The Holocene Evolution of the Volturno Coastal Plain (Northern Campania, Southern Italy): Implications for the Understanding of Subsidence Patterns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
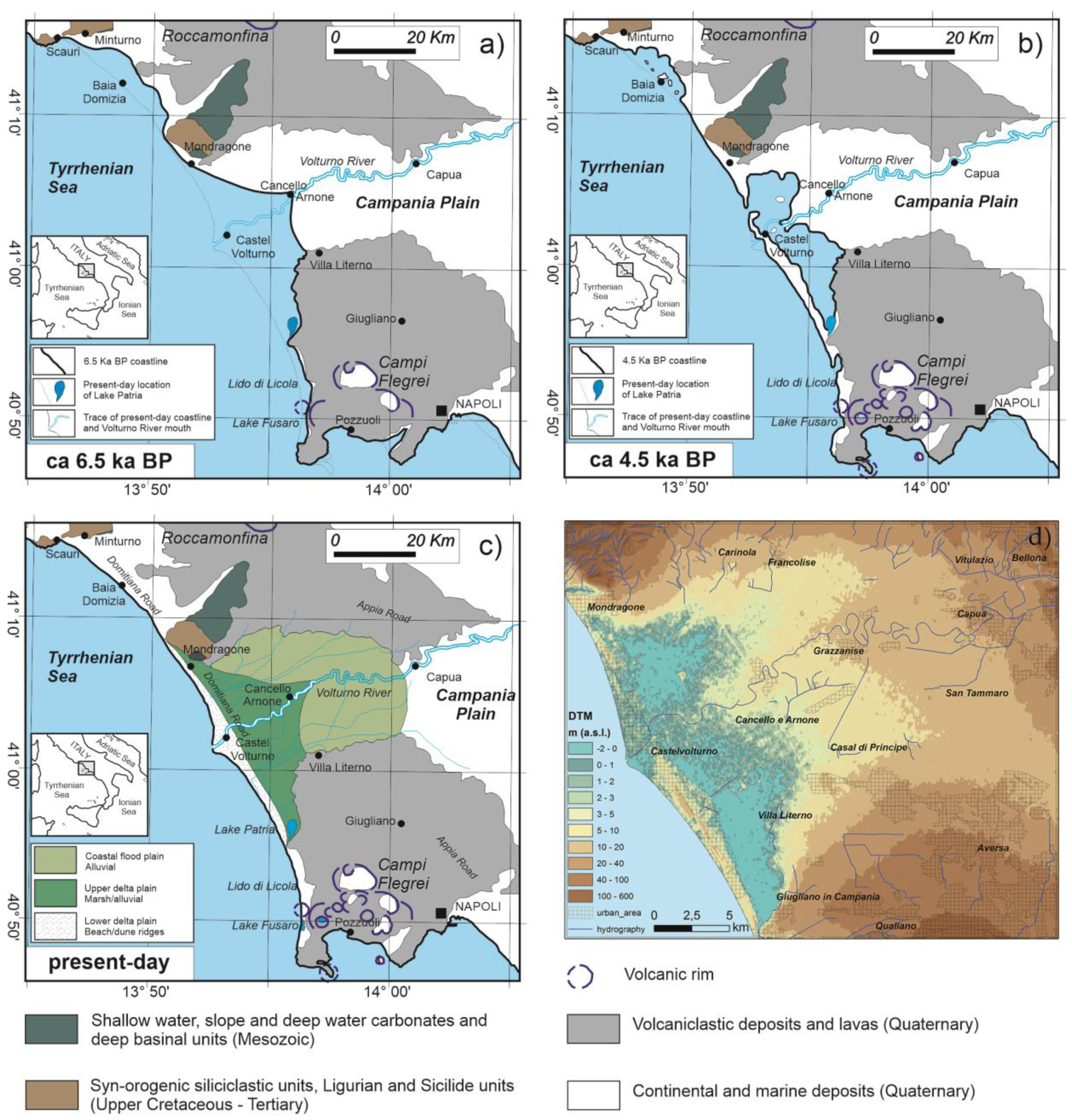
2. Geological Setting
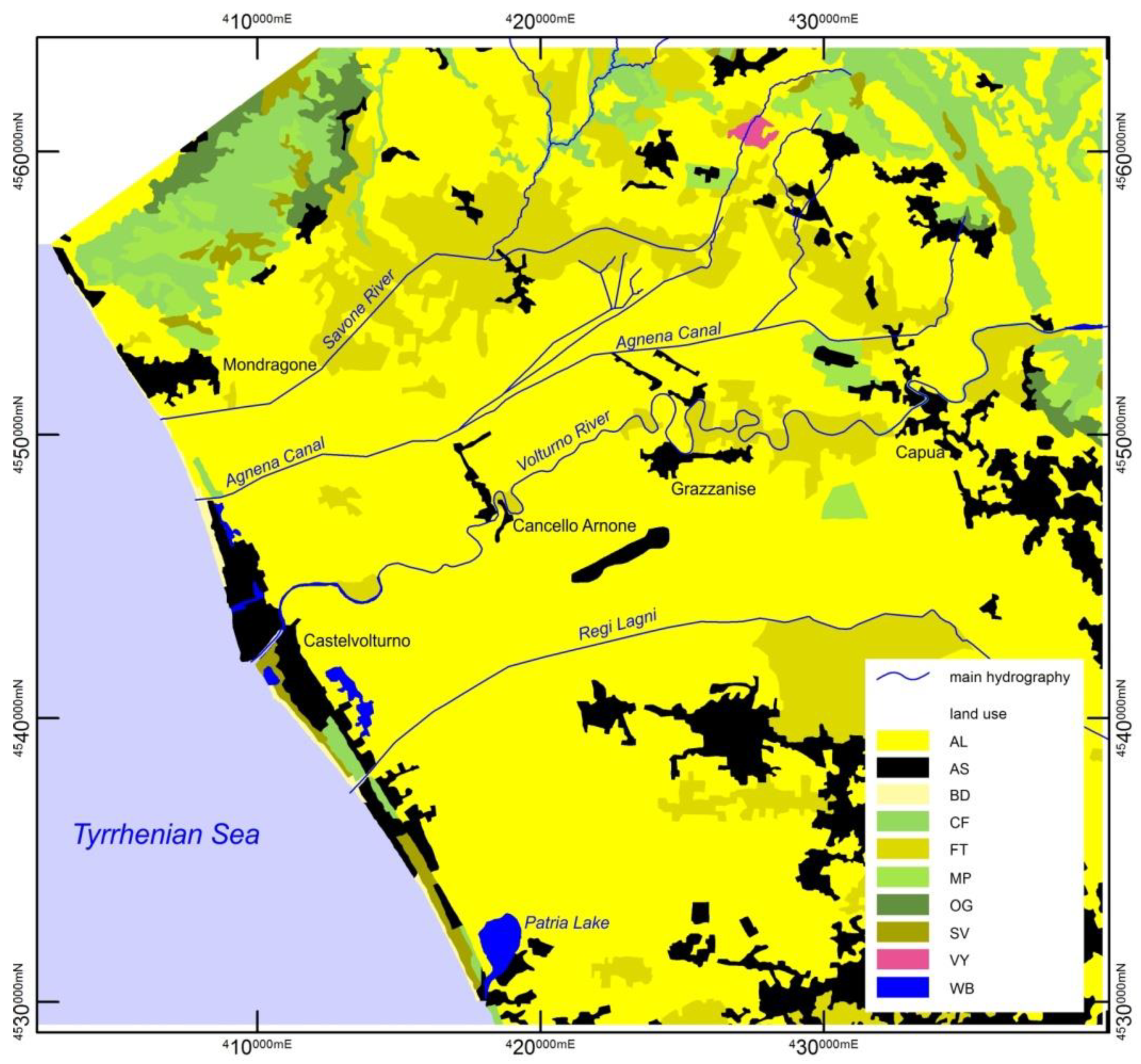
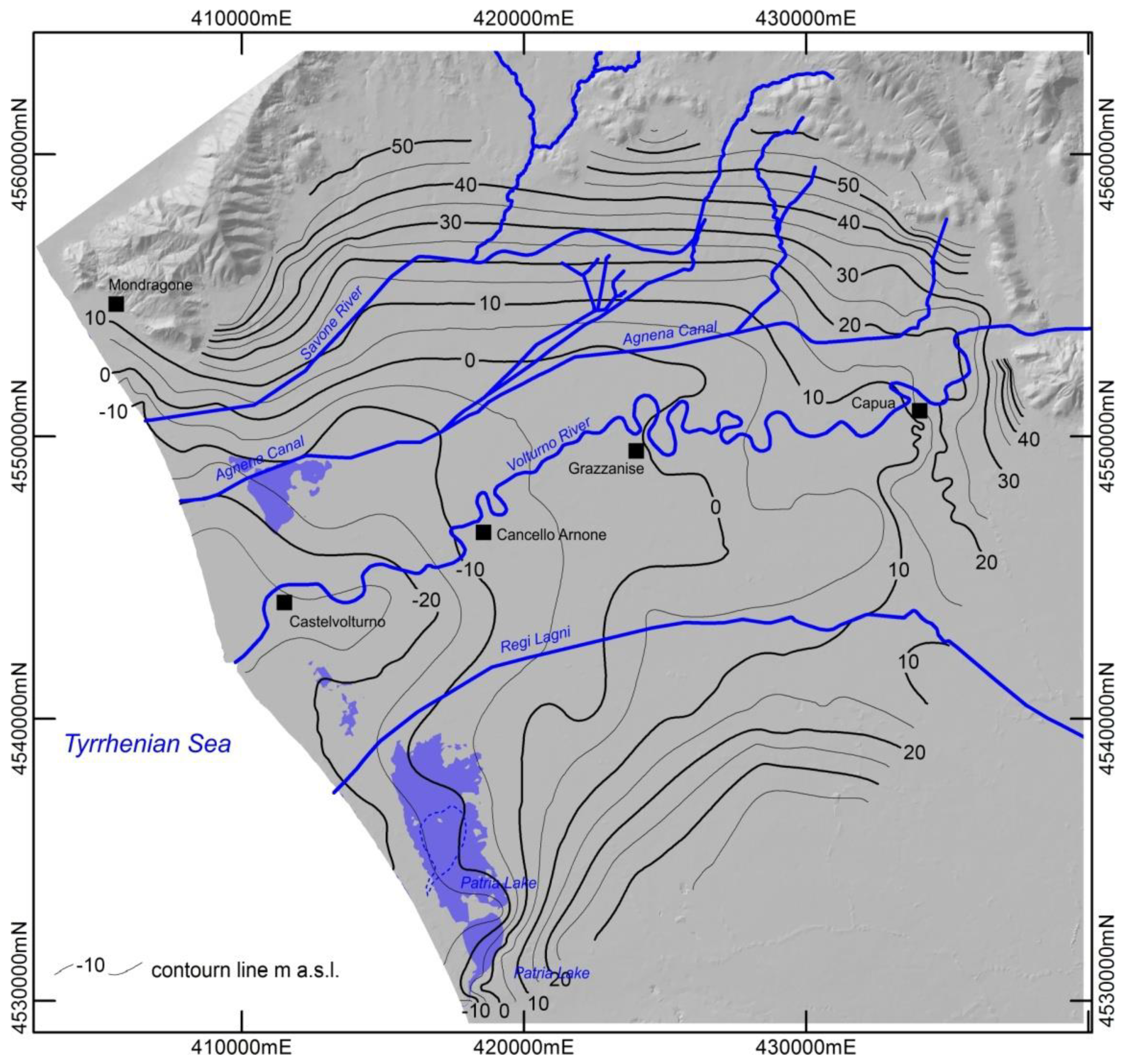
Geomorphology of the Plain and Land Use
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
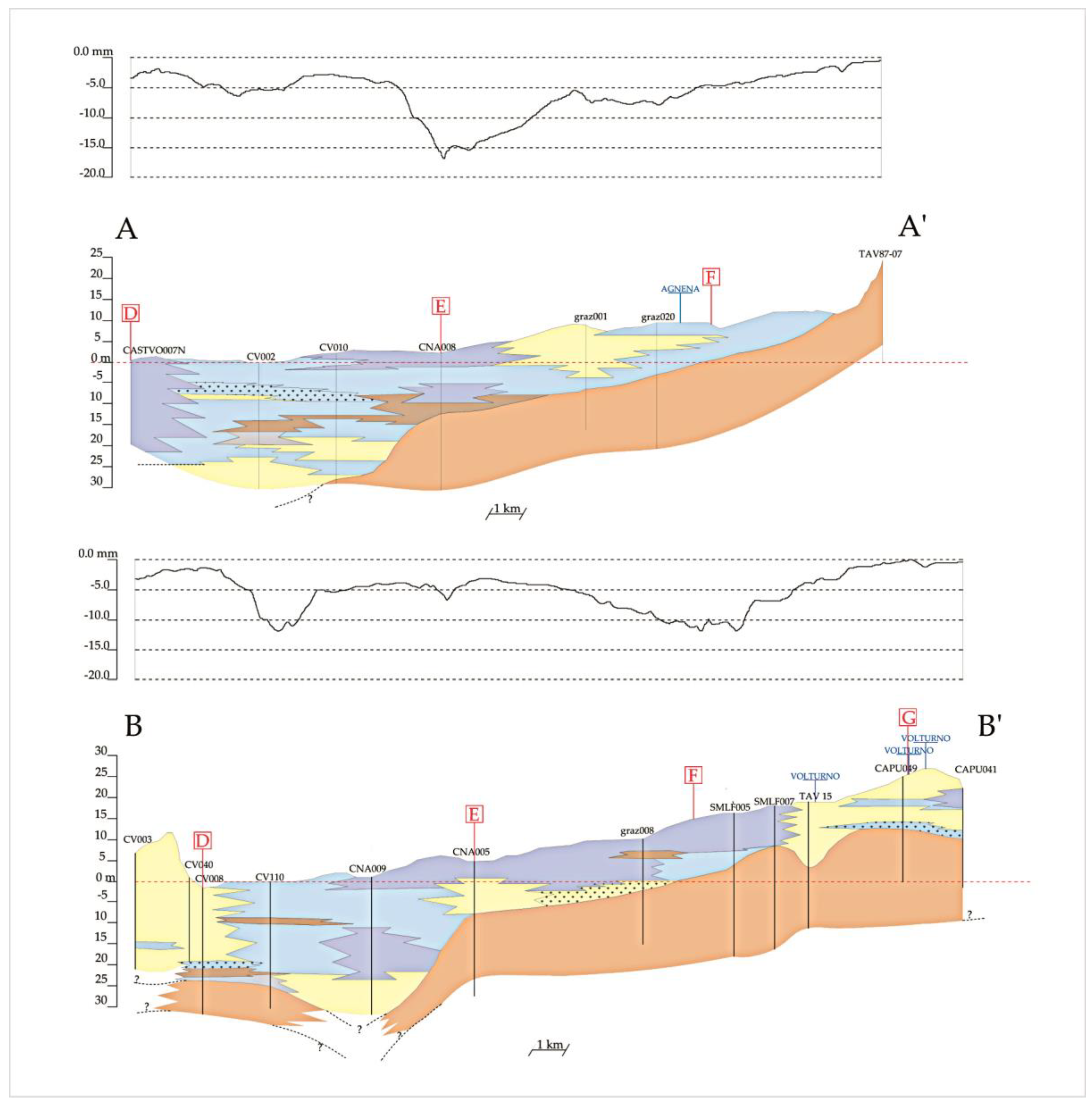
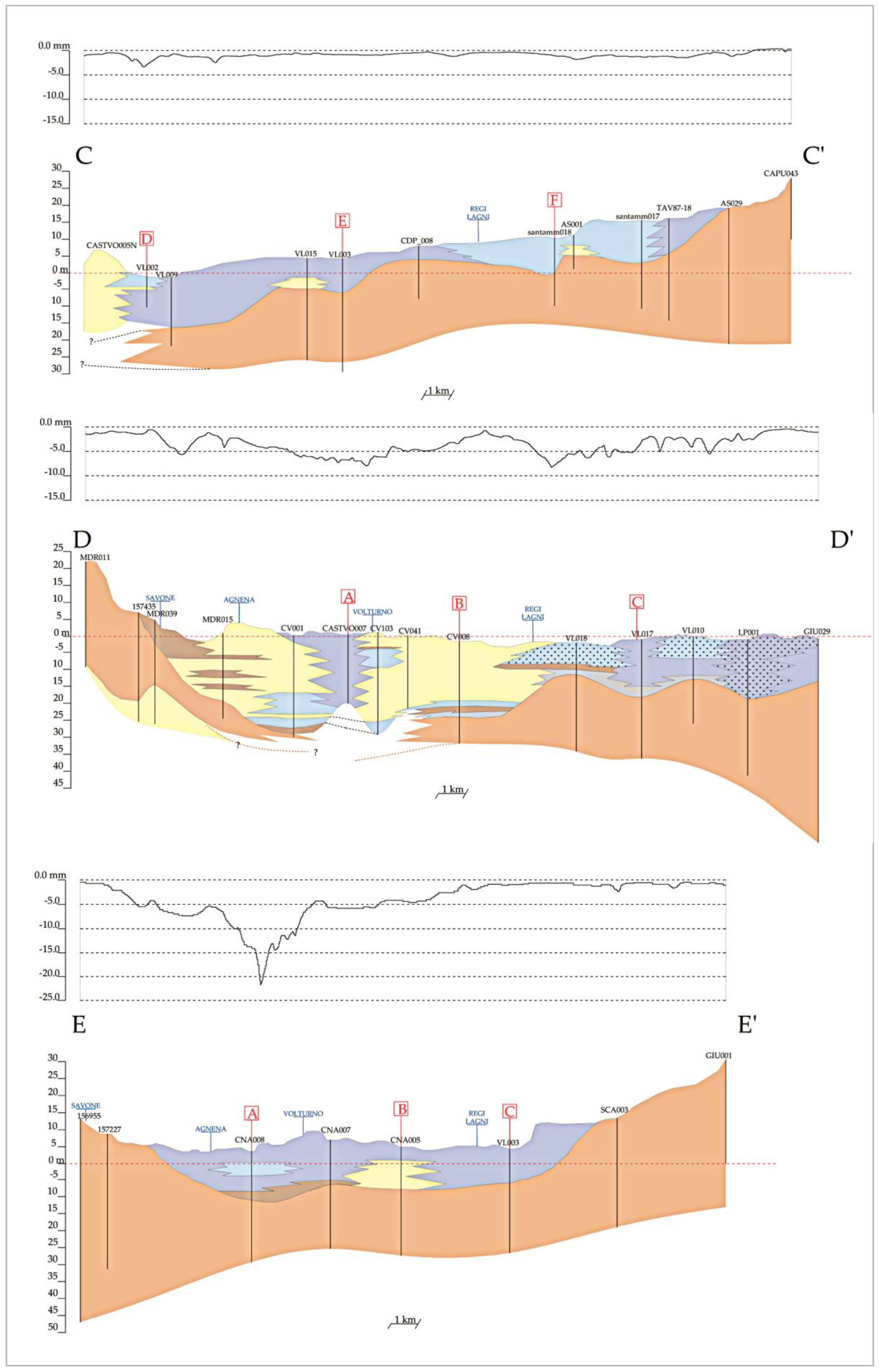
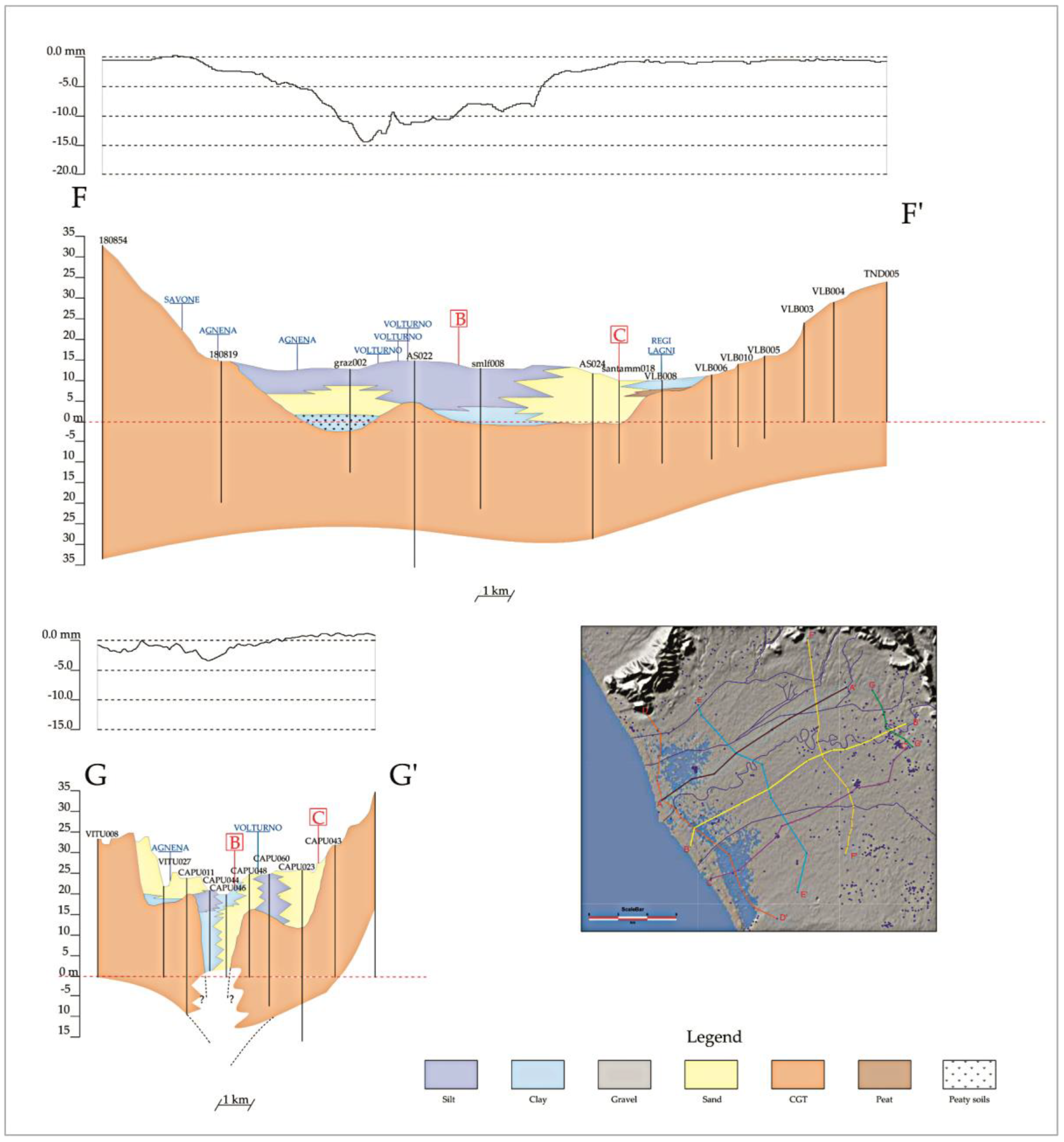
4.1. Subsoil Architecture
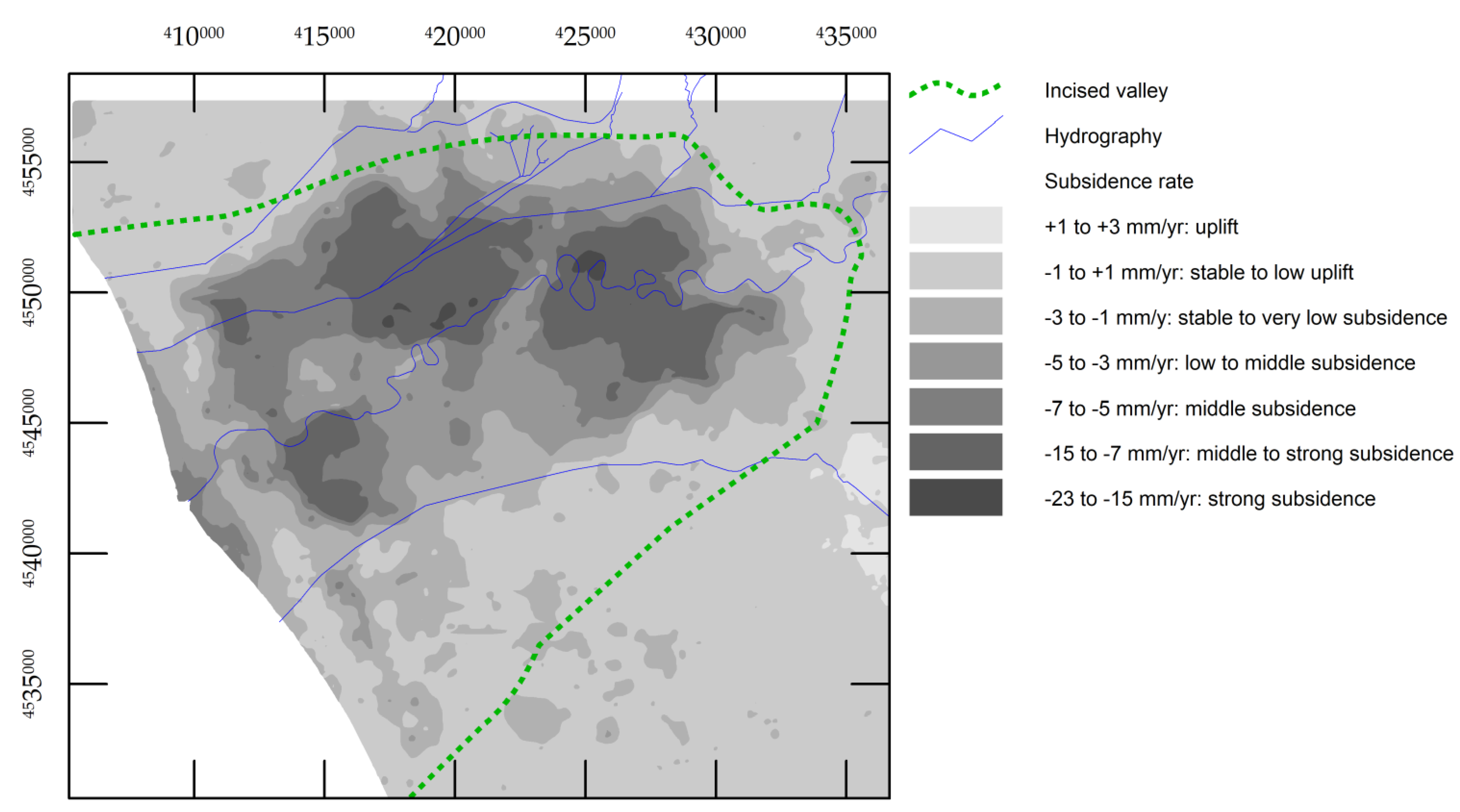
4.2. Vertical Ground Displacement
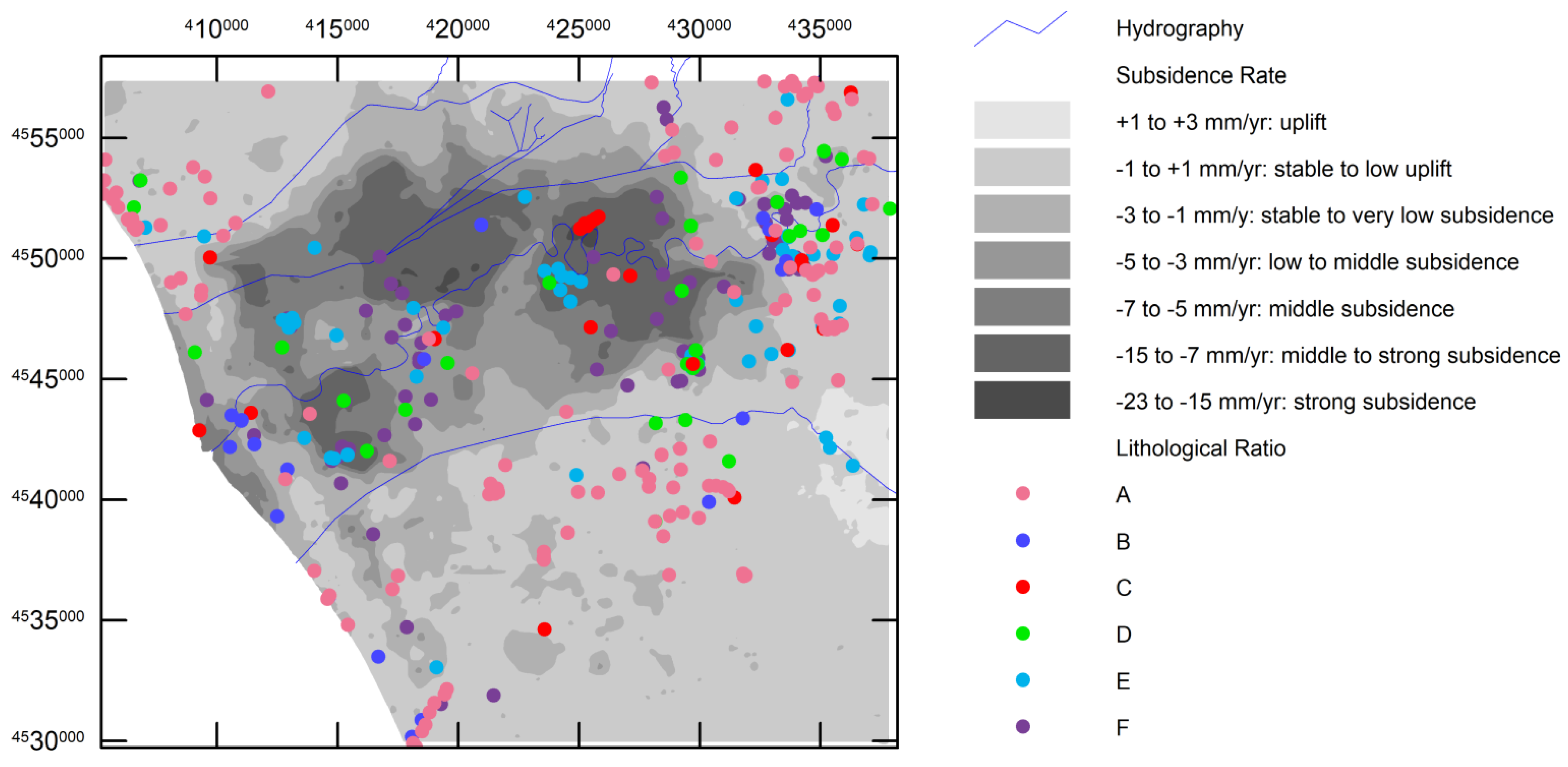
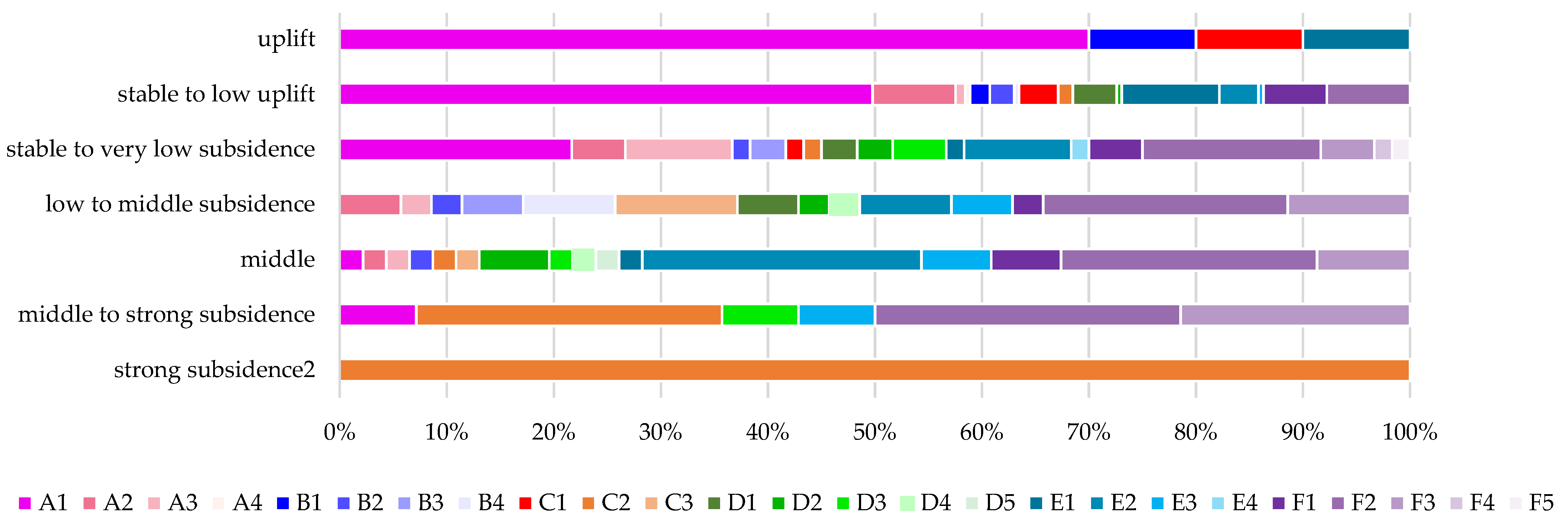
4.3. Subsidence vs. Stratigraphic Structure
5. Discussion
5.1. Geological Subsoil Model
5.2. Subsidence vs. Geology
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warrick, R.A.; Provost, C.L.; Meier, M.F.; Oerlemans, J.; Woodworth, P.L. Changes in sea level. In Houghton; Meira Filho, L.G., Houhton, J.T., Callander, B.A., Harris, N., Klattenberg, A., Maskell, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 359–405. [Google Scholar]
- Lambeck, K.; Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Ferranti, L.; Leoni, G.; Scicchitano, G.; Silenzi, S. Sea level change along the Italian coast during the Holocene and projections for the future. Quat. Int. 2011, 232, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkens, G.; Bucx, T.; Dam, R.; De Lange, G.; Lambert, J. Sinking coastal cities. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, S.A. Review: Advances in delta-subsidence research using satellite methods. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 24, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.; Yuill, B.; Törnqvist, T.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.; Erkens, G.; Stuurman, R.; Jones, C.; Milne, G.; Steckler, M.; et al. Global risks and research priorities for coastal subsidence. Eos 2016, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, J.F.; Davis, G.H. Land subsidence due to withdrawal of fluids. In Reviews in Engineering Geology; Varnes, D.J., Kiersch, G., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1969; Volume 2, pp. 187–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.; Waller, M.; Stupples, P. Driving mechanisms of coastal change: Peat compaction and the destruction of late Holocene coastal wetlands. Mar. Geol. 2006, 225, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Heller, P. Plate tectonics and basin subsidence history. GSA Bull. 2006, 19, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrio, C.J.; Zazo, C.; Goy, J.L.; Sierro, F.; Borja, F.; Lario, J.; A González, J.; A Flores, J. Depositional history of estuarine infill during the last postglacial transgression (Gulf of Cadiz, Southern Spain). Mar. Geol. 2000, 162, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wellner, R.W.; Bartek, L.R. The effect of sea level, climate, and shelf physiography on the development of incised-valley complexes: A modern example from the East China sea. J. Sediment. Res. 2003, 73, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Tanabe, S.; Saito, Y.; Haruyama, S.; Nguyen, V.; Kitamura, A. Delta initiation and Holocene sea-level change: Example from the Song Hong (Red River) delta, Vietnam. Sediment. Geol. 2004, 164, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.D.; Tomkin, J.H.; Purcell, A.; Lancaster, R.R. Ups and downs of the mississippi delta. Geology 2008, 36, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Rossi, V.; Sarti, G.; Mattei, R. Coalescent valley fills from the late quaternary record of tuscany (Italy). Quat. Int. 2013, 288, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, R.W.; Zaitlin, B.A.; Boyd, R. Estuarine facies models; conceptual basis and stratigraphic implications. J. Sediment. Res. 1992, 62, 1130–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckel, T.A.; Brink, U.S.T.; Williams, S.J. Current subsidence rates due to compaction of Holocene sediments in southern Louisiana. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckel, T.A.; Brink, U.S.T.; Williams, S.J. Sediment compaction rates and subsidence in deltaic plains: Numerical constraints and stratigraphic influences. Basin Res. 2007, 19, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massey, A.C.; Paul, M.A.; Gehrels, W.R.; Charman, D.J. Autocompaction in Holocene coastal back-barrier sediments from south Devon, southwest England, UK. Mar. Geol. 2006, 226, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnqvist, T.E.; Wallace, D.J.; Storms, J.E.; Wallinga, J.; van Dam, R.; Blaauw, M.; Derksen, M.S.; Klerks, C.J.W.; Meijneken, C.; Snijders, E.M.A. Mississippi delta subsidence primarily caused by compaction of Holocene strata. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, D.; You, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, O. Land subsidence as a result of sediment consolidation in the Yellow River Delta. J. Coast Res. 2007, 23, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Van Asselen, S. The contribution of peat compaction to total basin subsidence: Implications for the provision of accom-modation space in organic-rich deltas. Basin Res. 2011, 23, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, A.L. Peat Accumulation and Compaction in a Connecticut Coastal Marsh. J. Sediment. Res. 1964, 34, 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Van Asselen, S.; Stouthamer, E.; van Asch, T.W. Effects of peat compaction on delta evolution: A review on processes, responses, measuring and modeling. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 92, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, K.; Erkens, G.; Zwanenburg, C. A new soil mechanics approach to quantify and predict land subsidence by peat compression. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10792–10799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruno, L.; Campo, B.; Di Martino, A.; Hong, W.; Amorosi, A. Peat layer accumulation and post-burial deformation during the mid-late Holocene in the Po coastal plain (Northern Italy). Basin Res. 2019, 31, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckel, T. An attempt to reconcile subsidence rates determined from various techniques in southern Louisiana. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-García, G.; Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; López-Vinielles, J.; Rossi, M.; Mateos, R.M.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Lambert, J.; Teatini, P.; et al. Mapping the global threat of land subsidence. Science 2021, 371, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, F.; Sacchi, M.; Vigliotti, M.; Ruberti, D. Subsidence trends of volturno river coastal plain (Northern Campania, Southern Italy) Inferred by SAR Interferometry Data. Geosci. 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amorosi, A.; Pacifico, A.; Rossi, V.; Ruberti, D. Late quaternary incision and deposition in an active volcanic setting: The Volturno valley fill, southern Italy. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 282, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Molisso, F.; Pacifico, A.; Vigliotti, M.; Sabbarese, C.; Ruberti, D. Late-Holocene to recent evolution of Lake Patria, South Italy: An example of a coastal lagoon within a Mediterranean delta system. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 117, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberti, D.; Vigliotti, M.; Rolandi, R.; Di Lascio, M. Effect of paleomorphology on facies distribution of the campania ignimbrite in the northern campania plain, southern Italy. In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism; De Vivo, B., Belkin, H.E., Rolandi, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberti, D.; Sacchi, M.; Pepe, F.; Vigliotti, M. LGM incised valley in a volcanic setting. The northern campania plain (Southern Italy). In Alpine and Mediterranean Quaternary. In Proceedings of the Quaternary: Past, Present, Future—AIQUA Conference, Florence, Italy, 13–14 June 2018; pp. 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti, D.; Vigliotti, M. Land use and landscape pattern changes driven by land reclamation in a coastal area: The case of Volturno delta plain, Campania Region, southern Italy. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocicco, M.; Busico, G.; Colombani, N.; Vigliotti, M.; Ruberti, D. Modelling actual and future seawater intrusion in the variconi coastal wetland (Italy) due to climate and landscape changes. Water 2019, 11, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donadio, C.; Vigliotti, M.; Valente, R.; Stanislao, C.; Ivaldi, R.; Ruberti, D. Anthropic vs. natural shoreline changes along the northern Campania coast, Italy. J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 22, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberti, D.; Vigliotti, M.; Di Mauro, A.; Chieffi, R.; Di Natale, M. Human influence over 150 years of coastal evolution in the Volturno delta system (southern Italy). J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 22, 897–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberti, D.; Vigliotti, M.; Marzaioli, R.; Pacifico, A.; Ermice, A. Stratigraphic architecture and anthropic impacts on subsoil to assess the intrinsic potential vulnerability of groundwater: The northeastern Campania plain case study, southern Italy. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolani, F.; Aprile, F. Principali caratteristiche stratigrafiche e strutturali dei depositi superficiali della Piana Campana. Boll. Soc. Geol. Itl. 1985, 104, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, S.A.; Overeem, I.; Steckler, M.S.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Seeber, L.; Akhter, S.H. InSAR measurements of compaction and subsidence in the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, Bangladesh. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.E.; An, K.; Blom, R.G.; Kent, J.D.; Ivins, E.R.; Bekaert, D. Anthropogenic and geologic influences on subsidence in the vicinity of New Orleans, Louisiana. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 3867–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, L.; Campo, B.; Costagli, B.; Stouthamer, E.; Teatini, P.; Zoccarato, C.; Amorosi, A. Factors controlling natural subsidence in the Po Plain. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 382, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, T.; Xu, Y.; Tosi, L.; Stouthamer, E.; Andreas, H.; Minderhoud, P.; Ladawadee, A.; Hanssen, R.; Erkens, G.; et al. Advances and Practices on the Research, Prevention and Control of Land Subsidence in Coastal Cities. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolini, A.; Picarelli, L.; Viggiani, C. Un rilevato sperimentale su terreni limo-argillosi organici di origine palustre. Riv. Geoteeniea Ital. 1989, 3, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Riccio, T. Analysis of Subsidence in Campania Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”, Aversa, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti, D.; Mandolini, A.; Matano, F.; Picarelli, L.; Sacchi, M.; Vigliotti, M. Holocene stratigraphic architecture and current land subsidence of the Volturno coastal plain (northern Campania, southern Italy). J. Mediterr. Earth Sci. 2017, 9, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Phien-Wej, N.; Giao, P.H.; Nutalaya, P. Land subsidence in Bangkok, Thailand. Eng. Geol. 2006, 82, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolunghi, M.P.; Capelli, G.; Funiciello, R.; Lanzini, M. Geotechnical studies for foundation settlement in Holocenic alluvialdeposits in the city of Rome (Italy). Eng. Geol. 2007, 89, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Tosi, L.; Strozzi, T. Quantitative evidence that compaction of Holocene sediments drives the present land sub-sidence of the Po Delta, Italy. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Tosi, L.; Strozzi, T.; Carbognin, L.; Cecconi, G.; Rosselli, R.; Libardo, S. Resolving land subsidence within the Venice Lagoon by persistent scatterer SAR interferometry. Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 40, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, G.; Rossi, V.; Amorosi, A. Influence of Holocene stratigraphic architecture on ground surface settlements: A case study from the City of Pisa (Tuscany, Italy). Sediment. Geol. 2012, 281, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, K.; Stafleu, J.; Cohen, K.; Stouthamer, E.; Busschers, F.; Middelkoop, H. Three-dimensional distribution of organic matter in coastal-deltaic peat: Implications for subsidence and carbon dioxide emissions by human-induced peat oxidation. Anthropocene 2018, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | Easting | Northing | Total Thickness | Tuff Thickness | POST-CGT | Peat Thickness | Clay Thickness | Clay and Peat Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDR039 | 2,429,487.28 | 4,550,926.81 | 19.00 | 12.00 | 7.00 | 4.20 | 0.00 | 4.20 |
| CV106 | 2,435,452.90 | 4,542,001.03 | 31.00 | 1.50 | 29.50 | 0.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 |
| CV010 | 2,434,970.05 | 4,546,819.03 | 28.70 | 0.00 | 28.70 | 0.20 | 17.50 | 17.70 |
| LR | Thickness (m) |
|---|---|
| A | 0.00 |
| B | 0.00–0.20 |
| C | 0.20–0.40 |
| D | 0.40–0.60 |
| E | 0.60–0.85 |
| F | 0.85–1.00 |
| TC | Thickness Range (m) |
|---|---|
| P1 | 0–10 |
| P2 | 10–20 |
| P3 | 20–30 |
| P4 | 30–50 |
| P5 | 50–80 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Tot. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 148 | 26 | 15 | 1 | 190 | |
| B | 5 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 23 | |
| C | 13 | 12 | 5 | 30 | ||
| D | 15 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 30 |
| E | 29 | 29 | 7 | 1 | 66 | |
| F | 20 | 55 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 92 |
| Tot | 230 | 137 | 53 | 9 | 2 | 431 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buffardi, C.; Barbato, R.; Vigliotti, M.; Mandolini, A.; Ruberti, D. The Holocene Evolution of the Volturno Coastal Plain (Northern Campania, Southern Italy): Implications for the Understanding of Subsidence Patterns. Water 2021, 13, 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192692
Buffardi C, Barbato R, Vigliotti M, Mandolini A, Ruberti D. The Holocene Evolution of the Volturno Coastal Plain (Northern Campania, Southern Italy): Implications for the Understanding of Subsidence Patterns. Water. 2021; 13(19):2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192692
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuffardi, Carla, Regina Barbato, Marco Vigliotti, Alessandro Mandolini, and Daniela Ruberti. 2021. "The Holocene Evolution of the Volturno Coastal Plain (Northern Campania, Southern Italy): Implications for the Understanding of Subsidence Patterns" Water 13, no. 19: 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192692
APA StyleBuffardi, C., Barbato, R., Vigliotti, M., Mandolini, A., & Ruberti, D. (2021). The Holocene Evolution of the Volturno Coastal Plain (Northern Campania, Southern Italy): Implications for the Understanding of Subsidence Patterns. Water, 13(19), 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192692







