Heavy Metals in a High Arctic Fiord and Their Introduction with the Wastewater: A Case Study of Adventfjorden-Longyearbyen System, Svalbard
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
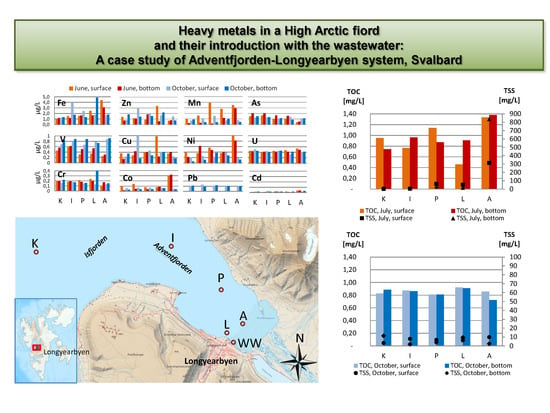
3.1. Heavy Metals Concentrations in the Wastewater and Adventfjorden
3.2. TSS, TOC and Correlations with Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
4.1. Heavy Metals in the Wastewater
4.2. Heavy Metals in the Adventfjorden
4.3. Correlations with TSS and TOC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Norway. This Is Svalbard 2016: What the Figures Say; Statistics Norway: Oslo, Norway, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, D.C.G.; Wagemann, R.; Hargrave, B.T.; Thomas, D.J.; Peakall, D.B.; Norstrom, R.J. Arctic marine ecosystem contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 122, 75–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, M. Abundance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Two Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants and Receiving Water in Atlantic Canada. Master’s Thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada, March 2017. Available online: https://dalspace.library.dal.ca/bitstream/handle/10222/72949/McConnell-Mandy-MASc-ENVE-March-2017.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Nakahara, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Sarai, Y.; Kondo, I. Frequency of heavy-metal resistance in bacteria from inpatients in Japan. Nature 1977, 266, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrin, T.R.; Maier, R.M. Impact of metals on the biodegradation of organic pollutants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crockett, A.B. Water and wastewater quality monitoring, McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1997, 47, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Smith, J.; King, C.K.; Lindsay, M.; Stark, S.; Palmer, A.S.; Snape, I.; Bridgen, P.; Riddle, M. Physical, chemical, biological and ecotoxicological properties of wastewater discharged from Davis Station, Antarctica. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2015, 113, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Bridgen, P.; Dunshea, G.; Galton-Fenzi, B.; Hunter, J.; Johnstone, G.; King, C.; Leeming, R.; Palmer, A.; Smith, J.; et al. Dispersal and dilution of wastewater from an ocean outfall at Davis Station, Antarctica, and resulting environmental contamination. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, J.R.; Edwards, R. Coal burning leaves toxic heavy metal legacy in the Arctic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12140–12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen-Gil, S.M.; Ford, J.; Lasorsa, B.K.; Monetti, M.; Vlasova, T.; Landers, D.H. Heavy metal contamination in the Taimyr Peninsula, Siberian Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 301, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, K.; Mikkelsen, Ø.; Berg, T.; Steinnes, E. The presence of mercury and other trace metals in surface soils in the Norwegian Arctic. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AMAP. AMAP Assessment 2002: Heavy Metals in the Arctic; Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP): Tromsø, Norway, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Chu, G.; Liu, J.; Gao, D. A 150-year Record of Heavy Metals in the Varved Sediments of Lake Bolterskardet, Svalbard. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2006, 38, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drbal, K.; Elster, J.; Komárek, J. Heavy metals in water, ice and biological material from Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Polar Res. 1992, 11, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, S.; Motoyama, H.; Narita, H.; Watanabe, O. Anthropogenic trace metals in an ice core at Vestfonna, Svalbard, Norway.pdf. Chin. J. Polar Sci. 2003, 14, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Łokas, E.; Zaborska, A.; Kolicka, M.; Różycki, M.; Zawierucha, K. Accumulation of atmospheric radionuclides and heavy metals in cryoconite holes on an Arctic glacier. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węgrzyn, M.; Wietrzyk, P.; Lisowska, M.; Klimek, B.; Nicia, P. What influences heavy metals accumulation in arctic lichen Cetrariella delisei in Svalbard? Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, H.; Kammann, U.; Aust, M.O.; Manthey-Karl, M.; Lüth, A.; Kanisch, G. Large scale distribution of dioxins, PCBs, heavy metals, PAH-metabolites and radionuclides in cod (Gadus morhua) from the North Atlantic and its adjacent seas. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauke, G.P.; Savinov, V.M.; Ritterhoff, J.; Savinova, T. Heavy metals in fish from the Barents Sea (summer 1994). Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 227, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norheim, G.; Skaare, J.U.; Wiig, Ø. Some heavy metals, essential elements, and chlorinated hydrocarbons in polar bear (Ursus maritimus) at Svalbard. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 77, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fant, M.L.; Nyman, M.; Helle, E.; Rudbäck, E. Mercury, cadmium, lead and selenium in ringed seals (Phoca hispida) from the Baltic Sea and from Svalbard. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 111, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jæger, I.; Hop, H.; Gabrielsen, G.W. Biomagnification of mercury in selected species from an Arctic marine food web in Svalbard. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4744–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdova, J.; Raclavska, H.; Raclavsky, K.; Skrobankova, H. Heavy metals in domestic wastewater with respect to urban population in Ostrava, Czech Republic. Water Environ. J. 2019, 33, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sörme, L.; Lagerkvist, R. Sources of heavy metals in urban wastewater in Stockholm. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 298, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comber, S.D.W.; Gunn, A.M. Heavy metals entering sewage-treatment works from domestic sources. Water Environ. J. 1996, 10, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Moilleron, R.; Lestel, L.; Gromaire, M.C.; Rocher, V.; Cambier, P.; Bonté, P.; Colin, J.L.; de Pontevès, C.; Meybeck, M. Critical budget of metal sources and pathways in the Seine River basin (1994–2003) for Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb and Zn. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 375, 180–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriyama, K.; Mori, T.; Arayashiki, H.; Saitot, H.; Chino, M. The amount of heavy metals derived from domestic wastewater. Water Pollut. Res. Control. Bright. 1988, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzinger, F.; Oldenburg, M. Characteristics of source-separated household wastewater flows: A statistical assessment. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, R.E.; Lartiges, B.S.; Samrani, A.E.; Faure, P.; Houhou, J.; Ghanbaja, J. Speciation of organic matter and heavy metals in urban wastewaters from an emerging Country. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4695–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aonghusa, C.N.; Gray, N.F. Laundry detergents as a source of heavy metals in Irish domestic wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2002, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E.; Donner, E. Metals in greywater: Sources, presence and removal efficiencies. Desalination 2009, 248, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.; Russell, L.L. Heavy metals contribution of household washing products to municipal wastewater. Water Environ. Res. 1994, 66, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłos, A.; Ziembik, Z.; Rajfur, M.; Dołhańczuk-Sródka, A.; Bochenek, Z.; Bjerke, J.W.; Tømmervik, H.; Zagajewski, B.; Ziółkowski, D.; Jerz, D.; et al. The Origin of Heavy Metals and Radionuclides Accumulated in the Soil and Biota Samples Collected in Svalbard, Near Longyearbyen. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2017, 24, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granberg, M.E.; Ask, A.; Gabrielsen, G.W. Local Contamination in Svalbard—Overview and Suggestions for Remediation Actions; Norsk Polarinstitutt: Tromsø, Norway, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S. Heavy metal pollution in China: Origin, pattern and control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenhamer, J.D.; Kobunski, P.A.; Kuepouo, G.; Corbin, R.W.; Gottesfeld, P. Lead exposure from aluminum cookware in Cameroon. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenhamer, J.D.; Fitzpatrick, M.P.; Biro, A.M.; Kobunski, P.A.; Hudson, M.R.; Corbin, R.W.; Gottesfeld, P. Metal exposures from aluminum cookware: An unrecognized public health risk in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhaiman, L.A. Estimating Aluminum Leaching from Aluminum Cookware in Different Vegetable Extracts. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 7283–7294. [Google Scholar]
- Bergkvist, C.; Kippler, M.; Hamadani, J.D.; Grandér, M.; Tofail, F.; Berglund, M.; Vahter, M. Assessment of early-life lead exposure in rural Bangladesh. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.S.; Al Zubaidy, E.A.H.; Bassioni, G. Effect of Aluminum Leaching Process of Cooking Wares on Food. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Al Zubaidy, E.A.H.; Mohammad, F.S.; Bassioni, G. Effect of pH, Salinity and Temperature on Aluminum Cookware Leaching During Food Preparation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 6424–6441. [Google Scholar]
- Houhou, J.; Lartiges, B.S.; Montarges-Pelletier, E.; Sieliechi, J.; Ghanbaja, J.; Kohler, A. Sources, nature, and fate of heavy metal-bearing particles in the sewer system. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6052–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Rehman, S.; Zeb Khan, A.; Amjad Khan, M.; Tahir Shah, M. Soil and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chino, M.; Moriyama, K.; Saito, H.; Morn, T. The amount of heavy metals derived from domestic sources in Japan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1991, 57, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno-García, E.; Andreu, V.; Boluda, R. Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soils. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 92, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjandraatmadja, G.; Diaper, C. Sources of Critical Contaminants in Domestic Wastewater: A Literature Review; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pawłowska, J.; Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Zajączkowski, M.; Nygård, H.; Berge, J. Seasonal variability of meio- and macrobenthic standing stocks and diversity in an Arctic fjord (Adventfjorden, Spitsbergen). Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zajaczkowski, M.; Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M. Dynamic sedimentary environments of an Arctic glacier-fed river estuary (Adventfjorden, Svalbard). I. Flux, deposition, and sediment dynamics. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyma, N.; Paw, J.; Kujawa, A.; Łącka, M.; Zajączkowski, M. ScienceDirect Impact of shelf-transformed waters (STW) on foraminiferal assemblages in the outwash and glacial fjords of Adventfjorden and Hornsund, Svalbard. Oceanologia 2017, 59, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen Ingerø, K. Longyearbyen Lokalstyre Annual Reports; Lokalstyre: Longyearbyen, Norway, 2002–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency. 2018 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories Tables; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Glabonjat, R.A.; Raber, G.; Van Mooy, B.A.S.; Francesconi, K.A. Arsenobetaine in Seawater: Depth Profiles from Selected Sites in the North Atlantic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.M. Oceanographic distributions of zinc, cadmium, copper and aluminium in waters of the central arctic. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.A.; Yeats, P.A. The distribution of manganese, iron, nickel, copper and cadmium in the waters of Baffin Bay and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Deep Sea Res. Part. B Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1982, 29, 764. [Google Scholar]
- Szopińska, M.; Łuczkiewicz, A.; Jankowska, K.; Fudala-Książek, S.; Potapowicz, J.; Kalinowska, A.; Bialik, R.J.; Chmiel, S.; Polkowska, Ż. Tracking of selected macro and micropollution in Admiralty Bay after wastewater discharge: Case study of Arctowski Station. Manuscr. Revis. Unpublished work. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lesage, E.; Rousseau, D.P.L.; Meers, E.; Tack, F.M.G.; De Pauw, N. Accumulation of metals in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland treating domestic wastewater in Flanders, Belgium. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvelas, M.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Samara, C. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in the wastewater treatment process. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipasa, K.B. Accumulation and fate of selected heavy metals in a biological wastewater treatment system. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gdańsk-Wschód Wastewater Treatment Plant; Gdańsk-Wschód Wastewater Treatment Plant Reports. Unpublished data. 2013–2014.
- Evenset, A. Adventfjorden Som Resipient for Sanitæravløp og Kvernet matavfall fra Longyearbyen; Akvaplan Niva; Polarmiljøsenteret: Tromsø, Norway, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.; Hodson, A. The Water Supply to Longyearbyen: Understanding the Present System and Future Uncertainties. 2013. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258515564_The_water_supply_to_Longyearbyen_understanding_the_present_system_and_future_uncertainties (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Bazzano, A.; Rivaro, P.; Soggia, F.; Ardini, F.; Grotti, M. Anthropogenic and natural sources of particulate trace elements in the coastal marine environment of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Mar. Chem. 2014, 163, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H. Seasonal Changes in Methylarsenic Distribution in Tosa Bay and Uranouchi Inlet. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1996, 10, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.R.; Yu, H.S.; Hu, H.; Monson, R.R. Arsenic in drinking water and skin cancers: Cell-type specificity (Taiwan, R.O.C.). Cancer Causes Control. 2001, 12, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurzau, E.S.; Gurzau, A.E. Arsenic in drinking water from groundwater in Transylvania, Romania: An overview. In Arsenic Exposure and Health Effects IV; Chappell, W.R., Abernathy, C., Calderon, R.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, C.F.; Swartz, C.H.; Badruzzaman, A.B.M.; Keon-Blute, N.; Yu, W.; Ali, M.A.; Jay, J.; Beckie, R.; Niedan, V.; Brabander, D.; et al. Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 2002, 298, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunduz, O.; Simsek, C.; Hasozbek, A. Arsenic pollution in the groundwater of Simav Plain, Turkey: Its impact on water quality and human health. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 205, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyler, P.; Martin, J.M. Arsenic and selenium in a pristine river-estuarine system: The Krka (Yugoslavia). Mar. Chem. 1991, 34, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.W.; Barrie, L.A.; Bidleman, T.F.; Diamond, M.L.; Gregor, D.J.; Semkin, R.G.; Strachan, W.M.J.; Li, Y.F.; Wania, F.; Alaee, M.; et al. Contaminants in the Canadian Arctic: 5 years of progress in understanding sources, occurrence and pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 254, 93–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajączkowski, M.; Szczuciński, W.; Bojanowski, R. Recent changes in sediment accumulation rates in Adventfjorden, Svalbard. Oceanologia 2004, 46, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, J.H.; Perdue, E.M. Importance of heavy metal-organic matter interactions in natural waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1977, 41, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Domestic Sources of Heavy Metals in Wastewater | Cu | Zn | Pb | Cr | Ni | Cd | Hg | Mn | Fe | Co | As | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Household contribution to heavy metals content in the typical municipal wastewater | 27–100% | 30–46% | 0.9–15% | 2.4–15% | 9–61% | 20–60% | 8% | 9% | 21% | [25,26,27,28,29] | ||
| Plumbing | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [25,26,27,30,31] | ||||||
| Laundry detergents | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [26,27,31,32,33,34] | |||
| Tap water | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [26,27,31,35,36,37] | |
| Kitchen utensils | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [25,26,27,38,39,40,41,42,43,44] | ||||||
| Food | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [26,37,45] | ||
| Cosmetics (PCP—personal care products): toothpaste, deodorant, shampoo | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [26] | ||||||||
| Medicines | ✓ | [25] | ||||||||||
| Feces | ✓ | ✓ | [29,46,47,48] | |||||||||
| Amalgam | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [26] | ||||||||
| Artist paint | ✓ | [26] |
| Analyte/Parameter | Measurement Instrumentation | MR | LOD | LOQ | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer Thermo XSERIES 2 ICP-MS (Thermo Fischer Scientific) | 0.01–500 | 0.01 | 0.03 | µg L−1 |
| Co | 0.01–500 | 0.01 | 0.03 | ||
| V,Cr,Mn,Ni,Cu,Zn,As,Pb,U | 0.10–500 | 0.10 | 0.30 | ||
| Fe | 0.15–500 | 0.15 | 0.45 | ||
| Total Organic Carbon (TOC) | Total Organic Carbon Analyzer TOC-V CSH (Shimadzu) | 0.03–200 | 0.03 | 0.10 | mg L−1 |
| Heavy Metal | Drinking Water Reservoirs | Potable Water System | Limit Values for Potable Water | Wastewater | Wastewater Recipient | Typical Values Found in the Marine Waters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isdammen | Gruvedalen | ||||||||||||||
| Concentration (µg/L) | |||||||||||||||
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Mean | Sd | Min | Max | Min | Max | ||
| As | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 10 | 1.57 | 2.55 | 1.25 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 2.01 | 1 | 2 |
| Cd | 0.02 | 1.0 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 1.0 | 5 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.07 |
| Co | 0.05 | 2.96 | 0.64 | 12.68 | no data | no data | - | 1.55 | 1.59 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 0.003 | 7.7 |
| Cr | 0.76 | 4.25 | 0.1 | 0.57 | no data | no data | 50 | 1.48 | 1.51 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.31 | 0.65 |
| Cu | 0.1 | 7.94 | 0.4 | 9.3 | no data | no data | 1000 | 1.69 | 2.73 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 1.58 | 0.1 | 1.07 |
| Fe | 5.0 | 1650 | 10.0 | 811 | 6.0 | 98 | 200 | 170 | 282 | 2.09 | 1.14 | 0.94 | 4.86 | 0.32 | 1.29 |
| Mn | 4.0 | 660 | 29.0 | 253 | 5.0 | 510 | 50 | 132 | 220 | 1.27 | 1.12 | 0.14 | 3.88 | 0.01 | 1.1 |
| Ni | 0.1 | 6.3 | 3.78 | 30.9 | no data | no data | 20 | 11.9 | 13.1 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 1.01 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| Pb | 0.93 | 1.32 | 0.04 | 0.27 | no data | no data | 10 | 0.74 | 1.49 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| U | no data | no data | no data | no data | no data | no data | 30 | 0.1 | 0.12 | 0.44 | 0.04 | 0.32 | 0.53 | 1.5 | 4.7 |
| V | <LOD | 0.03 | <LOD | 0.06 | no data | no data | - | 1.47 | 2.61 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.91 | 0.1 | 1 |
| Zn | 0.9 | 29.7 | 4.79 | 77.44 | no data | no data | - | 3.9 | 12.3 | 1.45 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 3.35 | 0.07 | 2.14 |
| Reference | [53] | [53] | [53] | [54] | This survey | This survey | [3,55,56,57] | ||||||||
| Research Area | Mean ± SD/Median | Concentration (μg/L) | Reference | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Zn | Pb | Cr | Ni | Cd | Mn | Fe | As | Co | V | |||
| untreated wastewater, Longyearbyen, Svalbard | mean | 2.21 | 8.10 | 1.12 | 1.50 | 12.51 | 0.03 | 176 | 226 | 2.06 | 1.57 | 2.04 | This survey |
| SD | 0.74 | 5.88 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.83 | 0.01 | 62 | 79 | 0.69 | 0.03 | 0.81 | ||
| untreated wastewater, McMurdo Antarctic Station | mean | 564 | 513 | 376 | 32 | 31 | 3.41 | 13.1 | 1646 | 3.33 | [8] | ||
| SD | 1073 | 230 | 1169 | 16.8 | 14 | 2.92 | 8.0 | 1205 | 0.98 | ||||
| untreated wastewater, Davis Station, Antarctica | mean | 870 | 1210 | 37 | 20 | 42 | 4.2 | 176 | [9] | ||||
| SD | 499 | 939 | 8 | 22 | 146 | ||||||||
| Untreated wastewater, Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station | mean | 4.27 | 37.3 | 0.48 | 4.44 | 23.30 | 0.45 | 28.9 | 428 | 1.68 | [58] | ||
| Domestic wastewater, residential area, Stockholm | mean | 78 | 150 | 3.6 | 4 | 6.2 | 0.23 | [26] | |||||
| Domestic wastewater, Ostrava, Czech Republic | median | 19.5 | 167 | 5.5 | 2.546 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 77.0 | 872 | 0.6 | [25] | ||
| Wastewater influent to WWTP Kravare, Czech Republic | median | 21.3 | 181 | 5.0 | 2.761 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 69.0 | 963 | 0.5 | |||
| Urban wastewater, inflow to WWTP Ostrava, Czech Republic | mean | 35.0 | 230.0 | 17.25 | 12.65 | 18.0 | 0.8 | 452 | 4785 | 1.4 | |||
| Domestic wastewater, constructed wetland influent, Zemst, Belgium | mean | 7 | 36 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0.1 | 33 | 45 | [59] | |||
| SD | 9 | 28 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.0 | 8 | 19 | |||||
| Treated wastewater, constructed wetland efluent, Zemst, Belgium | mean | 3 | 26 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0.1 | 227 | 28 | ||||
| SD | 1 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.1 | 46 | 8 | |||||
| Raw municipal wastewater, Thessaloniki, Greece | mean | 79 | 470 | 39 | 40 | 770 | 3.3 | 67 | 480 | [60] | |||
| SD | 35 | 140 | 9.4 | 12 | 200 | 1.1 | 12 | 87 | |||||
| Raw municipal wastewater, WWTP Gdańsk | mean | 125.38 | 439 | 62.58 | 20.59 | [61] | |||||||
| SD | 56.17 | 141 | 27.38 | 14.05 | |||||||||
| Raw municipal wastewater, WWTP Gdańsk | mean | 93 | 300 | 16.00 | 20.60 | 13 | 0.50 | 4.00 | 6.00 | [62] | |||
| SD | 30 | 60 | 12.00 | 16.90 | 7 | 0.30 | 5.00 | 5.00 | |||||
| Analyzed Parameter | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | U | TOC | TSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Cr | 0.832 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| Mn | 0.896 | 0.958 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| Fe | 0.721 | 0.955 | 0.870 | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| Co | 0.774 | 0.968 | 0.950 | 0.957 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| Ni | 0.835 | 0.984 | 0.977 | 0.952 | 0.990 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Cu | 0.592 | 0.833 | 0.744 | 0.876 | 0.827 | 0.820 | 1.000 | |||||||
| Zn | 0.504 | 0.801 | 0.638 | 0.907 | 0.779 | 0.764 | 0.908 | 1.000 | ||||||
| As | 0.392 | 0.487 | 0.384 | 0.545 | 0.399 | 0.453 | 0.443 | 0.538 | 1.000 | |||||
| Cd | 0.006 | 0.173 | 0.145 | 0.273 | 0.311 | 0.218 | 0.349 | 0.296 | −0.430 | 1.000 | ||||
| Pb | 0.706 | 0.913 | 0.807 | 0.985 | 0.907 | 0.901 | 0.873 | 0.936 | 0.544 | 0.296 | 1.000 | |||
| U | −0.841 | −0.914 | −0.876 | −0.897 | −0.870 | −0.905 | −0.758 | −0.767 | −0.622 | 0.021 | −0.878 | 1.000 | ||
| TOC | 0.824 | 0.988 | 0.958 | 0.975 | 0.987 | 0.995 | 0.841 | 0.813 | 0.494 | 0.223 | 0.937 | −0.919 | 1.000 | |
| TSS | −0.536 | −0.154 | 0.541 | 0.361 | 0.862 | 0.669 | −0.006 | −0.270 | −0.565 | 0.671 | −0.334 | 0.457 | 0.707 | 1.000 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalinowska, A.; Szopińska, M.; Chmiel, S.; Kończak, M.; Polkowska, Ż.; Artichowicz, W.; Jankowska, K.; Nowak, A.; Łuczkiewicz, A. Heavy Metals in a High Arctic Fiord and Their Introduction with the Wastewater: A Case Study of Adventfjorden-Longyearbyen System, Svalbard. Water 2020, 12, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030794
Kalinowska A, Szopińska M, Chmiel S, Kończak M, Polkowska Ż, Artichowicz W, Jankowska K, Nowak A, Łuczkiewicz A. Heavy Metals in a High Arctic Fiord and Their Introduction with the Wastewater: A Case Study of Adventfjorden-Longyearbyen System, Svalbard. Water. 2020; 12(3):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030794
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalinowska, Agnieszka, Małgorzata Szopińska, Stanisław Chmiel, Magdalena Kończak, Żaneta Polkowska, Wojciech Artichowicz, Katarzyna Jankowska, Aga Nowak, and Aneta Łuczkiewicz. 2020. "Heavy Metals in a High Arctic Fiord and Their Introduction with the Wastewater: A Case Study of Adventfjorden-Longyearbyen System, Svalbard" Water 12, no. 3: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030794