Effects of Grazing and Nutrients on Phytoplankton Blooms and Microplankton Assemblage Structure in Four Temperate Lakes Spanning a Eutrophication Gradient
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
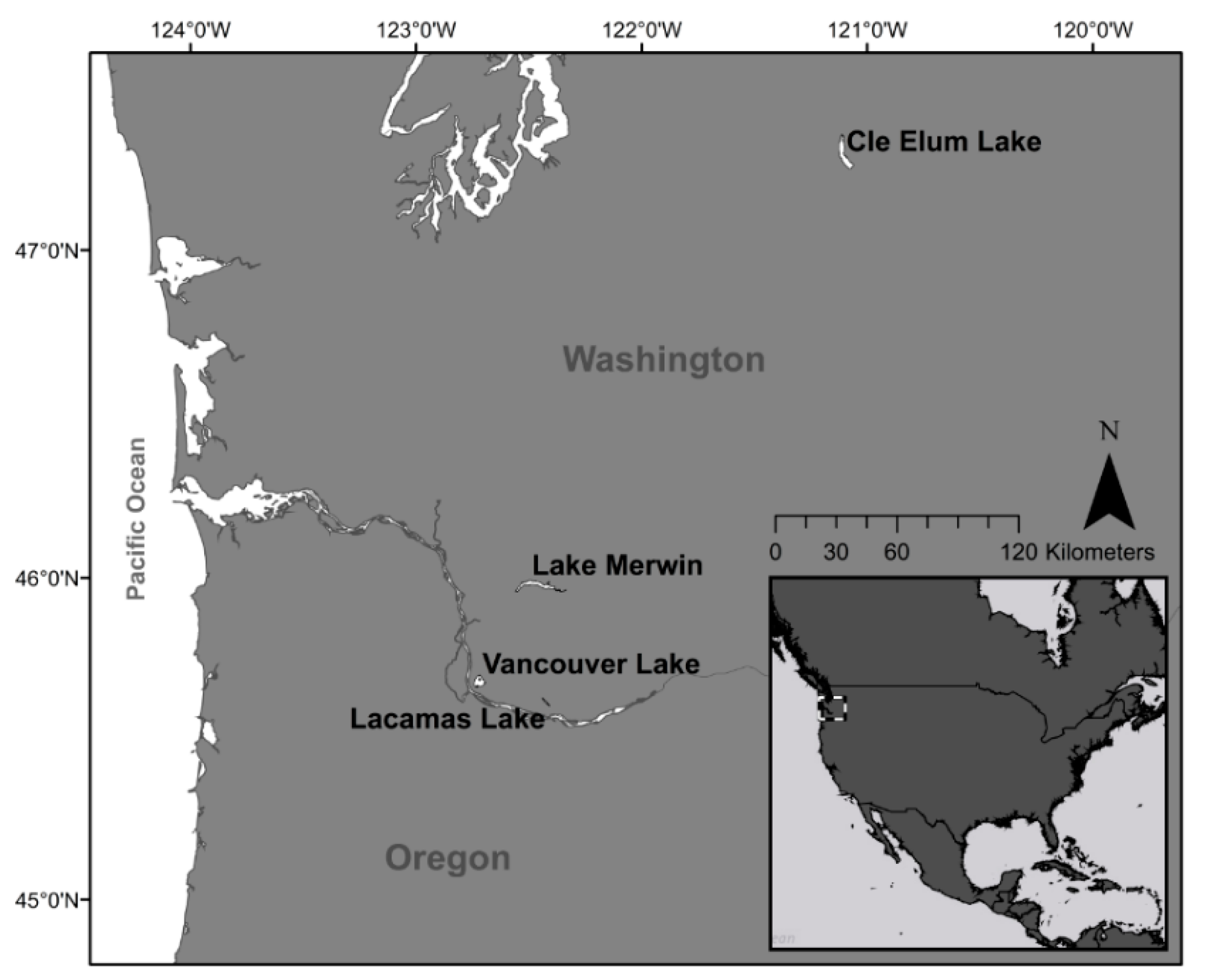
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. Grazing and Nutrient Enhancement Experiments
2.4. Taxonomic Enumeration and Identification
2.5. Rate Calculations and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Field Observations
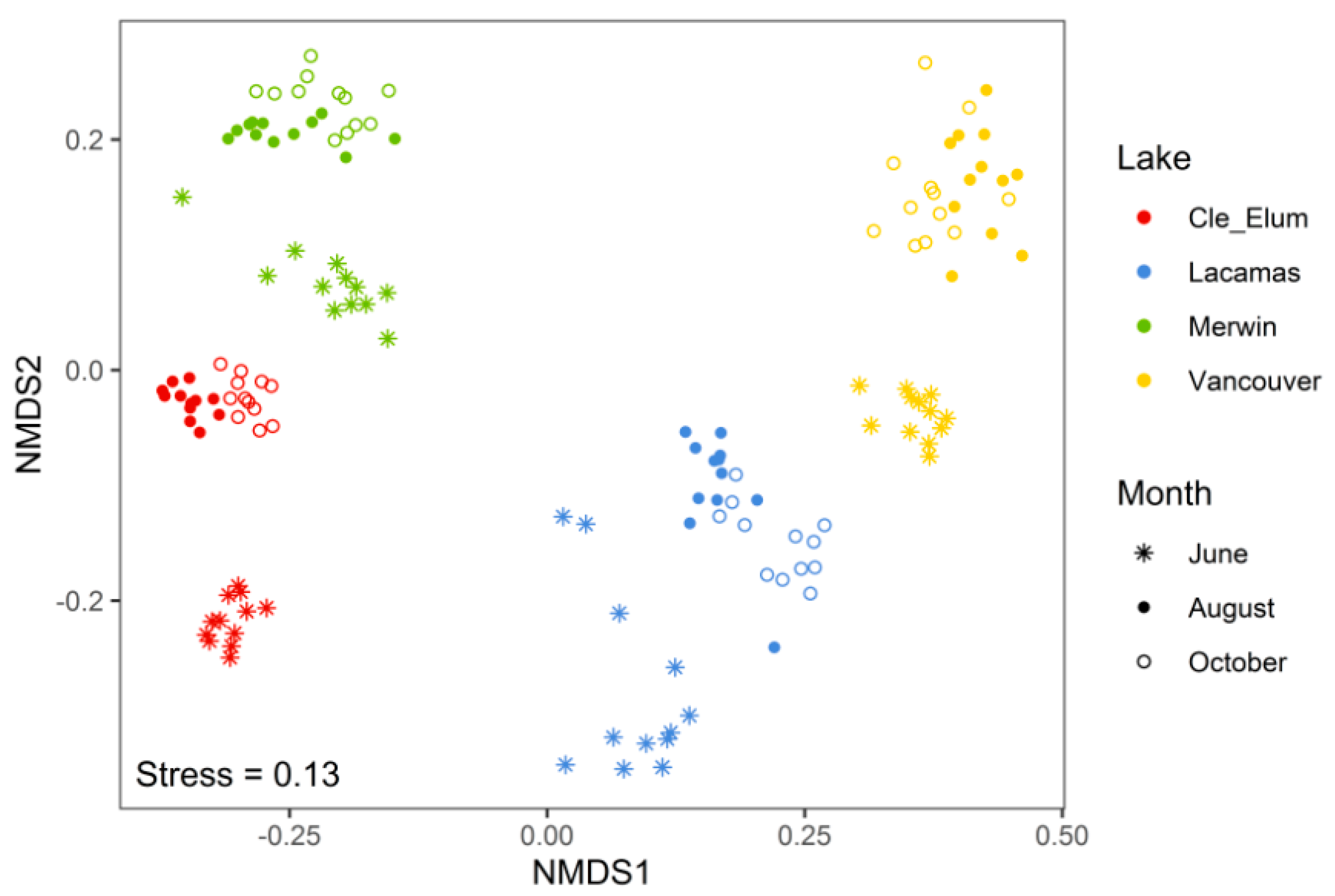
3.2. Succession of Microplankton and Zooplankton Assemblage Structure
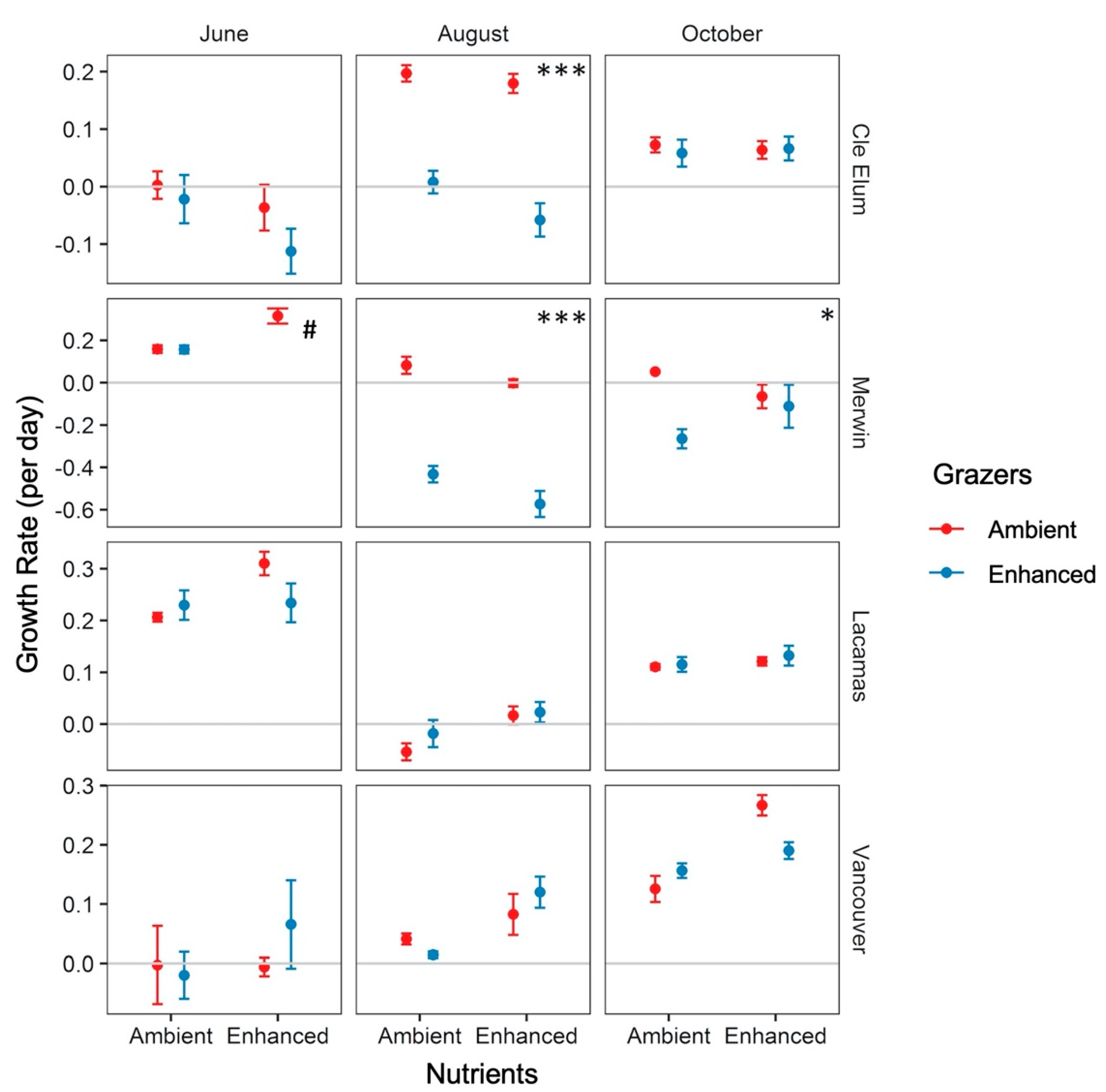
3.3. Responses to Grazer and Nutrient Enhancement
4. Discussion
4.1. Microplankton Assemblage Structure across Lakes of Varying Trophic State
4.2. Effects of Enhanced Grazing and Enhanced Nutrients on Microplankton Assemblages
4.3. Effects of Enhanced Grazing (“Top Down”) and Nutrients (“Bottom Up”) on Phytoplankton Growth
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeppesen, E.; Moss, B.; Bennion, H.; Carvalho, L.; DeMeester, L.; Feuchtmayr, H.; Friberg, N.; Gessner, M.; Hefting, M.; Lauridsen, T.; et al. Interaction of Climate Change and Eutrophication. In Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Ecosystems; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4443-2739-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, E.M.; McKnight, D.M.; Lewis, W.M.; Miller, M.P. Effects of Nutrient Enrichment on Phytoplankton in an Alpine Lake, Colorado, USA. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2008, 40, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havens, K.E. Cyanobacteria Blooms: Effects on Aquatic Ecosystems. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 619, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Davis, T.W.; Orr, P.T.; Sinha, R.; Willis, A.; Neilan, B.A. Nutrient-Related Changes in the Toxicity of Field Blooms of the Cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McQueen, D.J.; Johannes, M.R.S.; Post, J.R.; Stewart, T.J.; Lean, D.R.S. Bottom-Up and Top-Down Impacts on Freshwater Pelagic Community Structure. Ecol. Monogr. 1989, 59, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Peder Jensen, J.; SØndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Landkildehus, F. Trophic Structure, Species Richness and Biodiversity in Danish Lakes: Changes along a Phosphorus Gradient: A Detailed Study of Danish Lakes along a Phosphorus Gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; García-Berthou, E.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z. Analyzing the Importance of Top-down and Bottom-up Controls in Food Webs of Chinese Lakes through Structural Equation Modeling. Aquat. Ecol. 2015, 49, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Resource Competition and Community Structure; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1982; ISBN 978-0-691-08302-5. [Google Scholar]
- Interlandi, S.J.; Kilham, S.S. Limiting Resources and the Regulation of Diversity in Phytoplankton Communities. Ecology 2001, 82, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. The Ecology of Phytoplankton (Ecology, Biodiversity and Conservation); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Glibert, P.M. Margalef Revisited: A New Phytoplankton Mandala Incorporating Twelve Dimensions, Including Nutritional Physiology. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, J.A. Productivity of freshwater ecosystems and climate change. In Global Environmental Change; Handbook of Global Environmental Pollution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial Blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms in a World Experiencing Anthropogenic and Climatic-Induced Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosten, S.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Bécares, E.; Costa, L.S.; Donk, E.; Hansson, L.-A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kruk, C.; Lacerot, G.; Mazzeo, N.; et al. Warmer Climates Boost Cyanobacterial Dominance in Shallow Lakes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The Rise of Harmful Cyanobacteria Blooms: The Potential Roles of Eutrophication and Climate Change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Risk Management for Health Protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Al osman, M.; Yang, F. An Overview on Cyanobacterial Blooms and Toxins Production: Their Occurrence and Influencing Factors. Toxin Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Cole, J.J.; Hodgson, J.R.; Kitchell, J.F.; Pace, M.L.; Bade, D.; Cottingham, K.L.; Essington, T.E.; Houser, J.N.; Schindler, D.E. Trophic Cascades, Nutrients, and Lake Productivity: Whole-Lake Experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 2001, 71, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knisely, K.; Geller, W. Selective Feeding of Four Zooplankton Species on Natural Lake Phytoplankton. Oecologia 1986, 69, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, U.; Sommer, F. Cladocerans versus Copepods: The Cause of Contrasting Top–down Controls on Freshwater and Marine Phytoplankton. Oecologia 2006, 147, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampert, W.; Fleckner, W.; Rai, H.; Taylor, B.E. Phytoplankton Control by Grazing Zooplankton: A Study on the Spring Clear-Water Phase1: Spring Clear-Water Phase. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1986, 31, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Adrian, R.; De Senerpont Domis, L.; Elser, J.J.; Gaedke, U.; Ibelings, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Lürling, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Mooij, W.M.; et al. Beyond the Plankton Ecology Group (PEG) Model: Mechanisms Driving Plankton Succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U. Trophic Cascades in Marine and Freshwater Plankton. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.; Gonzalez, A.; Zimmerman, J.; Lee, T.; Emerson, J. Feeding Dynamics of the Copepod Diacyclops Thomasi before, during and Following Filamentous Cyanobacteria Blooms in a Large, Shallow Temperate Lake. Hydrobiologia 2013, 705, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Lee, T.; Rose, V.; Bollens, S. Beyond Eutrophication: Vancouver Lake, WA, USA as a Model System for Assessing Multiple, Interacting Biotic and Abiotic Drivers of Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms. Water 2018, 10, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epp, G.T. Grazing on Filamentous Cyanobacteria by Daphnia Pulicaria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Ekvall, M.K.; Hansson, L.-A. Controlling Harmful Cyanobacteria: Taxa-Specific Responses of Cyanobacteria to Grazing by Large-Bodied Daphnia in a Biomanipulation Scenario. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, A.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M.; Zimmerman, J. Feeding of the Invasive Copepod Pseudodiaptomus Forbesi on Natural Microplankton Assemblages within the Lower Columbia River. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ger, K.A.; Naus-Wiezer, S.; De Meester, L.; Lürling, M. Zooplankton Grazing Selectivity Regulates Herbivory and Dominance of Toxic Phytoplankton over Multiple Prey Generations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Physical Determinants of Phytoplankton Succession. In Plankton Ecology; Brock/Springer Series in Contemporary Bioscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.S. The Ecology of Phytoplankton. Available online: /core/books/the-ecology-of-phytoplankton/7E14FD43792ECC717C9E90E3519A1803 (accessed on 17 March 2018).
- Sterner, R.W. The Role of Grazers in Phytoplankton Succession. In Plankton Ecology: Succession in Plankton Communities; Sommer, U., Ed.; Brock/Springer Series in Contemporary Bioscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 107–170. ISBN 978-3-642-74890-5. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.S. The Ecological Basis for the Successful Biomanipulation of Aquatic Communities. Arch. Fur Hydrobiol. 1994, 130, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Benndorf, J.; Böing, W.; Koop, J.; Neubauer, I. Top-down Control of Phytoplankton: The Role of Time Scale, Lake Depth and Trophic State: Top-down Control of Phytoplankton. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 2282–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, D.G. Top-down versus Bottom-up Control in Planktonic Systems: Some Case Studies from the English Lake District. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A Trophic State Index for Lakes1: Trophic State Index. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratzer, C.; Brezonik, P. A Calrson-Type Tropic State Index for Nitrogen in Florida Lakes. Water Resour. Bull. 1981, 17, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Cole, J.J. Expanding the Concept of Trophic State in Aquatic Ecosystems: It’s Not Just the Autotrophs. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naselli-Flores, L.; Barone, R. Phytoplankton Dynamics and Structure: A Comparative Analysis in Natural and Man-Made Water Bodies of Different Trophic State. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliwicz, Z.M. Why Do Cladocerans Fail to Control Algal Blooms? Hydrobiologia 1990, 200–201, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Goldman, C.R. Zooplankton Effects on Phytoplankton in Lakes of Contrasting Trophic Status. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, L.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Ordoñez, J.; Armengol, J. Phytoplankton Distribution along Trophic Gradients within and among Reservoirs in Catalonia (Spain). Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Sommer, F.; Santer, B.; Jamieson, C.; Boersma, M.; Becker, C.; Hansen, T. Complementary Impact of Copepods and Cladocerans on Phytoplankton. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zöllner, E.; Santer, B.; Boersma, M.; Hoppe, H.-G.; Jürgens, K. Cascading Predation Effects of Daphnia and Copepods on Microbial Food Web Components: Zooplankton Impact on Microbial Food Web. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 2174–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.A.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M. The Influence of Water Quality Variables on Cyanobacterial Blooms and Phytoplankton Community Composition in a Shallow Temperate Lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, D.M.; Grabowski, S.J. Physical, Chemical, and Biological Characteristics of Cle Elum and Bumping Lakes in the Upper Yakima River Basin; Bureau of Reclamation: Boise, ID, USA, 2007; p. 83.
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. Final Environmental Impact Statement for the Lewis River Projects; Federal Energy Regulatory Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 434.
- Nolan, S.; Bollens, S.M.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G. Diverse Taxa of Zooplankton Inhabit Hypoxic Waters during Both Day and Night in a Temperate Eutrophic Lake. J. Plankton Res. 2019, 4, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, K.R.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M.; Harrison, J.A. Variability in the Vertical Distribution of Chlorophyll in a Spill-Managed Temperate Reservoir. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2019, 35, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, V.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M. Interactive Effects of Phosphorus and Zooplankton Grazing on Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Shallow Temperate Lake. Hydrobiologia 2017, 788, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arar, E.J.; Collins, G. In Vitro Determination of Chlorophyll a and Pheophytin a in Marine and Freshwater Algae by Fluorescence; US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1997; p. 22.
- Lee, T.A.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M.; Faber-Hammond, J.J. Environmental Influence on Cyanobacteria Abundance and Microcystin Toxin Production in a Shallow Temperate Lake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehoff, B.; Klenke, U.; Hirche, H.; Irigoien, X.; Head, R.; Harris, R. A High Frequency Time Series at Weathership M, Norwegian Sea, during the 1997 Spring Bloom:The Reproductive Biology of Calanus Finmarchicus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 176, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D. Statistical analysis of direct counts of microbial abundance. In Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-0-87371-564-5. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, D.J.; Hedley, S. Free-Living Freshwater Protozoa: A Colour Guide; Wolfe Publishing: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-0-7234-1683-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wehr, J.D.; Sheath, R.G.; Kociolek, J.P. Freshwater Algae of North America: Ecology and Classification, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-385876-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.-D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume Calculation for Pelagic and Benthic Microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menden-Deuer, S.; Lessard, E.J. Carbon to Volume Relationships for Dinoflagellates, Diatoms, and Other Protist Plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balcer, M.D.; Korda, N.L.; Dodson, S.I. Zooplankton of the Great Lakes: A Guide to the Identification and Ecology of the Common Crustacean Species; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-0-299-09820-9. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, J.H.; Covich, A.P. Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-12-374855-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cordell, J.R. Invasive copepods of North America. In A Handbook of Global Freshwater Invasive Species; Earthscan Publications Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 161–172. ISBN 978-1-84971-228-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. LmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Soft. 2017, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-1-118-44511-2. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- R Core Team R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- Sommer, U.; Gliwicz, Z.; Lampert, W.; Duncan, A. The PEG-Model of Seasonal Succession of Planktonic Events in Fresh Waters. Arch. Fur Hydrobiol. 1986, 106, 433–471. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-12-744760-5. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, B.; Stansfield, J.; Irvine, K. Development of Daphnid Communities in Diatom- and Cyanophyte-Dominated Lakes and Their Relevance to Lake Restoration by Biomanipulation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1991, 28, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatzky, C.L.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Luecke, C. The Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Deep Chlorophyll Layers in High-Mountain Lakes: Effects of Nutrients, Grazing and Herbivore Nutrient Recycling as Growth Determinants. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kagami, M.; Gurung, T.B.; Yoshida, T.; Urabe, J. To Sink or to Be Lysed? Contrasting Fate of Two Large Phytoplankton Species in Lake Biwa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2775–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Burford, M.A.; Ralph, P.J.; Udy, J.W.; Doblin, M.A. The Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis Raciborskii Is Facilitated by Copepod Selective Grazing. Harmful Algae 2013, 29, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, E.; Ger, K.A.; Panosso, R. Selective Grazing by a Tropical Copepod (Notodiaptomus Iheringi) Facilitates Microcystis Dominance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandgren, C.; Smol, J.P.; Kristiansen, J. Chrysophyte Algae: Ecology, Phylogeny and Development; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; ISBN 978-0-521-46260-0. [Google Scholar]
- Palsson, C.; Graneli, W. Nutrient Limitation of Autotrophic and Mixotrophic Phytoplankton in a Temperate and Tropical Humic Lake Gradient. J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olrik, K. Ecology of mixotrophic flagellates with special reference to Chrysophyceae in Danish lakes. In Phytoplankton and Trophic Gradients; Alvarez-Cobelas, M., Reynolds, C.S., Sánchez-Castillo, P., Kristiansen, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 329–338. ISBN 978-90-481-5067-0. [Google Scholar]





| Location | Date | Incubation Temperature (°C) | Dark:Light (h) | Grazer Taxon Amended |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cle Elum Lake | 18 June | 13 | 8:16 | Daphnia spp. |
| 21 August | 20 | 10:14 | Daphnia spp. | |
| 20 October | 17 | 13:11 | Leptodiaptomus spp. | |
| Lake Merwin | 20 June | 17 | 8:16 | Daphnia spp. |
| 15 August | 23 | 10:14 | Daphnia spp. | |
| 15 October | 18 | 13:11 | Daphnia mendotae | |
| Lacamas Lake | 9 June | 19 | 8:16 | Daphnia retrocurva |
| 5 August | 25 | 10:14 | Daphnia retrocurva | |
| 6 October | 20 | 13:11 | Mesocyclops spp. | |
| Vancouver Lake | 13 June | 20 | 8:16 | Acanthocyclops robustus |
| 11 August | 23 | 10:14 | Acanthocyclops robustus | |
| 10 October | 19 | 13:11 | Acanthocyclops robustus * |
| Month | Factor | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June | Grazers | 0.003 | 0.450 | 0.506 |
| Nutrients | 0.001 | 0.169 | 0.683 | |
| Grazers x Nutrients | 0.001 | 0.176 | 0.677 | |
| Site (random) | <0.001 *** | |||
| August | Grazers | 2.132 | 16.042 | <0.001 *** |
| Nutrients | 0.014 | 0.102 | 0.750 | |
| Grazers x Nutrients | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.895 | |
| Site (random) | <0.001 *** | |||
| October | Grazers | 0.308 | 5.671 | 0.021* |
| Nutrients | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.991 | |
| Grazers x Nutrients | 0.216 | 3.980 | 0.051 | |
| Site (random) | <0.001 *** |
| Month | Factor | MS | F | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| June | Grazers | 0.037 | 0.191 | 0.004 | 0.062 |
| Nutrients | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.982 | |
| Grazers x Nutrients | 0.014 | 0.073 | 0.002 | 0.704 | |
| August | Grazers | 0.030 | 0.146 | 0.003 | 0.104 |
| Nutrients | 0.012 | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.778 | |
| Grazers x Nutrients | 0.021 | 0.103 | 0.002 | 0.354 | |
| October | Grazers | 0.041 | 0.200 | 0.005 | 0.051 |
| Nutrients | 0.015 | 0.075 | 0.002 | 0.718 | |
| Grazers x Nutrients | 0.006 | 0.029 | 0.001 | 0.937 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rose, V.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M.; Zimmerman, J. Effects of Grazing and Nutrients on Phytoplankton Blooms and Microplankton Assemblage Structure in Four Temperate Lakes Spanning a Eutrophication Gradient. Water 2021, 13, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081085
Rose V, Rollwagen-Bollens G, Bollens SM, Zimmerman J. Effects of Grazing and Nutrients on Phytoplankton Blooms and Microplankton Assemblage Structure in Four Temperate Lakes Spanning a Eutrophication Gradient. Water. 2021; 13(8):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081085
Chicago/Turabian StyleRose, Vanessa, Gretchen Rollwagen-Bollens, Stephen M. Bollens, and Julie Zimmerman. 2021. "Effects of Grazing and Nutrients on Phytoplankton Blooms and Microplankton Assemblage Structure in Four Temperate Lakes Spanning a Eutrophication Gradient" Water 13, no. 8: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081085
APA StyleRose, V., Rollwagen-Bollens, G., Bollens, S. M., & Zimmerman, J. (2021). Effects of Grazing and Nutrients on Phytoplankton Blooms and Microplankton Assemblage Structure in Four Temperate Lakes Spanning a Eutrophication Gradient. Water, 13(8), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081085







