Formation Mechanisms and Characteristics of the Marine Nepheloid Layer: A Review
Abstract
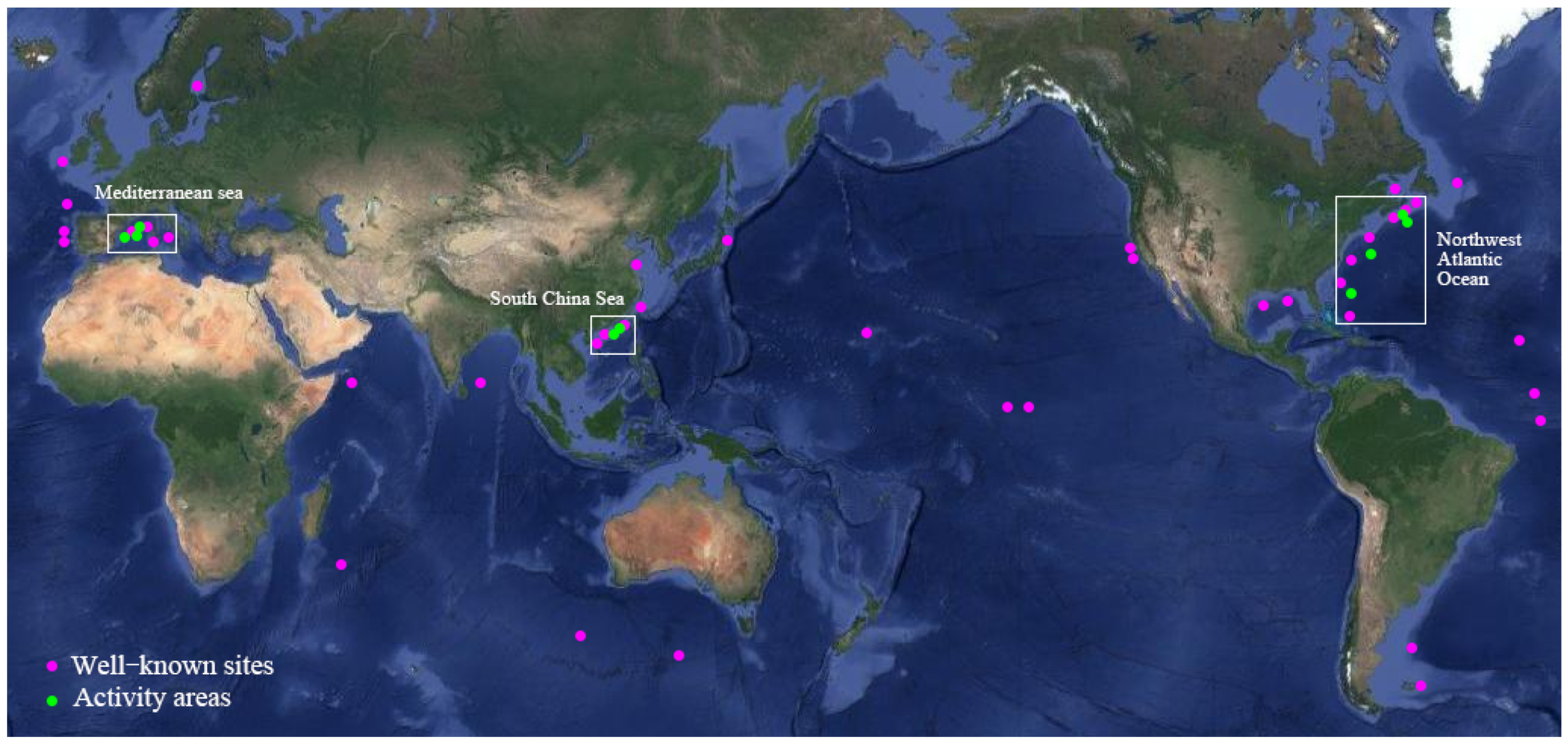
:1. Introduction
2. Characteristic of Marine Nepheloid Layer
2.1. Marine Nepheloid Layer of the Ocean
2.2. Marine Nepheloid Layer in the Marginal Sea
3. Formation Mechanisms of Marine Nepheloid Layer
3.1. Formation Mechanisms of Bottom Nepheloid Layer
3.1.1. Bottom Boundary Mixing Processes
3.1.2. Formation Mechanisms
3.2. Formation Mechanisms of Intermediate Nepheloid Layer
3.2.1. Reflection Characteristics of Internal Solitary Wave
3.2.2. Formation Mechanisms of Intermediate Nepheloid Layer by Internal Solitary Wave
3.3. Formation Mechanisms of Surface Nepheloid Layer
4. Observational, Experimental, and Numerical Results
4.1. Observation Methods of Marine Nepheloid Layer
4.2. Laboratory Experiments and Numerical Simulation on Nepheloid Layer
5. Summary and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ransom, B.; Shea, K.F.; Burkett, P.J. Comparison of pelagic and nepheloid layer marine snow: Implications for carbon cycling. Mar. Geol. 1998, 150, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Peng, X.; Wang, H. Formation cause of nepheloid layer and its effect on ocean carbon cycle process. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2004, 22, 364–369. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Madron, X.D.D.; Ramondenc, S.; Berline, L.; Houpert, L.; Bosse, A.; Martini, S.; Guidi, L.; Conan, P.; Curtil, C.; Delsaut, N.; et al. Deep sediment resuspension and thick nepheloid layer generation by open-ocean convection. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 2291–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diercks, A.-R.; Dike, C.; Asper, V.L.; DiMarco, S.F.; Chanton, J.P.; Passow, U. Scales of seafloor sediment resuspension in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2018, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCave, I.N. Local and global aspects of the bottom nepheloid layers in the world ocean. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1986, 20, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCave I, N. Nepheloid Layers. Encycl. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 1, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchione, D.A.; Pratson, L.F.; Ogston, A.S. The shaping of continental slopes by internal tides. Science 2002, 296, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Guillén, J.; El Khatab, M. Role of internal waves in the generation of nepheloid layers on the northwestern Alboran slope: Implications for continental margin shaping. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puig, P.; Greenan, B.J.W.; Li, M.Z.; Prescott, R.H.; Piper, D.J.W. Sediment transport processes at the head of Halibut Canyon, eastern Canada margin: An interplay between internal tides and dense shelf-water cascading. Mar. Geol. 2013, 341, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puig, P.; Martín, J.; Masqué, P.; Palanques, A. Increasing sediment accumulation rates in La Fonera (Palamós) submarine canyon axis and their relationship with bottom trawling activities. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8106–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arjona-Camas, M.; Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Durán, R.; White, M.; Paradis, S.; Emelianov, M. Natural vs. trawling-induced water turbidity and suspended sediment transport variability within the Palamós Canyon (NW Mediterranean). Mar. Geophys. Res. 2021, 42, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azetsu-Scott, K.; Johnson, B.D.; Petrie, B. An intermittent, intermediate nepheloid layer in Emerald Basin, Scotian Shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1995, 15, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerlov, N.C. Particle distribution in the ocean. Rep. Swed. Deep-Sea Exped. 1953, 3, 73–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, M.; Thorndike, E.M. Suspended matter in deep ocean water. Science 1965, 147, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biscaye, P.E.; Eittreim, S.L. Variations in benthic boundary layer phenomena: Nepheloid layer in the North American Basin. In Suspended Solids in Water; Gibbs, R.J., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 227–260. [Google Scholar]
- Biscaye, P.E.; Eittreim, S.L. Suspended particulate loads and transports in the nepheloid layer of the abyssal Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Geol. 1977, 23, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, C.D.; McCave, I.N. Sedimentation under deep-sea storms. Nature 1984, 309, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.D.; Richardson, M.J.; Mishonov, A.V.; Biscaye, P.E. Global comparison of benthic nepheloid layers based on 52 years of nephelometer and transmissometer measurements. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 168, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubnova, E.S.; Kapustina, M.V.; Krechik, V.A.; Sivkov, V.V. Suspended Matter Distribution in the Surface Layer of the East Equatorial Atlantic. Oceanology 2020, 60, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivkov, V.; Bubnova, E. Distribution of suspended particulate matter at the equatorial transect in the Atlantic Ocean. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 1421–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriton, O.M.; McPhee-Shaw, E.E.; Shaw, W.J.; Stanton, T.P.; Bellingham, J.G.; Storlazzi, C.D. Suspended particulate layers and internal waves over the southern Monterey Bay continental shelf: An important control on shelf mud belts?: Suspended Particulate Layers. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunaga, E.; Homma, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Fringer, O.B.; Nagai, T.; Kitade, Y.; Okayasu, A. Mixing and sediment resuspension associated with internal bores in a shallow bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 110, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, L.S.; Vitorino, J.; Oliveira, A.; da Silva, J. Evidence of sediment resuspension by nonlinear internal waves on the western Portuguese midshelf. Mar. Geol. 2007, 246, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.; Bourgault, D.; Galbraith, P.S.; Hay, A.; Kelley, D.E. Measurements of shoaling internal waves and turbulence in an estuary: Shoaling Internal Waves And Turbulence. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Y. Characteristics of suspended particles in the Pacific Ocean and discussion about near-bottom nepheloid layers. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2007, 29, 74–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.L.; Huang, L.L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Liu, S. Flux and its seasonal variation of suspended particulate matter in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Geol. J. 2016, 51, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qiao, L.; Li, G. Transport and flux of suspended sediment and its seasonal variation over the inner shelf of the east China sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2018, 49, 24–39. [Google Scholar]
- Reeder, D.B.; Ma, B.B.; Yang, Y.J. Very large subaqueous sand dunes on the upper continental slope in the South China Sea generated by episodic, shoaling deep-water internal solitary waves. Mar. Geol. 2011, 279, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Xiang, L.; Fang, J.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.; Ou, Y.; Fan, Y. A preliminary study on the characteristics of nepheloid layers in the northern South China Sea and their influential factors. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 36, 51–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Liu, J.T. Particle dynamics of the surface, intermediate, and benthic nepheloid layers under contrasting conditions of summer monsoon and typhoon winds on the boundary between the Taiwan Strait and East China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 156, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Bottom and intermediate nepheloid layer induced by shoaling internal solitary waves: Impacts of the angle of the wave group velocity vector and slope gradients. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Jia, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.P.; Zhang, S.; Ji, C.; Liu, X.; Shan, H.; Shi, X.; Tian, J. Internal solitary waves induced deep-water nepheloid layers and seafloor geomorphic changes on the continental slope of the northern South China Sea. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 053312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novigatsky, A.N.; Lisitzin, A.P.; Klyuvitkin, A.A.; Shevchenko, V.P.; Kravchishina, M.D.; Politova, N.V. Vertical Fluxes of Suspended Sedimentary Matter in Arctic Sedimentogenesis of Intracontinental Seas. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2018, 479, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgault, D.; Morsilli, M.; Richards, C.; Neumeier, U.; Kelley, D.E. Sediment resuspension and nepheloid layers induced by long internal solitary waves shoaling orthogonally on uniform slopes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 72, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masunaga, E.; Arthur, R.S.; Fringer, O.B.; Yamazaki, H. Sediment resuspension and the generation of intermediate nepheloid layers by shoaling internal bores. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 170, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weering, T.C.E.V.; Stigter, H.C.D.; Balzer, W.; Epping, E.H.G.; Graf, G.; Hall, I.R.; Helder, W.; Khripounoff, A.; Lohse, L.; McCave, N.I.; et al. Benthic dynamics and carbon fluxes on the NW European continental margin. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 48, 3191–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaye, P.E.; Flagg, C.N.; Falkowski, P.G. The Shelf Edge Exchange Processes experiment, SEEP-II: An introduction to hypotheses, results and conclusions. Deep-Sea Res. II 1994, 41, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollast, R.; Chou, L. Ocean margin exchange in the northern Gulf of Biscay: OMEX I, an introduction. Deep.-Sea Res. II 2001, 48, 2971–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee-Shaw, E. Boundary–interior exchange: Reviewing the idea that internal-wave mixing enhances lateral dispersal near continental margins. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2006, 53, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Colin, C.; Stattegger, K.; Wiesner, M.G.; Huh, C.-A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sompongchaiyakul, P.; You, C.-F.; et al. Source-to-sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 153, 238–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Vitorino, J.; Rodrigues, A.; Jouanneau, J.; Dias, J.; Weber, O. Nepheloid layer dynamics in the northern Portuguese shelf. Prog. Oceanogr. 2002, 52, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, P.; de Madron, X.D.; Salat, J.; Schroeder, K.; Martín, J.; Karageorgis, A.P.; Palanques, A.; Roullier, F.; Lopez-Jurado, J.L.; Emelianov, M.; et al. Thick bottom nepheloid layers in the western Mediterranean generated by deep dense shelf water cascading. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 111, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Washburn, L.; Swenson, M.S.; Largier, J.L.; Kosro, P.M.; Ramp, S.R. Cross-Shelf Sediment Transport by an Anticyclonic Eddy Off Northern California. Science 1993, 261, 1560–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Tian, J.; Zhao, W. Polarity variations of internal solitary waves over the continental shelf of the northern South China Sea: Impacts of seasonal stratification, mesoscale eddies and internal tides. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2018, 48, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.D.; Southard, J.B.; Hollister, C.D. Sedimentation and resuspension in the western North Atlantic. Mar. Geol. 1985, 65, 199–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eittreim, S.; Thorndike, E.M.; Sullivan, L. Turbidity distribution in the Atlantic Ocean. Deep-Sea Res. 1976, 23, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A.; McDowell, S.E.; Sullivan, L.G.; Biscaye, P.E. Abyssal hydrography, nephelometry, currents and benthic boundary layer structure in the Vema Channel. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 5771–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.D.; Sullivan, L.G. Benthic storms: Temporal variability in a deep ocean nepheloid layer. Science 1981, 213, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, H. Fluctuations of beam-attenuation coefficient in the lowest 2 m on the continental rise off Nova Scotia. Mar. Geol. 1983, 51, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, H.; Zaneveld, J.R.V. Temporal variations of beam attenuation coefficient on the continental rise off Nova Scotia. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 4427–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, C.D.; Nowell, A.R.M. HEBBLE epilogue. Mar. Geol. 1991, 99, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isley, A.E.; Pillsbury, R.D.; Laine, E.P. The genesis and character of benthic turbid events, northern Hatteras Abyssal Plain. Deep-Sea Res. 1990, 37, 1099–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, H.; Mittelstaedt, E. Currents and dispersion in the abyssal Northeast Atlantic: Results from the NOAMP field program. Deep-Sea Res. 1992, 39, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.J.; Weatherly, G.L.; Gardner, W.D. Benthic storms in the Argentine Basin. Deep-Sea Res. 1993, 40, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.D.; Tucholke, B.E.; Richardson, M.J.; Biscaye, P.E. Benthic storms, nepheloid layers, and linkage with upper ocean dynamics in the western North Atlantic. Mar. Geol. 2017, 385, 304–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, C.; Canals, M.; De Madron, X.D.; Houpert, L.; Lefèvre, D.; Martini, S.; D’Ortenzio, F.; Robert, A.; Testor, P.; Aguilar, J.A.; et al. Deep-sea bioluminescence blooms after dense water formation at the ocean surface. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puig, P.; Palanques, A.; Orange, D.L.; Lastras, G.; Canals, M. Dense shelf water cascades and sedimentary furrow formation in the Cap de Creus Canyon, northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Weidemann, A.; Pegau, W.S. Internal tidal bores and bottom nepheloid layers. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosegood, P.; Bonnin, J.; van Haren, H. Solibore-induced sediment resuspension in the Faeroe-Shetland Channel: Solibores Above The Continental Slope. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palanques, A.; Puig, P.; Latasa, M.; Scharek, R. Deep sediment transport induced by storms and dense shelf-water cascading in the Northwestern Mediterranean basin. Deep. Sea Res. Part I 2009, 56, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boegman, L.; Stastna, M. Sediment Resuspension and Transport by Internal Solitary Waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2019, 51, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorke, A.; Macintyre, S. The Benthic Boundary Layer (in Rivers, Lakes, and Reservoirs); Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.; Davies, P.A. Boundary layer flow beneath an internal solitary wave of elevation. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 026601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghsaee, P.; Boegman, L.; Diamessis, P.J.; Lamb, K.G. Boundary-layer-separation-driven vortex shedding beneath internal solitary waves of depression. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 690, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Forgia, G.; Tokyay, T.; Adduce, C.; Constantinescu, G. Bed shear stress and sediment entrainment potential for breaking of internal solitary waves. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 135, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Silva, J.C.B.D.; Jeans, G. The Generation of Nonlinear Internal Waves. Oceanography 2012, 25, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.T.; Hickey, B.M. Contemporary sedimentation processes in and around an active West Coast submarine canyon. Mar. Geol. 1986, 71, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bogucki, D.; Redekopp, L. Internal solitary waves in a structured thermocline with implications for resuspension and the formation of thin particle laden layers. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 9565–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, R.-C.; Henyey, F.; Ma, B.; Yang, Y.J. Large-Amplitude Internal Solitary Waves Observed in the Northern South China Sea: Properties and Energetics. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 1095–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, J.R.; Holbrook, J.R.; Liu, A.K.; Tsai, J.J. The Sulu Sea internal soliton experiment. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1985, 15, 1625–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helfrich, K.R.; Melville, W.K. Long nonlinear internal waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2006, 38, 395–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroyer, E.L.; Moum, J.N.; Nash, J.D. Vertical heat flux and lateral mass trans- port in nonlinear internal waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L08601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Forgia, G.; Adduce, C.; Falcini, F. Laboratory investigation on internal solitary waves interacting with a uniform slope. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 120, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, C. Internal tides and ocean mixing. Science 2003, 301, 1858–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedlowsky, J.; Miles, J. Waves in the ocean and atmosphere: Introduction to wave dynamics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2004, 57, B20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, B.R.; Barrett, K.J.; Ivey, G.N. Shoaling internal solitary waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 4111–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchione, D.; Wunsch, C. Experimental study of internal waves over a slope. J. Fluid Mech. 1974, 66, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, I.P.D.; Imberger, J.; Ivey, G.N. Localized mixing due to a breaking internal wave ray at a sloping bottom. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 350, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrett, C. The role of secondary circulation in boundary mixing. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 3181–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, O.M.; Shyu, J.H.; Salmun, H. An experiment on boundary mixing: Mean circulation and transport rates. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 173, 473–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, C. Marginal mixing theories. Atmosphere-Ocean 1991, 29, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsilli, M.; Pomar, L. Internal waves vs. surface storm waves: A review on the origin of hummocky cross-stratification: Hummocky cross-stratification formed by internal waves. Terra Nova 2012, 24, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Yu, L.; Jia, Y. Experimental investigation of sediment dynamics in response to breaking high-frequency internal solitary wave packets over a steep slope. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 199, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, L.; Thunell, R.C.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Hollander, D.; Martinez, N.; Tappa, E.; Varela, R.; Astor, Y.; Muller-Karger, F.E. The importance of subsurface nepheloid layers in transport and delivery of sediments to the eastern Cariaco Basin, Venezuela. Deep Sea Res. Part I 2009, 56, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribó, M.; Puig, P.; Salat, J.; Palanques, A. Nepheloid layer distribution in the Gulf of Valencia, northwestern Mediterranean. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 111–112, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudin, J.J.; Cauwet, G. Transfer mechanisms and biogeochemical implications in the bottom nepheloid layer. A case study of the coastal zone off the Rhone River (France). Deep. Sea Res. Part II 1997, 44, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainright, S. Stimulation of Heterotrophic Microplankton Production by Resuspended Marine Sediments. Science 1987, 238, 1710–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.M.; Raine, R.; Mohn, C.; White, M. Nepheloid layer distribution in the Whittard Canyon, NE Atlantic Margin. Mar. Geol. 2015, 367, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Gelfenbaum, G.; Pennock, J.R. Wind and tidal forcing of a buoyant plume. Mob. Bay Ala. Cont. Shelf Res. 1993, 13, 1281–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, J.A.; Mertes, L.A.K.; Washburn, L.; Siegel, D.A. Dispersal forcing of southern California river plumes, based on field and remote sensing observations. Geo.-Mar. Lett. 2004, 24, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoulaki, G.; MacDonald, D.; Horner-Devine, A.R. The role of wind in the near field and midfield of a river plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5132–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Hetland, R.D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Current–wave interaction in the Mississippi-Atchafalaya river plume on the Texas-Louisiana shelf. Ocean Model. 2014, 84, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halfman, B.M.; Johnson, T.C. Surface and Benthic Nepheloid Layers in the Western Arm of Lake Superior, 1983. J. Great Lakes Res. 1989, 15, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Song, H.; Guan, Y.; Jun, C. Research on the distribution and characteristics of the nepheloid layers in the northern South China Sea by use of seismic oceanography method. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, K.R. Internal solitary wave breaking and run-up on a uniform slope. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 243, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, G.N. Nokes, R.I. Vertical mixing due to the breaking of critical internal waves on sloping boundaries. J. Fluid Mech. 1989, 204, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee-Shaw, E.E. Kunze, E. Boundary layer intrusions from a sloping bottom: A mechanism for generating intermediate nepheloid layers. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.; Imberger, J. Residual circulation due to internal waves shoaling on a slope. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Jia, Y.; Du, Q.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Tian, W.; Zhang, M.; Song, L. Shearing stress of shoaling internal solitary waves over the slope. Ocean Engineering 2021, 241, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, R.; Fringer, O. Transport by breaking internal gravity waves on slopes. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 789, 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| References | Method | Location | Number of INLs | Thickness and Length of the BNLs (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [59] | Field observations | Shetland slope, Scotland | 2 | 100 and 10,000 |
| [8] | Field observations | Alboran continental slope, Mediterranean | 1 | >100 and 600 |
| [23] | Field observations | Western Portuguese mid-shelf | 0 | 10~15 and >1500 |
| [28] | Field observations | Shelf break, South China Sea | 0 | 200 and 20,000 |
| [24] | Field observations | St. Lawrence Estuary, Canada | 1 | 5 and 400 |
| [22] | Field observations | Otsuchi Bay, Japan | 1 | 2 and 1000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Formation Mechanisms and Characteristics of the Marine Nepheloid Layer: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050678
Tian Z, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhang M. Formation Mechanisms and Characteristics of the Marine Nepheloid Layer: A Review. Water. 2022; 14(5):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050678
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Zhuangcai, Yang Liu, Xiaojiang Zhang, Yan Zhang, and Mingwei Zhang. 2022. "Formation Mechanisms and Characteristics of the Marine Nepheloid Layer: A Review" Water 14, no. 5: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050678
APA StyleTian, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, M. (2022). Formation Mechanisms and Characteristics of the Marine Nepheloid Layer: A Review. Water, 14(5), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050678







