Aquatic Worm Assemblages along the Danube: A Homogenization Warning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
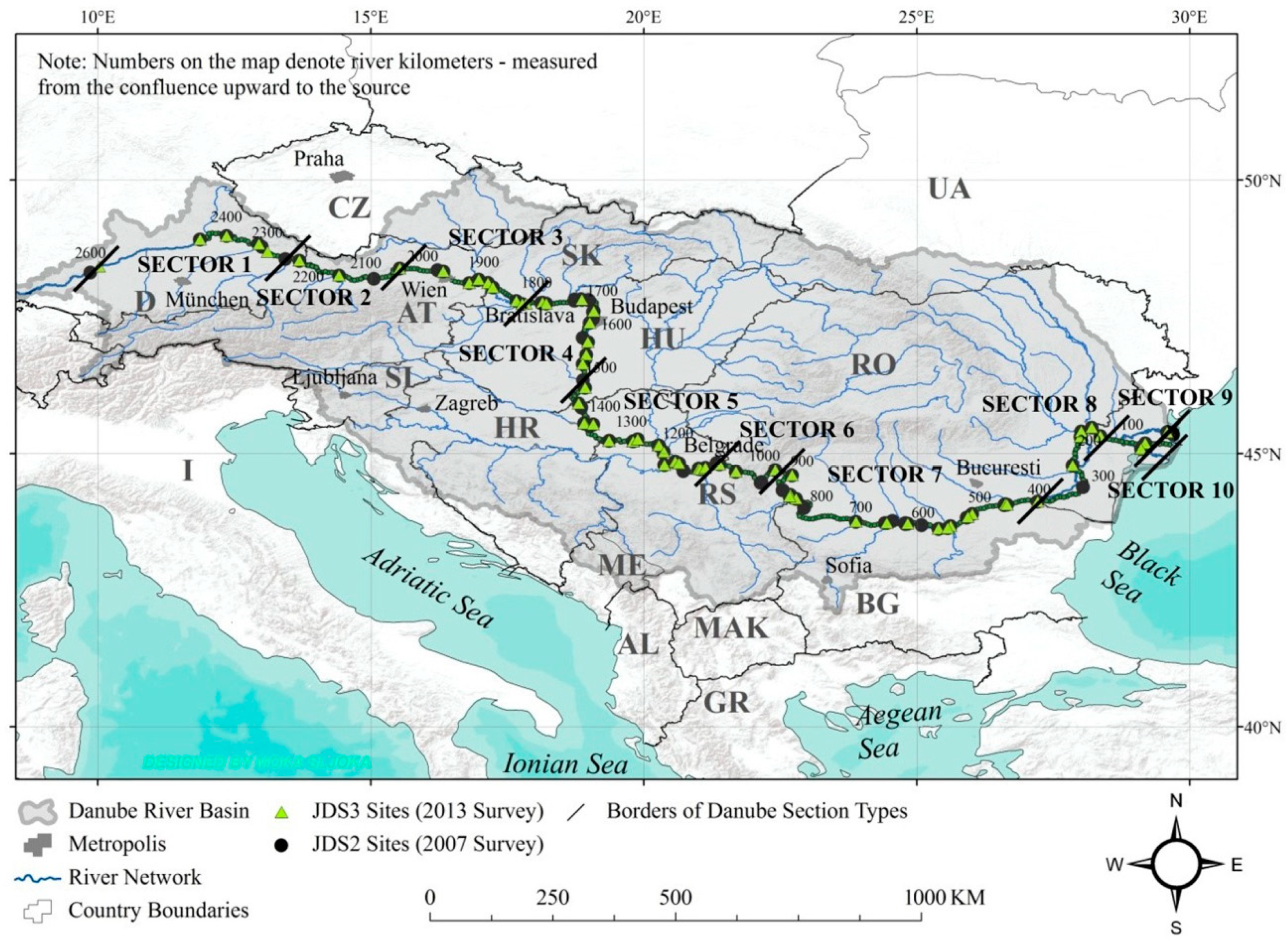
2.1. Study Area and Selection of Sampling Points
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
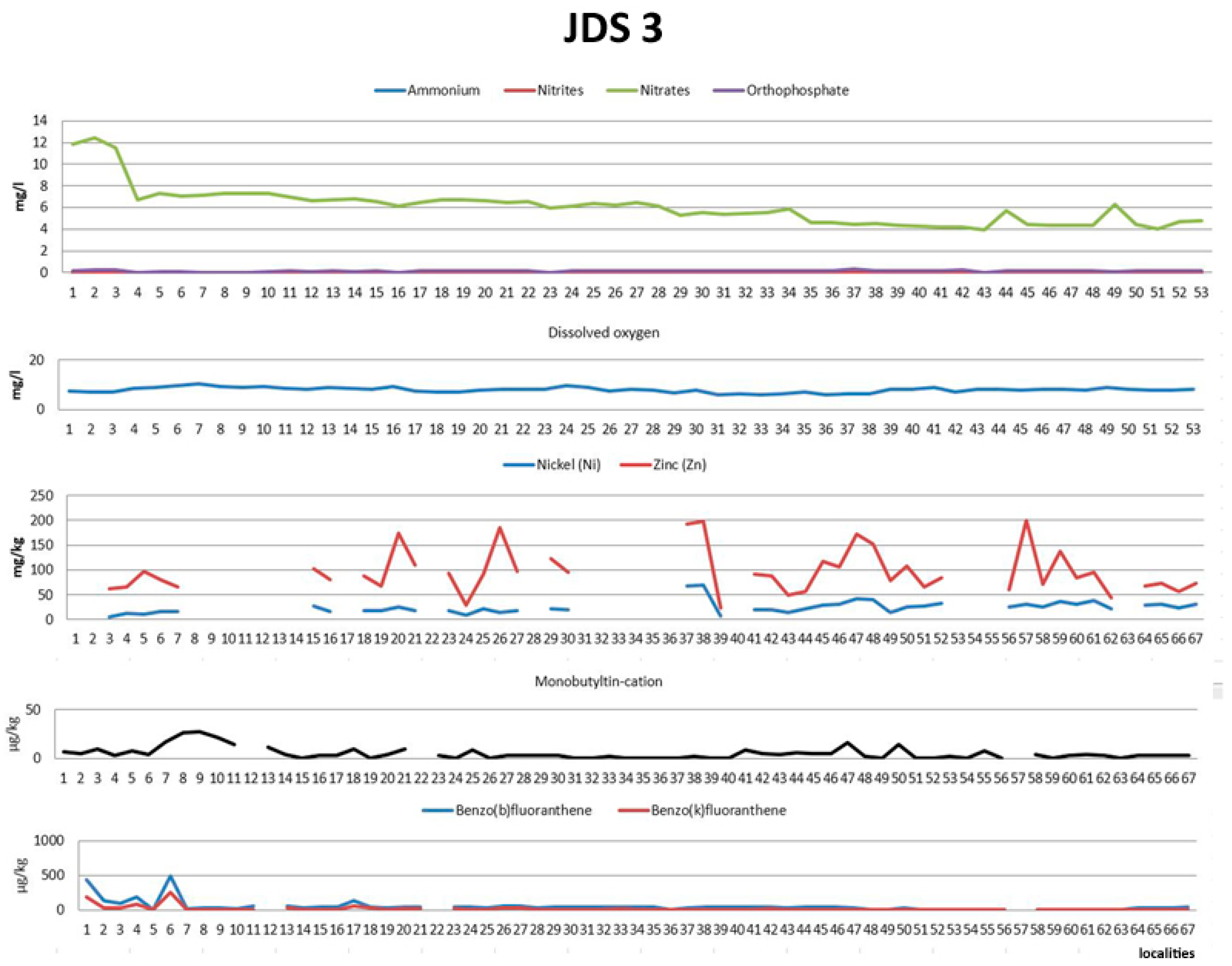
3.1. Environmental Data
3.2. Fauna
3.3. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liepolt, R. Limnologie der Donau; Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung: Stuttgart, Germany, 1967; p. 591. [Google Scholar]
- Titizer, T.; Banning, M. Biological assessment in the Danube catchement area: Indications in shifts in species composition induced by human activities. Eur. Water Manag. 2000, 3, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerwerk, N.; Hein, T.; Schneider-Jakoby, M.; Baumgartner, C.; Ostojic, A.; Paunovic, M.; Bloesch, J.; Siber, R.; Tockner, K. The Danube River Basin, Part 3. In Rivers of Europe; Tockner, K., Uehlinger, U., Robinson, C.T., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 59–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zavadsky, I.; Liska, I. A Comprehensive monitoring and assessment survey on the Danube. Water Res. Manag. 2015, 5, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Directive:, W.F. Water framework directive—Directive 2000/60/ec of the European parliament and of the council establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2000, 22, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- JDS1. Summary of the Final Report Joint Danube Survey ICPDR—International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River/Permanent Secretariat; Vienna International Centre: Vienna, Austria, 2002; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Liška, I.; Wagner, F.; Slobodnik, J. Joint Danube Survey—Final Report; ICPDR—International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River: Vienna, Austria, 2008; p. 235. [Google Scholar]
- Liška, I.; Wagner, F.; Sengl, M.; Deutsch, K.; Slobodnik, J. Joint Danube Survey 3—A Comprehensive Analysis of Danube Water Quality, Final Report; ICPDR—International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River: Vienna, Austria, 2015; p. 369. [Google Scholar]
- Schmedtje, U. (Ed.) The Danube River Basin District—Part A Basin-Wide Overview, ICPDR WFD Roof Report 2004; International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River in Cooperation with the Countries of the Danube River Basin District: Wien, Austria, 2005; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Woitke, P.; Wellmitz, J.; Helm, D.; Kube, P.; Lepom, P.; Litheraty, P. Analysis and assessment of heavy metal pollution in suspended solids and sediments of the river Danube. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumnicka, E. The effect of dam reservoirs on oligochaeta communities in the River Dunajec (Southern Poland). Acta Hydrobiol. 1987, 29, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Šporka, F. The typology of floodplain water bodies of the Middle Danube (Slovakia) on the basis of the superficial polychaete and oligochaeta fauna. Hydrobiologia 1998, 386, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, O.; Brunner, S.; Humpesch, U.H.; Schmidt-Kloiber, A. The distribution of benthic invertebrates along the Austrian stretch of the River Danube and its relevance as an indicator of zoogeographical and water quality patterns—Part 2. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2000, 11, 473–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, T.; Seire, A.; Pall, P. Half a century of oligochaeta research in Estonian running waters. Hydrobiologia 2001, 463, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rîşnoveanu, G.; Vadineanu, A. Long term functional changes within the Oligochaeta communities within the Danube River Delta, Romania. Hydrobiologia 2003, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanacković, A.; Šporka, F.; Csányi, B.; Vasiljević, B.; Tomović, J.; Paunović, M. Oligochaeta of the Danube River—A faunistical review. Biologia 2013, 68, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levashova, E.A.; Mikhailov, V.N.; Mikhailova, M.V.; Morozov, V.N. Natural and Human-Induced Variations in Water and Sediment Runoff in the Danube River Mouth. Water Resour. 2004, 31, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Olden, J.D.; Merritt, D.M.; Pepin, D.M. Homogenization of regional river dynamics by dams and global biodiversity implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5732–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahel, F.J. Homogenization of Freshwater Faunas. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafont, M. Oligochaeta communities as biological descriptors of pollution in the fine sediments of rivers. Hydrobiologia 1984, 115, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prygiel, J.; Rosso-Darmet, A.; Lafont, M.; Lesniak, C.; Durbec, A.; Ouddane, B. Use of oligochaeta communities for assessment of ecotoxicological risk in fine sediment of rivers and canals of the Artois-Picardie water basin (France). Hydrobiologia 2000, 410, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.M. Utility and relevance of aquatic oligochaetes in ecological risk assessment. Hydrobiologia 2001, 463, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.; Reynoldson, T.B. The Pollution Biology of Aquatic Oligochaetes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, S.; Birk, S.; Somenhauser, M. Typology of the Danube River—part 1: Top-down approach. In UNDP/GEF Danube Regional Project, Activity 1.1.6, Typology of Surface Waters and Definition of Reference Conditions for the Danube River—Final Report; ICPDR—International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River: Vienna, Austria, 2003; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Aqem Consortium. Manual for the application of the AQEM system. In A Comprehensive Method to Assess European Streams Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates, Developed for the Purpose of the Water Framework Directive, Version 1; The AQEM consortium: Duisburg-Esen, Germany, 2002; pp. 619–630. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardisation. Water Quality—Methods for Biological Testing—Methods of Biological Sampling: Guidance on Handnet Sampling of Aquatic Benthic Macroinvertebrates; EN 27828:1994, ISO 7828-1985; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lynden, G.W.J.; Mantel, S.; van Oostrumvan, A. Guiding Principles for the Quantitative Assessment of Soil Degradation with a Focus on Salinization, Nutrient Decline and Soil Pollution; International Soil Reference and Information Centre, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.A. The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann. Eugen. 1936, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenbruch, P.A.; Goldstein, M. Discriminant Analysis. Biom. Perspect. Biometry 1979, 35, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J. Canonical Correspondence Analysis: A New Eigenvector Technique for Multivariate Direct Gradient Analysis. Ecology 1986, 67, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ter Braak, C.J.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 57, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, A.C.A. A Simplified Monte Carlo Significance Test Procedure. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1968, 30, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadžić, B. FLORA: A software package for statistical analysis of ecological data. Water Res. Manag. 2013, 3, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Milosevic, D.; Mančev, D.; Čerba, D.; Piperac, M.S.; Popović, N.; Atanackovic, A.; Đuknić, J.; Simić, V.; Paunović, M. The potential of chironomid larvae-based metrics in the bioassessment of non-wadeable rivers. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 616, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, O. Fauna Aquatica Austriaca—Katalog zur Autecolologischen Einsfung; Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture Forestry Environment and Water Management: Vienna, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Russev, B. Influence of some ecological factors on changes of the standing crop of zoobenthos of the Danube in the Bulgarian stretch. In Proceedings of the IBP-UNESCO Symposium on Productivity Problems of Freshwaters, Kazimierz Dolny, Poland, 6–12 May 1970; Kajak, Z., Hillbricht-Ilkowska, A., Eds.; PWN-Polish Scientific Publishers: Warsaw, Poland, 1972; pp. 813–826. [Google Scholar]
- Šporka, F.; Nagy, Š. The macrozoobenthos of parapotamon-type side arms of the Danube River and its response to flowing conditions. Biologia 1998, 53, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Elexová, E.; Némethová, D. The effect of abiotic environmental variables on the Danube macrozoobenthic communities. Lirnnologica 2003, 33, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdonschot, P.F.M. The role of oligochaetes in the management of waters. Hydrobiologia 1989, 180, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kračun-Kolarević, M.; Kolarević, S.; Atanackovic, A.; Marković, V.; Gačić, Z.; Paunovic, M.; Vuković-Gačić, B. Effects of 5-Fluorouracil, Etoposide and CdCl2 in Aquatic Oligochaeta Limnodrilus udekemianus Claparede (Tubificidae) Measured by Comet Assay. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmutz, S.; Мооg, O. Dams: Ecological Impacts and Management. In Riverine Ecosystem Management; Aquatic Ecology Series 8; Schmutz, S., Sendzimir, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 111–127. [Google Scholar]






| JDS2 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Percentage Participation of Oligochaetes (%) | ||||||||||||
| Taksa | Code | F | Sector 1 | Sector 2 | Sector 3 | Sector 4 | Sector 5 | Sector 6 | Sector 7 | Sector 8 | Sector 9 | Sector 10 |
| Naidinae | ||||||||||||
| Dero obtusa d’Udekem, 1835 | Dob | 0.05 | 0.46 | 1.75 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Nais alpina Sperber, 1948 | Nal | 0.01 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| Nais bretscheri Michaelsen, 1899 | Nbr | 0.02 | 1.47 | 0.06 | ||||||||
| Nais christinae Kasprzak, 1973 | Nch | 0.01 | 0.09 | |||||||||
| Nais communis Piguet, 1906 | Nco | 0.02 | 0.05 | 2.04 | ||||||||
| Nais pardalis Piguet, 1906 | Npa | 0.02 | 0.18 | 1.19 | ||||||||
| Nais pseudobtusa Piguet, 1906 | Nps | 0.01 | 0.04 | |||||||||
| Nais simplex Piguet, 1906 | Nsi | 0.01 | 0.11 | |||||||||
| Ophiodonais serpentina (Müller, 1773) | Ose | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 2.64 | 1.56 | ||||||
| Piguetiella blanci (Piguet, 1906) | Pbl | 0.01 | 0.02 | |||||||||
| Stylaria lacustris (Linnaeus, 1767) | Sla | 0.04 | 9.46 | 1.07 | 1.15 | 1.56 | ||||||
| Tubificinae | ||||||||||||
| Aulodrilus japonicus Yamaguchi, 1953 | Aja | 0.02 | 0.02 | 12.98 | ||||||||
| Aulodrilus pluriseta (Piguet, 1906) | Apl | 0.05 | 0.79 | 0.27 | 0.54 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Aulodrilus limnobius Bretscher, 1899 | Ali | 0.05 | 3.11 | 0.87 | 0.74 | |||||||
| Bothrioneurum vejdovskyanum Štolc, 1888 | Bve | 0.01 | 0.13 | |||||||||
| Branchiura sowerbiy Beddard, 1892 | Bso | 0.27 | 0.07 | 1.19 | 10.33 | 16.44 | 7.41 | 8.33 | ||||
| Embolocephalus velutinus (Grube, 1879) | Eve | 0.03 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.13 | |||||||
| Isochaetides michaelseni (Lastočkin, 1936) | Imi | 0.47 | 2.41 | 0.51 | 0.90 | 19.30 | 24.75 | 17.23 | 29.86 | |||
| Limnodrilus claparedeanus Ratzel, 1868 | Lcl | 0.41 | 0.79 | 18.18 | 10.65 | 15.93 | 16.49 | 14.88 | 8.99 | 2.50 | 10.73 | |
| Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri Claparède, 1862 | Lho | 0.59 | 23.35 | 29.23 | 7.98 | 7.42 | 11.69 | 18.45 | 3.23 | 2.52 | 11.24 | |
| Limnodrilus profundicola (Verrill, 1871) | Lpr | 0.31 | 3.97 | 4.20 | 1.03 | 1.72 | 1.57 | 2.38 | 2.07 | 0.02 | 7.31 | |
| Limnodrilus udekemianus Claparède, 1862 | Lud | 0.37 | 0.53 | 0.71 | 4.45 | 5.82 | 1.64 | 2.34 | 14.23 | 8.33 | ||
| Potamothrix bavaricus Oschmann, 1913) | Pba | 0.01 | 2.74 | |||||||||
| Potamothrix danubialis (Hrabě, 1941) | Pda | 0.18 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 3.62 | 0.30 | 1.40 | 1.30 | 2.50 | |||
| Potamothrix hammoniensis (Michaelsen, 1901) | Pha | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 2.51 | ||||||
| Potamothrix isochaetus (Hrabě, 1941) | Pis | 0.16 | 0.70 | 1.05 | 2.21 | 1.80 | 4.08 | 1.56 | ||||
| Potamothrix moldaviensis Vejdovsky and Mrázek, 1902 | Pmo | 0.38 | 11.36 | 10.10 | 8.61 | 10.79 | 6.23 | 5.51 | 0.65 | 2.08 | ||
| Potamothrix vejdovskyi (Hrabě, 1941) | Pve | 0.12 | 1.35 | 4.15 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 5.05 | 0.57 | 0.62 | |||
| Psammoryctides albicola (Michaelsen, 1901) | Psl | 0.22 | 1.24 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 1.84 | 1.64 | 2.33 | 1.64 | |||
| Psammoryctides barbatus (Grube, 1861) | Psb | 0.38 | 1.65 | 5.24 | 4.81 | 6.11 | 3.91 | 3.26 | 4.08 | 0.94 | 2.81 | |
| Psammoryctides moravicus (Hrabě, 1934) | Psm | 0.16 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.32 | 1.51 | 1.63 | |||||
| Rhyacodrilus coccineus (Vejdovský, 1875) | Rco | 0.01 | 22.26 | |||||||||
| Tubifex ignotus (Štolc, 1886) | Tig | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.13 | ||||||||
| Tubifex tubifex (Müller, 1774) | Ttu | 0.22 | 0.56 | 4.74 | 0.47 | 0.94 | 3.73 | |||||
| Enchytraeidae | ||||||||||||
| Enchytraeidae Gen. sp. | 0.03 | 0.22 | 6.39 | |||||||||
| Propappidae | ||||||||||||
| Propappus volki (Michaelsen, 1916) | Pvo | 0.06 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 8.15 | |||||||
| Lumbriculidae | ||||||||||||
| Lumbriculus variegatus (Müller, 1774) | Lva | 0.01 | 0.34 | |||||||||
| Rhynchelmis limosella Hoffmeister, 1843 | Rli | 0.01 | 1.03 | |||||||||
| Stylodrilus lemani Grube, 1879 | Sle | 0.01 | 0.68 | |||||||||
| Stylodrilus heringianus Claparède, 1862 | She | 0.29 | 19.85 | 34.95 | 11.27 | 24.00 | 22.21 | 1.85 | 1.56 | |||
| Lumbricidae | ||||||||||||
| Eiseniella tetraedra (Savigny, 1826) | Eta | 0.14 | 7.69 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 6.18 | |||
| Criodrilidae | ||||||||||||
| Criodrilus lacuum Hoffmeister, 1845 | Cla | 0.35 | 1.59 | 0.18 | 1.23 | 0.77 | 1.10 | 2.07 | 14.33 | 1.22 | ||
| Haplotaxidae | ||||||||||||
| Haplotaxis gordioides (Hartmann, 1821) | Hgo | 0.05 | 1.68 | |||||||||
| Number of taxa | 11 | 12 | 20 | 23 | 28 | 22 | 16 | 28 | 13 | 10 | ||
| JDS3 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Percentage Participation of Oligochaetes (%) | ||||||||||||
| Taxa | Code | F | Sector 1 | Sector 2 | Sector 3 | Sector 4 | Sector 5 | Sector 6 | Sector 7 | Sector 8 | Sector 9 | Sector 10 |
| Naididae | ||||||||||||
| Dero digitata Müller, 1773 | Ddi | 1.79 | 0.14 | 1.21 | 1.70 | |||||||
| Dero obtusa d’Udekem, 1835 | Dob | 1.52 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.32 | ||||||
| Nais alpina Sperber, 1948 | Nal | 0.28 | 0.02 | 0.36 | ||||||||
| Nais barbata Müller, 1773 | Nba | 1.10 | 1.09 | 1.62 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |||||
| Nais bretscheri Michaelsen, 1899 | Nbr | 6.76 | 0.59 | 1.88 | 4.99 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.03 | 0.13 | ||
| Nais christinae Kasprzak, 1973 | Nch | 4.28 | 0.04 | 2.52 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.40 | 4.53 | ||||
| Nais communis Piguet, 1906 | Nco | 0.69 | 0.01 | 0.30 | ||||||||
| Nais elinguis Müller, 1774 | Nel | 0.14 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| Nais pardalis Piguet, 1906 | Npa | 3.03 | 0.63 | 4.95 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.63 | ||||
| Ophiodonais serpentina (Müller, 1773) | Ose | 2.76 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 12.93 | 1.49 | ||||||
| Paranais frici Hrabě, 1941 | Pfr | 0.14 | 0.46 | |||||||||
| Piguetiella blanci (Piguet, 1906) | Pbl | 0.14 | 4.09 | |||||||||
| Specaria josinae (Vejdovksy, 1883) | Sjo | 2.48 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 1.41 | 0.59 | 4.69 | ||||
| Stylaria lacustris (Linnaeus, 1767) | Sla | 7.03 | 0.89 | 1.37 | 0.03 | 0.54 | 9.30 | 5.05 | 0.11 | |||
| Uncinais uncinata (Orsted, 1842) | Uun | 0.55 | 0.15 | |||||||||
| Pristinidae | ||||||||||||
| Pristina aequiseta | Pae | 0.28 | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Pristina longiseta Ehrenberg, 1828 | Plo | 0.14 | ||||||||||
| Pristina rosea (Piguet, 1906) | Pro | 0.14 | 0.29 | |||||||||
| Tubificidae | ||||||||||||
| Aulodrilus japonicus Yamaguchi, 1953 | Aja | 1.24 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.26 | ||||||
| Aulodrilus pluriseta (Piguet, 1906) | Apl | 0.28 | 0.17 | |||||||||
| Bothrioneurum vejdovskyanum Štolc, 1888 | Bve | 0.55 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Branchiura sowerbyi Beddard, 1892 | Bso | 6.07 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.92 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 1.59 | ||
| Embolocephalus velutinus (Grube, 1879) | Eve | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.48 | 0.04 | |||||||
| Isochaetides michaelseni (Lastočkin, 1936) | Imi | 16.55 | 0.10 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 5.67 | 1.36 | 0.03 | 27.42 | 50.64 | 1.22 | |
| Haber speciosus (Hrabě, 1931) | Hsp | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.59 | ||||||||
| Limnodrilus claparedeanus Ratzel, 1868 | Lcl | 13.26 | 0.15 | 1.49 | 1.78 | 4.48 | 43.77 | 28.34 | 20.26 | 16.10 | 40.35 | |
| Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri Claparède, 1862 | Lho | 25.66 | 3.44 | 68.51 | 24.50 | 16.28 | 28.84 | 11.17 | 18.77 | 5.53 | 11.10 | |
| Limnodrilus profundicola (Verrill, 1871) | Lpr | 0.69 | 0.62 | 6.22 | ||||||||
| Limnodrilus udekemianus Claparède, 1862 | Lud | 7.59 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 6.67 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.78 | |
| Potamothrix bavaricus Oschmann, 1913) | Pba | 0.14 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| Potamothrix danubialis (Hrabě, 1941) | Pda | 4.55 | 0.98 | 1.74 | 2.47 | 2.50 | 13.43 | 19.22 | ||||
| Potamothrix hammoniensis (Michaelsen, 1901) | Pha | 4.83 | 0.02 | 0.26 | 1.07 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.48 | ||
| Potamothrix moldaviensis Vejdovsky and Mrázek, 1902 | Pmo | 13.39 | 54.70 | 0.65 | 6.57 | 40.38 | 2.39 | 7.33 | 3.21 | 3.85 | 16.39 | |
| Potamothrix vejdovskyi (Hrabě, 1941) | Pve | 7.45 | 0.65 | 2.55 | 1.29 | 4.06 | 0.08 | 5.02 | 0.68 | |||
| Psammoryctides albicola (Michaelsen, 1901) | Psl | 1.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |||||
| Psammoryctides barbatus (Grube, 1861) | Psb | 10.62 | 4.20 | 2.54 | 1.24 | 1.45 | 0.11 | 1.88 | 1.25 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |
| Psammoryctides moravicus (Hrabě, 1934) | Psm | 0.41 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| Spirosperma ferox | Sfe | 0.14 | 0.02 | |||||||||
| Tubifex ignotus (Štolc, 1886) | Tig | 0.83 | 0.19 | 0.22 | ||||||||
| Tubifex newaensis (Michaelsen, 1903) | Tne | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.01 | ||||||||
| Tubifex tubifex (Müller, 1774) | Ttu | 3.86 | 0.14 | 2.28 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 0.02 | |||
| Enchytraeidae | ||||||||||||
| Enchytraeus sp. | Enc sp | 0.14 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| Henlea ventriculosa (d’Udekem, 1854) | Hve | 0.14 | 0.11 | |||||||||
| Propappidae | ||||||||||||
| Propappus volki (Michaelsen, 1916) | Pvo | 0.97 | 0.43 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |||||
| Lumbriculidae | Lrl | |||||||||||
| Lumbriculus variegatus (Müller, 1774) | Lva | 0.14 | ||||||||||
| Stylodrilus brachystylus Hrabě, 1929 | Sbr | 0.14 | 0.15 | |||||||||
| Stylodrilus lemani Grube, 1879 | Sle | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| Stylodrilus heringianus Claparède, 1862 | She | 11.59 | 18.19 | 0.33 | 46.74 | 8.76 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |||
| Rhynchelmis limosella Hoffmeister, 1843 | Rli | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |||||||
| Lumbricidae | ||||||||||||
| Eiseniella tetraedra (Savigny, 1826) | Ete | 2.76 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.01 | |||||
| Criodrilidae | ||||||||||||
| Criodrilus lacuum Hoffmeister, 1845 | Cla | 1.10 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.01 | |||||||
| Number of taxa | 27 | 21 | 18 | 27 | 27 | 25 | 34 | 15 | 15 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atanacković, A.; Šporka, F.; Marković, V.; Slobodnik, J.; Zorić, K.; Csányi, B.; Paunović, M. Aquatic Worm Assemblages along the Danube: A Homogenization Warning. Water 2020, 12, 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092612
Atanacković A, Šporka F, Marković V, Slobodnik J, Zorić K, Csányi B, Paunović M. Aquatic Worm Assemblages along the Danube: A Homogenization Warning. Water. 2020; 12(9):2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092612
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtanacković, Ana, Ferdinand Šporka, Vanja Marković, Jaroslav Slobodnik, Katarina Zorić, Bela Csányi, and Momir Paunović. 2020. "Aquatic Worm Assemblages along the Danube: A Homogenization Warning" Water 12, no. 9: 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092612
APA StyleAtanacković, A., Šporka, F., Marković, V., Slobodnik, J., Zorić, K., Csányi, B., & Paunović, M. (2020). Aquatic Worm Assemblages along the Danube: A Homogenization Warning. Water, 12(9), 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092612





