Estimation and Compensation of the Ionospheric Path Delay Phase in PALSAR-3 and NISAR-L Interferograms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulation of PALSAR-3 Single-Look Complex (SLC) Data with Two Spectral Bands Based on PALSAR-2 SM1 Mode SLC Data
2.2. Adapting the Split-Spectrum Method to the PALSAR-3 and NISAR L-Band SAR Cases
2.3. Processing-Related Aspects
2.3.1. Band-Pass Filtering
2.3.2. Effects of the SLC Co-Registration on the Interferogram
2.3.3. Interferogram Filtering and Unwrapping
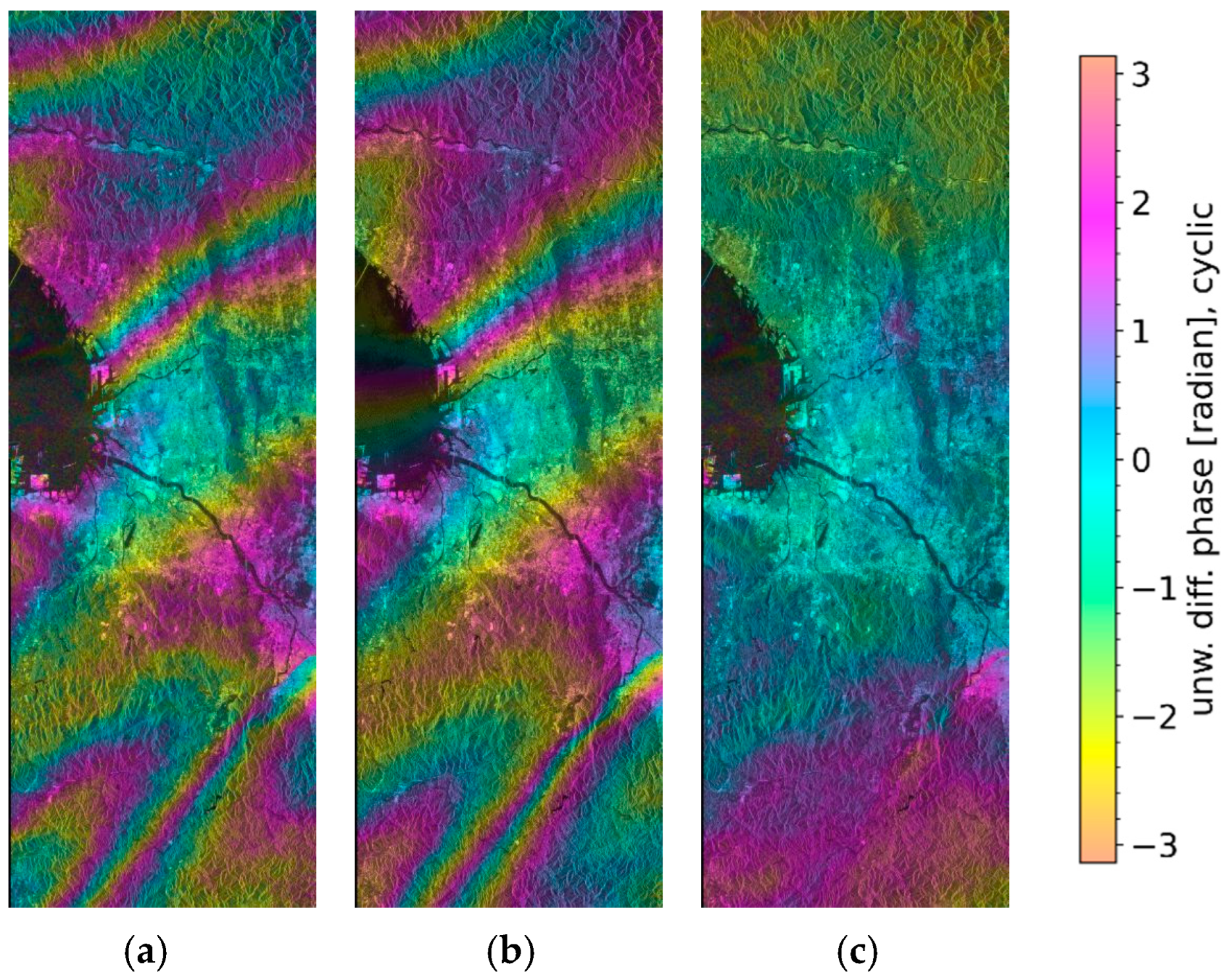
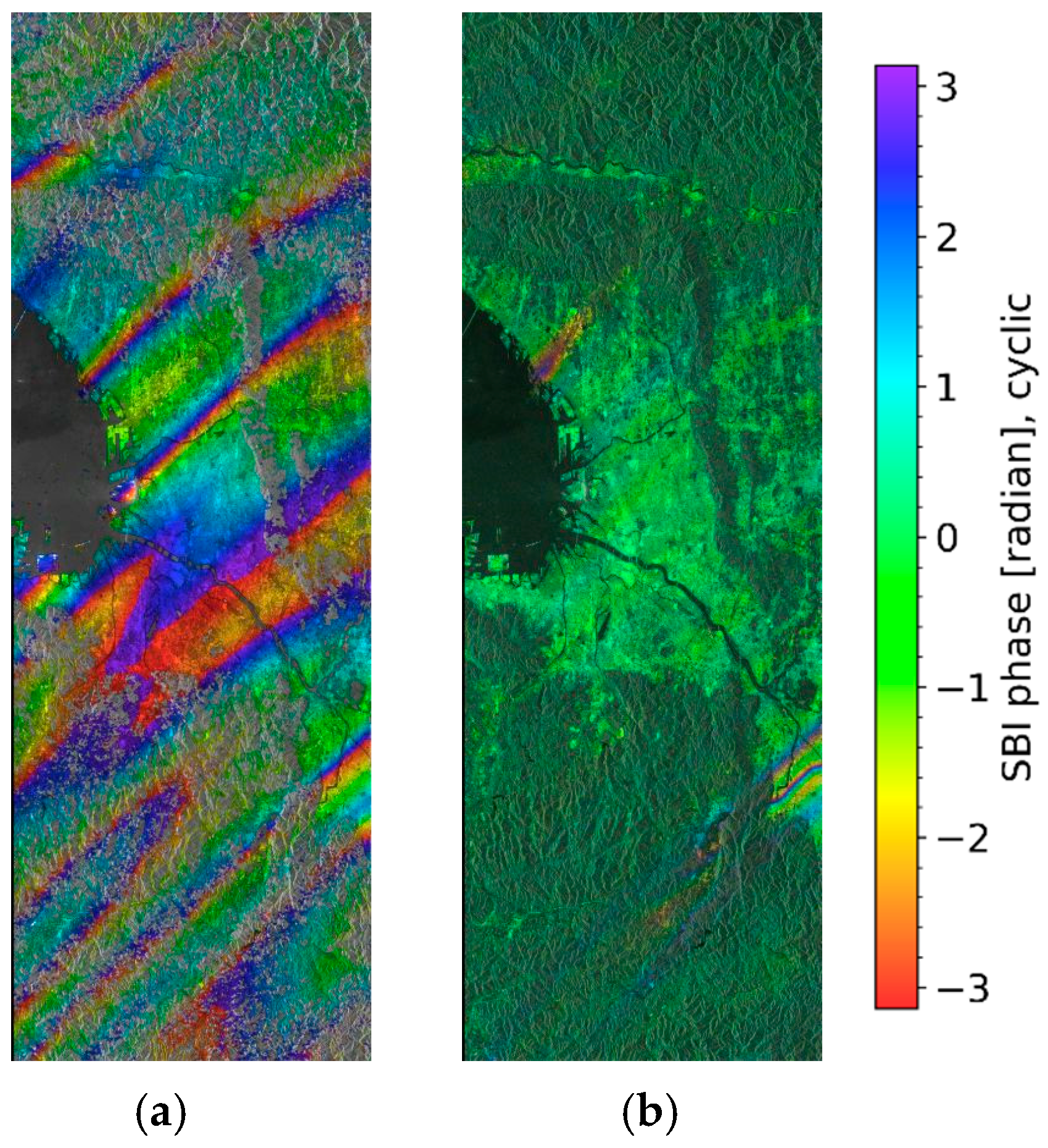
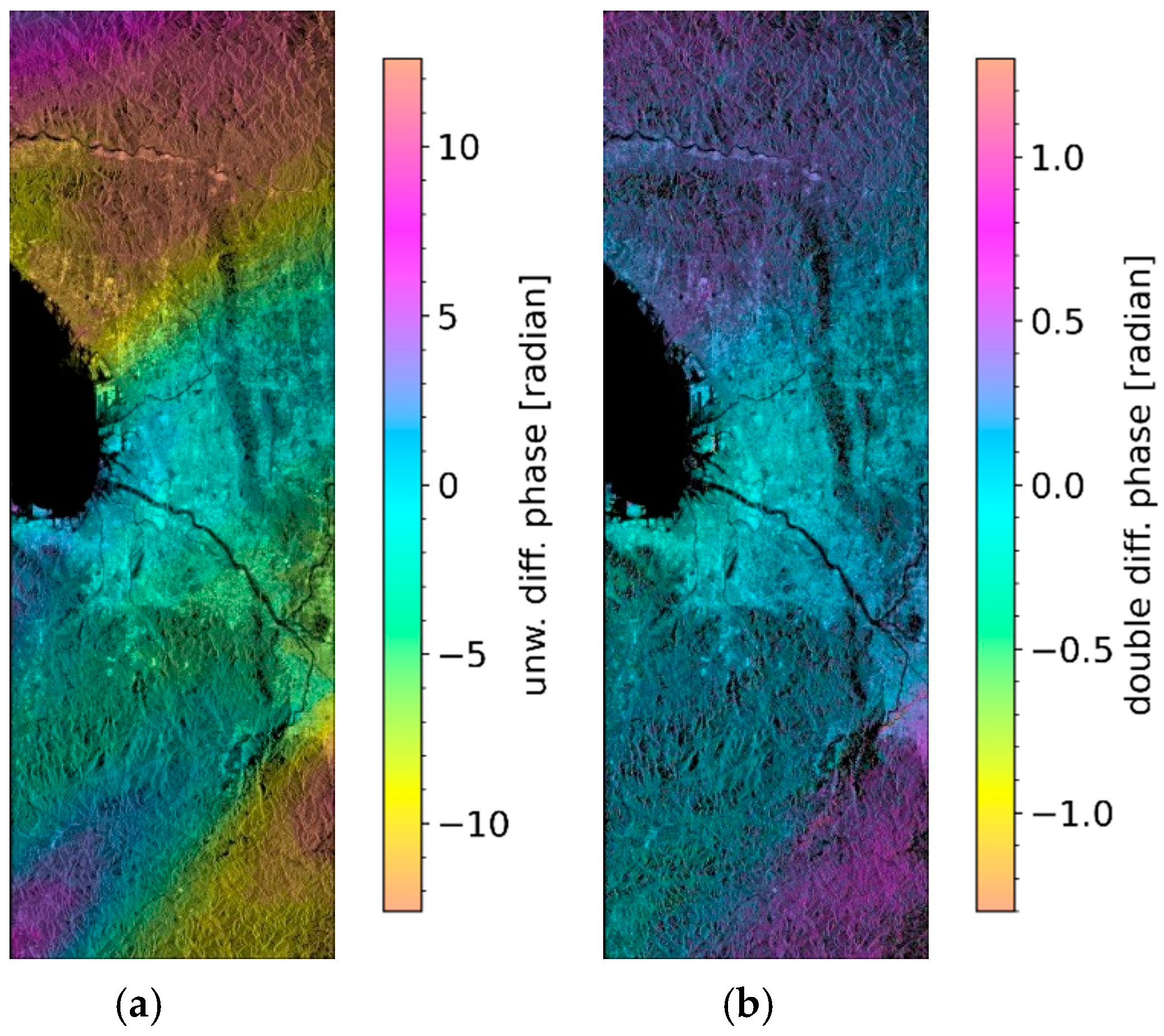
3. Results Using Simulated PALSAR-3 Data over Osaka
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Information on PALSAR-3 Instrument. 2023. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/2982981/10_191120SARwgcv_tadono.pdf/ee6db1c8-1910-7eed-3661-d25200df3abc (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) Mission Science Users’ Handbook. Available online: https://nisar.jpl.nasa.gov/documents/26/NISAR_FINAL_9-6-19.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, R1–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.; Li, F.; Madsen, S.; Rodriguez, E.; Goldstein, R. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, M.; Moreira, A. TanDEM-X mission status: The new topography of the earth takes shape. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 3386–3389. [Google Scholar]
- Massonet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, G.; Feigl, K.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by SAR interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.P.; Harp, E.L. Interpretation of earthquake-induced landslides triggered by the 12 May 2008, M7.9 Wenchuan earthquake in the Beichuan area, Sichuan Province, China, using satellite imagery and Google Earth. Landslides 2009, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.; Myer, D.; Mellors, R.; Shimada, M.; Brooks, B.; Foster, J. Accuracy and Resolution of ALOS Interferometry: Vector Deformation Maps of the Father’s Day Intrusion at Kilauea. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3524–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Wasowski, J. Investigating landslides with space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 173–199. [Google Scholar]
- Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P.; Berthier, E.; Raucoules, D.; Casson, B.; Grandjean, P.; Pambrun, C.; Varel, E. Remote-sensing techniques for analysing landslide kinematics: A review. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 2007, 178, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Ambrosi, C.; Raetzo, H. Interpretation of Aerial Photographs and Satellite SAR Interferometry for the Inventory of Landslides. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2554–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joughin, I.; Kwok, R.; Fahnestock, M. Estimation of ice-sheet motion using satellite radar interferometry: Method and error analysis with application to Humboldt Glacier, Greenland. J. Glaciol. 1996, 42, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Engelhardt, R.; Kamb, B.; Frolich, R. Satellite Radar Interferometry for Monitoring Ice Sheet Motion: Application to an Antarctic Ice Stream. Science 1993, 262, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, J.J.; Reeh, N.; Madsen, S.N. Three-dimensional glacial flow and surface elevation measured with radar interferometry. Nature 1998, 391, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.; Mattar, D.E.; Sofko, G. Influence of ionospheric electron density fluctuations on satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Bamler, R.; Jakowski, N.; Fritz, T. The potential of low-frequency SAR systems for mapping ionospheric TEC distributions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brcic, R.; Parizzi, A.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R.; Meyer, F. Estimation and compensation of ionospheric delay for SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 2908–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Brcic, R.; Parizzi, A.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R.; Meyer, F. Ionospheric effects in SAR interferometry: An analysis and comparison of methods for their estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 1497–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Chen, C. Measurement and mitigation of the ionosphere in L-band interferometric SAR data. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 10–14 May 2010; pp. 1459–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Gomba, G.; De Zan, F. Estimation of ionospheric height variations during an aurora event using multiple semi-focusing levels. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 4065–4068. [Google Scholar]
- Gomba, G.; Parizzi, A.; De Zan, F.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R. Toward operational compensation of ionospheric effects in SAR interferograms: The split-spectrum method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, M.; Suzuki, T.; Maeda, J.; Heki, K. Midlatitude sporadic-E episodes viewed by L-band split-spectrum InSAR. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Meyer, F.J.; Scheuchl, B.; Mouginot, J.; Joughin, I.; Rignot, E. Ionospheric correction of InSAR data for accurate ice velocity measurement at polar regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Simons, M.; Agram, P. InSAR Time-Series Estimation of the Ionospheric Phase Delay: An Extension of the Split Range-Spectrum Technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5984–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymofyeyeva, E.; Fialko, Y. Mitigation of atmospheric phase delays in InSAR data, with application to the eastern California shear zone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 5952–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C.; Frey, O.; Magnard, C.; Strozzi, T. Reformulating the Split-Spectrum Method to Facilitate the Estimation and Compensation of the Ionospheric Phase in SAR Interferograms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 138, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Ionospheric electron concentration effects on SAR and INSAR. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, Colorado, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamma Software Information. 2018. Available online: https://www.gamma-rs.ch/software (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Costantini, M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mode | f0 [GHz] | fL [GHz] | fH [GHz] | a | b | c | d | x | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PALSAR-3 28 MHz | 1.2330 | 1.2330 | 1.2910 | 11.38 | −10.87 | −10.39 | 10.87 | 0.511 | −10.87 |
| NISAR L 20 MHz | 1.2275 | 1.2275 | 1.2950 | 9.85 | −9.34 | −8.85 | 9.34 | 0.513 | −9.34 |
| NISAR L 40 MHz | 1.2375 | 1.2375 | 1.2950 | 11.52 | −11.01 | −10.52 | 11.01 | 0.511 | −11.01 |
| PALSAR-1 14 MHz | 1.2700 | 1.2653 | 1.2747 | 68.24 | −67.74 | −67.74 | 68.24 | 0.500 | −67.99 |
| PALSAR-1 28 MHz | 1.2700 | 1.2607 | 1.2793 | 34.28 | −33.78 | −33.78 | 34.28 | 0.500 | −34.03 |
| PALSAR-2 12 MHz | 1.2365 | 1.2325 | 1.2405 | 78.17 | −77.67 | −77.67 | 78.17 | 0.500 | −77.92 |
| PALSAR-2 25 MHz | 1.2700 | 1.2617 | 1.2783 | 38.50 | −38.00 | −38.00 | 38.50 | 0.500 | −38.25 |
| PALSAR-2 80 MHz | 1.2575 | 1.2310 | 1.2840 | 12.12 | −11.62 | −11.62 | 12.12 | 0.500 | −11.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C.; Frey, O.; Magnard, C. Estimation and Compensation of the Ionospheric Path Delay Phase in PALSAR-3 and NISAR-L Interferograms. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060632
Wegmüller U, Werner C, Frey O, Magnard C. Estimation and Compensation of the Ionospheric Path Delay Phase in PALSAR-3 and NISAR-L Interferograms. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(6):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060632
Chicago/Turabian StyleWegmüller, Urs, Charles Werner, Othmar Frey, and Christophe Magnard. 2024. "Estimation and Compensation of the Ionospheric Path Delay Phase in PALSAR-3 and NISAR-L Interferograms" Atmosphere 15, no. 6: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060632
APA StyleWegmüller, U., Werner, C., Frey, O., & Magnard, C. (2024). Estimation and Compensation of the Ionospheric Path Delay Phase in PALSAR-3 and NISAR-L Interferograms. Atmosphere, 15(6), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060632








