Identifying the Mechanisms behind the Positive Feedback Loop between Nitrogen Cycling and Algal Blooms in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Field Surveys
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Sediment Profile Measurements
2.3.1. In Situ Measurements
2.3.2. DGT Probe Measurements of Ammonium, Nitrate, and Fe (II)
2.3.3. HR-Peeper Probes for Nitrite and DOM Measurements
2.4. Ex Situ Measurements of Denitrifier Abundance and Microbial Composition
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water and Sediment Physicochemical Profiles
3.2. Sediment NO and N2O Profiles
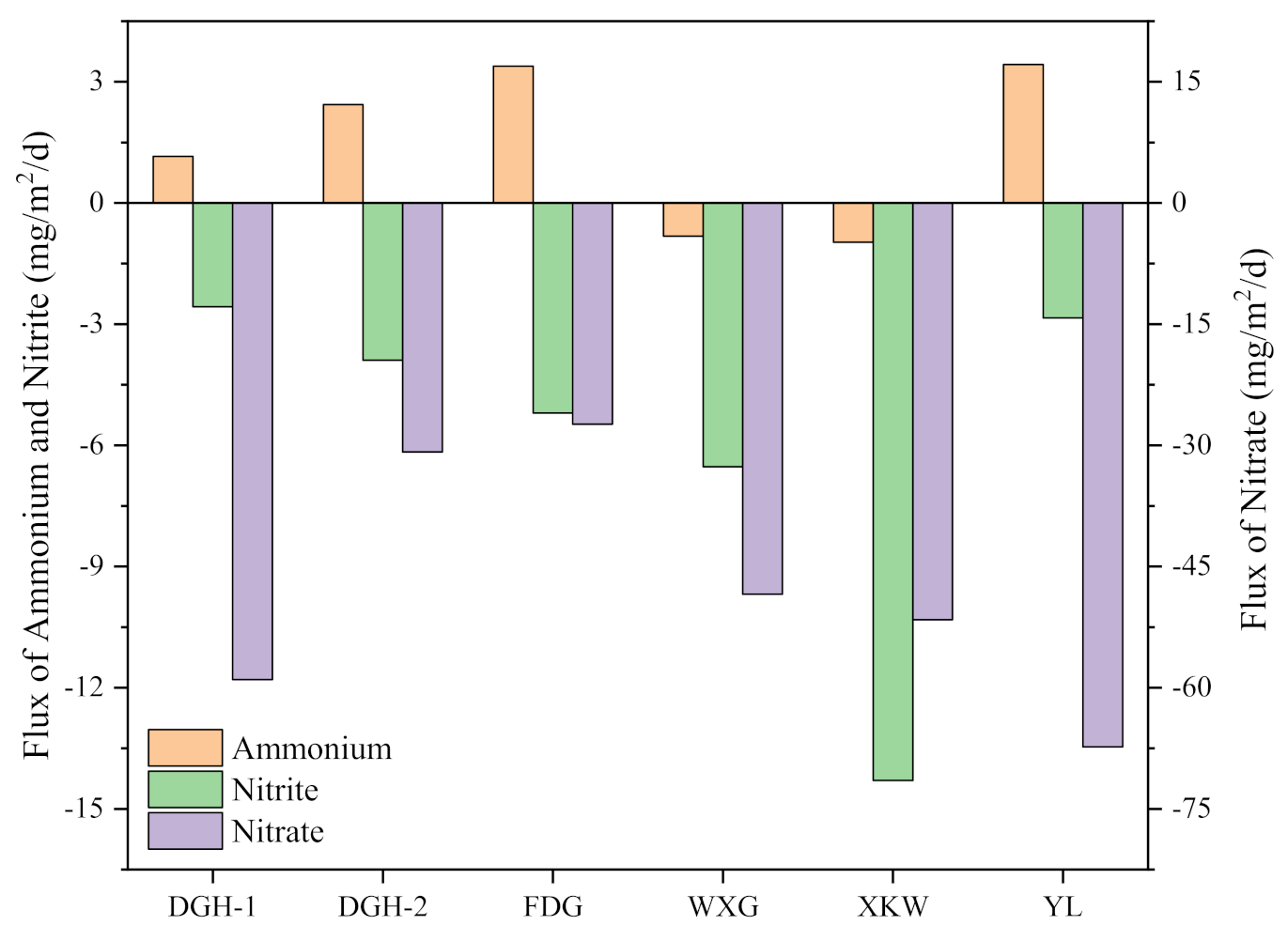
3.3. Sediment NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and NO2−-N Profiles
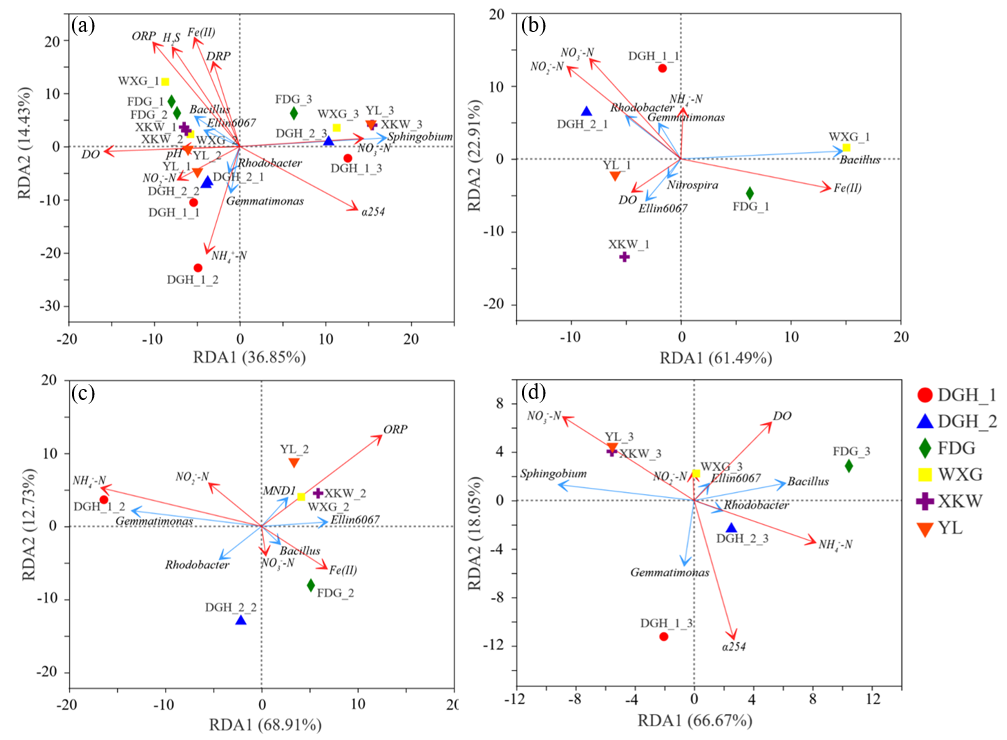
3.4. Sediment Taxonomic Composition of Microbial Communities
3.5. Sediment DOM Profiles
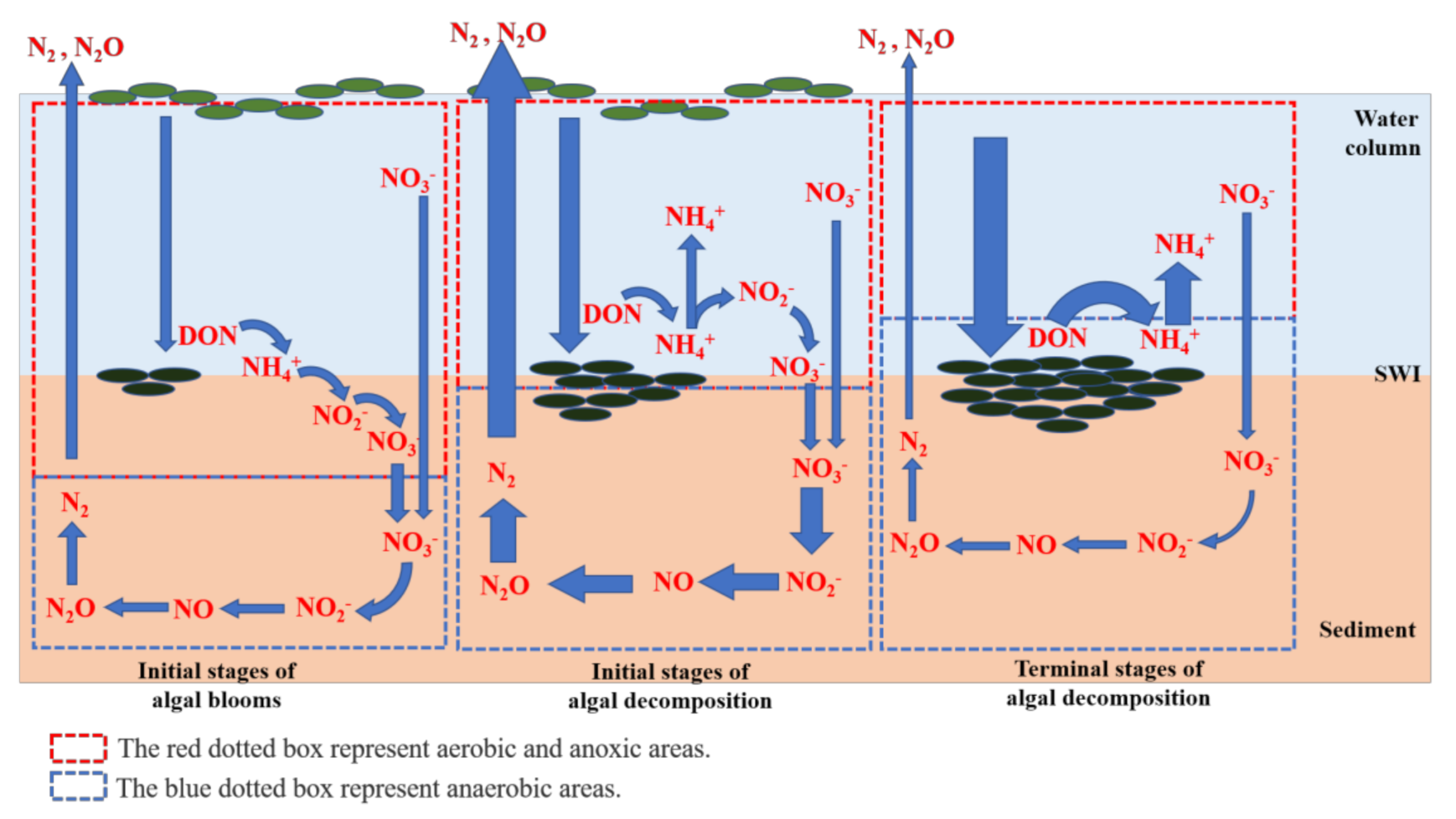
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Moal, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Ménesguen, A.; Souchon, Y.; Étrillard, C.; Levain, A.; Moatar, F.; Pannard, A.; Souchu, P.; Lefebvre, A.; et al. Eutrophication: A new wine in an old bottle? Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 651, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to Climatic Variability and Lake Management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinçon-Leite, B.; Casenave, C. Modelling eutrophication in lake ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 651, 2985–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Mun, H.; Shin, H.; Park, S.; Yu, C.; Lee, J.; Yoon, Y.; Chung, H.; Yun, H.; Lee, K.; et al. Nitrogen Stimulates Microcystis-Dominated Blooms More than Phosphorus in River Conditions That Favor Non-Nitrogen-Fixing Genera. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7185–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, G.P.; Sarnelle, O.; White, J.D.; Hamilton, S.K.; Kaul, R.B.; Bressie, J.D. Nitrogen availability increases the toxin quota of a harmful cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res. 2014, 54, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salk, K.R.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.L.; Chaffin, J.D.; Ostrom, N.E. Nitrogen cycling in Sandusky Bay, Lake Erie: Oscillations between strong and weak export and implications for harmful algal blooms. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2891–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shatwell, T.; Köhler, J. Decreased nitrogen loading controls summer cyanobacterial blooms without promoting nitrogen-fixing taxa: Long-term response of a shallow lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 64, S166–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Gao, H.; Glibert, P.M.; Wang, Y.; Tong, M. Rates of nitrogen uptake by cyanobacterially-dominated assemblages in Lake Taihu, China, during late summer. Harmful Algae 2017, 65, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, J. Emerging role of dissolved organic nitrogen in supporting algal bloom persistence in Lake Taihu, China: Emphasis on internal transformations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Brookes, J.D.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Gao, G.; Wu, P.; Zhang, W.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Environmental factors controlling colony formation in blooms of the cyanobacteria Microcystis spp. in Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Könneke, M.; Bernhard, A.E.; De La Torre, J.R.; Walker, C.B.; Waterbury, J.B.; Stahl, D.A. Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 437, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitzinger, S.P. Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: Ecological and geochemical significance. Limnology Oceanography 1988, 33, 702–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, P.; Miao, L.; Fan, X.; You, G.; Xu, Y. Effects of Ag and Ag2S nanoparticles on denitrification in sediments. Water Res. 2018, 137, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valett, H.M.; Thomas, S.A.; Mulholland, P.J.; Webster, J.R.; Dahm, C.N.; Fellows, C.S.; Crenshaw, C.L.; Peterson, C.G. Endogenous and exogenous control of ecosystem function: N cycling in headwater streams. Ecology 2008, 89, 3515–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Brookes, J.D.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Feng, J. Spatial distribution of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Taihu from a hydrodynamics-induced transport perspective. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 650, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, L. Molecular size-dependent abundance and composition of dissolved organic matter in river, lake and sea waters. Water Res. 2017, 117, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Gao, G.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Shao, K.; Hu, Y. Denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in freshwater lakes of the Eastern Plain, China: Influences of organic carbon and algal bloom. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 710, 136303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Kong, F. Bacterial community dynamics and functional variation during the long-term decomposition of cyanobacterial blooms in-vitro. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shi, W.; Van Dam, B.; Kong, L.; Yu, J.; Qin, B. Algal Accumulation Decreases Sediment Nitrogen Removal by Uncoupling Nitrification-Denitrification in Shallow Eutrophic Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6194–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolle, D.; Zhu, G.; Hamilton, D.; Luo, L.; McBride, C.; Zhang, L. The influence of water quality and sediment geochemistry on the horizontal and vertical distribution of phosphorus and nitrogen in sediments of a large, shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 2009, 627, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hollstein, M.; Podder, A.; Gupta, V.; Barber, M.; Goel, R. Cyanotoxin impact on microbial-mediated nitrogen trans-formations at the interface of sediment-water column in surface water bodies. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, M.; Chen, M.; Fan, X.; Lichtfouse, E. Diffusive gradients in thin films: Devices, materials and applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 801–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnken, K.W.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W. Accuracy of the Diffusive Gradients in Thin-Films Technique: Diffusive Boundary Layer and Effective Sampling Area Considerations. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3780–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Zhang, L.; Fang, J.; Lei, B.; Tang, X.C.; Huang, H.X.; Wang, Z.S.; Si, Z.J.; Wang, G.X. Benthic cyanobacterial detritus mats in lacustrine sediment: Characterization and odorant producing potential. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sima, W.; Hu, M.; He, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Dai, L.; Shao, Q.; Zhou, T.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.; et al. Regulation of nitrogen dynamics at the sediment-water interface during HAB degradation and subsequent reoccurrence. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13480–13488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, G.; Qin, B. Influence of algal bloom degradation on nutrient release at the sediment–water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.A.; Audet, J.; Svenning, J.-C.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Søndergaard, M.; Landkildehus, F.; Larsen, S.E.; Jeppesen, E. Eutrophication effects on greenhouse gas fluxes from shallow-lake mesocosms override those of climate warming. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 4449–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Han, R.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, G. Isotopic evidence revealing spatial heterogeneity for source and composition of sedimentary organic matters in Taihu Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lyu, H.; Li, Y.; Bi, S.; Xu, J.; Lei, S.; Mu, M.; Wang, Q. A Semianalytical Algorithm for Mapping Proportion of Cyanobacterial Biomass in Eutrophic Inland Lakes Based on OLCI Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2020, 58, 5148–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.; Kjær, T.; Revsbech, N.P. An oxygen insensitive microsensor for nitrous oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 81, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, P.; Nygren, A.; Revsbech, N.P.; Ulfendahl, H.R. Measurements of oxygen tension in the rat kidney after contrast media using an oxygen microelectrode with a guard cathode. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1997, 411, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabouille, C.; Denis, L.; Dedieu, K.; Stora, G.; Lansard, B.; Grenz, C. Oxygen demand in coastal marine sediments: Comparing in situ microelectrodes and laboratory core incubations. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 285, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.L.M.; Revill, A.T.; Butler, E.C.V.; Eyre, B.D. Carbon and nitrogen cycling on intertidal mudflats of a temperate Australian estuary. II. Nitrogen cycling. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 280, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elberling, B.; Christiansen, H.H.; Hansen, B.U. High nitrous oxide production from thawing permafrost. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, D.; Han, C.; Zhang, C. Iron-coupled inactivation of phosphorus in sediments by macrozoobenthos (chironomid larvae) bioturbation: Evidences from high-resolution dynamic measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.S.; Ding, S.M.; Wu, Y.X.; Fan, X.F.; Jin, Z.F.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.S. Phosphorus mobilization in lake sediments: Experimental evidence of strong control by iron and negligible influences of manganese redox reactions. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Chen, Y.; Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ding, D. Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films Technique Equipped with a Mixed Binding Gel for Simultaneous Measurements of Dissolved Reactive Phosphorus and Dissolved Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10477–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Gao, S.; Fu, Z.; Tang, W.; Wu, Y.; Gong, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Efficacy of dredging engineering as a means to remove heavy metals from lake sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, C.; Tsang, D.C.W. Synergistic adsorption of phosphorus by iron in lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock (R)): New insight into sediment phosphorus immobilization. Water Res. 2018, 134, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wu, W.; Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, C. A high-resolution dialysis technique for rapid determination of dissolved reactive phosphate and ferrous iron in pore water of sediments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 422, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; Bru, D.; Stres, B.; Hallet, S.; Philippot, L. Quantitative Detection of the nosZ Gene, Encoding Nitrous Oxide Reductase, and Comparison of the Abundances of 16S rRNA, narG, nirK, and nosZ Genes in Soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5181–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, B.; Zhong, J.; Fan, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S. Effects of hydrodynamics processes on phosphorus fluxes from sediment in large, shallow Taihu Lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Osburn, C.L.; Shin, K.H.; Hur, J. New insight into the applicability of spectroscopic indices for dissolved organic matter (DOM) source discrimination in aquatic systems affected by biogeochemical processes. Water Res. 2018, 147, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittar, T.B.; Stubbins, A.; Vieira, A.A.H.; Mopper, K. Characterization and photodegradation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) from a tropical lake and its dominant primary producer, the cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.H.; Hur, J. Utilization of UV-Vis spectroscopy and related data analyses for dissolved organic matter (DOM) studies: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Yang, L.; Hur, J. Lipid biomarkers and spectroscopic indices for identifying organic matter sources in aquatic environments: A review. Water Res. 2017, 112, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Han, R.; Huang, Z.; Luo, L.; Cao, D.; Zhang, S. Relationship between Molecular Components and Reducing Capacities of Humic Substances. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2018, 2, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Baudon, A.; Chow, A. Improved Fluorescence Excitation-Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Fluorescent Dissolved Organic Matter. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, G.; Dong, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, R.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, K.; et al. Multivariate relationships between microbial communities and environmental variables during co-composting of sewage sludge and agricultural waste in the presence of PVP-AgNPs. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Xiao, L. The roles of cyanobacterial bloom in nitrogen removal. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 609, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Yin, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J. Littoral zones as the “hotspots” of nitrous oxide (N2O) emission in a hyper-eutrophic lake in China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5522–5527. [Google Scholar]





| Sample Sites | pH | ORP (mV) | DO (µM L−1) | NH4+-N (mg L−1) | NO3−-N (mg L−1) | NO2−-N (mg L−1) | SRP (mg L−1) | Chl-a (μg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XKW | 6.95 | 464.28 | 252.76 | 0.20 | 3.78 | 1.29 | 2.63 | 8.23 |
| WXG | 7.73 | 491.38 | 245.48 | 0.18 | 3.71 | 1.24 | 5.63 | 53.04 |
| DGH-1 | 6.65 | 141.01 | 230.25 | 0.23 | 3.83 | 1.25 | 1.21 | 61.63 |
| DGH-2 | 7.74 | 140.12 | 210.56 | 0.11 | 3.84 | 1.26 | 1.78 | 38.22 |
| FDG | 7.3 | 219.10 | 260.58 | 0.22 | 2.84 | 1.26 | 1.31 | 64.98 |
| YL | 7.91 | 382.43 | 244.13 | 0.16 | 4.34 | 1.30 | 0.99 | 43.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Liu, H.; Han, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, L. Identifying the Mechanisms behind the Positive Feedback Loop between Nitrogen Cycling and Algal Blooms in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake. Water 2021, 13, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040524
Yao Y, Liu H, Han R, Li D, Zhang L. Identifying the Mechanisms behind the Positive Feedback Loop between Nitrogen Cycling and Algal Blooms in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake. Water. 2021; 13(4):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040524
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yu, Huaji Liu, Ruiming Han, Dujun Li, and Limin Zhang. 2021. "Identifying the Mechanisms behind the Positive Feedback Loop between Nitrogen Cycling and Algal Blooms in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake" Water 13, no. 4: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040524
APA StyleYao, Y., Liu, H., Han, R., Li, D., & Zhang, L. (2021). Identifying the Mechanisms behind the Positive Feedback Loop between Nitrogen Cycling and Algal Blooms in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake. Water, 13(4), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040524







