The Influence of Sudden Stratospheric Warming on the Development of Ionospheric Storms: The Alma-Ata Ground-Based Ionosonde Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
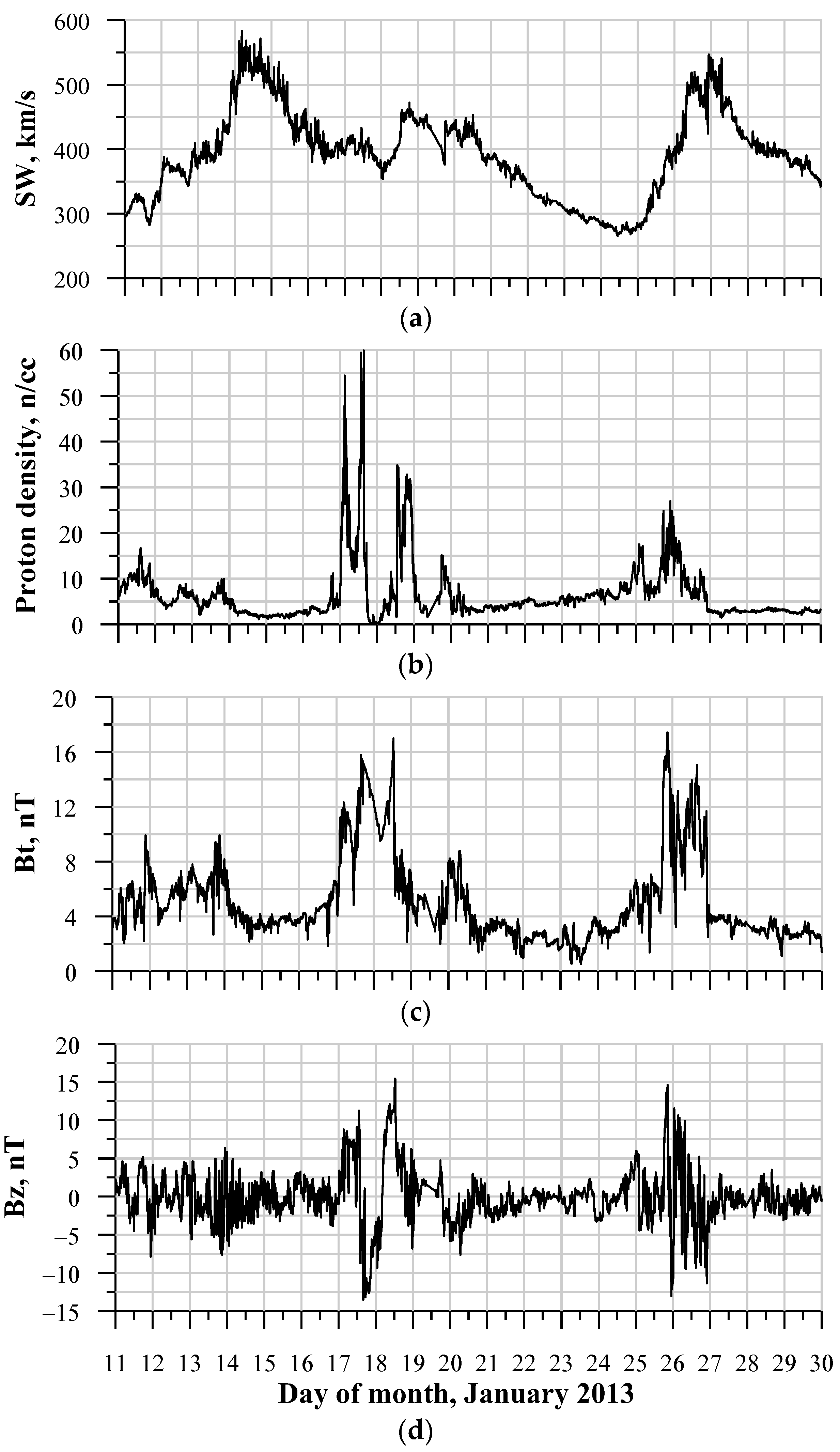
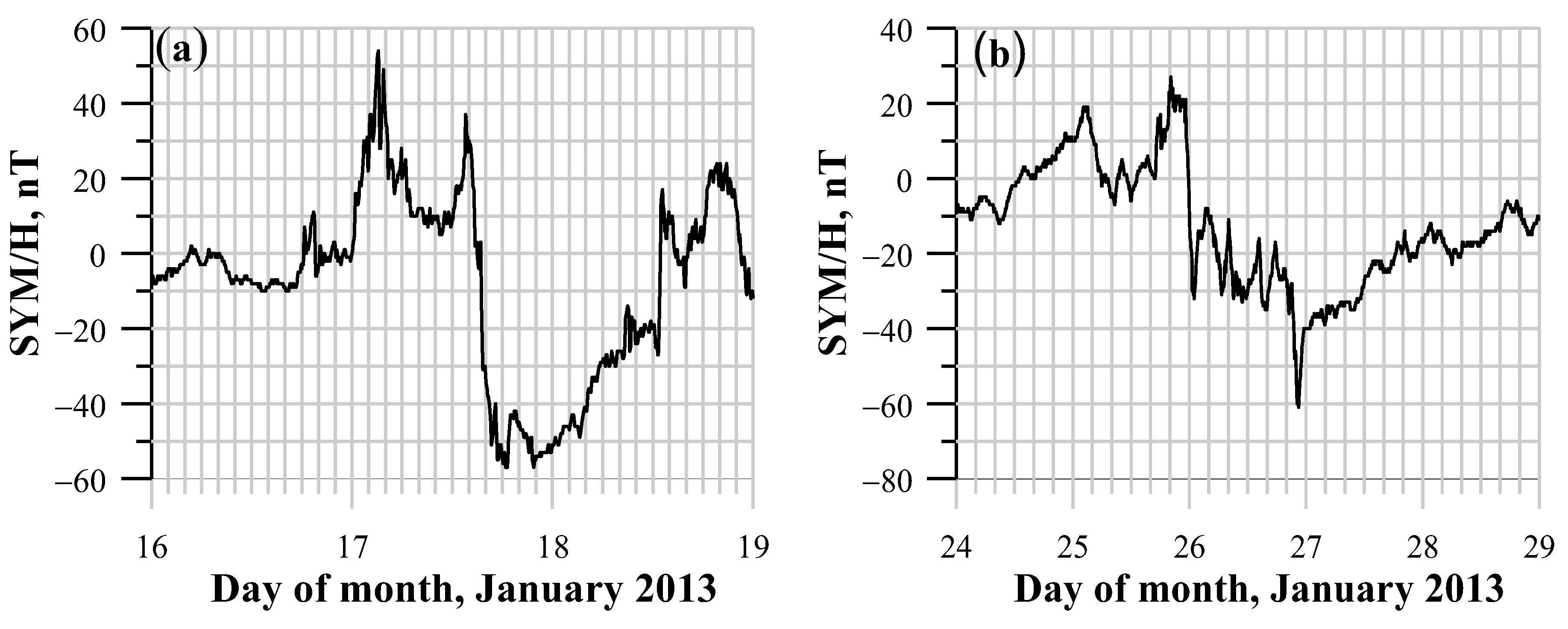
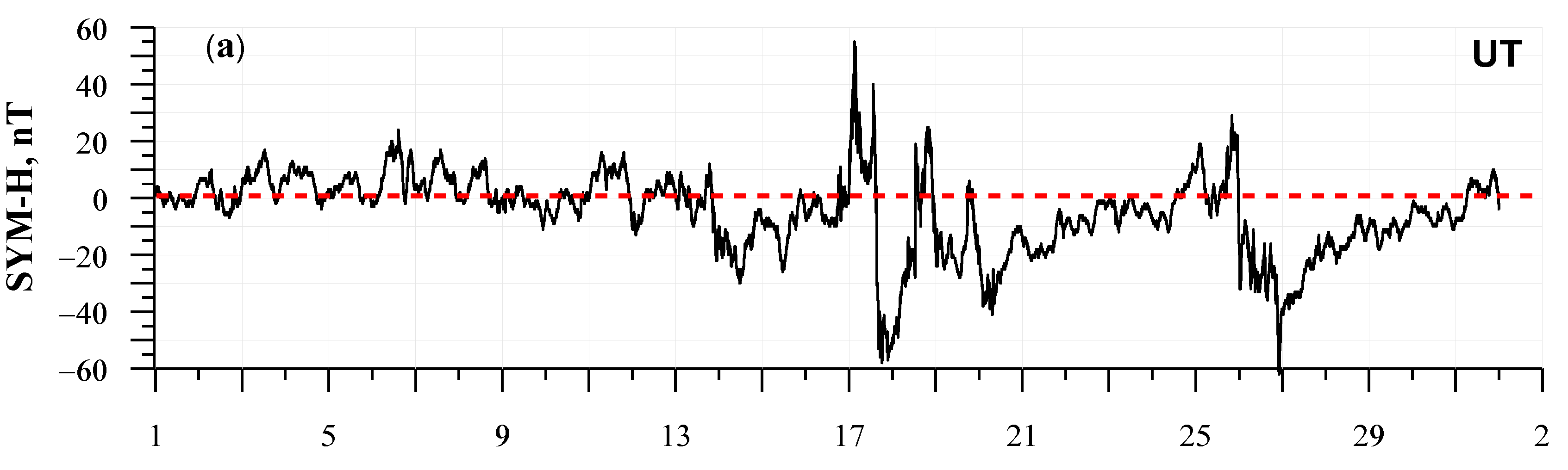
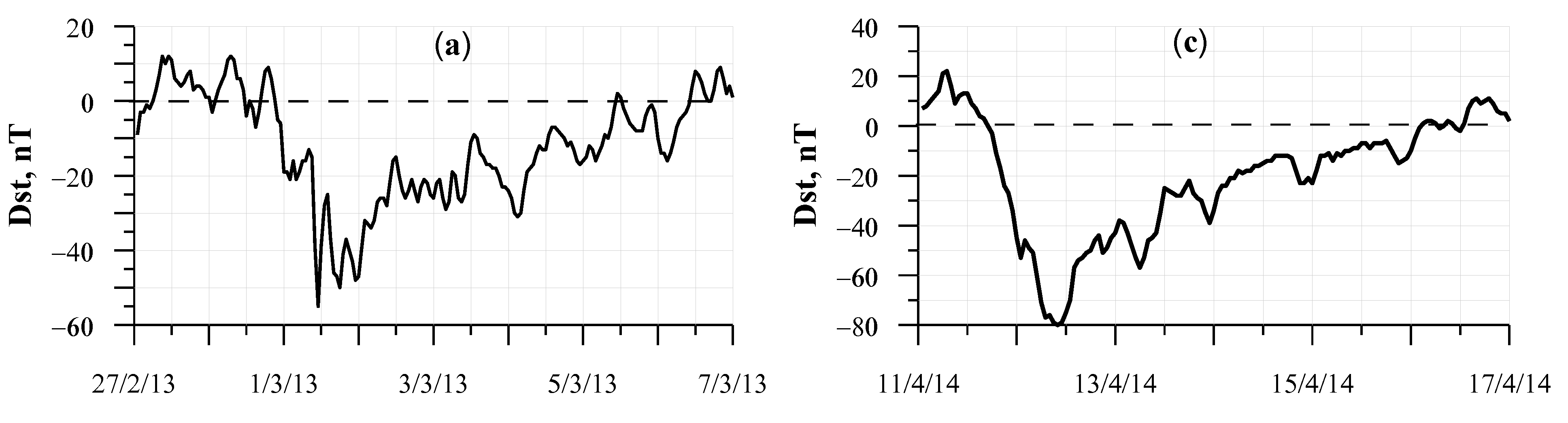
3.1. The January 2013 Solar and Geomagnetic Conditions
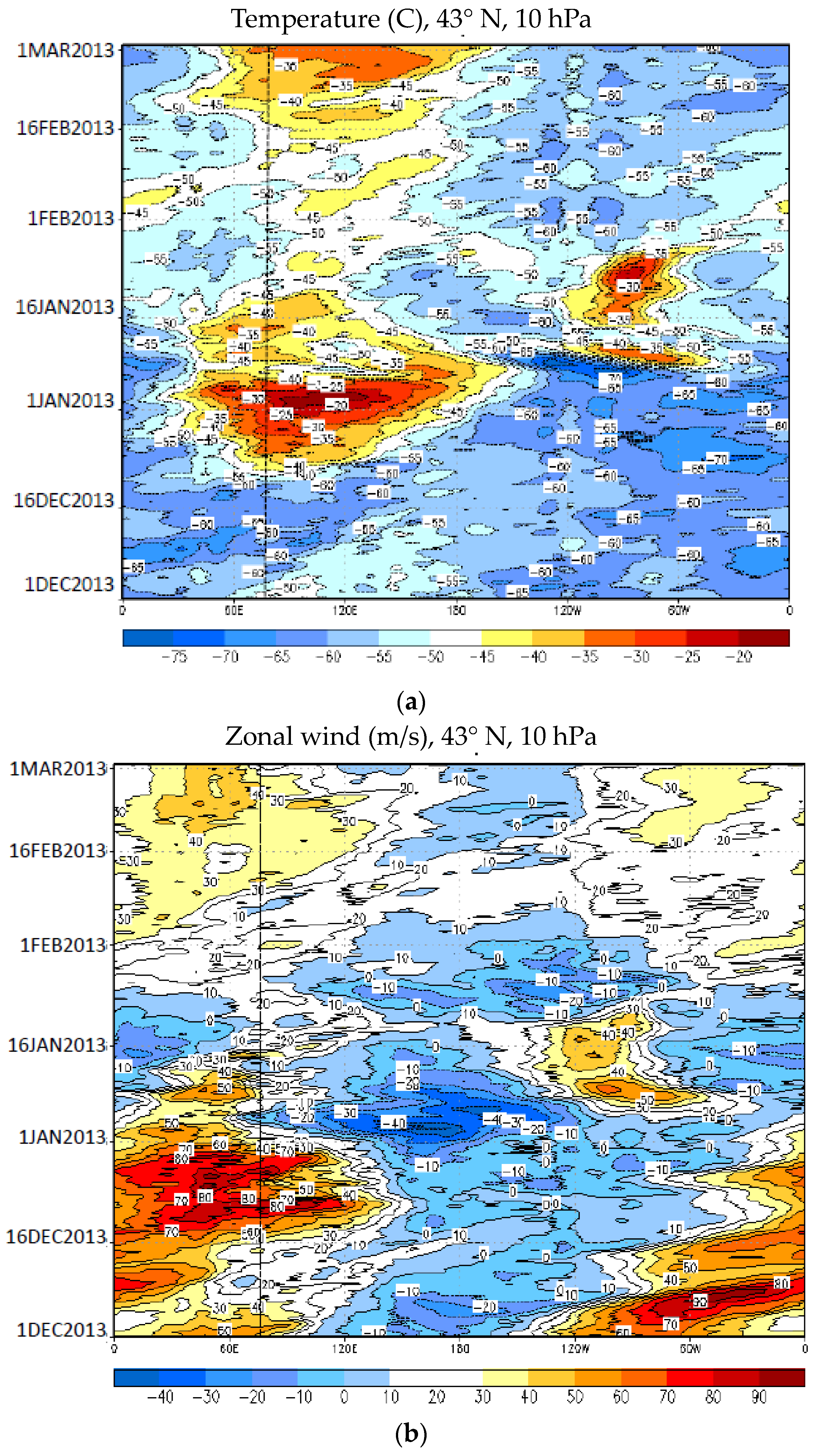
3.2. The January 2013 Major Stratospheric Warming: Temperatures and Dynamics
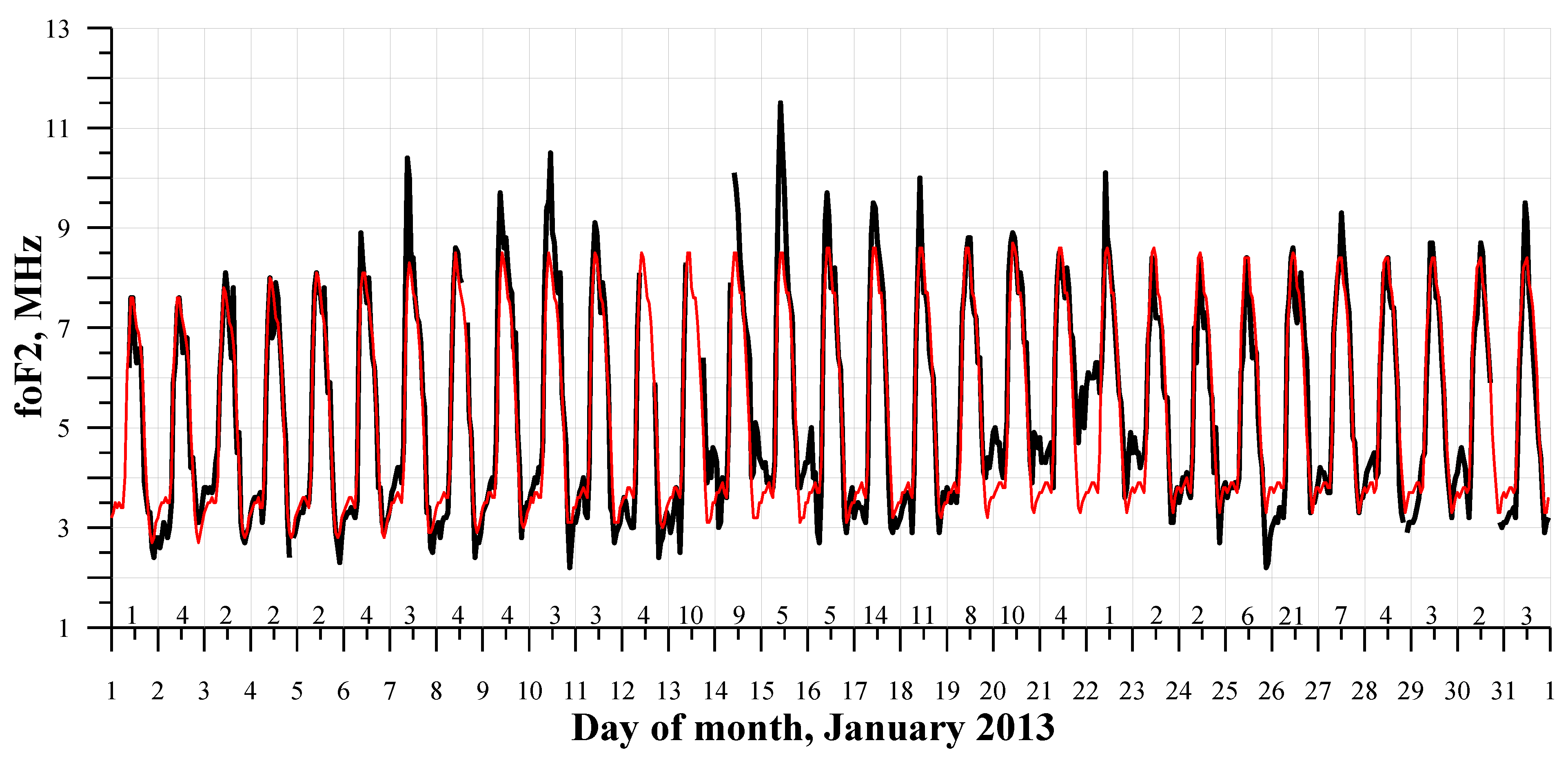
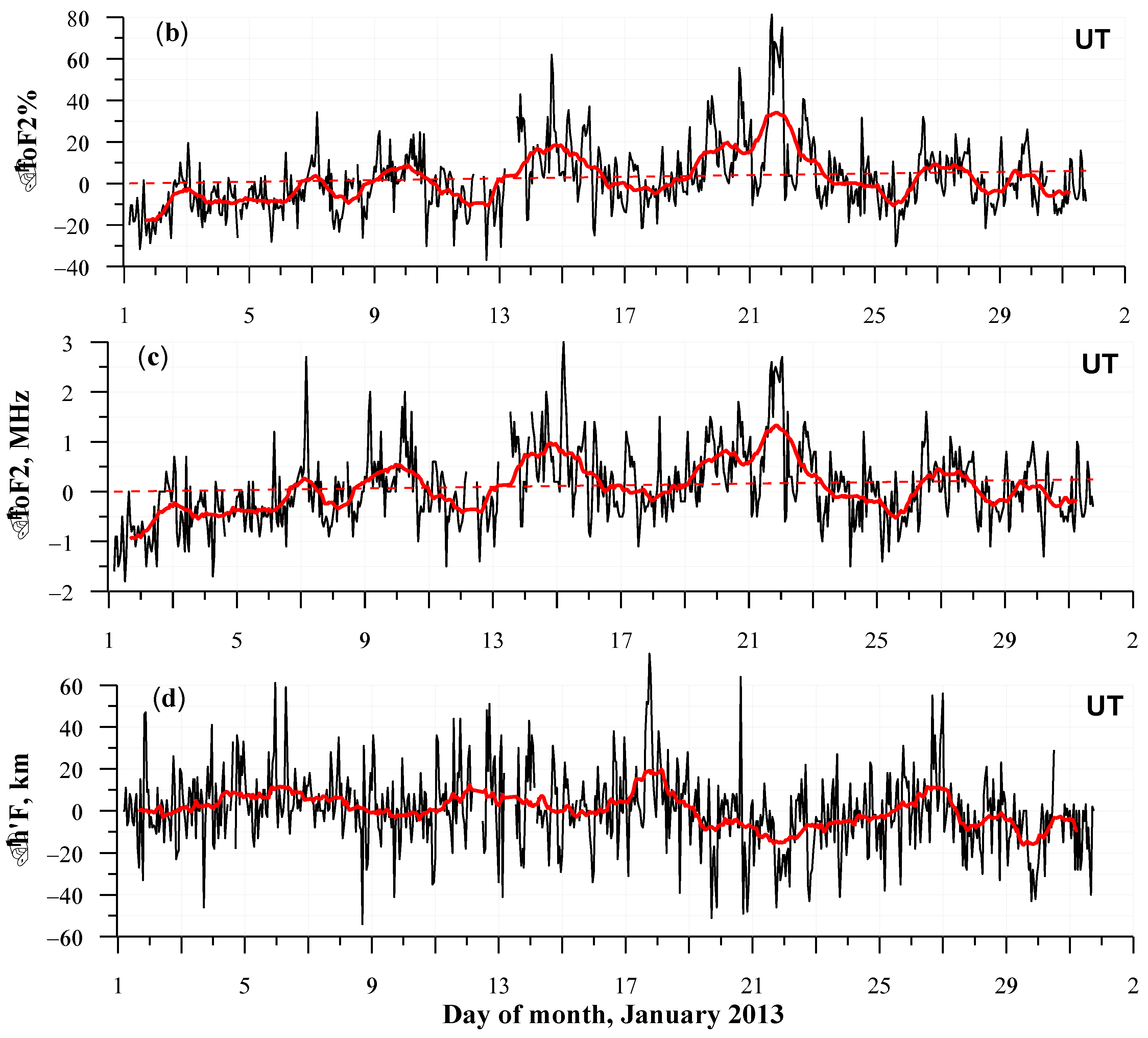
3.3. The January 2013 Dynamics of the Ionosphere
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The ionosonde observations show no significant ionospheric storms to the 17 and 26–27 January minor (−100 < Dst < −50 nT) geomagnetic storms that indicates that the development of geomagnetic storms does not correspond to the scheme accepted in [5] for the formation of ionospheric storms during geomagnetic disturbances.
- Large foF2 (up to 60%) deviations from the running median observed at the night/morning periods on 13–15 and 20–23 January which cannot be associated with either solar or geomagnetic activity. Spread and forked F traces observed in the ionograms at the periods indicate the appearance of different scale irregularities and tilts in the ionosphere.
- Wave-like disturbances in ΔfoF2, Δh’F, and daily averaged foF2 values with quasi-period of 5–8 h and peak-to-peak amplitude from about 1 MHz to 2 MHz (~from 20% to ~40%) are observed during the 9–28 January period, after registration of the occurrence of the major SSW event on 6 January.
- The observed variations in the OH emission rate are found to be quite similar to those observed in the ionospheric parameters that assume a community of processes in the stratosphere/mesosphere/ionosphere system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forbes, J.M.; Palo, S.E.; Zhang, X. Variability of the ionosphere. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2000, 62, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.D.; Morozova, L.D. Ionospheric storms in the F2 region: Morphology and physics (Review). Geomagn. Aeron. 1985, 25, 593–605. [Google Scholar]
- Buonsanto, M.J. Ionospheric Storms—A Review. Space Sci. Rev. 1999, 88, 563–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, A.V. Ionospheric F region storms. Fis. Tierra 2000, 12, 223–262. [Google Scholar]
- Danilov, A.D.; Lastovicka, J. Effects of geomagnetic storms on the ionosphere and atmosphere. Geomagn. Aeron. 2001, 2, 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Echer, E.; Gonzalez, W.D.; Tsurutani, B.T. Interplanetary conditions leading to superintense geomagnetic storms (Dst 250 nT) during solar cycle 23. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L06S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echer, E.; Gonzalez, W.D.; Tsurutani, B.T. Statistical studies of geomagnetic storms with peak Dst 50 nT from 1957 to 2008. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2011, 73, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paznukhov, V.V.; Altadill, D.; Reinisch, B.W. Experimental evidence for the role of the neutral wind in the development of ionospheric storms in midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A12319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.D. Ionospheric F-region response to geomagnetic disturbances. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 52, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, L.; Mikhailov, A.V.; Sabbagh, D. Thermospheric Parameters during Ionospheric G-Conditions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordiyenko, G. Ionospheric response over the Middle Asian region to the May 1967 geomagnetic storm. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2023, 253, 106151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordienko, G.I.; Vodyannikov, V.V.; Yakovets, A.F. Geomagnetic storm effects in the ionospheric E- and F-regions. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2011, 73, 1818–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cander, L.R. Mid-Latitude Single Station F region Storm Morphology and Forecast. Acta Geophys. 2016, 64, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, T.A. Dynamical Model of the Stratospheric Sudden Warming. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 1479–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, A.J.; Polvani, L.M. A New Look at Stratospheric Sudden Warmings. Part I: Climatology and Modeling Benchmarks. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Chen, W.; Zelin, C.; Pogoreltsev, A.I.; Wei, K. Dynamics of 2013 Sudden Stratospheric Warming event and its impact on cold weather over Eurasia: Role of planetary wave Reflection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedatella, N.M.; Chau, J.L.; Schmidt, H.; Goncharenko, L.P.; Stolle, C.; Hocke, K.; Harvey, V.L.; Funke, B.; Siddiqui, T.A. How sudden stratospheric warming affects the whole atmosphere. EOS 2018, 99, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Ayarzagüena, B.; Birner, T.; Butchart, N.; Butler, A.H.; Charlton-Perez, A.J.; Domeisen, D.I.V.; Garfinkel, C.I.; Garny, H.; Gerber, E.P.; et al. Sudden Stratospheric Warmings. Rev. Geophys. 2021, 59, e2020RG000708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, L.P.; Chau, J.L.; Liu, H.L.; Coster, A.J. Unexpected connections between the stratosphere and ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, L.; Zhang, S.R. Ionospheric signatures of sudden stratospheric warming: Ion temperature at middle latitude. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L21103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, J.L.; Fejer, B.G.; Goncharenko, L.P. Quiet variability of equatorial E × B drifts during a sudden stratospheric warming event. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L05101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Schreiner, W.S.; Lei, J.; Rocken, C.; Hunt, D.C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Wan, W. Global ionospheric response observed by COSMIC satellites during the January 2009 stratospheric sudden warming event. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A00G09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.G.; Shepherd, G.G. Stratospheric warming effects on thermospheric O(1S) dayglow dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, A11327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P. Stratospheric warmings: The atmosphere–ionosphere coupling paradigm. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2011, 73, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessarab, F.S.; Korenkov, Y.N.; Klimenko, M.V.; Klimenko, V.V.; Karpov, I.V.; Ratovsky, K.G.; Chernigovskaya, M.A. Modeling the effect of sudden stratospheric warming within the thermosphere-ionosphere system. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2012, 90–91, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumod, S.G.; Pant, T.K.; Jose, L.; Hossain, M.M.; Kumar, K.K. Signatures of Sudden Stratospheric Warming on the Equatorial Ionosphere-Thermosphere System. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 63–64, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.W.; Fuller-Rowell, T.; Akmaev, R.; Wu, F.; Wang, H.; Anderson, D. Longitudinal variation of ionospheric vertical drifts during the 2009 sudden stratospheric warming. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, A03324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polekh, N.M.; Kurkin, V.I.; Zolotukhina, N.A.; Chernigovskaya, M.A. On the connection between nighttime winter ionization increase in midlatitude F region and stratosphere warming. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2013, 22, 41–46. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Polyakova, A.S.; Chernigovskaya, M.A.; Perevalova, N.P. Ionospheric effects of sudden stratosperic warmings in eastern Siberia region. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2014, 120, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, F.I.; Pallamraju, D.; Veenadhari, B. Vertical coupling of atmospheres: Dependence on strength of sudden stratospheric warming and solar activity. Earth Planets Space 2014, 66, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedatella, N.M. Impact of the lower atmosphere on the ionosphere response to a geomagnetic superstorm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9383–9389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mošna, Z.; Edemskiy, I.; Laštovička, J.; Kozubek, M.; Koucká Knížová, P.; Kouba, D.; Siddiqui, T.A. Observation of the Ionosphere in Middle Latitudes during 2009, 2018 and 2018/2019 Sudden Stratospheric Warming Events. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, T.A.; Yamazaki, Y.; Stolle, C.; Maute, A.; Laštovička, J.; Edemskiy, I.K.; Mošna, Z.; Sivakandan, M. Understanding the total electron content variability over Europe during 2009 and 2019 SSWs. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, A.L.; Leshchenko, L.N.; Manaenkova, N.I. Peculiarities and perspectives of network digital ionospheric station ‘‘PARUS”. In Proceedings of the Progress in Electromagnetics Research (PIERS) Symposium Proceedings 2009, Moscow, Russia, 18–21 August 2009; pp. 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Sargoytchev, S.; Brown, S.; Solheim, B.; Cho, Y.-M.; Shepherd, G.; López-Gonzàlez, M.-J. Spectral Airglow Temperature Imager (SATI)—A ground based instrument for temperature monitoring of the mesosphere region. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncharenko, L.; Chau, J.L.; Condor, P.; Coster, A.; Benkevitch, L. Ionospheric effects of sudden stratospheric warming during moderate-to-high solar activity: Case study of January 2013. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4982–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, L.P.; Coster, A.J.; Zhang, S.R.; Erickson, P.J.; Benkevitch, L.; Aponte, N.; Harvey, V.L.; Reinisch, B.W.; Galkin, I.; Spraggs, M.; et al. Deep ionospheric hole created by sudden stratospheric warming in the nighttime ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 7621–7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, F.I.; McCormack, J.P.; Chau, J.L.; Pallamraju, D.; Hoffmann, P.; Singh, R.P. Interhemispheric meridional circulation during sudden stratospheric warming. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 7112–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Overview of the major 2012–2013 Northern Hemisphere stratospheric sudden warming: Evolution and its association with surface weather. J. Meteor. Res. 2014, 28, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coy, L.; Pawson, S. The Major Stratospheric Sudden Warming of January 2013: Analyses and Forecasts in the GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2015, 143, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, R.J.; Hibbins, R.E.; Espy, P.J.; Orsolini, Y.J.; Limpasuvan, V.; Kinnison, D.E. Observations of gravity wave forcing of the mesopause region during the January 2013 major Sudden Stratospheric Warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4745–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpynev, B.G.; Kurkin, V.I.; Ratovsky, K.G.; Chernigovskaya, M.A.; Belinskaya, A.Y.; Grigorieva, S.A.; Stepanov, A.E.; Bychkov, V.V.; Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P. High-midlatitude ionosphere response to major stratospheric warming. Earth Planets Space 2015, 67, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, A.S.; Kulikov, Y.Y.; Klimenko, M.V.; Klimenko, V.V.; Bessarab, F.S.; Korenkov, Y.N.; Marichev, V.N.; Ratovsky, K.G.; Kolesnik, S.A. Changes in the stratosphere and ionosphere parameters during the 2013 major stratospheric warming. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2018, 4, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.G.; Cho, Y.M.; Shepherd, G.G.; Ward, W.; Drummond, J.R. Mesospheric temperature and atomic oxygen response during the January 2009 major stratospheric warming. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A07318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Ning, B.; Huang, X.; Zhong, D.; Qi, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, L. Midlatitude ionospheric responses to the 2013 SSW under high solar activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Matthias, V.; Miyoshi, Y.; Stolle, C.; Siddiqui, T.; Kervalishvili, G.; Laštovička, J.; Kozubek, M.; Ward, W.; Themens, D.R.; et al. September 2019 Antarctic sudden stratospheric warming: Quasi-6-Dday wave burst and ionospheric effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordiyenko, G.; Yakovets, A.; Litvinov, Y.; Andreev, A. The Influence of Sudden Stratospheric Warming on the Development of Ionospheric Storms: The Alma-Ata Ground-Based Ionosonde Observations. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060626
Gordiyenko G, Yakovets A, Litvinov Y, Andreev A. The Influence of Sudden Stratospheric Warming on the Development of Ionospheric Storms: The Alma-Ata Ground-Based Ionosonde Observations. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(6):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060626
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordiyenko, Galina, Artur Yakovets, Yuriy Litvinov, and Alexey Andreev. 2024. "The Influence of Sudden Stratospheric Warming on the Development of Ionospheric Storms: The Alma-Ata Ground-Based Ionosonde Observations" Atmosphere 15, no. 6: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060626
APA StyleGordiyenko, G., Yakovets, A., Litvinov, Y., & Andreev, A. (2024). The Influence of Sudden Stratospheric Warming on the Development of Ionospheric Storms: The Alma-Ata Ground-Based Ionosonde Observations. Atmosphere, 15(6), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060626




