Some Early Studies of Isotropic Turbulence: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Remarkable Work of Saint-Venant and Boussinesq on Turbulence
3. James Thomson’s Laminar Theory of the Flow in Rivers and Other Open Channels
4. Kelvin’s Elementary Studies of Homogeneous, Isotropic Turbulence
4.1. The Early Ideas of Turbulence and Laminar and Turbulent Motion
4.2. The ‘Reynolds Stresses’ Anticipated by Kelvin
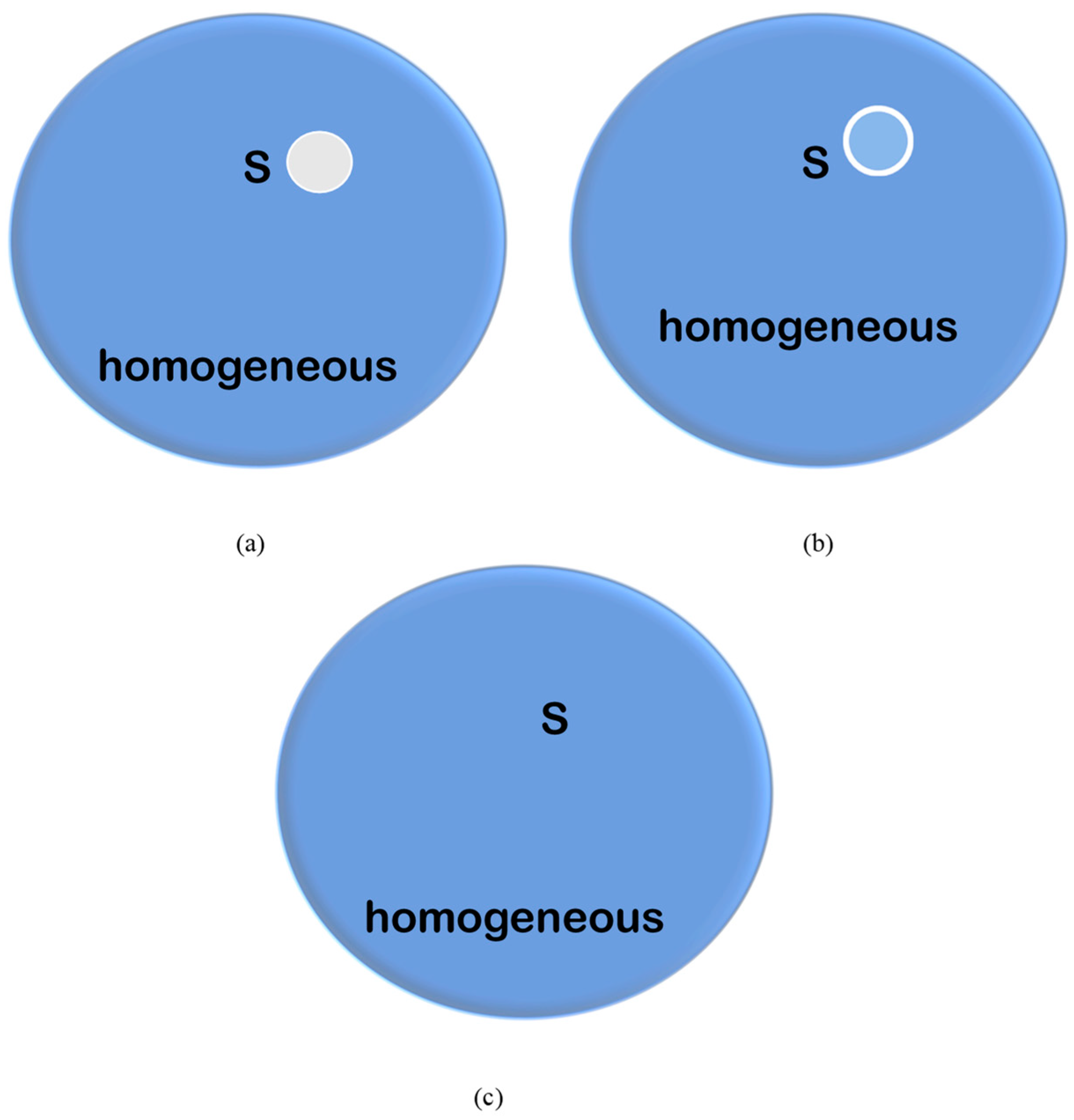
4.3. The Early Concepts of Homogeneous Isotropic Turbulence, Homogeneousness, and Isotropy
- ‘homogeneously’ appears four times in Thomson [57] (1887e, page 345, 7. line 1, 8. lines 1, 2, and 8);
- ‘homogeneous’ eight times in Thomson [57] (1887e, page 346, lines 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11, 15; page 352, 24. line 13);
- ‘homogeneousness’ three times in Thomson [57] (1887e, page 350, line 7; page 352, 24. line 12; page 352, 24. line 12);
- ‘isotropic’ four times in Thomson [57] (1887e, page 345, 9. line 1; page 346, 13. line 3; page 348, line 19, 17. line 4);
- ‘isotropy’ seven times in Thomson [57] (1887e, page 348, lines 1–2; page 349, 18. line 9, 19. 8; page 350, 20. lines 8, 14, 16 and 18);
- ‘homogeneous and isotropic’ two times in Thomson [57] (1887e, page 346, 14. lines 1–2; page 347, 15. lines 2–3).
4.4. The Introduction of Fourier Principles into the Turbulent Flow
4.5. Transformations Which the Distribution of Turbulent Motion Will Experience
4.6. The Kelvin Elementary Concept of the Direct Energy Cascade
4.7. The Concept of the Symmetrical Motion of Vortex Rings
5. The Maxwell–Reynolds Decomposition of Turbulent Flow Velocity
- Mean-mean-motion: mean-molar ;
- Relative-mean-motion: relative-molar .
6. The Taylor Statistical Theory of Isotropic Turbulence: A Revisit
6.1. The Taylor Concepts of the Average Height and a Coefficient of Eddy Viscosity
6.2. The Taylor Concept of the “Age” of the Eddy
6.3. The Early Taylor Concept of the Integral Scale
6.4. How Was the Concept of the Correlation Coefficient Introduced into Turbulence?
6.5. The Application of the Discontinuous Motion
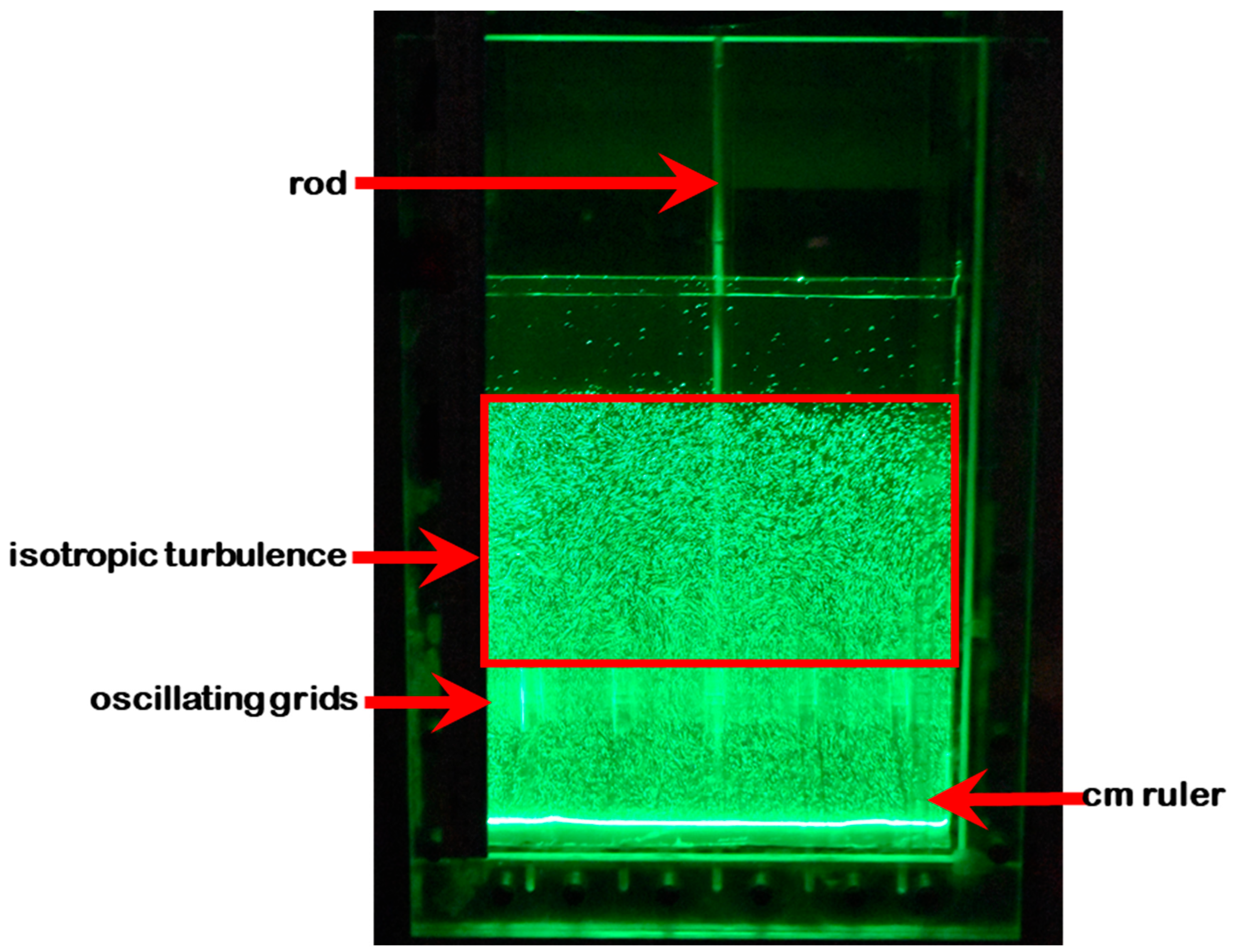
6.6. Taylor’s Own Experimental Studies of the Isotropy of Turbulence
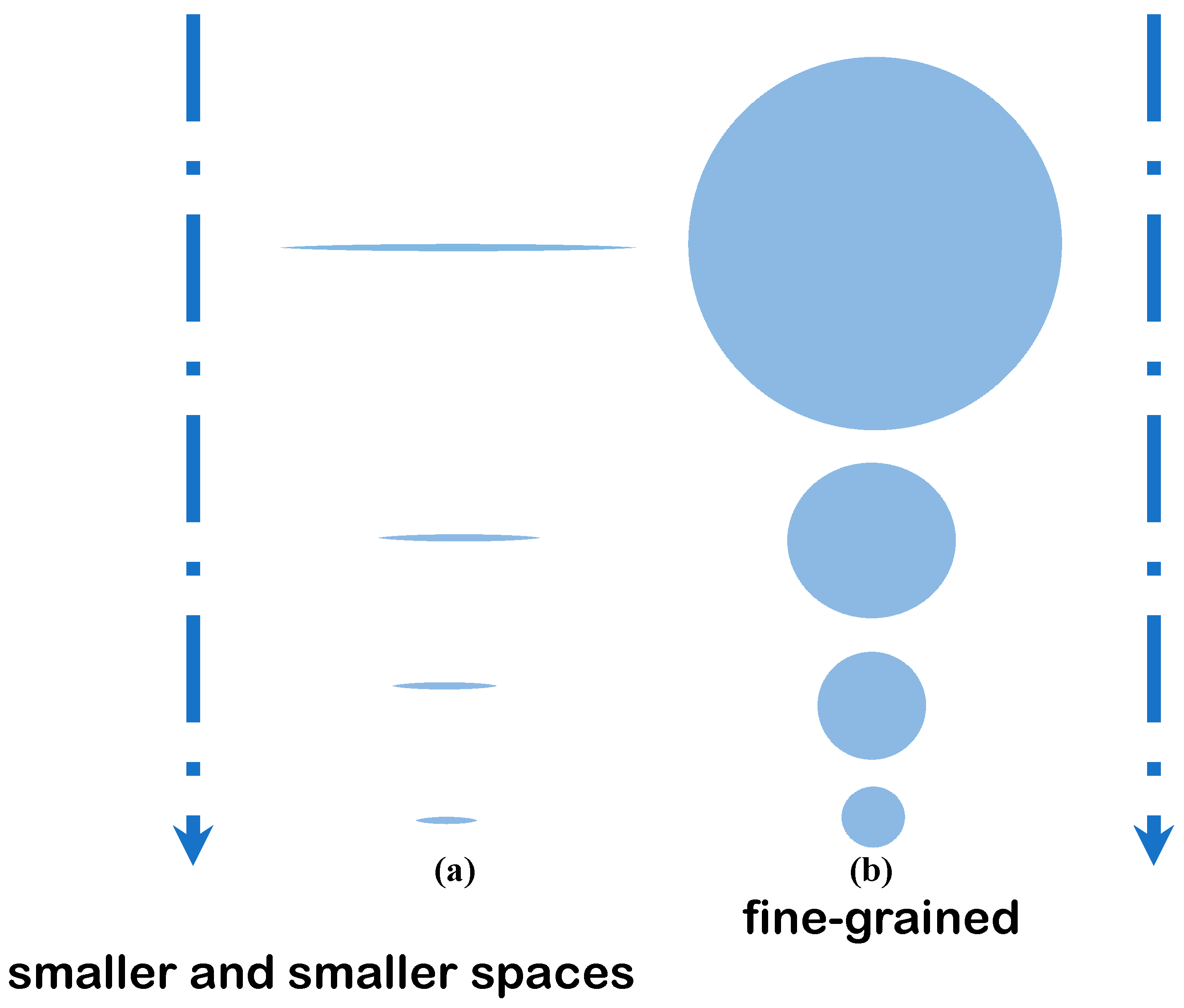
6.7. The Concept of Small Eddies or Microturbulence or Small-Scale Turbulence
7. The Kolmogorov–Obukhov Scaling Laws: A Revisit
7.1. The Power Law for the Turbulence Energy Spectrum Function
7.2. Obukhov’s [86] (1941a) Motivation of Studies of the Spectral Balance of Energy
7.3. The Obukhov Concept of a Function of the Inner Reynolds Number
7.4. The Relationship between Kolmogorov [28,29] (1941a, c) and Obukhov [86,87,88,89] (1941a, b, c, d)
7.5. Batchelor’s Dissemination of Kolmogorov’s Theory of Local Isotropy: A Revisit
8. The Heisenberg Statistical Theory of Homogeneous, Isotropic Turbulence
8.1. Heisenberg’s Inverse Seventh Power Spectrum
8.2. Chandrasekhar’s Thought on Heisenberg [31,32] (1948a, b)
8.3. Heisenberg’s Own Thoughts on His Inverse Seventh Power Spectrum

8.4. Batchelor’s Thoughts on Heisenberg [31,32] (1948a, b)
8.5. Corrsin’s Indirect Thought on Heisenberg [31,32] (1948a, b)
8.6. C-M Tchen’s Thoughts on Heisenberg [31,32] (1948a, b)
8.7. Monin and Yaglom’s Thought on Heisenberg [31,32] (1948a, b)
8.8. Townsend’s Thought on Heisenberg [31,32] (1948a, b)
9. Discussion
9.1. Does (James) Thomson’s [56] (1878) Laminar Theory Inspire William Thomson [57] (1887d)?
9.2. Does Kelvin Anticipate the Correlation Coefficient of the Velocities at Two Different Points?
9.3. The Relationship between Kelvin’s and G.I. Taylor’s Studies of Isotropic Turbulence
9.4. Implication of Kelvin’s Elementary Fourier Analysis of Turbulent Motion
9.5. Does Kelvin Anticipate the Concept of the Energy Cascade?
9.6. Does the Taylor Age of ‘Eddy’ Anticipate the Kolmogorov Time Scale?
9.7. What Was the Genesis of the Concept/Theory of Isotropic Turbulence?
9.8. Does Obukhov Anticipate the Finite Reynolds Number Effect of Turbulence?
9.9. Some Remarks on the Different Derivations of the Power Law
9.10. Is Heisenberg’s Inverse Seventh Power Spectrum Significant or Insignificant?
9.11. Where Do These Modern Approaches Currently Stand?
10. Summary
- (1)
- The present author strongly believes that there are still many hidden pearls of mathematical and physical aspects of turbulence in Kelvin’s elementary studies of isotropic turbulence. They were/or will be inspirational to our studies of isotropic turbulence.
- (2)
- There is about a five-decade span between Kelvin’s early studies of isotropic turbulence and Taylor’s statistical theory of isotropic turbulence. It is still unclear how they are linked. Nevertheless, there must be some connections between them.
- (3)
- The whole but brief historical narrative may be interpreted as follows: Firstly, the birth of the concept of isotropy in turbulent flow is credited to Kelvin. Secondly, from a historical perspective, Kelvin provided a mathematical and physical study of isotropic turbulence first. Thirdly, Taylor himself first made his observational or experimental investigations of the vertical component and the horizontal component of eddy motion in the atmosphere and did statistical analysis of those results. Fourthly, the early experimental discoveries of isotropy seem to be made by Fage and Townend. The statistical theory of isotropy was further developed by Taylor.
- (4)
- Kelvin’s introduction of the Fourier Principle into turbulent flow may have anticipated/stimulated the development of Direct Numerical Simulation.
- (5)
- Coincidently, 26 June 2024 will mark the bicentenary of the birth of Kelvin, while May 7, 2024, the 110th anniversary of Taylor’s first paper on the turbulence of Eddy Motion in the Atmosphere since he read it on 7 May 1914. The present review can be a tribute to Kelvin and G.I. Taylor.
- (6)
- The Obukhov concept of a function of the inner Reynolds number (i.e., the Reynolds dependent coefficient) anticipates the Finite Reynolds number effect of the turbulence.
- (7)
- The Kolmogorov–Obukhov scaling laws are indeed significant, but the significance of Heisenberg’s inverse seventh power law should not be underestimated.
- (8)
- It is hoped that the revisionist aspects, and especially the role of Kelvin presented in this review, are of interest and perhaps inspirational to those studying aspects of isotropic turbulence.
- (9)
- It is also hoped that this review can be one on establishment and attempts to complete the isotropic turbulence theory.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frisch, U. Turbulence. The Legacy of A.N. Kolmogorov; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; p. xiii+296. [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Venant, A.J.C. (Barre) de. Note a joindre au Memoire sur la dynamique des fluids. Comptes Rendus Des Seances De L’Academie Des Sci. 1843, XVII, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Helmholtz, L.F. On discontinuous movements of fluids. Philos. Mag. 1868, 36, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandtl, L. Beitrag Zum Turbulenz Symposium. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of Applied Mechanics, Cambridge, MA, USA, 12–16 September 1938; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1938; pp. 340–346. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Hinze, J.O. Turbulence an Introduction to Its Mechanisms and Theory; McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1959; p. ix+586. [Google Scholar]
- Gence, J.N. Homogeneous turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1983, 15, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Eddy motion in the atmosphere. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1915, A215, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Turbulence. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1927, 53, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, H.L.; Kuethe, A.M. The Measurements of Fluctuations of Air Speed by the Hot-Wire Anemometer; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Report No. 320; Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1929; pp. 357–382. [Google Scholar]
- Mock, W.C.; Dryden, H.L. Improved Apparatus for the Measurement of Fluctuations of Air Speed in Turbulent Flow; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Report No. 448; Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1932; pp. 131–154. [Google Scholar]
- Fage, A.; Townend, H.C.H. An examination of turbulent flow with an ultramicroscope. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1932, A135, 656–677. [Google Scholar]
- Townend, H.C.H. Statistical measurements of turbulence in the flow of air through a pipe. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1934, A145, 180–211. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. Diffusion by continuous movements. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1921, 2, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Statistical theory of turbulence. I. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1935, A151, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Statistical theory of turbulence. II. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1935, A151, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Statistical theory of turbulence. III. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1935, A151, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. Statistical theory of turbulence. IV. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1935, A151, 465–478. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. Statistical theory of turbulence. V. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1936, A156, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. The statistical theory of isotropic turbulence. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 1937, 4, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, L.F.G.; Salter, C. Experimental investigation and analysis of the velocity variations in turbulent flow. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1934, A145, 212–234. [Google Scholar]
- Dryden, H.L. The theory of isotropic turbulence. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 1937, 4, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, H.L.; Schubauer, G.B.; Mock, W.C., Jr.; Skramstad, H.K. Measurements of Intensity and Scale of Wind-Tunnel Turbulence and Their Relation to the Critical Reynolds Number of Spheres; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Report No. 581; Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1937; pp. 109–140. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, L.F.G.; Salter, C. An experimental determination of the spectrum of turbulence. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1938, A165, 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dryden, H.L. Turbulence and diffusion. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1939, 31, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Kármán, T. The fundamentals of the statistical theory of turbulence. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 1937, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kármán, T.; Howarth, L. On the statistical theory of isotropic turbulence. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1938, A164, 192–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, H.P. The invariant theory of isotropic turbulence. Math. Proc. Philos. Soc. 1940, 36, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. The local structure of turbulence in incompressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds numbers. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1941, XXX, 299–303. reprinted in Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1991, A434, 9–13(In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Dissipation of energy in the locally isotropic turbulence. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1941, XXXII, 19–21. reprinted in Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1991, A434, 15–17(In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Millionschikov, M.D. On the uniform isotropic turbulent theory. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1941, XXXII, 611–614. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg, W. Zur statistischen theorie der turbulenz. Z. Fur Phys. 1948, 124, 628–657. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisenberg, W. On the theory of statistical and isotropic turbulence. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1948, A195, 402–406. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C. Note on the law of decay of isotropic turbulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1948, 34, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, S. The theory of statistical and isotropic turbulence. Phys. Rev. 1949, 75, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. On the decay of isotropic turbulence. Phys. Rev. 1949, 75, 1454–1455, Erratum in Phys. Rev. 1949, 76, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. On Heisenberg’s elementary theory of turbulence. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1949, 200, 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Dryden, H.L. A review of the statistical theory of turbulence. Q. J. Appl. Math. 1943, 1, 7–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Turbulence–a physical theory of astrophysical interest. Astrophys. J. 1949, 110, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, L.; Bass, J. The Theories of Turbulence (Translation of Les Theories de la Turbulence. Publications Scientifiques et Techniques du Minjstb de L‘Air, No. 237, 1950); National Advisory Committee For Aeronautics Technical Memorandum No. 1377; Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1950; p. iii+163. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, G.K. The Theory of Homogeneous Turbulence; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1953; p. xi+197. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, D.C. Developments in the Theory of Turbulence; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973; 368p. [Google Scholar]
- Monin, A.S.; Yaglom, A.M. Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence. Volume I; English ed.; revised by the authors and edited by J.L. Lumley; The Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; p. xii+769. [Google Scholar]
- Monin, A.S.; Yaglom, A.M. Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence. Volume II; English ed.; revised by the authors and edited by J.L. Lumley; The Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975; p. xi+874. [Google Scholar]
- McComb, W.D. The Physics of Fluid Turbulence; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990; p. xxiv+572. [Google Scholar]
- McComb, W.D. Theory of turbulence. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1995, 58, 1117–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, K.R.; Antonia, R.A. The phenomenology of small-scale turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1997, 29, 435–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, H.K. Homogeneous turbulence: An introductory review. J. Turbul. 2012, 13, N39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComb, W.D. Homogeneous, Isotropic Turbulence; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; 429p. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.Z. George Keith Batchelor’s interaction with Chinese fluid dynamicists and inspirational influence: A historical perspective. Notes Rec. R. Soc. 2021, 75, 461–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Z. Qian Jian (1939–2018) and his contribution to small-scale turbulence studies. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panickacheril, J.J.; Donzis, D.A.; Sreenivasan, K.R. Laws of turbulence decay from direct numerical simulations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2022, A380, 20210089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussinesq, J. Mémoires Présentés par Divers Savants à l‘Académie des Sciences de l‘Institut de France Paris. Essai sur la theorie des eaux courantes. Extr. Des Tomes XXIII Et XXIV 1877, XXII+666. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Prandtl, L. Bericht uber untersuchungen zur ausgebildeten turbulenz. Z. Fur Angew. Math. Und Mech. 1925, 5, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J.T.B. Obituary Notices of Fellows Deceased. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1893, 52, i–x. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, W. On the propagation of laminar motion through a turbulently moving inviscid liquid. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. Ser. 1887, 24, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J. On the flow of water in uniform regime in rivers and other open channels. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1878, 28, 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, W. Stability of motion (continued from the May, June, and August Numbers)—Broad river flowing down an inclined plane bed. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1887, 24, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandtl, L. Uber Flussigkeitsbewegung bei sehr kleiner Rfibung. In Verhandlungen des Dritten Internationalen Mathematiker-Kongresses; Krazer, A., Ed.; in Heidelberg 1904; Teubner: Leipzig, Germany, 1905; pp. 391–484. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Fourier, J. Theorie Analytique de la Chaleur; A Paris, Chez Firmin Didot, Pere et Fils; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1822; p. xii+639 pp+2 plates. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, W. On the stability of steady and of periodic fluid motion. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1887, 23, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, W. On the stability of steady and of periodic fluid motion (continued from May number)—Maximum and minimum energy in vortex motion. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1887, 23, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, W. Stability of fluid motion (continued from the May and June numbers)—Rectilineal motion of viscous fluid between two parallel planes. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1887, 24, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecke, R. The turbulence problem an experimentalist’s perspective. Los Alamos Sci. 2005, 29, 124–141. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, U.; Bec, J.; Aurell, E. Locally homogeneous turbulence: Is it an inconsistent framework? Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 081706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, A.D.D. Lord Kelvin on fluid mechanics. Eur. Phys. J. H 2012, 37, 75–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.G. Turbulence from 1870 to 1920: The birth of a noun and of a concept. Comptes Rendus Mec. 2017, 345, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.C. On the dynamical theory of gases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1867, 157, 49–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, G.G. On some cases of fluid motion. Trans. Camb. Philos. Trans. 1843, VIII, 105–137. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, G.G. On the theories of the internal friction of fluids in motion, and of the equilibrium and motion of elastic solids. Trans. Camb. Philos. Trans. 1845, VIII, 287–319. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, G.G. On the steady motion of incompressible fluids. Trans. Camb. Philos. Trans. 1842, VII, 439–453. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, U. Fully developed turbulence and intermittency. In Turbulence and Predictability in Geophysical Fluid Dynamics and Climate Dynamics; LXXXVIII Corso Soc. Italiana di Fisica: Bologua, Italy, 1985; pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli, U. Large eddy simulations in 2030 and beyond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 2014, A372, 20130320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, O. On the dynamical theory of incompressible viscous fluids and the determination of the criterion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, A186, 123–164. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, G.K. Geoffrey Ingram Taylor 7 March 1886–27 June 1975. Biogr. Mem. Fellows R. Soc. Lond. 1976, 22, 565–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. The Life and Legacy of G.I. Taylor; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; p. xv+285. [Google Scholar]
- Sreenivasan, K.R. G.I. Taylor: The inspiration behind the Cambridge school. In A Voyage through Turbulence; Davidson, P.A., Kaneda, Y., Moffatt, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. v+127–186. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. Phenomena connected with turbulence in the lower atmosphere. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1918, A94, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Some early ideas about turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1970, 41, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjalic, K.; Launder, B.E. Eddy-viscosity transport modelling: A historical review. In 50 Years of CFD in Engineering Sciences. A Commemorative Volume in Memory of D. Brian Spalding; Runchal, A., Ed.; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2020; pp. 295–316. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. On the Dissipation of Eddies; Reports and Memoranda No. 598 of Advisory for Committee Aeronautics; Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1919; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. The conditions necessary for discontinuous motion in gases. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1910, A84, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, G.G. On a difficulty in the theory of sound. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1848, 33, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPhail, D.C. An experimental verification of the isotropy of turbulence produced by a grid. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 1940, 8, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. An unfinished dialogue with G.I. Taylor. J. Fluid Mech. 1975, 70, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Kolmogorov’s work on turbulence (part of Obituary: Andrei Nikolaevich Kolmogorov 1903–1987). Bull. Lond. Math. Soc. 1990, 22, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov, A. Spectral energy distribution in a turbulent flow. Bull. De L’Academie Des Sci. De L’URSS Ser. Geogr. Et Geophys. 1941, 5, 453–463. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov, A. Uber die energieverteilung im spektrum des turbulenzstromes. Bull. De L’Academie Des Sci. De L’URSS Ser. Geogr. Et Geophys. 1941, 5, 463–466. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov, A. On the energy distribution in the spectrum of a turbulent flow. Comptes Rendus (Dokl.) De L’academie Des Sci. De L’urss 1941, XXXII, 22–24. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov, A. On the energy distribution in the spectrum of a turbulent flow [in English. Translated by V. Levin]. Comptes Rendus (Dokl.) De L’academie Des Sci. De L’urss 1941, XXXII, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, G.K.; Townsend, A.A. The nature of turbulent motion at large wave-numbers. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1949, 199, 238–255. [Google Scholar]
- Yaglom, A.M. Obituary Alexander Mikhailovich Obukhov, 1918–1989. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1990, 53, v–xi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Double velocity correlation function in turbulent motion. Nature 1946, 4024, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Kolmogoroff’s theory of locally isotropic turbulence. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1947, 43, 533–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.A. Early days of turbulence research in Cambridge. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 212, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. The distribution of energy in turbulence (Abstract). Phys. Rev. 1945, 68, 286. [Google Scholar]
- von Weizsaecker, W. Zur statistischen theorie der turbulenz. Z. Fur Phys. 1948, 124, 628–657. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Liepmann, H. Aspects of the turbulence problem. Z. Fur Angew. 1952, 3, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, K.R. Chandrasekhar’s fluid dynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2019, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchen, C.M. Transport processes as foundations of the Heisenberg and Obukhoff theories of turbulence. Phys. Rev. 1954, 93, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.A.; Kaneda, Y.; Moffatt, K.; Sreenivasan, K.R. (Eds.) A Voyage through Turbulence; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; p. xv+434. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, G.K. The theory of axisymmetric turbulence. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1946, A186, 450–502. [Google Scholar]
- Orszag, S.A.; Kruskal, M.D. Formulation of the theory of turbulence. Phys. Fluids 1968, 11, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orszag, S.A. Analytical theories of turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1970, 41, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orszag, S.A.; Patterson, G.S. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional homogeneous isotropic turbulence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1972, 28, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.F. Weather Prediction by Numerical Process; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1922; p. xiii+236. [Google Scholar]
- Gamard, S.; George, W.K. Reynolds number dependence of energy spectra in the overlap region of isotropic turbulence. Flow Turbul. Combust. 1999, 63, 443–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J. Inertial range and the finite Reynolds number effect of turbulence. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 55, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenidi, L.; Antonia, R.A. Assessment of large-scale forcing in isotropic turbulence using a closed Karman-Howarth equation. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 055104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhov, A.M. Some specific features of atmospheric turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1962, 13, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenidi, L.; Antonia, R.A. A general self-preservation analysis for decaying homogeneous isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 773, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. Statistical hydrodynamics. II Nuovo C. 1949, 6 (Suppl. S2), 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, T.S. Kolmogorov two-thirds law by matched asymptotic expansion. Phys. Fluids 2002, 15, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenidi, L.; Antonia, R.A.; Tang, S.L. Scale invariance in finite Reynolds number homogeneous isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 864, 244–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenidi, L.; Antonia, R.A.; Tang, S.L. Scaling of turbulent velocity structure functions: Plausibility constraints. J. Fluid Mech. 2023, 965, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.L.; Antonia, R.A.; Djenidi, L. Dual scaling and the n-thirds law in grid turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2023, 975, A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buaria, D.; Sreenivasan, K.R. Dissipation range of the energy spectrum in high Reynolds number turbulence. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2020, 5, 092691(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsinga, G.E.; Ishihara, T.; Hunt, J.C.R. Intermittency across Reynolds numbers—The influence of large-scale shear layers on the scaling of the enstrophy and dissipation in homogeneous isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2023, 974, A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
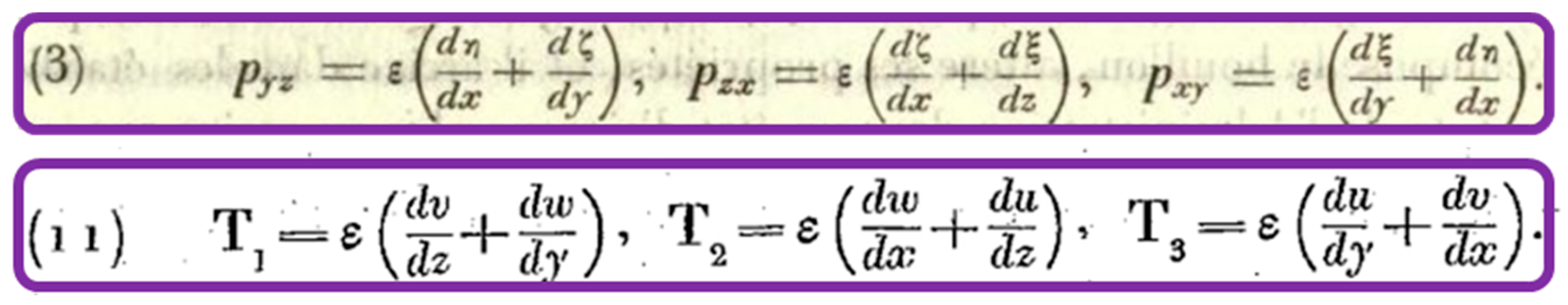




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.Z. Some Early Studies of Isotropic Turbulence: A Review. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040494
Shi JZ. Some Early Studies of Isotropic Turbulence: A Review. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040494
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, John Z. 2024. "Some Early Studies of Isotropic Turbulence: A Review" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040494
APA StyleShi, J. Z. (2024). Some Early Studies of Isotropic Turbulence: A Review. Atmosphere, 15(4), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040494





