Assessing the Hydrologic Impacts of Land Use Change in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2010
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
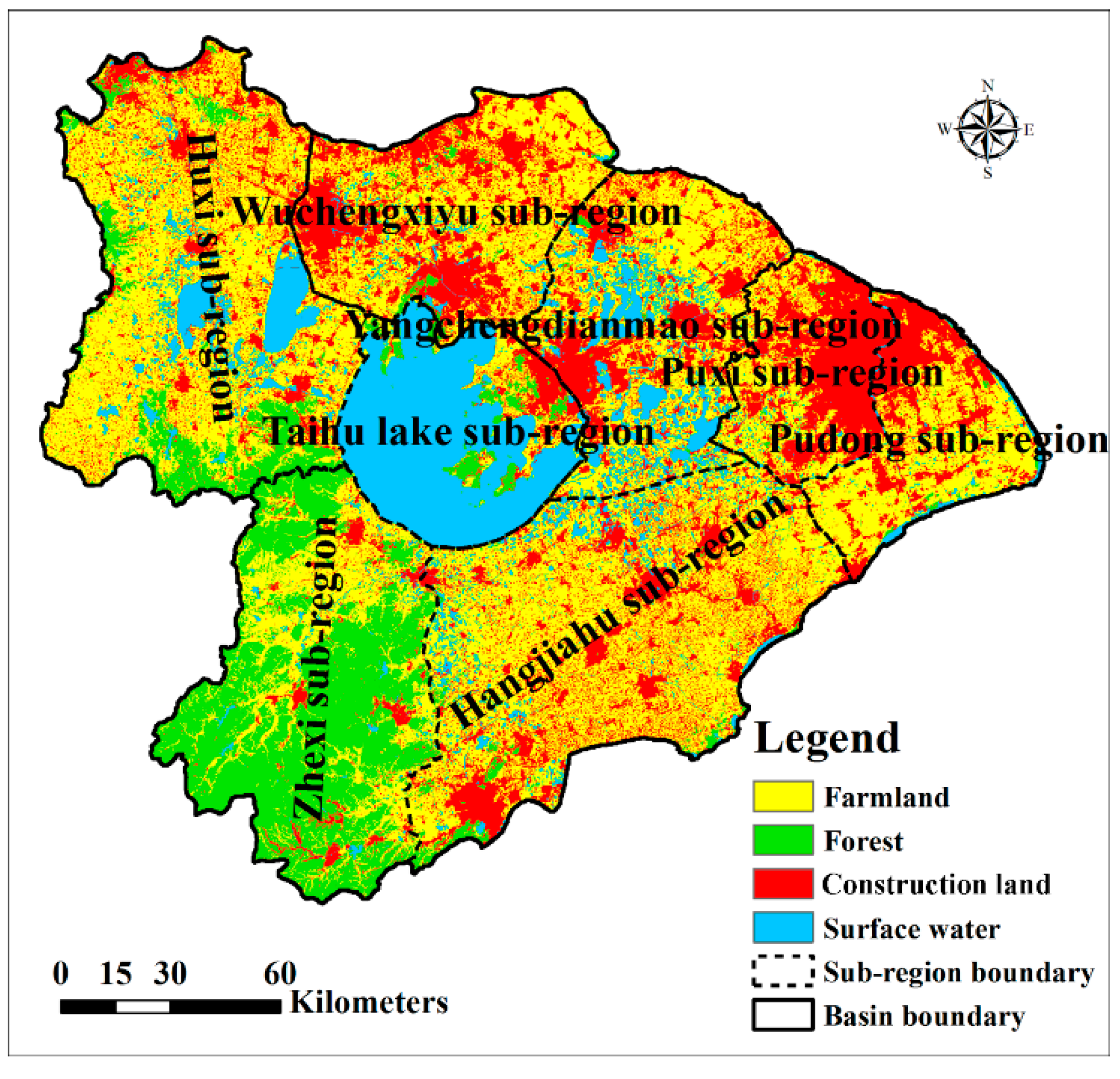
2.1. The Study Area
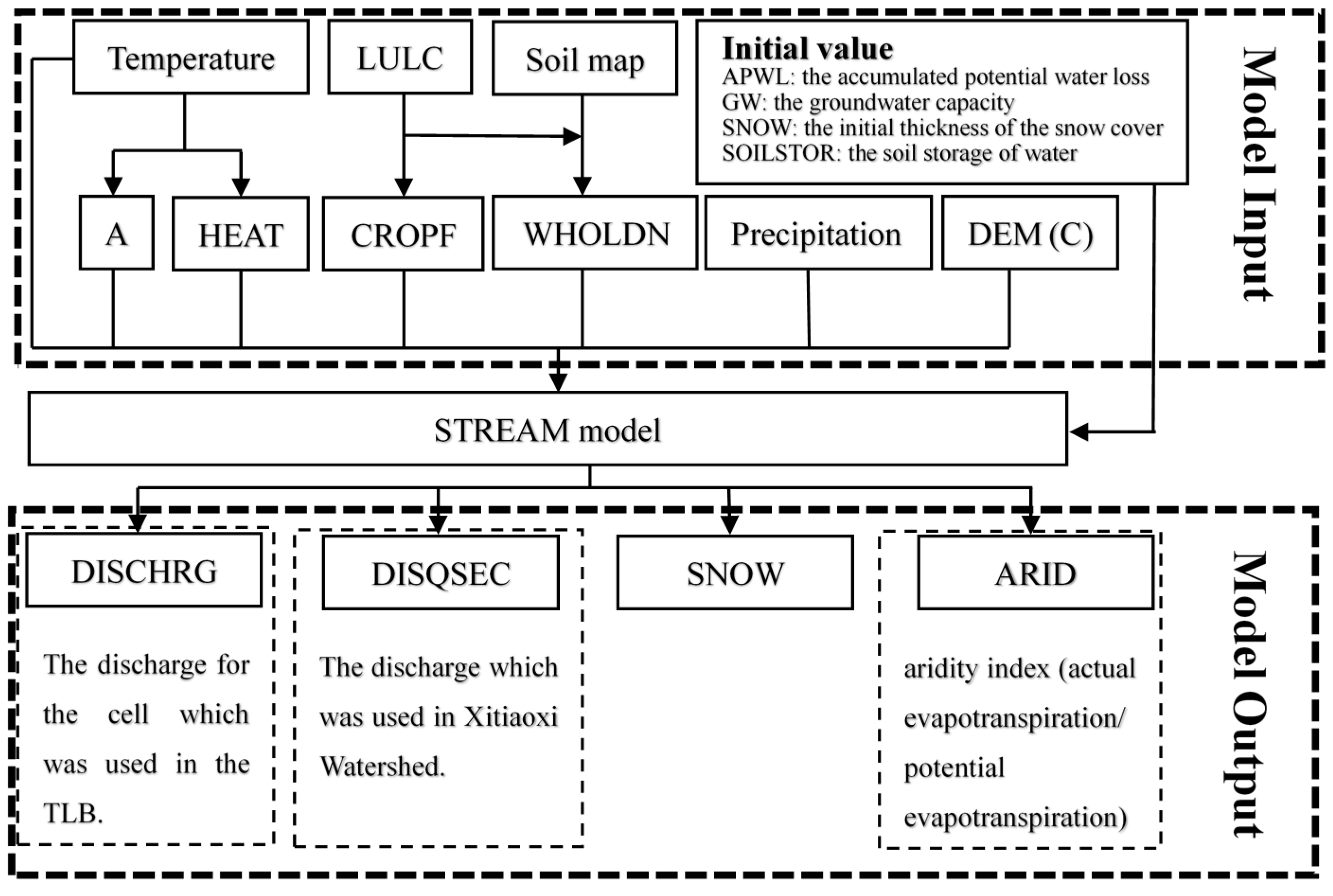
2.2. The STREAM Model
2.3. Data Collection and Preparation
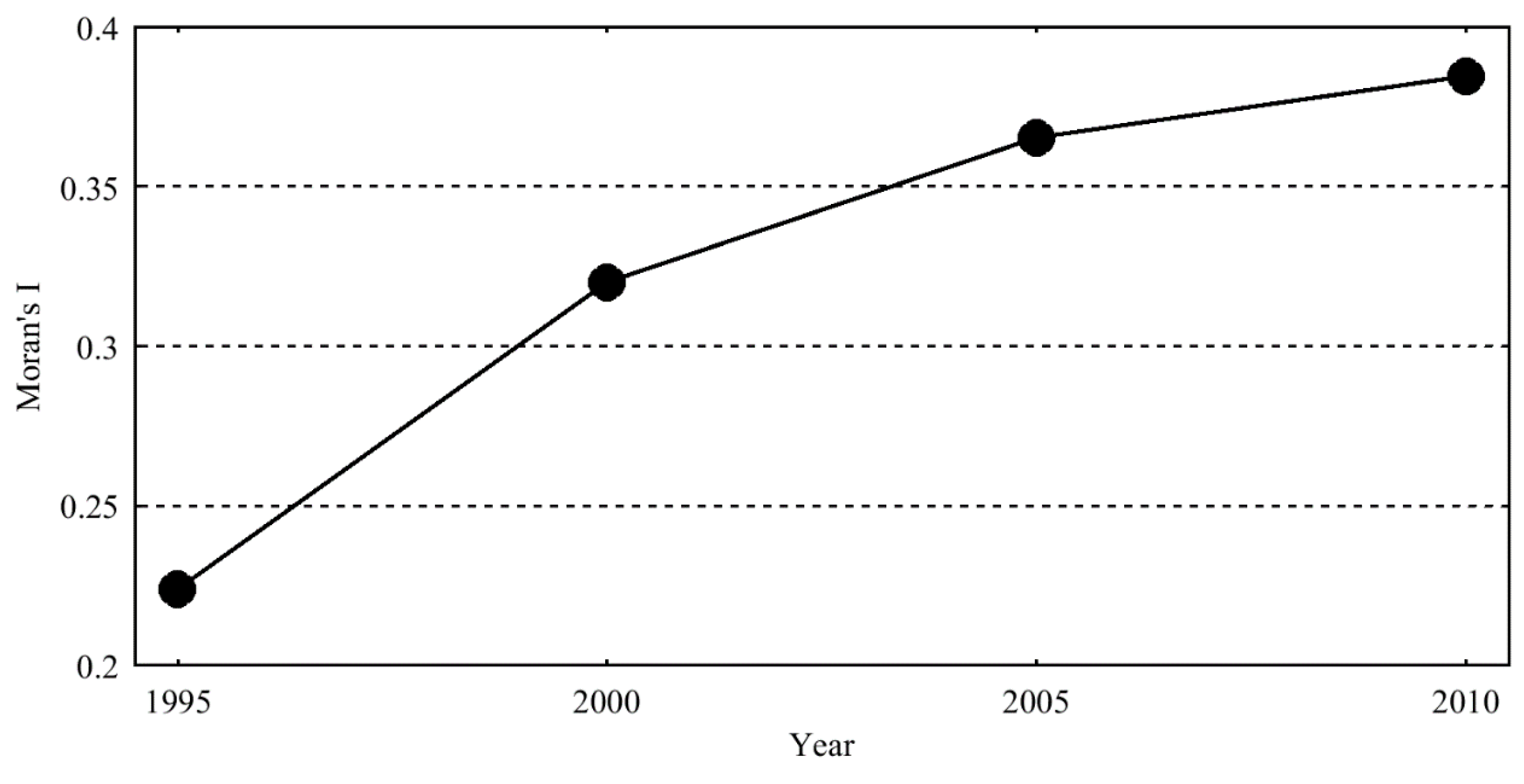
2.4. Moran’s I
3. Results
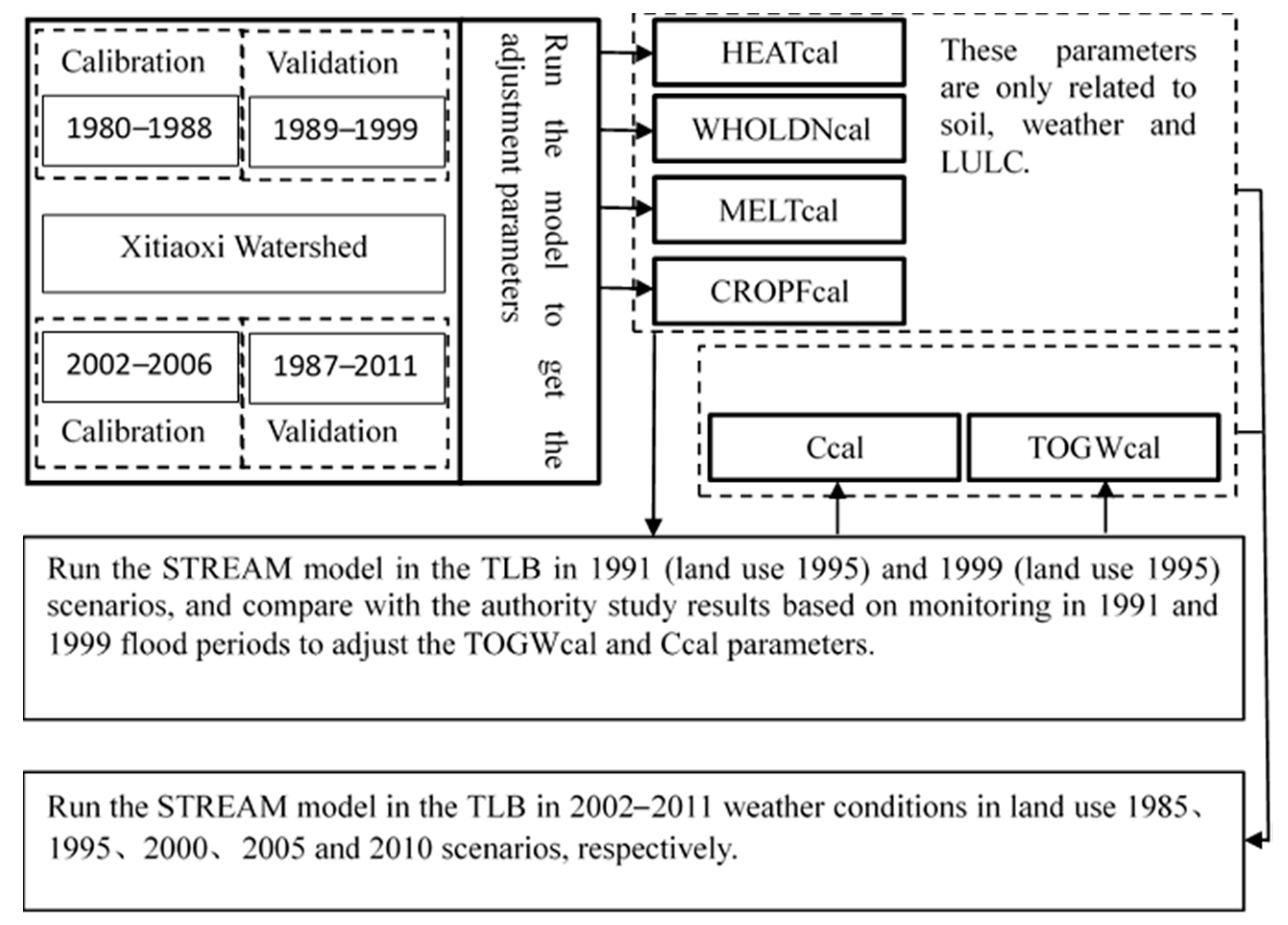
3.1. Model Calibration and Validation
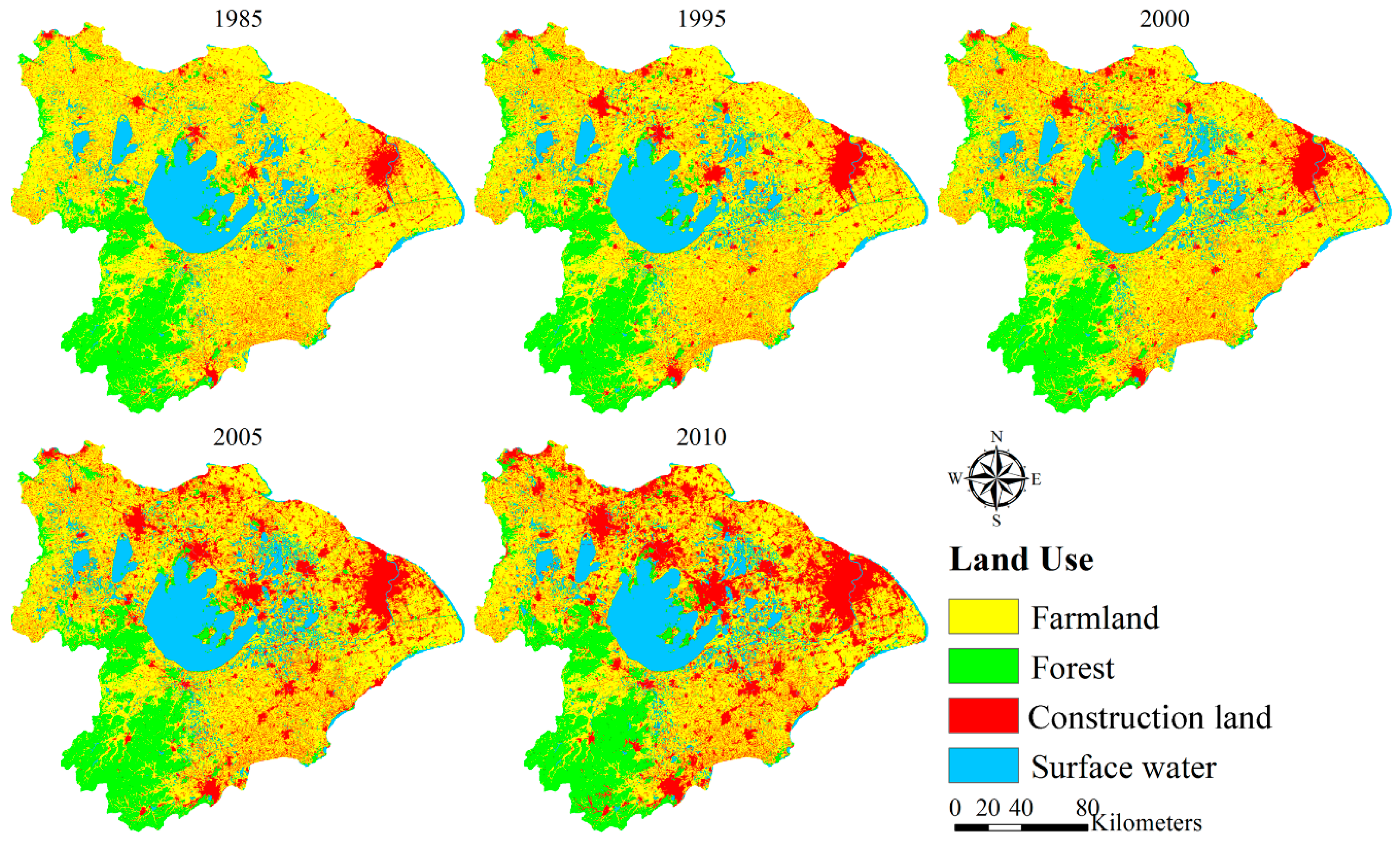
3.2. LULC Change
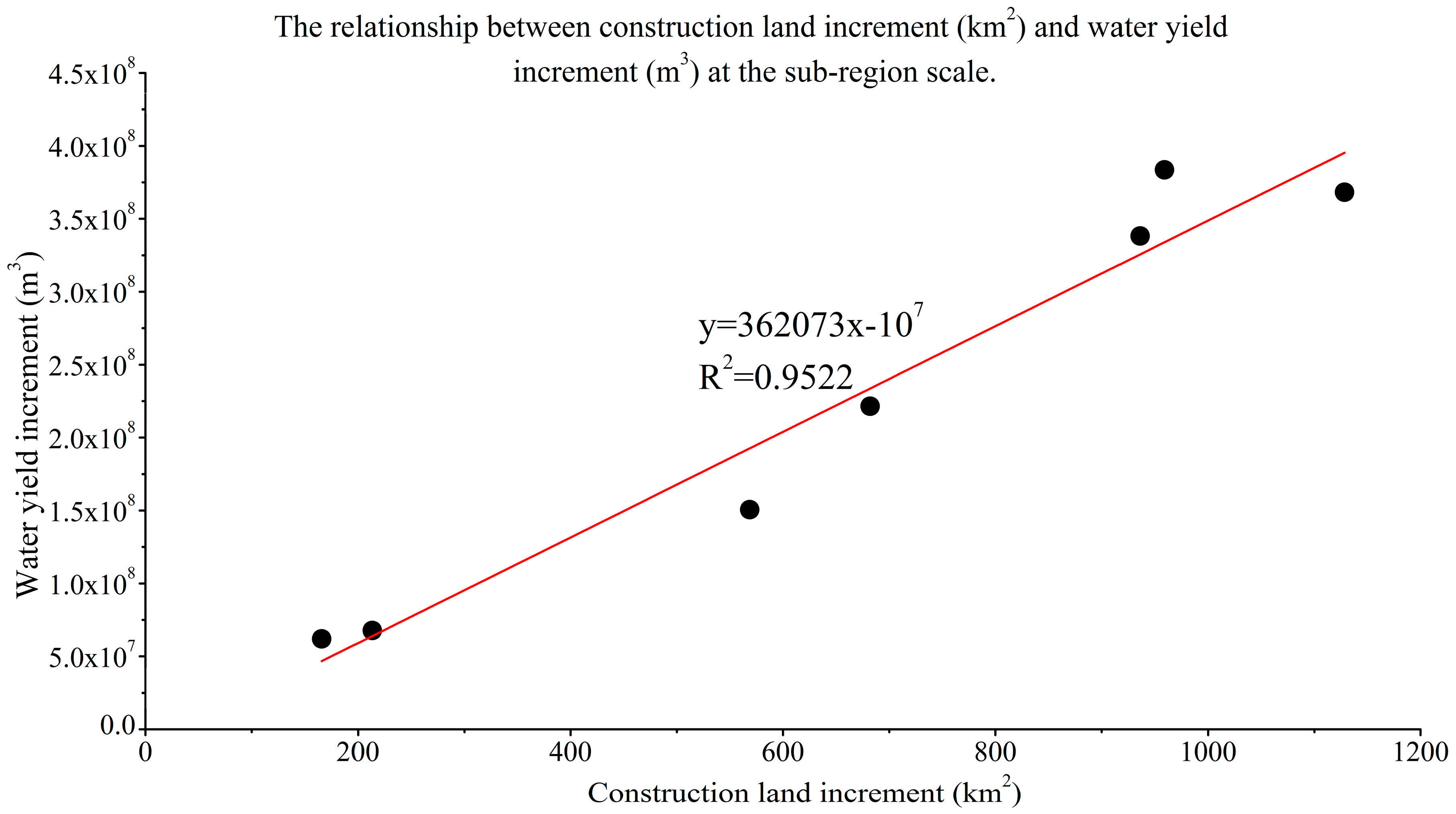
3.3. Water Yield Response to Land Use Change
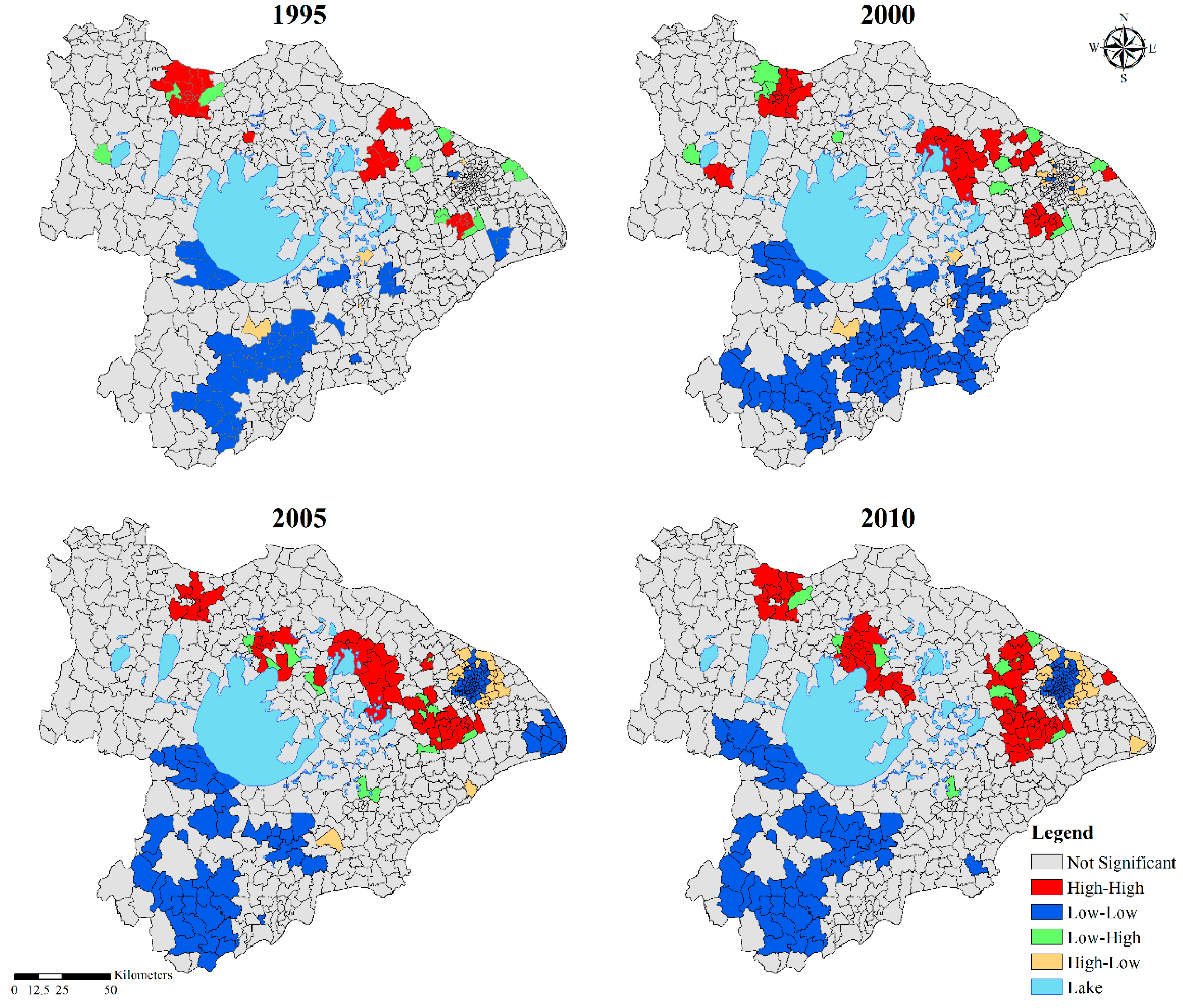
3.4. Spatial Variation Difference of Water Yield
3.4.1. Water Yield Changes in Hydrological Subregions
3.4.2. Water Yield Changes in the Town Scale
4. Discussion
4.1. Influences of Urbanization on Local Hydrological Characteristics
4.2. Urban Waterlogging and Urbanization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olson, J.M.; Alagarswamy, G.; Andresen, J.A.; Campbell, D.J.; Davis, A.Y.; Ge, J.; Huebner, M.; Lofgren, B.M.; Lusch, D.P.; Moore, N.J.; et al. Integrating diverse methods to understand climate and interactions in East Africa. Geoforum 2008, 39, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, W.; Guo, Q.; Wu, S. Effects of landuse change on surface run-off and sediment yield at different watershed scales on the Loess Plateau. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2010, 25, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rientjes, T.; Haile, A.; Kebede, E.; Mannaerts, C.; Habib, E.; Steenhuis, T. Changes in land cover, rainfall and stream flow in Upper Gilgel Abbay catchment, Blue Nile Basin Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoi, D.; Suetsugi, T. Impact of climate and land-use changes on hydrological processes and sediment yield: A case study of the Be River catchment, Vietnam. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.J.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.A.; Ge, Y.; Qiu, G.Y. The effect of land use/cover change on surface runoff in Shenzhen region, China. Catena 2007, 69, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldesenbet, T.A.; Elagib, N.A.; Ribbe, L.; Heinrich, J. Hydrological responses to land use/cover changes in the source region of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y. Impact of land use change scenarios on storm-runoff generation in Xitiaoxi Basin, China. Quatern. Int. 2009, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiablame, L.; Shakya, R. Modeling flood reduction effects of low impact development at a watershed scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 171, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fohrer, N.; Haverkamp, S.; Eckhardt, K.; Frede, H.G. Hydrologic response to land use changes on the catchment scale. Phys. Chem. Earth B 2001, 26, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yuan, Y.; Kepner, W.; Nash, M.S.; Jackson, M.; Erickson, C. Assessing impacts of land use and land cover changes on hydrology for the upper San Pedro watershed. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, C.; Ndambuki, J.M.; Salim, R.W. Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Cover Changes in the Olifants Basin, South Africa. Water 2016, 8, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.J.; Miller, S.N. Using the Soil and Water Assessmnent Tool (SWAT) to assess land use impact on water resources in an East African watershed. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneti, S.; Sunkara, S.L.; Roy, P.S. Hydrological Modeling with Respect to Impact of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change on the Runoff Dynamics in Godavari River Basin Using the HEC-HMS Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Bowling, L.C.L.; Cherkauer, K.A.L.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Niyogi, D. Hydroclimatic response of watersheds to urban intensity: An observational and modeling-based analysis for the White River Basin, Indiana. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, S.E.; Band, L.E. Simulating runoff behavior in an urbanizing watershed. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2000, 24, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.; Salavati, B.; Percot, C.F.; Ribstein, P.; Saadi, M. Hydrological impacts of urbanization at the catchment scale. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.H.; Li, Y.K. Long-term hydrological impacts of land use/land cover change from 1984 to 2010 in the Little River Watershed, Tennessee. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014, 2, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Fang, N.F.; Zhang, P.C.; Shi, Z.H. Impacts of land use change on watershed streamflow and sediment yield: An assessment using hydrologic modelling and partial least squares regression. J. Hydrol. 2013, 484, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjad, B.; Gupta, A.; Razavi, S.; Faramarzi, M.; Marceau, D.J. An Integrated Modelling System to Predict Hydrological Processes under Climate and Land-Use/Cover Change Scenarios. Water 2017, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, T.; Mejía, A.; Gall, H.; Gironás, J. Effect of urbanization on the long-term persistence of streamflow records. Phys. A 2016, 447, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Smith, J.A.; Wright, D.B.; Baeck, M.L.; Villarini, G.; Tian, F.Q.; Hu, H.P. Urbanization and climate change: An examination of nonstationarities in urban flooding. J. Hydro Meteorol. 2013, 14, 1791–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J.; McDonnell, J.J. Land-cover impacts on streamflow: A changedetection modelling approach that incorporates parameter uncertainty. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.-Z.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zheng, F.-L. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Kim, H.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Packman, J.; Grebby, S.; Dearden, R. Assessing the impact of urbanization on storm runoff in a peri-urban catchment using historical change in impervious cover. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zope, P.E.; Eldho, T.I.; Jothiprakash, V. Impacts of land use–land cover change and urbanization on flooding: A case study of Oshiwara River Basin in Mumbai, India. Catena 2016, 145, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundecha, Y.; Bárdossy, A. Modeling of the effect of land use changes on the runoff generation of a river basin through parameter regionalization of a watershed model. J. Hydrol. 2004, 292, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadore, E.; Bronders, J.; Batelaan, O. Hydrological modelling of urbanized catchments: A review and future directions. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.R.; Yang, G.S. Influence of Land Use/Cover Change on Storm Runoff—A Case Study of Xitiaoxi River Basin in Upstream of Taihu Lake Watershed. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solecki, W.D.; Oliveri, C. Downscaling climate change scenarios in an urban land use change model. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 72, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.N.; Almeida, A.C.D.; Coelho, C.O.A. Impacts of land use and cover type on runoff and soil erosion in a marginal area of Portugal. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, Z.X.; Reynard, N.S.; Hu, C.W.; Jones, R.G. Hydrological analysis for water level projections in Taihu Lake, China. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2013, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hall, J.W.; Cheng, X.; Evans, E.P. Broad scale quantified flood risk analysis in the Taihu Basin, China. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2013, 6, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Yin, Y.X. Assessment of effects of land use changes on storm runoff generation—A Case Study of Xitiaoxi Basin. Sci. Geogra. Sinica. 2009, 29, 117–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rong, J.; Zeng, C.F.; Wang, L.C. The impact of land use/cover change on hydrological processes of Lake Taihu Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 305–312. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.F. Flood response to land use change in Taihu Lake Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 17, 150–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.Y.; Guan, W.Q. The Flood in Taihu Lake Basin in 1991; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 20–33. ISBN 7-5084-0186-7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Kriek, M.; Schepel, M. STREAM (Spatial Tools for River Basins and Environment and Analysis of Management Options): ‘Set Up and Requirements’. Phys. Chem. Earch (B) 1999, 24, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.M. Detection of urban-induced rainfall anomalies in a major coastal city. Earth Interact. 2003, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.M. Evidence of urban-induced precipitation variability in arid climate regimes. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 67, 607–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.P.; Ding, J.J.; Chen, Y. Impacts of urbanization on hydrology in the Yangtze River delta. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2009, 12, 67–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, G.B.; Su, W.Z.; Chen, W.X. The Elevation Characteristics Variation of Urban and Rural Construction Land Expansion in Taihu Lake Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 938–950. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, H.Y.; Wu, H.Y. The Flood in Taihu Lake Basin in 1999; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 22–31. ISBN 7-5084-0851-9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.J.; Wang, J.A.; Zhou, J.H.; Ding, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.C. Integrated risk management of flood disaster in China: To balance flood disaster magnitude and vulnerability in metropolitan regions. J. Nat. Disaster 2004, 4, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Balica, S.F.; Wright, N.G.; van der Meulen, F. A flood vulnerability index for coastal cities and its use in assessing climate change impacts. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.G.; Wu, T.L.; Jiang, J.H.; Mao, R. 1999 heavy flooding in the Taihu Basin: Investigation, analysis and further suggestions on the integrated harnessing in the basin. J. Lake Sci. 2000, 12, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.W.; Wu, Y.N.; Yao, S.J. Key issues of water conservancy in the Taihu Lake Basin and sci-tech demands under fast urbanization. China Water Resour. 2015, 8, 18–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.M.; Jin, H.Z.; Chen, Y.H. Countermeasures for new problems of urban flood and waterlogging prevention in east Taihu Lake Basin. Yangtze River 2013, 44, 7–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Description | Range | Fitted Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WHOLDNcal | Water holding capacity of the soil | >0 | 1.5 |
| MELTcal | How fast snow melts | >0 | 10 |
| CROPFcal | Parameter steering the evapotranspiration | >0 | 1 |
| TOGWcal | Parameter separating the fraction going to groundwater and to direct runoff | >0 | 0.4 |
| Ccal | Parameter steering how fast groundwater flows | >1 | 2 |
| Heatcal | parameter (constant) used to calculate PE | >0 | 1 |
| Landuse | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | Change of 1985–1995 | Change of 1995–2000 | Change of 2000–2005 | Change of 2005–2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 63.65% | 60.23% | 58.98% | 53.20% | 47.90% | −3.41% | −1.25% | −5.79% | −5.29% |
| Vegetation | 13.92% | 14.00% | 13.98% | 13.89% | 14.30% | 0.08% | −0.03% | −0.09% | 0.41% |
| construction land | 9.68% | 12.53% | 13.41% | 18.57% | 24.24% | 2.85% | 0.88% | 5.16% | 5.67% |
| Water | 12.75% | 13.24% | 13.63% | 14.34% | 13.55% | 0.49% | 0.39% | 0.71% | −0.79% |
| Landuse | Farmland | Vegetation | Construction Land | Water | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | |
| 1985 | 47.20 | 54.26 | 38.15 | 17.36 | 19.88 | 14.71 | 10.50 | 11.53 | 9.53 | 24.94 | 31.24 | 18.70 |
| 1995 | 44.05 | 51.06 | 35.41 | 16.99 | 19.27 | 14.57 | 13.99 | 15.53 | 12.96 | 24.97 | 30.79 | 19.02 |
| 2000 | 44.75 | 51.05 | 37.29 | 16.97 | 19.23 | 14.59 | 13.77 | 14.88 | 13.13 | 24.50 | 30.03 | 18.88 |
| 2005 | 40.21 | 45.72 | 33.43 | 16.05 | 17.84 | 14.07 | 19.28 | 20.82 | 18.05 | 24.46 | 29.76 | 19.28 |
| 2010 | 35.20 | 40.43 | 28.82 | 16.11 | 17.84 | 14.25 | 25.82 | 27.98 | 24.30 | 22.88 | 27.77 | 18.21 |
| 1985–1995 | 1995–2000 | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase Rate | Increment (mm) | Increase Rate | Increment (mm) | Increase Rate | Increment (mm) | Increase Rate | Increment (mm) | |
| Zhexi sub-region | 0.19% | 1.16 | 0.20% | 1.21 | 0.48% | 2.88 | 1.02% | 6.16 |
| Hangjiahu sub-region | 0.90% | 3.64 | 0.53% | 2.16 | 6.10% | 24.95 | 3.23% | 14.02 |
| Taihu Lake sub-region | 0.28% | 2.11 | 0.25% | 1.90 | 1.55% | 11.73 | 0.48% | 3.67 |
| Pudong sub-region | 2.61% | 7.99 | 2.46% | 7.74 | 4.34% | 13.97 | 9.57% | 32.15 |
| Puxi sub-region | 4.64% | 14.64 | 4.50% | 14.84 | 10.62% | 36.60 | 9.39% | 35.82 |
| Yangchengdianmao sub-region | 7.53% | 27.79 | 3.83% | 15.22 | 10.69% | 44.04 | 0.47% | 2.13 |
| Wuchengxiyu sub-region | 7.66% | 23.16 | 2.93% | 9.53 | 8.57% | 28.72 | 8.35% | 30.38 |
| Huxi sub-region | 4.69% | 18.22 | 0.65% | 2.64 | 3.68% | 15.06 | 1.32% | 5.60 |
| Total Taihu Lake Basin | 2.74% | 11.91 | 1.23% | 5.49 | 4.61% | 20.85 | 2.75% | 13.01 |
| City | Per Capita GDP in 2010 (Yuan) | Construction Land Growth Rate | Water Yield Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | 73,297 | 57.73% | 40.79% |
| Suzhou | 87,607 | 72.23% | 54.84% |
| Wuxi | 90,355 | 64.25% | 43.43% |
| Changzhou | 64,824 | 63.06% | 43.89% |
| Huzhou | 44,982 | 50.78% | 18.45% |
| Jiaxing | 51,003 | 45.64% | 24.85% |
| City/Basin | 1985–1995 | 1995–2000 | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | 1985–2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | 6.77% | 3.64% | 12.41% | 13.19% | 40.79% |
| Suzhou | 11.64% | 2.99% | 19.29% | 12.90% | 54.84% |
| Wuxi | 11.41% | 2.41% | 12.58% | 11.66% | 43.43% |
| Changzhou | 15.42% | 1.97% | 9.18% | 11.97% | 43.89% |
| Huzhou | 1.50% | 0.10% | 7.37% | 8.57% | 18.45% |
| Jiaxing | 1.18% | 0.11% | 16.21% | 6.06% | 24.85% |
| Taihu Lake Basin | 2.99% | 1.34% | 4.97% | 2.94% | 12.85% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Diao, Y. Assessing the Hydrologic Impacts of Land Use Change in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2010. Water 2018, 10, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111512
Li P, Li H, Yang G, Zhang Q, Diao Y. Assessing the Hydrologic Impacts of Land Use Change in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2010. Water. 2018; 10(11):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111512
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pengcheng, Hengpeng Li, Guishan Yang, Qi Zhang, and Yaqin Diao. 2018. "Assessing the Hydrologic Impacts of Land Use Change in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2010" Water 10, no. 11: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111512
APA StyleLi, P., Li, H., Yang, G., Zhang, Q., & Diao, Y. (2018). Assessing the Hydrologic Impacts of Land Use Change in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2010. Water, 10(11), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111512




