Impact of Dissolved Oxygen on the Performance and Microbial Dynamics in Side-Stream Activated Sludge Hydrolysis Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
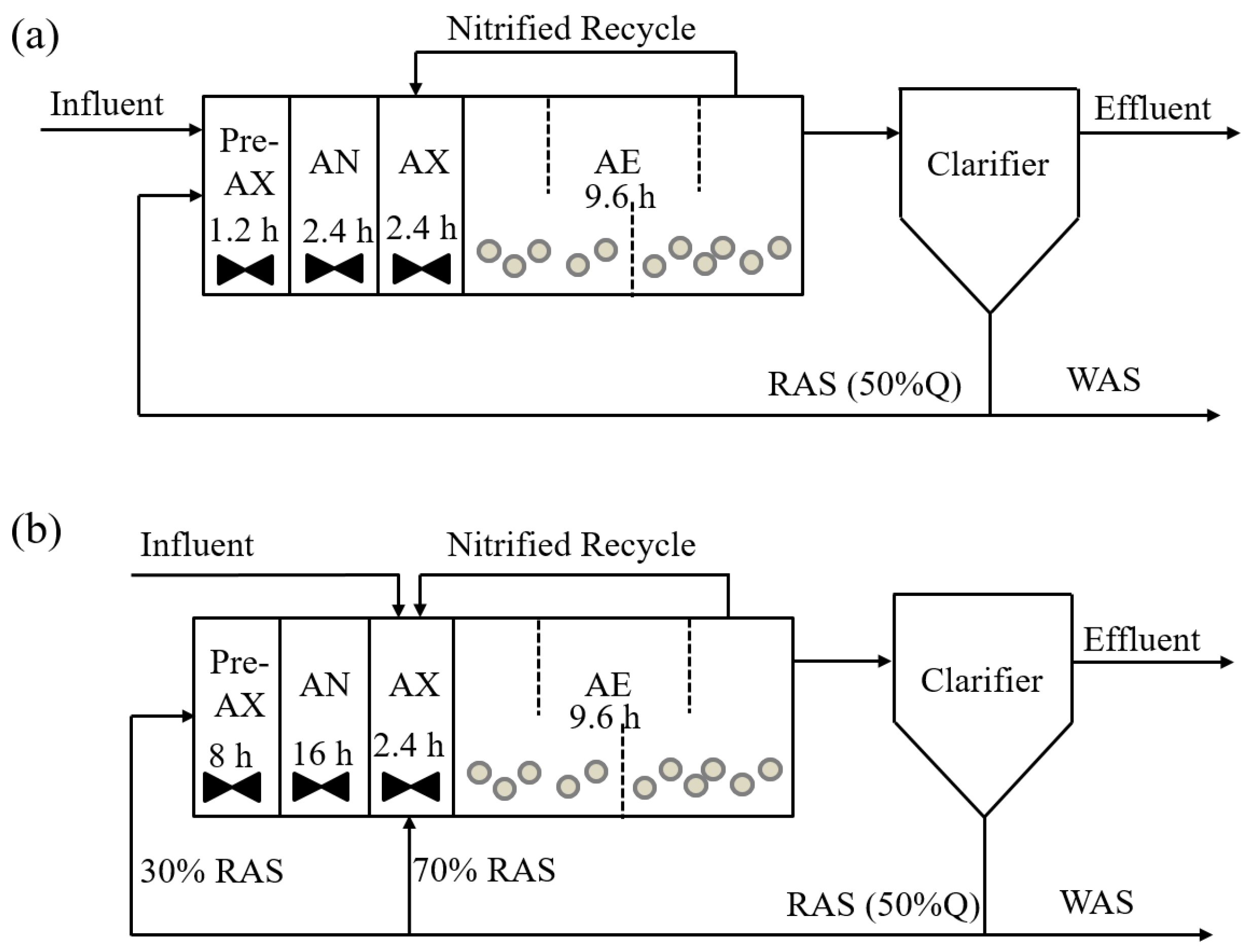
2.1. Reactor Setup and Operational Conditions
2.2. Biological P Removal Activity Batch Tests
2.3. Microbial Community Analysis
2.4. Chemical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of DO on Pollutant Removal Performance
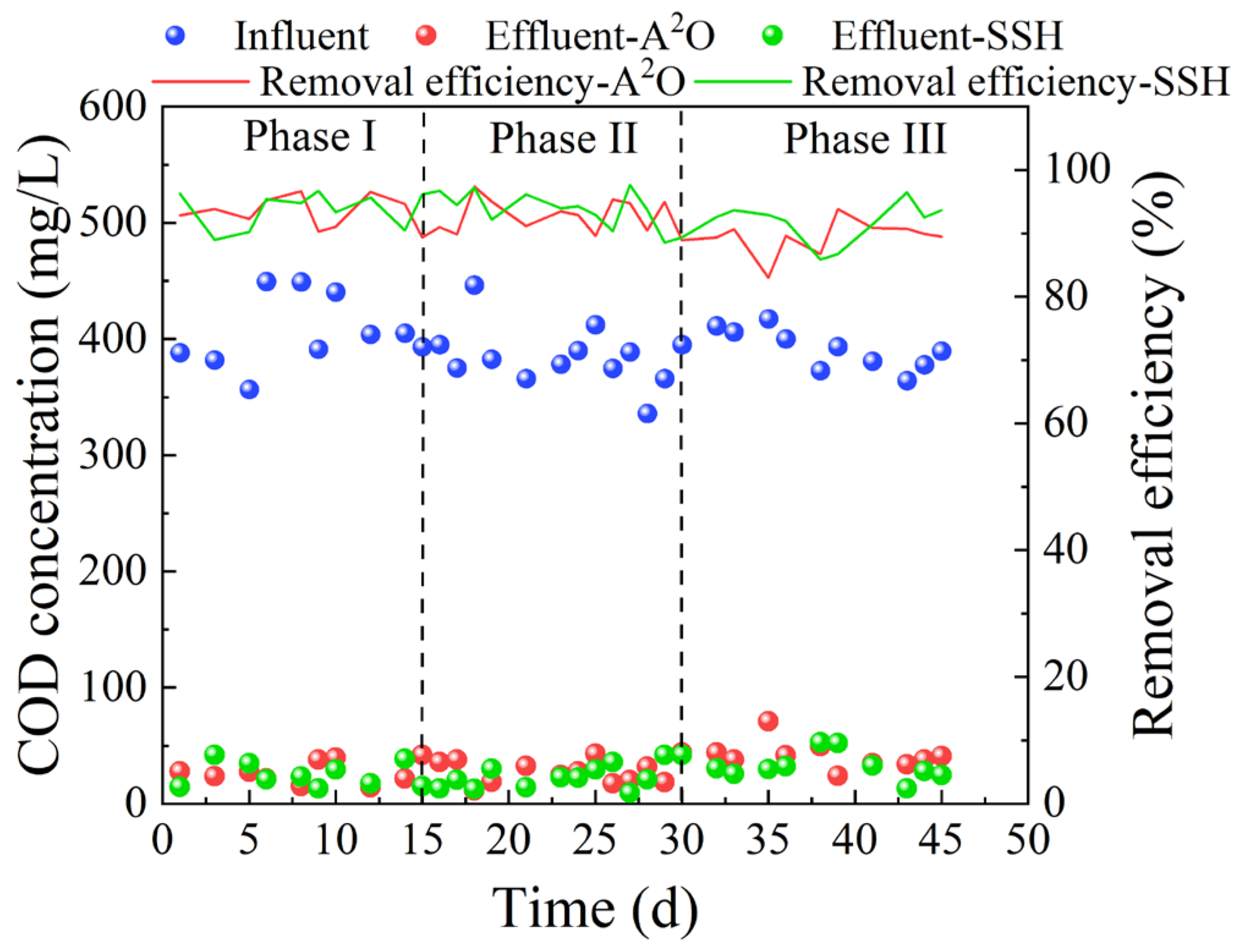
3.1.1. COD Removal Performance
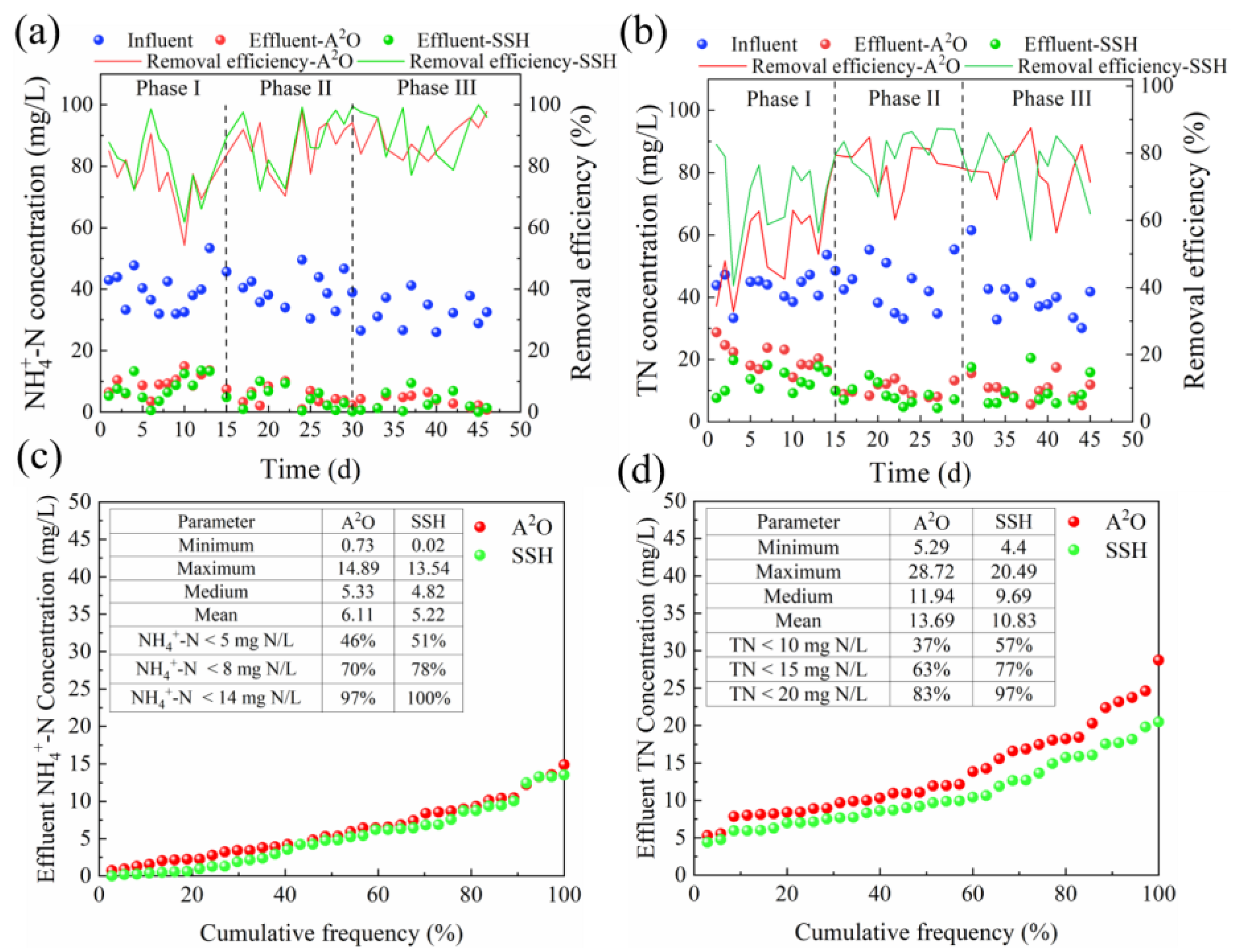
3.1.2. Nitrogen Removal Performance
3.1.3. Phosphorus Removal Performance
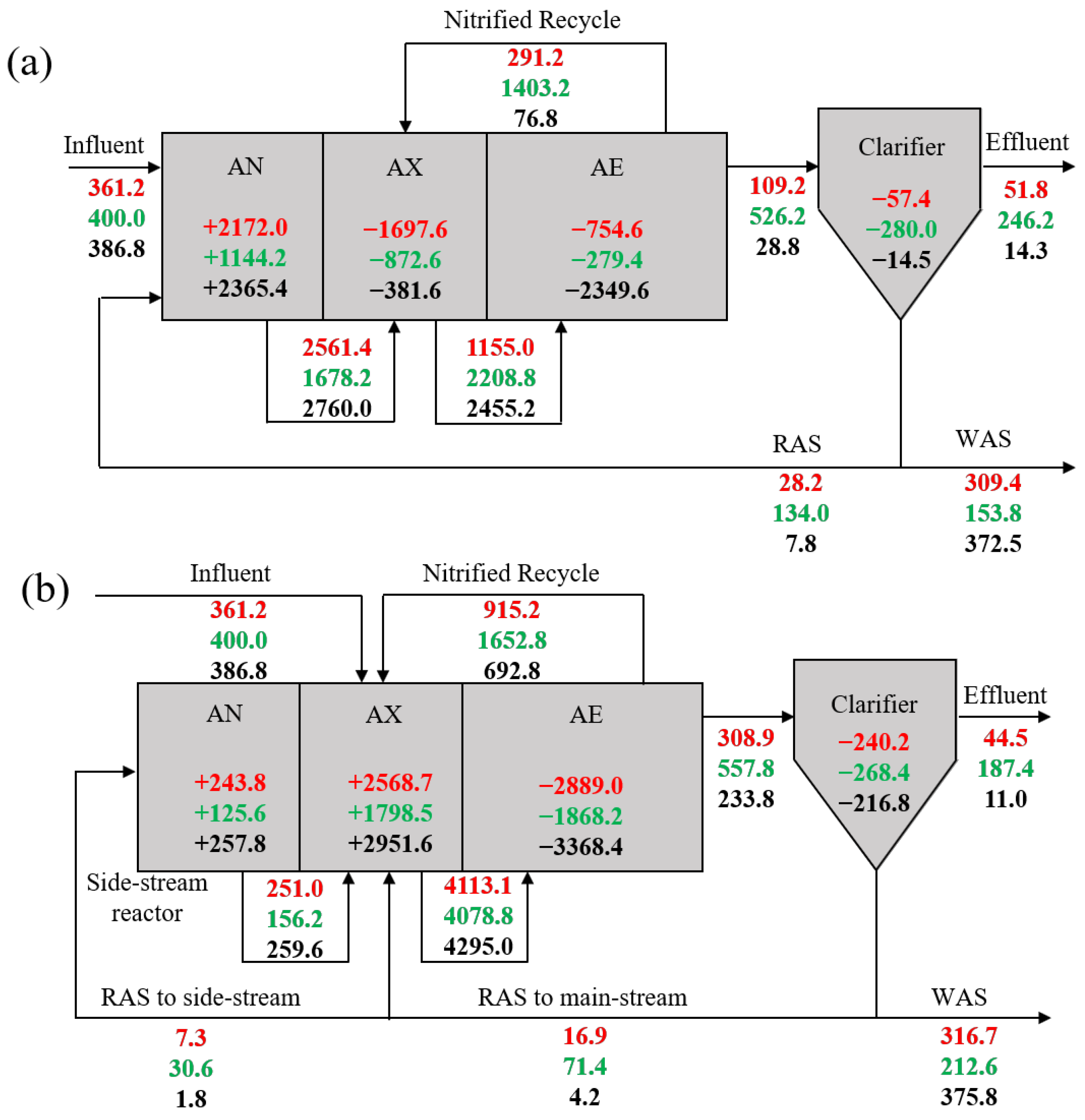
3.2. Mass Balance of Phosphorus
3.3. EBPR Activity
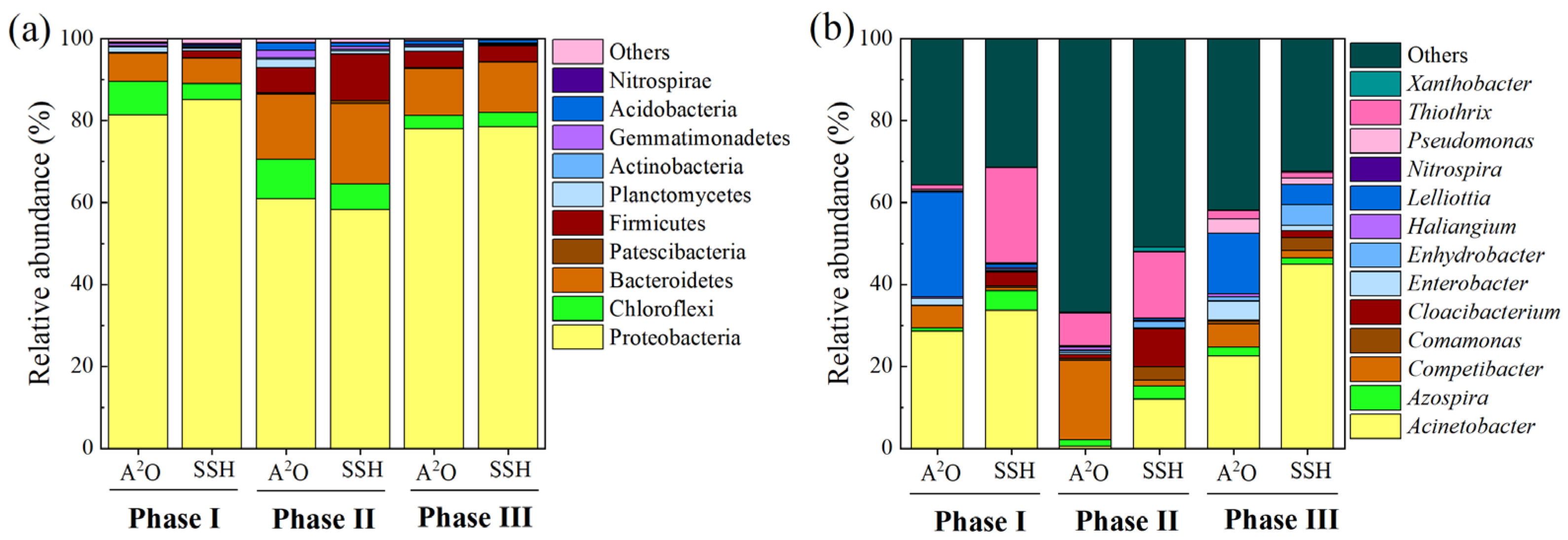
3.4. Effects of DO on Microbial Community
3.4.1. Microbial Community Composition
3.4.2. Functionally Relevant Populations
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Changes in DO had little impact on the COD removal performance. At low and moderate DO levels, the SSH reactor had better NH4+-N and TN removal performance. The direct decrease in the DO concentration from high to low depressed the EBPR performance, while the EBPR performance improved substantially when the DO concentration increased to moderate levels.
- (2)
- Due to the side-stream anaerobic tank providing stress resistance and additional VFAs, the SSH reactor had more stable and better nutrient removal performance than the A2O reactor at various DO levels, highlighting its potential to promote energy saving, carbon neutrality, and sustainable development.
- (3)
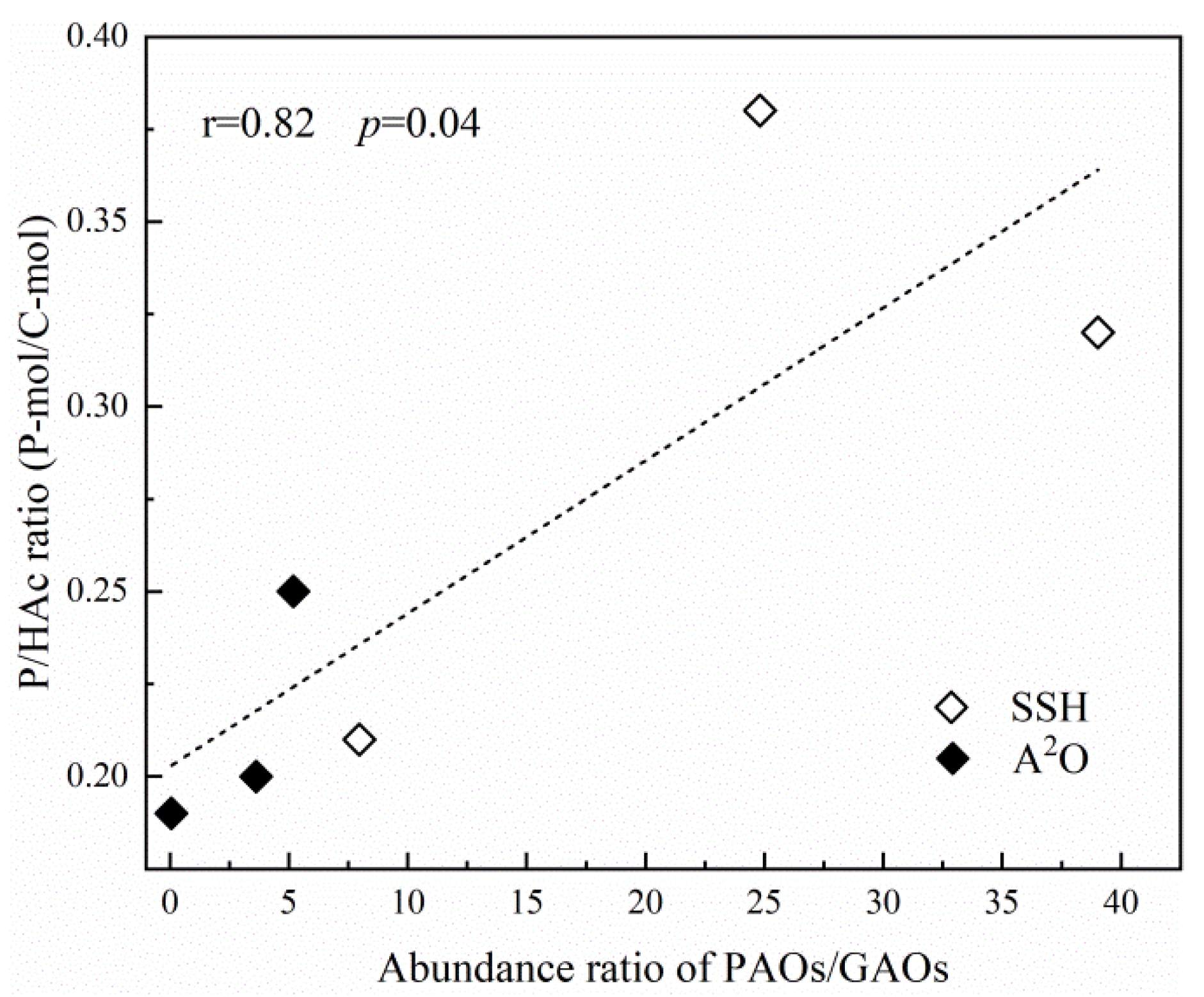
- Higher EBPR metabolic activities were observed in the SSH reactor. P/HAc ratios were positively correlated with the abundance ratios of PAOs/GAOs. Compared to the A2O reactor, the SSH reactor showed better resilience to changing the DO concentrations, which is related to its special configuration.
- (4)
- As the DO concentrations declined rapidly, the relative abundance of PAOs (dominated by Acinetobacter) decreased, but the relative abundance of GAOs (dominated by Competibacter) increased, which were likely the drivers of the deterioration in the EBPR performance. Higher relative abundance of PAOs and fermentative microorganisms were observed in the SSH reactor, which would have potentially enhanced the pollutant removal performance and stability.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, W.; Wan, R.; Luo, J.; Su, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y. Increasing municipal wastewater BNR by using the preferred carbon source derived from kitchen wastewater to enhance phosphorus uptake and short-cut nitrification-denitrification. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Bai, M. Advanced nutrient removal and functional microorganism enrichment in AOA system reinforced by side-stream sludge fermentation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y. Denitrifying phosphorus removal and impact of nitrite accumulation on phosphorus removal in a continuous anaerobic–anoxic–aerobic (A2O) process treating domestic wastewater. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 48, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, F.; Orchard, M.; Muñoz, C.; Zamorano, M.; Antileo, C. Advanced strategies to improve nitrification process in sequencing batch reactors—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehmen, A.; Lemos, P.; Carvalho, G.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J.; Blackall, L.; Reis, M. Advances in enhanced biological phosphorus removal: From micro to macro scale. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2271–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayà, C.; Guerrero, J.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J. Assessment of crude glycerol for Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal: Stability and role of long chain fatty acids. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, J.L.; Dunlap, P.; Steichen, M. Rethinking the Mechanisms of Biological Phosphorus Removal. Water Environ. Res. 2017, 89, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P.; Liu, Y.; Jing, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, L.; Chai, G.; Lv, T.; et al. Performance and microbial dynamics of side-stream activated sludge hydrolysis process at different influent food-to-microorganism (F/M) ratios. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Tooker, N.B.; Onnis-Hayden, A.; Wang, D.; Srinivasan, V.; Li, G.; Takács, I.; Vargas, E. Optimization and design of a side-stream EBPR process as a sustainable approach for achieving stable and efficient phosphorus removal. Water Res. Found. 2019, 226, U1R13/4869. [Google Scholar]
- Onnis-Hayden, A.; Srinivasan, V.; Tooker, N.B.; Li, G.; Wang, D.; Barnard, J.L.; Bott, C.; Dombrowski, P.; Schauer, P.; Menniti, A.; et al. Survey of full-scale sidestream enhanced biological phosphorus removal (S2EBPR) systems and comparison with conventional EBPRs in North Americarocess stability, kinetics, and microbial populations. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tooker, N.B.; Srinivasan, V.; Li, G.; Fernandez, L.A.; Schauer, P.; Menniti, A.; Maher, C.; Bott, C.B.; Dombrowski, P.; et al. Side-stream enhanced biological phosphorus removal (S2EBPR) process improves system performance—A full-scale comparative study. Water Res. 2019, 167, 115109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lan, S.; Wang, L.; Dong, S.; Zhou, H.; Tan, Z.; Li, X. A review: Driving factors and regulation strategies of microbial community structure and dynamics in wastewater treatment systems. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keene, N.A.; Reusser, S.; Scarborough, M.; Grooms, A.L.; Seib, M.; Domingo, J.S.; Noguera, D.R. Pilot plant demonstration of stable and efficient high rate biological nutrient removal with low dissolved oxygen conditions. Water Res. 2017, 121, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulkerrins, D.; Dobson, A.; Colleran, E. Parameters affecting biological phosphate removal from wastewaters. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, D.; Larson, L.; Stenstrom, M. Aeration of large-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants: State of the art. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J. Long-Term Low DO Enriches and Shifts Nitrifier Community in Activated Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5109–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Liu, R.; Huang, X. Evaluation of the potential for operating carbon neutral WWTPs in China. Water Res. 2015, 87, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Miao, J.; Abulimiti, A.; Jing, X.; Ren, N. Carbon neutrality of wastewater treatment—A systematic concept beyond the plant boundary. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2022, 11, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Luo, K.; Zeng, G.; Tang, M.; Xiong, W.; Yang, G. Effect of dissolved oxygen on biological phosphorus removal induced by aerobic/extended-idle regime. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 90, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.C.; Stratton, H.; Seviour, R. Environmental factors contributing to the “G bacteria” population in full-scale EBPR plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-T.; Mino, T.; Nakamura, K.; Matsuo, T. Glycogen accumulating population and its anaerobic substrate uptake in anaerobic-aerobic activated sludge without biological phosphorus removal. Water Res. 1996, 30, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, A.M.; Oehmen, A.; Blackall, L.L.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J. The effect of GAOs (glycogen accumulating organisms) on anaerobic carbon requirements in full-scale Australian EBPR (enhanced biological phosphorus removal) plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cech, J.S.; Hartman, P. Competition between polyphosphate and polysaccharide accumulating bacteria in enhanced biological phosphate removal systems. Water Res. 1993, 27, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheira, M.; Oehmen, A.; Carvalho, G.; Eusébio, M.; Reis, M.A. The impact of aeration on the competition between polyphosphate accumulating organisms and glycogen accumulating organisms. Water Res. 2014, 66, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y. Research on polyhydroxyalkanoates and glycogen transformations: Key aspects to biologic nitrogen and phosphorus removal in low dissolved oxygen systems. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2011, 5, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Gu, G. The effect of propionic to acetic acid ratio on anaerobic–aerobic (low dissolved oxygen) biological phosphorus and nitrogen removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4400–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochmatter, S.; Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Holliger, C. Optimized aeration strategies for nitrogen and phosphorus removal with aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6187–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginige, M.P.; Kayaalp, A.S.; Cheng, K.Y.; Wylie, J.; Kaksonen, A.H. Biological phosphorus and nitrogen removal in sequencing batch reactors: Effects of cycle length, dissolved oxygen concentration and influent particulate matter. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschreur, M.J.; Temmink, H.; Kleerebezem, R.; Jetten, M.S.M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Nitrous oxide emission during wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4093–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikola, A.; Rautiainen, J.; Vahala, R. Secondary clarifier conditions conducting to secondary phosphorus release in a BNR plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.M.P.; Heijnen, J.; van Loosdrecht, M. Effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on sludge settleability. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, G.J.F.; van der Meij, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process: Stoichiometry and pH influence. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 43, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.Z.; Saunders, A.; Neethling, J.B.; Stensel, H.D.; Blackall, L.L. Functionally Relevant Microorganisms to Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal Performance at Full-Scale Wastewater Treatment Plants in the United States. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q. Simultaneous denitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal in a full-scale anoxic–oxic process without internal recycle treating low strength wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y.; Miao, Z. Biological nutrient removal by applying modified four step-feed technology to treat weak wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Tai, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, M. Influence of turbulent mixing on the composition of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and aggregate size of aerated activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Mei, X.; Wu, Z. Correlating microbial community structure and composition with aeration intensity in submerged membrane bioreactors by 454 high-throughput pyrosequencing. Water Res. 2013, 47, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-D.; Noguera, D.R. Evaluating the effect of dissolved oxygen on ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in activated sludge. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3275–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z. The effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on long-term stability of partial nitrification process. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 90, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plósz, B.G.; Jobbágy, A.; Grady, C. Factors influencing deterioration of denitrification by oxygen entering an anoxic reactor through the surface. Water Res. 2003, 37, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Silverstein, J. Oxygen inhibition of activated sludge denitrification. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1925–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-Z.; Wang, X.-L.; Li, B.-K. Anoxic biological phosphorus uptake and the effect of excessive aeration on biological phosphorus removal in the A2O process. Desalination 2006, 189, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, P.; Izadi, P.; Eldyasti, A. Understanding microbial shift of Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal process (EBPR) under different Dissolved Oxygen (DO) concentrations and Hydraulic Retention Time (HRTs). Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 166, 107833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camejo, P.Y.; Owen, B.R.; Martirano, J.; Ma, J.; Kapoor, V.; Domingo, J.S.; McMahon, K.D.; Noguera, D.R. Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis clades enriched under cyclic anaerobic and microaerobic conditions simultaneously use different electron acceptors. Water Res. 2016, 102, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, P.; Izadi, P.; Eldyasti, A. Evaluation of PAO adaptability to oxygen concentration change: Development of stable EBPR under stepwise low-aeration adaptation. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Zuniga-Montanez, R.; Law, Y.; Thi, S.S.; Nguyen, T.Q.N.; Eganathan, K.; Liu, X.; Nielsen, P.H.; Williams, R.B.H.; Wuertz, S. Polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in full-scale tropical wastewater treatment plants use diverse carbon sources. Water Res. 2019, 149, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majed, N.; Gu, A.Z. Phenotypic dynamics in polyphosphate and glycogen accumulating organisms in response to varying influent C/P ratios in EBPR systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilles, J.L.; Peccia, J.; Kim, M.W.; Hung, C.H.; Noguera, D.R. Involvement of Rhodocyclus-Related Organisms in Phosphorus Removal in Full-Scale Wastewater Treatment Plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2763–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, A.J.; Jenkins, D. Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal from Wastewater by Biomass with Different Phosphorus Contents, Part I: Experimental Results and Comparison with Metabolic Models. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Du, R.; Dan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y. Rapidly achieving partial nitrification of municipal wastewater in enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) reactor: Effect of heterotrophs proliferation and microbial interactions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.H.; Mielczarek, A.T.; Kragelund, C.; Nielsen, J.L.; Saunders, A.M.; Kong, Y.; Hansen, A.A.; Vollertsen, J. A conceptual ecosystem model of microbial communities in enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5070–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, G.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Chai, G.; Liu, T.; Cao, X.; Pan, B.; Li, J.; Sheng, G.; et al. Long-term impact of heavy metals on the performance of biological wastewater treatment processes during shock-adaptation-restoration phases. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.E.; Strachan, B.J.; Hanson, N.W.; Hahn, A.S.; Hall, E.R.; Rabinowitz, B.; Mavinic, D.S.; Ramey, W.D.; Hallam, S.J. Rare taxa have potential to make metabolic contributions in enhanced biological phosphorus removal ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4979–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Lei, C.; Zhang, T.C.; Wu, W. Effect of organic matter strength on anammox for modified greenhouse turtle breeding wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujii, N.; Yamada, Y.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community analysis of an anaerobic up-flow granular bed anammox reactor. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Wang, R. Effect of dissolved oxygen concentration (microaerobic and aerobic) on community structure and activity of culturable heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qian, Y.; Xi, P.; Cao, R.; Qin, L.; Zhang, S.; Chai, G.; Huang, M.; Li, K.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Partial Nitrification and Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal in a Sequencing Batch Reactor Treating High-Strength Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierychlo, M.; Andersen, K.S.; Xu, Y.; Green, N.; Jiang, C.; Albertsen, M.; Dueholm, M.S.; Nielsen, P.H. MiDAS 3: An ecosystem-specific reference database, taxonomy and knowledge platform for activated sludge and anaerobic digesters reveals species-level microbiome composition of activated sludge. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Martínez, N.; Badia-Fabregat, M.; Albert, G.; Baeza, J.A. Glutamate as sole carbon source for enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J. Exploring the stability of an A-stage-EBPR system for simultaneous biological removal of organic matter and phosphorus. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, P.; Izadi, P.; Eldyasti, A. Design, operation and technology configurations for enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) process: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 561–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Kim, M.; Nakhla, G. Simultaneous partial nitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal (PNDPR) in a sequencing batch reactor process operated at low DO and high SRT for carbon and energy reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, H.; Takahashi, K.; Tsuzuki, Y.; Toda, K. Uptake and release of phosphate by a pure culture of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Water Res. 1985, 19, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafiri, C.; Kornaros, M.; Lyberatos, G. Kinetic modelling of biological phosphorus removal with a pure culture of Acinetobacter sp. under aerobic, anaerobic and transient operating conditions. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2769–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-H.; Fu, T.; Wang, S.S.; Yu, H.T.; Xiang, P.; Zhang, W.; Chen, D.L.; Li, M. Efficient phosphate accumulation in the newly isolated Acinetobacter junii strain LH4. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weon, S.-Y.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, S.; Koopman, B. Nitrite inhibition of aerobic growth of Acinetobacter sp. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4471–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, E.Y.; McIlroy, S.J.; Nierychlo, M.; Herbst, F.A.; Petriglieri, F.; Schmid, M.C.; Wagner, M.; Nielsen, J.L.; Nielsen, P.H. Resolving the individual contribution of key microbial populations to enhanced biological phosphorus removal with Raman–FISH. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Cope, H.A.; Li, X.; He, P.; Liu, C.; Li, G.; Rahman, S.M.; Tooker, N.B.; Bott, C.B.; et al. Intracellular polyphosphate length characterization in polyphosphate accumulating microorganisms (PAOs): Implications in PAO phenotypic diversity and enhanced biological phosphorus removal performance. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cope, H.A.; Rahman, S.M.; Li, G.; Nielsen, P.H.; Elfick, A.; Gu, A.Z. Toward Better Understanding of EBPR Systems via Linking Raman-Based Phenotypic Profiling with Phylogenetic Diversity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8596–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Majed, N.; Gu, A.Z. Advances in single cell Raman spectroscopy technologies for biological and environmental applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 64, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Brdjanovic, D.; van Loosdrecht, M. Effect of nitrite on phosphate uptake by phosphate accumulating organisms. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3760–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijuan, M.; Ye, L.; Yuan, Z. Free nitrous acid inhibition on the aerobic metabolism of poly-phosphate accumulating organisms. Water Res. 2010, 44, 6063–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Li, D.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Z.; Fang, X.; Wen, X.; Wan, J.; Li, A. Effect of free nitrous acid on nitrous oxide production and denitrifying phosphorus removal by polyphosphorus-accumulating organisms in wastewater treatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pijuan, M.; Yuan, Z. Free nitrous acid inhibition on anoxic phosphorus uptake and denitrification by poly-phosphate accumulating organisms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 98, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Duan, H.; Oehmen, A.; Carvalho, G.; Yuan, Z.; Ye, L. Achieving combined biological short-cut nitrogen and phosphorus removal in a one sludge system with side-stream sludge treatment. Water Res. 2021, 203, 11756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, A.; Álvarez-Pérez, S.; de Breij, A.; De Brabanter, J.; Willems, K.A.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Lievens, B. Phylogenetic signal in phenotypic traits related to carbon source assimilation and chemical sensitivity in Acinetobacter species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, C.P.L.J.; Daigger, G.T.; Lim, H.C. Biological Wastewater Treatment, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Henze, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ekama, G.A.; Brdjanovic, D. Biological Wastewater Treatment: Principles, Modelling, and Design; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wentzel, M.; Dold, P.; Ekama, G.; Marais, G. Enhanced polyphosphate organism cultures in activated sludge systems. Part III: Kinetic model. Water SA 1989, 15, 89–102. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Phase I (Days 1–15) | Phase II (Days 16–27) | Phase III (Days 28–45) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2O | SSH | A2O | SSH | A2O | SSH | |
| DO (mg/L) | 5.0 ± 0.9 | 5.1 ± 1.1 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.6 | 3.4 ± 0.5 |
| Influent COD (mg/L) | 406 ± 29 | 391 ± 23 | 392 ± 16 | |||
| Influent NH4+-N (mg/L) | 40.0 ± 6.2 | 39.3 ± 5.7 | 32.4 ± 5.0 | |||
| Influent PO43−-P (mg/L) | 8.92 ± 0.85 | 10.43 ±1.45 | 9.52 ± 1.22 | |||
| Phase | Samples | P Release (mg P/g VSS/h) | Hac Uptake (mg HAc/g VSS/h) | P Uptake (mg P/g VSS/h) | P/HAc Ratio (P-mol/C-mol) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | A2O | 7.7 | 30.0 | 2.3 | 0.25 | This study |
| SSH | 8.0 | 23.9 | 2.4 | 0.32 | ||
| II | A2O | 6.6 | 34.4 | 2.0 | 0.19 | |
| SSH | 7.0 | 38.5 | 3.7 | 0.21 | ||
| III | A2O | 9.2 | 44.7 | 3.7 | 0.20 | |
| SSH | 11.0 | 27.8 | 4.5 | 0.38 | ||
| Full-scale sludge | 2.8–31.9 | 13.5–47.0 | 1.9–11.0 | 0.11–0.66 | [10,11,33,47] | |
| Lab-scale sludge | 4.4–50.6 | 7.7–32.7 | 9.8–23.8 | 0.22–0.60 | [48] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Chai, G.; Lin, Y.; Liu, C.; Cao, R.; Song, Y.; Meng, H.; et al. Impact of Dissolved Oxygen on the Performance and Microbial Dynamics in Side-Stream Activated Sludge Hydrolysis Process. Water 2023, 15, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15111977
Qin L, Wang D, Zhang Z, Li X, Chai G, Lin Y, Liu C, Cao R, Song Y, Meng H, et al. Impact of Dissolved Oxygen on the Performance and Microbial Dynamics in Side-Stream Activated Sludge Hydrolysis Process. Water. 2023; 15(11):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15111977
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Lu, Dongqi Wang, Zhe Zhang, Xiaoxiao Li, Guodong Chai, Yishan Lin, Cong Liu, Rui Cao, Yuxin Song, Haiyu Meng, and et al. 2023. "Impact of Dissolved Oxygen on the Performance and Microbial Dynamics in Side-Stream Activated Sludge Hydrolysis Process" Water 15, no. 11: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15111977
APA StyleQin, L., Wang, D., Zhang, Z., Li, X., Chai, G., Lin, Y., Liu, C., Cao, R., Song, Y., Meng, H., Wang, Z., Wang, H., Jiang, C., Guo, Y., Li, J., & Zheng, X. (2023). Impact of Dissolved Oxygen on the Performance and Microbial Dynamics in Side-Stream Activated Sludge Hydrolysis Process. Water, 15(11), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15111977









