Using Age Tracers to Estimate Ecological Rates in a Phytoplankton Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Overview of Approach
2.3. Hydrodynamic Model
2.4. Water Age and Property Tracking
2.5. Predicting Chlorophyll
2.6. Estimating Phytoplankton Growth and Loss
2.7. Chlorophyll Observations
3. Results
3.1. Hydrodynamic Model Calibration
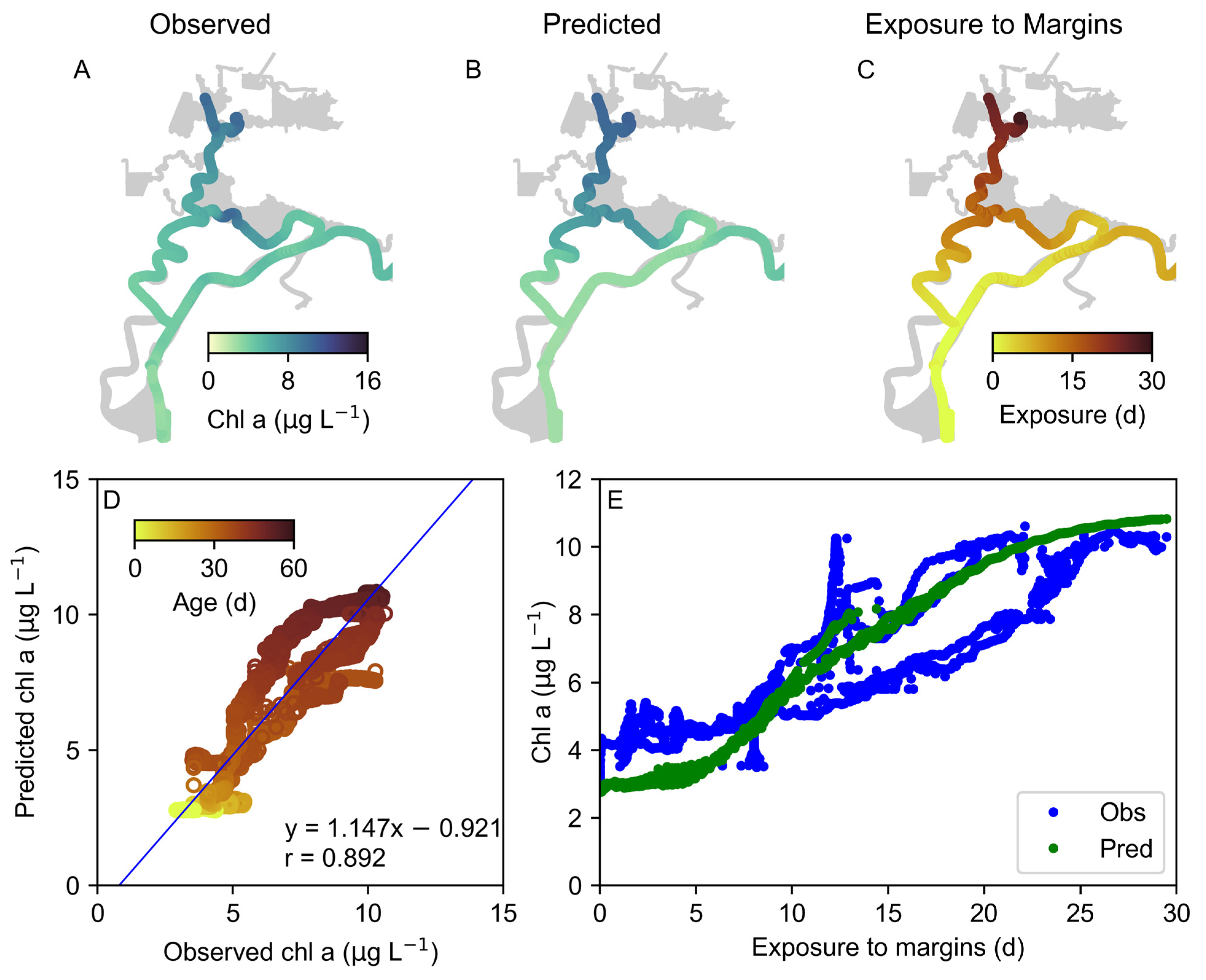
3.2. Age and Property Exposure Predictions
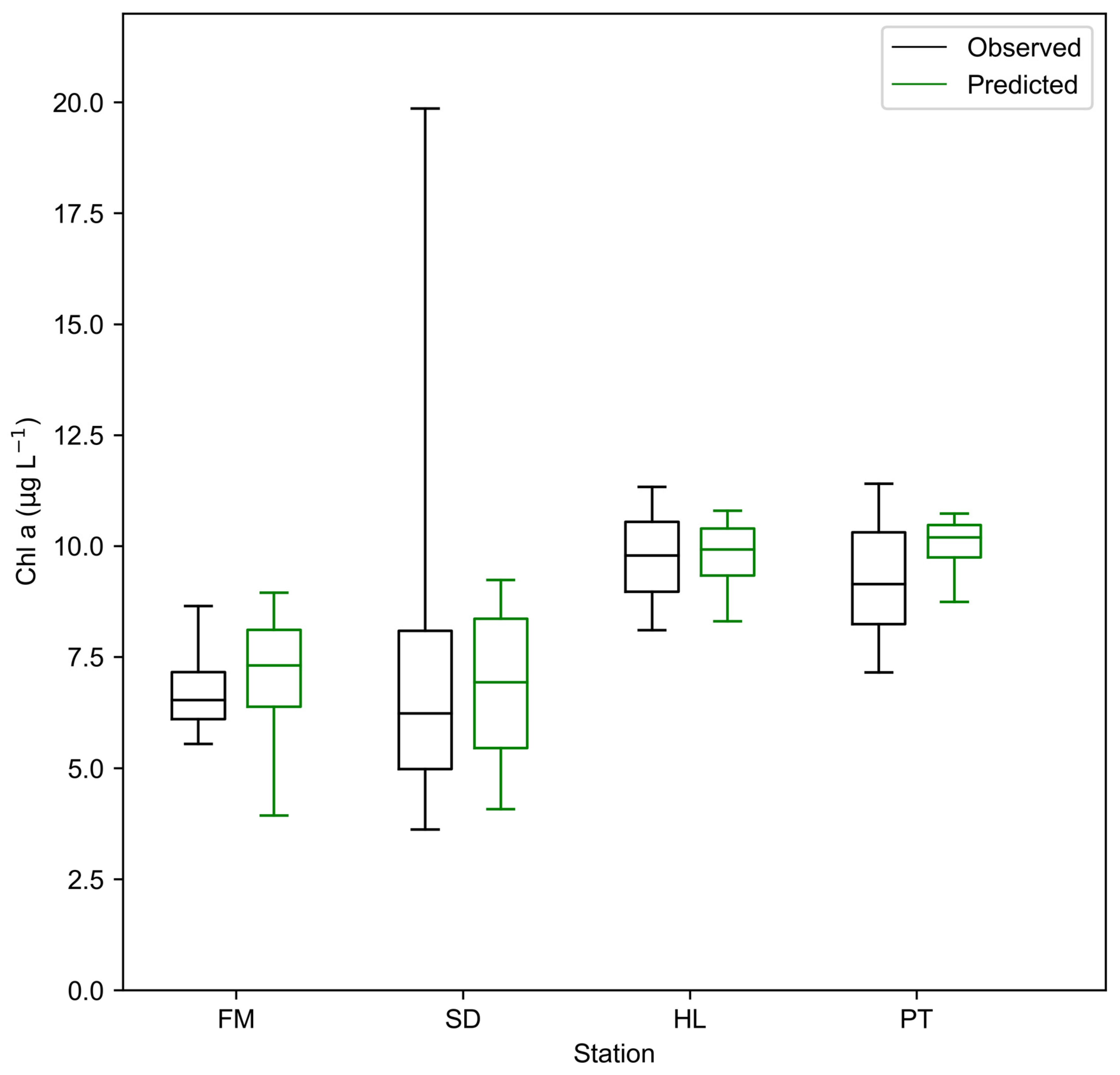
3.3. Chlorophyll-a Predictions at Stations
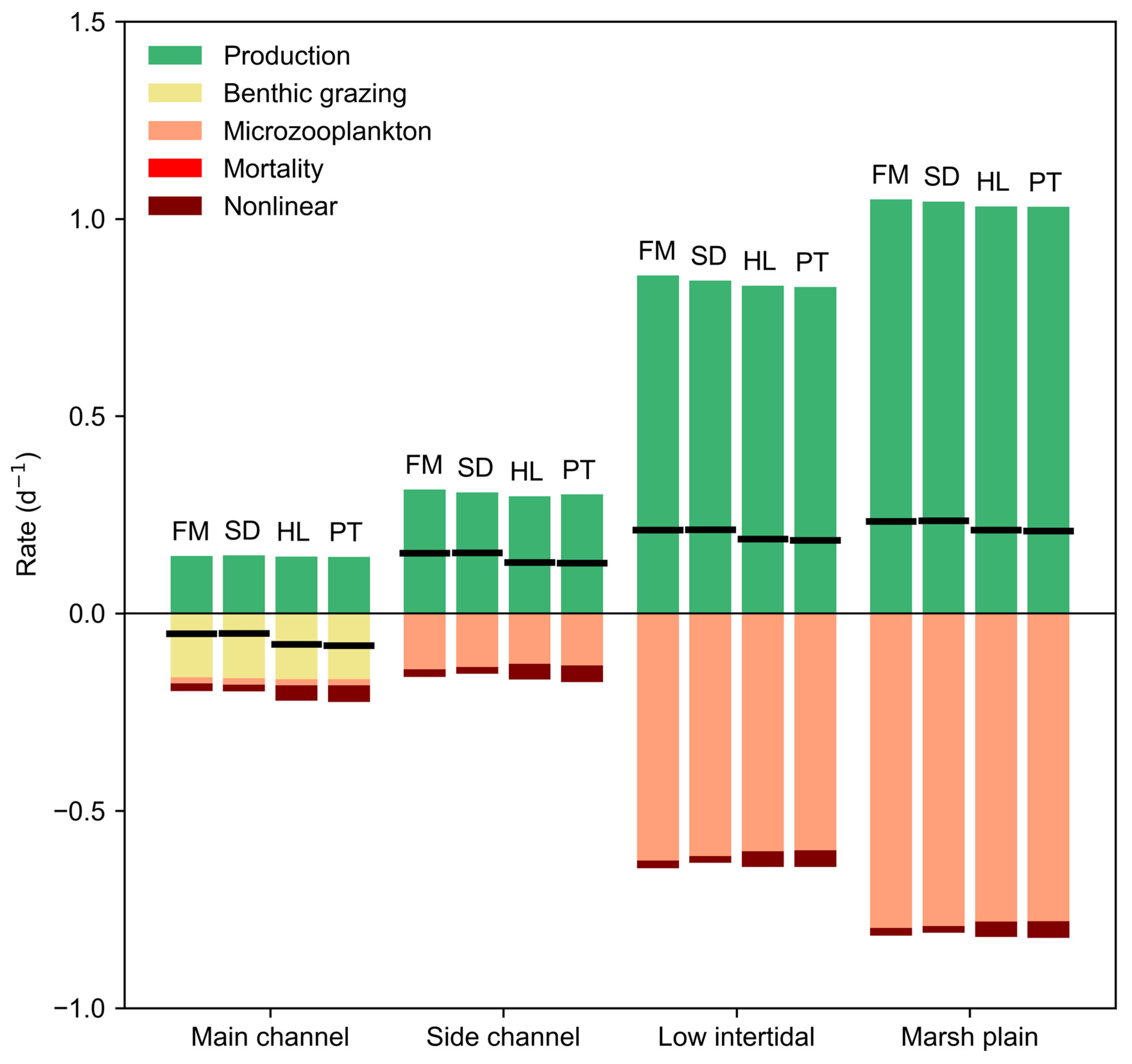
3.4. Chlorophyll Growth and Loss Terms
3.5. Phytoplankton Model Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Suisun Marsh Phytoplankton Dynamics
4.2. General Applicability
4.3. Management Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Liu, Q.; Chai, F.; Dugdale, R.; Chao, Y.; Xue, H.; Rao, S.; Wilkerson, F.; Farrara, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. San Francisco Bay Nutrients and Plankton Dynamics as Simulated by a Coupled Hydrodynamic-Ecosystem Model. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 161, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.K.; Koseff, J.R.; Monismith, S.G.; Lucas, L.V. Shallow Water Processes Govern System-Wide Phytoplankton Bloom Dynamics: A Field Study. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerer, W.J.; Thompson, J.K. Phytoplankton Growth Balanced by Clam and Zooplankton Grazing and Net Transport into the Low-Salinity Zone of the San Francisco Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 1202–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauw, A.N.; Los, H.F.J.; Bokhorst, M.; Erftemeijer, P.L.A. GEM: A Generic Ecological Model for Estuaries and Coastal Waters. Hydrobiologia 2009, 618, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassby, A.D. Phytoplankton in the Upper San Francisco Estuary: Recent Biomass Trends, Their Causes, and Their Trophic Significance. SFEWS 2008, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Ye, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, F.; Liu, Z.; Du, J. An Analytical Phytoplankton Model and Its Application in the Tidal Freshwater James River. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 224, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E.; Campin, J.-M.; Delhez, E.J.M. The Concept of Age in Marine Modelling: I. Theory and Preliminary Model Results. J. Mar. Syst. 2001, 28, 229–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, A.; Cornaton, F.; Deleersnijder, É.M.; Delhez, É.J. Partial Ages: Diagnosing Transport Processes by Means of Multiple Clocks. Ocean Dyn. 2016, 66, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.; Andrews, S.; Bergamaschi, B.; Downing, B.; Holleman, R.; Burdick, S.; Durand, J. The Use of Stable Isotope-Based Water Age to Evaluate a Hydrodynamic Model. Water 2019, 11, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.V.; Deleersnijder, E. Timescale Methods for Simplifying, Understanding and Modeling Biophysical and Water Quality Processes in Coastal Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review. Water 2020, 12, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.B.; Cloern, J.E.; Schraga, T.S.; Little, A.J.; Lucas, L.V.; Thompson, J.K.; Burau, J.R. Ecological Values of Shallow-Water Habitats: Implications for the Restoration of Disturbed Ecosystems. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 422–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpine, A.E.; Cloern, J.E. Trophic Interactions and Direct Physical Effects Control Phytoplankton Biomass and Production in an Estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, J.K.; McManus, G.B.; Kimmerer, W.J.; Slaughter, A.M.; Ignoffo, T.R. Trophic Links in the Plankton in the Low Salinity Zone of a Large Temperate Estuary: Top-down Effects of Introduced Copepods. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E. Habitat Connectivity and Ecosystem Productivity: Implications from a Simple Model. Am. Nat. 2007, 169, E21–E33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumsteiger, J.; Schroeter, R.E.; O’Rear, T.; Cook, J.D.; Moyle, P.B. Long-Term Surveys Show Invasive Overbite Clams (Potamocorbula Amurensis) Are Spatially Limited in Suisun Marsh, California. SFEWS 2017, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.; Manfree, A.; Fiedler, P. The Future of Suisun Marsh: Balancing Policy with Change. SFEWS 2013, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, T.; Hartman, R.; Koller, M.; Koohafkan, M.; Conrad, J.L.; MacWilliams, M.; Bever, A.; Burdi, C.; Hennessy, A.; Beakes, M. Evaluation of a Large-Scale Flow Manipulation to the Upper San Francisco Estuary: Response of Habitat Conditions for an Endangered Native Fish. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.B.; Baltz, D.M. Patterns in Distribution and Abundance of a Noncoevolved Assemblage of Estuarine Fishes in California. Fish. Bull. 1987, 84, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, T.; Mejia, F. A Place to Call Home: A Synthesis of Delta Smelt Habitat in the Upper San Francisco Estuary. SFEWS 2013, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldo, L.; Feyrer, F.; Burns, J.; Maniscalco, D. Sampling Uncharted Waters: Examining Rearing Habitat of Larval Longfin Smelt (Spirinchus Thaleichthys) in the Upper San Francisco Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyrer, F.; Nobriga, M.L.; Sommer, T.R. Multidecadal Trends for Three Declining Fish Species: Habitat Patterns and Mechanisms in the San Francisco Estuary, California, USA. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 64, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, G.H.; Lee, C.M.; Hestir, E.L.; Hulley, G.C.; Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Hook, S.J.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Acuña, S.; Tufillaro, N.B.; Radocinski, R.G.; et al. Decline in Thermal Habitat Conditions for the Endangered Delta Smelt as Seen from Landsat Satellites (1985–2019). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.E.; Cocherell, D.E.; Sommer, T.; Baxter, R.D.; Hung, T.-C.; Todgham, A.E.; Fangue, N.A. Sensitivities of an Endemic, Endangered California Smelt and Two Non-Native Fishes to Serial Increases in Temperature and Salinity: Implications for Shifting Community Structure with Climate Change. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, coy076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E. Patterns, Pace, and Processes of Water-quality Variability in a Long-studied Estuary. Limnol Ocean. 2019, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerer, W.J.; Gartside, E.; Orsi, J.J. Predation by an Introduced Clam as the Likely Cause of Substantial Declines in Zooplankton of San Francisco Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 113, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, K.; Moyle, P.; Durand, J.; Hung, T.-C.; Rypel, A.L. Small Populations in Jeopardy: A Delta Smelt Case Study. Envtl. L. Rep. 2020, 50, 10714. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, L.V.; Thompson, J.K. Changing Restoration Rules: Exotic Bivalves Interact with Residence Time and Depth to Control Phytoplankton Productivity. Ecosphere 2012, 3, art117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J. Foodweb Dynamics in Shallow Tidal Sloughs of the San Francisco Estuary; University Of California, Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Casulli, V.; Walters, R.A. An Unstructured Grid, Three-Dimensional Model Based on the Shallow Water Equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2000, 32, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, V. A High-Resolution Wetting and Drying Algorithm for Free-Surface Hydrodynamics. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2009, 60, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, V.; Stelling, G.S. Semi-Implicit Subgrid Modelling of Three-Dimensional Free-Surface Flows. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2011, 67, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the Validation of Models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Deleersnijder, E. The Concept of Age in Marine Modelling: II. Concentration Distribution Function in the English Channel and the North Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2001, 31, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA National Estuarine Research Reserve System (NERRS). System-Wide Monitoring Program; NOAA: Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://coast.noaa.gov/digitalcoast/data/nerr.html (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Stumpner, E.B.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Kraus, T.E.C.; Parker, A.E.; Wilkerson, F.P.; Downing, B.D.; Dugdale, R.C.; Murrell, M.C.; Carpenter, K.D.; Orlando, J.L.; et al. Spatial Variability of Phytoplankton in a Shallow Tidal Freshwater System Reveals Complex Controls on Abundance and Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmerer, W.; Wilkerson, F.; Downing, B.; Dugdale, R.; Gross, E.; Kayfetz, K.; Khanna, S.; Parker, A.; Thompson, J. Effects of Drought and the Emergency Drought Barrier on the Ecosystem of the California Delta. SFEWS 2019, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential Evolution—A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for Global Optimization over Continuous Spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nature Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clescrei, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E. Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; United Book Press, Inc.: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschi, B.; Stumpner, E.; O’Donnell, K.; Hansen, A.; Gelber, A.; Richardson, E.; Kraus, T.; Downing, B.; Senn, D. Spatial Assessment of Nutrients and Water-Quality Constituents in Suisun Marsh with the Salinity Control Gate Reoperation Experiment; a Delta Smelt Resiliency Strategy Experiment 2018. 2021. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/data/spatial-assessment-nutrients-and-water-quality-constituents-suisun-marsh-salinity-control-gate (accessed on 9 April 2023).
- Durand, J. A Conceptual Model of the Aquatic Food Web of the Upper San Francisco Estuary. SFEWS 2015, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Nally, R.; Thomson, J.R.; Kimmerer, W.J.; Feyrer, F.; Newman, K.B.; Sih, A.; Bennett, W.A.; Brown, L.; Fleishman, E.; Culberson, S.D.; et al. Analysis of Pelagic Species Decline in the Upper San Francisco Estuary Using Multivariate Autoregressive Modeling (MAR). Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 1417–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aha, N.M.; Moyle, P.B.; Fangue, N.A.; Rypel, A.L.; Durand, J.R. Managed Wetlands Can Benefit Juvenile Chinook Salmon in a Tidal Marsh. Estuaries Coasts 2021, 44, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, M.; Khanna, S.; Drexler, J.; Young, M. Ecology and Ecosystem Impacts of Submerged and Floating Aquatic Vegetation in the Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta. SFEWS 2023, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettinger, M.; Anderson, J.; Anderson, M.; Brown, L.; Cayan, D.; Maurer, E. Climate Change and the Delta. SFEWS 2016, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoellhamer, D.H. Sudden Clearing of Estuarine Waters upon Crossing the Threshold from Transport to Supply Regulation of Sediment Transport as an Erodible Sediment Pool Is Depleted: San Francisco Bay, 1999. Estuaries Coasts 2011, 34, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, V.; Zanolli, P. High resolution methods for multidimensional advection–diffusion problems in free-surface hydrodynamics. Ocean Model. 2005, 10, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
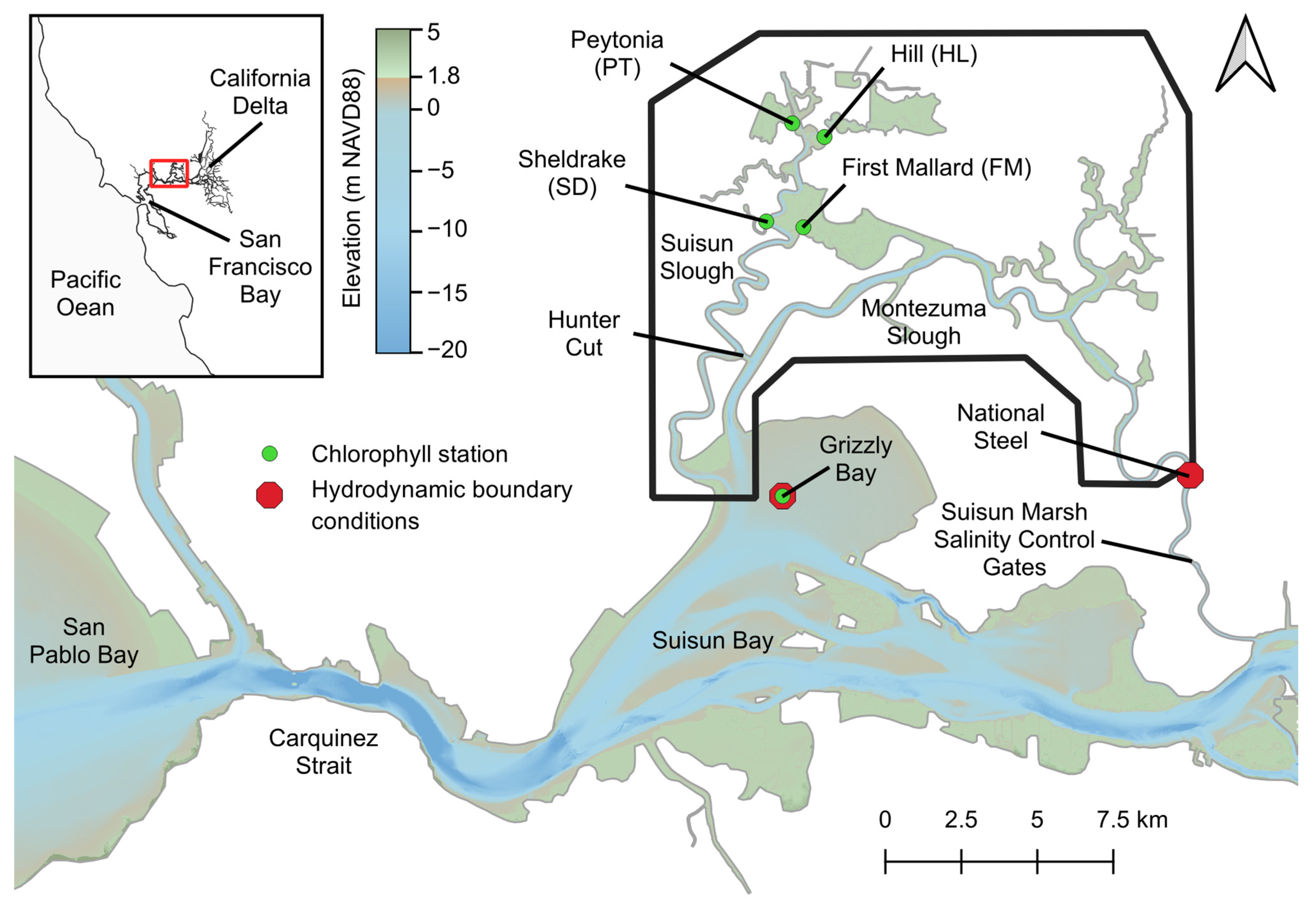
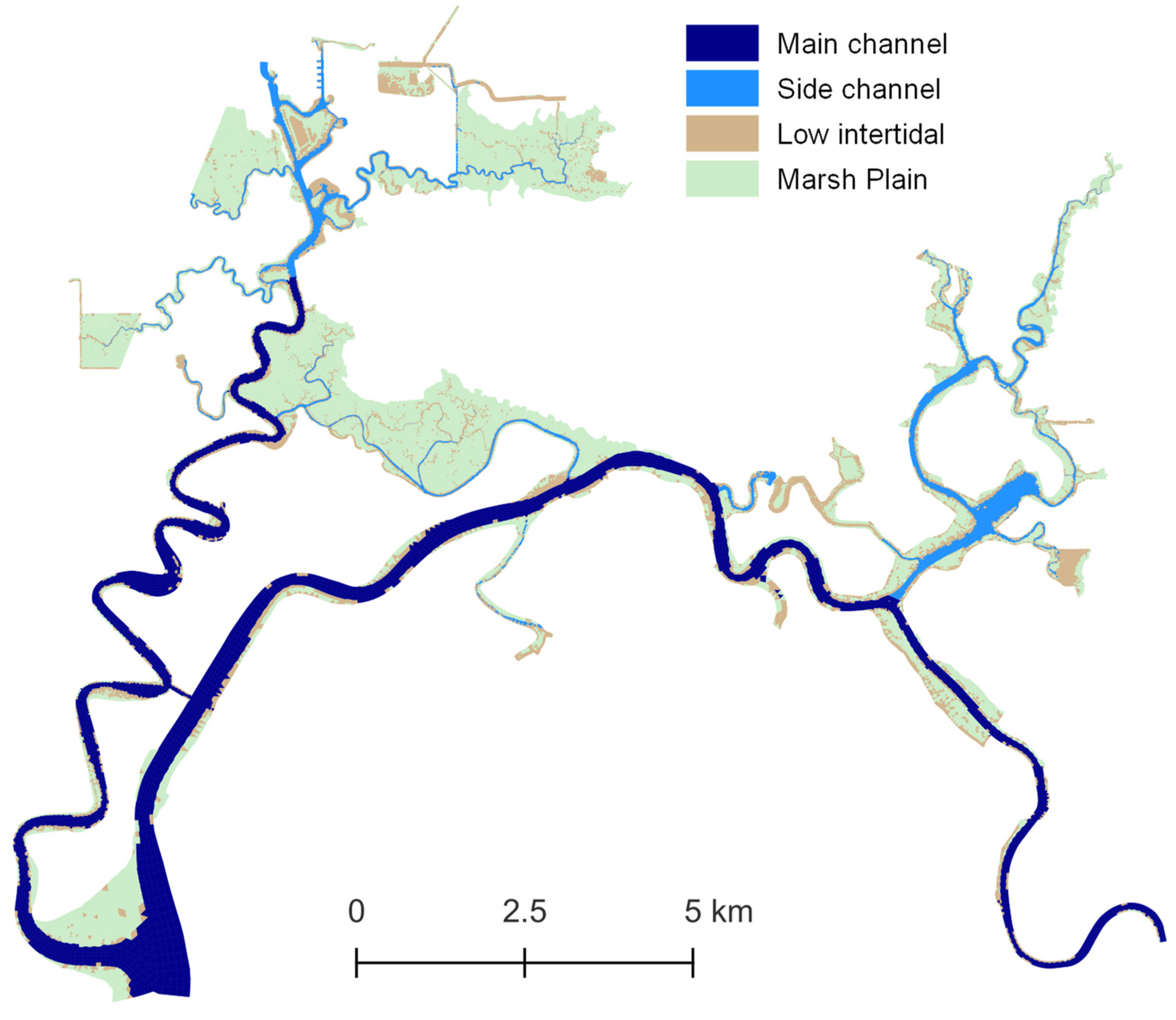
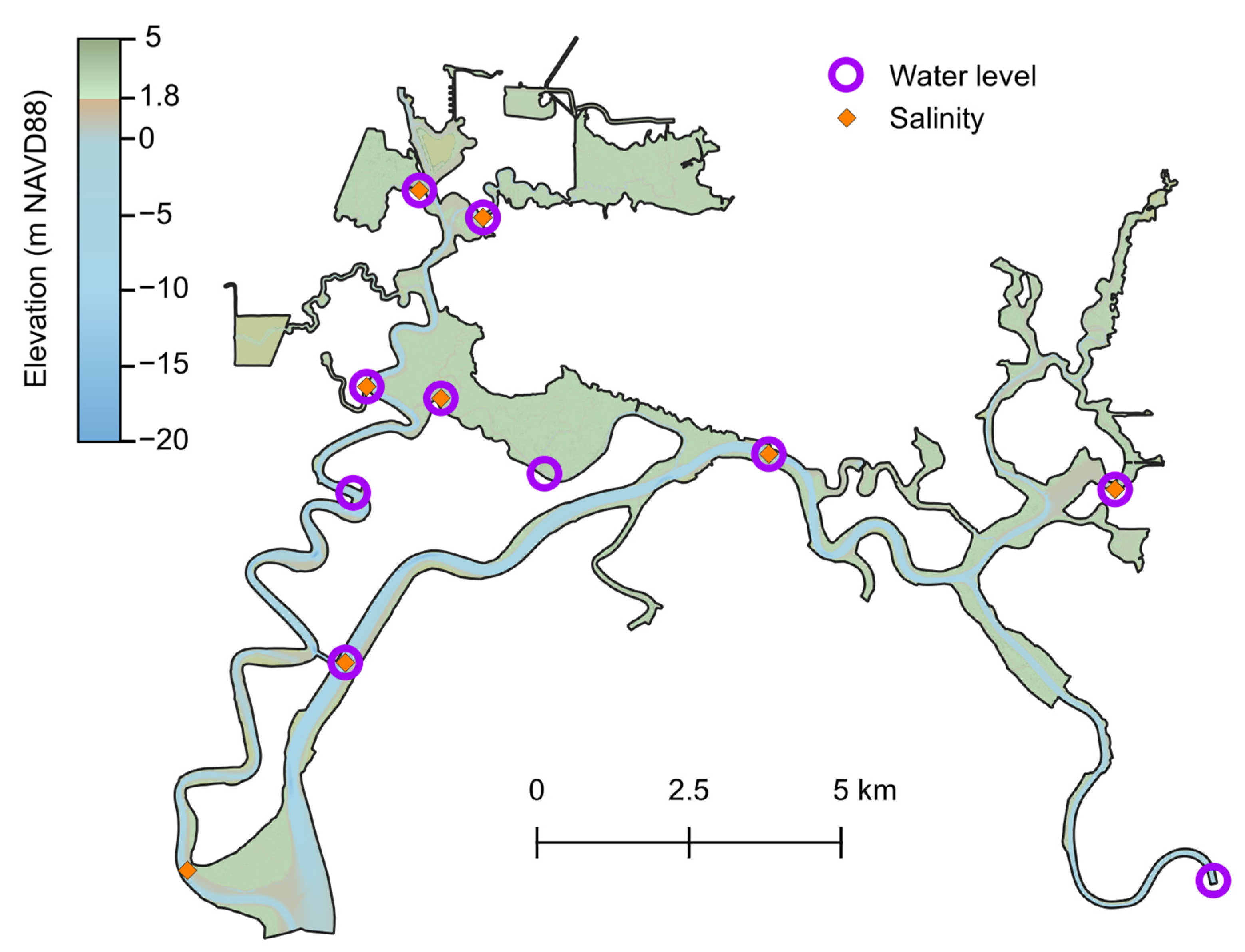



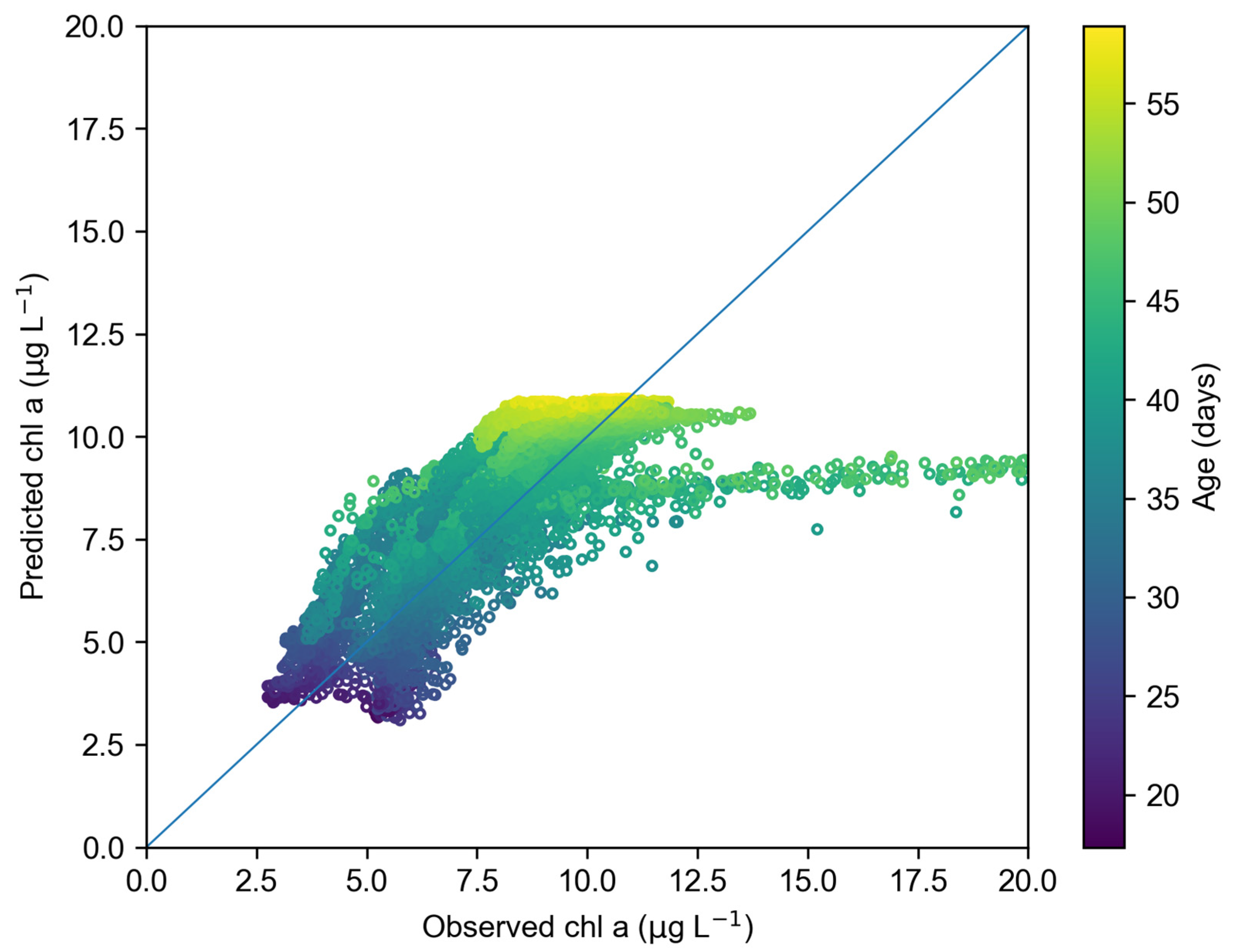

| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Chlorophyll concentration (μg L−1) | |
| Hydrodynamic velocity vector (m s−1) | |
| Phytoplankton growth rate (d−1) | |
| Phytoplankton loss rate (d−1) | |
| Net phytoplankton growth rate (d−1) | |
| Mean age (d) | |
| Phytoplankton density-dependent gain/loss term (-) | |
| Horizontal position vector (m) | |
| Boundary concentration of chlorophyll (μg L−1) | |
| Time-averaged net phytoplankton growth rate (d−1) | |
| Mean exposure time to compartment j (d) | |
| j | Compartment index (-) |
| Maximum growth rate at a given temperature (d−1) | |
| Temperature (degrees C) | |
| Light limitation factor (-) | |
| Water column depth (m) | |
| Water column mean photosynthetically active radiation (moles m−2 d−1) | |
| Irradiance supporting maximum water column growth (moles m−2 d−1) | |
| Light attenuation coefficient (m−1) | |
| Turbidity (FNU) | |
| Phytoplankton mortality rate (d−1) | |
| Microzooplankton grazing rate (d−1) | |
| Clam grazing rate (m d−1) | |
| Clam grazing rate in main channel (m d−1) | |
| Clam grazing rate in side channel (m d−1) |
| Station | Continuous (mg L−1) | Underway (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| First Mallard | 2.08 | 6.49 |
| Sheldrake | 4.54 | 5.39 |
| Peytonia | 7.60 | 10.01 |
| Hill | 5.86 | 9.43 |
| Parameter | R2 | Bias | RMSE | Skill |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water level | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 1.00 |
| Salinity | 0.81 | −0.35 | 0.72 | 0.84 |
| Parameter | Location | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmain | Main channel | 1.13 | m d−1 |
| Cside | Side channel | 0.0 | m d−1 |
| kc | Global | −0.091 | L μg−1 |
| M | Global | 0.0 | d−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gross, E.; Holleman, R.; Kimmerer, W.; Munger, S.; Burdick, S.; Durand, J. Using Age Tracers to Estimate Ecological Rates in a Phytoplankton Model. Water 2023, 15, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112097
Gross E, Holleman R, Kimmerer W, Munger S, Burdick S, Durand J. Using Age Tracers to Estimate Ecological Rates in a Phytoplankton Model. Water. 2023; 15(11):2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112097
Chicago/Turabian StyleGross, Edward, Rusty Holleman, Wim Kimmerer, Sophie Munger, Scott Burdick, and John Durand. 2023. "Using Age Tracers to Estimate Ecological Rates in a Phytoplankton Model" Water 15, no. 11: 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112097
APA StyleGross, E., Holleman, R., Kimmerer, W., Munger, S., Burdick, S., & Durand, J. (2023). Using Age Tracers to Estimate Ecological Rates in a Phytoplankton Model. Water, 15(11), 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15112097







