Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Phosphorus Fractions and Their Relationship in Water–Sediment Phases in the Tuojiang River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
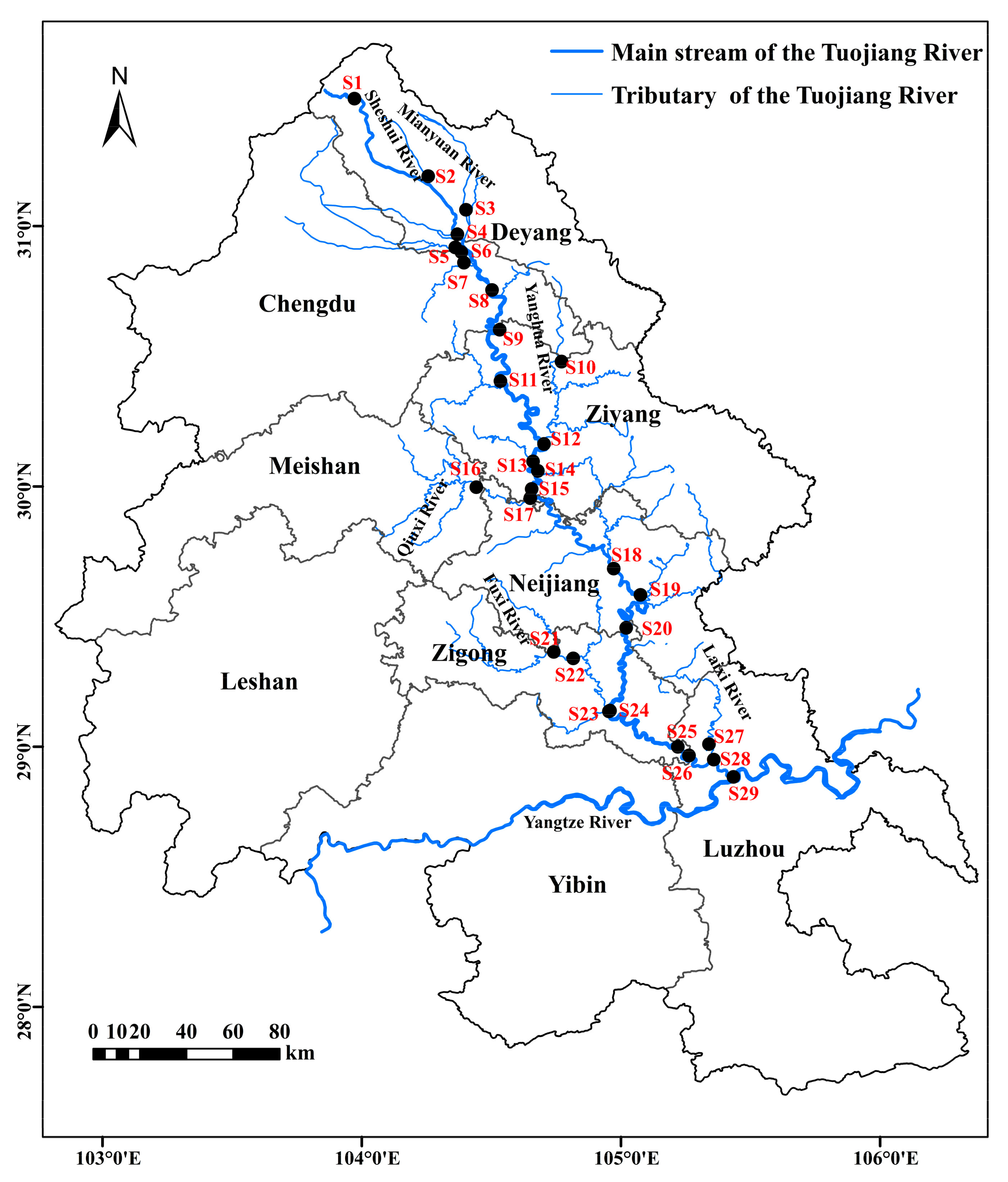
2.1. Study Region and Sampling Sites
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Physicochemical Parameters of Water and Sediments
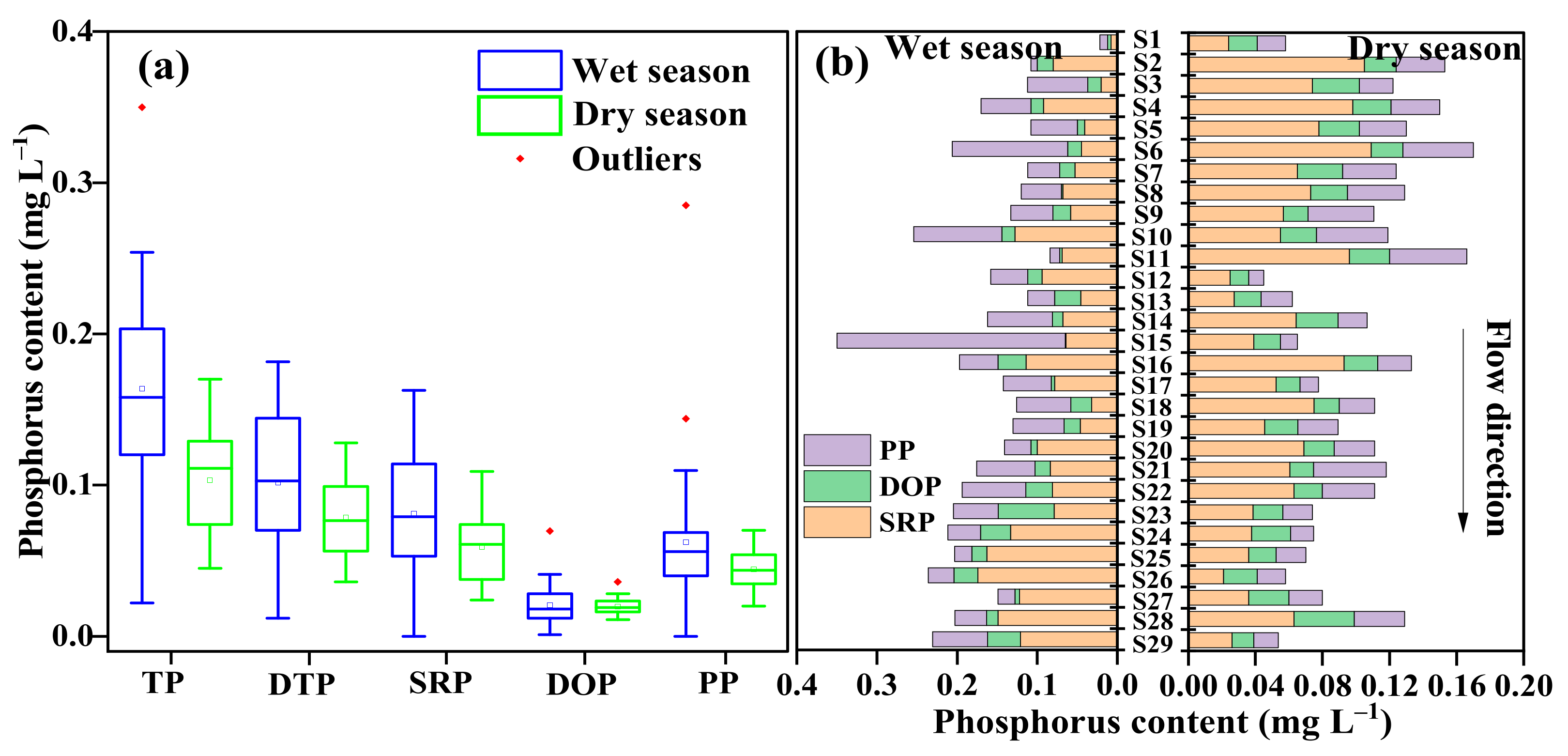
3.2. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Phosphorus Fractions in the Water
3.3. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Phosphorus Fractions in the Sediment
4. Discussions
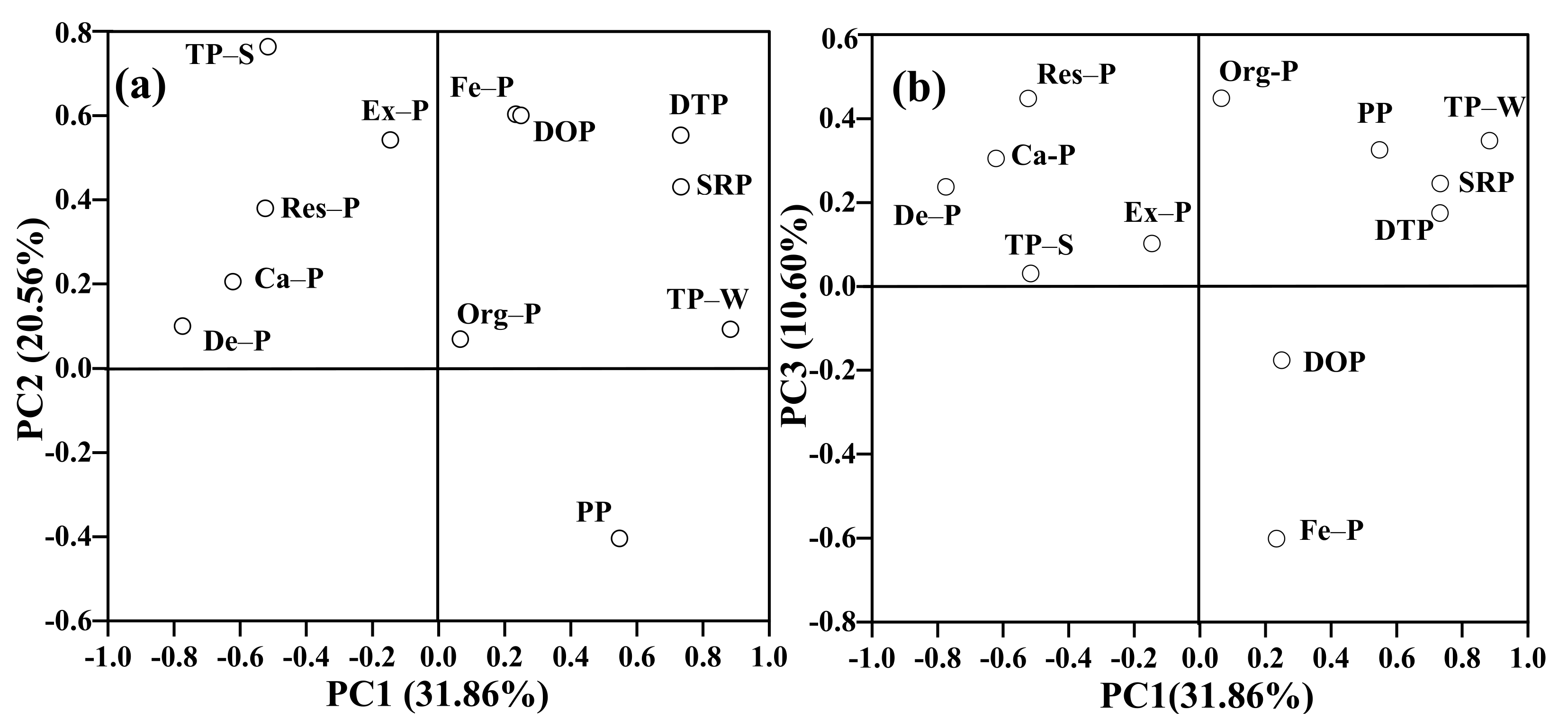
4.1. Relationship between Phosphorus Fractions in the Water–Sediment Phases
4.2. Effect of Physicochemical Properties of Water and Sediments on Phosphorus Fractions
4.3. Identification of the Sources of Phosphorus in the Tuojiang River
4.4. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.5. Study Uncertainties and Limitations
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The average of most phosphorus fractions showed significant seasonal variations, with relatively high contents of phosphorus fractions in water in the wet season and high contents in sediment in the dry season. The SPR and Fe-P were the dominant phosphorus fractions in the water and sediment, respectively. The TP-W, DTP, SRP, and DOP in water and the TP-S, Ex-P, Fe-P, and Ca-P in sediment were larger in the upper reaches than in the middle and lower reaches in the wet season. All the phosphorus fractions (except De-P and Re-P in the sediment) in the water–sediment phases were larger in the lower reaches than in the middle and upper reaches in the dry season.
- (2)
- The Fe-P, Org-P, and TP in the sediments of the Tuojiang River would be released to the water interface, resulting in an increase in phosphorus in the water. The spatial–temporal distribution of phosphorus fractions was attributed to a superposition of various factors in the Tuojiang River. The PH-S and OM may majorly affect phosphorus fractions with spatial–temporal variations in the Tuojiang River.
- (3)
- Most phosphorus fractions mainly originated from anthropogenic activities (industrial or domestic wastewater and agricultural production). More attention should be given to strengthening the management of anthropogenic sources in the Tuojiang River.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, C.N.; Zheng, B.H.; Qin, Y.W.; Ma, Y.Q.; Yang, C.C.; Liu, Z.C.; Cao, W.; Chi, M.H. Impact of upstream river inputs and reservoir operation on phosphorus fractions in water-particulate phases in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Bai, L.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Lu, Z.B.; Liu, J.Y. Spatial characteristics and driving forces of anthropogenic phosphorus emissions in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Wang, S.R.; Ni, Z.K.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.F.; Wu, T.; Wu, H.X. Implications of phosphorus partitioning at the suspended particle-water interface for lake eutrophication in China’s largest freshwater lake, Poyang Lake. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lin, H.; Bartlett, S.L.; Houghton, E.M.; Robertson, D.M.; Guo, L.D. Partitioning and transformation of organic and inorganic phosphorus among dissolved, colloidal and particulate phases in a hypereutrophic freshwater estuary. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.L.; Huang, Y.N.; Pu, X.C.; An, R.D.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Li, R. Spatial and seasonal distribution and transportation of different forms of phosphorus in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Water 2018, 10, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, Z.D.; Wang, Y.W.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Lin, X.Y.; Czapar, G.F. Properties of phosphorus retention in sediments under different hydrological regimes: A laboratory-scale simulation study. J. Hydrol. 2011, 404, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Q.; Wu, M.; Li, R. Phosphorus distribution and bioavailability dynamics in the mainstream water and surface sediment of the Three Gorges Reservoir between 2003 and 2010. Water Res. 2018, 145, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, S.L.; Zhao, H.D.; Deng, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.H.; Dong, S.K. The phosphorus speciations in the sediments up- and down-stream of cascade dams along the middle Lancang River. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.D.; He, Y.L.; Kirumba, G.; Hassan, Y.; Li, J.B. Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption-release characteristics of the sediment in the Yangtze River estuary reservoir. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 55, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Gan, Z.W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.W.; Ma, X.; Chen, M.Q.; Qu, B.; Ding, S.L.; Su, S.J. Occurrence and risk assessment of anthelmintics in Tuojiang River in Sichuan, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Wu, X.F.; Chen, Y.C.; Yi, Z.Y. Spatial variation and source apportionment of surface water pollution in the Tuo River, China, using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Jin, X.; Cao, H.M.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, B.Q. Water quality in representative Tuojiang River network in Southwest China. Water 2018, 864, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.D.; Bai, L.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, R.N.; Liu, J.Y. Anthropogenic total phosphorus emissions to the Tuojiang River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Qin, Y.W.; Ma, Y.Q.; Han, C.N.; Liu, Z.C.; Yang, C.C. Phosphorus forms and potential release characteristics of phosphogypsum in Tuojiang River basin. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 8, 610–616. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.J.; Zhang, X.B.; Ai, N.S. Effect of sediment on concentration of dissolved phosphorus in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.P.; Guo, Y.F.; Deng, T.L. Vertical distribution of phosphorus species at the sediment-water interface of the Tuojiang River and its spatial and temporal characteristics. Rock Miner. Anal. 2019, 38, 668–680. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Liang, T. Distribution patterns and dynamics of phosphorus forms in the overlying water and sediment of Dongting Lake. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Qin, Y.W.; Han, C.N.; Ma, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.C.; Yang, C.C. Environmental Science. Distribution of phosphorus fractions in surface sediments of Minjiang mainstreams. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 2165–2173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otim, O. To freeze, or not to freeze: The impact of subzero temperature on quantifying organic contaminants in ocean sediments. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2019, 21, 1580–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China’s Ministry of Environmental Protection. Water Quality-Determination of Total Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method (GB 11893-89). 1989. Available online: http://c.gb688.cn/bzgk/gb/showGb?type=online&hcno=E3834D3D19D975F69C69CB359BCB762E (accessed on 22 August 2021). (In Chinese)
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Du, Y.H.; Yin, H.B.; Fan, C.X.; Chen, K.N.; Zhong, J.; Gu, X.Z. Exchanges of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface influenced by the external suspended particulate matter and the residual matter after dredging. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, H.; Araujo, F.; Noyma, N.P.; Becker, V. Phosphorus fractionation in sediments of tropical semiarid reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Fang, F.; Guo, J.S.; Chen, Y.P.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.S. Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption-release characteristics relevant to the soil composition of water-level-fluctuating zone of Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.K.; Wang, S.R.; Wu, Y.; Pu, J. Response of phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments to anthropogenic activities in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.X.; Gao, X.L.; Yuan, H.M.; Song, J.M.; Chen, C.T.A.; Lui, H.K.; Zhang, Y. Geochemical forms and seasonal variations of phosphorus in surface sediments of the East China Sea shelf. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 159, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Ouyang, W.; He, M.C.; Han, F.X.; Lin, C.Y. Sorption dynamics, geochemical fraction and driving factors in phosphorus transport at large basin scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wen, S.L.; Yao, S.C.; Zheng, X.L.; Kang, D.Y.; Zhong, J.C. Environmental significance of phosphorus existing forms in the sediments of Yuqiao Reservoir in Tianjin. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 628–639. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varol, M. Spatio-temporal changes in surface water quality and sediment phosphorus content of a large reservoir in Turkey. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyen, D.; Van Gaelen, N.; Ronchi, B.; Batelaan, O.; Struyf, E.; Govers, G.; Merckx, R.; Diels, J. Dissolved phosphorus transport from soil to surface water in catchments with different land use. Ambio 2015, 44, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.X.; Wu, X.; Lu, R.; Yang, W.J.; Zhao, Y. Total phosphorus pollution, countermeasures and suggestions of the Yangtze River economic belt. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 10, 70–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Krom, M.D.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, L.J.; Dai, L.C.; Sheng, Y.Q.; Mortimer, R.J. Impact of suspended inorganic particles on phosphorus cycling in the Yellow River (China). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9685–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samadi-Maybodi, A.; Saffar, H.T.; Khodadoust, S.; Saravi, H.N.; Najafpour, S. Study on different forms and phosphorus distribution in the coastal surface sediments of Southern Caspian Sea by using UV-Vis spectrophotometery. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2013, 113, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudheesh, V.; Movitha, M.; Hatha, A.A.M.; Renjith, K.R.; Resmi, P.; Rahiman, M.; Nair, S.M. Effects of seasonal anoxia on the distribution of phosphorus fractions in the surface sediments of southeastern Arabian Sea shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 150, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, S.M.; Zhang, G.L. Geochemical characteristics of phosphorus in surface sediments from the continental shelf region of the northern South China Sea. Mar. Chem. 2018, 198, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.S.; Guo, X.P.; Cai, Z.H.; Gao, X.F.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.L.; Long, X.J.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Liang, Y.R. Characteristics of various forms of phosphorus and their relationships in the sediments of Haizi Lake, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.J.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, X.Y.; Yang, M.F.; Chen, J. Study on the characteristics of total phosphorus in the Qiuxi River basin, Renshou, Sichuan. Sichuan Environ. 2019, 38, 23–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Study Area | Sampling Time | TP-W | SRP | Ca-P | Fe-P | TP-S | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg L−1 | mg L−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||
| Southern Caspian Sea | Summer 2009 | - | - | 146.0 | 45.7 | 287.0 | [33] |
| South Eastern Arabian Sea | August 2013 | - | - | 294.0 | 10.0 | 508.0 | [34] |
| South China Sea | March–April 2014 | - | - | 100.7 | 27.3 | 412.9 | [35] |
| East China Sea shelf | May–June, October–November 2014 | - | - | 164.0 | 21.0 | 466.8 | [26] |
| Three Gorges Reservoir | October and November 2010 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 431.2–592.8 | 0.1–2.2 | 744.9 | [7] |
| Qingcaosha Reservoir | April–November 2011 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 481.7 | 41.1 | 649.0 | [9] |
| Dongting Lake | - | 0.06 | - | 281.5 | 168 | 705.6 | [17] |
| Haizi Lake | April 2011 | - | 0.48 | 36.4 | 55.9 | 503.0 | [36] |
| Yarlung Zangbo River | August and November 2016, April 2017 | - | - | 355.6 | 12.4 | 408.2 | [6] |
| Yellow River | September and October 2019 | - | - | 517.0 | 14.7 | 619.9 | [27] |
| Yellow River | November 2006, April 2007 | - | 0.01 | 586.5 | 15.3 | 650.1 | [32] |
| Minjiang River | December 2016 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 67.0 | 82.9 | 745.0 | [18] |
| Qiuxi River | June 2018 | 0.59 | 0.37 | - | - | - | [37] |
| Tuojiang River | September 2020 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 27.5 | 306.6 | 438.2 | This study |
| March 2021 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 85.6 | 250.7 | 594.7 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Bai, L.; Qiao, Q.; Liu, J. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Phosphorus Fractions and Their Relationship in Water–Sediment Phases in the Tuojiang River, China. Water 2022, 14, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010027
Liu D, Li X, Zhang Y, Lu Z, Bai L, Qiao Q, Liu J. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Phosphorus Fractions and Their Relationship in Water–Sediment Phases in the Tuojiang River, China. Water. 2022; 14(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dandan, Xueying Li, Yue Zhang, Zhibo Lu, Lu Bai, Qi Qiao, and Jingyang Liu. 2022. "Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Phosphorus Fractions and Their Relationship in Water–Sediment Phases in the Tuojiang River, China" Water 14, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010027
APA StyleLiu, D., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Lu, Z., Bai, L., Qiao, Q., & Liu, J. (2022). Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Phosphorus Fractions and Their Relationship in Water–Sediment Phases in the Tuojiang River, China. Water, 14(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14010027





