North Sea Ecosystem-Scale Model-Based Quantification of Net Primary Productivity Changes by the Benthic Filter Feeder Mytilus edulis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Abundance Reconstruction, Numerical Models, and Experimental Setup
2.1. Numerical Models
2.2. Experiment Setup
2.3. Data for Model Evaluation
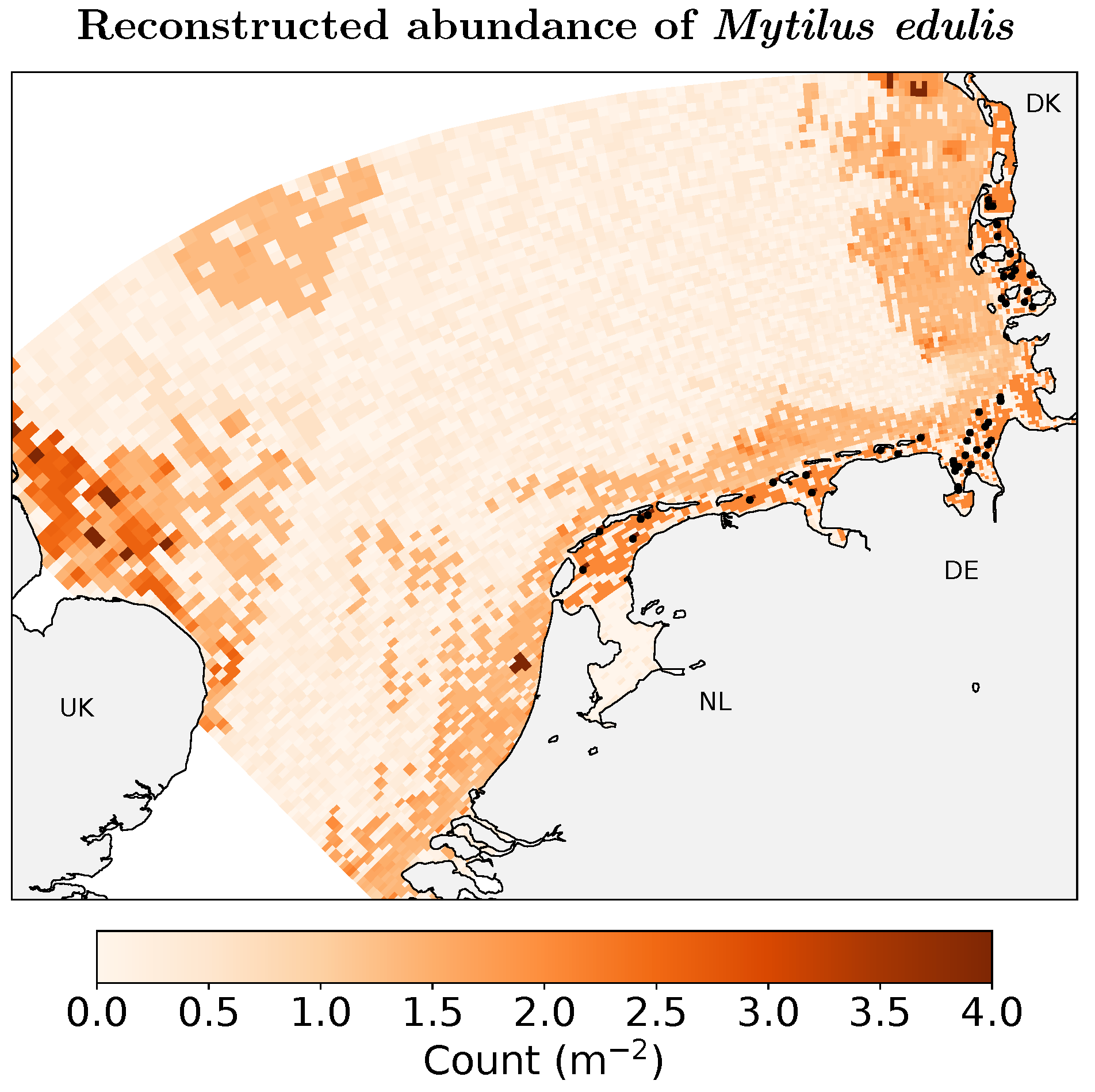
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Data and Code Availability Statement
5.2. Supporting Online Material
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFDW | ash-free dry weight |
| BFM | Biogeochemical Flux Model |
| BMDB | Belgian Marine Data Centre |
| DASSH | Archive for Marine Species and Habitats Data |
| DW | dry weight |
| ECOHAM | Ecosystem Model Hamburg |
| ECOSMO | Ecosystem Model |
| ERSEM | European Regional Seas Ecosystem Model |
| ESA-CCI | European Space Agency Climate Change Initiative |
| ESMF | Earth System Modeling Framework |
| FABM | Framework for Aquatic Biogeochemistry |
| FR | filtration rate |
| GBIF | Global Biodiversity Information Facility |
| GETM | General Estuarine Transport Model |
| HAMSOM | Hamburg Shelf Ocean Model |
| ICES | International Council for the Exploration of the Seas |
| JNCC | Joint Nature Conservation Committee |
| MAECS | Model for Adaptive Ecosystems in Coastal Seas |
| MOSSCO | Modular System for Shelves and Coasts |
| NEMO | Nucleus for European Modelling of the Ocean |
| NERC | Natural Environment Research Council |
| NOAH | North Sea Assessment of Habitats |
| NORWECOM | NORWegian ECOlogical Model |
| NPP | net primary productivity |
| NPZD | nutrient, phytoplankton, zooplankton, detritus |
| OBIS | Ocean Biogeographic Information System |
| OMExDia | Ocean Margin Experiment Diagenesis model |
| OSPAR | Oslo-Paris agreement |
| POLCOMS | Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory Coastal Ocean Modelling System |
| PSU | Practical Salinity Unit |
| RF | Random forest |
| SeaWiFS | Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor |
| SIBES | Synoptic Intertidal BEnthic Survey |
| SNS | southern North Sea |
| TPM | total particulate matter |
References
- Darr, A.; Gogina, M.; Zettler, M.L. Detecting hot-spots of bivalve biomass in the south-western Baltic Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 134, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Con Iomaire, M. No The history of Seafood in Irish Cuisine and Culture. In Oxford Symposium on Food and Cookery 2005; Prospect Books: Devon, UK, 2006; pp. 219–233. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, J.L.; Jones, C.G.; Strayer, D.L.; Iribarne, O.O. Mollusks as ecosystem engineers: The role of shell production in aquatic habitats. Oikos 2003, 101, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations FAO Fishstat, Database. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/software/fishstatj/en (accessed on 6 June 2017).
- Slavik, K.; Lemmen, C.; Zhang, W.; Kerimoglu, O.; Klingbeil, K.; Wirtz, K.W. The large-scale impact of offshore wind farm structures on pelagic primary productivity in the southern North Sea. Hydrobiologia 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, T.; Stank, J.; Schernewski, G.; Krost, P. The impact of a mussel farm on water transparency in the Kiel Fjord. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 101, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, J.; Green, N.W.; Brooks, S.; Allan, I.J.; Ruus, A.; Gomes, T.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Schøyen, M. Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis spp.) as sentinel organisms in coastal pollution monitoring: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, T.C.; Smaal, A.C.; Pouwer, A.J. Selective ingestion of phytoplankton by the bivalves Mytilus edulis L. and Cerastoderma edule (L.). Hydrobiol. Bull. 1991, 25, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmus, H.; Asmus, R.M.; Prins, T.C.; Dankers, N.; Francés, G.; Maaß, B.; Reise, K. Benthic-pelagic flux rates on mussel beds: Tunnel and tidal flume methodology compared. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1992, 46, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekhuizen, N.; Zeldis, Z.; Stephens, S.A.; Oldman, J.W.; Ross, A.H.; Ren, J.; James, M.R. Factors Related to the Sustainability of Shellfish Aquaculture Operations in the Firth of Thames: A Preliminary Analysis; NIWA Client Report: EVW02243; National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research Ltd.: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bayne, B.L.; Iglesias, J.; Hawkins, A.J.S. Feeding behaviour of the mussel, Mytilus edulis: Responses to variations in quantity and organic content of the seston. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1993, 73, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, P.; Hill, P. Seasonal variation in food utilization by the suspension-feeding bivalve molluscs Mytilus edulis and Placopecten magellanicus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 190, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, C.; Davenport, J. A 15-month study of zooplankton ingestion by farmed mussels (Mytilus edulis) in Bantry Bay, Southwest Ireland. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riisgård, H.U.; Kittner, C.; Seerup, D.F. Regulation of opening state and filtration rate in filter-feeding bivalves (Cardium edule, Mytilus edulis, Mya arenaria) in response to low algal concentration. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 284, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milke, L.M.; Ward, J. Influence of diet on pre-ingestive particle processing in bivalves. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 293, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.; Maar, M. Effects of a blue mussel Mytilus edulis bed on vertical distribution and composition of the pelagic food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 339, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmus, R.M.; Asmus, H. Mussel beds: Limiting or promoting phytoplankton? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 148, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekhuizen; Zeldis, J.; Stevens, S.; Ren, J. Ecological Sustainability Assessment for Firth of Thames Shellfish Aquaculture; NIWA Client Report: HAM2003-120; National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research Ltd.: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ICES Ecosystem Overviews: Greater North Sea Ecoregion. In ICES Advice 2016; International Council for the Exploration of the Seas: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016; Volume 6, p. 22.
- Emeis, K.-C.; van Beusekom, J.; Callies, U.; Ebinghaus, R.; Kannen, A.; Kraus, G.; Kröncke, I.; Lenhart, H.-J.; Lorkowski, I.; Matthias, V.; et al. The North Sea—A shelf sea in the Anthropocene. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 141, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint, I.; Pomroy, A. Phytoplankton biomass and production in the southern North Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 99, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogen, M.D.; Svendsen, E.; Berntsen, J.; Aksnes, D.; Ulvestad, K.B. Modelling the primary production in the North Sea using a coupled three-dimensional physical-chemical-biological ocean model. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 41, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daewel, U.; Schrum, C. Simulating long-term dynamics of the coupled North Sea and Baltic Sea ecosystem with ECOSMO II: Model description and validation. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 119-120, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, S.M.; van der Molen, J.; Ruardij, P.; Fernand, L.; Jickells, T. Modelling the contribution of deep chlorophyll maxima to annual primary production in the North Sea. Biogeochemistry 2013, 113, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riginos, C.; Cunningham, C.W. INVITED REVIEW: Local adaptation and species segregation in two mussel (Mytilus edulis × Mytilus trossulus) hybrid zones. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelle, J.; van Stralen, M.; Wijsman, J.; Herman, P.; Smaal, A. Population dynamics of subtidal blue mussels Mytilus edulis and the impact of cultivation. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2017, 9, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saier, B. Direct and indirect effects of seastars Asterias rubens on mussel beds (Mytilus edulis) in the Wadden Sea. J. Sea Res. 2001, 46, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.; Esler, D.; Boyd, W. Effects of predation by sea ducks on clam abundance in soft-bottom intertidal habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büttger, H.; Asmus, H.; Asmus, R.; Buschbaum, C.; Dittmann, S.; Nehls, G. Community dynamics of intertidal soft-bottom mussel beds over two decades. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2008, 62, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reise, K.; Buschbaum, C.; Büttger, H.; Wegner, K.M. Invading oysters and native mussels: From hostile takeover to compatible bedfellows. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krone, R.; Gutow, L.; Joschko, T.J.; Schröder, A. Epifauna dynamics at an offshore foundation—Implications of future wind power farming in the North Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, S.; de la Vega, C.; Asmus, R.; Schwemmer, P.; Enners, L.; Garthe, S.; Binder, K.; Asmus, H. Interaction between birds and macrofauna within food webs of six intertidal habitats of the Wadden Sea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehls, G.; Thiel, M. Large-scale distribution patterns of the mussel Mytilus edulis in the Wadden Sea of Schleswig-Holstein: Do storms structure the ecosystem? Neth. J. Sea Res. 1993, 31, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armonies, W.; Buschbaum, C.; Hellwig-Armonies, M. The seaward limit of wave effects on coastal macrobenthos. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2014, 68, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBIF.org. Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Occurrence Download. Dataset 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glockzin, M.; Zettler, M.L. Spatial macrozoobenthic distribution patterns in relation to major environmental factors—A case study from the Pomeranian Bay (southern Baltic Sea). J. Sea Res. 2008, 59, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS). Data Selection: Region “North Sea”, Taxon “Mytilus edulis”. 2018. Available online: www.iobis.org (accessed on 30 June 2017).
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M.; Elith, J.; Graham, C.H.; Lehmann, A.; Leathwick, J.; Ferrier, S. Sample selection bias and presence—Only distribution models: Implications for background and pseudo—Absence data. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OSPAR Commission Intertidal Mytilus edulis Beds on Mixed and Sandy Sediments. In Quality Status Report 2010: Case Reports for the Ospar List of Threatened and/or Declining Species and Habitats—Update; Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic Commission: Texel, The Netherlands, 2010.
- Compton, T.J.; Holthuijsen, S.; Koolhaas, A.; Dekinga, A.; ten Horn, J.; Smith, J.; Galama, Y.; Brugge, M.; van der Wal, D.; van der Meer, J.; et al. Distinctly variable mudscapes: Distribution gradients of intertidal macrofauna across the Dutch Wadden Sea. J. Sea Res. 2013, 82, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanek, T.H. The ecology of Mytilus edulis L. in exposed rocky intertidal communities. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1978, 31, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reise, K.; Schubert, A. Macrobenthic turnover in the subtidal Wadden Sea: The Norderaue revisited after 60 years. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1987, 41, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, H.; Diekmann, R.; Emeis, K.-C.; Kleeberg, U.; Moll, A.; Kröncke, I. Full-coverage spatial distribution of epibenthic communities in the south-eastern North Sea in relation to habitat characteristics and fishing effort. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Slavik, K. Assessing the Impact of Offshore Windfarms on Pelagic Primary Production in the Southern North Sea: A 3-D Modelling Approach. Master’s Thesis, Manchester University, Manchester, UK, 2016; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmen, C.; Hofmeister, R.; Klingbeil, K.; Nasermoaddeli, M.H.; Kerimoglu, O.; Burchard, H.; Kösters, F.; Wirtz, K.W. Modular System for Shelves and Coasts (MOSSCO v1.0)—A flexible and multi-component framework for coupled coastal ocean ecosystem modelling. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2017, 138, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, R.; Lemmen, C.; Kerimoglu, O.; Wirtz, K.W.; Nasermoaddeli, M.H. The predominant processes controlling vertical nutrient and suspended matter fluxes across domains—Using the new MOSSCO system form coastal sea sediments up to the atmosphere. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Hydroscience and Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2014; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Kerimoglu, O.; Hofmeister, R.; Maerz, J.; Riethmüller, R.; Wirtz, K.W. The acclimative biogeochemical model of the southern North Sea. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 4499–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wirtz, K. Mutual Dependence Between Sedimentary Organic Carbon and Infaunal Macrobenthos Resolved by Mechanistic Modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2509–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasermoaddeli, M.; Lemmen, C.; Stigge, G.; Kerimoglu, O.; Burchard, H.; Klingbeil, K.; Hofmeister, R.; Kreus, M.; Wirtz, K.; Kösters, F. A model study on the large-scale effect of macrofauna on the suspended sediment concentration in a shallow shelf sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, H.; Bolding, K.; Rippeth, T.P.; Stips, A.; Simpson, J.H. Microstructure of turbulence in the northern North Sea: A comparative study of observations and model simulations. J. Sea Res. 2002, 47, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingbeil, K.; Burchard, H. Implementation of a direct nonhydrostatic pressure gradient discretisation into a layered ocean model. Ocean Model. 2013, 65, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräwe, U.; Flöser, G.; Gerkema, T.; Duran-Matute, M.; Badewien, T.H.; Schulz, E.; Burchard, H. A numerical model for the entire Wadden Sea: Skill assessment and analysis of hydrodynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 5231–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purkiani, K.; Becherer, J.; Klingbeil, K.; Burchard, H. Wind-induced variability of estuarine circulation in a tidally energetic inlet with curvature. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 3261–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurich, G.; DeLuca, C.; Campbell, T.; Liu, F.; Saint, K.; Vertenstein, M.; Chen, J.; Oehmke, R.; Doyle, J.; Whitcomb, T.; et al. The Earth System Prediction Suite: Toward a Coordinated U.S. Modeling Capability. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1229–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wirtz, K.W.; Kerimoglu, O. Autotrophic Stoichiometry Emerging from Optimality and Variable Co-limitation. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruggeman, J.; Bolding, K. A general framework for aquatic biogeochemical models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 61, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soetaert, K.; Herman, P.M.; Middelburg, J.J. A model of early diagenetic processes from the shelf to abyssal depths. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1019–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, A.; Bourget, E. Weight-to-weight conversion factors for marine benthic macroinvertebrates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 163, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glazier, D.S. A unifying explanation for diverse metabolic scaling in animals and plants. Biol. Rev. 2010, 85, 111–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Große, F.; Greenwood, N.; Kreus, M.; Lenhart, H.-J.; Machoczek, D.; Pätsch, J.; Salt, L.; Thomas, H. Looking beyond stratification: A model-based analysis of the biological drivers of oxygen deficiency in the North Sea. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 2511–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geyer, B. High-resolution atmospheric reconstruction for Europe 1948–2012: CoastDat2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2014, 6, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Grant, M.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Brockmann, C.; Brotas, V.; Chuprin, A.; Doerffer, R.; Dowell, M.; Farman, A.; Groom, S.; et al. ESA Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative (Ocean_Colour_cci): Version 3.1 Data. CEDA Arch. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijkswaterstaat Waterbase. Available online: http://live.waterbase.nl (accessed on 30 March 2017).
- Voynova, Y.G.; Brix, H.; Petersen, W.; Weigelt-Krenz, S.; Scharfe, M. Extreme flood impact on estuarine and coastal biogeochemistry: The 2013 Elbe flood. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daewel, U.; Schrum, C. Low-frequency variability in North Sea and Baltic Sea identified through simulations with the 3-D coupled physical–biogeochemical model ECOSMO. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2017, 8, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenhart, H.-J.; Mills, D.K.; Baretta-Bekker, H.; van Leeuwen, S.M.; van der Molen, J.; Baretta, J.W.; Blaas, M.; Desmit, X.; Kühn, W.; Lacroix, G.; et al. Predicting the consequences of nutrient reduction on the eutrophication status of the North Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 81, 148–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.A.; van der Molen, J.; Hyder, K.; Bacon, J.; Barciela, R.; Creach, V.; McEwan, R.; Ruardij, P.; Forster, R. Observing and modelling phytoplankton community structure in the North Sea. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 1419–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butenschön, M.; Clark, J.; Aldridge, J.N.; Allen, J.I.; Artioli, Y.; Blackford, J.; Bruggeman, J.; Cazenave, P.W.; Ciavatta, S.; Kay, S.; et al. ERSEM 15.06: A generic model for marine biogeochemistry and the ecosystem dynamics of the lower trophic levels. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1293–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heip, C.; Craeymeersch, J.A. Benthic community structures in the North Sea. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1995, 49, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arntz, W.E.; Gili, J.M.; Reise, K. Unjustifiably Ignored: Reflections on the Role of Benthos in Marine Ecosystems. In Biogeochemical Cycling and Sediment Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar]






| Method | NPP g m−2 a−1 | Reference | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECOSMO | 150, 60 | Daewel and Schrum 2013 [23] | Near coast, offshore |
| ERSEM | 318 | van Leeuwen et al. 2013 [24] | Southern Bight |
| MAECS | 142 | (this study) | - |
| NERC in suit | 119, 261, 119 | Joint and Pomroy 1993 [21] | W, E Wadden sea, Central NS |
| NORWECOM | 90–200 | Skogen et al. 1995 [22] | - |
| (review) | 250 | Emeis et al. 2015 [20] | Continental coast |
| Scenario | Factor | NPP g m−2 a−1 | NPPq50 g m−2 a−1 | ΔNPP % | ΔNPPq50 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NONE | 170 | 169 | 0 | 0 | |
| REF | 171 | 170 | 0.6 | 0.2 | |
| 168 | 168 | −0.9 | −0.3 | ||
| 161 | 161 | −4.7 | −1.3 | ||
| REF | 1 | 152 | 150 | −9.3 | −2.6 |
| 2 | 140 | 136 | −15 | −4.0 | |
| 5 | 116 | 117 | −27 | −8.9 | |
| 10 | 97 | 105 | −37 | −17 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lemmen, C. North Sea Ecosystem-Scale Model-Based Quantification of Net Primary Productivity Changes by the Benthic Filter Feeder Mytilus edulis. Water 2018, 10, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111527
Lemmen C. North Sea Ecosystem-Scale Model-Based Quantification of Net Primary Productivity Changes by the Benthic Filter Feeder Mytilus edulis. Water. 2018; 10(11):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111527
Chicago/Turabian StyleLemmen, Carsten. 2018. "North Sea Ecosystem-Scale Model-Based Quantification of Net Primary Productivity Changes by the Benthic Filter Feeder Mytilus edulis" Water 10, no. 11: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111527
APA StyleLemmen, C. (2018). North Sea Ecosystem-Scale Model-Based Quantification of Net Primary Productivity Changes by the Benthic Filter Feeder Mytilus edulis. Water, 10(11), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111527





