Physicochemical Characterization of Air Pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM>2.5) in an Urban Area of Cotonou, Benin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods (See the Schematic Diagram, Figure S1)
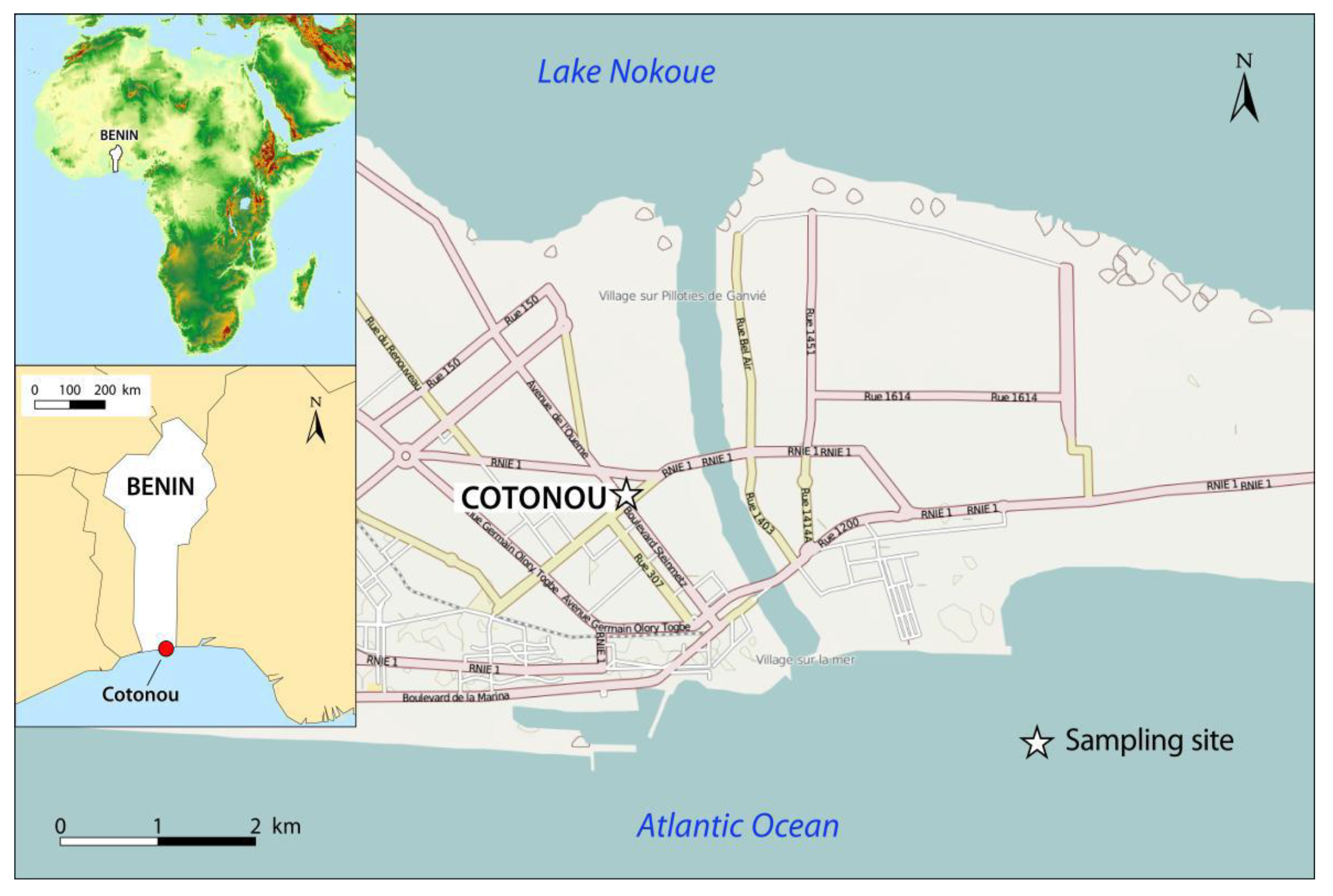
2.1. Site Description and PM Sampling
2.2. Experimental Analysis
2.2.1. PM Physical Characterization
PM Size Distribution
Specific Surface Area
2.2.2. Inorganic Elements and Water-Soluble Ions
2.2.3. Element Composition
2.2.4. Organic Compounds
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PM Physical Characteristics
3.2. Inorganic Elements and Water-Soluble Ions
3.3. Element Composition
3.4. Organic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baulig, A.; Singh, S.; Marchand, A.; Schins, R.; Barouki, R.; Garlatti, M.; Marano, F.; Baeza-Squiban, A. Role of Paris PM2.5 Components in the pro-Inflammatory Response Induced in Airway Epithelial Cells. Toxicology 2009, 261, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osornio-Vargas, A.R.; Serrano, J.; Rojas-Bracho, L.; Miranda, J.; García-Cuellar, C.; Reyna, M.A.; Flores, G.; Zuk, M.; Quintero, M.; Vázquez, I.; et al. In Vitro Biological Effects of Airborne PM2.5 and PM10 from a Semi-Desert City on the Mexico–US Border. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.G.; Gualtieri, M.; Ferrero, L.; Porto, C.L.; Udisti, R.; Bolzacchini, E.; Camatini, M. Seasonal Variations in Chemical Composition and in Vitro Biological Effects of Fine PM from Milan. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, J. Will the Circle Be Unbroken: A History of the U.S. National Ambient Air Quality Standards. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 652–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., 3rd; Burnett, R.T.; Krewski, D.; Jerrett, M.; Shi, Y.; Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J. Cardiovascular Mortality and Exposure to Airborne Fine Particulate Matter and Cigarette Smoke: Shape of the Exposure-Response Relationship. Circulation 2009, 120, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachwenkizi, J.; Liu, C.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Hammer, M.S.; Chen, R.; Kan, H. Fine Particulate Matter Constituents and Infant Mortality in Africa: A Multicountry Study. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachwenkizi, J.; Liu, C.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Hammer, M.S.; Chen, R.; Kan, H. Maternal Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight in Africa. Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergham, M.; Lepers, C.; Verdin, A.; Billet, S.; Cazier, F.; Courcot, D.; Shirali, P.; Garçon, G. Prooxidant and Proinflammatory Potency of Air Pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5–0.3) Produced in Rural, Urban, or Industrial Surroundings in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 904–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieme, D.; Cabral-Ndior, M.; Garçon, G.; Verdin, A.; Billet, S.; Cazier, F.; Courcot, D.; Diouf, A.; Shirali, P. Relationship between Physicochemical Characterization and Toxicity of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected in Dakar City (Senegal). Environ. Res. 2012, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisa, E.; Kuuire, V.; Adams, M. Children’s Exposure to Indoor and Outdoor Black Carbon and Particulate Matter Air Pollution at School in Rwanda, Central-East Africa. Environ. Adv. 2023, 11, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, M.A.; Onwunzo, C.S.; Adesina, O.A.; Sonibare, J.A. Particulate Matters Pollution in Selected Areas of Nigeria: Spatial Analysis and Risk Assessment. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanker, A.; Barnett, W.; Chartier, R.; MacGinty, R.; Zar, H.J. Personal Monitoring of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Exposure in Mothers and Young Children in a South African Birth Cohort Study—A Pilot Study. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 294, 119513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Fujimura, M.; Kayamuro, H.; Yamashita, K.; Higashisaka, K.; Nakanishi, R.; Morishita, Y.; Nabeshi, H.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Urban Aerosols Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Macrophages and Cause Airway Inflammation in Vivo. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, B.; Kan, H. Fine Particulate Matter Constituents and Cardiopulmonary Mortality in a Heavily Polluted Chinese City. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Size, Source and Chemical Composition as Determinants of Toxicity Attributable to Ambient Particulate Matter. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 504–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Deng, F.; Liu, Y.; Yao, W. The Relationship between Particulate Matter (PM 10) and Hospitalizations and Mortality Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Meta-Analysis. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2013, 10, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazier, F.; Dewaele, D.; Delbende, A.; Nouali, H.; Garçon, G.; Verdin, A.; Courcot, D.; Bouhsina, S.; Shirali, P. Sampling Analysis and Characterization of Particles in the Atmosphere of Rural, Urban and Industrial Areas. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delfino, R.J.; Gillen, D.L.; Tjoa, T.; Staimer, N.; Polidori, A.; Arhami, M.; Sioutas, C.; Longhurst, J. Electrocardiographic ST-Segment Depression and Exposure to Traffic-Related Aerosols in Elderly Subjects with Coronary Artery Disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocbach, A.; Li, Y.; Yttri, K.E.; Cassee, F.R.; Schwarze, P.E.; Namork, E. Physicochemical Characterisation of Combustion Particles from Vehicle Exhaust and Residential Wood Smoke. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouassi, K.S.; Billet, S.; Garçon, G.; Verdin, A.; Diouf, A.; Cazier, F.; Djaman, J.; Courcot, D.; Shirali, P. Oxidative Damage Induced in A549 Cells by Physically and Chemically Characterized Air Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Hvidberg, M.; Jensen, S.S.; Ketzel, M.; Sørensen, M.; Loft, S.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A. Lung Cancer Incidence and Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution from Traffic. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senlin, L.; Zhenkun, Y.; Xiaohui, C.; Minghong, W.; Guoying, S.; Jiamo, F.; Paul, D. The Relationship between Physicochemical Characterization and the Potential Toxicity of Fine Particulates (PM2.5) in Shanghai Atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7205–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.M.; Kim, H.R.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Chung, K.H. Organic Extracts of Urban Air Pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5)-Induced Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Human Lung Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B Cells). Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2011, 723, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, J.L.; Anderson, H.R.; Bremner, S.A.; Marston, L.; Seemungal, T.A.; Strachan, D.P.; Wedzicha, J.A. Outdoor Air Pollution and Respiratory Health in Patients with COPD. Thorax 2011, 66, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Inambao, F.L.; Ampah, J.D. Evaluation of Biodiesel on Speciated PM2.5, Organic Compound, Ultrafine Particle and Gaseous Emissions from a Low-Speed EPA Tier II Marine Diesel Engine Coupled with DPF, DEP and SCR Filter at Various Loads. Energy 2022, 239, 121837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varenik, A.V. The Characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 and Elemental Carbon Air Pollution in Sevastopol, Crimean Peninsula. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Inambao, F.L. Effect of Low Bioethanol Fraction on Emissions, Performance, and Combustion Behavior in a Modernized Electronic Fuel Injection Engine. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2021, 11, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwumiju, A.S.; Ajisafe, T.; Adelodun, A.A. Airborne Particulate Matter Pollution in Akure Metro City, Southwestern Nigeria, West Africa: Attribution and Meteorological Influence. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2021, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nducol, N.; Tchuente Siaka, Y.F.; Younui Yakum-Ntaw, S.; Saidou; Dika Manga, J.; Vardamides, J.C.; Hamadou, Y.A.; Simo, A. Ambient Air Particle Mass Concentrations in the Urban Area of the Capital City of Yaoundé (Cameroon, Central Africa): Monthly and Seasonal Behaviour. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 2909–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, A.; Garçon, G.; Diop, Y.; Ndiaye, B.; Thiaw, C.; Fall, M.; Kane-Barry, O.; Ba, D.; Haguenoer, J.M.; Shirali, P. Environmental Lead Exposure and Its Relationship to Traffic Density among Senegalese Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbo, K.E.; Walgraeve, C.; Eze, J.I.; Ugwoke, P.E.; Ukoha, P.O.; Van Langenhove, H. A Review on Ambient and Indoor Air Pollution Status in Africa. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, E.P.; Jack, D.W.; Volavka-Close, N.H.; Kinney, P.L. Particulate Matter Pollution in African Cities. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, W.; Kumie, A.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.; Lai, A.; Sricharoenvech, P.; Patz, J.; Samet, J.; Schauer, J.J. Source Apportionment of Fine Organic Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in Central Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogbe, P.H.; Ayi-Fanou, L.; Cachon, B.; Chabi, N.; Debende, A.; Dewaele, D.; Aissi, F.; Cazier, F.; Sanni, A. Hematological Changes among Beninese Motor-Bike Taxi Drivers Exposed to Benzene by Urban Air Pollution. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachon, B.; Ayi-Fanou, L.; Cazier, F.; Genevray, P.; Adéoti, K.; Dewaele, D.; Debende, A.; Aissi, F.; Sanni, A. Analysis of Gasoline Used by Motorbike-Taxi Drivers in Cotonou. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kounouhewa, B.; Koto N’Gobi, G.; Houngue, H.; Müller, L.; Wirtz, M.; Yurtsever-Kneer, S.; Fink, H.; Kneer, A.; Barbe, S. Cotonou’s next Breath: Particulate Matter Monitoring and Capturing. Sci. Afr. 2020, 8, e00367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Leite, A.; Léon, J.-F.; Macouin, M.; Rousse, S.; da Trindade, R.I.F.; Proietti, A.; Drigo, L.; Antonio, P.Y.J.; Akpo, A.B.; Yoboué, V.; et al. PM2.5 Magnetic Properties in Relation to Urban Combustion Sources in Southern West Africa. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kèlomé, N.C.; Lévêque, J.; Andreux, F.; Milloux, M.-J.; Oyédé, L.-M. C4 Plant Isotopic Composition (δ13C) Evidence for Urban CO2 Pollution in the City of Cotonou, Benin (West Africa). Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avogbe, P.H.; Ayi-Fanou, L.; Autrup, H.; Loft, S.; Fayomi, B.; Sanni, A.; Vinzents, P.; Møller, P. Ultrafine Particulate Matter and High-Level Benzene Urban Air Pollution in Relation to Oxidative DNA Damage. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayi Fanou, L.; Mobio, T.A.; Creppy, E.E.; Fayomi, B.; Fustoni, S.; Møller, P.; Kyrtopoulos, S.; Georgiades, P.; Loft, S.; Sanni, A.; et al. Survey of Air Pollution in Cotonou, Benin—Air Monitoring and Biomarkers. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 358, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billet, S.; Garçon, G.; Dagher, Z.; Verdin, A.; Ledoux, F.; Cazier, F.; Courcot, D.; Aboukais, A.; Shirali, P. Ambient Particulate Matter (PM2.5): Physicochemical Characterization and Metabolic Activation of the Organic Fraction in Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549). Environ. Res. 2007, 105, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baneschi, I.; Dallai, L.; Giazzi, G.; Guidi, M.; Krotz, L. A Method for the Definition of the Carbon Oxidation Number in the Gases Dissolved in Waters and the Redox Variations Using an Elemental Analyser (FlashEA 1112). Preliminary Data from a Stratified Lake. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 124, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksperiandova, L.P.; Fedorov, O.I.; Stepanenko, N.A. Estimation of Metrological Characteristics of the Element Analyzer EuroVector EA-3000 and Its Potential in the Single-Reactor CHNS Mode. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplain, I.; Cazier, F.; Nouali, H.; Mercier, A.; Déchaux, J.-C.; Nollet, V.; Joumard, R.; André, J.-M.; Vidon, R. Emissions of Unregulated Pollutants from European Gasoline and Diesel Passenger Cars. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5954–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeleke, M.A.; Bamgbose, J.T.; Oguntoke, O.; Itua, E.O.; Bamgbose, O. Assessment of Health Impacts of Vehicular Pollution on Occupationally Exposed People in Lagos Metropolis, Nigeria. Trace Elem. Electrolytes 2011, 28, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndong Ba, A.; Cazier, F.; Verdin, A.; Garcon, G.; Cabral, M.; Courcot, L.; Diouf, A.; Courcot, D.; Gualtieri, M.; Fall, M. Physico-Chemical Characterization and in Vitro Inflammatory and Oxidative Potency of Atmospheric Particles Collected in Dakar City’s (Senegal). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchrif, A.; Tahri, M.; Guinot, B.; Chakir, E.M.; Zahry, F.; Bagdhad, B.; Bounakhla, M.; Cachier, H.; Costabile, F. Aerosols in Northern Morocco-2: Chemical Characterization and PMF Source Apportionment of Ambient PM2.5. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, W.; Kumie, A.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.; Lai, A.; Sricharoenvech, P.; Samet, J.; Patz, J.; Schauer, J.J. Chemical Characterization and Seasonality of Ambient Particles (PM2.5) in the City Centre of Addis Ababa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, P.L.; Gichuru, M.G.; Volavka-Close, N.; Ngo, N.; Ndiba, P.K.; Law, A.; Gachanja, A.; Gaita, S.M.; Chillrud, S.N.; Sclar, E. Traffic Impacts on PM2.5 Air Quality in Nairobi, Kenya. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, J.P.; Hedges, S.R.; Kimbrough, S. Characterization and Aerosol Mass Balance of PM2.5 and PM10 Collected in Conakry, Guinea during the 2004 Harmattan Period. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, K.L.; Rooney, M.S.; Arku, R.E.; Friedman, A.B.; Hughes, A.F.; Vallarino, J.; Agyei-Mensah, S.; Spengler, J.D.; Ezzati, M. Within-Neighborhood Patterns and Sources of Particle Pollution: Mobile Monitoring and Geographic Information System Analysis in Four Communities in Accra, Ghana. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.-P.; Cai, M.-J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.-B.; Yan, J.-P.; Schwab, J.J.; Yuan, C.-S. Chemical Nature of PM2.5 and PM10 in the Coastal Urban Xiamen, China: Insights into the Impacts of Shipping Emissions and Health Risk. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 227, 117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mandal, T.K. Chemical Composition of Fine Mode Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in an Urban Area of Delhi, India and Its Source Apportionment. Urban Clim. 2017, 21, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Shirasuna, Y.; Hirano, K.; Masunaga, S. Characterization of PM2.5, PM2.5–10 and PM> 10 in Ambient Air, Yokohama, Japan. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diapouli, E.; Manousakas, M.; Vratolis, S.; Vasilatou, V.; Maggos, T.; Saraga, D.; Grigoratos, T.; Argyropoulos, G.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C.; et al. Evolution of Air Pollution Source Contributions over One Decade, Derived by PM10 and PM2.5 Source Apportionment in Two Metropolitan Urban Areas in Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrica, D.; Tamburo, E.; Vultaggio, M.; Di Carlo, I. ATR-FTIR Spectral Analysis and Soluble Components of PM10 And PM2.5 Particulate Matter over the Urban Area of Palermo (Italy) during Normal Days and Saharan Events. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sillanpää, M.; Hillamo, R.; Saarikoski, S.; Frey, A.; Pennanen, A.; Makkonen, U.; Spolnik, Z.; Van Grieken, R.; Braniš, M.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Chemical Composition and Mass Closure of Particulate Matter at Six Urban Sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40 (Suppl. 2), 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, B.T.; Guizellini, F.C.; Hojo, O.; Pastre, I.A.; de Marchi, M.R.R.; Silva, H.F.; Fertonani, F.L.; Oliveira, C.M. Chemical and Morpho-Structural Characterization of Atmospheric Aerosol (PM10 and PM2.5) in a City of São Paulo State, Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 59486–59498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240034228 (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Okuda, T. Measurement of the Specific Surface Area and Particle Size Distribution of Atmospheric Aerosol Reference Materials. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courcot, D.; Laversin, H.; Ledoux, F.; Cazier, F.; Matta, J.; Cousin, R.; Aboukais, A. Composition and Textural Properties of Soot and Study of Their Oxidative Elimination by Catalytic Process. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 39, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, S.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Viana, M.-M.; Alarcón, M.; Mantilla, E.; Ruiz, C.R. Comparative PM10–PM2.5 Source Contribution Study at Rural, Urban and Industrial Sites during PM Episodes in Eastern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 328, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.E.; Im, U.; Mezuman, K.; Gao, C.Y. Desert Dust, Industrialization, and Agricultural Fires: Health Impacts of Outdoor Air Pollution in Africa. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4104–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Smith, S.J.; Easter, R.; Ma, P.-L.; Qian, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Rasch, P.J. Global Source Attribution of Sulfate Concentration and Direct and Indirect Radiative Forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8903–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Yin, D. A Review of Secondary Organic Aerosols Formation Focusing on Organosulfates and Organic Nitrates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P. The Characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4959–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. Heavy Metal Pollution in China: Origin, Pattern and Control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Daher, N.; Kam, W.; Shafer, M.M.; Ning, Z.; Schauer, J.J.; Sioutas, C. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Chemical Composition and Mass Closure of Ambient Coarse Particulate Matter (PM10–2.5) in the Los Angeles Area. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2651–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.-C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Huang, J.-H. Study of Atmospheric Metallic Elements Pollution in Asia during 2000–2007. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbi, A.; Kerchich, Y.; Kerbachi, R.; Boughedaoui, M. Assessment of Annual Air Pollution Levels with PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and Associated Heavy Metals in Algiers, Algeria. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Mustafa, A.-R.A.; El-Sheikh, A.A. Geochemistry and Spatial Distribution of Selected Heavy Metals in Surface Soil of Sohag, Egypt: A Multivariate Statistical and GIS Approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of Mediterranean: Insights from Argolida Basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma 2014, 221–222, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiec, E.; Jarosz-Krzemińska, E.; Wieszała, R. Heavy Metals from Non-Exhaust Vehicle Emissions in Urban and Motorway Road Dusts. Environ. Monit. Assess 2016, 188, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.; Tan, J. Atmospheric Heavy Metals and Arsenic in China: Situation, Sources and Control Policies. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; O’Connor, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Liu, A.; Hou, D. Assessment of Sources of Heavy Metals in Soil and Dust at Children’s Playgrounds in Beijing Using GIS and Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:152:0001:0044:FR:PDF (accessed on 28 April 2013).
- Lee, P.-K.; Youm, S.-J.; Jo, H.Y. Heavy Metal Concentrations and Contamination Levels from Asian Dust and Identification of Sources: A Case-Study. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gietl, J.K.; Lawrence, R.; Thorpe, A.J.; Harrison, R.M. Identification of Brake Wear Particles and Derivation of a Quantitative Tracer for Brake Dust at a Major Road. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S. Contamination Characteristics and Possible Sources of PM10 and PM2.5 in Different Functional Areas of Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckner, P.; Reemtsma, T.; Eisentraut, P.; Braun, U.; Ruhl, A.S.; Wagner, S. Tire and Road Wear Particles in Road Environment—Quantification and Assessment of Particle Dynamics by Zn Determination after Density Separation. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choplin, A. Cementing Africa: Cement Flows and City-Making along the West African Corridor (Accra, Lomé, Cotonou, Lagos). Urban Stud. 2020, 57, 1977–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soussia, T.; Guedenon, P.; Lawani, R.; Gbaguidi, C.D.; Edorh, P.A. Assessment of Cement Dust Deposit in a Cement Factory in Cotonou (Benin). J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 06, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Belosi, F.; Gambaro, A.; Cesari, D.; Stortini, A.M.; Bove, M.C. Comparison of PM10 Concentrations and Metal Content in Three Different Sites of the Venice Lagoon: An Analysis of Possible Aerosol Sources. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1954–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldabe, J.; Elustondo, D.; Santamaría, C.; Lasheras, E.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Santamaría, J.M. Chemical Characterisation and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 at Rural, Urban and Traffic Sites in Navarra (North of Spain). Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofosu, F.G.; Hopke, P.K.; Aboh, I.J.K.; Bamford, S.A. Characterization of Fine Particulate Sources at Ashaiman in Greater Accra, Ghana. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2012, 3, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mkoma, S.L.; Chi, X.; Maenhaut, W. Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosols in Ambient PM10 and PM2.5 Particles in Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engling, G.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Chan, C.-Y.; Sang, X.-F.; Lin, M.; Ho, K.-F.; Li, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lee, J.J. Characterization and Sources of Aerosol Particles over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau during the Southeast Asia Biomass-Burning Season. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczynska, A.J.; Krata, A.; Stranger, M.; Locateli Godoi, A.F.; Kontozova-Deutsch, V.; Bencs, L.; Naveau, I.; Roekens, E.; Van Grieken, R. Atmospheric BTEX-Concentrations in an Area with Intensive Street Traffic. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z. Atmospheric Levels of BTEX Compounds during the 2008 Olympic Games in the Urban Area of Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Xu, X.; Grgicak-Mannion, A.; Brook, J.; Wheeler, A. Multi-Season, Multi-Year Concentrations and Correlations amongst the BTEX Group of VOCs in an Urbanized Industrial City. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Lemke, L.D.; Xu, X.; Molaroni, S.M.; You, H.; Wheeler, A.J.; Booza, J.; Grgicak-Mannion, A.; Krajenta, R.; Graniero, P.; et al. Intra-Urban Correlation and Spatial Variability of Air Toxics across an International Airshed in Detroit, Michigan (USA) and Windsor, Ontario (Canada). Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, C.; Moreno, T.; Amato, F.; Viana, M.; van Drooge, B.L.; Chuang, H.-C.; Bérubé, K.; Jones, T.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Characterise Exposure Risk and Toxicological Effects of PM10 and PM2.5 Samples in Urban Environments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y. Seasonal Variation and Source Apportionment of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in PM2.5 and PM10 Particulates in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Drooge, B.L.; Ballesta, P.P. Seasonal and Daily Source Apportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Concentrations in PM10 in a Semirural European Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7310–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrogrande, M.C.; Abbaszade, G.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Bacco, D.; Mercuriali, M.; Zimmermann, R. Seasonal Variation and Source Estimation of Organic Compounds in Urban Aerosol of Augsburg, Germany. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindado, O.; Pérez, R.M.; García, S.; Sánchez, M.; Galán, P.; Fernández, M. Characterization and Sources Assignation of PM2.5 Organic Aerosol in a Rural Area of Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2796–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callén, M.S.; de la Cruz, M.T.; López, J.M.; Mastral, A.M. PAH in Airborne Particulate Matter.: Carcinogenic Character of PM10 Samples and Assessment of the Energy Generation Impact. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorská, A.; Lammel, G.; Klánová, J. Use of Diagnostic Ratios for Studying Source Apportionment and Reactivity of Ambient Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons over Central Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladji, R.; Yassaa, N.; Balducci, C.; Cecinato, A.; Meklati, B.Y. Distribution of the Solvent-Extractable Organic Compounds in Fine (PM1) and Coarse (PM1–10) Particles in Urban, Industrial and Forest Atmospheres of Northern Algeria. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. PAH Diagnostic Ratios for the Identification of Pollution Emission Sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Van Grieken, R. Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Source Attribution, Emission Factors and Regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsoyiannis, A.; Terzi, E.; Cai, Q.-Y. On the Use of PAH Molecular Diagnostic Ratios in Sewage Sludge for the Understanding of the PAH Sources. Is This Use Appropriate? Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazier, F.; Genevray, P.; Dewaele, D.; Nouali, H.; Verdin, A.; Ledoux, F.; Hachimi, A.; Courcot, L.; Billet, S.; Bouhsina, S.; et al. Characterisation and Seasonal Variations of Particles in the Atmosphere of Rural, Urban and Industrial Areas: Organic Compounds. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landkocz, Y.; Ledoux, F.; André, V.; Cazier, F.; Genevray, P.; Dewaele, D.; Martin, P.J.; Lepers, C.; Verdin, A.; Courcot, L.; et al. Fine and Ultrafine Atmospheric Particulate Matter at a Multi-Influenced Urban Site: Physicochemical Characterization, Mutagenicity and Cytotoxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadel, M.; Ledoux, F.; Farhat, M.; Kfoury, A.; Courcot, D.; Afif, C. PM2.5 Characterization of Primary and Secondary Organic Aerosols in Two Urban-Industrial Areas in the East Mediterranean. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyüz, M.; Çabuk, H. Gas–Particle Partitioning and Seasonal Variation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Atmosphere of Zonguldak, Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5550–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Bencs, L.; Wauters, E.; de Hoog, J.; Deutsch, F.; Roekens, E.; Bleux, N.; Berghmans, P.; Van Grieken, R. Seasonal and Site-Specific Variation in Vapour and Aerosol Phase PAHs over Flanders (Belgium) and Their Relation with Anthropogenic Activities. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, P.Q.; Kawamura, K.; Pavuluri, C.M.; Swaminathan, T. Molecular Characterization of Urban Organic Aerosol in Tropical India: Contributions of Biomass/Biofuel Burning, Plastic Burning, and Fossil Fuel Combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Disc. 2009, 9, 21669–21716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotianová, P.; Puxbaum, H.; Bauer, H.; Caseiro, A.; Marr, I.L.; Čík, G. Temporal Patterns of N-Alkanes at Traffic Exposed and Suburban Sites in Vienna. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2993–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Pio, C.; Alves, C.; Evtyugina, M.; Santos, P.; Gonçalves, V.; Nunes, T.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Palmgren, F.; Wåhlin, P.; et al. Seasonal Distribution of Polar Organic Compounds in the Urban Atmosphere of Two Large Cities from the North and South of Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5555–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, W.F.; Medeiros, P.M.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Organic Marker Compounds for Surface Soil and Fugitive Dust from Open Lot Dairies and Cattle Feedlots. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Continent | City/Country | Concentration (µg/m3) | Sulphate | Nitrate | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | PM10 | PM2.5 | PM10 | |||||||||
| PM2.5 | PM10 | µg/m3 | % | µg/m3 | % | µg/m3 | % | µg/m3 | % | |||
| Africa | ||||||||||||
| Present study Cotonou (Benin) | 180.9 | 94.5 | 1.4 | 21.5 | 0.5 | 16.6 | 0.8 | 13.0 | 0.2 | 5.8 | ||
| Tetouan (Morocco) | 18 | - | 3 | 17 | - | - | 1 | 6 | - | - | [47] | |
| Addis Ababa (Ethiopia) | 19–127 | - | 1.3–5.3 | 5.7 | - | - | 0.1–0.5 | 0.6 | - | - | [48] | |
| Dakar (Senegal) | 87 | 57 | 2.5 | - | 1.6 | - | 1.9 | - | 0.5 | - | [46] | |
| Dakar (Senegal) | 75.1 | - | 1.9 | 17.3 | - | - | 1.6 | 14.3 a | - | - | [9] | |
| Nairobi (Kenya) | 10.7–98.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [49] | |
| Abidjan (Côte d’Ivoire) | 105.1 | - | 1.1 | 21.6 | - | - | 1.6 | 31.7 a | - | - | [20] | |
| Conakry (Guinea) | 38–177 | 80–358 | 1.5 | 31.1 a | 2.2 | 21.3 a | 0.9 | 20.2 a | 3.4 | 32.9 a | [50] | |
| Accra (Ghana) | 21–39 | 49–96 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [51] | |
| Asia | ||||||||||||
| Xiamen (China) | 32.8 | 54.5 | 4.1 | - | 4.6 | - | 2.2 | - | 3.9 | - | [52] | |
| Delhi (India) | 125.5 | - | 13.1 | - | - | - | 10.8 | - | - | - | [53] | |
| Yokohama (Japan) | 20.6 | 9.6 | 3.8 | 48.3 a | 0.2 | 7.6 a | 1.0 | 12.2 a | 1.0 | 34.7 a | [54] | |
| Europe | ||||||||||||
| Athens (Greece) | 18.0 | 33.5 | 3.7 | - | 6.0 | - | 1.0 | - | 2.0 | - | [55] | |
| Palermo (Italy) | 29 | 42 | 2.5 | - | 2.3 | - | 2.9 | - | 4.1 | - | [56] | |
| Dunkerque (France) | 9.9 | - | 0.5 | 18.2 a | - | - | 0.8 | 32.5 a | - | - | [8] | |
| Barcelona (Spain) | 20.0 | 26.3 | - | 24 | - | 2.1 | - | 6.8 | - | 11 | [57] | |
| Duisburg (Germany) | 14.7 | 7.2 | - | 19 | - | 3.4 | - | 13 | - | 12 | ||
| Amsterdam (Netherland) | 25.4 | 8.4 | - | 14 | - | 5.3 | - | 18 | - | 14 | ||
| America | ||||||||||||
| São Paulo (Brazil) | 11–43 | 17–60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [58] | |
| Metal and Trace | PM2.5 | PM>2.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| µg/m3 | % | µg/m3 | % | |
| Al | 4.5 | 42 | 2.3 | 40 |
| Ba | 0.04 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 0.4 |
| Ce | 0.006 | 0.1 | 0.003 | 0.1 |
| Co | 0.001 | 0 | 0.0005 | 0 |
| Cr | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.1 |
| Cu | 0.03 | 0.3 | 0.007 | 0.1 |
| Fe | 3.7 | 34 | 2 | 35 |
| La | 0.002 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 |
| Li | 0.001 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 |
| Mg | 0.8 | 7 | 0.4 | 7 |
| Mn | 0.07 | 0.6 | 0.03 | 0.6 |
| Na | 1.3 | 12 | 0.8 | 14 |
| Ni | 0.002 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 |
| Pb | 0.02 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.2 |
| Rb | 0.002 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 |
| Sn | 0.001 | 0 | 0.0005 | 0 |
| Sr | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 0.2 |
| Ti | 0.13 | 1 | 0.06 | 1.0 |
| V | 0.003 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.0 |
| Zn | 0.1 | 1 | 0.07 | 1.3 |
| Total | 10.8 | 5.7 | ||
| City/Country | Pb | Zn | Ni | Cu | Cd | As | Cr | V | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present study Cotonou (Benin) | PM2.5 | 22 | 145 | 2 | 29 | - | - | 11 | 3 | This study |
| PM>2.5 | 11 | 71 | 1 | 7 | - | - | 5 | 2 | ||
| Xiamen (China) | PM2.5 | 19 | 87 | 7 | 7 | 0.5 | 2 | 8 | 11 | [52] |
| PM10 | 22 | 116 | 8 | 11 | 0.6 | 2 | 11 | 12 | ||
| Addis Ababa (Ethiopia) | PM2.5 | 8 | 3 | - | - | 0.5 | 1 | - | - | [48] |
| Athens (Greece) | PM2.5 | 11 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 | [55] |
| PM10 | 15 | 6 | 7 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 13 | ||
| Delhi (India) | PM2.5 | 2 | 13 | - | 4 | - | 7 | 8 | - | [53] |
| Baoshan (China) | PM2.5 | 133 | 465 | 27 | 29 | 3 | - | 31 | - | [79] |
| PM10 | 137 | 590 | 32 | 41 | 3 | - | 56 | - | ||
| Beijing (China) | PM2.5 | 261 | 0.2 | 29 | 117 | 13 | 51 | 86 | 18 | [74] |
| Dakar (Senegal) | PM2.5 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 5 | - | - | 2 | 2 | [9] |
| Dunkerque (France) | PM2.5 | 4 | 17 | 2 | 9 | - | 0.2 | 4 | 1 | [8] |
| Punta Sabbioni (Italy) | PM10 | 21 | 57 | 4 | 10 | - | 2 | 5 | 4 | [83] |
| Navarra (Spain) | PM2.5 | 2 | 18 | 1 | 12 | - | 0.2 | 2 | - | [84] |
| PM10 | 3 | 29 | 2 | 27 | - | 0.2 | 3 | - | ||
| Conakry (Guinea) | PM2.5 | 36 | 69 | 8 | 179 | - | - | 24 | 14 | [50] |
| PM10 | 42 | 37 | 18 | 10 | - | - | 144 | 22 |
| Element | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | PM>2.5 | |
| Total C | 22.97 ± 0.11 | 14.09 ± 0.02 |
| Organic C | 21.21 ± 0.10 | 12.81 ± 0.02 |
| Nitrogen | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 0.85 ± 0.01 |
| Hydrogen | 3.04 ± 0.01 | 1.81 ± 0.01 |
| Sulphur | 1.16 ± 0.00 | 0.96 ± 0.01 |
| EC/TC | 0.076 | 0.09 |
| VOCs | Concentration (ng/m3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | PM>2.5 | ||
| Benzene | 0.5 | 0.05 | |
| Toluene | 1.8 | 0.07 | |
| Ethylbenzene | 0.8 | 0.10 | |
| o-Xylene | 3.5 | 0.07 | |
| 123Trimethylbenzene | 1.2 | 0.71 | |
| Trimethylbenzene | 0.5 | <LQ | |
| Tetramethylbenzene | 0.3 | 0.20 | |
| Pentamethylbenzene | 0.3 | <LQ | |
| Total | 8.9 | 1.2 | |
| PAHs | |||
| Naphtalene | Nap | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Acenaphtylene | Ace | <LQ | 0.004 |
| Phenanthrene | Phe | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Fluoranthene | Flu | 0.1 | 0.03 |
| Pyrene | Pyr | 0.3 | 0.06 |
| Benzo[a]Anthracene | BaA | 0.2 | <LQ |
| Chrysene | Chr | 0.3 | 0.01 |
| Benzo[b]Fluoranthene | BbF | <LQ | 0.02 |
| Benzo[k]Fluoranthene | BkF | 0.3 | <LQ |
| Benzo[a]Pyrene | BaP | 0.2 | 0.01 |
| Dibenzo[a.h]Anthracene | DahA | 0.2 | <LQ |
| Indeno[1.2.3-c.d]Pyrene | Ind | <LQ | 0.07 |
| Benzo[g.h.i]Perylene | BghiP | 0.4 | <LQ |
| Total | 2 | 0.2 | |
| PAH Ratio | Value Range | Origin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ∑COMB/∑PAHs | ~1 | Combustion | [101] |
| BaP/BghiP | <0.6 | Non-traffic emissions | [102] |
| >0.6 | Traffic emissions | ||
| BaP/(BaP + Chr) | 0.5 | Diesel emissions | [103,104,105] |
| >0.5 | Gasoline emissions | ||
| BaA/(BaA + Chr) | 0.2–0.35 | Coal combustion | [106] |
| >0.35 | Vehicle emissions | ||
| Flu/(Flu + Pyr) | >0.5 | Diesel emissions | [107] |
| <0.5 | Gasoline emissions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cachon, F.B.; Cazier, F.; Verdin, A.; Dewaele, D.; Genevray, P.; Delbende, A.; Ayi-Fanou, L.; Aïssi, F.; Sanni, A.; Courcot, D. Physicochemical Characterization of Air Pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM>2.5) in an Urban Area of Cotonou, Benin. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020201
Cachon FB, Cazier F, Verdin A, Dewaele D, Genevray P, Delbende A, Ayi-Fanou L, Aïssi F, Sanni A, Courcot D. Physicochemical Characterization of Air Pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM>2.5) in an Urban Area of Cotonou, Benin. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020201
Chicago/Turabian StyleCachon, Fresnel Boris, Fabrice Cazier, Anthony Verdin, Dorothée Dewaele, Paul Genevray, Agnès Delbende, Lucie Ayi-Fanou, Faustin Aïssi, Ambaliou Sanni, and Dominique Courcot. 2023. "Physicochemical Characterization of Air Pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM>2.5) in an Urban Area of Cotonou, Benin" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020201
APA StyleCachon, F. B., Cazier, F., Verdin, A., Dewaele, D., Genevray, P., Delbende, A., Ayi-Fanou, L., Aïssi, F., Sanni, A., & Courcot, D. (2023). Physicochemical Characterization of Air Pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM>2.5) in an Urban Area of Cotonou, Benin. Atmosphere, 14(2), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020201




