Abstract
This study evaluated watershed health (WH) change using reference values for environmental changes at various times. Land use in 1985 was defined as the reference value under the most natural conditions, and the WH for the years 1995 to 2019 was calculated in comparison to 1985. The proposed method was used to assess the WH of 78 standard subbasins in South Korea’s Geum River Basin (GRB), where complex land-use change has occurred since 1995. For evaluating hydrology and water quality (WQ) health index, Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) and four land-use maps (1985, 1995, 2008, and 2019) were used to simulate the hydrology and WQ. A multivariate normal distribution (MND) from poor (0) to good (1) was used to assess WH based on SWAT modeling results. Based on the reference value, the WQ health from 1995 to 2019 changed to within 0.1, while the range of changes in the hydrology index was analyzed over 0.18. As a result of WH changes from 1985 to 2019, hydrological health deteriorated in high-density urbanized subbasins, while WQ health deteriorated in upland-cultivation-increased subbasins. This study provides useful information for recognizing potential WH issues related to long-term environmental changes.
1. Introduction
Watersheds have been the bases of many local communities and an important source of livelihood for people [1]. Although many countries have achieved rapid economic growth, water quality (WQ) and quantity and the ecological environmental conditions in watersheds are facing serious problems [2,3]. Recently, stream watersheds have undergone increases in impermeable areas and water intake due to climate change and urbanization, and these watersheds are also affected by river improvement projects. In this situation, the exiting normal water cycle system of the watershed collapses, lowering the groundwater level and reducing the stream flow. Consequently, streams lose their normal functions. In addition, the shortage of maintenance flow caused by the drying of streams results in an increase in water pollutants, especially in streams [4,5,6,7].
Such a change in the watershed environment and the inefficient utilization of water resources seriously distort the hydrologic health of watershed. Increased surface flow, decreased groundwater flow, increased flooding, soil erosion, water pollution, and urban desertification are all side effects of this crisis [8]. Accordingly, to maintain a sustainable and healthy water cycle, it is desirable to accurately identify the overall water cycle systems of each watershed and develop an analysis technology that enables the water availability to be sustained [9]. In particular, an evaluation technology that can objectively quantify the efficiency and health of the water cycle in watersheds should be established [10,11].
The concept of watershed health (WH) has been applied mainly to the hydrophilic properties, habitats, flow rates, and WQ of large streams [12]. Researchers working in different fields adopt various criteria for evaluating WH. Considering the water cycle in watershed, WH is defined as “a state where the water cycle system of a stream maintains its normal functions including the usual flow, groundwater level, WQ and ecosystem” or “a state of equilibrium in a particular watershed, where the water cycle system of nature has been established over a long stretch of time under the influence of the sun and gravity” [13,14,15,16].
By considering the concept of WH from an ecological viewpoint focusing on the watershed environment, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines a healthy watershed system as a dynamic system with interconnections that enable health to be identified and protected [17]. In other words, it can be understood as an integrated system that can be evaluated with respect to dynamic interactions among main characteristics or conditions related to hydrology, WQ, land use, and aquatic ecology and biology. The watershed management approach has recently been introduced to secure WH and thus to prevent problems related to the flow, WQ, and environment from arising. However, only a few studies have attempted to find appropriate means of watershed management. Ahn and Kim [18,19] noted that WH needs to be evaluated by considering both water quantities (evapotranspiration (ET), stream outflow, soil water (SW), groundwater, and dam/reservoir discharge) and watershed environments (vegetation and land use). They reported the evaluation results of WH for the Han River. Hazbavi et al. [20] evaluated WH in different climates for the UK, Portugal, and Iran. Sadeghi et al. [21] propose that hydrologic and anthropogenic behaviors have interactive effects on WH through precipitation, remote sensing, and soil erosion. Mosaffaie et al. [22] conducted assessment of the Goranroun watershed in Iran, and they found that socioeconomic activities and related pressures impact watershed health.
However, existing methods used for calculating the watershed health index (WHI), proposed by previous studies, were intended to calculate the current WH. The method developed here evaluates the most vulnerable watershed, which needs to be protected and restored in preference to the other watersheds, through the comparison of the current states of health among watersheds considered. As this method lacks a reference value for chronological analysis or analysis of each evaluation period, absolute comparison for the same watershed is impossible. In other words, it is difficult to derive the health variation within a watershed according to the long-term environmental change using this method. Accordingly, this study calculated the probability density function for the reference value by using the multivariate normal distribution of two WHIs (hydrology and WQ) out of six WHIs proposed by the EPA [17] and Ahn and Kim [18,19]. Thus, the present WHIs were improved to enable the change in WH to be analyzed according to long-term environmental change.
A focus of this study was to (1) investigate WH variation in accordance with long-term land-use change using the multivariate normal distribution (MND) approach; and (2) quantify the consequence of land-use transition factors on WH in terms of absolute comparison. The input data for the study of the land-use map were collected first. After the design and input specifications were developed and the data for dams, weirs, and point sources were released, the hydrology and WQ of the watershed were calibrated and validated using Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). We established a reference condition for hydrology and WQ to the subindex by MND and calculated WH as a consequence of a transition in land use.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
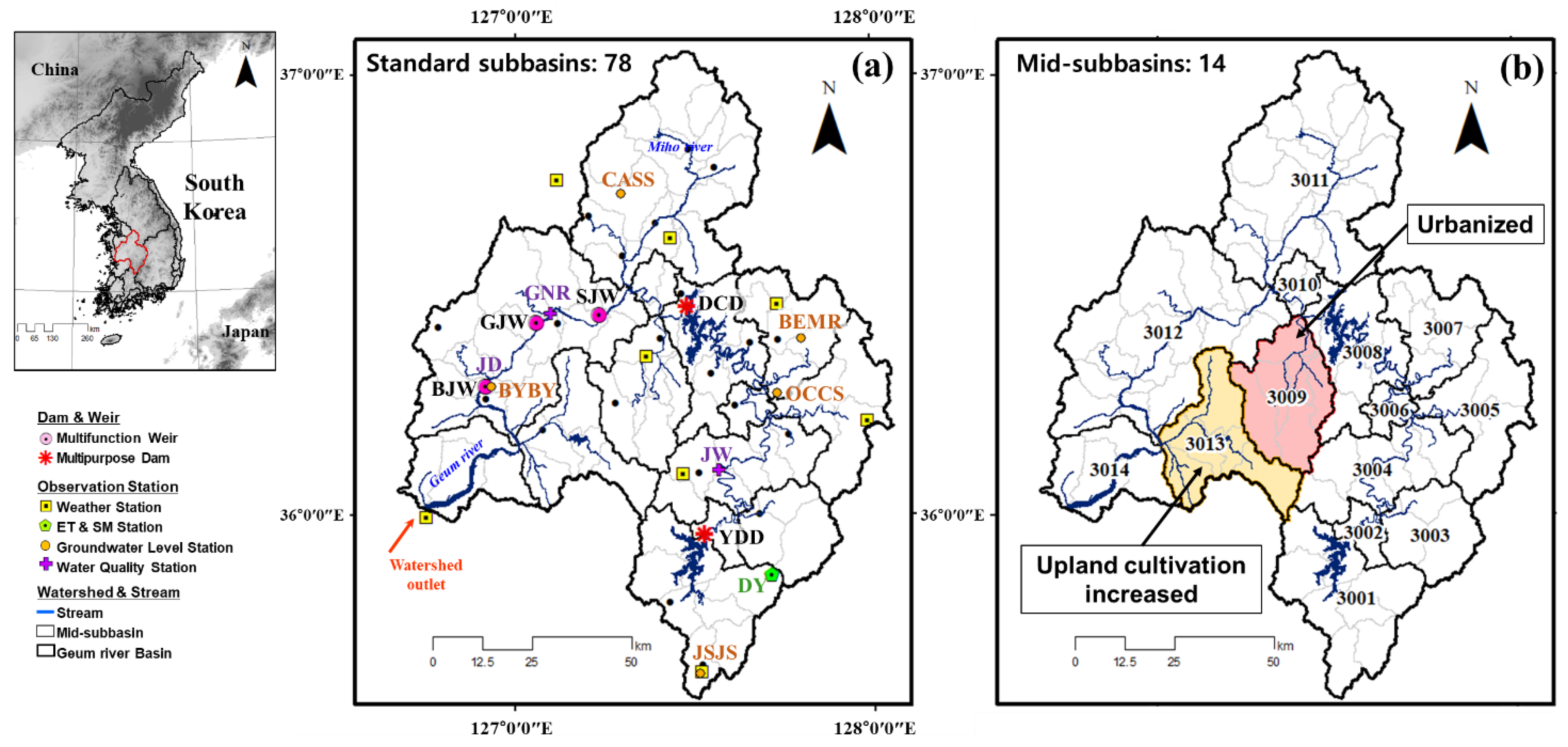
The Geum River Basin (GRB) is located in the most western area of South Korea (35°08′00″ N–37°09′00″ N and 126°07′00″ E–128°00′00″ E). The basin serves 12% of South Korea’s population and has the largest proportion of land use dedicated for agriculture (29.5% of the basin area). The metropolitan city of Daejeon occupies midstream of the Geum River and urbanization has expanded around this city. The downstream is an important agricultural production area and in recent years, the rice paddy area has been changed to upland crop area. The water management issues in this basin include water scarcity and high rates of water pollution incidents in comparison with other basins. In the GRB, two multipurpose dams (Daecheong (DCD) and Yongdam (YDD)) and three multifunctional weirs (Backje (BJW), Gongju (GJW), and Sejong (SJW)) have been installed and are currently in operation. GRB is under temperature monsoon climates; annually, the temperature is 12.2 °C. Annual rainfall is 1261 mm and 50–60% of rainfall has occurred during summer (June–August) for 35 years (1985–2019). Figure 1a shows GRB and 78 standard subbasins that were designed for modeling of SWAT and WH evaluation, and Figure 1b illustrates two mid-subbasins for comparison of the WH changes by land use. The hydrology and WQ health of 78 standard subbasins were evaluated based on the SWAT simulation results. In addition, two subbasins with rapid changes in land use among the evaluation results were analyzed in detail.
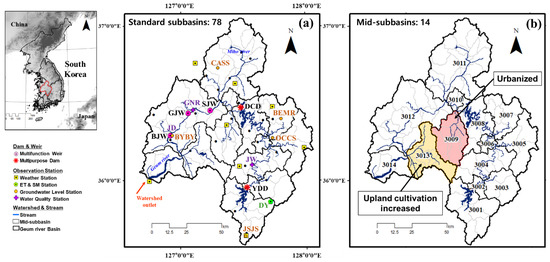
Figure 1.
Locations of (a) the Geum River Basin’s boundaries and gauging stations for the SWAT modeling, (b) subbasins with increased urban and upland cultivation.
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. WH Evaluation Method
Hydrologic factors (surface runoff (SQ), ET, SW, and groundwater flow (GWQ)) and WQ factors (suspended solids (SS), total phosphorus (T-P), and total nitrogen (T-N)) can be derived by the following equations for WH (Equations (1)–(3)), which were proposed by Ahn and Kim [18,19]. For each of the four hydrologic factors and three WQ factors, Equation (1) was utilized to derive the normalized component values. Based on these values, two subindices for hydrology and WQ were obtained (Equation (2)). A comprehensive health evaluation for hydrology and WQ was conducted by deriving one index from the two subindices and Equation (3). The normalized values were calculated based on percentile ranks; each index ranged from 0 to 1. An index closer to 1 represents a healthier watershed. This study evaluated hydrology and WQ health via SWAT simulations using land-use data from 1985. The evaluation result was utilized as the reference value to analyze the change in health under long-term environmental change.
The MND is a generalization of the univariate normal distribution. For correlated variable random vectors, it is a distribution with a univariate normal distribution for each vector element. There is no connection between variables in the simplest case, and the vector components are separate univariate normal random variables. The MND has the mean vector μ and the covariance matrix Σ as parameters. These are similar to the mean parameter μ and the variance parameter σ2 of the univariate normal distribution. The diagonal element of Σ includes the variance for each parameter, while the nondiagonal element of Σ includes the covariance of variables. As a megavariate distribution that can be easily dealt with, the MND is usually used as a model for multivariate data [23]. If the bivariate normal distribution is defined as two discrete random variables X and Y, which are different from each other, the bivariate probability function expressed as P (X = x, Y = y) shows a joint probability where the random variables X and Y have the particular values of x and y, respectively.
where, is the variable following the bivariate normal distribution, is the mean value of each variable, is the variance of the variable , is the variance of the variable , is , and denotes the mean value [24,25].
To improve the existing evaluation index for WH, which is applicable only to relative evaluations, this study calculated the reference value by applying the MND probability function. Based on the SWAT modelling results using the 1985 land use, the hydrology and WQ health were evaluated using Equations (1)–(3). The evaluation results were defined as the reference values under the most natural conditions. The SWAT simulation results, which were necessary to derive WH indices from the reference values, were set as variables. A python program was implemented for the variables. Thus, a probability density function was derived from the MND [26].
2.2.2. SWAT Description
The SWAT, which was released by the USDA-ARS [27], was conducted to simulate the long-term runoff from the GRB. The SWAT is a physically dependent continuous model that can simulate hydrology and WQ for various types of land use. The model simulates SQ, SW, and GWQ using the water balance equation for HRU. The SCS-CN method is used in SWAT to calculate daily streamflow. The MUSLE was used to simulate phosphorus and nitrogen transport and concentration estimation. The water bodies considered included streams, dams and weirs, and streamflow; SS and nutrients were considered [28].
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Land-Use Data from 1985 to 2019
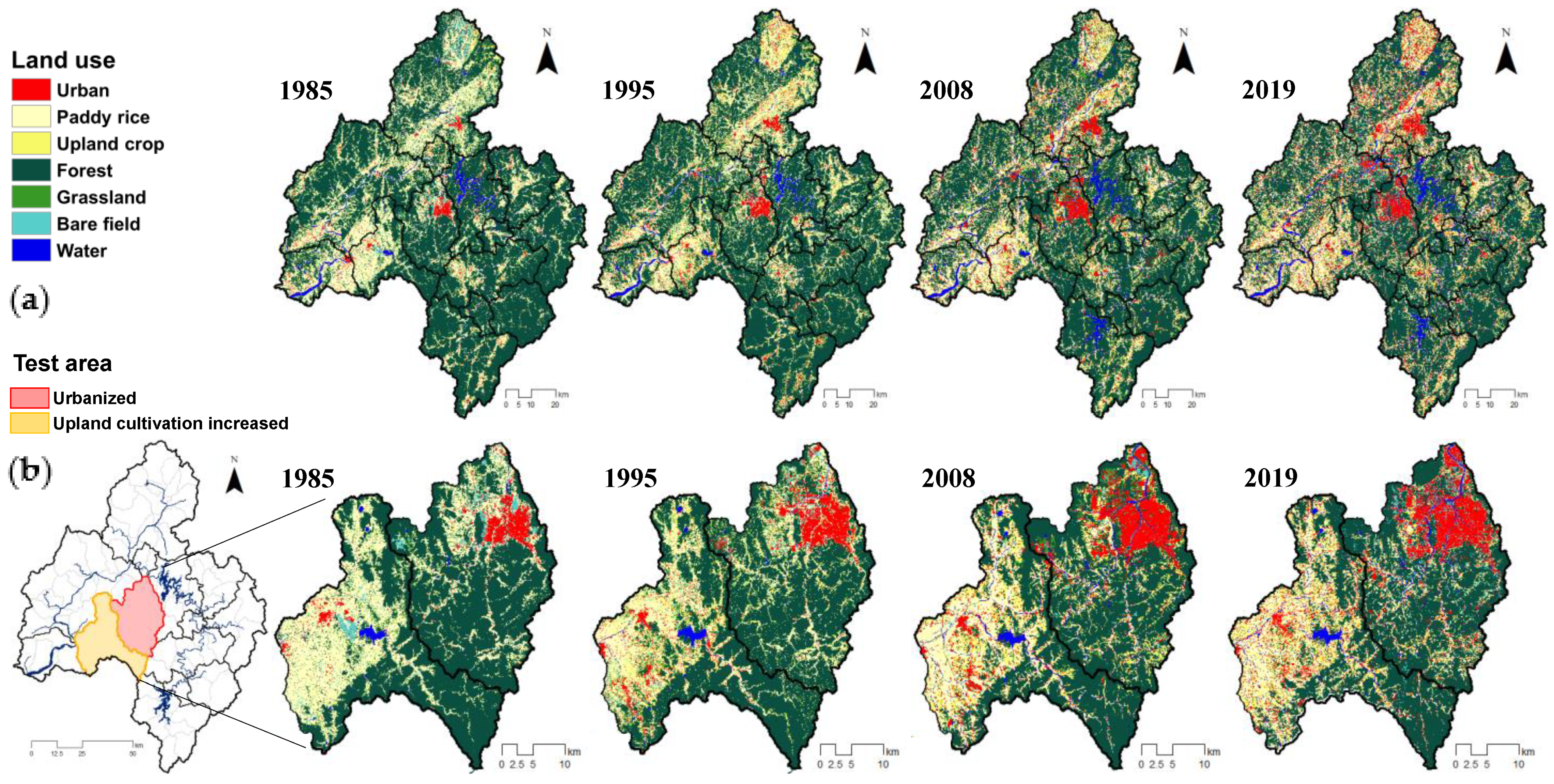
Before analyzing the hydrologic conditions and WQ according to the change in land use, this study gathered seven categories of land-use maps from the Water Resources Management Information System (WAMIS) for the years 1985 and 1995, and land-use maps of 2008 and 2019 were provided by the Environmental Geographic Information Service (EGIS) (Figure 2). WAMIS classifies land cover into the following eight categories: urban, crop, paddy, grass, forest, wetland, bare field, and water [29]. The land-use map was composed of Landsat TM, Landsat ETM, and Korea Multi-Purpose Satellite-2 (KOMPSAT-2) images.
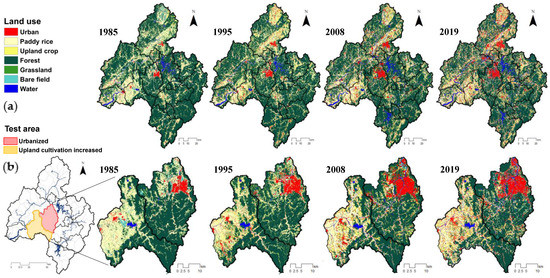
Figure 2.
Land-use data of (a) Geum River Basin and (b) two test subbasins.
2.3.2. GIS and Measured Data for SWAT Evaluation
The 30 m DEM and soil map from WAMIS were conducted as the GIS spatial data for the SWAT. Sandy loam occupied high proportions of 58% of the soil types in GRB. The 35-year period (1985–2019) SWAT weather inputs were daily data from nine weather stations [30].
The two dams (DCD and YDD) and three weirs (BJW, GJW, and SJW) operation data were collected from Korea Water Resources Corporation (K-water). The dam storage and daily inflow data for DCD collected over 35 years were used. For YDD, the dam daily inflow and storage data were collected from January 2002 to December 2019. For BJW, GJW, and SJW, the daily weir storage and inflow data were collected from August 2012 to December 2019. The groundwater level data observed by the National Groundwater Information Center (GIMS) groundwater level observation stations were collected. Five sites (BYBY, JSJS, BEMR, CASS, and OCCS) in the GRB were selected (Figure 1a) [31]. The flux tower DY, operated by K-water, is in the upper GRB within the forested area [31]. The DY daily ET (mm) and soil moisture (%) data were collected from April 2011 to December 2019. For 11 years (2005–2019), dam weir, groundwater, ET, and soil moisture were used to calibrate and validate the watershed hydrology.
Point source data for SWAT and daily sewage treatment plant monitoring data were aggregated from the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). From 2005 to 2019, SS, T-P, and T-N weekly data were collected from three WQ monitoring stations (Jewon (JW), Gomnaru (GNR), and Jeongdong (JD)) for evaluation of stream WQ. The fertilizers applied were the measured fertilizers of upland crops and paddy rice in South Korea [32].
2.3.3. Data Reconstruction for Evaluating Hydrology and Water Quality Health
The EPA [17] uses the ratio of the water storage of a dam to the annual average stream flow before the development of the watershed to evaluate the WH at the side of the flood gate. However, the water resource characteristics of watersheds in South Korea require that stream flow, ET, SW, and GWQ be considered very important factors. Accordingly, this study evaluated WH by considering all hydrologic and water cycle factors for watershed management focusing on water quantity. This study utilized the SWAT verification and calibration results of Lee et al. [31] to evaluate hydrologic WH. The evaluation results were analyzed with respect to the following four factors: ET, SQ, SW, and GWQ.
For the WH evaluation with respect to WQ, the distributions of the SS, T-P, and T-N were calculated as evaluation factors for each standard watershed. Among the SWAT simulation result files, Output.rch was used to arrange the WQ simulation results. As Output.rch converted the simulation results of WQ to loads (ton/day or kg/day), the concentrations (mg/L) were calculated based on the simulation result of stream flow.
3. Results
3.1. SWAT Evaluation for Hydrology and Water Quality
This study validated and calibrated SWAT before simulating the hydrology and WQ according to the land-use trend from 1985 to 2019. For the hydrologic validation and calibration of SWAT for the GRB, the parameters proposed by Lee et al. [31] were applied. As shown in Table 1, validation and calibration were conducted for two dams (YDD and DCD), and three weirs (SJW, GJW, and BJW). The NSE of dam inflow was analyzed and found to range from 0.57 to 0.67. The RMSE was 0.82 mm/day–1.66 mm/day. The PBIAS ranged from −5.65% to 8.02%. Thus, the calibration results were consistent with the SWAT calibration guidelines (NSE 0.5, PBIAS 28.0%, and R2 0.6) and were found to be satisfactory [19].

Table 1.
SWAT evaluation results for GRB.
Based on the hydrologic validation and calibration results, the WQ at 3 points (JW, GNR, JD) in GRB was validated and calibrated. For the validation and calibration of WQ, the stream WQ measurement data between 2005 and 2019 were collected from the water environment information system. As nutritive substances are affected by the movement and discharge of sediment load in the SWAT, the SS load was calibrated before nutritive substances were calibrated [33,34]. The applicability of the SWAT applicability was evaluated using the R². It was calculated that the statistical values of SS, T-P, and T-N were 0.72–0.81, 0.64–0.78, and 0.69–0.76, respectively (Table 1).
3.2. Impact of Land-Use Change on Hydrology and WQ
3.2.1. Land-Use Change Analysis
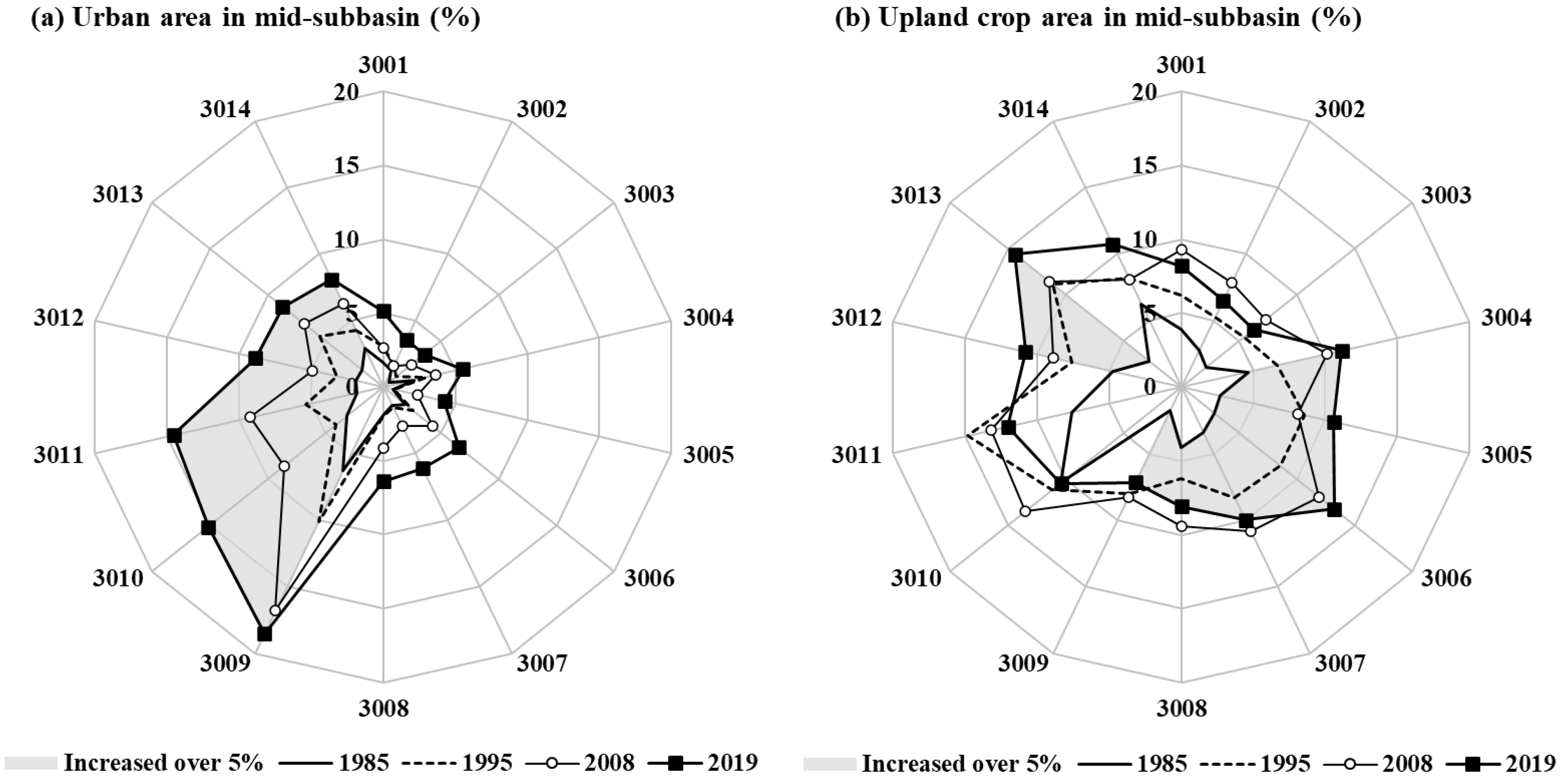
In GRB, there are dominant land-use types of area forest and paddy, which encompass up to 73% of the total area over the 35 years. In 1985, forests accounted for 63.6% of the total area, and this value decreased to 54.1% by 2019. In contrast, the urban area increased every year and accounted for 9.0% in 2019 (Table 2). Comparing the land-use data of 1985, 1995, 2008, and 2019, the obvious change occurred in urban, agricultural, and forest land-use classes. Figure 3 represents the proportions of urban and upland crop area for each of the 14 mid-subbasins in the GRB. The mid-subbasins where urban area expanded by more than 5% compared to 1985 were 3009, 3010, 3011, 3012, 3013, and 3014 mid-subbasins (Figure 3a). In particular, the urban area of the 3009 mid-subbasins increased by up to 12.3% compared to 1985. From 1985 to 2019, the upland crop area increased by more than 5% at eight mid-subbasins, and in 3013 mid-subbasin, where the change was the greatest, 11.6% of the watershed was converted into upland crop. (Figure 3b).

Table 2.
Land-use occupation in the GRB.
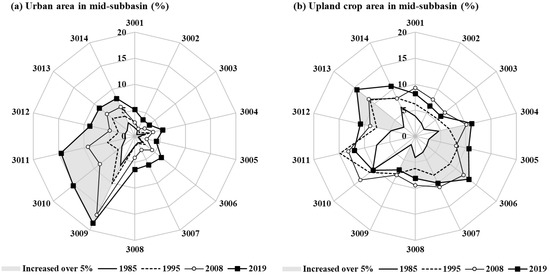
Figure 3.
Area changes in the mid-subbasins from 1985 to 2019, (a) urban area (%) and (b) upland crop area (%).
The areas of urban and upland crop increased while the area of forest and paddy decreased. As the forest area was generally reduced for the 14 mid-subbasins as shown in Figure 2, in this study, we selected the test areas where urbanized and upland crop cultivation increased rapidly. Table 2 describes occupied land use classification in the most urbanized (3009) and upland-cultivation-increased (3013) subbasins. The urban area increases in 3009 subbasin was at the expense of paddy field. Daejeon city is located in this subbasin, and the city was expanded to high density every year, resulting in the largest increase in urban area within the total watershed. The urban expanded rate in 3009 mid-subbasin was 75% higher than the average expanded rate in the GRB. The 3013 mid-subbasin is a representative agricultural area in the GRB. This subbasin is a representative agricultural area in the GRB, with paddy area accounting for 42.8% of the basin in 1985. The paddy area of 2019 decreased by 12.8% while upland crop area increased by 11.6%. This change is due to policies that encourage the cultivation of economic crops other than rice.
3.2.2. Hydrology and WQ Simulation Results of SWAT According to Land-Use Change
Table 3 shows the hydrologic and WQ simulation results of SWAT according to the conservation of land use. Four land-use maps for the years 1985–2019 were utilized and meteorological data were set to the constant period from 1980 to 2019 for the SWAT simulation. For the average of GRB, the average SCS-CN value of 2019 was 4.4 greater than the 1985 CN value. In 1985, the urban area accounted for 2.0% (202.0 km2) of the GRB and increased to 6.0% (587.1 km2) in 2008 and to 9.0% (892.4 km2) in 2019. From 1985 to 2019, the ET, SW, and GWQ decreased by 1.7%, 9.3%, and 11.0%, respectively. However, the SQ increased by 81.4% (Table 3). The change of the hydrology changed more severely in the area where high-density urbanization was concentrated. In 3009 mid-subbasin, the SCS-CN value of 2019 was 9.3 greater than the 1985 CN value and surface runoff of 2019 was 248.3% greater than 1985’s. Due to the high-density urban area increase, the ET, SW, and GWQ reduced by 5.8%, 17.7%, and 25.9%, respectively. In 3013 mid-subbasins, where the rice paddy area was changed to upland crop area, the SQ increased; however, that was lower than the increase rate of the total watershed. SW and GWQ also decreased by 8.6% and 9.6%, respectively.

Table 3.
The change on hydrology and WQ component behavior.
The WQ simulation results of total area showed an increasing pattern over time. Between 1985 and 2019, the SS, T-P, and T-N increased by 13.5 mg/L, 0.009 mg/L, and 0.031 mg/L. However, 3009 urbanized area showed that the T-P and T-N concentration decreased by 2.7% and 7.4%, respectively. This phenomenon could be because N and P were not leaching to groundwater in high-density urban areas and were washed off to downstream of 3009 mid-subbasin. The 3013, which is an upland-cultivation-increased area, showed that the SS, T-P, and T-N concentration increased by 24.9 mg/L, 0.013 mg/L, and 0.063 mg/L, respectively. In particular, the rate of increase in WQ in 3013 upland-crop-increase area was greater than the overall average of the GRB and the increase rate in urbanized areas.
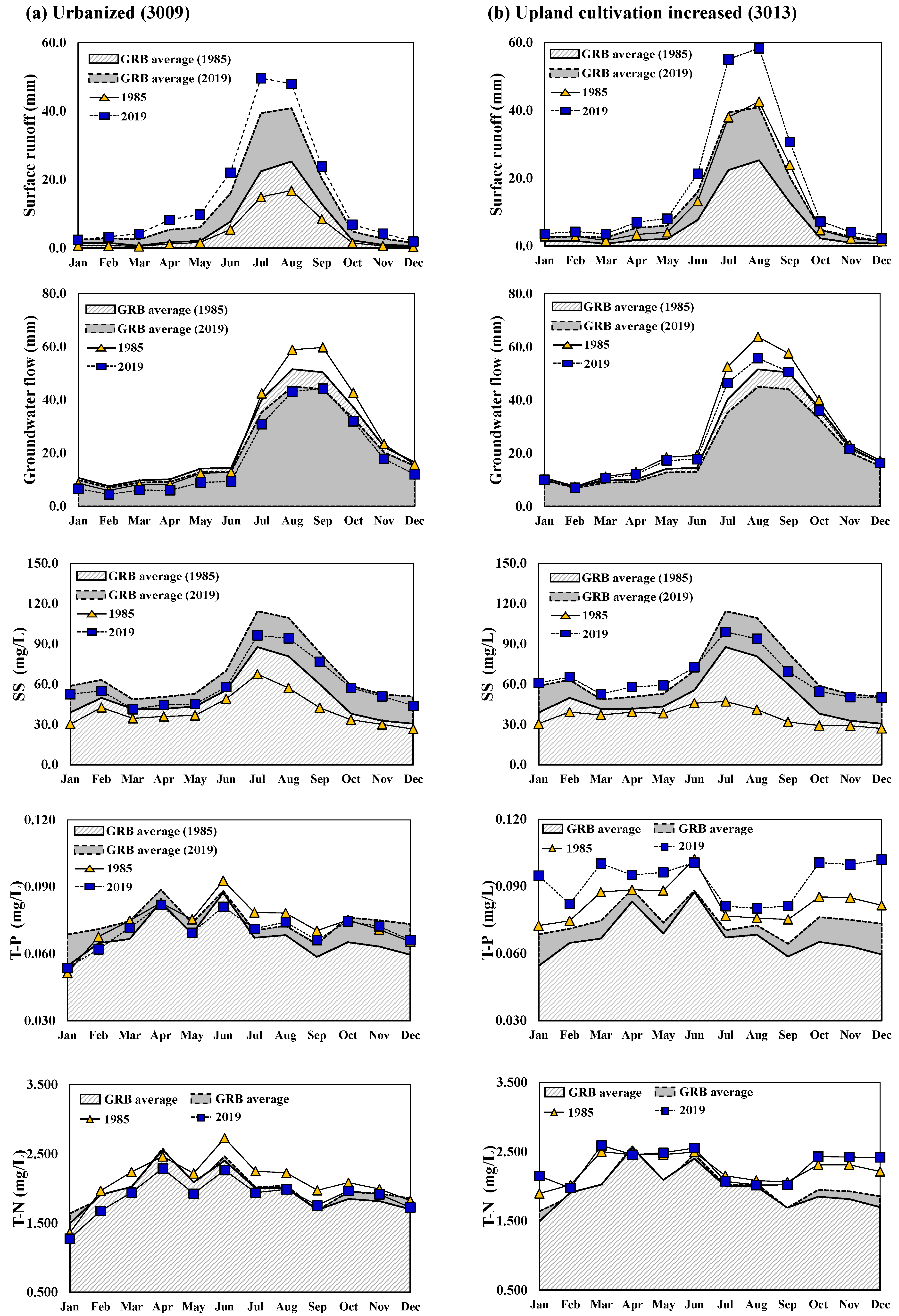
Figure 4 shows the monthly average changes in hydrology (SQ and GWQ) and WQ (SS, T-P, and T-N) according to urbanized (Figure 4a) and upland-cultivation-increased area (Figure 4b). In the figure, the grey area is the simulation result of GRB average, the yellow triangle line represents the 1985 results of each test subbasin, and the blue square line represents the 2019 results of test subbasins. In urbanized watershed, the increase in the overall impervious area increased the SQ, and the decreases were in GWQ. The SS concentration was shown to increase compared to the reference year (1985), which caused the increase in the SQ. The T-P and T-N concentration decreased compared to the reference year; in particular, the T-P decreased the most from June to September when the SQ increased (Figure 4a). In 3013 subbasin, which is an upland-cultivation-increased area, the increase is in SQ and WQ concentration. The T-P and T-N increased in spring and winter when the SQ decreased (Figure 4b).
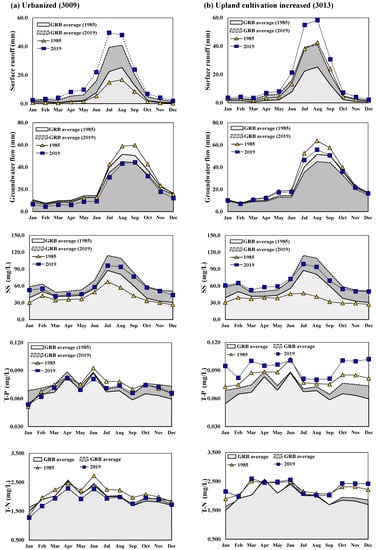
Figure 4.
The monthly changes in hydrology and WQ resulting from land-use change.
3.3. Evaluation of WH Change
This study defined the result obtained from the land use of 1985 as the reference value under the most natural conditions and derived the hydrologic and WQ health for the years from 1995 to 2019 compared to that in 1985. Using the SWAT results, WH analyses of each component were implemented for 78 standard watersheds as the GRB.
3.3.1. WH Evaluation Results for the Reference Year
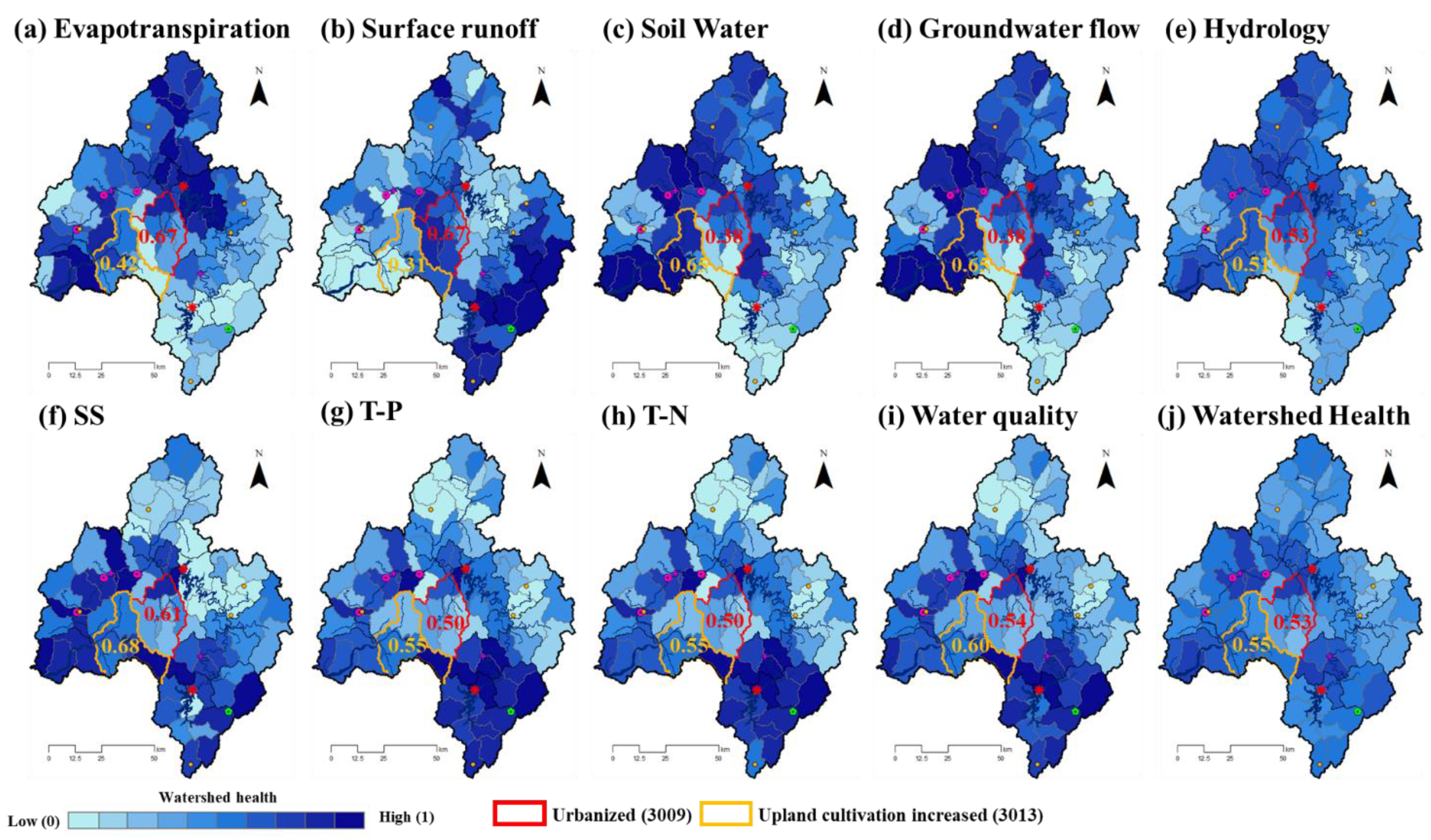
Figure 5 shows the four hydrologic and three WQ normalized health components for the GRB in the reference year. Hydrology subindices were evaluated by four hydrologic normalized components, and WQ subindex was calculated by SS, T-P, and T-N health components. An index value closer to 1 indicates a healthier watershed.
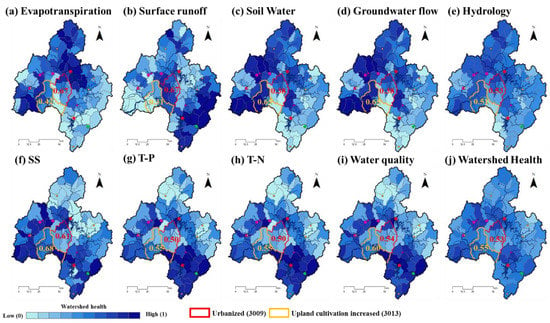
Figure 5.
Hydrology and water quality results of the WHI in reference year.
Throughout the GRB, SQ was evaluated as healthy in upstream (Figure 5a), while SW and GWQ were evaluated as healthy in downstream of the GRB (Figure 5c,d). The T-P and T-N health index was evaluated as healthy in upstream (Figure 5g,h), and the WQ subindex was evaluated in the same pattern (Figure 5i). In the reference year, the WH of total watershed was evaluated between 0.17 and 0.80. The scores of ET, SQ, SW, and GWQ health evaluations before the high-density urban expansion in 3009 mid-subbasin were 0.67, 0.67, 0.38, and 0.38, respectively, with ET and SQ healthy above the overall average of GRB. In the 3013 mid-subbasin, where paddy fields account for 42.8%, the health evaluation results of ET and SQ were 0.42 and 0.31, respectively, lower than the overall average of GRB, while SW and GWQ were healthy at 0.65. WQ health for 3009 and 3013 mid-subbasins was assessed at 0.54 and 0.60, respectively.
3.3.2. WH Change Based on Reference Year
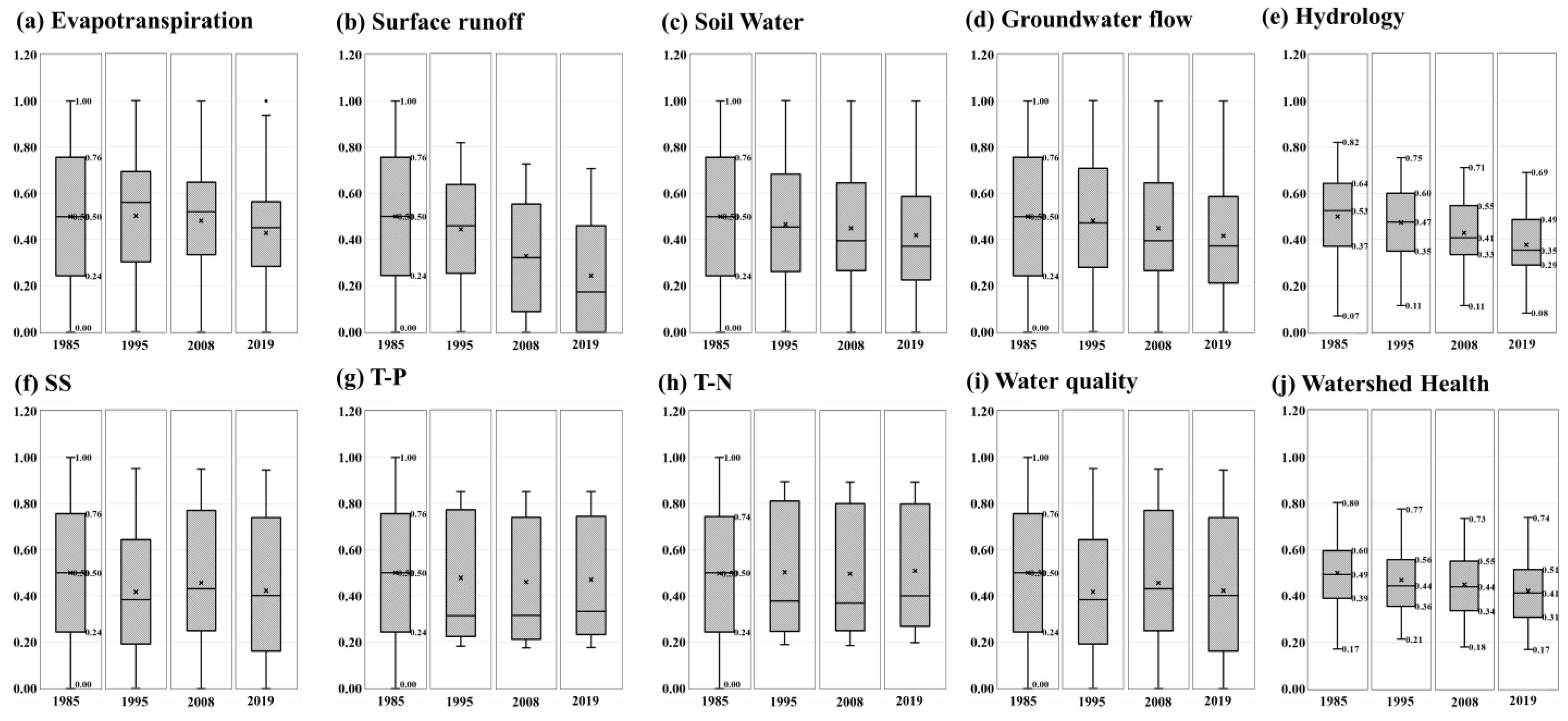
Compared to the reference value, changes in hydrological and WQ health according to land-use changes from 1995 to 2019 were absolutely evaluated. Figure 6 presents the boxplot of the evaluated health index for the 78 standard subbasins of GRB from 1985 to 2019. The total average of the 2019 SQ index evaluated value decreased to 0.17 as a result of the increase in impervious area. The SQ health index for the reference year was distributed between 0 and 1; this index from 1995 to 2019 was determined to range from 0 to 0.71 (Figure 6b), indicating that the health was worse than that in the reference year. The increase in impervious area caused a decrease in SW (Figure 6c) which resulted in the GWQ (Figure 6d) index tending to decrease every year. In 2019, the integrated hydrological health index decreased by an average of 0.18 compared to the reference year (Figure 6e).
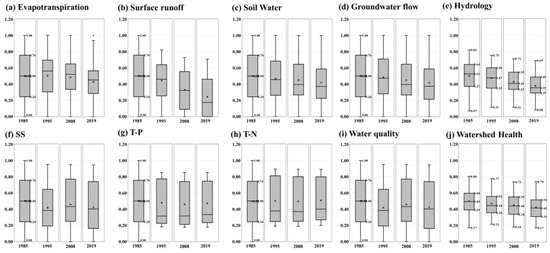
Figure 6.
Boxplot of each component of WHI in Geum River Basin.
Compared to that in the base year, the WQ health from 1995 to 2019 changed to within 0.1, while the range of changes in the hydrology index was analyzed very largely. The T-P health index for the reference year was distributed between 0 and 1, but the SS index from 1990 to 2019 was determined to range from 0 to 0.95 (Figure 6f), indicating that the health was worse than that in the reference year. The T-N and T-P also showed poor health compared to the reference year (Figure 6g,h). The integrated WQ health index for the three subindices (SS, T-P, and T-N) has been shown to deteriorate every year compared to the reference year. As a result of evaluating the health of the watershed by combining four hydrological health indicators and three WQ health indicators, WH has deteriorated since the reference year (Figure 6i). In particular, hydrological health tended to decrease compared to WQ (Figure 6j).
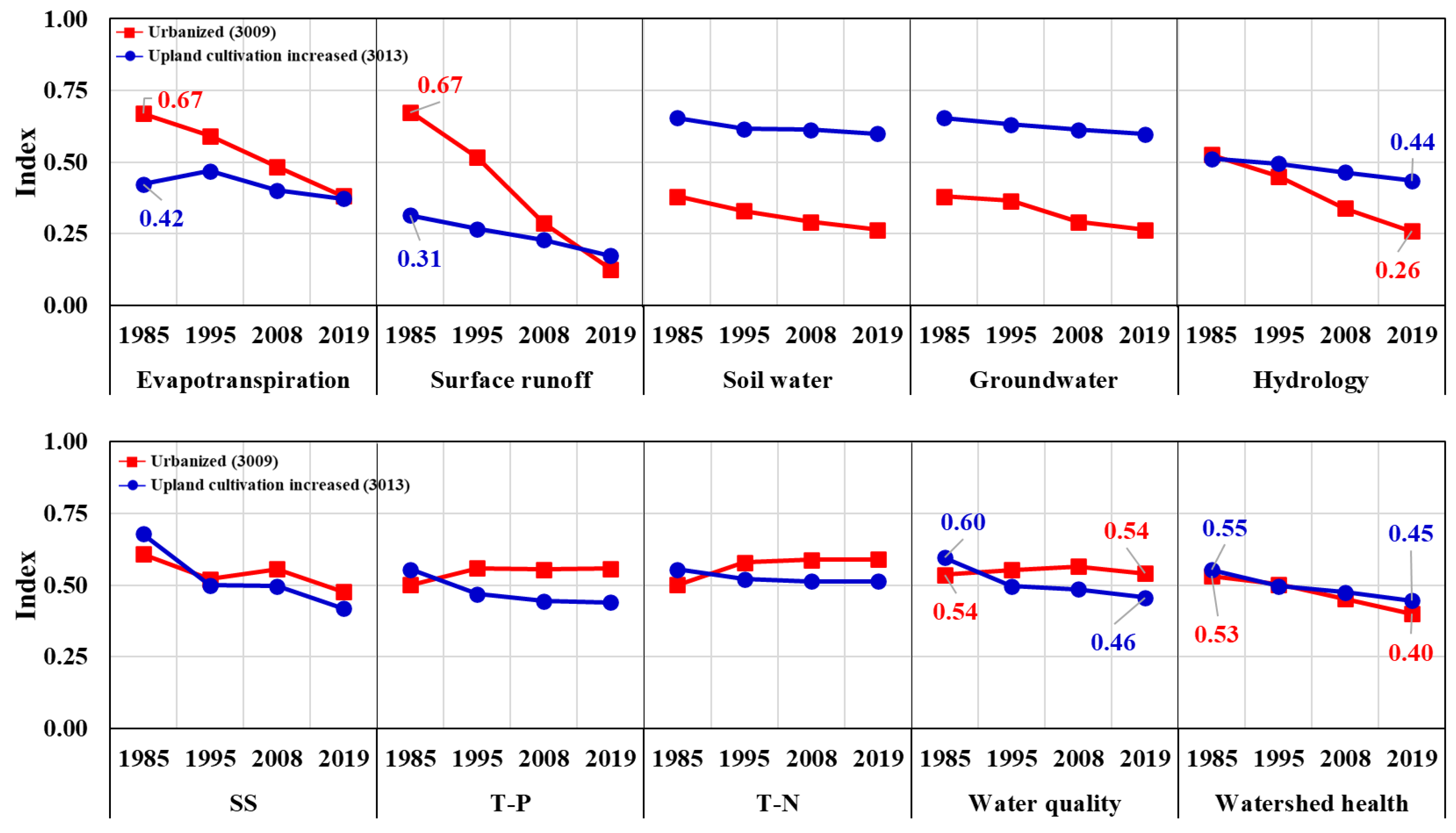
Figure 7 presents the WH indices in two study subbasins (3009 and 3013) between 1985 and 2019, which were obtained based on the SWAT results for 1985. In Figure 7, the change in the value of each subindex and the changes compared with the reference year are shown on the basis of each average value of the mid-subbasin. When the WH changes were analyzed according to two test subbasins, the hydrologic WHIs decreased in the analysis periods compared to the reference value of 1985. In the urbanized subbasin (3009), the hydrology health index decreased to 0.26. In particular, the health of the SQ showed a deteriorating trend from 1995 to 2019. In comparison with the upland-crop-cultivation-increased subbasin (3013), the SQ health worsened in 2019. Similar to the study, it was shown that the expansion in urban area and the decrease in forest area reduced SW, resulting in a decrease in GWQ [35,36,37].
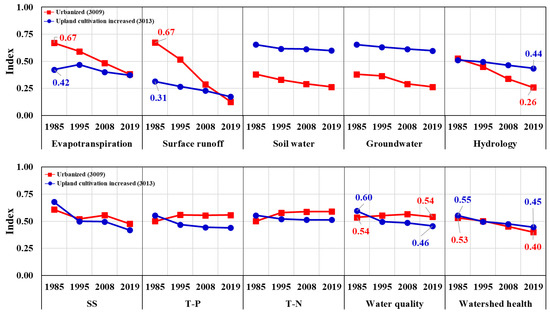
Figure 7.
Results of WH changes in urbanized (3009) and upland-cultivation-increased watershed (3013).
The SS health index deteriorated rapidly in both study watersheds; however, the T-P and T-N health showed a conflicted trend. In urbanized subbasin (3009), T-P and T-N concentration was decreased from 1985 to 2019, and consequently the evaluated T-P and T-N health was healthier than the reference year. Meanwhile, the evaluated T-P and T-N health of upland-cultivation-increased watershed (3013) was slightly poorer than the reference year. Compared to the reference year, the distribution range of health indices changed. In the case of the urbanized subbasin, which was found to have undergone the most serious health degradation, the change in land use alone under the same weather conditions caused a significant change in hydrology and WQ health.
4. Discussion
4.1. Land-Use Change Impact on WH
Land-use changes influence ecosystems by altering water cycles and WQ [38,39,40]. Many studies have confirmed that the land-use change alters regional hydrology [41,42,43], and WQ conditions and cities amplify ecosystem changes in natural watersheds [43,44,45] and urban sprawl impact on the agricultural area [46]. The results of the WH assessment show that its present land use is worse than its natural state in the past (Figure 6). Although only satellite land-use data were analyzed from 1985 to 2019 under the same meteorological conditions, the hydrology and WQ simulation results for these years are greatly different. The surface runoff increased due to the increase in impervious area, but groundwater decreased, resulting in a change in the hydrology in the watershed (Figure 4). Our results in hydrological cycle and WQ corresponded with a considerable number of studies [47,48,49,50,51].
The newly revealed 12.3 % increase in 3009 mid-subbasin urban areas was shown to increase surface runoff in the 2019 SWAT simulation (Table 2 and Table 3). Therefore, it affected the decrease in ET, soil water, and groundwater flow. The decreased ET corresponded to mid-subbasin, where the major land use changes from paddy to urban. This phenomenon can be explained as follows: as urbanization increased impervious areas, surface runoff increased and reduction ET, the ground inflow of rain, also decreased, which affected the groundwater level, and decreased the groundwater flow, while the runoff rate increased during flood seasons [52,53,54,55].
While urban areas increased, the rainfall runoff and pollutant emissions in residential and commercial areas showed various characteristics depending on the population density and economic activities in each area. However, as impervious areas, including parking lots and roads, increased in most urban areas, the rainfall runoff and flow and the WQ displayed rapid changes. In particular, because an urban area shows a remarkable initial runoff, by which pollutants are emitted at the beginning of rainfall events, a maximum outflow of pollutants occurs, which has a great impact on the downstream of urban areas [56]. However, in this study, it was found that the T-P and T-N health in the 3009 mid-subbasin, which was the most high-density urbanized area (Figure 2), improved compared to the reference year (Figure 7). The increase in the impermeable area caused a rapid increase in surface runoff and the first flush of water pollutants, which caused a decrease in infiltration and spread of groundwater depletion, preventing N and P from leaching into the soil. Similar findings are presented in some other studies. Hobbie et al. [57] confirmed that urban watersheds, characterized by high-density urbanized areas, lose phosphorus to surface runoff. Wang et al. [58] also found the effect of urbanization on stream WQ and high correlations according to the groundwater results, and that high-density urban growth was more efficient in reducing NO3-N and T-P concentration than sprawl development.
The 3013 mid-subbasin was a representative area where paddy rice fields were converted to upland cultivation area. In comparison to paddy rice fields, upland crops have different discharge characteristics due to the slope, scale, and shape of the field, as well as the characteristics of the rainfall. Because of the characteristics of the land used for paddy field, most of the upland reclamation is flat land with a slope close to 0%, so the characteristics of runoff are different from those of conventional farming on the sloping land [59]. In 3013 mid-subbasin, the amount of SQ increased while SW and GWQ decreased due to increased crop water demand (Figure 7). Compared to paddy fields, SQ health was poor due to the increase of SQ loss due to frequent water use for cultivating field crops.
SS health s rapidly became poor due to increased SQ, and the T-P and T-N health score decreased due to frequent fertilizer use (Figure 7). The results of this phenomenon are analogous to those of previous studies about crop fertilization. Jang et al. [60] reported that the reclamation of upland areas has been expanded with the use of fertilizers to improve the productivity of crops. They have since had a negative impact on WQ issues in streams and groundwater. Zhang et al. [61] point out that the factors influencing T-N in crops and paddy fields differed. This was primarily due to variations in crops and paddy fields runoff, N fertilization rates, and management strategies. Ni et al. [62] published similar findings about SS, T-P, and T-N concentration increases in crop land as a result of improvements in crop management activities, including fertilization. Pollutant content in agricultural areas is a critical environmental concern due to the high risk of pollutants reaching nearby bodies of water by leaching or runoff [63].
4.2. Assessment of WH Using MND
Hydrologists and ecologists interested in encouraging sustainable activities are heavily involved in assessing watersheds in terms of human and ecosystem health [64]. The US EPA has moved toward integrated watershed assessment at the state level; they suggested that managers use integrated watershed evaluations to help them determine WH and building priority of watersheds for protecting and restoring [17]. Ahn and Kim [18,19] have proposed an application strategy to evaluate WH in the central area of South Korea. They assessed six indices of WHIs for 237 subbasins and found that the WH decreased further downstream in the watershed. In this study, we evaluated WH according to the consequence in land use and the findings showed that WH decreases in high-density urbanized area and upland-cultivation-increased area. These results are similar to previous studies for WH evaluation. Alilou et al. [65] used fuzzy logic theory to assess WH in the Khoy watershed and suggest a method for sub-watershed prioritization. To assess WH, they focused on climate vulnerability, relative surficial rock erosion rate, topographic indexes, thirteen morphometric characteristic features, and slope-weighted K-factor possible non-point source pollution. Human-caused activities and habitat changes had degraded the WH in the Khoy watershed (e.g., such as agriculture and expanding urbanization). Moreover, Mosaffaie et al. [22] suggest a framework for assessment for the WH during 2004–2018 in the Gorganroud watershed. In this framework, the key issues for WH are the lack of soil erosion rate, supplies of groundwater, and flood capacity. According to this study, the WH of the Gorganroud watershed deteriorates gradually as a result of socioeconomic activities such as agriculture and industry. These results have clearly shown that changes in land use such as urban expansion and an increase in crop area affect watershed health. They also imply that a long-term evaluation of health is necessary.
Using the proposed previous method to calculate distributed WHIs between 0 and 1 for every analysis, it was possible to compare only the WH of each sub-watershed for every analysis. This method is effective in comparing WH among sub-watersheds in the present state. However, when the change in the watershed environment takes place over a long period of time from the past to the future, ratings change at different times. In this case, the method could not provide any reference value. This study solved this problem by ensuring that changes in WH could be absolutely analyzed by using reference values for environmental changes at different times. Reference values could be provided for analyzing WH for each period or each evaluation period. In addition, an absolute comparison could now be possible for the same watershed. Thus, the environmental change in a watershed caused by human activity could be identified and compared to past natural conditions, and influential factors on WH could be analyzed.
We found that the changing hydrology and WQ of the basin could be assessed by the health index through the absolute comparison. The results of hydrological modeling, which utilizes land use as input, were used, and the results of the land use for the homogenous year were calculated as the reference year to derive the absolute value for health. Although only land-use data were analyzed under the same meteorological conditions using SWAT modelling, it can be extended to the analysis of WH for various indicators and data, such as climate change, socioeconomic change, vulnerabilities, and recovery priorities of the basin. The derived method from this study has the advantage of being able to intuitively judge how much the current WH has improved and deteriorated compared to the past.
4.3. Limitations of this Study
Although this study selected and analyzed only two out of six subindices evaluated by existing studies, it is also possible to analyze the change in WH by comparing reference values with land cover, vegetation, stream, habitat, aquatic ecology, organic matter, and heavy metal. Based on such an analysis, decision-making data for basin management could be produced. The bias and incompleteness of WH indices will cause uncertainty for this study. Moreover, because the modeling results for reference values and the data used for identifying the change in land use contain uncertainties, additional studies are required to produce reliable evaluation results. In particular, the national portal site provides observational hydrological and WQ data for 1990 and after. If a reference value is calculated by considering the period, more reliable results regarding hydrology and WQ health can be obtained. In addition, this study did not sufficiently verify the statistical adequacy of the probability distribution method that was adopted to calculate the reference value. For this reason, various statistical methods also need to be verified. If uncertainties are improved and nationwide hydrology and WQ models are constructed on a national scale, the long-term patterns of WH in terms of hydrology and WQ could be studied.
5. Conclusions
This study was aimed at establishing a reference condition for WHI based on MND and calculated WH change by land use. Among the previous study variables, two WH evaluation indices (hydrology and WQ) were selected. The urbanized area caused a rapid increase in surface runoff and the first flush of water pollutants, which caused a decrease in infiltration and spread of groundwater depletion, limiting N and P from leaching into the soil. In upland-crop-cultivation-increased area, the amount of SQ increased while SW and GWQ decreased due to increased crop water demand. This study indicated that the health of GRB deteriorates over time as a result of human activities (i.e., urbanization and upland reclamation). The findings of this study indicate that the derived approach has the advantage of providing an absolute comparison of WH change. Based on such an analysis, it can be extended to the analysis of WH for various indicators and data, such as climate change, socioeconomic change, vulnerabilities, and recovery priorities of the basin. To conclude, this study can provide the decision-making data for basin management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and C.J.; funding acquisition, J.L. and S.K.; data curation and investigation, J.C., S.W. and Y.L.; methodology, J.L. and S.K; software, C.J.; supervision, D.P.; writing original draft, J.L.; writing—review and editing, S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) through the Aquatic Ecosystem Conservation Research Program, funded by the Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (2020003050001) and this paper was supported by Konkuk University Researcher Fund in 2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mirchooli, F.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Darvishan, A.K.; Strobl, J. Multi-dimensional assessment of watershed condition using a newly developed barometer of sustainability. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 791, 148389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Liu, J.; Savenije, H.H. A simple approach to assess water scarcity integrating water quantity and quality. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A.T.; Darabi, H.; Karimidastenaei, Z.; Davudirad, A.A.; Rouzbeh, S.; Rahmati, O.; Klöve, B. Land degradation risk mapping using topographic, human-induced, and geo-environmental variables and machine learning algorithms, for the Pole-Doab watershed, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. Streams in Mediterranean climate regions: Abiotic influences and biotic responses to predictable seasonal events. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1999, 30, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menció, A.; Mas-Pla, J. Assessment by multivariate analysis of groundwater–surface water interactions in urbanized Mediterranean streams. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, M.; Yackulic, C.B.; Lim, Y.; Arce-Nazario, J.A. Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: A multi-scale analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chadli, K.; Boufala, M.H. Assessment of water quality using Moroccan WQI and multivariate statistics in the Sebou watershed (Morocco). Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.W.; Lin, J.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Establishment of the watershed health indicators and health check of reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Sheng, Z. Assessment of water availability and scarcity based on hydrologic components in an irrigated agricultural watershed using SWAT. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2021, 57, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.M.; Hermoso, V.; Pantus, F.; Olley, J.; Linke, S.; Poff, N.L. A proposed framework to systematically design and objectively evaluate non-dominated restoration tradeoffs for watershed planning and management. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 127, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Xiang, M.; Yang, J.; Fan, W.; Yi, Y. Distributed hierarchical evaluation and carrying capacity models for water resources based on optimal water cycle theory. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.I.; Yun, J.U.; Lee, J.W. Comparative Analysis of QUAL2E. QUAL2K and CAP Steady State Water Quality Modelling Results in Downstream Areas of the Geum River, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Water Wastewater 2008, 22, 121–129. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Hascic, I.; Wu, J. Land use and watershed health in the United States. Land Econ. 2006, 82, 214–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Nazif, S. Reliability-based flood management in urban watersheds considering climate change impacts. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H. Assessing water scarcity by simultaneously considering environmental flow requirements, water quantity, and water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, W.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Evaluation method for regional water cycle health based on nature-society water cycle theory. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Identifying and Protecting Healthy Watersheds: Concepts, Assessments, and Management Approaches; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; EPA, 841-B-11-002.
- Ahn, S.R.; Kim, S.J. Assessment of integrated watershed health based on the natural environment, hydrology, water quality, and aquatic ecology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 1607, 7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, S.R.; Kim, S.J. Assessment of watershed health, vulnerability and resilience for determining protection and restoration Priorities. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbavi, Z.; Keesstra, S.D.; Nunes, J.P.; Baartman, J.E.; Gholamalifard, M.; Sadeghi, S.H. Health comparative comprehensive assessment of watersheds with different climates. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Hazbavi, Z.; Gholamalifard, M. Interactive impacts of climatic, hydrologic and anthropogenic activities on watershed health. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 648, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosaffaie, J.; Jam, A.S.; Tabatabaei, M.R.; Kousari, M.R. Trend assessment of the watershed health based on DPSIR framework. Land Use Policy 2021, 100, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, D.V.; Ahmed, N.A.; Res, B.C. Entropy expressions and their estimators for multivariate distributions, Information Theory. IEEE Trans. 1989, 35, 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacker, R.E. Using R with Multivariate Statistics; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Manly, B.F.; Alberto, J.A.N. Multivariate Statistical Methods: A Primer; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, J.Y.; Jung, C.G.; Kim, S.J. Evaluation of Land Use Change Impact on Hydrology and Water Quality Health in Geum River Basin. J. Korean Assoc. Geogr. Inf. Stud. 2019, 22, 82–96. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Williams, J.R.; Srinivasan, K.; King, W. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Manual. In Agricultural Research Service and Black land Research Center; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Temple, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R.; Kingm, K.W. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation; Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Park, Y.G.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jung, C.G. A Study on the Use of GIS-based Time Series Spatial Data for Streamflow Depletion Assessment. J. Korean Assoc. Geogr. Inf. Stud. 2018, 21, 50–63. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S. The Modified SEBAL for Mapping Daily Spatial Evapotranspiration of South Korea Using Three Flux Towers and Terra MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Jung, C.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Future Groundwater-Level Behavior Using SWAT Groundwater-Consumption Function in Geum River Basin of South Korea. Water 2019, 11, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Park, G.; Park, M.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Evaluation of non-point source pollution reduction by applying Best Management Practices using a SWAT model and QuickBird high resolution satellite imagery. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Jha, M.K. SWAT: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagó, A.; Bouraoui, F.; Vigiak, O.; Grizzetti, B.; Pastori, M. Modelling water and nutrient fluxes in the Danube River Basin with SWAT. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 603, 196–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, Y.M.; Tripathi, S.; Hantush, M.M.; Govindaraju, R.S. Watershed reliability, resilience and vulnerability analysis under uncertainty using water quality data. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 109, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, Y.M.; Raj, C.; Hantush, M.M.; Chaubey, I.; Govindaraju, R.S. How do land-use and climate change affect watershed health? A scenario-based analysis. Water Quality Expo. Health 2014, 6, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbavi, Z.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Gholamalifard, M.; Davudirad, A.A. Watershed health assessment using the pressure–state–response (PSR) framework. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Hallema, D.; Asbjornsen, H. Ecohydrological processes and ecosystem services in the Anthropocene: A review. Ecol. Process. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razali, A.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Awang, S.; Praveena, S.M.; Abidin, E.Z. Land use change in highland area and its impact on river water quality: A review of case studies in Malaysia. Ecol. Process. 2018, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.; Hao, L.; Huang, X.; Sun, L.; Sun, G. Effects of Urbanization on Watershed Evapotranspiration and Its Components in Southern China. Water 2020, 12, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, J.R. Joseph Fourier, the ‘greenhouse effect’, and the quest for a universal theory of terrestrial temperatures. Endeavour 1999, 23, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broecker, W. Climatic change: Are we on the brink of a pronounced global warming. Science 1975, 189, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Hu, C.; Ma, B.; Mu, X. Rapid Urbanization Impact on the Hydrological Processes in Zhengzhou, China. Water 2020, 12, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oni, S.K.; Futter, M.N.; Buttle, J.; Dillon, P. Hydrological footprints of urban developments in the Lake Simcoe watershed, Canada: A combined paired-catchment and change detection modelling approach. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1829–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Gao, S.; Tong, L.; Qiu, F.; Yan, H. Spatio-temporal Differentiation and Driving Factors of Industrial Ecology of Restricted Development Zone from Adaptive Perspective: A Case Study of Shandong, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, K.; Shabnam, S.; Das, S.; Mitran, T. Assessment of Urban Sprawl Impact on Agricultural Land Use Using Geospatial Techniques. In Geospatial Technologies for Crops and Soils; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 489–521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.X.; Liu, J.E.; Qin, P. Impacts of an alien species (Spartina alterniflora) on the macrobenthos community of Jiangsu coastal inter-tidal ecosystem. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.C.; Versace, V.L.; Lester, R.E.; Walter, M.T. Assessing the impact of drought and forestry on streamflows in south-eastern Australia using a physically based hydrological model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6047–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zuo, Q.; Shao, Q. A new framework for assessing river ecosystem health with consideration of human service demand. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 640, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Li Liu, D.; Zhang, M.; Leslie, L.M.; Yu, Q. Using an improved SWAT model to simulate hydrological responses to land use change: A case study of a catchment in tropical Australia. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Shao, Q.; Zuo, Q.; Cui, Y. Impact of land use and urbanization on river water quality and ecology in a dam dominated basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, J. Hydrological response to urbanization at different spatio-temporal scales simulated by coupling of CLUE-S and the SWAT model in the Yangtze River Delta region. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.D.; Du, J.K.; Song, M.M.; Xu, Y.P.; Xie, S.P.; Zheng, W.L.; Xu, C.Y. A procedure for quantifying runoff response to spatial and temporal changes of impervious surface in Qinhuai River basin of southeastern China. Catena 2017, 157, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, J.; Gosain, A.K.; Khosa, R. Prediction of land use changes based on Land Change Modeler and attribution of changes in the water balance of Ganga basin to land use change using the SWAT model. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 644, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghsaei, H.; Dinan, N.M.; Moridi, A.; Asadolahi, Z.; Delavar, M.; Fohrer, N.; Wagner, P.D. Effects of dynamic land use/land cover change on water resources and sediment yield in the Anzali wetland catchment, Gilan, Iran. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 712, 136449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, B.; Harbor, J.O.N.; Engel, B.; Grove, M. Assessing watershed-scale, long-term hydrologic impacts of land-use change using a GIS-NPS model. Environ. Manag. 2000, 26, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, S.E.; Finlay, J.C.; Janke, B.D.; Nidzgorski, D.A.; Millet, D.B.; Baker, L.A. Contrasting nitrogen and phosphorus budgets in urban watersheds and implications for managing urban water pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4177–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Kim, J.H.; Li, M.H. Predicting stream water quality under different urban development pattern scenarios with an interpretable machine learning approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 761, 144057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Oh, C.; Choi, S.K.; Na, C.I.; Hwang, S. Monitoring the Hydrologic Water Quality Characteristics of Discharge from a Flat Upland Field. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 62, 109–121. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.S.; Ahn, S.R.; Kim, S.J. Evaluation of executable best management practices in Haean highland agricultural catchment of South Korea using SWAT. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 180, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yao, M.; Zhou, J.; Wu, K.; Hu, M.; Shen, D.; Chen, D. Estimation of nitrogen runoff loss from croplands in the Yangtze River Basin: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Parajuli, P.B.; Ouyang, Y.; Dash, P.; Siegert, C. Assessing land use change impact on stream discharge and stream water quality in an agricultural watershed. Catena 2021, 198, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Yang, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, Q.; Bai, J.; Hao, F.; Wu, L. Phosphorus risk in an intensive agricultural area in a mid-high latitude region of China. Catena 2015, 127, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranagalage, M.; Estoque, R.C.; Zhang, X.; Murayama, Y. Spatial Changes of Urban Heat Island Formation in the Colombo District, Sri Lanka: Implications for Sustainability Planning. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alilou, H.; Rahmati, O.; Singh, V.P.; Choubin, B.; Pradhan, B.; Keesstra, S.; Sadeghi, S.H. Evaluation of watershed health using Fuzzy-ANP approach considering geo-environmental and topo-hydrological criteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).