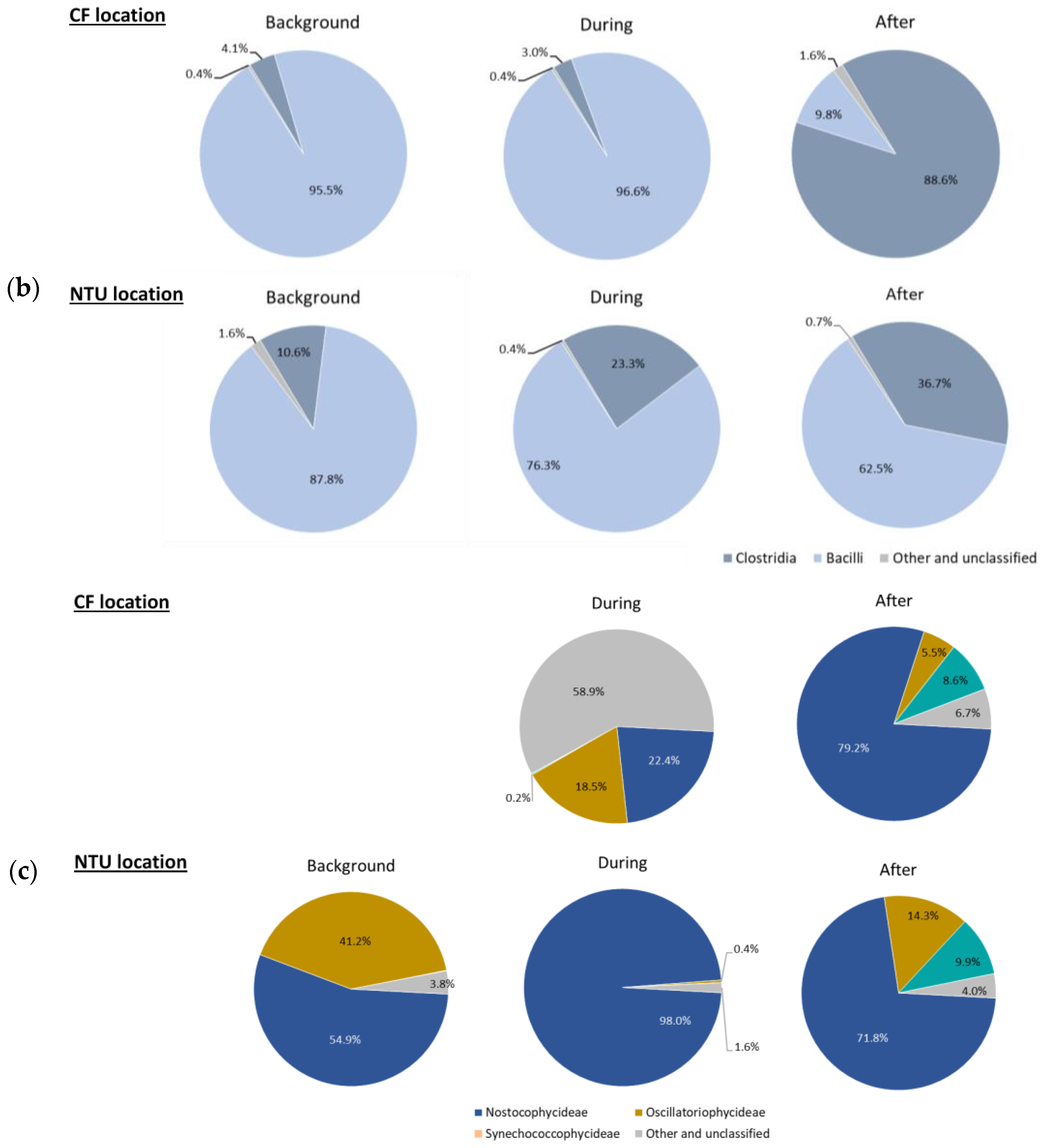
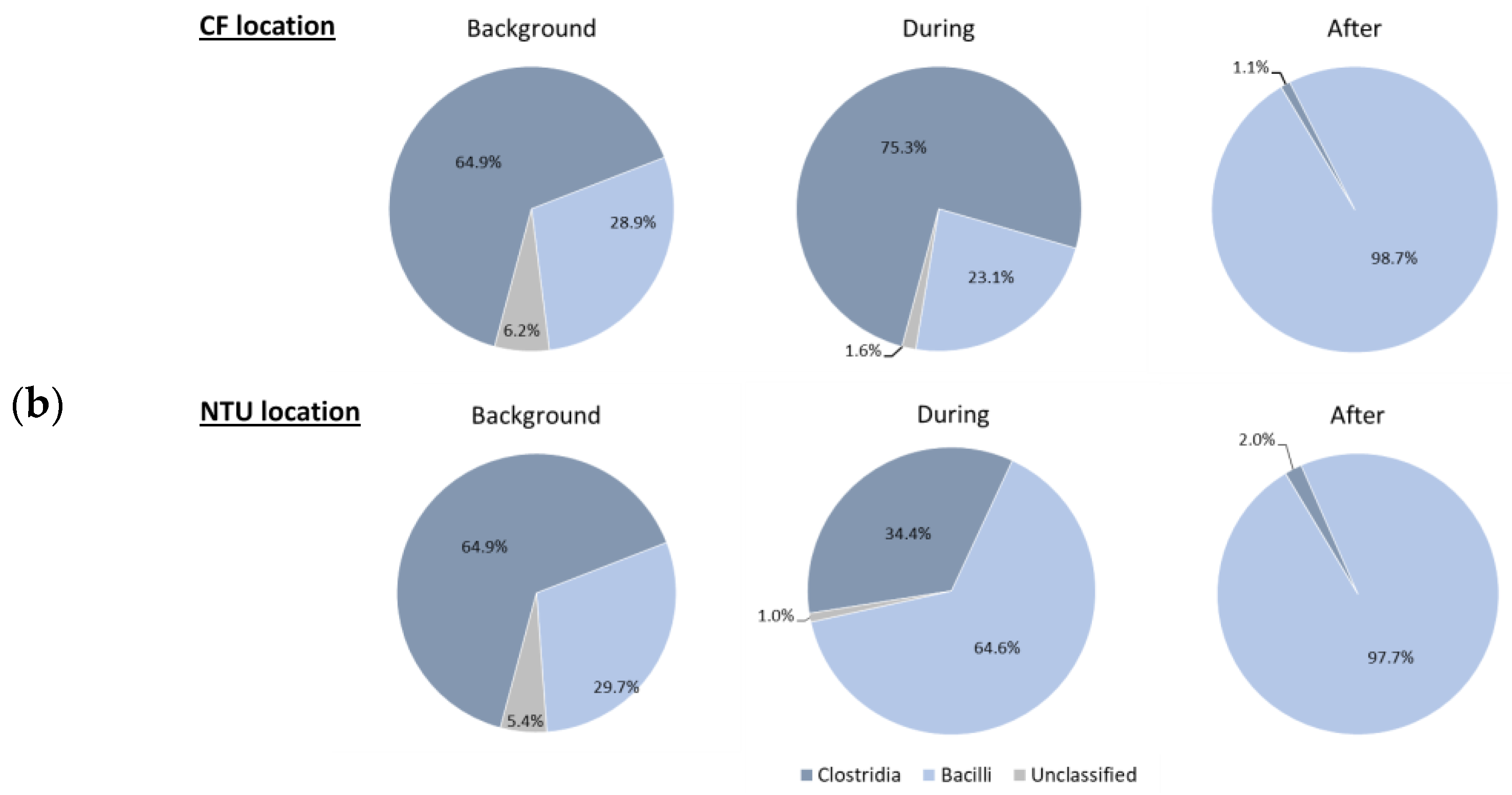
Figure 3.
Classes of Proteobacteria (a), Firmicutes (b); and Cyanobacteria (c) on background days as well as during and after the FP1 (frontal pollution case 1). The classes with the relative abundance of less than 1% were not listed.
Regarding Firmicutes-related classes (Figure 3b), Bacilli was dominant at CF on background days and during FP1 (95.5% and 96.6%, respectively). However, after FP1, the relative abundance of Bacilli at CF dramatically decreased (9.8%); Clostridia became prevalent (88.6%). For NTU, although Bacilli was the most abundant class during our three sampling periods, its proportion decreased during and after FP1 and the lowest one was found after FP1. Correspondingly, the prevalence of Clostridia increased from 10.6% to 36.7%.
For Cyanobacteria-related classes (Figure 3c), at CF, the relative abundance on background days was less than 1%, whereas the sequence frequency increased during FP1 with a higher proportion of Nostocophycideae (22.4%) and Oscilatoriophycideae (18.5%) classes. Interestingly, during FP1, half of the Cyanobacteria-related classes (58.9%) belong to other and unclassified classes. After FP1, the relative abundance of Nostocophycideae at CF drastically increased (79.2%), Oscilatoriophycideae significantly decreased (6.7%), and Synechococcophycideae appeared. For NTU, the major class of Cyanobacteria was Nostocophycideae, and its abundance increased during FP1 and then moderately declined after FP1. Oppositely, the proportion of Oscilatoriophycideae at NTU decreased from 41.2% on background days to 0.4% during FP1 and then slightly increased to 14.3% after FP1. Moreover, Synechococcophycideae appeared at NTU after FP1.
3.1.3. Genus Taxon
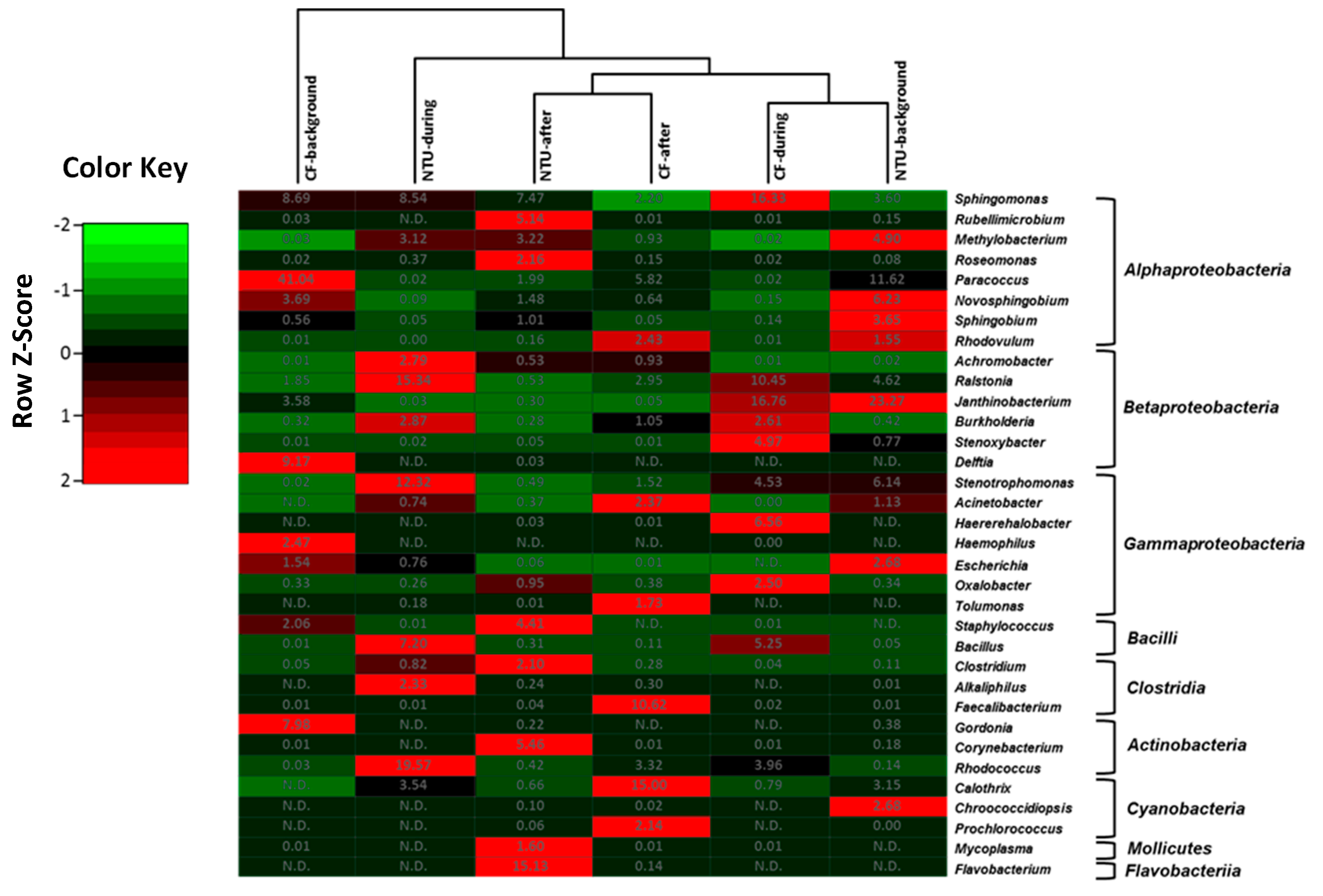
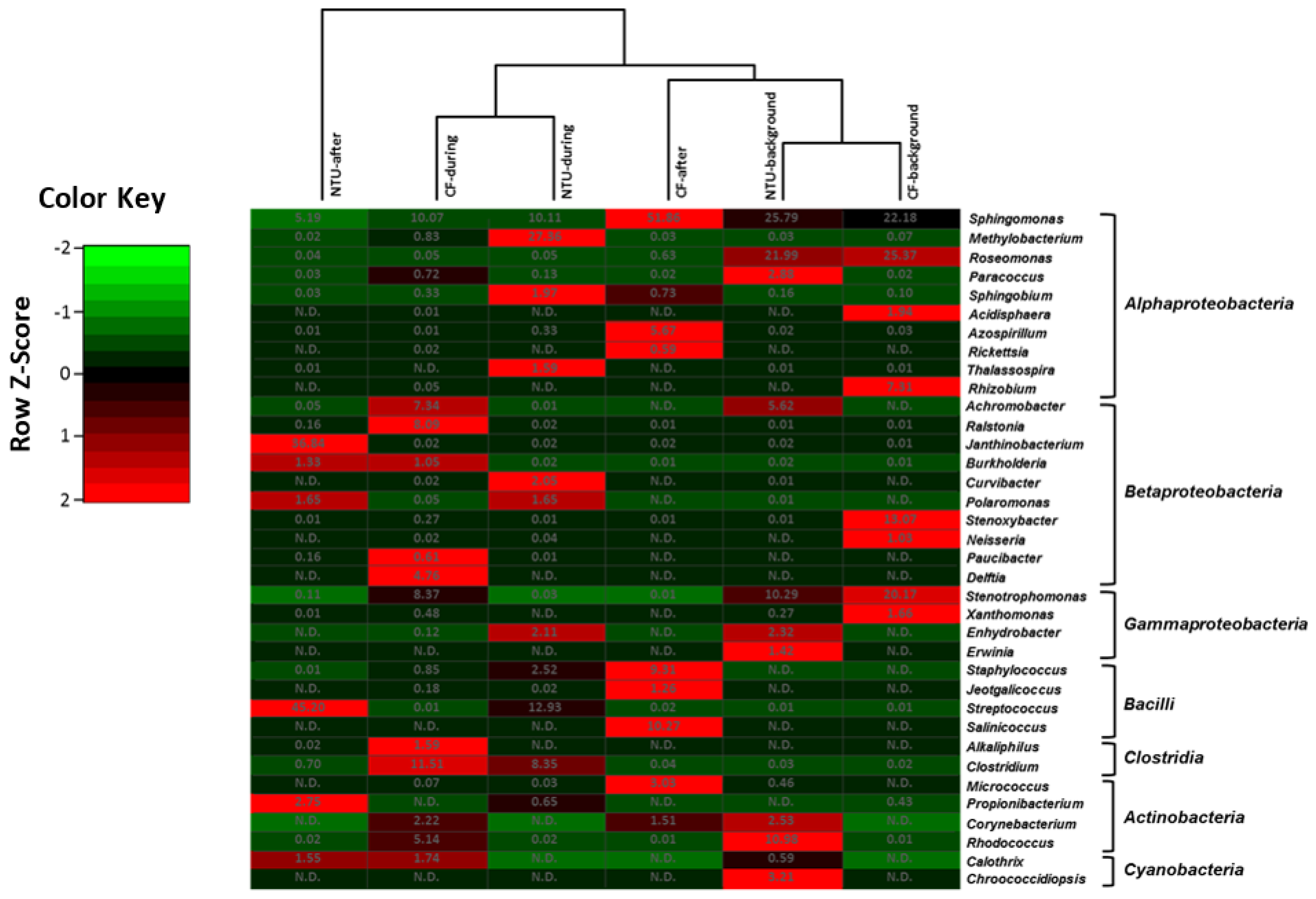
Four community groups were identified in the genus taxon, namely CF-during and NTU-background cluster, CF-after, and NTU-after cluster, NTU-during cluster, and CF-background cluster (Figure 4). The CF-during and NTU-background cluster was distinguished by predominant populations of Janthinobacterium from class Betaproteobacteria, with relative abundances of 16.76–23.27%. In addition to Janthinobacterium, three genera have >10% of the relative abundance: Sphingomonas (16.33%) and Raistonia (10.45%) for the CF-during and Paracoccus (11.62%) for the NTU-background. In terms of the cluster of NTU-after and CF-after, the typical populations observed for CF-after were Faecalibacterium (10.62%) and Calothri (15%), whereas, in the NTU-after, Flavobacterium (15.13%) was dominant. For the NTU-during cluster, Rhodococcus (19.57%), Raistonia (15.34%), and Stenotrophomonas (12.32%) were dominant. As for the CF-background cluster, Paracoccus (41.04%) was highly prevalent.
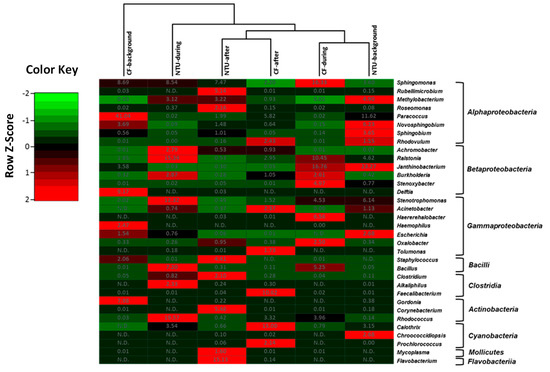
Figure 4.
Heat map displaying the similarity among bacterial community structures in samples collected on background days as well as during and after the FP1 (frontal pollution case 1) based on the sequence frequencies of the top 10 genera. The numbers in the heat map refer to the relative abundance (%) of all genera in a specific sample. The color key shows the standard deviations of sequence frequency from the mean, with light green depicting low frequency and light red depicting high frequency. The genera with the relative abundance of less than 1% were not listed.
Overall, although the bacterial community structures on background days and during FP1 differed between CF and NTU in the hierarchical analysis, a high abundance of Paracoccus was observed on background days, and a high proportion of Bacillus and Raistonia were found during FP1 at both sampling locations. Moreover, the cluster analysis indicated that Sphingomoas (2.20–16.33%) was generally the major contributor to bacterial communities in all samples.
3.2. Compositions of Bacterial Community: ADS
3.2.1. Phylum Taxon
Figure 5 shows that the six dominant phyla with relative abundance >1% accounted for 96.8–99.1% of all sequences. The others and unclassified phyla among all samples accounted for <3.2% of all sequences. In general, Proteobacteria had the highest relative abundance (57.0–99.1%), followed by Firmicutes, regardless of sampling location. The sequence abundance of Proteobacteria decreased during and after the FP1 case compared with that on background days at both sampling locations, whereas that of Firmicutes increased significantly. Members of Actinobacteria and Cyanobacteria were detected at both sampling locations.

Figure 5.
Compositions of the bacterial community at phylum taxon for the Asian dust storm. The phyla with the relative abundance of less than 1% were not listed.
3.2.2. Class Taxon
The three main bacterial phyla (Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Cyanobacteria) that accounted for 62.5–93.4% of all sequences were further examined at the class level.
At CF, the community of Proteobacteria on background days and after an ADS event was dominated by Alphaproteobacteria (Figure 6a). During an ADS, Betaproteobacteria was the most abundant in the Proteobacteria-related classes, and Deltaproteobacteria appeared. At NTU, the Proteobacteria community on background days was dominated by Alphaproteobacteria, similar to the finding at CF. During an ADS, the community was still primarily composed of Alphaproteobacteria, which was then dominated by Betaproteobacteria after the ADS.


Figure 6.
Classes of Proteobacteria (a) and Firmicutes (b) on background days as well as during and after the Asian dust storm. The classes with the relative abundance of less than 1% were not listed.
Regarding the Firmicutes-related community (Figure 6b), the bacterial compositions on background days and after an ADS were the same between CF and NTU. Clostridia (64.9%) and Bacilli (>97%) were the most abundant on background days and after an ADS, respectively. During an ADS, Clostridia was highly represented at CF, whereas Bacilli dominated at NTU.
In terms of the Cyanobacteria-related community, the relative abundance of Cyanobacteria at both locations on background days and at CF after an ADS was less than 1%. During an ADS, Nostocophycideae and Oscillatoriophycideae were dominant at CF and NTU, respectively. At NTU after an ADS, the predominant class of Cyanobacteria was Nostocophycideae.
3.2.3. Genus Taxon
The heat map based on the sequence frequencies of the top 10 genera accounting for 76.71–94.69% of all sequences shows similar bacterial community structures between CF and NTU on background days (Figure 7). The bacterial communities on background days were distinguished by dominant populations of Sphingomonas, Roseomonas, and Stenotrophomonas. Moreover, the community structures of samples collected at CF and NTU during an ADS were in the same cluster, with especially large populations (>8.3%) of Clostridium and Sphingomonas. Streptococcus was also dominant at NTU during an ADS. After an ADS, the bacterial community at CF was relatively similar to that found in the cluster of NTU-background and CF-background, dominated by Sphingomonas (51.86%), Salinicoccus, and Staphylococcus. However, the bacterial community in the NTU-after cluster represented the farthest branch in the cluster analysis, with the characteristic populations being Streptococcus and Janthinobacterium. The heat map shows that Sphingomoas was the major contributor to the bacterial communities at both locations regardless of sampling periods.
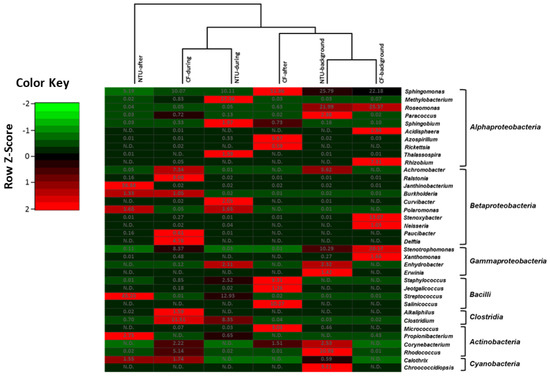
Figure 7.
Heat map displaying the similarity among bacterial community structures in samples collected on background days as well as during and after the Asian dust storm based on the sequence frequencies of the top 10 genera. The numbers in the heat map refer to the relative abundance (%) of all genera in a specific sample. The color key shows the standard deviations of sequence frequency from the mean, with light green depicting low frequency and light red depicting high frequency. The genera with the relative abundance of less than 1% were not listed.
Generally, specific phylotypes were observed in the bacterial communities at different periods and locations. In particular, extensive populations of Rhizobium and Stenoxybacter were detected in CF-background samples. Roseomonas dominated in the NTU-background and CF-background samples. The populations of Ralstonia and Delftia were detected in CF-during samples, and Methylobacterium was detected predominately in NTU-during samples. Furthermore, Streptococcus populations were detected at a relatively high level in the communities during and after an ADS at NTU.
3.3. Impact of FP Cases on Bacterial Community Diversity: T-RFLP
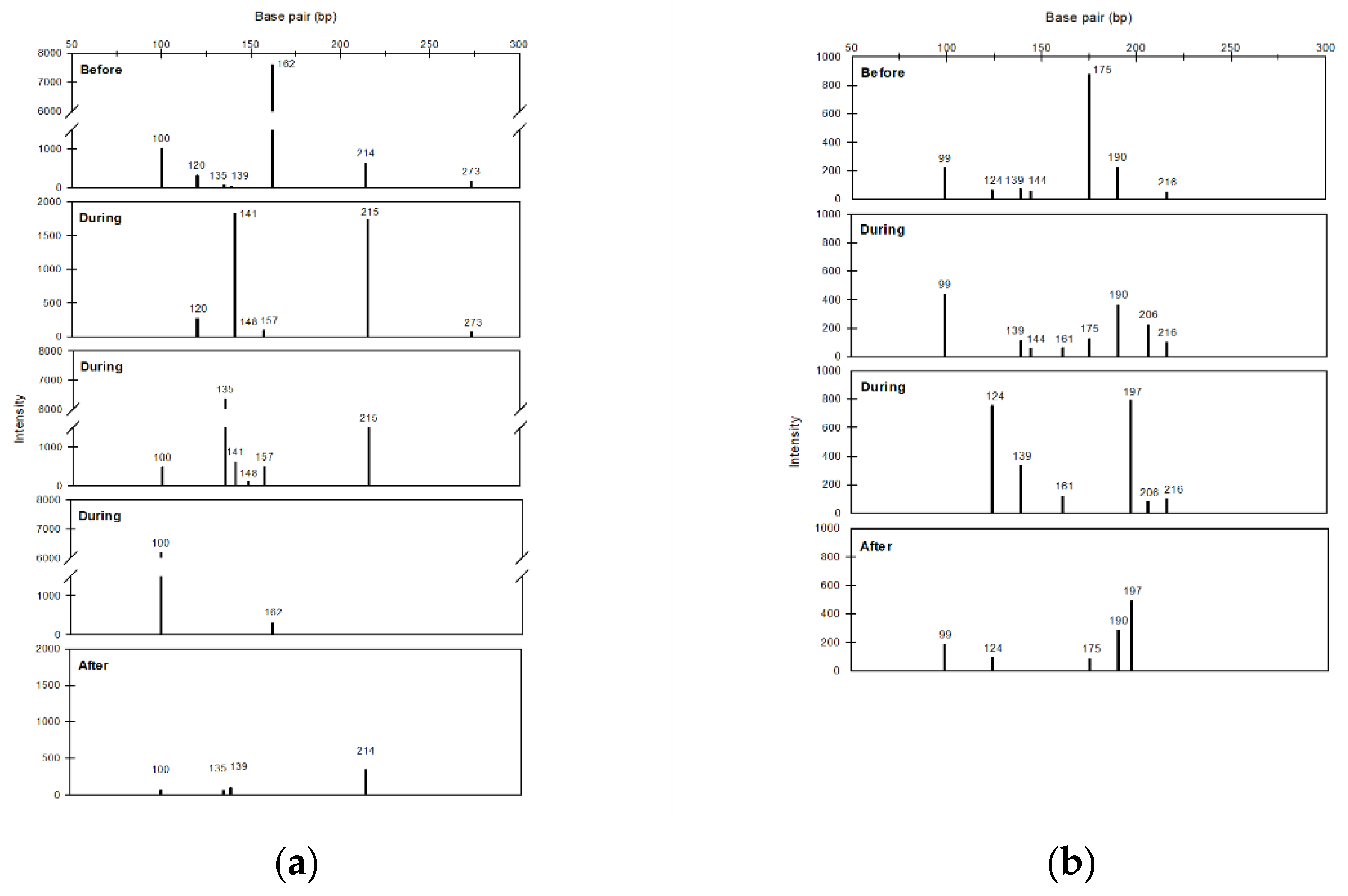
This study also used air samples collected in NTU during 2014–2015 to further assess the impact of FP cases on bacterial community diversity. As shown in Table 2, the richness, H index, and evenness increased during FPs compared with those before FPs, and most of these values decreased in the period after FPs. Furthermore, the T-RFs at different sampling periods were investigated by assessing two FP cases (FP2 and FP6) having the complete sampling period (i.e., before, during, and after FP). The electropherogram generated from the T-RFLP analysis showed that the DNA fragments ranging in size from 50 to 300 bp can be separated well (Figure 8). The T-RFs that only found in the ‘during’ period were at the lengths of 141, 148, 157, and 215 bp for FP2 and 161 and 206 bp for FP6.

Table 2.
Estimated diversity indices of total bacteria at NTU for the five FP cases that occurred during 2014–2015.
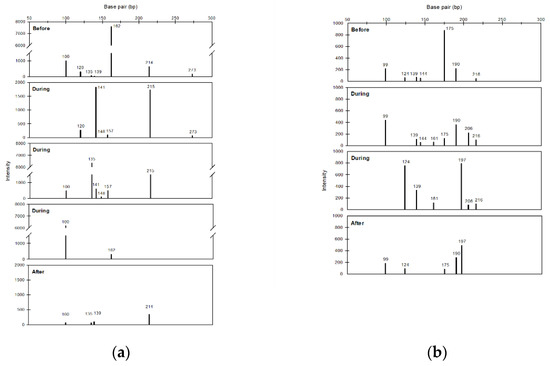
Figure 8.
Histograms of particular terminal restructure fragments of bacteria in samples of NTU before, during and after frontal pollution cases (FP2 (a) and FP6 (b)).
4. Discussion
LRT has been known to worsen air pollution and bioaerosols in downwind areas [4,6,9,10,42,43,44]. However, studies focused on airborne microbes are few, especially for FP cases. Our previous study [6] demonstrated that not only ADSs, but also FPs can transport bioaerosols. This study further revealed that the bacterial community was different before (or background days), during, and after LRT events (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7, Table 2). Based on these findings, both ADSs and FPs can transport bioaerosols to the downwind area, and thereby change the bacterial community among others. Previous studies reported the effect of ADSs on the bacterial community by comparing the results between dusty and non-dusty days [9,10]. This study provided more direct evidence and further showed that the impacts can last days after ADSs (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). Additionally, the effect of FP cases on the bacterial community was first reported.
Our T-RFLP quantitative analysis results provided insights into the bacterial structures dominant during FP cases. Importantly, the richness, H index, and evenness increased during FP cases compared with those on days before FPs and decreased after the end of such cases (Table 2). These findings revealed that the bacterial community structures became more complex and even during the FP cases. Furthermore, some specific T-RFs were only detected during the FP cases (Figure 8). The more complex bacterial community and the specific T-FRs observed during FP cases revealed the increase in bacterial diversity rather than just changing the relative abundance among the pre-existing bacterial taxa. These findings supported that the northeast monsoon wind of the FP cases did long-range transport non-native bacterial strains/species to downwind areas.
The present study also went deep into investigating the bacterial community compositions among three sampling periods of LRT events using high-throughput sequencing. For the FP1 and the ADS event, the major bacterial phyla were Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Cyanobacteria (Figure 2 and Figure 5), which originate from a wide range of terrestrial and marine environments [35]. Among these phyla, Proteobacteria that can survive in the free troposphere [35] were predominant regardless of the sampling site and period. Notably, the prevalence of Firmicutes increased during and after the FP1 and ADS. Firmicutes originate from various natural (e.g., soil, freshwater, and seawater) and artificial sources (e.g., fermented foods, wastewater, compost, and clinical specimens) [45]. Firmicutes were also reported to be a dominant phylum on the surface of desert sand [46,47]. Additionally, some Firmicutes populations can form spores that are resistant to environmental stresses and can survive in extreme atmospheric environments [48], which is in favor of the transport by the LRT. Therefore, when LRT events occur, Firmicutes are lifted and carried by the strong wind from the sources and pathway of LRTs and dispersed to downwind areas, resulting in an increase in their abundance in these areas. It should also be noted that some considerable pathogens, such as Staphylococcus and Clostridium, belong to the Firmicutes phylum.
The present study also analyzed the bacterial community compositions at the class and genera taxa levels. On background days of the FP1 case, Alphaproteobacteria, which includes the genus Paracoccus (Figure 4), was the most abundant among Proteobacteria-related communities at both locations (Figure 3a). In addition, most of these sequences were similar to those of P. homiensis, which has been isolated from the sea sand in South Korea [49]. The HYSPLIT model indicated that part of the air mass swept over Japan and the East China Sea, which are neighboring areas of South Korea (Figure S1a). However, during the FP1 case with the air mass source from the coast of eastern China, the major component at CF and NTU changed to Betaproteobacteria (Figure 3a), indicating that the bacterial community structure was associated with the sources of airflow and the LRT pathway. A genus particularly prevalent was Ralstonia, classed under Betaproteobacteria (Figure 4), and most of the sequences were similar to those of R. insidiosa. R. insidiosa has been isolated from river, pond, and artificial sources (such as activated sludge) and is clinically important and resistant to some antibiotics, such as aminoglycoside gentamicin or the ß-lactam antibiotic aztreonam [50]. Moreover, the populations of Firmicutes increased during FP at both locations (Figure 2), and most of these were similar to Bacillus (class Bacilli) populations (Figure 3b and Figure 4). Although Bacillus was a major phylotype of soil bacteria [51], the number of Bacillus strains that were only detected during the FP1 case was high (Supplementary Material, Figure S3). These results agree with the finding of T-RFLP that the FPs could increase the bacterial diversity (Table 2 and Figure 8) and support that the increase in Bacillus prevalence was associated with the FP1 case. Bacillus can form endospores and has extreme environmental tolerance [52], allowing its long-range transport. It also should be noted that during FP1, other and unclassified Cyanobacteria-related classes increased from <1% to 58.9%. Although the proportion of other and unclassified Cyanobacteria to all bacteria was not high because the relative abundance of Cyanobacteria was only 6.4% at CF location during the FP1 (Figure 1), this large increase revealed the significant impact of FP1 on Cyanobacteria community. Further research is needed to assess the bacterial taxa of this other and unclassified Cyanobacteria. Overall, based on our findings, the FP case could carry bacterial species that are present in its source of air mass and transmission pathway to downwind areas and the transported species might affect human and plant health.
According to the results of clustering (Figure 4), the CF-after and NTU-after were grouped in the same cluster, showing similar bacterial community compositions. During the period of FP1, NTU and CF both had a higher relative abundance of Rasitonia (>10%), Sphingomonas (>8%), Bacillus (>5%), and Stenotrophomonas (>4.5%). Additionally, their relative abundance increased during the FP1 and then decreased after the event. These findings supported that the genera that were affected most by the FP1 in Taiwan were Rasitonia, Sphingomonas, Bacillus, and Stenotrophomonas. We also found that during the FP1, the relative abundance of some bacterial genera increased in only one sampling location, e.g., Janthinobacterium, Stenoxybacter, and Haererehalobacter in CF and Rhodococcus in NTU. Because of the inconsistency between the two sampling locations, we cannot confirm that such increases in these four bacterial genera, especially Rhodococcus (an increase in NTU only), are due to the long-range transport or the stronger local emission of bacteria into the air caused by the intense disturbance and dispersion during the FP case.
As for the ADS-related changes in the bacterial community composition at class and genera levels, we observed that the dominant class of Proteobacteria was correlated with the occurrence of ADS. During an ADS, the abundance of Betaproteobacteria increased regardless of the sampling locations (Figure 6a), indicating that this bacterial population may have multiplied due to ADS events. Among Betaproteobacteria at CF, the prevalence of Ralstonia and Delftia were increased during ADS (Figure 7). A high abundance of Ralstonia was also observed during the FP1 (Figure 4), showing Ralstonia can be long-range transported from China regardless of FP and ADS events. Delftia is found in freshwater and sludge [53,54], and is even an infection bacterium [55]. They are easily carried to downwind areas through LRT because they can use inorganic energy sources (such as inorganic air pollutants that were also transported during ADSs) as food [56].
At NTU, the genus community of Alphaproteobacteria was altered (Figure 7) although its proportion did not change during an ADS and was still the highest among Proteobacteria (Figure 6a). The top two abundant Alphaproteobacteria genera in the NTU-background cluster were Sphinogomonas and Roseomonas, whereas those in the NTU-during were Methylobacterium and Sphingomonas, showing Methylobacterium could be associated with the transport of an ADS. Methylobacterium is broadly distributed in natural environments, including soil, dust, sediments, freshwater, air, and plants [57]. Their high resistance to dehydration [58] favors their transmission through LRT. Methylobacterium species have been reported to be opportunistic pathogens in immunocompromised patients [58]. Another predominant population at NTU-during was Streptococcus belonging to the class Bacilli (Figure 7), and many species have been reported to originate from clinical specimens and cause infectious diseases in humans [59]. However, the increment in Methylobacterium and Streptococcus was not observed in CF, the location where LRT arrives in Taiwan first. Therefore, we suppose that the stronger wind during ADSs may enhance the dispersion of these two genera from the local source around NTU, thereby increasing their relative abundance. Because Methylobacterium and Streptococcus are both infectious and the wind flows primarily from the east and northeast during an ADS, the hospital facility on the east side of the NTU sampling location was one potential emission source. However, further studies are needed to demonstrate this speculation, and to clarify where Methylobacterium are from (natural environments, hospitals, or others?).
During an ADS, there were also large amounts of Firmicutes populations at both locations, particularly Clostridium (class Clostridia). Clostridium species can form endospores against environmental stresses, which favors the long-range transport, and have been detected in dust particles carried to downwind areas during ADSs [60]. The species also act as opportunistic pathogens through the release of exotoxin [61]. Notably, the number of Clostridium strains only detected during the ADS remained large, particularly at CF (Supplementary Material, Figure S4). These findings support the premise that ADSs transported Clostridium to Taiwan, thereby increasing the diversity of Clostridium. For example, at CF, the strain numbers of Clostridium increased from 14 to 37 at CF (Figure S4). Because CF is located at the northernmost point of Taiwan, the earliest arrival point for LRT in winter, the impact of ADSs on CF was higher than that on NTU.
Based on this and our previous study, both ADS and FP events can transport airborne bacteria to the downwind areas and thereby increase the bacterial concentrations [6] and change the community structure of airborne bacteria in these areas. However, the differences between ADSs and FPs on trajectories of the air masses arriving in Taiwan (Supplementary Material, Figures S1 and S2) might lead to varied impacts of ADSs and FPs on bacterial communities. Although Ralstonia, Delftia, Methylobacterium, and Clostridium increased and were dominant during ADSs, an increase in Methylobacterium was found in NTU rather than CF (the earliest arrival point for LRT). Therefore, we suppose that Ralstonia, Delftia, and Clostridium were the bacterial genera related to the long-range transport of ADSs, especially Clostridium, which were increased at both sampling locations. As for the FP, Rasitonia, Sphingomonas, Bacillus, and Stenotrophomonas were the most affected genera in Taiwan. The increment was especially high in Rasitonia and Bacillus. According to our results, the bacteria transported by ADS and FP events have similarities and differences. Ralstonia populations were abundant during ADS and FP events, indicating that they might be the representative population for LRT events. Additionally, Clostridium and Bacillus were the indicator genus for ADSs and FPs, respectively. Because Clostridium and Ralstonia are opportunistic pathogens and have severe health impacts, threats of infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria should be considered when studying the health impacts of LRT. In addition, studies focusing on the viable pathogenic microbes are needed, which could help to provide a greater understanding of the potential risk of infection.
5. Conclusions
This is a pioneering study that simultaneously investigated the community composition of ambient bacteria associated with ADS and FP events in Taiwan. During FP cases, the community structure became more complex and even, and specific T-FRs were observed, showing that FP cases increased bacterial diversity rather than just changing the relative abundance among the pre-existing bacterial taxa. In addition, the bacterial community compositions were varied among background days, the during and after periods of LRT events (including ADS and FP events). The abundance of Firmicutes increased during and after the FP case and the ADS event regardless of sampling locations. At the class level, the increase in populations of Gammaproteobacteria (FP) and Betaproteobacteria (FP and ADS), and Nostocophycideae (FP and ADS) was associated with LRT events. At the genus level, Sphinogomonas was the important contributor to bacterial communities regardless of sampling locations and periods. Generally, the indicator genus of the ADS was Clostridium, whereas that of the FP was Bacillus. Ralstonia was a representative genus of both ADS and FP. In addition, both LRT types can carry air pollutants and bacteria that have adverse effects on human health. Therefore, people in northern Taiwan should carefully consider outdoor activities during the FP case and the ADS event, and even after the LRT events.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13050841/s1, Figure S1: Analysis of 48-h backward trajectories by using the HYSPLIT model on background days (a) and on days during (b,c) and after (d) the FP1; Figure S2: Analysis of 48-h backward trajectories by using the HYSPLIT model on background days (a,b) and on days during (c,d) and after (e,f) an ADS; Figure S3: Venn diagrams comparing the strain numbers of Bacillus on background days and during the FP1 at CF and NTU; Figure S4: Venn diagrams comparing the strain numbers of Clostridium on background days and during an Asian dust storm (ADS); Table S1: Numbers of 16S clusters and OTUs for ADS and FP events in 2013.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.-T.C. and H.-J.S.; methodology, N.-T.C., J.-H.W., C.-Y.L. and C.-C.T.; validation, L.-M.T. and N.-T.C.; formal analysis, L.-M.T.; investigation, N.-T.C., L.-M.T. and N.-S.C.; resources, H.-J.S., C.-Y.L., C.-C.T. and J.-H.W.; data curation, L.-M.T. and N.-S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, N.-T.C. and L.-M.T.; writing—review and editing, N.-T.C.; visualization, L.-M.T.; supervision, J.-H.W. and H.-J.S.; project administration, H.-J.S.; funding acquisition, C.-C.T. and H.-J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan [grant numbers NSC 102-2621-M-006-001 and MOST103-2621-M-006-001].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Center for Genomic Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan, for its assistance in performing NGS, optimizing the NGS procedures, initial data analysis, and quality control. The authors also thank the Research Center of Environmental Changes, Academia Sinica, Taiwan, for the assistance in providing sampling sites.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miao, J.P.; Wang, T. Decadal variations of the East Asian winter monsoon in recent decades. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, e960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Lu, M.M. Intraseasonal predictability of Siberian high and East Asian winter monsoon and its interdecadal variability. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A. Intercontinental Transport of Air Pollution; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Chou, C.C.; Liu, T.H.; Lee, C.T.; Yuan, C.S.; Shiu, C.J.; Young, C.Y. Long-range transport of Asian dust and air pollutants to Taiwan. TAO 2004, 15, 759–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihui, D. Monsoons over China; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.T.; Cheong, N.S.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, C.C.; Su, H.J. Ambient viral and bacterial distribution during long-range transport in Northern Taiwan. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, S.; Elbert, W.; Lawrence, M.; Pöschl, U. Bacteria in the global atmosphere–Part 1: Review and synthesis of literature data for different ecosystems. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9263–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, J.Y.; Kuznetsova, M.R.; Jahns, C.J.; Kemp, P.F. The sea surface microlayer as a source of viral and bacterial enrichment in marine aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, E.; Petroselli, C.; Montalbani, E.; Casagrande, C.; Ceci, E.; Moroni, B.; La Porta, G.; Castellini, S.; Selvaggi, R.; Sebastiani, B.; et al. Airborne bacteria and persistent organic pollutants associated with an intense Saharan dust event in the Central Mediterranean. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazar, Y.; Cytryn, E.; Erel, Y.; Rudich, Y. Effect of dust storms on the atmospheric microbiome in the Eastern Mediterranean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4194–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, M.; Han, H.M.; Dittmann, C.; Setlow, O. Intracellular membranes of bacterial endospores are reservoirs for spore core membrane expansion during spore germination. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, N.P.; Kobayashi, F.; Iwasaka, Y.; Shi, G.Y.; Naganuma, T. Detailed identification of desert-originated bacteria carried by Asian dust storms to Japan. Aerobiologia 2007, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, C.A.; Griffin, D.W. Aerobiology and the global transport of desert dust. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macher, J. Bioaerosols: Assessment and Control; American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH): Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Maki, T.; Susuki, S.; Kobayashi, F.; Kakikawa, M.; Tobo, Y.; Yamada, M.; Higashi, T.; Matsuki, A.; Hong, C.; Hasegawa, H. Phylogenetic analysis of atmospheric halotolerant bacterial communities at high altitude in an Asian dust (KOSA) arrival region, Suzu City. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4556–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polymenakou, P.N.; Mandalakis, M.; Stephanou, E.G.; Tselepides, A. Particle size distribution of airborne microorganisms and pathogens during an intense African dust event in the eastern Mediterranean. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochu, P.; Bouchard, M.; Haddad, S. Physiological daily inhalation rates for health risk assessment in overweight/obese children, adults, and elderly. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darquenne, C. Aerosol deposition in the human lung in reduced gravity. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2014, 27, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatani, K.T.; Ito, I.; Al-Delaimy, W.K.; Adachi, Y.; Mathews, W.C.; Ramsdell, J.W. Desert dust exposure is associated with increased risk of asthma hospitalization in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.C.; Yang, C.H.; Yu, H.L. Estimated effects of Asian Dust Storms on spatiotemporal distributions of clinic visits for respiratory diseases in Taipei children (Taiwan). Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, W.W.; Wong, T.W.; Wong, A.H.; Hui, D.S. Effect of dust storm events on daily emergency admissions for respiratory diseases. Respirology 2012, 17, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.K. Effects of Asian dust events on daily asthma patients in Seoul, Korea. Meteorol. Appl. 2013, 21, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekema, A.; Hirsch, P.; Hooykaas, P.; Schilperoort, R. A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir-and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 1983. 303, 179–180. [CrossRef]
- Lee, R., Jr; Warren, G.J.; Gusta, L.V. Biological Ice Nucleation and Its Applications, 1st ed.; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, C.E.; Sands, D.C.; Vinatzer, B.A.; Glaux, C.; Guilbaud, C.; Buffiere, A.; Yan, S.; Dominguez, H.; Thompson, B.M. The life history of the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae is linked to the water cycle. ISME J. 2008, 2, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. Saharan dust storms: Nature and consequences. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2001, 56, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganor, E.; Osetinsky, I.; Stupp, A.; Alpert, P. Increasing trend of African dust, over 49 years, in the eastern Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D07201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Oanh, N.T.K.; Abuduwaili, J. Variation trends of dust storms in relation to meteorological conditions and anthropogenic Impacts in the northeast edge of the Taklimakan desert, China. Open J. Air Pollut. 2016, 5, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, I.D.S.A.; Briant, R.M.; Engels, S. Drought severity and increased dust storm frequency in the Middle East: A case study from the Tigris–Euphrates alluvial plain, central Iraq. Weather 2019, 74, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Chou, C.C.K.; Huang, S.J.; Liu, C.M.; Kuo, C.H.; Young, C.Y. Long-range transport of aerosols and their impact on the air quality of Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6066–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chou, C.C.; Wang, Z.; Lung, S.C.; Lee, C.T.; Yuan, C.S.; Chen, W.N.; Chang, S.Y.; Hsu, S.C.; Chen, W.C. Impact of different transport mechanisms of Asian dust and anthropogenic pollutants to Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.T.; Marsh, T.L.; Cheng, H.; Forney, L.J. Characterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, B.; Yi, S.M.; Ko, G. Characterization of microbial community during Asian dust events in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5308–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.M.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, Y.P.; Ka, J.O. Impact of Asian dust events on airborne bacterial community assessed by molecular analyses. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4313–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, T.; Kakikawa, M.; Kobayashi, F.; Yamada, M.; Matsuki, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Iwasaka, Y. Assessment of composition and origin of airborne bacteria in the free troposphere over Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.J.; Kretzer, A.M.; Rygiewicz, P.T.; Topa, M.A. Soil bacterial diversity in a loblolly pine plantation: Influence of ectomycorrhizas and fertilization. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 57, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Timonen, H.J.; Jaffe, D.A.; Griffin, D.W.; Birmele, M.N.; Perry, K.D.; Ward, P.D.; Roberts, M.S. Intercontinental dispersal of bacteria and archaea by transpacific winds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Chang, J.E. Pyrosequencing analysis reveals high population dynamics of the soil microcosm degrading octachlorodibenzofuran. Microbes Environ. 2014, 29, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.M.; Kang, H.; Kim, Y.P. Identification of airborne bacterial and fungal community structures in an urban area by T-RFLP analysis and quantitative real-time PCR. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewling, Ł.; Bogawski, P.; Kryza, M.; Magyar, D.; Šikoparija, B.; Skjøth, C.A.; Udvardy, O.; Werner, M.; Smith, M. Concomitant occurrence of anthropogenic air pollutants, mineral dust and fungal spores during long-distance transport of ragweed pollen. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celenk, S. Detection of reactive allergens in long-distance transported pollen grains: Evidence from Ambrosia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.D.; Schevin, P.; Ferrier, J.; Jolly, D.; Andreasen, T.; Ascanius, T.; Ascanius, S.E.; Hendriksen, S.E.; Poulsen, U. Long-distance pollen transport from North America to Greenland in spring. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2008, 113, G02013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, C.N.; Kang, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, S.Y.; Woo, J.J.; Park, C.; Bae, K.S.; Kim, M.S. Taxonomic hierarchy of the phylum Firmicutes and novel Firmicutes species originated from various environments in Korea. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Couteau, C.; Luo, F.; Neveu, J.; DuBow, M.S. Bacterial diversity of surface sand samples from the Gobi and Taklamaken Deserts. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belov, A.A.; Cheptsov, V.S.; Vorobyova, E.A. Soil bacterial communities of Sahara and Gibson deserts: Physiological and taxonomical characteristics. Aims Microbiol. 2018, 4, 685–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueche, M.; Wunderlin, T.; Roussel-Delif, L.; Junier, T.; Sauvain, L.; Jeanneret, N.; Junier, P. Quantification of Endospore-Forming Firmicutes by Quantitative PCR with the Functional Gene spo0A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5302–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Weon, H.Y.; Yoo, S.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Cho, Y.H.; Stackebrandt, E.; Go, S.J. Paracoccus homiensis sp. nov., isolated from a sea-sand sample. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2387–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryan, M.P.; Adley, C.C. The antibiotic susceptibility of water-based bacteria Ralstonia pickettii and Ralstonia insidiosa. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felske, A.; Wolterink, A.; Van Lis, R.; Akkermans, A.D. Phylogeny of the main bacterial 16S rRNA sequences in Drentse A grassland soils (The Netherlands). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, W.L.; Munakata, N.; Horneck, G.; Melosh, H.J.; Setlow, P. Resistance of Bacillus endospores to extreme terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 548–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, N.O.; Brandt, K.K.; Nybroe, O.; Hansen, M. Delftia lacustris sp. nov., a peptidoglycan-degrading bacterium from fresh water, and emended description of Delftia tsuruhatensis as a peptidoglycan-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2195–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, T.; Yumihara, K.; Ueda, Y.; Numaguchi, M.; Morimura, S.; Kida, K. Delftia tsuruhatensis sp. nov., a terephthalate-assimilating bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Sistla, S.; Dhodapkar, R.; Parija, S.C. Fatal Delftia acidovorans infection in an immunocompetent patient with empyema. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 923–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, G.M.; Bell, J.A.; Lilburn, T. Class II. Betaproteobacteria class. nov. In Bergey’s Manual® of Systematic Bacteriology; Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knief, C.; Frances, L.; Cantet, F.; Vorholt, J.A. Cultivation-independent characterization of Methylobacterium populations in the plant phyllosphere by automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaleva, J.; Degener, J.E.; van der Mei, H.C. Methylobacterium and its role in health care-associated infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facklam, R. What happened to the streptococci: Overview of taxonomic and nomenclature changes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Baba, T.; Ichijo, T.; Himezawa, Y.; Enoki, K.; Saraya, M.; Li, P.F.; Nasu, M. Abundance and community structure of bacteria on Asian dust particles collected in Beijing, China, during the Asian dust season. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.P.; Gibson, G.; Maczulak, A.; Schoemaker, P.J.H.; Schoemaker, J.A. Germs, Genes, and Bacteria: How They Influence Modern Life (Collection); Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).