Alum and Gypsum Amendments Decrease Phosphorus Losses from Soil Monoliths to Overlying Floodwater under Simulated Snowmelt Flooding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Soil Monoliths and Soil Characterization
2.2. Incubation Study with Intact Soil Monoliths
2.3. Predicting Phosphorus Transformations with Flooding in Amended and Unamended Soil
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Characterization
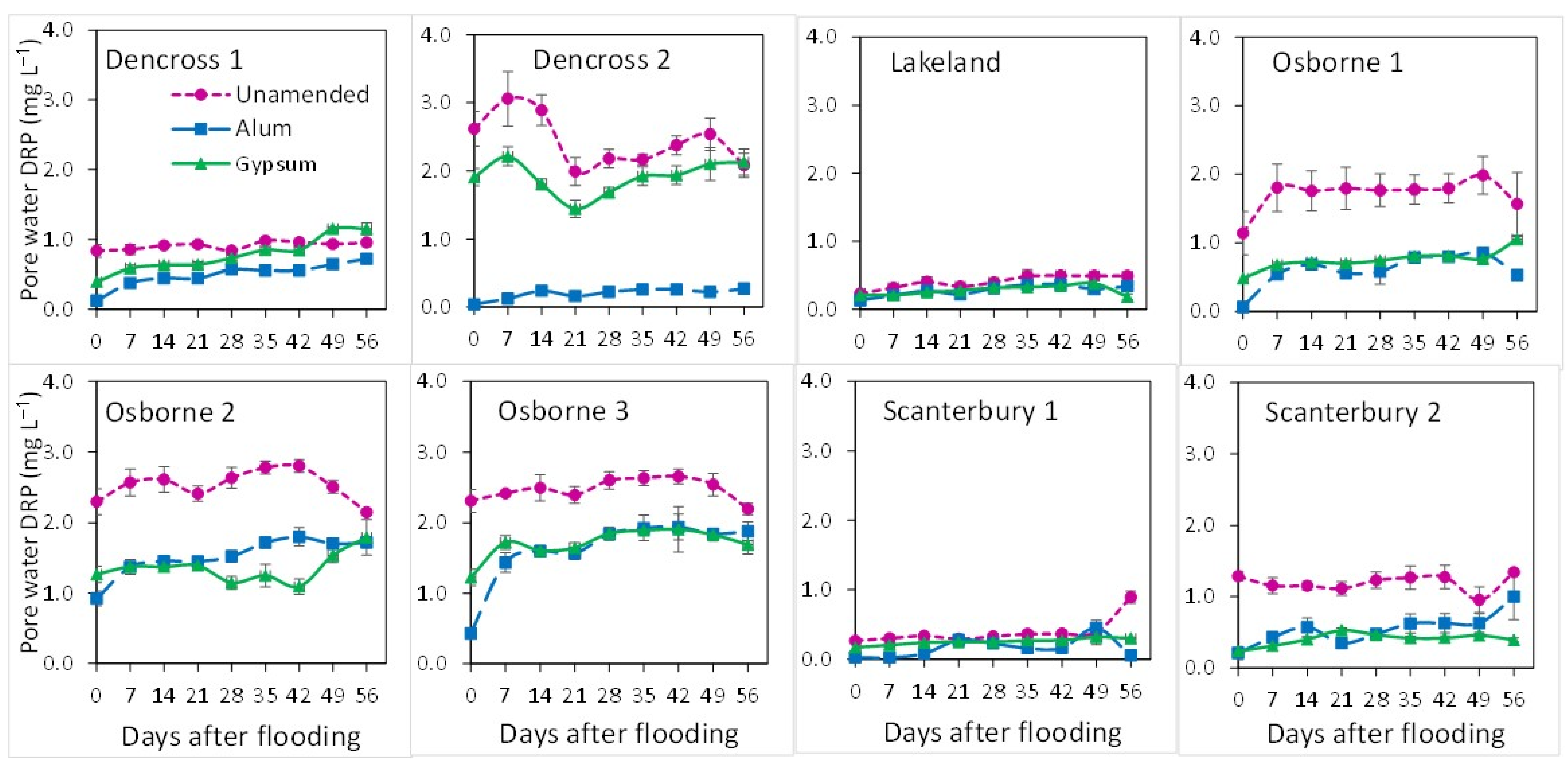
3.2. Dissolved Reactive P and Total P Concentrations in Porewater and Floodwater with Days of Flooding (DAF)
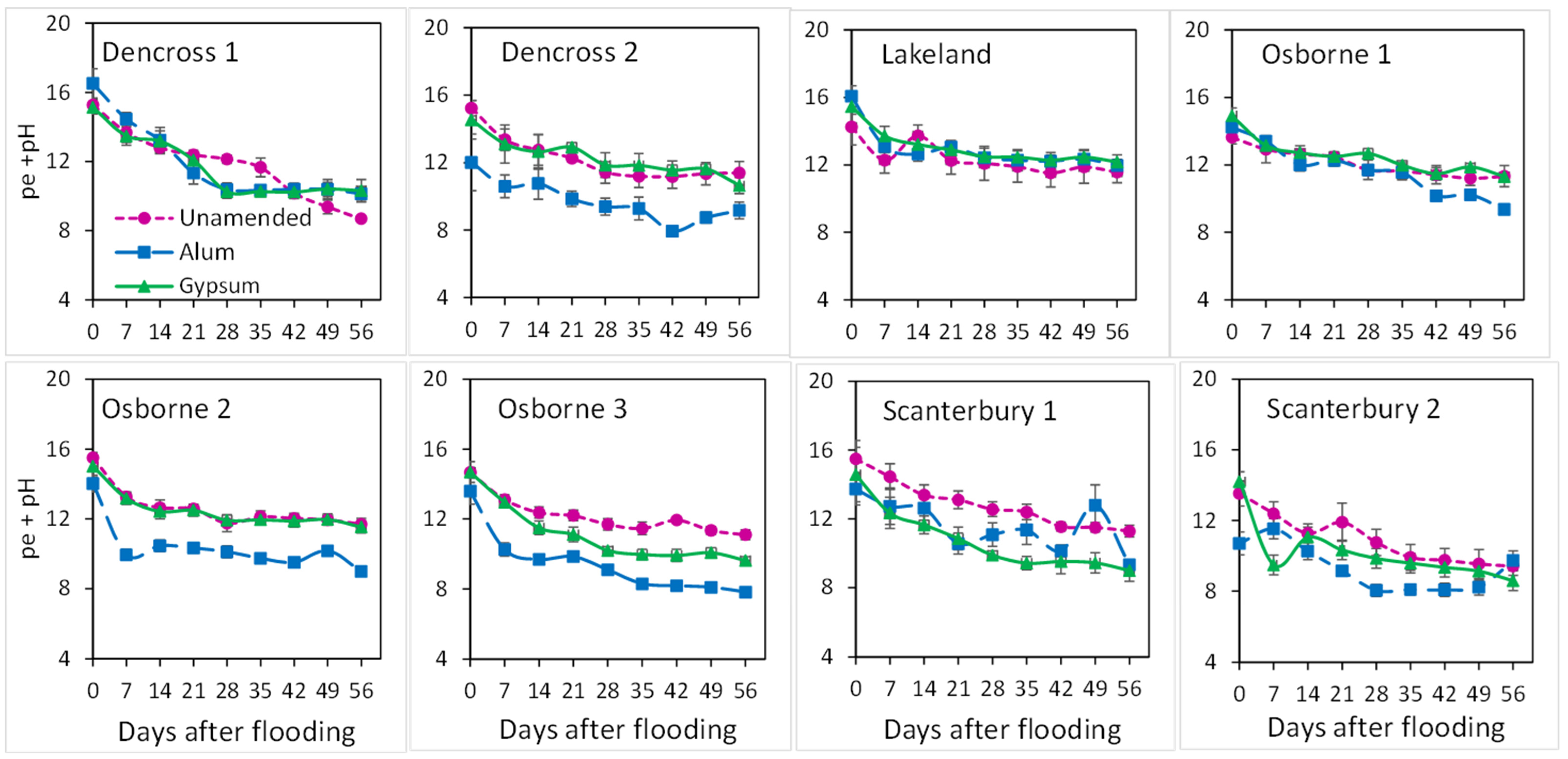
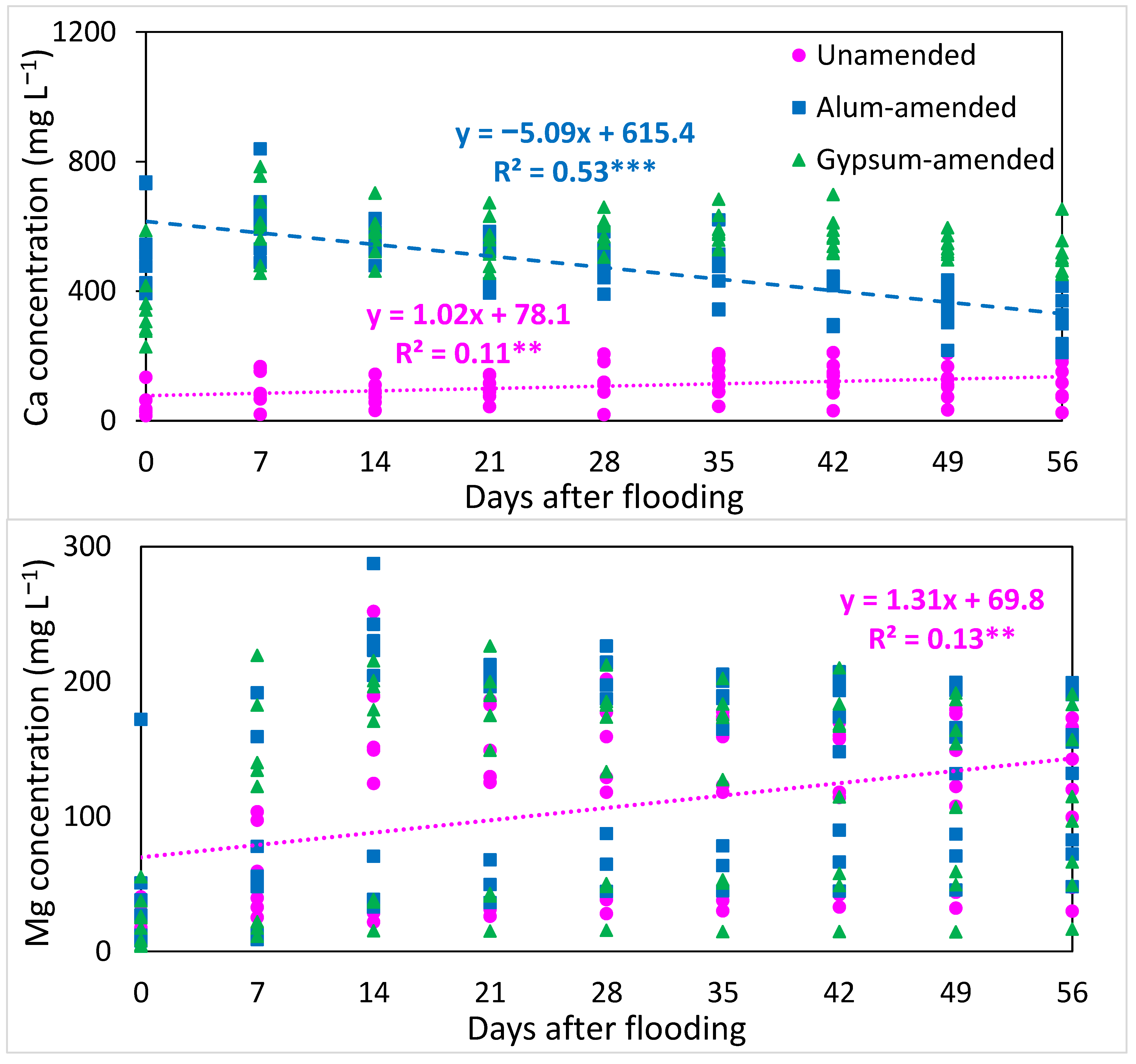
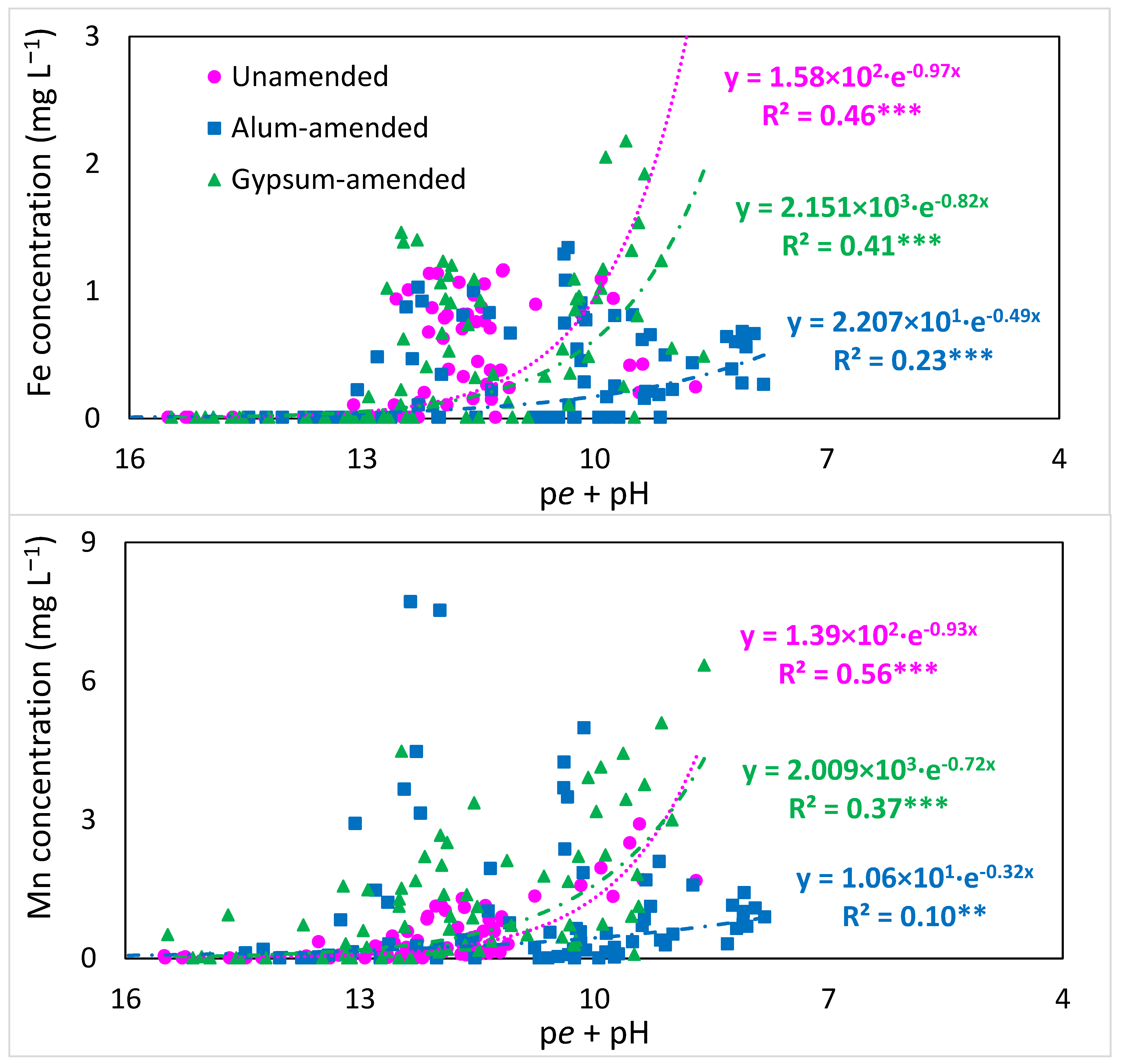
3.3. Changes in Overall Redox Status and Release of Cations with Time of Flooding
3.4. Predicted P Transformations with Amended Treatments and Flooding
4. Discussion
4.1. Redox, Ionic Strength, and pH Changes with Flooding and Amendments
4.2. P Transformations and Release at Early Stages of Flooding in Amended and Unamended Soils
4.3. P Transformations and Release with Prolonged Flooding in Amended and Unamended Soils
4.4. Effectiveness of Alum and Gypsum in Reducing P Release from Flooded Soils
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; McDowell, R.W.; Flaten, D.N.; Buda, A.R.; Tao, L.; Bergstrom, L.; Zhu, Q. Managing Agricultural Phosphorus for Water Quality Protection: Principles for Progress. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Gburek, W.J.; Folmar, G.; Pionke, H.B. Sources of Phosphorus Exported from an Agricultural Watershed in Pennsylvania. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 41, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Evolution of Phosphorus Limitation in Lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; McCullough, G.K. The Rapid Eutrophication of Lake Winnipeg: Greening under Global Change. J. Great Lakes Res. 2012, 38, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.; Foy, B.; Withers, P. Practical and Innovative Measures for the Control of Agricultural Phosphorus Losses to Water: An Overview. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Elliott, J.A.; Lobb, D.A.; Flaten, D.N.; Yarotski, J. Nutrient and Sediment Losses in Snowmelt Runoff from Perennial Forage and Annual Cropland in the Canadian Prairies. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattan, K.J.; Corriveau, J.C.; Brua, R.B.; Culp, J.M.; Yates, A.G.; Chambers, P.A. Quantifying Seasonal Variation in Total Phosphorus and Nitrogen from Prairie Streams in the Red River Basin, Manitoba Canada. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulén, B. Concentrations and Transport of Different Forms of Phosphorus during Snowmelt Runoff from an Illite Clay Soil. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.; Elliott, J.; Macrae, M.; Glenn, A. Near-Surface Soils as a Source of Phosphorus in Snowmelt Runoff from Cropland. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bedard-Haughn, A. Managing Excess Water in Canadian Prairie Soils: A Review. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2009, 89, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnamperuma, F.N. The Chemistry of Submerged Soils. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1972; Volume 24, pp. 29–96. ISBN 978-0-12-000724-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaragamage, D.; Concepcion, A.; Gregory, C.; Goltz, D.; Indraratne, S.; Amarawansha, G. Temperature and Freezing Effects on Phosphorus Release from Soils to Overlying Floodwater under Flooded-Anaerobic Conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasekara, C.; Kumaragamage, D.; Akinremi, W.; Indraratne, S.; Goltz, D. Phosphorus Mobilization from Intact Soil Monoliths Flooded under Simulated Summer versus Spring Snowmelt with Intermittent Freeze–Thaw Conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, W.H., Jr.; Jugsujinda, A. Sequential Reduction and Oxidation of Inorganic Nitrogen, Manganese, and Iron in Flooded Soil. Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarawansha, E.A.G.S.; Kumaragamage, D.; Flaten, D.; Zvomuya, F.; Tenuta, M. Phosphorus Mobilization from Manure-Amended and Unamended Alkaline Soils to Overlying Water during Simulated Flooding. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maranguit, D.; Guillaume, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of Flooding on Phosphorus and Iron Mobilization in Highly Weathered Soils under Different Land-Use Types: Short-Term Effects and Mechanisms. Catena 2017, 158, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaragamage, D.; Amarawansha, G.S.; Indraratne, S.P.; Jayarathne, K.; Flaten, D.N.; Zvomuya, F.; Akinremi, O.O. Degree of Phosphorus Saturation as a Predictor of Redox-Induced Phosphorus Release from Flooded Soils to Floodwater. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalenghe, R.; Edwards, A.C.; Ajmone Marsan, F.; Barberis, E. The Effect of Reducing Conditions on the Solubility of Phosphorus in a Diverse Range of European Agricultural Soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2002, 53, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalenghe, R.; Edwards, A.C.; Barberis, E.; Ajmone-Marsan, F. Release of Phosphorus under Reducing and Simulated Open Drainage Conditions from Overfertilised Soils. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarawansha, G.; Kumaragamage, D.; Flaten, D.; Zvomuya, F.; Tenuta, M. Predicting Phosphorus Release from Anaerobic, Alkaline, Flooded Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayarathne, P.D.K.D.; Kumaragamage, D.; Indraratne, S.; Flaten, D.; Goltz, D. Phosphorus Release to Floodwater from Calcareous Surface Soils and Their Corresponding Subsurface Soils under Anaerobic Conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Van Kempen, M.M.L.; Van der Heide, T.; Manschot, J.J.A.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; Lamers, L.P.M.; Smolders, A.J.P. A Tool for Easily Predicting Short-Term Phosphorus Mobilization from Flooded Soils. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Jianhua, L. Organic Phosphorus Fractions in Organically Amended Paddy Soils in Continuously and Intermittently Flooded Conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, P.A.; Miller, D.M. Decreasing phosphorus solubility in poultry litter with aluminum, calcium, and iron amendments. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shreve, B.R.; Moore, P.A., Jr.; Daniel, T.C.; Edwards, D.R.; Miller, D.M. Reduction of Phosphorus in Runoff from Field-Applied Poultry Litter Using Chemical Amendments. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, N.; Norton, L.D.; Joern, B.C.; Brouder, S.M. Gypsum Amendment and Exchangeable Calcium and Magnesium Affecting Phosphorus and Nitrogen in Runoff. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, P.N.C.; Stevens, R.J. Lime and Gypsum as Source Measures to Decrease Phosphorus Loss from Soils to Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; Dick, W.A.; LaBarge, G.A. Decreasing Phosphorus Loss in Tile-Drained Landscapes Using Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, N.; Norton, L.D.; Johnston, C.T.; Bigham, J.; Sperrin, M. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Leaching as Affected by Gypsum Amendment and Exchangeable Calcium and Magnesium. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.B.; Torbert, H.A. Influence of Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum on Reducing Soluble Phosphorus in Successive Runoff Events from a Coastal Plain Bermudagrass Pasture. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekholm, P.; Valkama, P.; Jaakkola, E.; Kiirikki, M.; Lahti, K.; Pietola, L. Gypsum Amendment of Soils Reduces Phosphorus Losses in an Agricultural Catchment. Agric. Food Sci. 2012, 21, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lizarralde, C.A.; McDowell, R.W.; Condron, L.M.; Brown, J.; Whelan, M.; Lizarralde, C.A.; McDowell, R.W.; Condron, L.M.; Brown, J.; Whelan, M. Amending Soils of Different PH to Decrease Phosphorus Losses. Soil Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, Y.; Reddy, K.R.; Delfino, J.J. Influence of Chemical Amendments on Phosphorus Immobilization in Soils from a Constructed Wetland. Ecol. Eng. 1999, 14, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmakeerthi, R.S.; Kumaragamage, D.; Goltz, D.; Indraratne, S.P. Phosphorus Release from Unamended and Gypsum- or Biochar-Amended Soils under Simulated Snowmelt and Summer Flooding Conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dharmakeerthi, R.S.; Kumaragamage, D.; Indraratne, S.P.; Goltz, D. Gypsum Amendment Reduces Redox-Induced Phosphorous Release from Freshly Manured, Flooded Soils to Floodwater. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitharana, U.W.A.; Kumaragamage, D.; Balasooriya, B.L.W.K.; Indraratne, S.P.; Goltz, D. Phosphorus Mobilization in Unamended and Magnesium Sulfate-Amended Soil Monoliths under Simulated Snowmelt Flooding. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Yosef, B.; Rosenberg, R.; Kafkafi, U.; Sposito, G. Phosphorus adsorption by kaolinite and montmorillonite: I. Effect of time, ionic strength, and pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1988, 52, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Shaw, T.C. Effects of ionic strength and nature of the cation on desorption of phosphate from soil. J. Soil Sci. 1979, 30, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, J.C.; Syers, J.K. Desorption and isotopic exchange relationships of phosphate sorbed by soils and hydrous ferric oxide gel. J. Soil Sci. 1977, 28, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G.; Coves, J. SOILCHEM: A Computer Program for the Calculation of Chemical Speciation in Soil; The Kearney Foundation of Soil Science; University of California: Riverside, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, J.P. Visual MINTEQ—Visual MINTEQ—A Free Equilibrium Speciation Model. 2013. Available online: https://vminteq.lwr.kth.se/ (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Attanayake, C.; Dharmakeerthi, R.S.; Kumaragamage, D.; Indraratne, S.P.; Goltz, D. Flooding Induced Inorganic Phosphorus Transformations in Two Soils, with and without Gypsum Amendment. J. Environ. Qual. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concepcion, A.; Kumaragamage, D.; Akinremi, W.; Dharmakeerthi, S.; Goltz, D.; Indraratne, S. Phosphorus Release from Intact Soil Monoliths of Manure-Amended Fields under Simulated Snowmelt Flooding. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Classification Working Group; NRC Press: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1998.
- FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources, by ISSS-ISRIC-FAO; World Soil Resources Reports No. 103, FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed.; Klute, A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. ISBN 978-0-8911-8088-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich-3 soil test extractant. A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Comm. Soil Sci. Pl. Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, W.E. Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: Comparison with other methods. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1974, 44, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, W. Chemical Equilibria in Soils; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water And Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and the Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-087553-013-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sposito, G. The Chemistry of Soils, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-19-063088-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mosley, L.M.; Daly, R.; Palmer, D.; Yeates, P.; Dallimore, C.; Biswas, T.; Simpson, S.L. Predictive Modelling of PH and Dissolved Metal Concentrations and Speciation Following Mixing of Acid Drainage with River Water. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 59, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. SAS for Windows. Version 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom, S.M.; White, J.R. Reducing Phosphorus Flux from Organic Soils in Surface Flow Treatment Wetlands. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, J.; Anderson, M.A.; Graham, R.C. Laboratory Investigation of Aluminum Solubility and Solid-Phase Properties Following Alum Treatment of Lake Waters. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3918–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Moore, P.A., Jr.; Griffis, C.L.; Daniel, T.C.; Edwards, D.R.; Boothe, D.L. Effects of Alum and Aluminum Chloride on Phosphorus Runoff from Swine Manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Walthall, P.M. The solubility of aluminum in soils. In The Environmental Chemistry of Aluminum.; Sposito, G., Ed.; Lewis Publishers: Washington DC, USA, 1995; ISBN 1-56670-030-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, E.A.; Marcos, M.L.F.; Martínez, C.M. Solubility Equilibria Controlling Solution Phosphorus Concentration in Minesoils in Galicia, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 180, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Wang, J.; Fenton, O.; Daly, K.; Ezzati, G.; Chen, Q. Strategic Differences in Phosphorus Stabilization by Alum and Dolomite Amendments in Calcareous and Red Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4842–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak, D.; Sims, J.T.; Sparks, D.L. Solid-State Speciation of Natural and Alum-Amended Poultry Litter Using XANES Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4253–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; El-sharkawi, H.; Irshad, M.; Honna, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Al-busaidi, A.S. Changes in Water-Extractability of Soil Inorganic Phosphate Induced by Chloride and Sulfate Salts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2008, 15, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Jiang, T.; Yao, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Q.; Wei, S. Preliminary Investigation of Phosphorus Adsorption onto Two Types of Iron Oxide-Organic Matter Complexes. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 42, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.B.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Nielsen, N.E.; Magid, J. Phosphate Mobilization and Immobilization in Two Soils Incubated under Simulated Reducing Conditions. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 1998, 48, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Dong, G.; Karthikeyan, R.; Li, L.; Harmel, R.D. Phosphorus Dynamics in Long-Term Flooded, Drained, and Reflooded Soils. Water 2017, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, E.O.; Ross, D.S. Phosphate Release from Seasonally Flooded Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.B.; Fenton, O.; Grant, J.; Healy, M.G. Impact of Chemical Amendment of Dairy Cattle Slurry on Phosphorus, Suspended Sediment and Metal Loss to Runoff from a Grassland Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5111–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, P.A., Jr.; Daniel, T.C.; Gilmour, J.T.; Shreve, B.R.; Edwards, D.R.; Wood, B.H. Decreasing Metal Runoff from Poultry Litter with Aluminum Sulfate. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaif, N.I.; Gharaibeh, M.A. Impact of Alum on Crust Prevention and Aggregation of Calcareous Soil: Laboratory Studies. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 424–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibiandehkordi, R.; Quinton, J.N.; Surridge, B.W. Long-Term Effects of Drinking-Water Treatment Residuals on Dissolved Phosphorus Export from Vegetated Buffer Strips. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6068–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mineral | SI at 0 DAF | SI at 28 DAF | SI at 56 DAF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unamended | Alum-Amended | Gypsum-Amended | Unamended | Alum-Amended | Gypsum-Amended | Unamended | Alum-Amended | Gypsum-Amended | |
| Dencross 2 soil | |||||||||
| AlPO4·1·5H2O | −4.1 | −0.9 | −1.1 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.6 | −1.1 | −0.4 | 0.6 |
| Ca3(PO4)2 (beta) | 1.6 | −6.8 | 2.6 | 1.4 | −1.1 | 1.8 | 0.3 | −0.8 | 2.0 |
| Hydroxyapatite | 8.6 | −6.0 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 4.1 | 8.7 | 6.1 | 4.5 | 8.9 |
| MnHPO4(s) | 1.3 | −0.6 | 0.5 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 1.8 | 2.5 |
| Variscite | −2.5 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 2.3 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 2.2 |
| Lakeland soil | |||||||||
| Ca3(PO4)2 (beta) | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| Hydroxyapatite | 7.8 | 6.6 | 7.2 | 8.1 | 8.9 | 8.5 | 7.8 | 7.3 | 8.2 |
| MnHPO4(s) | −0.1 | −0.7 | −0.5 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| Variscite | −3.3 | 0.6 | 0.3 | −1.2 | 0.6 | 0.5 | −0.1 | 0.7 | −2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumaragamage, D.; Weerasekara, C.S.; Perry, M.; Akinremi, O.O.; Goltz, D. Alum and Gypsum Amendments Decrease Phosphorus Losses from Soil Monoliths to Overlying Floodwater under Simulated Snowmelt Flooding. Water 2022, 14, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040559
Kumaragamage D, Weerasekara CS, Perry M, Akinremi OO, Goltz D. Alum and Gypsum Amendments Decrease Phosphorus Losses from Soil Monoliths to Overlying Floodwater under Simulated Snowmelt Flooding. Water. 2022; 14(4):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040559
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumaragamage, Darshani, Chamara S. Weerasekara, Madelynn Perry, Olalekan O. Akinremi, and Doug Goltz. 2022. "Alum and Gypsum Amendments Decrease Phosphorus Losses from Soil Monoliths to Overlying Floodwater under Simulated Snowmelt Flooding" Water 14, no. 4: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040559
APA StyleKumaragamage, D., Weerasekara, C. S., Perry, M., Akinremi, O. O., & Goltz, D. (2022). Alum and Gypsum Amendments Decrease Phosphorus Losses from Soil Monoliths to Overlying Floodwater under Simulated Snowmelt Flooding. Water, 14(4), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040559






