Interaction Analysis of Urban Blue-Green Space and Built-Up Area Based on Coupling Model—A Case Study of Wuhan Central City
Abstract
:1. Introduction
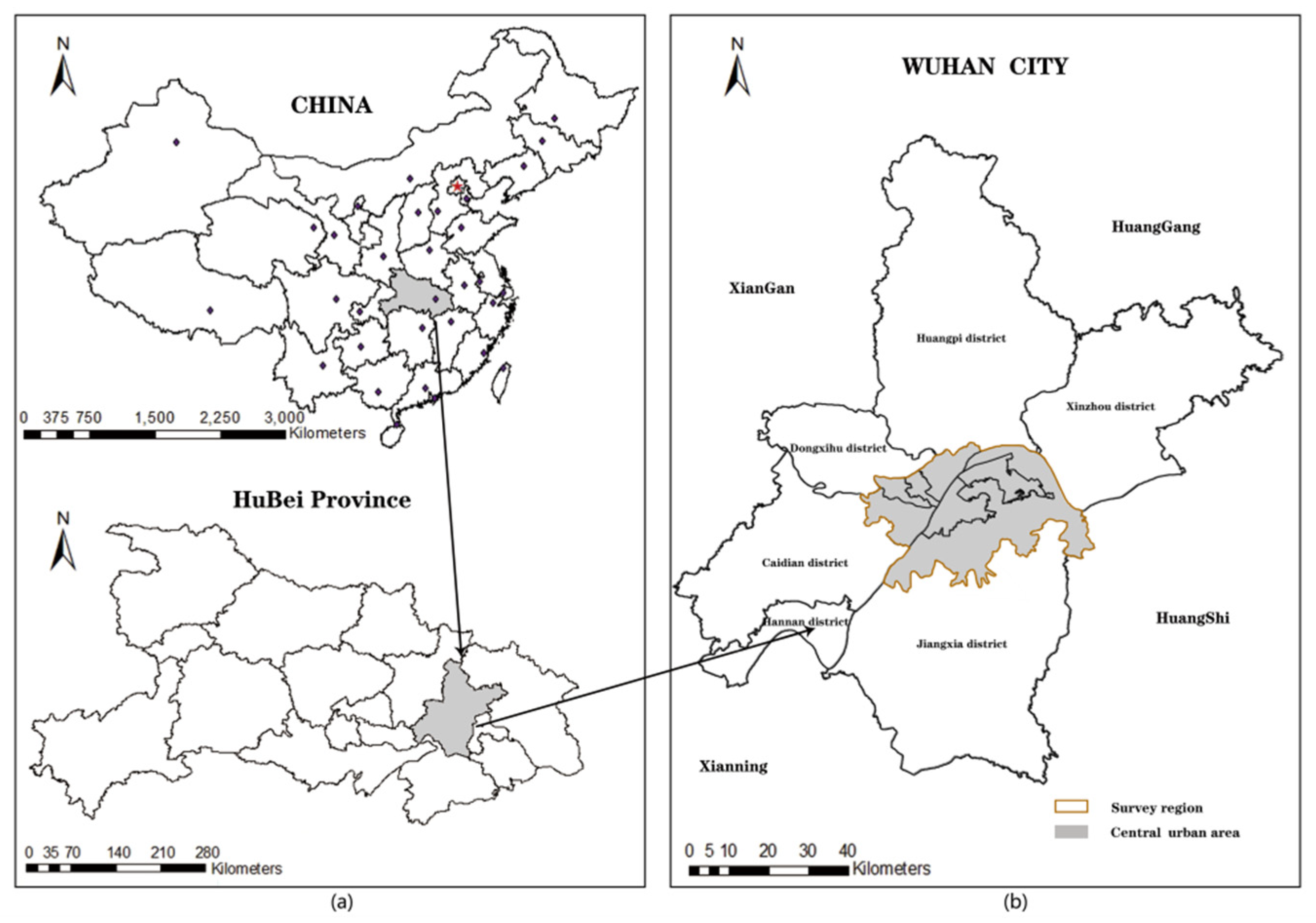
2. Study Area and Data Source
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Methods
3.1. Land Use Mapping and Analysis
3.1.1. Classification of Land Use Types
3.1.2. Accuracy Evaluation
3.2. Blue-Green Space Landscape Pattern Index
3.3. Urban Expansion Intensity
3.4. Sector Analysis and Gradient Direction Analysis
3.5. Coupling Analysis
3.5.1. Data Standardization
3.5.2. System Development Level Measurement
3.5.3. Coupling Model
4. Results
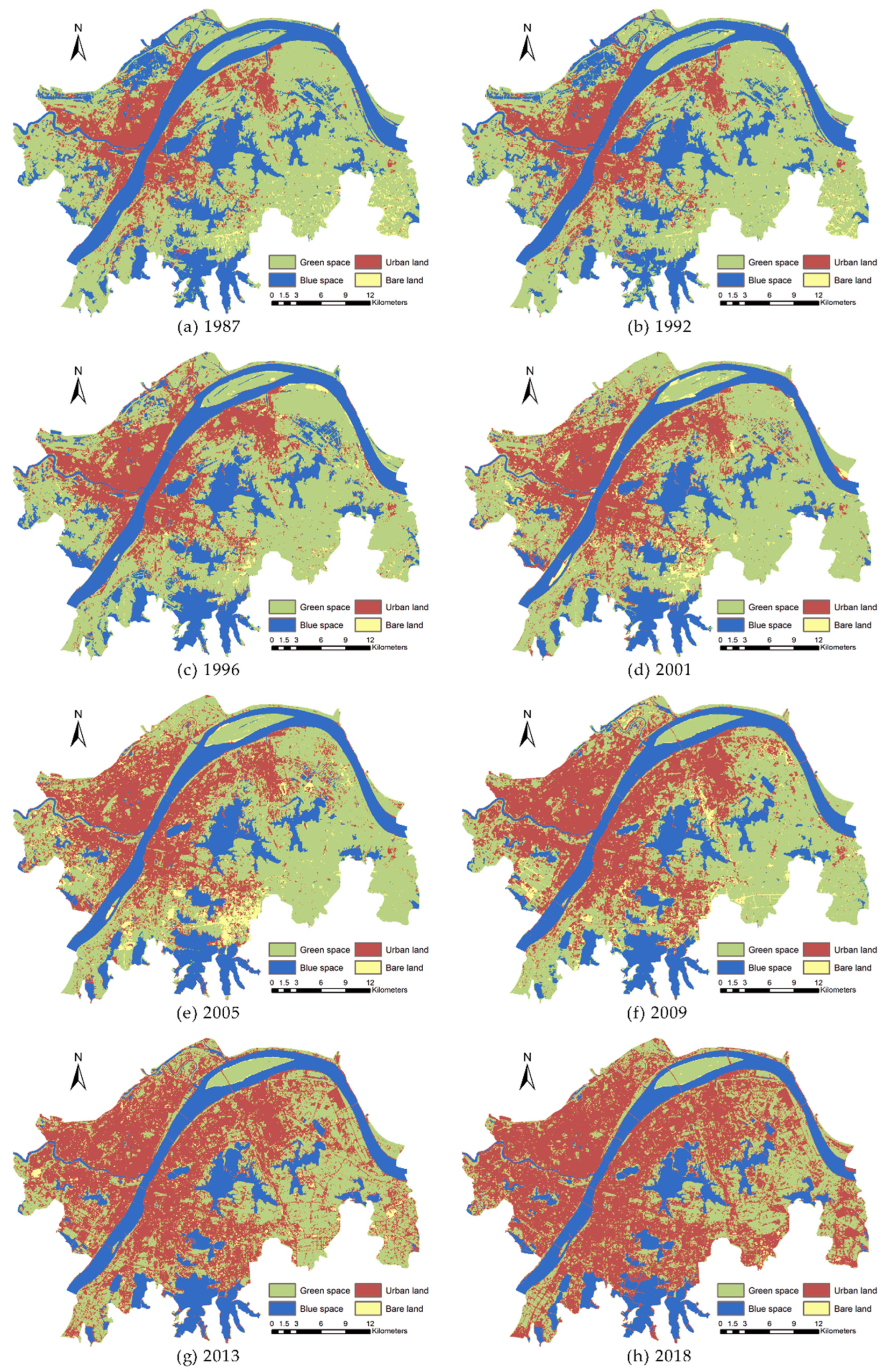
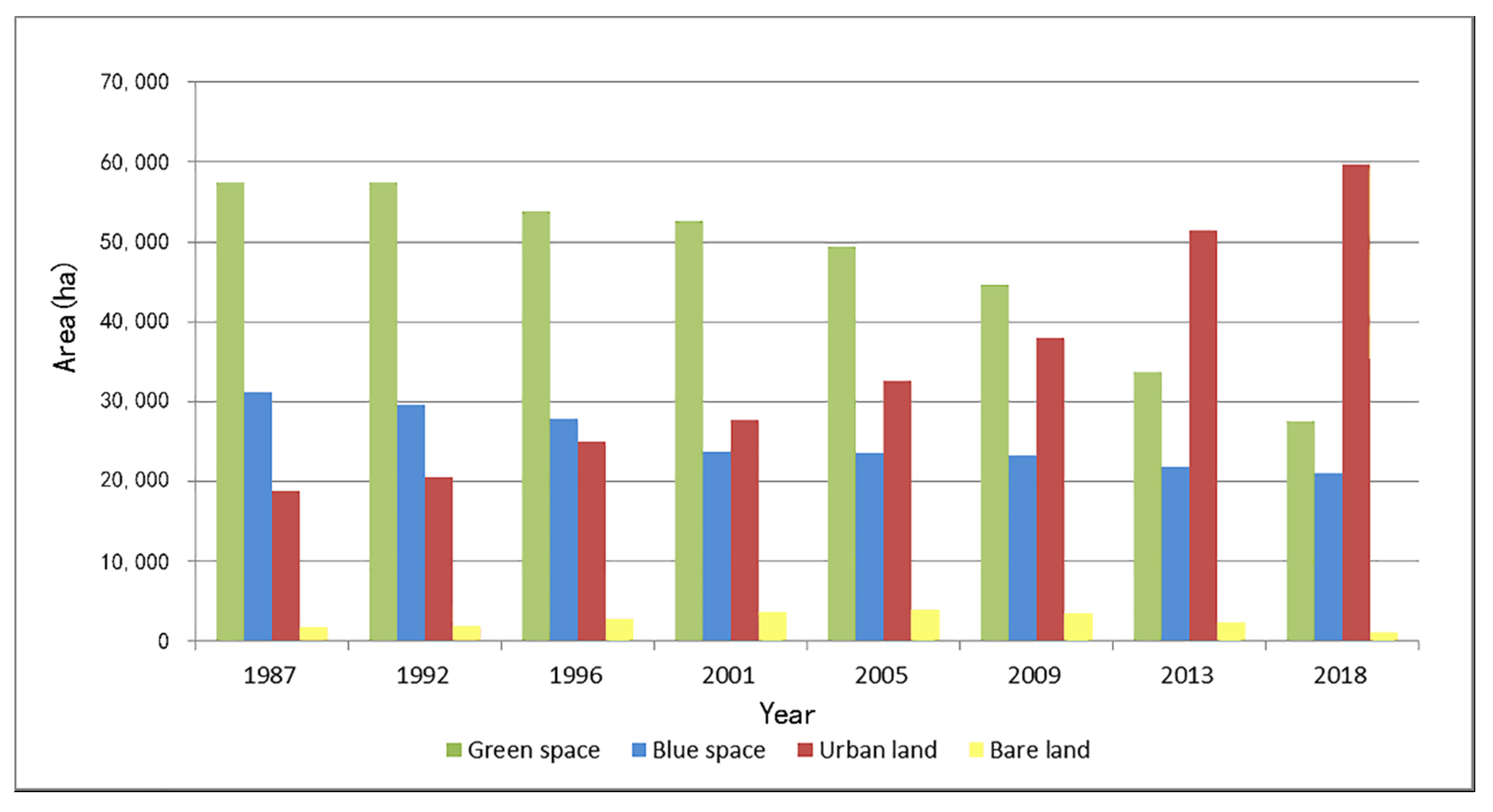
4.1. Results of Land Use Change
4.1.1. Accuracy Assessment of Land Classification
4.1.2. Dynamic Changes of Blue-Green Space and Urban Built-Up Area
4.2. Analysis of Land Use Transfer Results
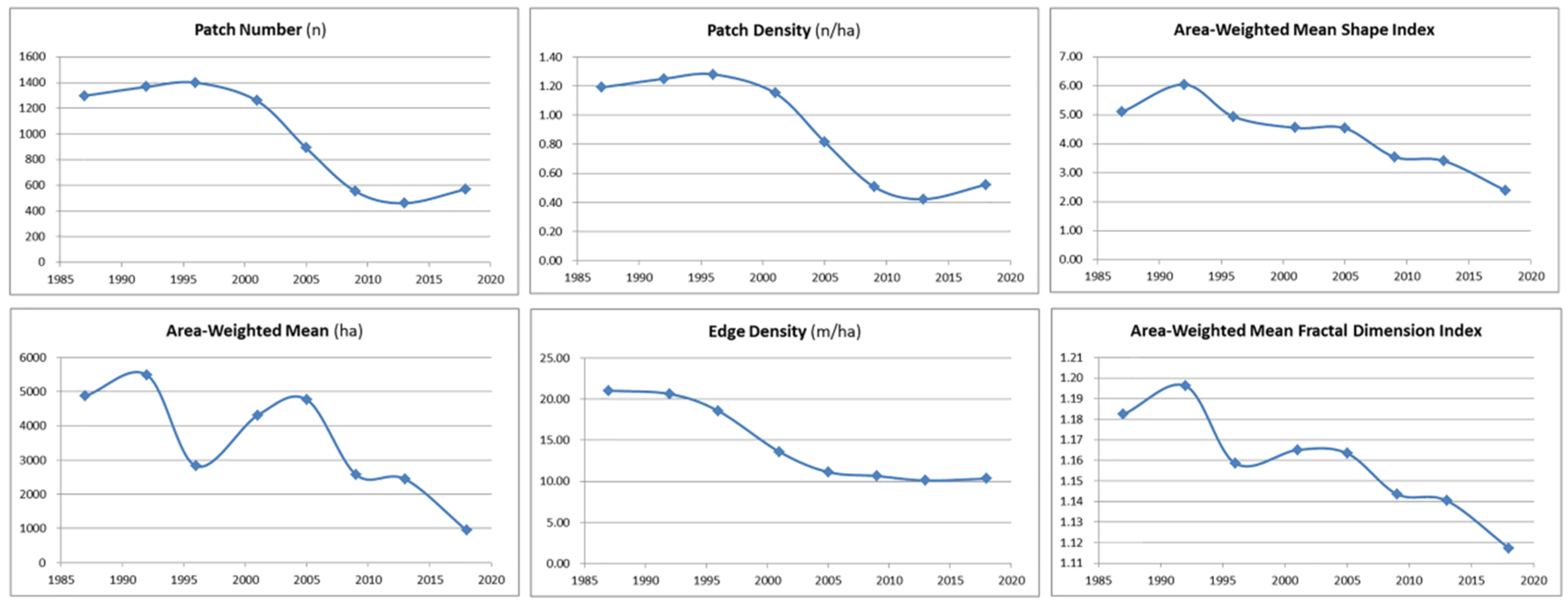
4.3. Analysis of Blue-Green Space Landscape Pattern
4.4. Analysis of Urban Expansion
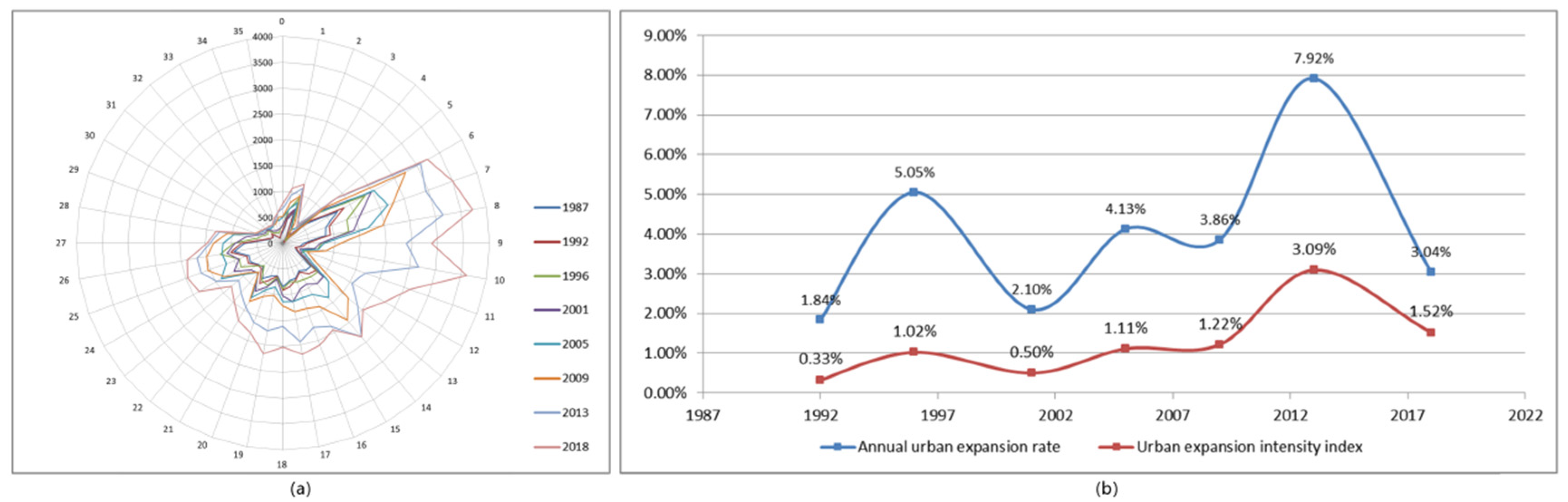
4.4.1. Urban Expansion Intensity
4.4.2. Effect of Urban Expansion on Blue-Green Space
4.5. Coupling Analysis Results of Blue-Green Space and City
4.5.1. Measurement of Blue-Green Space Development Level
4.5.2. Coupling Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.1.1. Urban Built-Up Area
5.1.2. Urban Green Space
5.1.3. Urban Blue Space
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashem, D.; Parviz, A.; Mahdis, M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in landscape pattern in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; He, X.S.; Yang, L. Compilation conception of special planning for blue and green space system at city and county level under the background of land space planning system. Landsc. Archit. 2020, 27, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.; Kim, G.; Mayer, A.; He, R.; Tian, G. Assessing the Ecosystem Services of Various Types of Urban Green Spaces Based on i-Tree Eco. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuliani, S.; Hardiman, G.; Setyowati, E. Green-Roof: The Role of Community in the Substitution of Green-Space toward Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schüle, S.A.; Hilz, L.K.; Dreger, S.; Bolte, G. Social Inequalities in Environmental Resources of Green and Blue Spaces: A Review of Evidence in the WHO European Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaeztavakoli, A.; Lak, A.; Yigitcanlar, T. Blue and Green Spaces as Therapeutic Landscapes: Health Effects of Urban Water Canal Areas of Isfahan. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caplat, P.; Lepart, J.; Marty, P. Landscape patterns and agriculture: Modelling the long-term effects of human practices on Pinus sylvestris spatial dynamics (Causse Mejean, France). Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geri, F.; Amici, V.; Rocchini, D. Human activity impact on the heterogeneity of Mediterranean landscape. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Research on strategies of urban “blue and green” space construction from the perspective of green development concept—A case study of Wuhan [C]. Urban Ecol. Plan. 2019, 12, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, S. Determinants of urban expansion and their relative importance: A comparative analysis of 30 major metropolitans in China. Habitat Int. 2016, 58, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Luo, J.M.; Tang, L. Coupling Relationship between Urban Expansion and Lake Change—A Case Study of Wuhan. Water 2019, 11, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Song, Y. Decision-Making of Green Space Utilization and Protection in Urban Fringe Based on Biodiversity Trade-Off. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.Q.; Yu, Q.; Chen, W. Spatial-Temporal Dynamic Analysis of Land Use and Landscape Pattern in Guangzhou, China: Exploring the Driving Forces from an Urban Sustainability Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Examining the relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment using a coupling analysis: Case study of Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; He, C.Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Dou, Y.Y. How Did Urban Land Expand in China between 1992 and 2015? A Multi-Scale Landscape Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, X. Spatiotemporal variation of landscape patterns and their spatial determinants in Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhong, S.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y. Land Use Change in Coastal Cities during the Rapid Urbanization Period from 1990 to 2016: A Case Study in Ningbo City, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.N.; Yang, S.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, H. Response of land use change to human activities in Beiluo River Basin since 1976. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Characterizing landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes for urbanization impacts at an eco-regional scale. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.; Jian, L.; Chen, J.L.; Gao, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urban Land Use Change in Typical Cities in the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 801. [Google Scholar]
- Mottet, A.; Ladet, S.; Coque, N.; Gibon, A. Agricultural land-use change and its drivers in mountain landscapes: A case study in the Pyrenees. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, X.L.; Kuang, W.X.; Zhou, W.C. Analysis of spatial pattern and driving force of land use change in China in the early 21st century. J. Geogr. 2009, 64, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Mundia, C.N.; Aniya, M. Dynamics of land use/cover changes and degradation of Nairobi City, Kenya. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 17, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K. Predicting Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using a CA-Markov Model under Two Different Scenarios. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twisa, S.; Kazumba, S.; Kurian, M.; Buchroithner, M.F. Evaluating and Predicting the Effects of Land Use Changes on Hydrology in Wami River Basin, Tanzania. Hydrology 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.L.; Feng, J.M.; Gao, H. Numerical simulation of the impact of land cover change on regional climate in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Li, S.M.; Lu, H.C. Quantitative Influence of Land-Use Changes and Urban Expansion Intensity on Landscape Pattern in Qingdao, China: Implications for Urban Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, G.; Zheng, S.; Sun, C.; Kong, X.; Liu, Z. Land Cover Change Detection in Urban Lake Areas Using Multi-Temporary Very High Spatial Resolution Aerial Images. Water 2018, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, R.V.; KrummelR, J.R.; Gardner, H.; Sugihara, G.; Jackson, B.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Milne, B.T.; Turner, M.G.; Zygmunt, B.; Christensen, S.W.; et al. Indices of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1988, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, B.; Xu, M.; Fukushima, T. Characterizing the changes in landscape structure in the Lake Kasumigaura Basin, Japan using a high-quality GIS dataset. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.C. Spatiotemporal changes of landscape pattern in response to urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 81, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Hu, M.; Xia, B. Spatiotemporal dynamic simulation of land-use and landscape-pattern in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M. Monitoring land use/land cover change, urban growth dynamics and landscape pattern analysis in five fastest urbanized cities in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nana, L.; Chuanzhe, L.; Yufei, X. Examining the coordination between urbanization and eco-environment using coupling and spatial analyses: A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Yin, C.; Huixia, H. An empirical analysis of the coupling coordination among decomposed effects of urban infrastructure environment benefit: Case study of four Chinese autonomous municipalities. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, J.; Yang, w.g.; Wang, L. Spatial characteristics of urban green space under different health influence pathways. Landsc. Archit. 2020, 27, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.D.; Tang, Y.H.; Wu, X.F. Evaluation of the Equity of Urban Park Green Space Based on Population Data Spatialization: A Case Study of a Central Area of Wuhan, China. Sensors 2019, 19, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X. Evaluation of the Fairness of Urban Lakes’ Distribution Based on Spatialization of Population Data: A Case Study of Wuhan Urban Development Zone. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, T.; Mayer, A.L.; Shuster, W.D.; Tian, G. The Hydrologic Role of Urban Green Space in Mitigating Flooding (Luohe, China). Sustainability 2018, 10, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Lee, D.K.; Sung, S. Effect of Urban Green Spaces and Flooded Area Type on Flooding Probability. Sustainability 2016, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.L.; Chen, N.; Ye, W.T.; Zhang, M.M. Analysis of urban green space landscape pattern of xiamen island based on ALOS data. Geospat. Inf. 2020, 18, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.W.; Li, Y.N.; Li, F.Z. Research on the influence of urban green landscape pattern on the quality of “core habitat”. Landsc. Archit. 2020, 27, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Chen, Z.H.; Huang, G.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.K.; Tu, X.Y.; Hua, Y.Y. Research progress on relationship between urban green space pattern and residents’ social and economic characteristics. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3303–3315. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Fang, J.Y.; Xie, P. Land use change in urban lake areas: A case study of East Lake in Wuhan. Resour. Environ. Yangtze River Basin 2004, 3, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Masser, I. Urban growth pattern modeling: A case study of Wuhan city, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 12, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, C.S.; Jorge, L.B. Delineation of suitable areas for crops using a multi-criteria evaluation approach and land use/cover mapping: A case study in Central Mexico. Agric. Syst. 2003, 77, 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mcfeeters, S.K. The use of normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Extraction of water information by improved normalized differential water index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 590–595. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, J.F. Analysis and mapping of urban land image based on NDBI index. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 8, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Analysis of impervious surface and its impact on urban heat environment using the normalized difference impervious surface index (NDISI). Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.H.; Tan, W.; Xu, X. Precision Comparison of different classification methods in land use information Extraction. Mod. Surv. Mapp. 2016, 41, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, A.I.R.; Costa, F.L. Land cover changes and landscape pattern dynamics in Senegal and Guinea Bissau borderland. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 82, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Min, X. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban expansion in China using remote sensing data. Cities 2013, 35, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, F. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Urban Expansion along the Guangzhou–Foshan Inter-City Rail Transit Corridor, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A meta-analysis of global urban land expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F.; Mei, A. Urban spatial restructuring in transitional economy—Changing land use pattern in Shanghai. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, W. Urban land expansion and the transitional mechanisms in Nanjing, China. Habit. Int. 2016, 53, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Yang, G.; Luo, L. Urban Expansion and Its Impact on the Land Use Pattern in Xishuangbanna since the Reform and Opening up of China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hugh, S.; Mark, S.F. Homelessness and Open City Data: Addressing a Global Challenge. Open Cities Open Data 2019, 9, 29–55. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, D.; Shen, S.; Lu, Y. Coupling of county transportation superiority and regional economic space in central plains economic zone. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 32, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y. Coupling ecosystem services supply and human ecological demand to identify landscape ecological security pattern: A case study in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Urban Ecosyst. 2016, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M. Analysis of spatial-temporal characteristics of urbanization and socio-economic coupling and coordinated development degree—A case study of anhui province. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 32, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z. Quantitative evaluation of coordinated development of environment and economy and its classification system—A case study of urban agglomeration in pearl river delta. Trop. Geogr. 1999, 19, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. 70-year planning process of landscape and ecological space in Wuhan. Urban Rural Plan. 2019, 5, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Zuo, H. Discussion on lake protection and management in Wuhan. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2008, 47, 149–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H. Study on the model of public participation in lakes protection in Wuhan, China—An Example of “Love Our 100 Lakes” Volunteer Action. Adv. Environ. Prot. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, C. The pace and pattern of urban expansion in China’s 32 major cities over the past three decades. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1541–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Region | Name | Area (km2) | Permanent Residents | Household Registration Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central city | Jiang’an District | 64.24 | 895,635 | 659,192 |
| Jianghan District | 33.43 | 683,492 | 468,497 | |
| Tongkou District | 46.39 | 828,644 | 536,411 | |
| Hanyang District | 108.34 | 584,077 | 511,168 | |
| Wuchang District | 87.42 | 1,199,127 | 1,136,551 | |
| Hongshan District | 480.20 | 1,049,434 | 851,264 | |
| Qingshan District | 85.5 | 485,375 | 452,870 | |
| Peripheral city | Dongxihu District | 439.19 | 451,880 | 261,408 |
| Hannan District | 287.70 | 114,970 | 107,052 | |
| Caidian District | 1108.10 | 410,888 | 472,130 | |
| Jiangxia District | 2010.00 | 644,835 | 721,435 | |
| Huangpi District | 2261.00 | 874,938 | 1,118,474 | |
| Xinzhou District | 1500.00 | 848,760 | 985,685 | |
| Total | Wuhan | 8494.41 | 9,785,392 | 8,282,137 |
| Satellite | Sensor | Resolution | Data Identification | Date | Cloudiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 | TM | 30 M | LT51230391987253BJC00 | 1987/9/10 | No |
| LT51230391992299BJC00 | 1992/10/25 | No | |||
| LT51230391996278CLT00 | 1996/9/2 | No | |||
| LT51230392001067BJC00 | 2001/916 | No | |||
| LT51230392005110BJC00 | 2005/9/11 | No | |||
| LT51230392009249BJC00 | 2009/9/6 | No | |||
| Landsat 8 | OLI | 30/15 M | LC81230392013260LGN01 | 2013/9/17 | No |
| LC81230392018098LGN0 | 2018/4/8 | No |
| Accidentally and Coordination Degree | Accidentally and Coordination Degree Level | Accidentally and Coordination Degree | Accidentally and Coordination Degree Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0000–0.1 | Extreme disorder | 0.5001–0.6 | Barely coordination |
| 0.1001–0.2 | Severe disorder | 0.6001–0.7 | Primary coordination |
| 0.2001–0.3 | Moderate disorder | 0.7001–0.8 | Intermediate coordination |
| 0.3001–0.4 | Mild disorder | 0.8001–0.9 | Good coordination |
| 0.4001–0.5 | On the verge of disorder | 0.9001–1.0 | Excellent coordination |
| Date Year | Overall Accuracy (%) | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| 1987 | 93.57 | 0.9249 |
| 1992 | 93.46 | 0.9215 |
| 1996 | 92.84 | 0.9172 |
| 2001 | 94.61 | 0.9354 |
| 2005 | 92.78 | 0.9227 |
| 2009 | 95.12 | 0.9463 |
| 2013 | 94.27 | 0.9375 |
| 2018 | 93.34 | 0.9283 |
| System | Primary | Weight (%) | Secondary Indicators | Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green space | Change index | 73.01 | Area | 12.01 |
| Patch number | 10.95 | |||
| Area weighted average patch area | 19.49 | |||
| Area weighted shape index | 17.04 | |||
| Area weighted average fractal dimension | 13.52 | |||
| Fragmentation index | 26.99 | Patch density | 10.95 | |
| Edge density | 16.04 | |||
| Blue space | Change index | 59.41 | Area | 16.51 |
| Patch number | 15.20 | |||
| Area weighted average patch area | 9.36 | |||
| Area weighted shape index | 9.15 | |||
| Area weighted average fractal dimension | 9.19 | |||
| Fragmentation index | 40.59 | patch density | 15.22 | |
| Edge density | 25.37 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X. Interaction Analysis of Urban Blue-Green Space and Built-Up Area Based on Coupling Model—A Case Study of Wuhan Central City. Water 2020, 12, 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082185
Wu J, Yang S, Zhang X. Interaction Analysis of Urban Blue-Green Space and Built-Up Area Based on Coupling Model—A Case Study of Wuhan Central City. Water. 2020; 12(8):2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082185
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jing, Shen Yang, and Xu Zhang. 2020. "Interaction Analysis of Urban Blue-Green Space and Built-Up Area Based on Coupling Model—A Case Study of Wuhan Central City" Water 12, no. 8: 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082185
APA StyleWu, J., Yang, S., & Zhang, X. (2020). Interaction Analysis of Urban Blue-Green Space and Built-Up Area Based on Coupling Model—A Case Study of Wuhan Central City. Water, 12(8), 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082185




