Abstract
Hydrological modeling is an important tool for water resources management, providing a feasible solution to represent the main hydrological processes and predict future streamflow regimes. The literature presents a set of hydrological models commonly used to represent the rainfall-runoff process in watersheds with different meteorological and geomorphological characteristics. The response of such models could differ significantly for a single precipitation event, given the uncertainties associated with the input data, parameters, and model structure. In this way, a correct hydrological representation of a watershed should include the evaluation of different hydrological models. This study explores the use and performance of five hydrological models to represent daily streamflow regimes at six hydropower plants located in the Tocantins river basin (Brazil). The adopted models include the GR4J, HYMOD, HBV, SMAP, and MGB-IPH. The evaluation of each model was elaborated considering the calibration (2014–2019) and validation period (2005–2010) using observed data of precipitation and climatological variables. Deterministic metrics and statistical tests were used to measure the performance of each model. For the calibration stage, results show that all models achieved a satisfactory performance with NSE values greater than 0.6. For the validation stage, only the MGB-IPH model present a good performance with NSE values greater than 0.7. A bias correction procedure were applied to correct the simulated data of conceptual models. However, the statistical tests exposed that only the MGB-IPH model could preserve the main statistical properties of the observed data. Thus, this study discusses and presents some limitations of the lumped model to represent daily streamflows in large-scale river basins (>50,000 km).
1. Introduction
Reservoirs are an important infrastructure for water resources management, providing social and economic benefits such as hydropower production, water supply, drought and flood control, irrigation, and recreation. A suitable reservoir operation requires inflow forecasting procedures in order to achieve better operational policies and reduce the risk derived from hydrological extreme events [1,2]. Among many water reservoir operation methodologies, the use of simulation models has the advantage to provide a more detailed and realistic representation with lower computational demands as well as being more readily accepted by operators in practice [3,4].
Hydrological models have been an important tool for assessing future streamflow conditions in water reservoirs and evaluating the impact of climate and for land-use change in watersheds [5,6]. Hydrological models help in making decisions, particularly where data are scarce and the understanding of a hydrological system is incomplete [7]. Three main classifications of hydrological models are found in the literature: data-driven empirical, conceptual, and physical models [8]. The selection of each approach commonly depends on data availability, the complexity and heterogeneity of the watershed, and the application of the model itself [9]. Empirical models seek to characterize the system response only from the available data by an input–output relationship [10]. The simplicity of such models allows us to apply them in ungauged catchments by regional analysis, relating model properties to physical and climatic descriptors of the catchment [11]. Examples of empirical models commonly applied in water resources are Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) [12,13], autoregressive models [14], copula functions [15] and fuzzy logic models [16].
Conceptual models employ simplified mathematical conceptualization of a watershed with the use of several interconnected storages to represent different components of the hydrological processes. This kind of model generally has a lumped configuration and assumes the same values of each parameter for the whole watershed, ignoring the spatial variability [17]. In that way, conceptual models strongly rely on observed data, and the quality of results depends highly on the calibration process. Finally, physical models represent the main hydrological processes through mass, momentum, and energy conservation equations. In this modeling approach, the involved partial differential equations are solved by finite difference or finite computation schemes. Physical models take account of the spatial variability of land use, and soil to deal with the hydrological processes in a semi or fully distributed nature. Parameters of physical-based models are measurable and can provide a continuous simulation of the runoff response without a calibration process [18]. Additionally, hybrid models combine, for example, a conceptual structure with physical-based equations. This kind of model has been developed to combine the strengths of different approaches. For instance, the rainfall-runoff process can be represented by a simple conceptual loss function, and the routing component is estimated by the Saint-Venant equations.
The use of distributed and/or semi-distributed models have been considerably increasing in water resources sciences as an alternative of implementing management strategies for flood control, land use and climate change impact assessments, pollution control, and hydropower operation [19]. This type of model can incorporate sub-grids to represent the spatial variability of soil characteristics, vegetation, land use and precipitation [20,21]. Such capacity can bring more detailed information about the hydrological condition and help to define integrated strategies for climate change impacts [22,23]. However, a suitable implementation of a fully distributed hydrological model required a lot of information, such as input data that can be scarce in large-scale watersheds and could present a high quantity of uncertainty [24]. Alternatively, semi- and fully distributed models present a higher number of parameters that are commonly increased with the number of the sub-catchments. This situation requires the use of more robust optimization techniques or multiobjective calibration functions in order to avoid converging in a bad local minimum. In that way, a correct hydrological modeling approach should be both robust and parsimonious in the representation of the main hydrological variables for the study area.
In the conceptual approach, selecting a specific model relies on whether the structure can adequately reflect the main hydrological characteristics of the study area [25]. Thus, errors in the modeling results may arise from the sum of three types of uncertainties including [26]: (1) uncertainty due to simplification and approximation in conceptualization; (2) parameter uncertainty, and (3) the numerical scheme and solution uncertainty. In particular, the uncertainties caused by the elements (2) and (3) rely on the adoption of an adequate calibration algorithm and the numerical method used to solve the governing model equations [27,28]. As the structure of a specific hydrological model remains fixed, many flexible approaches could be adopted in order to represent the hydrological conditions for a specific watershed. The authors of [26] comment on the emerging flexible hydrological modeling frameworks, such as the SUPERFLEX [29], the Framework for Understanding Structural Errors (FUSE) [30] and the Structure for Unifying Multiple Modeling Alternatives (SIMMA) [31]. In such cases, the authors argued that a single hydrological model structure could limit the representation of all hydrological processes in a watershed. Therefore, either the implementation of a flexible framework or the use of more than one single structure could bring a better understanding of hydrological processes and help for better water resource management. This concern increases in the study of large-scale watersheds, given the spatial variability and heterogeneity of soil and climate.
This study aims to analyze and compare the performance of four lumped hydrological models (GR4J, HYMOD, SMAP and HBV), and one semi-distributed model (MGB-IPH), as for characterizing daily streamflow regimes in six hydropower plants, in a large-scale and tropical river basin located in the North, Central West, and Southeast regions of Brazil. Deterministic metrics and probabilistic tests were executed to determine the more suitable and parsimonious hydrologic modeling approach for this region. Post-processing analysis based on statistical bias correction was applied to reduce the systematic error between observed and simulated data. Results show that all hydrological models can well represent the streamflow regimes at the six hydropower plants, with an excellent performance in the deterministic metrics. However, bigger differences were exposed when comparing the statistical properties between the observed and simulated data of each model. This study reflects that multiple modeling approaches should be considered in order to guarantee a better characterization of the daily streamflow regimes in large-scale watersheds as well as for dealing with the uncertainties associated with hydrological model structures. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the methodology and hydrological models used for this study. Section 3 presents the case study, main results, and discussions. Finally, Section 4 draws conclusions and presents future research directions.
2. Methodology
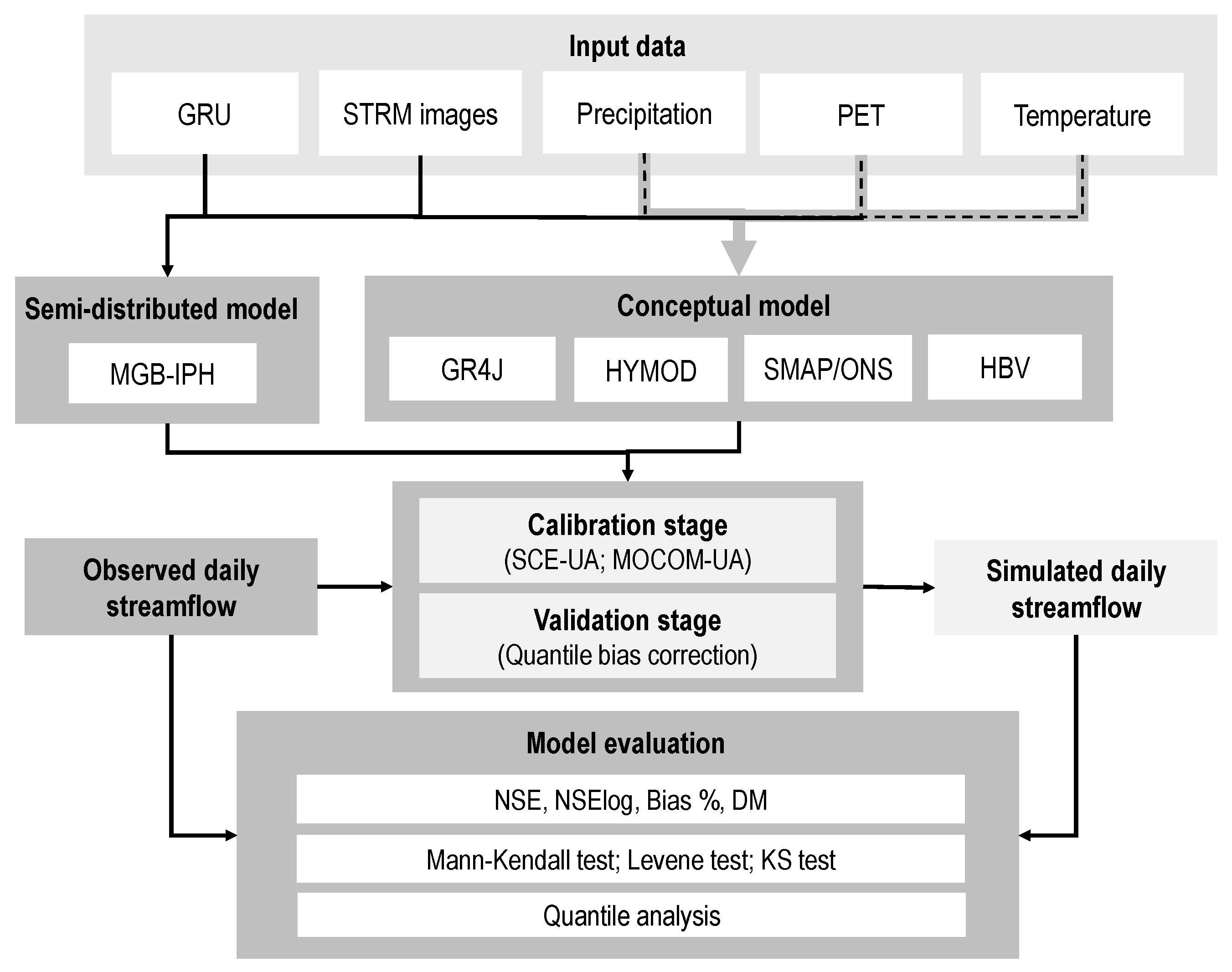
The methodology used in this study is based on the evaluation of five hydrological models to represent the daily streamflow regimes in six hydropower plants located in the Tocantins river basin (Figure 1). Four lumped rainfall-runoff models (GR4J, HBV, HYMOD, and SMAP) and one semi-distributed model (MGB-IPH) were used for this purpose. The selection of these models aims to compare numerical approaches that have been used to characterize the hydrological conditions in Brazilian river basins (SMAP and MGB-IPH model), with other models that have been developed and are commonly used in regions with different hydrological and climatological conditions (GR4J, HYMOD, and HBV). For instance, the SMAP model was adopted by the Brazilian National Electrical System Operator (ONS) [32] to simulate daily and monthly inflows for all hydropower reservoirs in Brazil, and the MGB-IPH model was developed and broadly apply to represent different Brazilian and South American watersheds [33,34,35]. This work also reinforces the analysis initially made by previous studies [9,36,37] that compare the use of hydrological models with different structure and parameter complexities. Table 1 summarizes the the main different characteristics of the structures of each hydrological model. Each one possess distinct complexities that are reflected by the number of parameters that varies based on their corresponding number of hydrologic processes and descriptions. For isntance, note that the conceptual models only consider two types of flows, mainly represented by a surface and a base flow, whereas the MGB-IPH also include a subsurface or interface flow. The following sections present a brief explanation of each hydrological model.
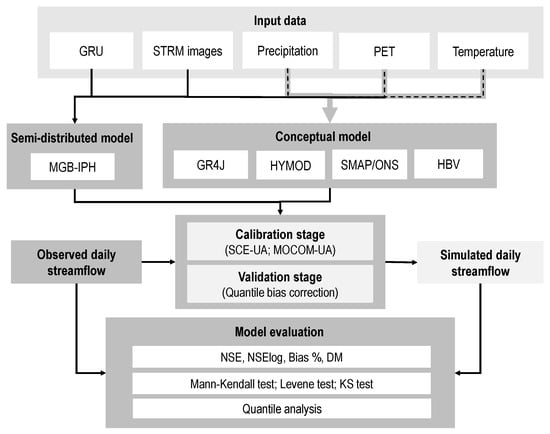
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the hydrological modeling procedure.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the model structure of the hydrologic models used in this study.
Lumped models only use precipitation and potential evapotranspiration time series as input data, except for the HBV model, which also requires temperature information. Additionally, the MGB-IPH model also requires a geoprocessing analysis that incorporates digital elevation models and hydrological response units information. The evaluation of each model was performed by using deterministic metrics including the Nash-Sutcliffe (NSE), the NSE of the logarithm of the streamflows (NSElog), the percent bias (PBIAS), and the Multi-criteria distance (DM). Probabilistic tests were also used to compare the mean, variance, and probability distribution between the observed and simulated data. For the calibration stage, we consider daily streamflow data observed between 2014 and 2019, which is longest period with observed continuous data in the selected watershed. Moreover, we look to adjust the parameters of each hydrological model with the most recent hydrological conditions observed in the river basin. For the validation stage, we selected the years between 2005 and 2010 with the aim of evaluating each model in an independent and far enough period of time of the calibration stage.
The SCE-UA method [38] was employed to calibrate the parameters for all lumped rainfall-runoff models, considering the NSE coefficient as the objective function. This method was employed given its flexibility and robustness, being broadly used by practitioners in water resources management and hydrology for modeling purposes [39,40]. Alternative, the MGB-IPH model employs the MOCOM-UA technique [41] for calibrating the parameters of each sub-watershed. In this case, the NSE, the NSElog and the Q90 are used as objective functions. Finally, for all lumped models we adopted a triangular weighting function for routing the hydrograph between sub-watersheds, whereas the MGB-IPH model uses the Muskingum–Cunge method.
2.1. HYMOD Model
HYMOD (The HYdrological MODel) is a parsimonious conceptual hydrological model with 5 parameters that simulate runoff on a daily scale [42]. The HYMOD allows representing different excess generation processes, as well as percolation and streamflow routing functions that can be put together in different combinations to describe a wide range of hydrological behaviors. The input data are daily precipitation and potential evapotranspiration time series. Figure 2 presents the structure of the HYMOD model and Table 2 describes the main parameter of this conceptual model. The excess precipitation is estimated based on the potential evapotranspiration (PET), and the soil moisture capacity, which is estimated according to the maximum soil moisture capacity (FC) and the degree of spatial variability of the soil moisture capacity (). A portion of the excess precipitation () goes directly to the quick flow reservoirs, represented by three quick-flow tanks, that simulate surface flow. The rest of the excess precipitation flows to the slow reservoir to generate slow runoff. The sum of the slow and quick compose the total runoff of the watershed. More information about the HYMOD model is presented in [42].
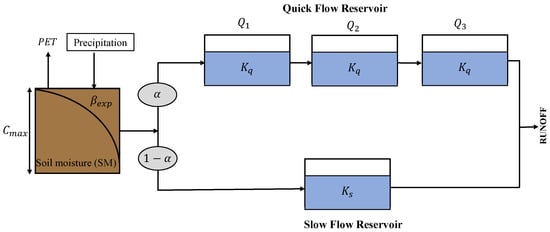
Figure 2.
Conceptual diagram of the HYMOD model.

Table 2.
Description of main parameters of HYMOD model.
2.2. GR4J Model
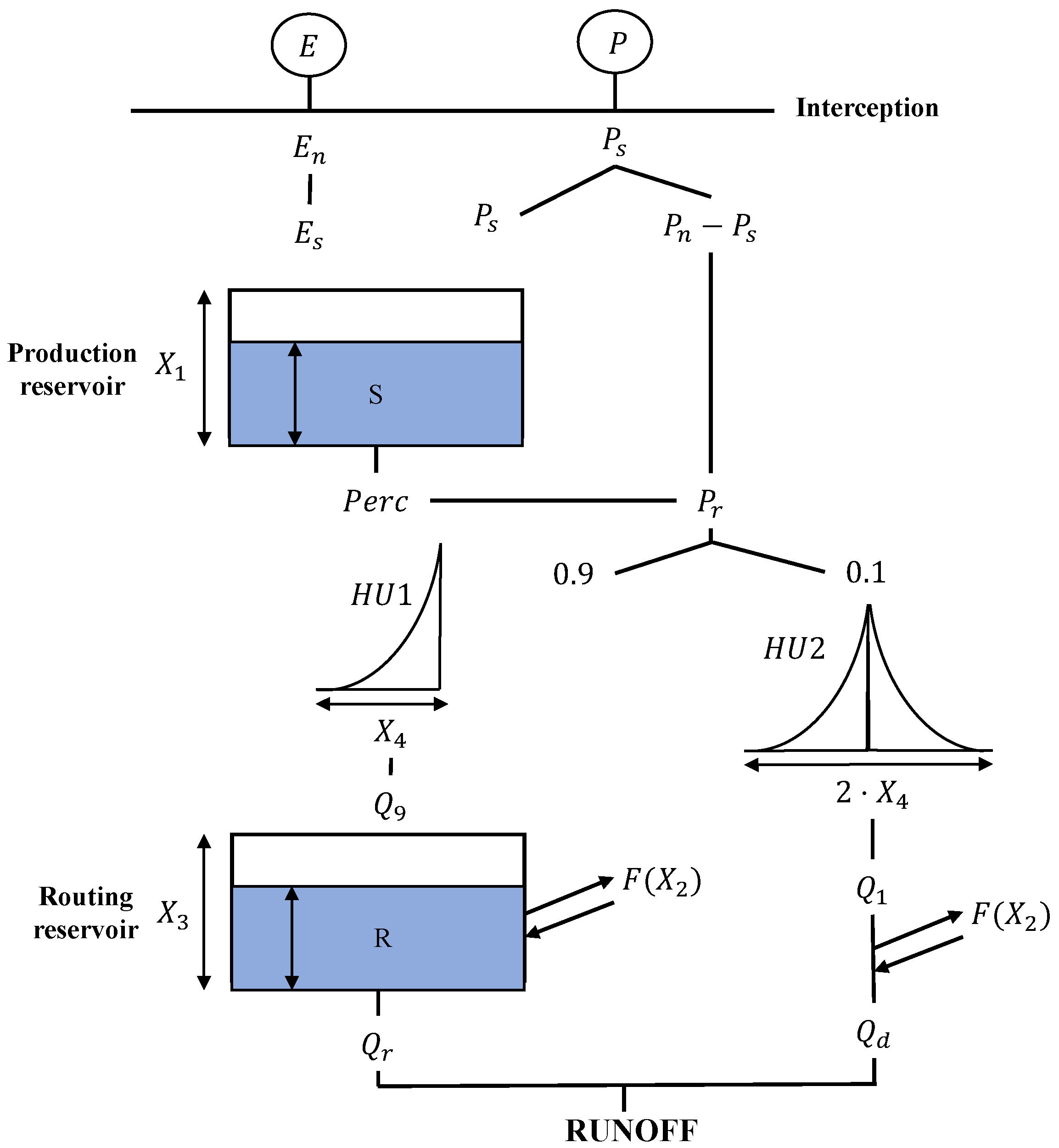
The GR4J (The Génie Rural à 4 paramètres Journalier) is a four-parameter lumped rainfall-runoff model developed by [43], being well recognized to be a parsimonious and robust approach for rainfall-runoff simulation. The GR4J has shown good performance on a wide range of catchments in Europe [44], China [45], Africa [46], and South America [47]. The GR4J model transforms the rainfall into runoff by the use of two reservoirs and two unit hydrographs, employing a daily time-step discretization of the water balance equations (Figure 3). The GR4J model firstly estimates the effective precipitation based on the daily evapotranspiration (PET), and through the interception, a portion of the net rainfall goes into the production storage [45]. In the production storage, the actual evaporation is calculated and percolation occurs. The flow routing occurs both by leakage of percolated water and direct precipitation. The flow component is split into 90% runoff routed by the unit hydrograph (HU1) and then into a non-linear routing store, and the other 10% runoff is routed by a single unit hydrograph (HU2). The total runoff is obtained by adding these to runoff components. Table 3 describes the four parameters considered in the GR4J model, as well as the limits employed in the calibration procedure.
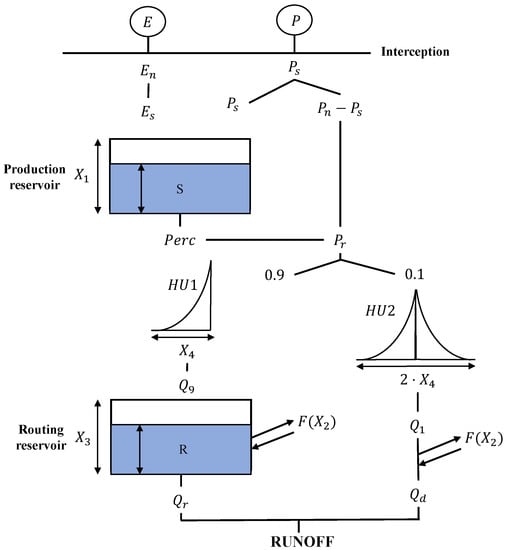
Figure 3.
Conceptual diagram of the GR4J model.

Table 3.
Description of main parameters of GR4J model.
2.3. SMAP Model
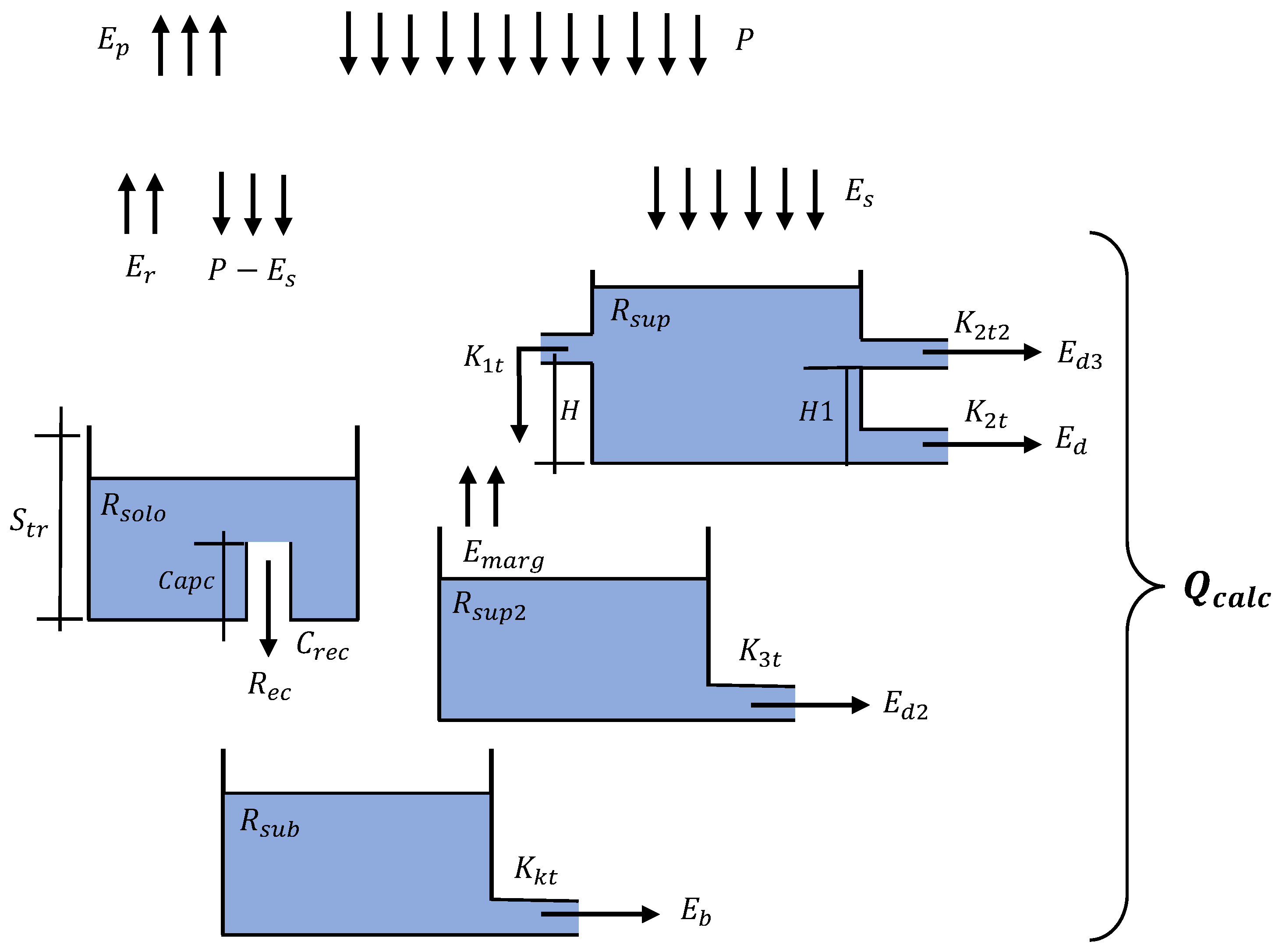
SMAP (Soil Moisture Accounting Procedure) is a conceptual hydrological model based on the application of the Stanford Watershed IV and the Mero model [48]. The SMAP model uses as input data series of daily precipitation and potential evapotranspiration to simulate streamflow at the outfall of the watershed. The original version of the SMAP model considers a simple structure with three linear reservoirs, employing the Soil Conservation Service (SCS) method for the separation of runoff. Looking for a better representation of different watersheds, the Brazilian National Electrical System Operator (ONS) [32] modified the SMAP model by increasing the number of linear reservoirs by four (Figure 4) and adding some coefficients to adjust the temporal representation of daily precipitation, potential evapotranspiration as well as the recession curves for the base and superficial flows. The SMAP model is broadly employed for operational purposes in the Brazilian National Interconnected System (SIN) and has been used for different applications including flash flood prevention [49,50], daily inflow forecast for hydropower generation [51], and water resources management in coastal watersheds [52]. Table 4 describes the main parameters of the SMAP/ONS model.
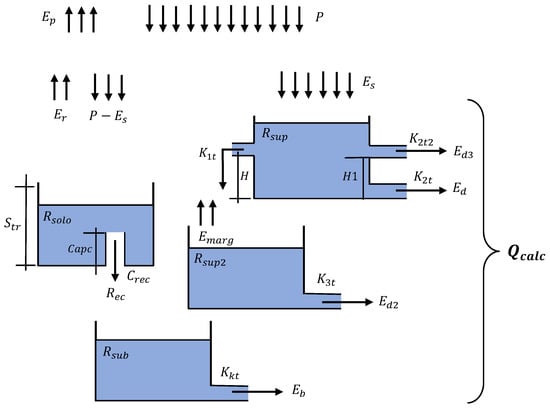
Figure 4.
Conceptual diagram of the SMAP/ONS model.

Table 4.
Description of main parameters of the SMAP/ONS model.
2.4. HBV Model
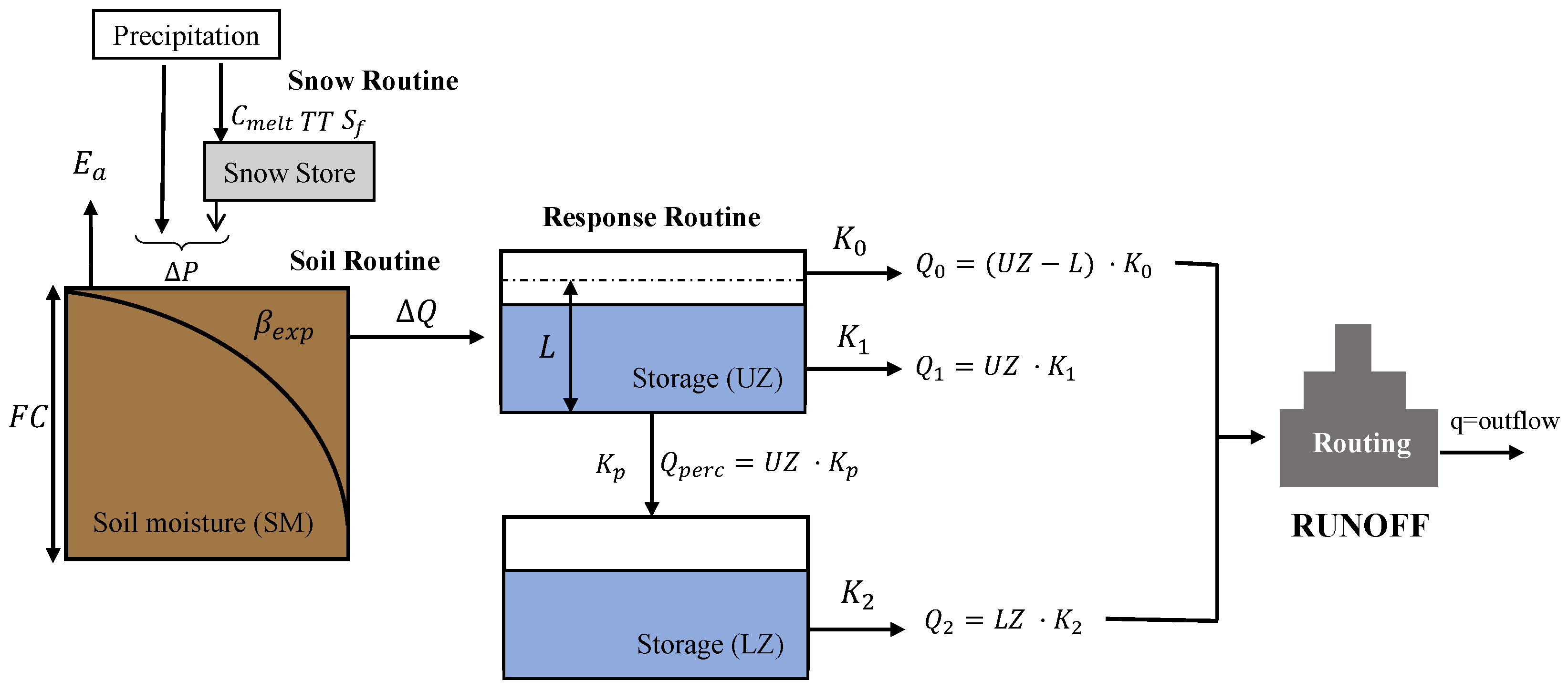
The HBV (Hydrologiska Byrans Vattenbalansavdelning) model is a semi-distributed conceptual snow–rain water balance model proposed by [53]. The HBV model simulates daily runoff based on daily precipitation and temperature records, and long-term evapotranspiration and temperature time series. This model includes a snow routine, a soil routine, and a response routine (Figure 5). Precipitation can be presented as snow or rain, depending on the temperature on the corresponding day above or below a threshold temperature (TT). If the actual temperature is greater than TT, there will be snowmelt. For the study area presented in this paper, snowmelt is seldom presented, and therefore the snow routine is not included in the HBV model. The total precipitation goes to the soil routine, where the actual evapotranspiration () is estimated by a linear function which decreases as the soil moisture drops. The HBV model includes two runoff reservoirs. The upper reservoir generates the quick flow expressed by a non-linear function and the other reservoir estimates the baseflow expressed by a linear function. The total runoff is generated from these two reservoirs and then routing through a transformation function. In this study, the simplified version of the original HBV model developed by [54] was used. Table 5 describes the parameters considered in the HBV model, as well as the limits employed in the calibration procedure.
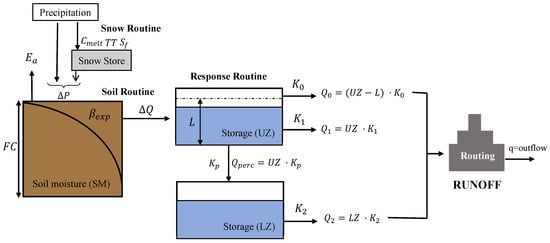
Figure 5.
Conceptual diagram of the HBV model.

Table 5.
Description of main parameters of HBV model.
2.5. MGB-IPH Model
The MGB-IPH (Large Basins Model—Modelo de Grandes Bacias) is a large-scale and semi-distributed hydrological model that uses physical- and conceptual-based equations to simulate continental hydrological cycles [55]. This model has been developed with a focus on large South American basins, considering the typical low spatial density and limited duration of hydrological records available in the region [34,35,56]. The MGB-IPH has been previosly applied to represent the hydrological of different tropical river basins [57,58], as well for the implementation of operational flood forecasting systems [59,60].
The MGB-IPH model employs land use, topography, vegetation cover, and soil types as guides to select parameter values, and divided the main hydrologic processes into modules, which are used to determine the groundwater, evapotranspiration, superficial, sub-superficial, and subterranean flow, as well as total discharge. Differently from conceptual the models previously presented, the MGB-IPH requires an initial geoprocessing analysis to estimate the spatial characteristics of soil, land use, vegetation, and elevation of the study area. The MGB-IPH model presents three main geospatial discretization units: unit-catchments, sub-basins, and the whole basin itself. Moreover, the unit-catchments are further divided into hydrological homogeneous regions termed grouped response unit (GRU) or hydrological response units, which are generally defined from a combination of soil and vegetation type maps [61].
The hydrological simulation of the MGB-IPH model begins from the balance of groundwater analysis of each individual cell accounting for the rainfall and its respective GRUs. The evapotranspiration is calculated through the Penman–Montheit equation and can occur in both intercepted water and the water in the soil through the vegetation. Determining the superficial and internal runoff as well as the subterranean flow takes into consideration the total accumulated in each cell and response time parameters. Finally, the Muskingum–Cunge or inertial flow equations can be used for routing hydrographs between interconnected sub-basins. The MGB-IPH employs three independent linear reservoirs to route the flow through the cell. Those reservoirs are used to represent each flow generation type: surface, interflow, and groundwater. The linear reservoirs collect the flow generated in every GRU of the cell, as represented schematically in Figure 6 for an example of a cell with two GRUs [55]. The variables Dsup, Dint and Dbas are the surface, interflow, and groundwater flow, respectively, generated in the soil layer of the GRU. Further information about the governing model equations of the MGB-IPH model is presented in [55,62].
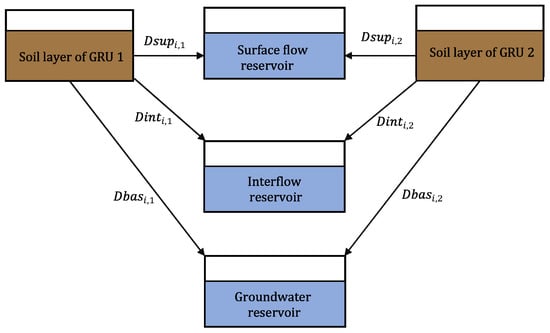
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of linear reservoirs used by the MGB-IPH model. Adapted from: [55].
2.6. Performance Metrics
Four performance metrics were used in this study to compare the simulated and observed streamflow time series for both calibration and validation periods. The employed metrics included the Nash–Sutcliffe (NSE), the logarithmic version of the NSE (NSElog), the percent bias (PBIAS), and the Multi-criteria distance (DM).
The Nash–Sutcliffe coefficient (NSE) is used to test the predictive power of hydrological models. The NSE has a range between and 1. When NSE is equal to 1, the model achieves a perfect representation for the observed data, whereas a value of 0 suggests that the predictions of the models are as accurate as the mean of observed data [63]. Since greater streamflow values are more weighted in the NSE coefficient, the logarithmic values of the streamflows are used to estimate the corresponding NSElog. The NSElog is useful to evaluate the performance of the models in dry periods. Hence, this metric takes importance in regions with significant dry periods. The NSE is calculated using Equation (1) as:
where is the observed streamflow at the tth time step; is the simulated streamflow at the tth time step; and is the mean of the observed data.
The percent bias (PBIAS) measures the average tendency of the simulated values to be larger or smaller than their observed ones. The optimal value of PBIAS is 0. Positive values of PBIAS indicates an underestimation of simulations and negative values represent the overestimation of simulations [64]. The PBIAS is estimated by the Equation (2) as:
In addition, metrics that use the average streamflows, such as the NSE (1), are useful to evaluate the long-term hydrological conditions in a watershed, whereas metrics that compare each individual realization are focused on evaluating the short-term hydrological response in the watershed. In that way, the Multi-criteria distance (DM) is considered in this study and is defined as the Euclidean distance between the inverse of the NSE coefficient and the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), which is estimated by Equation (3) as:
where the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) is calculated as:
2.7. Statistical Tests
The Mann–Whitney U test is a non-parametric statistical method that can be used to compare the mean of two independent samples [65]. In this case, the null hypothesis states that , where is the difference between both sample means. To perform this test, we first ranked each sample as and sum the ranks of each sample and . The values and are used to compute U, which is the lowest value obtained by the two expressions presented in the Equation (5).
The test statstic can be approximated by the normal distribution and calculated using the Equation (6) as:
Finally, is rejected for a significance level if Z exceeds the quantil.
Heteroscedasticity was assessed with the non-parametric Levene test, under the assumption that k subgroups of the same variable Y have equal variances [66]. For a given k subgroups, where is the sample size of the ith subgroup, the Levene test statistic W is estimated by the Equation (7) as:
where N is the total number of values in all subgroups; is the jth value of the ith subgroup; ; is the mean of the ith subgroup; Z is the mean of all ; is the mean of the subgroup. The null hypothesis of the Levene test is rejected if , where is the upper critica value of the F distribution with and degrees of freedom at a significance level of .
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (K-S) quantifies the vertical distance between the empirical distribution of a sample and the cumulative distribution function of the reference distribution [67]. Given n increasing ordered data points, , the K-S test stastistic is estimated using the Equation (8) as:
where stands for the specified distribution; represents the empirical distribution; and sup is the supremum function. The null hypothesis is: for all x from to ∞. For a significance level , the null hypothesis is rejected if T exceeds the quantil [68].
2.8. Bias Correction
For the validation period, a bias-correction methodology based on the work of [69] was applied as a post-processing analysis for the streamflow simulation. For each month, a single probability distribution function was fitted for both the observed and simulated time series. The non-exceedance probability is estimated for every simulated value and related to the observed streamflow value with the same non-exceedance probability. The implementation of this method can improve the accuracy of hydrological models in the prediction of future events. In this study, we adopted the Gamma probability distribution function. More details about this bias-correction method are presented in [70].
3. Case Study
3.1. Overview
For the case study, we selected the Tocantins river which is one of the most important water bodies in terms of hydropower production for Brazil [60,71]. The Tocantins river basin has a drainage area of 306,200 km, and it is located in the North, Central-West, and Northeast regions of Brazil, covering the states of Tocantins, Goiás, Maranhão, Pará, and Distrito Federal (Figure 5). This basin is characterized by its high potential for electricity generation, and the presence of many reservoirs for electricity production. According to the [72], the Tocantins river basin achieves 74% of the hydroelectric potential inventoried in the country. Furthermore, the reservoirs located in this region are also used to control and regulate water resources, providing water supply for irrigation, fishing, and recreation. For instance, the reservoir of the Serra da Mesa hydropower plant has a surface area of 1.784 km and a storage capacity of 54.4 km, being the largest reservoir in Brazil.
The predominant biome of the region is the Cerrado (Brazilian Savanna), corresponding to 97.8% of its area. Based on the Köppen type-climate classification [73], the climate in this basin is Aw (tropical with predominant summer precipitation and dry winter). The average annual temperature is 26 °C and the average annual precipitation is approximately 1770 mm [74]. The wet period extends from October to April, with a short dry period between January and February. The dry season is commonly presented between May and September. Figure 7 presents the localization of the Tocantins river basin, the localization of the hydropower plants, the rain gauges, and climatic stations as well as the results of the geoprocessing analysis included the digital elevation model, grouped response units (GRUs), and unit-catchments, used to construct the MGB-IPH hydrological model.
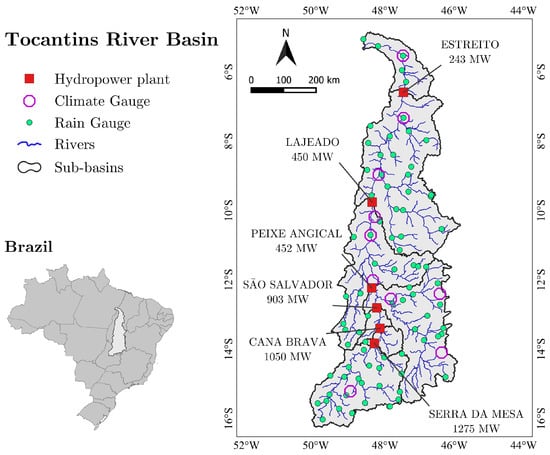
Figure 7.
Location of the Tocantins river basin and the main hydropower plants.
3.2. Data
Precipitation and potential evapotranspiration (PET) are two major inputs for the selected conceptual models. Acummulated daily precipitation data were obtained from 83 rain gauges located the Tocantins river basin for the period 2005–2019. The data were provided by the Brazilian National Agency of Waters (ANA). The days with missing data were infilled using the inverse distance weighting interpolation method (IDW). Daily PET is calculated using the Pennam-Monteith equation [75], which considers climatological records of sunshine, temperature, humidity, and wind speed. The variables were extracted from 10 climatic stations located in the Tocantins river basin, and the data were provided by the Brazilian National Institute of Meteorology (INMET). For the MGB-IPH model, we used STRM (shuttle radar topography mission) images with 90 × 90 m resolution. The data are available from the Consultative Group in Internation Agriculture Research (CGIAR) in GeoTiff format. The drainage area was subdivided in square cells containing information on both land use and soil type and classified according to the grouped response unit (GRU).
Daily streamflow records from the period 2005-2019 were used in this study. The streamflow data was provided by the Brazilian National Electrical System Operator (ONS) and consists of naturalized streamflows, i.e., without the influence of the dams nor consumptive water uses. The drainage area, total anual rainfall, and descriptive statistics of observed daily inflows at each hydropower plant are presented in Table 6. It is worth mentioning that the smallest incremental drainage area considered in this study is greater than 5700 km (São Salvador UHE). Additionally, the data depicts a high variability of the streamflow regimes, represented by coefficient of variations greater than 100%. In fact, this river presents a strong periodicity, characterized by drought periods in the middle of the year and wet periods at the beginning and end of the year.

Table 6.
Descriptive statistics of observed daily streamflow and precipitation for the period 2010–2019.
3.3. Results Analysis
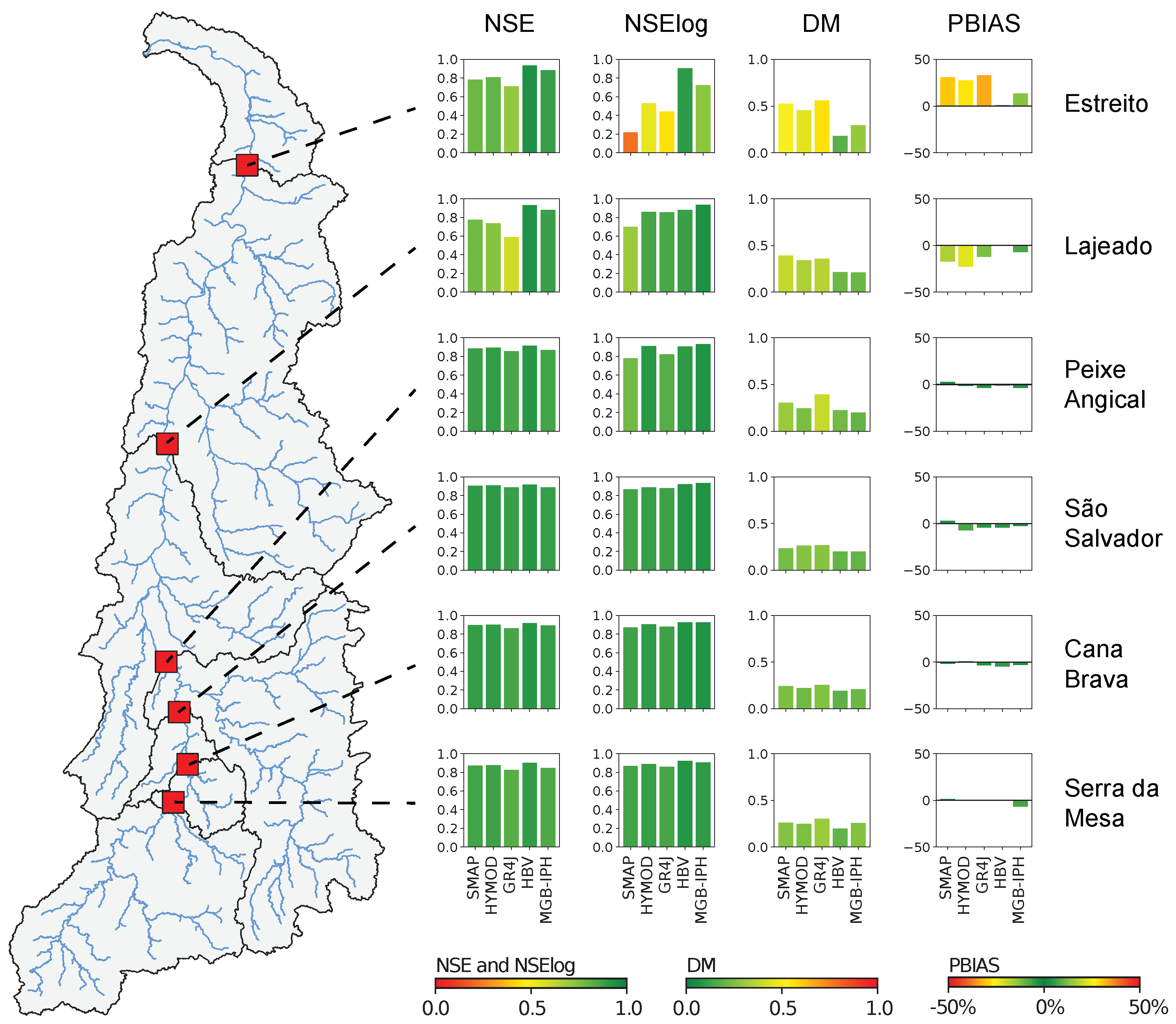
Figure 8 presents the results of the deterministic metrics obtained for each hydrological model in the calibration period (2014–2019). Based on the NSE metric, the results in this stage show that all modeling approaches present a satisfactory performance to represent the hydrological regime for all hydropower plants, and the results of more parsimonious models, such as the GR4J, are comparable with those obtained by the MGB-IPH model. In this stage, the HBV model exhibits the best adjustment to the observed data at all hydropower plants. Furthermore, it is also noted that the SMAP, GR4J, and HYMOD models exhibited a poor performance at the Estreito UHE, mainly exposed by the NSElog and the bias percentage. This result could indicate a limitation for representing lower streamflows in downstream areas, which could be associated with propagation errors of the modeling process along the watershed.
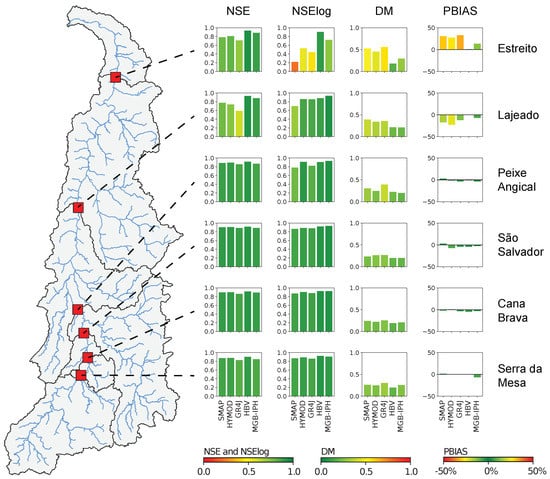
Figure 8.
Results of deterministric metrics in the calibration stage.
For the validation stage, a post-processing methodology based on correcting the non-exceedance probabilities of simulated data was applied to reduce the systematic error or bias between the simulated and observed data. To avoid overfitting, the observed data of the target year was excluded from the probability distribution fitting. Figure 9 compares the boxplots of the obtained deterministic metrics for both original and bias-corrected data. Results show a significant improvement after bias correction, mainly exposed by the DM and bias percentage values. Additionally, negative NSElog values were removed from the simulated data. However, it is worth mentioning that for the original valdation results, only the MGB-IPH model presents a satisfactory performance for all deterministic metrics. For instance, the NSE values are greater than 0.7, and the bias percentages are lower than 10%. For conceptual models, the HBV and the HYMOD exhibit bias percentages close to 30%, and negative NSElog values are observed for the SMAP, and GR4J models. Those differences show that the adopted conceptual models fail to represent daily streamflow conditions for another period of time, and exposed limitations that lumped hydrological models could have to represent hydrological regimes in large-scale river basins, mainly characterized by its spatial variability and heterogeneity conditions.
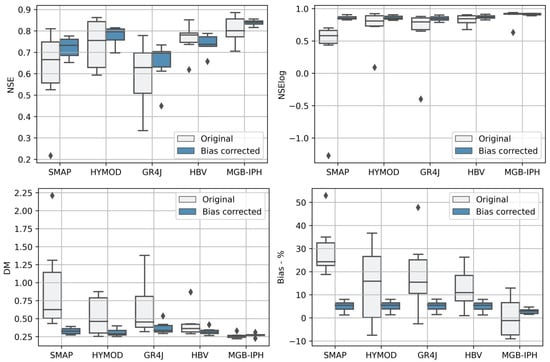
Figure 9.
Boxplots of deterministic metrics for the original and corrected simulated data for the vaildation period.
Figure 10 compares the observed and simulated hydrographs obtained for each hydrological model at the Estreito UHE in the validation stage. The first year was burned to set the initial conditions of each hydrological model similar to the observed data. Bias correction results show a significant improvement to represent the recession curves in the dry periods, specially for the simulated hydrographs of the SMAP, GR4J and HYMOD models. The figure also show that after bias correction, the peak flows were corrected in most of the cases. However, for the MGB-IPH model, an underestimation is observed in the peaks flow when compared to the observed and original simulated data.
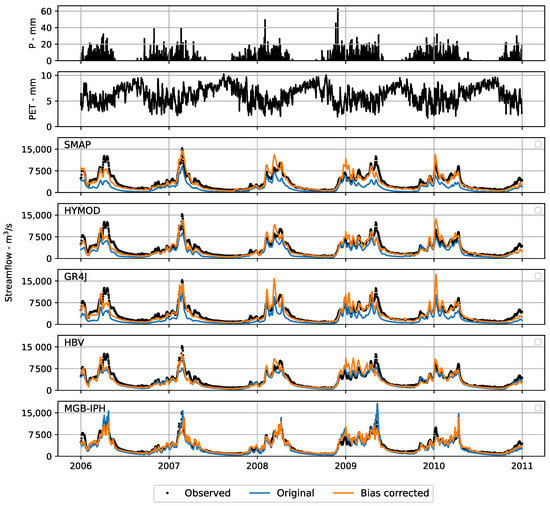
Figure 10.
Hydrographs for the validation stage comparing the observed and the simulated streamflows by different hydrological models at the Estreito UHE.
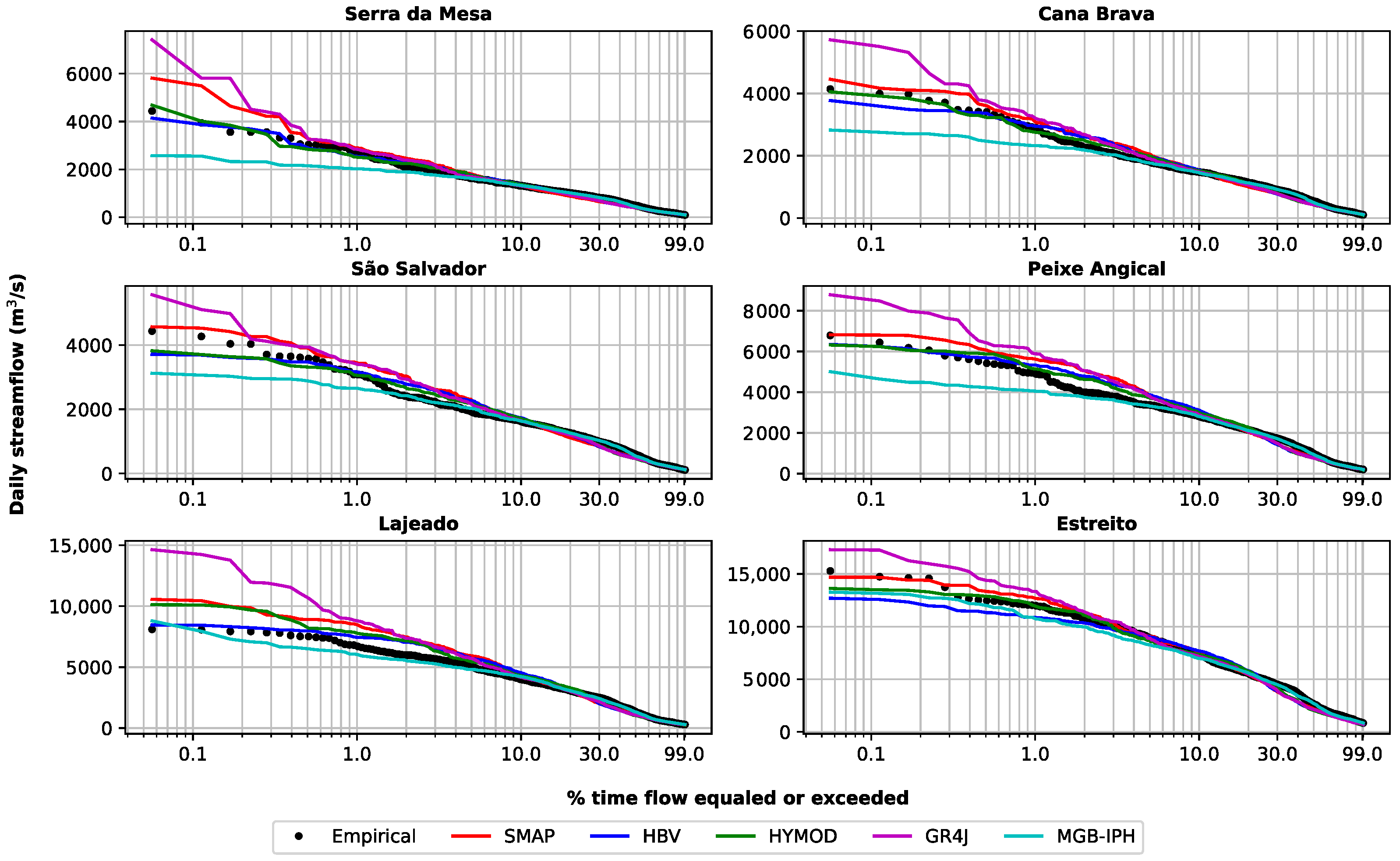
Figure 11 compares the flow duration curves between the observed and simulated data obtained for the validation period after applying the bias correction. The results show that all hydrological models have a good performance to represent daily streamflows that are below 10% of the exceedance flow duration curve. However, for the highest quantiles (<10%), the models exhibit some different behaviors. For instance. the GR4J model tends to overestimate the streamflow values and the MGB-IPH tends to underestimate the observed data. Meanwhile, the HBV, the HYMOD, and the SMAP models showed a better representation to achieve the observed peak flows of the hydrograph. Those results are derived in part from the uncertainties associated to each hydrological model structure, the calibration process, the routing method, and the bias correction method.
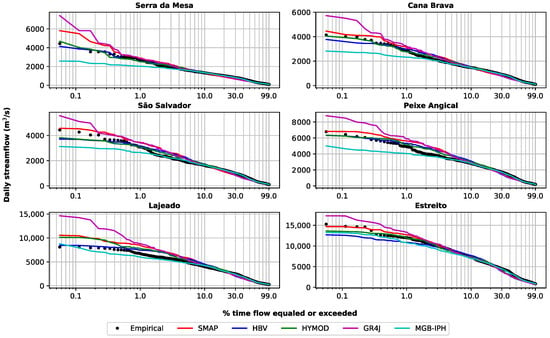
Figure 11.
Curves describing the duration of daily streamflow in the Tocantins river basin for the validation period (2005–2010).
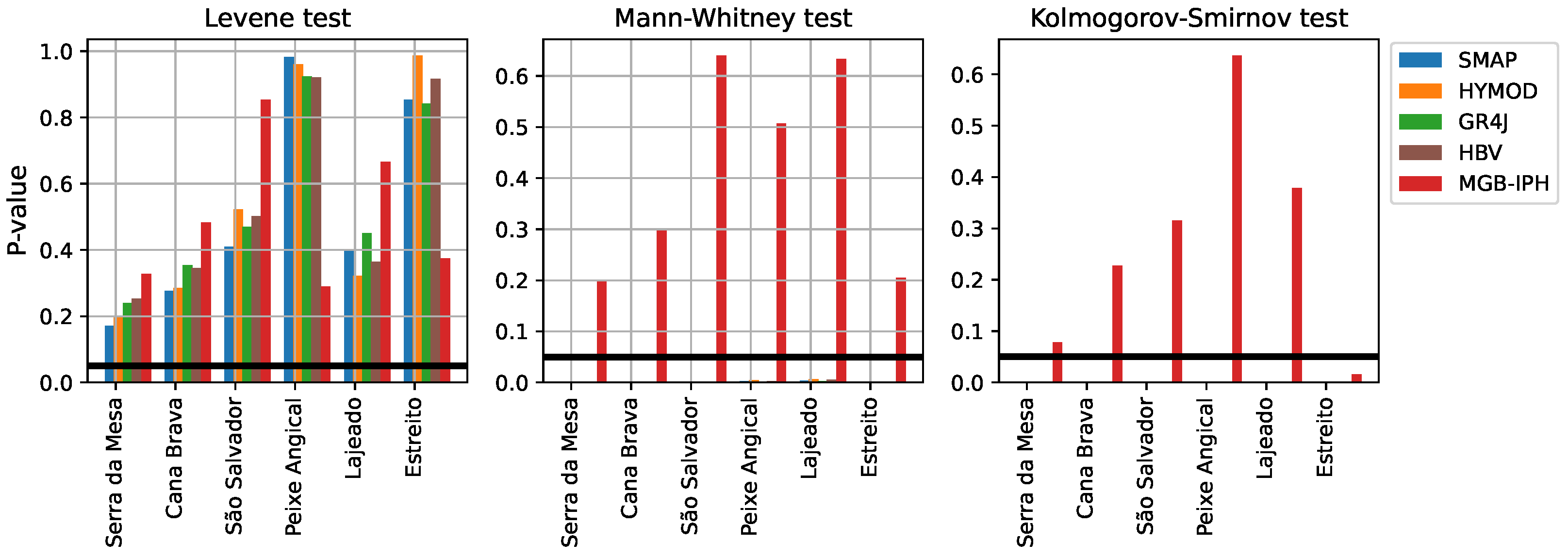
Figure 12 presents the results of different statistical tests, including the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, the Mann–Whitney test, and the Levene test, in order to compare the probability distribution, the mean, and the variance between the observed and simulated data. In this case, we present the estimated p-value for each hydrological model in the validation stage, after applying the bias correction procedure. For a significance level , expressed by a horizontal line, the results show that only the MGB-IPH model fails to reject the null hypothesis in all statistical tests, evidencing that this model follows the same statistical properties of the observed data in each hydropower plant. In the case of conceptual models, only the variance of the observed data were preserved, mainly derived from the capacity of representing the seasonal hydrological regime in the study area. Those results diverge significantly from those obtained for the deterministic evaluation after the bias correction, in which all conceptual hydrological models achieved a similar or better performance than the MGB-IPH model.
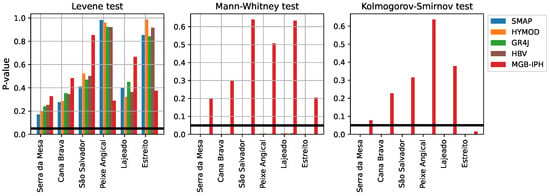
Figure 12.
Statistical tests of each hydrological model in the validation stage. The horizontal line indicates the significance level .
Finally, Figure 13 and Figure 14 present the violin plots that evaluate the capability of the models to simulate different quantiles of flows as low (Q95 and Q75), median (Q50), and high (Q25 and Q10) in the Tocantins river basin for the calibration and validation periods, respectively. For the calibration period (Figure 13), the results show that all hydrological models can well represent the highest quantiles (Q10, Q25), maintaining a similar density curve in comparison with the observed data. However, greater differences are presented for lower streamflows (Q75, Q95), where simulated data present an underestimation for all cases. In the validation stage, and after applying the bias correction procedure, the results indicate an improvement in the representation of lower streamflow values. For dry periods, the MGB-IPH model presented a better representation of the inflow for all hydropower plants, whereas for the highest quantiles, the better representation was achieved by the SMAP model.

Figure 13.
Violin plot describing the low, median, and high flows simulated in the Tocantins river basin by multiple hydrological models. Calibration period.
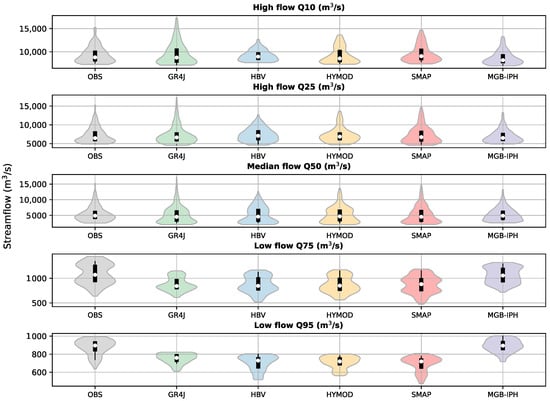

Figure 14.
Violin plot describing the low, median, and high flows simulated in the Tocantins river basin by multiple hydrological models. Validation period.
4. Conclusions
This study evaluated five hydrological models to represent daily streamflow time series at six hydropower plants located in the Tocantins river basin. The modeling approaches included four lumped conceptual models (GR4J, HBV, SMAP, and HYMOD) and one semi-distributed model (MGB-IPH). The selection of such models was based on covering a wide range of numerical schemes with different complexity that have been used in different regions around the world. For conceptual models, the data encompass daily rainfall records from 83 rainfall stations and climatic variables from 10 stations. The MGB-IPH model also required geospatial information, which was provided by satellite information. The performance indicators NSE, NSElog, PBIAS, and DM were computed by comparing model simulated streamflows against observed daily streamflows for calibration and validation periods of 2014–2019 and 2005–2010, respectively. Additionally, statistical tests including the Mann–Whitney, Levene, and Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests were estimated to validate the statistical significance of the mean, variance and probability distribution of simulated data.
For the calibration period, the deterministic metrics indicated that all of the employed models can well represent the daily streamflow regimes in the study area, with NSE values greater than 0.6, and mean NSElog values equal to 0.82. Additionally, the simulated data do not present a significant bias in comparison with the observed data. According to deterministic metrics, the HBV model achieved the best adjustment with the observed data in the calibration stage, whereas the GR4J show a lower performance.
For the validation period, only the MGB-IPH model preserved a satisfactory performance to represent daily streamflows for another period of time, whereas the conceptual hydrolological models exibited worse metrics when compared to the calibration stage. Those differences could be related to the optimization algorithms used to calibrate the parameters of each hydrological model, being the MOCOM-UA superior to the SCE-UA for considering more than one metric as objective functions, or even by the structure of the model itself, given that the MGB-IPH contains a more robust representation of different types of flows in the catchment. On the other hand, the results may indicate some limitations of lumped hydrological models to represent daily streamflows in large-scale river basins, considering that the greater spatial variability and heterogeneity of such drainage areas are commonly represented only by a set of parameters. For a better comparison, a bias-correction procedure was executed to reduce the systematic errors of all adopted hydrological models. A first evaluation showed that deterministic metrics of conceptual models improved significantly for the validation stage, presenting in some cases a similar or better performance than the MGB-IPH model. However, after applying statistical tests to the corrected simulated data, the results show that only the semi-distributed model could preserve the same statistical properties of the observed data at each hydropower plant.
Based on the obtained results, we highlight the importance of considering multiple hydrological approaches to simulate daily streamflow regimes. The results show some limitations that lumped and more simple hydrological models, such as the GR4J, could have for representing hydrological conditions in large-scale river basins, mainly characterized by their spatial heterogeneity. Considering the importance of this river basin for hydropower generation, the performance of all hydrological models was addressed in this study by only comparing daily streamflow data for two periods of time. However, based on different water uses, the comparison of hydrological models should include other variables of the water cycle. For future studies, the suggested directions are: (i) include and compare the performance of fully distributed hydrological models, as well as other conceptual and semi-distributed hydrological models in the selected river basin; (ii) expand the presented analysis to other river basins with different hydrological and climatological conditions; (iii) explore the use of more efficient optimization algorithms, such as the DSS, to calibrate the parameters of conceptual models and; (iv) Include uncertainty analyses in the calibration process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Á.; methodology, L.Á. and R.S.; software, L.Á.; validation, L.Á. and R.S.; formal analysis, L.Á.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Á.; funding acquisition C.F. and C.A.; project administration C.F., C.A., R.S. and F.F.; review and editing, R.S., A.C., N.R., C.F., C.A., F.F., A.S. and J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work presents part of the results obtained during the research project Project PD 6491-0503/2018—“Previsão Hidroclimática com Abrangência no Sistema Interligado Nacional de Energia Elétrica”, under development by the Parana State electric company (COPEL GeT), the Technological System for Environment Monitoring of Parana State (SIMEPAR) and the RHAMA Environment Consulting; Researchers of the Hydraulic Research Institute (IPH) from the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS) participate in part of the project through an agreement with the RHAMA company. This project is granted by the Brazilian Agency of Electrical Energy (ANEEL) under its Research and Development program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Coulibaly, P.; Anctil, F.; Bobée, B. Daily reservoir inflow forecasting using artificial neural networks with stopped training approach. J. Hydrol. 2000, 230, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Peng, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, J. Simulating reservoir operation using a recurrent neural network algorithm. Water 2019, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhao, B. Real-time reservoir operation using recurrent neural networks and inflow forecast from a distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cai, X.; Yang, D. Effect of streamflow forecast uncertainty on real-time reservoir operation. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneti, S.; Sunkara, S.L.; Roy, P.S. Hydrological modeling with respect to impact of land-use and land-cover change on the runoff dynamics in Godavari River Basin using the HEC-HMS model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysanova, V.; Donnelly, C.; Gelfan, A.; Gerten, D.; Arheimer, B.; Hattermann, F.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. How the performance of hydrological models relates to credibility of projections under climate change. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 696–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Pappenberger, F.; Wood, A.; Cloke, H.L.; Schaake, J. Handbook of Hydrometeorological Ensemble Forecasting; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Devia, G.K.; Ganasri, B.; Dwarakish, G. A review on hydrological models. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbandsari, P.; Coulibaly, P. Inter-comparison of lumped hydrological models in data-scarce watersheds using different precipitation forcing data sets: Case study of Northern Ontario, Canada. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 31, 100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheater, H.; Jakeman, A.; Beven, K. Progress and Directions in Rainfall-Runoff Modelling; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Pechlivanidis, I.; Jackson, B.; Mcintyre, N.; Wheater, H. Catchment scale hydrological modelling: A review of model types, calibration approaches and uncertainty analysis methods in the context of recent developments in technology and applications. Glob. NEST J. 2011, 13, 193–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, C.W.; Abrahart, R.J.; Shamseldin, A.Y.; Wilby, R.L. Flood estimation at ungauged sites using artificial neural networks. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, P.K.d.M.M.; Santos, C.A.G.; da Silva, G.B.L. Analysis of the use of discrete wavelet transforms coupled with ANN for short-term streamflow forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 80, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.; McLeod, A.I.; Hipel, K.W. Contemporaneous autoregressive-moving average (CARMA) modeling in water resources 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1985, 21, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Singh, V.P. Review of dependence modeling in hydrology and water resources. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 40, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Chang, Y.T. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for prediction of water level in reservoir. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Ali, S.; Bharti, B. Comparative evaluation of conceptual and physical rainfall–runoff models. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Freer, J. Equifinality, data assimilation, and uncertainty estimation in mechanistic modelling of complex environmental systems using the GLUE methodology. J. Hydrol. 2001, 249, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Chen, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Zhang, X.; Cai, T.; Fang, X.; Qu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Q. Evaluating the SWAT model for hydrological modeling in the Xixian watershed and a comparison with the XAJ model. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2595–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.J.; Clark, M.P.; Winstral, A.; Marks, D.; Seyfried, M. The use of similarity concepts to represent subgrid variability in land surface models: Case study in a snowmelt-dominated watershed. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1717–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xie, Z. A new surface runoff parameterization with subgrid-scale soil heterogeneity for land surface models. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. VIC distributed hydrological model to predict climate change impact in the Hanjiang basin. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 3234–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, L.A.; de Mello, C.R.; Colombo, A.; Chou, S.C.; Cuartas, L.A.; Viola, M.R. Impacts of climate change on the hydrology of a Small Brazilian headwater catchment using the distributed hydrology-soil-vegetation model. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2018, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreda, F.; Koren, V.; Zhang, Z.; Reed, S.; Smith, M. Parameterization of distributed hydrological models: Learning from the experiences of lumped modeling. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, M.; Beven, K. A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1979, 24, 43–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Al-Asadi, K. Evaluating the effect of numerical schemes on hydrological simulations: HYMOD as a case study. Water 2019, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.P.; Kavetski, D. Ancient numerical daemons of conceptual hydrological modeling: 1. Fidelity and efficiency of time stepping schemes. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetski, D.; Clark, M.P. Ancient numerical daemons of conceptual hydrological modeling: 2. Impact of time stepping schemes on model analysis and prediction. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenicia, F.; Kavetski, D.; Savenije, H.H. Elements of a flexible approach for conceptual hydrological modeling: 1. Motivation and theoretical development. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.P.; Slater, A.G.; Rupp, D.E.; Woods, R.A.; Vrugt, J.A.; Gupta, H.V.; Wagener, T.; Hay, L.E. Framework for Understanding Structural Errors (FUSE): A modular framework to diagnose differences between hydrological models. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.P.; Nijssen, B.; Lundquist, J.D.; Kavetski, D.; Rupp, D.E.; Woods, R.A.; Freer, J.E.; Gutmann, E.D.; Wood, A.W.; Brekke, L.D.; et al. The Structure for Unifying Multiple Modeling Alternatives (SUMMA), Version 1.0: Technical Description; NCAR Tech. Note NCAR/TN-5141STR; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ONS. Amplicação do Modelo SMAP/ONS Para PrevisãO de Vazões no Âmbito do SIN; ONS 0097/2018-RV3; ONS: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, V.A.; Paiva, R.C.; Fleischmann, A.S.; Fan, F.M.; Ruhoff, A.L.; Pontes, P.R.; Paris, A.; Calmant, S.; Collischonn, W. Toward continental hydrologic–hydrodynamic modeling in South America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4815–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, A.S.; Siqueira, V.A.; Wongchuig-Correa, S.; Collischonn, W.; Paiva, R.C.D.D. The great 1983 floods in South American large rivers: A continental hydrological modelling approach. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 1358–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brêda, J.P.L.F.; de Paiva, R.C.D.; Chou, S.C.; Collischonn, W. Assessing extreme precipitation from a regional climate model in different spatial–temporal scales: A hydrological perspective in South America. Int. J. Climatol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Srivastava, A.; Sahoo, B.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Bretreger, D. Identification of suitable hydrological models for streamflow assessment in the Kangsabati River Basin, India, by using different model selection scores. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 4187–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, U.; Agarwal, A.; Shrestha, N.K.; Daggupati, P.; Srinivasan, G.; Than, H.H. Applicability of lumped hydrological models in a data-constrained river basin of Asia. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 05020018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, M.R.; Analui, B.; Gupta, H.V.; Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S. Three decades of the Shuffled Complex Evolution (SCE-UA) optimization algorithm: Review and applications. Sci. Iran. 2019, 26, 2015–2031. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H. Automatic calibration of SWAT model using LH-OAT sensitivity analysis and SCE-UA optimization method. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 39, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.Y.; Biftu, G.F. Automatic calibration of conceptual rainfall-runoff models: Optimization algorithms, catchment conditions, and model structure. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 3513–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapo, P.O.; Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S. Multi-objective global optimization for hydrologic models. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, D.P. Multicriteria Calibration of Hydrologic Models. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, C.; Michel, C.; Andréassian, V. Improvement of a parsimonious model for streamflow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2003, 279, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grouillet, B.; Ruelland, D.; Vaittinada Ayar, P.; Vrac, M. Sensitivity analysis of runoff modeling to statistical downscaling models in the western Mediterranean. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 1031–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Zhang, X.J. Assessment of climate change impacts on river high flows through comparative use of GR4J, HBV and Xinanjiang models. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2871–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, V.B.; Sambou, S.; Tamba, S.; Fall, S.; Diaw, A.T.; Cisse, M.T. Calibrating the rainfall-runoff model GR4J and GR2M on the Koulountou river basin, a tributary of the Gambia river. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 3, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hublart, P.; Ruelland, D.; García De Cortázar Atauri, I.; Ibacache, A. Reliability of a conceptual hydrological model in a semi-arid Andean catchment facing water-use changes. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 371, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.E.G.; Braga, B., Jr.; Conejo, J. SMAP—A simplified hydrologic model. In Applied Modeling in Catchment Hydrology; Singh, V.P., Ed.; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante, M.R.G.; da Cunha Luz Barcellos, P.; Cataldi, M. Flash flood in the mountainous region of Rio de Janeiro state (Brazil) in 2011: Part I—calibration watershed through hydrological SMAP model. Nat. Hazards 2020, 102, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha Luz Barcellos, P.; Cataldi, M. Flash flood and extreme rainfall forecast through one-way coupling of WRF-SMAP models: Natural hazards in Rio de Janeiro state. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, G.M.; Cabral, V.A.; Marcato, A.L.M.; Júnior, I.C.S.; Honório, L.D.M. Daily Water Flow Forecasting via Coupling Between SMAP and Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 204660–204675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.O.; dos Santos2 Pablo, J.W.B.; de Assis, R. Application of the SMAP hydrological model in the determination of water production in a coastal watershed. Rev. Bras. De Geogr. Física 2018, 11, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, S. The HBV Model-Its Structure and Applications; SMHI: Norrkoping, Sweden, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Aghakouchak, A.; Habib, E. Application of a conceptual hydrologic model in teaching hydrologic processes. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2010, 26, 963–973. [Google Scholar]
- Collischonn, W.; Allasia, D.; Da Silva, B.C.; Tucci, C.E. The MGB-IPH model for large-scale rainfall—Runoff modelling. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 878–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, V.A.; Fan, F.M.; De Paiva, R.C.D.; Ramos, M.H.; Collischonn, W. Potential skill of continental-scale, medium-range ensemble streamflow forecasts for flood prediction in South America. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.F.d.; Zolin, C.A.; Victoria, D.d.C.; Lopes, T.R.; Vendrusculo, L.G.; Paulino, J. Hydrological calibration and validation of the MGB-IPH model for water resource management in the upper Teles Pires River basin in the Amazon-Cerrado ecotone in Brazil. Acta Amaz. 2019, 49, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, T.S.; Uliana, E.M.; Martins, C.A.d.S.; Rapalo, L.M.C. Regionalization of maximum, minimum and mean streamflows for the Juruena River basin, Brazil. Rev. Ambiente Água 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.M.; Pontes, P.R.M.; Beltrame, L.F.; Collischonn, W.; Buarque, D.C. Operational flood forecasting system to the Uruguay River Basin using the hydrological model MGB-IPH. In Proceedings of the ICFM-6 Proceedings, São Paulo, Brasil, 16–18 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.M.; Schwanenberg, D.; Collischonn, W.; Weerts, A. Verification of inflow into hydropower reservoirs using ensemble forecasts of the TIGGE database for large scale basins in Brazil. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 196–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghnegahdar, A.; Tolson, B.A.; Craig, J.R.; Paya, K.T. Assessing the performance of a semi-distributed hydrological model under various watershed discretization schemes. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4018–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, P.R.M.; Fan, F.M.; Fleischmann, A.S.; de Paiva, R.C.D.; Buarque, D.C.; Siqueira, V.A.; Jardim, P.F.; Sorribas, M.V.; Collischonn, W. MGB-IPH model for hydrological and hydraulic simulation of large floodplain river systems coupled with open source GIS. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 94, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: Comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, P.D.; Sawilowsky, S.S. Increasing physicians’ awareness of the impact of statistics on research outcomes: Comparative power of the t-test and Wilcoxon rank-sum test in small samples applied research. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1999, 52, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levene, H. Robust tests for equality of variances. In Contributions to Probability and Statistics. Essays in Honor of Harold Hotelling; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1961; pp. 279–292. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A. Sulla determinazione empirica di una lgge di distribuzione. Inst. Ital. Attuari, Giorn. 1933, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Razali, N.M.; Wah, Y.B. Power comparisons of shapiro-wilk, kolmogorov-smirnov, lilliefors and anderson-darling tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2011, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, W.H.; Over, T.M.; Kiang, J.E. Bias correction of simulated historical daily streamflow at ungauged locations by using independently estimated flow duration curves. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5741–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Lozano, J.; Romero Bustamante, G.; Hales, R.; Nelson, E.J.; Williams, G.P.; Ames, D.P.; Jones, N.L. A Streamflow Bias Correction and Performance Evaluation Web Application for GEOGloWS ECMWF Streamflow Services. Hydrology 2021, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.M.; Collischonn, W.; Quiroz, K.; Sorribas, M.; Buarque, D.; Siqueira, V. Flood forecasting on the Tocantins River using ensemble rainfall forecasts and real-time satellite rainfall estimates. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2016, 9, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA. Plano Estratégico de Recursos Hídricos da Bacia Hidrográfica dos Rios Tocantins e Araguaia: Relatório e Síntese; Agência Nacional de Águas: Brasília, Brazil, 2009; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.d.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, R.; Viola, M.R.; de Mello, C.R.; Vieira-Filho, M.; Alves, M.V.; Amorim, J.d.S. Drought severity indexes for the Tocantins River Basin, Brazil. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 141, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, K.; Jarvis, P. Using the Penman-Monteith equation predictively. Agric. Water Manag. 1984, 8, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).