Abstract
The study aimed to determine groundwater’s suitability for irrigation and cattle rearing in Kuwait. In this regard, groundwater samples were collected from Umm Al Aish (UA) and adjoining Rawdhatain (RA) water wellfields to develop groundwater suitability maps for irrigation purposes using the fuzzy logic technique in ArcGIS. RA was dominated by Na-Cl, Na-Ca, and Ca-SO4 water types, whereas UA was dominated by the Ca-Mg water type. Due to the influence of the temperature and pCO2, the carbonates were inferred to be more susceptible to precipitation in the soil than the sulfates. The ternary plots for both regions revealed that the samples’ suitability ranged from good to unsuitable. Spatial maps of nine significant parameters governing the irrigation suitability of water were mapped and integrated using the fuzzy membership values for both regions. The final suitability map derived by overlaying all the considered parameters indicated that 8% of the RA region was categorized as excellent, while UA showed only 5%. Samples situated in the study areas showed an excellent to very satisfactory range for livestock consumption. Developing a monitoring system along with innovative water resource management systems is essential in maintaining the fertility of the soil and existing groundwater reserves.
Keywords:
groundwater suitability; irrigation; fuzzy logic; GIS; water quality; water management; Kuwait; arid region 1. Introduction
The lack of freshwater availability is the primary challenge in the world’s driest regions. Water quality is quickly degrading because of the combined effects of the dry climate and global warming. Climate change has an immediate impact on the amount and quality of groundwater/surface water in arid and semi-arid regions [1,2]. Studies on long-term climate change, adopting modeling techniques using land use–land cover and meteorological parameters, have also yielded similar observations [3]. Additionally, the water quality is declining due to the rising demand for human consumption and agricultural purposes. These needs cannot be satisfied by existing water sources, where water quality is also crucial for farming in many deserts and semi-arid areas [4]. In arid regions such as Kuwait, evaporation rates are higher due to increased temperatures, lesser rainfall, and a lack of surface water bodies, and the dependency on groundwater has increased. Groundwater dependence has not only resulted in increased salinity but has also depleted the freshwater resources in arid regions [5], thus affecting its utility for agricultural purposes. Hence, agriculture in arid regions mainly focuses on the availability of sustainable freshwater resources. Therefore, the need for water in an arid region is heterogeneous; it varies with utility, availability, and proximity. However, due to increased rates of evaporation and poor precipitation, groundwater often becomes the main source for irrigation, despite its inferior quality. Because of this, the use of low- to medium-quality groundwater for irrigation is becoming increasingly important [6]. The increased use of agrochemicals, variability of land use, changes in climate, increase in population, etc., are a few major factors affecting the groundwater quantity and quality, especially in arid regions [7]. Further, due to the presence of certain ions at unsafe/harmful levels, groundwater that is not fit for industrial or drinking purposes may be fit for irrigation purposes [8,9].
As intensive crop production and irrigated agriculture [10] are rapidly increasing the water demand, the current groundwater requirements for crop production cannot keep pace with the demand [11]. This is because farmers, specifically in arid regions, are forced to use brackish to saline groundwater for irrigation purposes, which has a high concentration of dissolved salts. In most cases, this leads to crop failure and the development of saline or sodic soils, requiring expensive remediation to restore their productivity. In fact, studies have indicated that the extensive practice of pumping brackish groundwater for agricultural purposes has led to enhanced conductivity values and a drop in groundwater levels, thus affecting the suitability of the region’s future irrigation practices [12,13]. Hence, the irrigation suitability should be assessed when the low-quality water consumption rises.
Kuwait has three agricultural regions: Abdally, Wafra, and Kabd. Brackish groundwater is used for agriculture in these agricultural regions, with treatment in certain farms. The brackish groundwater serves as a substitute for irrigation due to the absence of fresh groundwater resources in Kuwait. This practice of brackish groundwater utilization for agriculture has been reported globally for food safety [14]. Since brackish groundwater serves as a source, the type and variety of crops cultivated are limited due to the higher salinity [15]. Nevertheless, when brackish/saline water is used in an innovative manner, it may contribute to the production of a variety of salt-tolerant crops. Therefore, brackish groundwater should be used with caution considering the chemical constituents and their concentration levels in water [16]. The treated water also results in the generation of brines, which affect the environment; hence, the cultivation of plants tolerant to the salinity of groundwater in arid regions is necessary [17].
In Kuwait, the Rawdhatain field (RA) and Umm Al Aish field (UA) are the only known groundwater fields with exploitable freshwater lenses. About 40 years ago, the groundwater in RA and UA was reported to range from 205 mg/L to 700 mg/L of TDS [18]. Later, the RA and UA freshwater lenses were protected with the study of the local conditions, which included the catchment boundary, size, lithology, rainfall rates, and drainage patterns [19]. Paleoenvironmental studies indicated that the wadis formed under varied environmental conditions in the Pleistocene transported rainfall runoff and infiltrated to form the freshwater lenses [19]. The wide catchment area and higher percolation rates have led to enormous volumes of water to recharge the lenses, despite the high temperatures of the region. The long-term assessment of groundwater in the RA and UA regions indicated that a small number of wells around UA were strongly contaminated with hydrocarbons [20], and these could reach parts of the RA field if no necessary action was taken to prevent this contaminated plume migration [21]; this was also later confirmed by groundwater modeling studies [22].
Al-Rashed [23] found that the Sabriya Oil Fields’ seawater pits infiltrated to the groundwater and thus seawater ingression impaired the groundwater by increasing its salinity. Hence, these studies suggest that the groundwater of the region needs to be protected from the infiltration of contaminants. Further, Mukhopadhyay [24] reported that the infiltration of surface runoff and the leaching of salts and hydrocarbons from the surface soil resulted in high groundwater TDS levels in Northern Kuwait.
It is worth noting that regions with different groundwater quality are to be mapped both spatially and temporally in lateral and vertical dimensions to ascertain the use and manage the resources strategically. A geographic information system (GIS) is a powerful tool for the monitoring and management of groundwater resources at a local or regional level, the analysis of water quality, and to provide tangible solutions [25,26]. The basic chemical parameters in determining the groundwater’s characteristics and its appropriateness for irrigation purposes include the electrical conductivity (EC), sodium percentage (Na%), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), Kelly’s ratio (KR), magnesium hazard (MAR), residual sodium carbonate (RSC), permeability index (PI), potential salinity (PS), and soluble sodium percentage (SSP). Many authors have investigated the irrigation suitability of groundwater (ISGW) based on some of the above-mentioned parameters [27,28,29,30]. Several studies have used fuzzy logic to assess land suitability for yield prediction [31], regions with promising irrigation water quality [32,33], and regions with fresh groundwater resources suitable for drinking purposes [34]. Apart from spatiotemporal variation studies, a ternary plot has also been used to integrate four different water quality parameters for the assessment of irrigation suitability [30].
A bibliometric review on the Scopus database using the keywords (groundwater, irrigation, fuzzy, and GIS) identified 25 research articles. The retrieved file was checked for duplicate research articles and similar words were merged to derive a meaningful representation in the plot (Figure 1). The network-based visualization map of the co-occurrence of keywords in the selected articles, was obtained with the VOSviewer software [35]. Later, filtering the articles with a minimum of five occurrences resulted in 14 frequently used keywords.
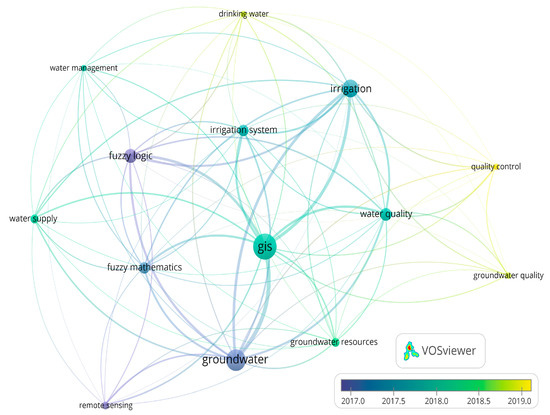
Figure 1.
A network-based visualization map derived from a bibliometric review on the Scopus database representing the frequency of keywords and their linkages. The size of the circles and the thickness of the lines are proportional to the number of uses and the frequency of the linkages, respectively. The colors reflect the chronology of the usage and their linkages.
Irrigation-related groundwater studies using fuzzy logic techniques initially focused on groundwater using remote sensing techniques. Later, studies concentrated more on irrigation, GIS, groundwater resources, water supply, water management, and water quality. Recently, more emphasis has been given to drinking water, groundwater quality, and quality control. Hence, it could be inferred that fuzzy logic techniques have been very recently adopted in studying the irrigation suitability of groundwater, as the oldest work in the database was reported by Dixon [36] for groundwater vulnerability assessment, followed by studies with an emphasis on irrigation systems and GIS. Recently, more studies on fuzzy logic have aimed to unravel the ISGW and focused on drinking water purposes by involving more related parameters through the analytic hierarchical process (AHP) [32,37,38].
Although the freshwater reserves are being preserved in the RA and UA wellfield regions, the quality of the resources is reported to be deteriorating [19,39]. Further, there are no detailed studies investigating the quality and suitability of brackish and fresh groundwater lenses for irrigation purposes. Thus, studying the hydrogeochemical characteristics of the region and identifying the wells/zones for ISGW is essential for the development and application of groundwater resources. Hydrochemical characterization associated with hydrological inferences is needed to evaluate and manage the groundwater resources [40]. Thus, the formation of policies and governance regarding the risk of damaging the potential aquifers and available freshwater resources are actions that urgently need to be executed. Hence, water management considering the future needs of the region is critical in arid regions for strategic planning.
Study Aims and Objectives
Water is one of the main focuses of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), particularly for SDG 6 (clean water and sanitation), and it also relates to agriculture, i.e., SDG 13 (climate change) and SDG 15 (life on land). Thus, the current study considered the pursuit of these SDGs by using a fuzzy GIS technique to develop a map of groundwater quality and ISGW. The study also attempted to identify areas suitable for the purpose of groundwater irrigation and cattle rearing, along with optimizing the groundwater utilization in the study area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Kuwait is an arid region, receiving average rainfall varying from 110 to 120 mm [41]. During the country’s dry hot summers (May to September), the temperature reaches 45 to 50 °C, while, in the winter (December to February), the temperature can fall below 10 °C [42]. The study area’s RW and UA fields are located north of Kuwait (Figure 2) and are bounded by latitudes 29°46′0″ to 29°46′0″ N and longitudes 47°38′0″ to 47°52′0″ E. The RA and UA regions, adjoining each other, are reported to have the only known economically viable freshwater lenses in Kuwait [24]. The RA and UA regions cover an area of 53 km2 and 44.5 km2, respectively. The Rawdhatain Oilfield lies to the southeast of the Rawdhatain groundwater field, whereas a portion of the Sabriya Oilfield is situated NE of the Umm Al Aish groundwater field.
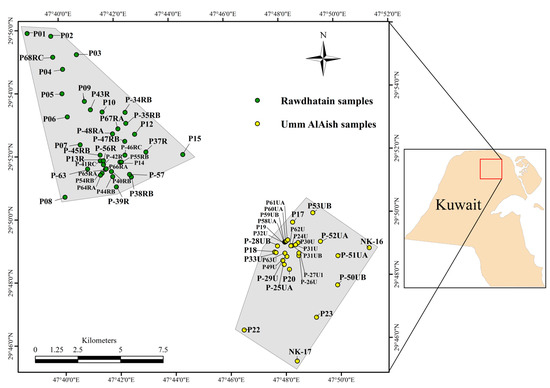
Figure 2.
Map of sampling locations in the studied groundwater fields of Rawdhatain (RA) and Umm Al Aish (UA) regions. The northwestern region in the figure indicates the RA wellfield and the southeastern region represents the UA wellfield.
The tertiary sediment sequence (Paleogene and Neogene) of Kuwait has been divided into two main groups [43]. The formation of the Neogene Aquifer System, which is also referred to as the Kuwait Group Aquifer, occurred during the Pleistocene pluvial. It is noteworthy that, during this phase, Wadi Ar-Rimah and Wadi al Batin [44] were the mainstream channels. The Dibdibba Formation (Upper Miocene to Pliocene), Fars Formation (Middle Miocene), and Ghar Formation (Lower Miocene) are the three formations that make up the Neogene Aquifer System. Moreover, the oldest group that is found to be overlain by the Kuwait Group is the Hasa Group, where it consists of the Dammam Formation, Umm Er Radhuma Formation, and Rus Formation [45]. Additionally, the Hassa Group, which is made up of Paleogene rocks, and the Neogene Formations, which are overlain by Quaternary sediments, are separated by a disconformity layer [44]. The Dibdibba Formation is characterized by the presence of fresh groundwater lenses in the northern area of Kuwait. Further, the Dibdibba Formation is generally defined by two main units. The first unit is the Pliocene–Pleistocene (upper unit), composed of gravel, sand, and gypsiferous cement. The second unit is the Miocene–Pliocene (lower unit), which contains pebble-sized sandstone cemented with chalky carbonates [22].
In general, the Neogene Aquifer System is considered an unconfined aquifer, although, in deeper layers of the aquifer, confined conditions may exist. The Neogene Aquifer System was recharged during the cold–humid period based on isotopic data, and it dates back to 30,000 years ago [22,44]. An analysis of more than 75 pumping tests carried out by the Ministry of Electricity and Water (MEW) in the study area for aquifer evaluation suggests that the transmissivity ranges between eighty thousand and twenty-six thousand gallons per day per foot, with a storage coefficient of 5.1 × 10−6 to 0.13 × 10−4 [46]. Hence, the transmissivity values that have been documented in Kuwait from the southwest to the northeast are 1.15 × 10−4 m2/s and 1.73 × 10−2 m2/s, respectively [22]. In addition, the hydraulic parameters of the same system vary widely according to the saturated thickness and lithological differences, ranging from 0.24 to 21 m per day, with an average value of 7.40 m per day [47].
For the studied wells in RA, the water level ranges from 29.4 to 38 mbgl, and the well depth ranges from 31 to 76 m. In the UA wells, the water level ranges from 17.3 to 29.1 mbgl, with a well depth of 22.4 to 57 m, covering only the top part of the Kuwait Group in both fields. The water level ranges from 2.4 to 8.4 m (amsl) in RA and from 6.2 to 16.5 m (amsl) in UA, reflecting the change in topography, where it has been recorded that the groundwater in Kuwait flows from SW to NE [48].
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
Thirty UA groundwater wells and thirty-eight RA groundwater wells were chosen for sampling. Using disposable Teflon bailers, a total of 68 samples were collected from the monitoring wells. All the samples were transported to the Water Research Center (WRC), Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research (KISR), and filtered before analysis. Temperature, electrical conductivity (EC), and pH analysis was conducted onsite and in the WRC laboratory by means of calibrated meters of a portable type. The analysis of total dissolved solids (TDS), cations of Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, Na+ type, and anions of HCO3−, Cl−, Br−, F−, NO3−, and SO42− were determined using the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (SMEWW) and American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standard methods. All the major ions (except HCO3) were analyzed with an ion chromatograph; calibration, duplication, standard checks, and certified reference materials were applied to the analytes as part of the quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA). The HCO3 was determined by the sulfuric acid titration method.
Ternary plots were developed for both the sampling locations using the SAR, EC, Na%, and PI values in AQUACHEM. The values of the parameters used for the study were calculated using the CHIDAM software [49], considering the analytical data of groundwater from both the wellfields. The saturation indexes (SIs) of carbonate and sulfate minerals, and their variation with respect to a temperature change from 5 to 50 °C, were determined in the PHREEQC software [50]. Based on the literature review summarized in a recent study [30], nine typical parameters, namely EC, Na% [51], SAR [52], KR [53], MAR [54], RSC [52], PI [55], PS [56], and SSP [57], were selected in the current study to validate the irrigation suitability of the groundwater. The recommendations of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) [58] were considered to study the groundwater’s suitability for livestock.
2.3. Geospatial Analysis Using Fuzzy Membership
Fuzzy logic membership [59] is a technique that enables the semantic descriptions of experts to be transformed into a numerical spatial model that forecasts the suitability zones of a certain parameter. Using a scale of 0 to 1, the fuzzy membership technique evaluates the input data depending on how likely they are to be part of a detailed set [60].
Any of the functions and operators of the Spatial Analyst extension tool in ArcGIS can be used to change the input data, reclassifying them to a 0 to 1 scale. The values of fuzzy membership for the current study were obtained by adopting the fuzzy linear membership function. The spatial maps of the fuzzy membership were developed using the inverse distance weighted (IDW) interpolation method. Using the Fuzzy Overlay tool, all the fuzzy membership maps were merged into a single integrated map for the studied regions. The ArcGIS software was also used to plot the groundwater level, ground elevation, and depth to water level along with the flow direction of the groundwater. The fuzzy gamma 0.9 operator was used in this study to overlay the maps, due to its ability to vary the amount of decreasing and increasing effects [34,61]. The schematic approach of fuzzy GIS adopted for the development of the map for ISGW is represented in Figure 3.
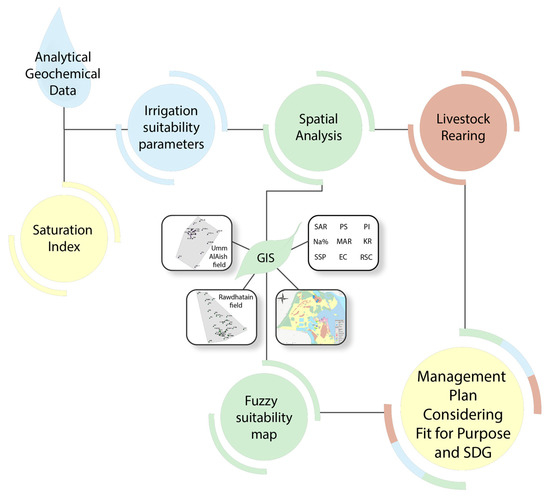
Figure 3.
Flowchart depicting the methodology used to derive a groundwater suitability map for irrigation purposes using fuzzy GIS method and agricultural management plan.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemistry
The maximum, minimum, and average values of all the chemical constituents of the groundwater samples for the RA and UA fields are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The results of physical and chemical analyses of the groundwater samples (mg/L is the unit for all parameters except electrical conductivity (EC) (µS/cm) and temperature (°C)).
The pH of the RA samples ranged from 6.80 to 9.20, while that for UA ranged from 6.91 to 8.80. Although the RA samples tended to be more alkaline, both the study areas had a similar average pH, with 7.60 and 7.70. Groundwater tends to be alkaline, owing to the presence of HCO3 percolated through rainfall runoff and aided by eroded soil [62]. The TDS of the RA and UA fields ranged from 328 to 9040 mg/L and 397 to 27,821 mg/L, respectively. There are a multitude of causes of the high TDS concentrations in groundwater, but the marine influence on geological formation and sabkhas is the most plausible explanation (the Arabic word sabkha describes both coastal and inland salt flats with the same meaning). Sabkha soil typically contains four to six times the amount of salt found in the seawater of the region [63]. Moreover, a dry climate, increased irrigation, and less rainfall recharge also contribute to elevated TDS levels [64]. The salinity also increases when water infiltrates a salty surface to reach the water table.
3.2. Mechanism Controlling the Type and Chemistry of the Groundwater
Earlier studies on the hydrochemical classification of UA groundwater performed by Robinson and Al-Ruwaih [18] identified the following four major groundwater groups: group 1, calcium bicarbonate water type in which Na > Cl; group 2, calcium chloride water type in which Na > Cl; group 3, calcium sulfate water type in which Na > Cl; group 4, calcium sulfate water type, with Cl > Na. In the present study, however, the southern and eastern parts of the RA and UA fields indicated the predominance of the Na water type, whereas the western and the northern areas were represented by the Ca water type (Figure 4). RA is mostly dominated in the east by Na-Cl, and in the north and south by Na-Ca and Ca-SO4 water types. However, Na-Ca is the dominant water type throughout the UA area, except for the southwestern part, where it is dominated by the Ca-Mg water type.
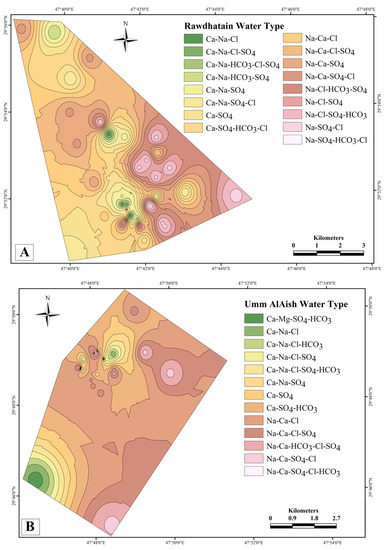
Figure 4.
Spatial map showing the different water types of (A) RA and (B) UA fields, where the eastern part is dominated by Na-Ca and Na-Cl water types in both wellfields.
By exchanging Ca2+ for Na+, the water is softened [65]. A 2001 study by Hidalgo and Cruz-Sanjulián [66] stated that the cation exchange mechanisms are typically indicated by the Na-HCO3 water type [67]. The term “exchange waters” is used to describe bodies of water in which the HCO3− concentration is greater than that of the alkaline-earth cations (Ca2+ + Mg2+) [67]. As a result of the exchange interaction with the exchange sites, the Na+ ions together with excess bicarbonate ions are released into the groundwater.
A correlation was found between the Na-SO4, Ca-Cl, and Ca-SO4, water types and samples with NO3− pollution. Groundwater samples of the Na-Ca-Cl-SO4 and Ca-SO4-Cl type were mainly due to interactions between rock and water (gypsum dissolution), and the exchange of ions. Both evaporation and the ion exchange process influenced the facies, as shown by the Na-Ca-SO4-Cl and Na-Ca-Cl-SO4 types.
3.3. Saturation Index
Compounds with values exceeding the solubility limits are most likely to precipitate, especially sulfates and carbonates. An increase in ions has a direct relationship with the saturation of minerals. However, the mixed precipitation of salts has not been determined with a definite pathway due to the non-availability of thermodynamic data for mixed or co-precipitation condition [68,69]. Authors have indicated that the presence of minor amounts of one compound may hinder the precipitation kinetics of another compound [68,69]. The solid form of a compound/mineral may contribute ions to the salt formation by the process of dissolution or behave similarly to a germination seed or as an adsorbent [70,71].
In general, the irrigated water salinity is related to biomass production and evapotranspiration. The yield of a crop is noted to be higher when there is a decrease in salinity and an increase in evapotranspiration [72,73]. The pores between the soil particles are generally clogged due to the precipitation of salts in these spaces, thereby increasing the bulk density. Thus, the soil salinity and the crop yield are mainly influenced by salt formation [74,75]. This situation is common in arid regions such as Kuwait, with increased rates of evaporation and irrigation with brackish water. The prolonged practice of using brackish groundwater for irrigation increases the salinization of the soil, thus affecting the permeability and crop yields. In this regard, the SI of a mineral provides the probability of salt precipitation on the soil based on the groundwater composition. Hence, the saturation states of carbonates (calcite, aragonite, and dolomite) and sulfates (gypsum and anhydrite) were determined for the analyzed samples.
The minerals of carbonate, aragonite, calcite, and dolomite, along with sulfate minerals like anhydrite and gypsum, were studied for variations in the SI values with respect to annual temperature fluctuations in Kuwait (5–50 °C) (Figure 5). The SI of anhydrite in UA (Figure 5A) at 5 °C varied from >−2.5 to <0.4, but an increase in temperature to 50 °C in the groundwater tends to increase the SI to range from >−2.0 to saturation around zero values. However, no significant variation was noted with the gypsum composition. All carbonate minerals reflected an increase in SI values with an increase in temperature from 5 to 50 °C. The lowest SI value for aragonite at 5 °C was noted to be −0.3, and, at 50 °C, it was calculated as 0.01. Similarly, the value of aragonite increased from 0.6 to 0.8 with an increase in temperature from 5 to 50 °C. Relatively, a greater increase in the SI of calcite was observed for a similar increase in temperature. The highest increase in the SI with regard to a rise in temperature was noticed for dolomite, tending towards supersaturation at 50 °C. Hence, there is a greater probability of the precipitation of dolomite at higher temperatures, followed by calcite and aragonite. However, at low temperatures, calcite tends to precipitate first, followed by aragonite and then dolomite. The SIs of sulfate minerals, irrespective of temperature variation, are noted to shift between saturated and undersaturated states, so they are less likely to be precipitated in soil. Groundwater samples from RA also showed a similar trend (Figure 5B) for all the studied minerals, but with relatively smaller ranges of SIs at both higher and lower temperatures compared to UA.
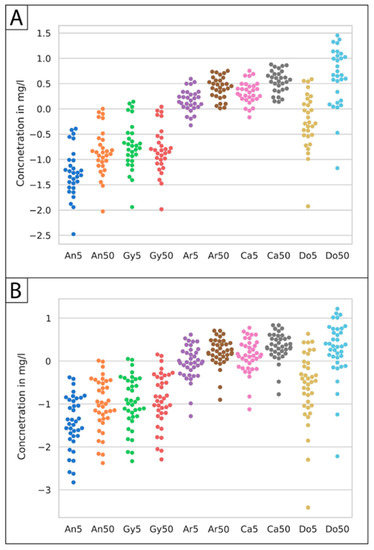
Figure 5.
The variations in saturation index (SI) values with respect to annual temperature (5–50 °C) for sulfate (An = anhydrite, Gy = gypsum) and carbonate (Ar = aragonite, Ca = calcite, Do = dolomite) minerals in (A) UA and (B) RA.
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2) governs the formation of carbonate salts along with the chemical composition of the groundwater and the temperature. The samples from the RA and UA fields had log pCO2 values above the atmospheric value (10−3.5) [76] of pCO2 computed for groundwater samples, ranging from 10−4.46 to 10−1.48 and from 10−4.8 to 10−1.61, respectively. The decomposition of organic matter and plant root respiration in the top soil leads to an increase in the pCO2 of the infiltrating water compared to that of the atmosphere (10−3.5). Thus, the soil carbon dioxide may easily enter the groundwater system [77]. The pCO2 value in a closed system is >10−2.5 [78,79] and it governs the saturation states of carbonate minerals in groundwater. The pCO2 of the Kuwaiti rainwater studied for a period of five years (2018–2023) ranged from 10−3.81 to 10−2.29, with an average of 10−2.86 in 2018; it ranged from 10−3.50 to 10−2.05 with an average value of 10−2.86 in 2019 [42], and from 10−4.29 to 10−2.09 with an average value of 10−3.15 in 2022, reflecting a higher value than the reported atmospheric pCO2 (10−3.5), indicating that carbonates remained in the solution due to the regional atmospheric pCO2 levels, in certain samples from the study area. However, at higher atmospheric temperatures and under the variation in the thermodynamic nature of the solution, carbonates are forced to precipitate.
The undersaturation of calcite, dolomite, and aragonite was observed in the samples due to the higher atmospheric pressure of the dissolved CO2, irrespective of the wellfield. The dissolution of carbonates is prominent under pCO2-rich conditions and the reverse reaction precipitates CaCO3 when CO2 escapes from the solution, either due to variations in pressure or variations in temperature, leading to the lowering of the pH. The pCO2, a significant factor in weathering, favors carbonate weathering, which is responsible for the higher HCO3 concentration [80]. As a result of a rise in HCO3−, Mg2+, and Ca2+ concentrations due to evaporation and mineral breakdown, groundwater becomes slightly supersaturated with regard to dolomite and calcite [80].
Due to the presence of secondary minerals inside the host rock, such as calcite and dolomite, the geochemistry of groundwater is more complicated. Cation exchange between groundwater and clay minerals and the dissolution and precipitation of secondary carbonate minerals impact the groundwater chemistry. High levels of bicarbonate in some waters might cause toxicity due to a lack of iron [81]. CaCO3 precipitation from these groundwaters reduces the dissolved Ca2+ concentrations, boosting the SAR and thereby the soil exchangeable Na+ [81]. In the study, the groundwater was subsaturated with gypsum and anhydrite, which is consistent with the lack of evaporites in the area, except for the presence of gypsum in the Lower Fars and Ghar Formation [82]. The disintegration of the gypsiferous formation of the aquifer is the source of the salinity [83]. The precipitation of gypsum is rather straightforward as it depends on the Ca2+ and SO42− concentrations at a given pressure and temperature. The concentration of Ca2+ may be altered by the removal of this ion during the formation of carbonates, as it leads to the common ion effect [84].
3.4. Irrigation Suitability Plot
In general, if the EC of groundwater ranges from 1000 to 2000 µS/cm, it is likely to be of good quality. Apart from EC, parameters that indicate its suitability for agricultural purposes are Na%, SAR, and PI. The samples of RA represented four categories, reflecting a few samples with low suitability for agricultural purposes. Similarly, samples of UA were also represented in all four categories, but only one sample was observed in the unsuitable category (Figure 6) as the EC was >10,000 µS/cm. It was also noted that although the EC was higher in a few samples, the samples fell under the moderate, good, and doubtful categories. Moreover, it was observed that samples with EC ranging from 2000 to 5000 µS/cm and 5000 to 10,000 µS/cm were classified as good to moderate, which could be due to their higher Ca2+ and Mg2+. Similarly, samples falling into the doubtful to unsuitable categories had higher Na% [30].
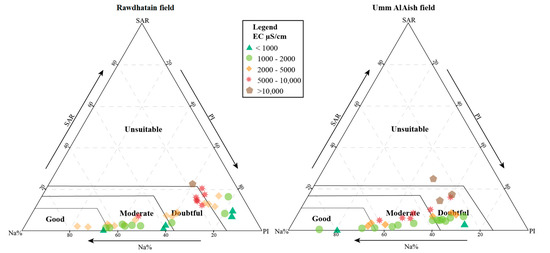
Figure 6.
Ternary plot of RA and UA groundwater samples to determine suitability for irrigation purposes using EC, sodium percentage (Na%), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), and permeability (PI).
3.5. Fuzzy GIS Maps and Irrigation Groundwater Quality Indices
The ISGW parameters used for the classification and determination of the fuzzy membership values were determined based on previous studies [30] (Table 2). In RA, based on the EC classification [85], only 7.8% of the samples were categorized as good, 36.8% were permissible, 36.8% were doubtful, and 18.4% were unsuitable. The EC map showed high fuzzy membership values in the southern part, which were identified as unsuitable, with small patches of lower values reflecting good suitability in the north (Figure S1).

Table 2.
Summary of the classification of fuzzy membership values adopted for the determination of irrigation water quality indices.
In UA, EC classification showed that only 3% of the samples were categorized as good, 50% as permissible, 23% as doubtful, and 23% as unsuitable. The EC fuzzy membership maps (Figure S2) showed that only small patches located in the north and southwest were suitable for irrigation use. The TDS results showed that out of the 30 samples, only 9 samples were freshwater and 21 were brackish. The major and minor ions in irrigated water serve as macro- and micronutrients for the growth of plants [86]. Higher concentrations of ions such as Na+ and Cl− affect the salinity and soil permeability, reduce crop yields, and hinder plant growth [87,88,89]. The Na+ concentration is observed to be higher in brackish/saline waters and treated wastewater [90]. Ozturk [75] recommends the limitation of the usage of RO water with higher Na+. Higher EC, indicative of high salinity, results in a drought scenario, where plants fail to compete with different ions in the soil [27]. The soil structure and crop growth are critically impacted by EC when irrigation water contains high salinity [91]. The higher EC concentration may be due to the process of weathering of rocks, leaching, and salt dissolution during rainfall. An increase in the salinity in water leads to a higher ionic concentration around the roots and the impact of osmotic processes in this zone, resulting in changes in biochemical and metabolic processes [92,93]. The irrigation of brackish groundwater with higher salinity increases the rate of chlorophyll degradation, prevents the synthesis of proteins, and inhibits the activity of enzymes and rates of photosynthesis [94].
The cationic ratio between the alkaline and alkaline-earth elements, where Na+ is considered as the main alkali, is referred to as Kelly’s ratio (KR). The KR determines the ISGW based on the concentration of Na+ and that of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions [53,95]; K+ is often neglected due to lesser concentrations. This ratio determines the excess sodium in the cations, such as Na%, indicating the probability of salt formation, thereby affecting the soil properties and crop yield. Na+ ions adsorb onto clay particles at high concentrations, expelling Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions. Substituting Na+ for Ca2+ and Mg2+ causes the soil to have a weak internal channel and reduces water and air movement in wet conditions [96]. Drought conditions cause the soil to harden into unworkable clods that destroy crops. According to the KR, only 44.7% of samples in the RA region were considered safe and fit for irrigation use. The fuzzy membership map of the KR in RA indicated that higher values were represented in the central and southern parts of the region (Figure S1). The northern part of the region had lower values, indicating that it was suitable for irrigation use. Similarly, in UA, 43% of samples were considered suitable and safe for irrigation based on the KR. It was observed from the KR fuzzy maps (Figure S2) that low membership values were only present in the NW and SW regions.
A negative impact on crop cultivation is reported due to the volume of water held between clay and excess Mg2+ [92], which increases the alkalinity, reducing the percolation rate by damaging the soil structure [97]. The crop yield can also be affected by the increase in soil alkalinity developed by excess Mg2+ in water, and it is referred to as the magnesium hazard [98]. Stomatal changes, leaf burn, and the varying uptake of Ca and Mg are associated with higher concentrations of these ions in brackish or RO brines, also modifying the osmotic variations to regulate the plant uptake of water [99]. Calcium and magnesium ions are usually balanced in groundwater [100], but they act differently in soil. Especially in brackish to saline water, the exchange of Mg2+ with Na+ in irrigated soils disperses soil assemblages and damages the soil structure [101], thus reducing crop yields [102,103]. In the RA field, all samples in the region were placed in the suitable category based on the MAR classification [104]. The MAR fuzzy membership map showed that the groundwater in the region was suitable and safe for irrigation (Figure S1). Similarly, the MAR values of groundwater samples in the UA field indicated that it was suitable and excellent for irrigation. The fuzzy membership maps of the MAR (Figure S2) revealed that the membership values were low throughout UA.
Similarly, the parameters associated with high Na+ in groundwater, such as SAR and Na%, can also reduce the permeability of the soil and the water-absorbing capacity of crops [91]. Soil properties are generally affected by sodium, especially by SAR [105]. The relative percentage of Na+ to that of other cations in irrigated water affects crops and the soil structure. The permeability, soil aeration, and physical structure of soil are affected by higher Na% in irrigated water [106]. Higher Na+ in water may be due to its brackish nature or derived from the pressure of ion exchange, the dissolution leaching of anthropogenic salts, or even agrochemicals or the intrusion of seawater in coastal regions. The sodicity issue is linked to permeability in the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) recommendations [58]. Regions with excess Na+ in their groundwater produce crops with inadequate water due to low infiltration rates resulting from the poor hydraulic conductivity of the soil. Montmorillonitic clays are more sensitive to Na+ than in kaolinite regions. Because sodium ions (Na+) are adsorbed onto soil exchange sites, they cause nonhomogeneous aggregates and thus decrease the soil permeability [107]. The potential effect of Na+ may be slightly amplified in Mg2+-dominated water, especially when Mg/Ca is >1 [80]. The Na% indicated that only 2% of the RA groundwater was excellent for irrigation use, whereas 28.9% fell within the good category, 21% in permissible, with 23.6% in the doubtful and unsuitable categories [85]. The fuzzy map of Na% showed that low membership values were seen in the northern part of the RA region, along with some small patches in the central part of the area (Figure S1). Thus, the samples from the central part of the RA field were considered permissible, whereas those along the eastern and southeastern parts were considered unsuitable for irrigation purposes.
In UA, according to the Na%, samples were categorized as excellent (2%), good (26%), permissible (30%), and doubtful (36%). From the fuzzy maps of Na% (Figure S2), it was observed that good groundwater was detected in the southwest, with moderate membership values in the central part of the UA field. Moreover, the eastern part of the region showed unsuitable groundwater quality for irrigation use.
Seedling growth is affected by decreasing soil aeration [86], which may also result from the irrigation of the soil with water with higher ionic concentrations [108]. The index of permeability is typically compared to the total concentration of ions, and if the index value exceeds 75%, the sample is suitable and fit for irrigation, while less than 25% is considered unsuitable [109]. Soil permeability is reduced, and hardening occurs with higher salt concentrations in the surface and on the pore spaces [110]. As stated earlier, the inability of plants to absorb water and nutrients via osmotic processes and metabolic responses is another route by which high salinity can harm plant growth [101]. Soil permeability and water quality for irrigation are influenced by the long-term presence of sodium, calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonate ions [111]. Most of the RA samples (55%) fell under the good category, with 42% being classified as suitable and only 2.6% in the unsuitable class. Furthermore, the fuzzy map of PI showed that RA was mostly characterized by low membership values, and high membership values were only observed in the southeastern part (Figure S1). However, among the UA samples, only 10% were found to be suitable and 83% of the samples represented the good category, whereas only 6% of the samples were unsuitable. The fuzzy membership map of PI (Figure S2) showed that the entire region was represented by low membership values, reflecting the suitability for irrigation in the UA area.
The potential salinity parameter Is specifically determined by the groundwater chloride ions containing half of the sulfate ions. Since chloride is a strongly electronegative ion, it facilitates the conductivity of water and then associates with other ions in arid environments to form salts. In RA, the PS values indicated that only 5% of the samples were suitable, 31.5% were moderate, and 63% were considered unsuitable for irrigation [56]. In addition, the PS fuzzy map showed low to moderate membership values along the northern part of the RA area, with minor patches in the central and southern parts (Figure S1). In the UA region, however, only 3% of the samples were suitable, 50% moderate, and 46% were considered unsuitable for irrigation based on the PS values [56]. In the fuzzy map of PS (Figure S2), most of the membership values were high, except for a small portion along the northern and southwestern parts of UA that had low membership values.
The surplus of carbonates or bicarbonates in irrigated water may result in the formation of salts, which precipitate in the soil pore spaces, thereby affecting its permeability, as reflected by the SI values of the carbonate minerals. The excess HCO3 relative to Ca2+ and Mg2+ tends to precipitate as NaHCO3 in the irrigated soil, affecting the soil fertility and thus the crop yields [112,113]. Water classification for irrigation according to the residual sodium carbonate [52] in the RA region showed that only 7% of the groundwater samples were in the medium category, and the rest (92%) was observed to represent the good category. The RSC spatial map showed that higher fuzzy values were represented in the entire RA region (Figure S1). Moreover, in the UA region, the RSC values and fuzzy membership map (Figure S2) revealed that all the groundwater samples were suitable for irrigation use.
The sodium absorption ratio can be used to evaluate the sodium in excess compared to magnesium and calcium, which decreases the permeability of the soil, resulting in water limitations for plants. An increase in SAR can reduce the water absorption capacity of plants [92], in addition to the impact on the soil structure and fertility. The irrigated water based on SAR was classified as unsuitable, doubtful, good, and excellent, based on the values of >26, 18–26, 10–18, and <10, respectively. The irrigation of plants with sodium-enriched water results in ion exchange reactions with Ca2+ and Mg2+ [78]. However, sodium that is bound to the adsorption sites on clay particles is generally released during irrigation with Ca-enriched water. According to the SAR classification [52], most of the RA samples (63%) were in the excellent category, with 21%, 13%, and 2% in the good, fair, and poor categories, respectively. The spatial map of SAR showed that the RA region was predominantly characterized by low fuzzy values, with a minor representation of high membership values in the east (Figure S1). Similarly, most of the UA samples (83%) were excellent for irrigation, whereas 6% were good, 6% were fair, and only 3% were in the unsuitable category. The SAR spatial distribution map (Figure S2) showed that most of the UA area had low fuzzy values, with a minor representation of high membership values along the eastern part of the area.
According to the classification of SSP [57], 2.6% of the RA samples were considered excellent, 28.9% good, 21% permissible, 23.6% doubtful, and 23.6% unsuitable. The fuzzy membership map of SSP in the RA region (Figure S1) showed that lower values were only noticed in the north, and they gradually increased towards the southeast. Similarly, the SSP values in UA showed that 10% of samples had excellent suitability, whereas 26.6% were good, 26.6% were permissible, and 36.6% were doubtful for irrigation use. Furthermore, the fuzzy membership map of UA (Figure S2) showed low values along the southwestern part of the area, with a gradual increase in value towards the eastern part of the area.
3.6. Final Fuzzy Overlay Map
In order to identify contamination levels, contaminated regions, and sources, and to map the extent of the contaminated areas, groundwater quality evaluation and spatial mapping using GIS approaches are required [114,115]. For this purpose, researchers across the world rely on inverse distance weighting (IDW) interpolation [30,37,116]. The fuzzy membership maps for the considered parameters were overlaid to create a final groundwater suitability map for irrigation purposes (Figure 7). Based on the values of fuzzy membership, the groundwater suitability for irrigation purposes was categorized into four classes: excellent, good, moderate, and poor.
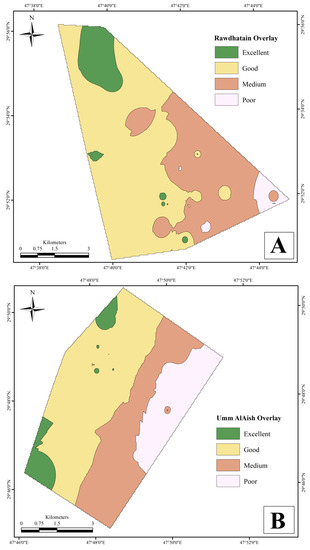
Figure 7.
Final fuzzy overlay map of (A) Rawdhatain and (B) Umm Al Aish regions, depicting the spatial distribution of different categories of groundwater for irrigation purposes (excellent, good, medium, and poor).
In the final overlay map of the RA region (Figure 7A), the excellent to good ISGW was dispersed from the northern to the southern parts, whereas medium to poor groundwater quality was predominantly observed along the eastern portion of the wellfield. However, in the UA region (Figure 7B), suitable zones of excellent to good ISGW were observed in the northern and eastern portions of the wellfield and the suitability gradually changed from moderate to poor towards the east and south of the area.
The final fuzzy overlay map of the RA field revealed that the region was categorized as excellent (8.36%), good (56.64%), medium (32.17%), and poor (2.81%). Meanwhile, the UA field was categorized as excellent (5.90%), good (46.50%), medium (29.70%), and poor (17.70%) (Table 3). Hence, the final overlay map of these two wellfields indicated that samples from the RA wellfield were relatively more suitable for irrigation purposes.

Table 3.
Area coverage of the Rawdhatain and Umm Al Aish regions and their water suitability categories.
3.7. Livestock Suitability
The health of biota can be deteriorated by the prolonged usage of drinking water with high salinity, and it can even lead to mortality [117]. Due to the high salt content of groundwater, desalination units are used by local poultry farms. The suitability of groundwater for animal rearing based on the salinity in the research area [58] was studied (Figure 8). The results indicated that among the 38 samples from RA, only 36 samples were rated as excellent (28.9%) and very satisfactory (52.6%) for livestock and poultry, whereas 13.1% were satisfactory for livestock and unfit for poultry. Similarly, out of the 31 samples from UA, 27 samples were rated as excellent (26.6%) and very satisfactory (46.6%) for all classes of poultry and livestock, whereas 13.3% were considered satisfactory for livestock and unsuitable for poultry, 10% could be considered for limited use for livestock and unsuitable for poultry, and 3.3% were not recommended for livestock and poultry consumption.
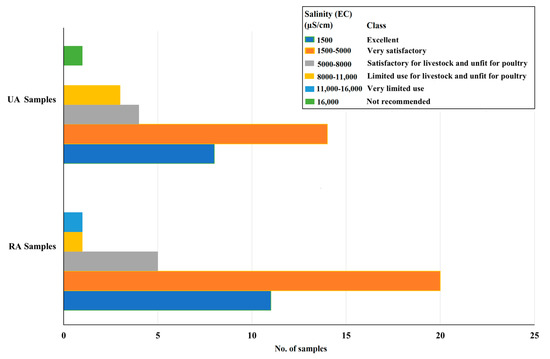
Figure 8.
Groundwater samples in UA and RA compared to the classification of Ayer and Westcot [58] regarding groundwater quality for livestock and poultry.
The composition of the diet has a considerable impact on the water salinity tolerance for goats and sheep [118,119]. Sheep and goats have different water salinity tolerances [118,119]. Sheep of different breeds and sizes should be provided drinking water with TDS generally lower than 5000 mg/L [117] (lactating females, dry adults, and young). EC of 6000 to 10,000 µS/cm for young and 9300 to 21,800 µS/cm is suggested as optimal for goats (dry adults) [117]. However, water with EC higher than 10,000 µS/cm should be used with caution. Under these circumstances, sheep and goats could use 97% and 90% of the groundwater samples from the RA and UA fields for drinking purposes, respectively.
3.8. Management of Brackish Groundwater
Since water is scarce and unevenly distributed, globally, eighteen countries are considered to be at “serious risk” [120]. Fifteen of these countries are in the Middle East. Water resource management is becoming increasingly difficult because of national development, irrigated agriculture, and water competition between urban areas, farming, and industry [121]. Groundwater has been seriously disrupted from its normal state due to irregular rainfall, scant recharge, and uncontrolled abstraction patterns, leading to the major depletion of underground aquifers and long-term water quality issues.
The demand for food and water increases with the population [122]. The salinity of groundwater used for irrigation may also lead to seed dormancy [123]. The selection of appropriate crops can offer a solution to soil salinity issues [124]. The salinity thresholds for different crops vary and thus suitable crops can be identified based on the soil fertility and electrical conductivity of the groundwater, although certain glycophytes [125], such as coconut, are moderately salinity-tolerant. The quantity of water used and the value of the threshold limit of salinity can be helpful in the utilization of brackish groundwater for irrigation. Similarly, the different crops grown annually have different criteria with respect to salinity and demand [126,127]. One of the main types of salt-tolerant crops are halophytes [128], which could be used for several purposes. The cultivation of halophytes could be a viable solution for disposed inland RO reject brines and brackish groundwater.
Certain plants used for animal feed, with more nutrients and carbohydrates, such as forage cactus, can be cultivated with brackish groundwater individually or in integrated multiple agricultural systems, along with aquaculture or through intercropping with Gliricidia [129,130]. The yields of crop are increased without the formation of salts in the soil and water use can be maintained through supplemental irrigation techniques. This method also enhances the rate of photosynthesis. The hydroponic production of tilapia can be performed under salinity with minimal water requirements [131]. Integrated systems involving halophytes such as forage cactus and seedling production to supplement irrigation along with pisciculture can be considered for brackish groundwater agriculture [131].
3.9. Fit for Purpose (FFP)
Brackish and freshwater mixing can be considered for certain crops that are salt-tolerant, such as cotton, but is not appropriate for freshwater-dependent crops such as corn [132]. Management strategies can also consider the utility of the available water resources based on their quality, referred to as “fit for purpose” (FFP) [133,134]. The FFP method addresses the UN’s Sustainable Developmental Goals by advocating for the use of recycling [135], the integration of different management techniques to sustain water resources [136], the implementation of water policies and modeling techniques [137], consideration of the use of the available water resources [138], and desalination and wastewater treatment [139]. Recent studies have tried to integrate these resources to address the FFP in water management and governance strategies as a step towards achieving SDG 6.
Developing a new water management system that takes into account rising temperatures, shifting precipitation patterns, along with shifts in the volume and distribution of rainfall is essential to satisfy future global water needs. To find workable and generally accepted water resource allocation solutions for different users and to speed up the development of non-conventional water resources, such as water reuse and the desalination of seawater, future studies should focus on innovative water resource management systems such as integrated water resource management (IWRM) [140]. The insitu monitoring of soil and water in irrigated regions is a basic requirement for planning and management strategies.
4. Conclusions and Limitations
The salination of soil is a key issue in arid regions, as it alters the physiochemical properties of the soil and reduces the crop yields. The study of the ISGW of fresh to brackish samples collected from the two adjacent water wellfields in RA and UA indicates Ca-Na water type in the central portions of the wellfields and are observed to be of the Na-Cl type along the southern and eastern portions of the study area, reflecting the increase in salinity along the regional groundwater flow. The geochemical modeling of the composition of the groundwater in both wellfields indicates that the saturation states of carbonates are greater, in contrast to sulfates, reflecting the probability of the precipitation of carbonate salts in the soil pores, affecting the permeability of the soil and thereby the crop yields. The probability salt formation on the soil surfaces and the pores is inferred to increase during high-temperature months. Further, the formation of salts is also identified to be governed by the ionic strength, pCO2, and changes in the thermodynamic properties of the system, which lead to drastic variations in salt formation, thus affecting permeability. The integrated plot of the ISGW shows that UA samples are more suitable for irrigation than RA samples. Cation exchange between groundwater and clay minerals, and the dissolution and precipitation of secondary carbonate minerals, affect the groundwater chemistry.
The ISGW for these two regions were evaluated by considering nine parameters (EC, KR, MAR, Na%, PI, PS, SAR, RSC, and SSP) adopting the fuzzy logic technique. The fuzzy membership maps of the nine parameters were then integrated into a final fuzzy overlay map of the RA and UA fields to investigate the ISGW. Based on the values of the fuzzy membership, the groundwater suitability for irrigation purposes was categorized into four classes: excellent, good, moderate, and poor. Na played a key role in most of these parameters and hence the higher values of Na+ ions in samples affected the irrigation quality of the water. The RA field 8.3% of samples were categorized as excellent,56.6% as good,32.1% as moderate, and 2.8% as poor. In the UA field, 5.9% of samples were excellent, 46.5% were good, 29.7% were moderate, and 17.7% were poor. It is inferred from the maps that most of the groundwater in RA can be used for irrigation, except those from the eastern side of the study area, with poor water quality. The groundwater in the northern and western parts of the UA region is suitable for agriculture, whereas that from the eastern and southern parts is unsuitable for irrigation. It is suggested that salt-tolerant crops could be prioritized in regions with poor suitability. Further, the water provided to the different parts of plants from the soil and subsurface is also affected due to the effect of salinity on the osmotic pressure of the stomatal cells. The study also indicates that most of the groundwater in the wellfield is suitable for consumption by livestock. However, this depends on the type of livestock, their age, size, breed, gender, etc., which also varies the quantity of consumption.
Due to irregular precipitation in arid regions and minimal aquifer recharge along with extensive abstraction patterns, groundwater has been substantially disturbed from its natural state, resulting in significant aquifer depletion and long-term water quality challenges. Therefore, soil and water monitoring in irrigated regions, along with innovative water resource management systems such as IWRM, are crucial for the sustainability of resources in arid regions such as Kuwait. Further, monitoring of the soil and quality of irrigated water in arid regions with brackish groundwater helps to maintain the crop yields and fertility of the soil. Moreover, in regions with inland desalination units, it is advisable to develop a monitoring system to observe the leaching of rejects and impacts on soil and to determine the maximum depth of leaching. This monitoring system would aid in conserving the fertility of the soil and existing groundwater reserves.
The hydrogeochemical interpretation of the saturation states regarding the precipitation of salts was not validated with XRD data, and this could be considered a major limitation of the study. The geochemical processes inferred during infiltration though vadose zone could be confirmed with litho-logs and core samples in future studies. Such interpretations could also help in assessing the geochemical environment of the topsoil region and the capillary zone. The water level data of all the wells were not obtained in the study, but these could have clearly illustrated the variations in the geochemistry along the flow direction. Furthermore, the isotopic evaluation of groundwater would assist in the interpretation of evaporation, recharge, and contaminated sources. Although the overall process of the region and its suitability was established in the current study, the abovementioned additional data and their integrated analysis would yield more concrete solutions for the future groundwater resource management of the region.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w15142674/s1, Figure S1: Rawdhatain fuzzy membership maps. Figure S2: Umm Al Aish membership maps.
Author Contributions
A.A.-R.—Conceptualization, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing, Methodology, Software; C.S.—Conceptualization, Project Administration, Supervision, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing; D.R.S.—Data Curation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing—Original Draft; B.A.—Writing—Review and Editing, Software, Visualization; T.R.—Sampling, Methodology, Writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the International Atomic Energy Agency through TC project KUW7010 and the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research through project WM084C.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be provided on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their appreciation to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) for their in-kind contribution to the study through IAEA-KUW7010. The support of the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research’s (KISR’s) management (WM084C) was pivotal in carrying out the various tasks of the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mahdian, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Siadatmousavi, S.M.; Chalipa, Z.; Delavar, M.; Guo, M.; Abolfathi, S.; Noori, R. Modelling Impacts of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities on Inflows and Sediment Loads of Wetlands: Case Study of the Anzali Wetland. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekmohammadi, B.; Uvo, C.B.; Moghadam, N.T.; Noori, R.; Abolfathi, S. Environmental Risk Assessment of Wetland Ecosystems Using Bayesian Belief Networks. Hydrology 2023, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Rezaie, F.; Cooper, J.; Kalantari, Z.; Abolfathi, S.; Hatamiafkoueieh, J. Soil Water Erosion Susceptibility Assessment Using Deep Learning Algorithms. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, H. Integrated Water Management: Emerging Issues and Challenges. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 45, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendiran, T.; Sabarathinam, C.; Panda, B.; Elumalai, V. Influence of Dissolved Oxygen, Water Level and Temperature on Dissolved Organic Carbon in Coastal Groundwater. Hydrology 2023, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahchi, Z.; Jalali, M. Effect of Water Quality on the Leaching of Potassium from Sandy Soil. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, R. Management of Declining Groundwater Resources and the Role of Policy Planning in Semi-Arid Economies: The Case of Texas High Plains. In Emerging Issues in Groundwater Resources. Advances in Water Security; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, A.R.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Tanninen, J.; Kamppinen, L.; Nystrom, M. Pre-Treatment and Hybrid Processes: Nanofiltration-Principles and Application; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 253–254. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, D.; Bailey, O.; Kim, P.; Mullaney, E.; Calabrese, J.; Walman, L.; Nelson, F.; Yao, X. Will Limits of the Earth’s Resources Control Human Numbers? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 1999, 1, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G. Use of Saline–Sodic Waters through Phytoremediation of Calcareous Saline–Sodic Soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 50, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E.; Tanji, K.K. Effects of Drainage on Water Quality in Arid and Semiarid Irrigated Lands. Agric. Drain. 1999, 38, 831–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, D.R.; Bruss, P.J.; Yang, X.; Staggenborg, S.A.; Welch, S.M.; Apley, M.D. Tapping Unsustainable Groundwater Stores for Agricultural Production in the High Plains Aquifer of Kansas, Projections to 2110. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3477–E3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, L.; Konar, M.; Cai, X.; Troy, T.J. Virtual Groundwater Transfers from Overexploited Aquifers in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8561–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.F.; Liu, X.; Suddarth, S.R.P.; Nguyen, C.; Sandhu, D. NaCl Accumulation, Shoot Biomass, Antioxidant Capacity, and Gene Expression of Passiflora edulis f. Flavicarpa Deg. in Response to Irrigation Waters of Moderate to High Salinity. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, R.; Borzelabad, M.J.; Feizi, H.; Azimi, A. Interaction of SiO Nanoparticles with Seed Prechilling on Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Tall Wheatgrass (Agropyron elongatum L.). Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2014, 16, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.; Schutte, B.; Shukla, M.; Picchioni, G.; Ulery, A. Time-Integrated Measurements of Seed Germination for Salttolerant Plant Species. Seed Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.W.; Al Ruwaih, F. The Stable-Isotopic Composition of Water and Sulfate from the Raudhatain and Umm Al Aish Freshwater Fields, Kuwait. Chem. Geol. Isot. Geosci. Sect. 1985, 58, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwarteng, A.; Viswanathan, M.; Al-Senafy, M.; Rashid, T. Formation of Fresh Ground-Water Lenses in Northern Kuwait. J. Arid Environ. 2000, 46, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akber, A.; Viswanathan, M.; Al Senafy, M.; Rashed, T. Assessment of Long-Term Pollution for the Groundwater of Raudhatain and Umm Al-Aish Areas (Phase II); Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Akber, A.; Al-Murad, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Rashid, A.; Al-Qallaf, H.; Al-Haddad, A.; Bhandary, H.; Marzouk, F.; Al-Salman, B. Long-Term Monitoring and Remediation Strategy for Hydrocarbon Pollutants in the Groundwater of Raudhatain and Umm Al-Aish Fields; Report No. KISR9902; Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Akber, A.; Rashed, T.; Kotwicki, V.; Uddin, S.; Bushehri, A. Establishing a Baseline to Evaluate Future Impacts to Groundwater Resources in North Kuwait. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashed, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; AlSenafy, M.; Ghoneim, H. Effect of Seawater Discharge on Groundwater Quality in the Northern Kuwait; Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Quinn, M.; Al-Haddad, A.; Al-Khalid, A.; Al-Qallaf, H.; Rashed, T.; Bhandary, H.; Al-Salman, B.; Bushehri, A.; Boota, A. Pollution of Fresh Groundwater from Damaged Oil Wells, North Kuwait. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjandra, F.L.; Kondhoh, A.; Mohammed, M. A Conceptual Database Design for Hydrology Using GIS. In Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology and Water Resources, Kyoto, Japan, 13–15 March 2003; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Selvam, S.; Dar, F.A.; Magesh, N.; Singaraja, C.; Venkatramanan, S.; Chung, S. Application of Remote Sensing and GIS for Delineating Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones of Kovilpatti Municipality, Tamil Nadu Using IF Technique. Earth Sci. Inform. 2016, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Hamza, S.; Bashir, E. Groundwater Geochemistry of Winder Agricultural Farms, Balochistan, Pakistan and Assessment for Irrigation Water Quality. Eur. Water 2010, 31, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kumarasamy, P.; Dahms, H.-U.; Jeon, H.-J.; Rajendran, A.; Arthur James, R. Irrigation Water Quality Assessment—An Example from the Tamiraparani River, Southern India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 5209–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadiati, M.; Nalley, D.; Adamowski, J.; Nakhaei, M.; Asghari-Moghaddam, A. A Comparative Study of Fuzzy Logic-Based Models for Groundwater Quality Evaluation Based on Irrigation Indices. J. Water Land Dev. 2019, 43, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.; Prasanna, M.; Venkatramanan, S.; Nepolian, M.; Pradeep, K.; Panda, B.; Thivya, C.; Thilagavathi, R. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Irrigation by Adopting New Suitability Plot and Spatial Analysis Based on Fuzzy Logic Technique. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnamasari, R.A.; Noguchi, R.; Ahamed, T. Land Suitability Assessments for Yield Prediction of Cassava Using Geospatial Fuzzy Expert Systems and Remote Sensing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 166, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovari, Y.; Beigi-Harchegani, H.; Asgari, K. A Fuzzy Logic Approach for Assessment and Mapping of Groundwater Irrigation Quality: A Case Study of Marvdasht Aquifer, Iran. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2015, 61, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafreshi, A.M.; Tafreshi, G.M. A New Approach in Qualitative Zoning of Groundwater to Assessment Suitable Irrigation Water Using Fuzzy Logic Spatial Modeling via GIS. Res. Sq. 2022. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Shekhar, A.; Jenifer, M.A. Assessing Groundwater Quality for Drinking Water Supply Using Hybrid Fuzzy-GIS-Based Water Quality Index. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B. Groundwater Vulnerability Mapping: A GIS and Fuzzy Rule Based Integrated Tool. Appl. Geogr. 2005, 25, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, F.B.; Boughariou, E.; Bouri, S. Multicriteria-Analysis of Deep Groundwater Quality Using WQI and Fuzzy Logic Tool in GIS: A Case Study of Kebilli Region, SW Tunisia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 180, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaoui, O.; Agoubi, B.; Antunes, I.M.; Tlig, L.; Kharroubi, A. Groundwater Quality for Irrigation in an Arid Region—Application of Fuzzy Logic Techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 29773–29789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misak, R.; Hussain, W. Groundwater in Kuwait. In The Geology of Kuwait; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Umar, R.; Ahmad, M. Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Framework of Regional Aquifer System in Kali-Ganga Sub-Basin, India. Environ. Geol. 2001, 40, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samayamanthula, D.R.; Sabarathinam, C.; Alayyadhi, N.A. Trace Elements and Their Variation with PH in Rain Water in Arid Environment. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, S.D.; Sabarathinam, C.; Al Otaibi, F.; Al-Sabti, B.T. Variation of Centennial Precipitation Patterns in Kuwait and Their Relation to Climate Change. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.; Nasr, S.N. Stratigraphy of the Kuwait-Basra Area: Middle East. In Habitat of Oil; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Edgell, H. Aquifers of Saudi Arabia and Their Geological Framework. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 1997, 22, 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Un-Escwa, B.; United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia. Bundesanstalt Für Geowissenschaften Und Rohstoffe; Inventory of Shared Water Resources in Western Asia: Beirut, Lebanon, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Parson Corporation. Groundwater Resources of Kuwait, I–III; Ministry of Electricity and Water: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer, H.; Rice, R. A Slug Test for Determining Hydraulic Conductivity of Unconfined Aquifers with Completely or Partially Penetrating Wells. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ruwaih, F.M.; Shehata, M. Hydrochemical Processes and Environmental Isotopic Study of Groundwater in Kuwait. Water Int. 2004, 29, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarathinam, C.; Bhandary, H.; Hadi, K. CHIDAM-A Software for Chemical Interpretation of the Dissolved Ions in Aqueous Media. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Thorstenson, D.C.; Plummer, L.N. PHREEQE: A Computer Program for Geochemical Calculations; US Geological Survey; Water Resources Division: Reston, VA, USA, 1982; Volume 80. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of Carbonates in Irrigation Waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, L. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils. In Agriculture Handbook; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 60, pp. 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, W.P. Permissible Composition and Concentration of Irrigated Waters. Proc. Am. Soc. Civil Eng. 1940, 66, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabolcs, I.; Darab, K. Radio-Active Technique for Examining the Improving Effect of CaCO3 on Alkali (Szik) Soils. Acta Agron. Hung 1964, 13, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Doneen, L. Water for Field and Truck Crops. Calif. Agric. 1948, 2, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, V.O.; Aceves, N.E. Instructions for Sampling, Data Recording and Interpretation of Water Quality for Agricultural Irrigation; Colegio de Postgraduados: Chapingo, Mexico, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.K.; Mays, L.W. Groundwater Hydrology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 0-471-05937-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985; Volume 29, Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/T0234E/T0234E00.htm (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Zadeh, L.A. Outline of a New Approach to the Analysis of Complex Systems and Decision Processes. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonham-Carter, G. Geographic Information Systems for Geoscientists: Modelling with GIS; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; ISBN 0-08-042420-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tafreshi, A.M.; Tafreshi, G.M. A Novel GIS-Based Approach to Assessment Suitable Irrigation Water Using a Fuzzy-Multi Indices Method in Astaneh-Kuchesfahan Plain, Iran. Res. Sq. 2021, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alati, H.N.; Gad, M. Study The Seasonal Fluctuations of Groundwater Characteristics in Al-Raudhatain And Umm Al-Aish Depressions, North Kuwait. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2018, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Homidy, A.A.; Dahim, M.H.; Abd El Aal, A.K. Improvement of Geotechnical Properties of Sabkha Soil Utilizing Cement Kiln Dust. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 9, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Katheeri, E.; Howari, F.; Murad, A. Hydrogeochemistry and Pollution Assessment of Quaternary–Tertiary Aquifer in the Liwa Area, United Arab Emirates. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, M.H.; Sanjulián, J.J.C.; Mendizábal, A.S. Evolución Geoquímica de Las Aguas Subterráneas En Una Cuenca Sedimentaria Semiárida: Acuífero de Baza-Caniles, Granada, España. Tierra Tecnol. Rev. Inf. Geol. 1995, 10, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, M.C.; Cruz-Sanjulián, J. Groundwater Composition, Hydrochemical Evolution and Mass Transfer in a Regional Detrital Aquifer (Baza Basin, Southern Spain). Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, M.N. Evolution of Saline Waters and Brines in the Benue-Trough, Nigeria. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, R. Mixed Salts—Scaling Limits and Propensity. Desalination 2003, 154, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, R. Nucleation and Kinetics of Mixed Salts in Scaling. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancollas, G.H.; Zieba, A. Constant Composition Kinetics Studies of the Simultaneous Crystal Growth of Some Alkaline Earth Carbonates and Phosphates. In Mineral Scale Formation and Inhibition; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.; Bhandary, H.; Al-Khalid, A. Modeling of Temperature Governed Saturation States and Metal Speciation in the Marine Waters of Kuwait Bay–Concern to the Desalination Process. Desalin Water Treat 2020, 176, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, F.; Benes, S.; Grattan, S. Field Performance of Halophytic Species under Irrigation with Saline Drainage Water in the San Joaquin Valley of California. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 118, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, P.; Shukla, M.; Mexal, J. Spatial Variability of Hydraulic Conductivity and Sodium Content of Desert Soils: Implications for Management of Irrigation Using Treated Wastewater. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.F. Irrigation Using Brackish Groundwater and RO Concentrate: Effects on Germination, Emergence, and Growth of Halophytes. Ph.D. Thesis, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wigley, T.; Plummer, L.; Pearson, F., Jr. Mass Transfer and Carbon Isotope Evolution in Natural Water Systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 42, 1117–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njitchoua, R.; Dever, L.; Fontes, J.C.; Naah, E. Geochemistry, Origin and Recharge Mechanisms of Groundwaters from the Garoua Sandstone Aquifer, Northen Cameroon. J. Hydrol. 1997, 190, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigter, T.; Van Ooijen, S.; Post, V.; Appelo, C.; Dill, A.C. A Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Explanation of the Groundwater Composition under Irrigated Land in a Mediterranean Environment, Algarve, Portugal. J. Hydrol. 1998, 208, 262–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, M. Salinization of Groundwater in Arid and Semi-Arid Zones: An Example from Tajarak, Western Iran. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1133–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, H.; Brain, L.; George, A.; O’Connor, G. Soil Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 129, p. 389. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Al-Sulaimi, J.; Al-Awadi, E.; Al-Ruwaih, F. An Overview of the Tertiary Geology and Hydrogeology of the Northern Part of the Arabian Gulf Region with Special Reference to Kuwait. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1996, 40, 259–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokeddem, I.; Belhachemi, M.; Merzougui, T.; Nabbou, N.; Lachache, S. Hydrochemical Assessment and Groundwater Pollution Parameters in Arid Zone: Case of the Turonian Aquifer in Béchar Region, Southwestern Algeria. J. Water Land Dev. 2018, 39, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarathinam, C.; Rashed, T.; Dashti, F.; Bhandary, H. Equilibrium States of Groundwater Chemistry in Coastal Region of Kuwait. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 263, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, S. An Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes around Brick Kilns in Three Districts of Balochistan Province, Pakistan, through Water Quality Index and Multivariate Statistical Approaches. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.-S.; Chen, J.-S. Probabilistic Assessment of Groundwater Mixing with Surface Water for Agricultural Utilization. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Qian, H.; Fang, Y. Assessment of Soil Salinization Based on a Low-Cost Method and Its Influencing Factors in a Semi-Arid Agricultural Area, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3465–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H. Hydrochemical Appraisal of Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes and the Major Influencing Factors: A Case Study in and around Hua County, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.; Shukla, M.K.; Mexal, J.G. Spatial Variability of Soil Properties in an Arid Ecosystem Irrigated with Treated Municipal and Industrial Wastewater. Soil Sci. 2012, 177, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, M.J.; Ebrahimi, P.; Ebrahimi, M. Evaluating Hydrogeochemical Processes Regulating Groundwater Quality in an Unconfined Aquifer. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 1021–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Mahmudy-Gharaie, M.H.; Ghassemzadeh, F.; Karimi Karouyeh, A. Assessment of Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation in a Gold Mine Surrounding Area, NE Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, H. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Irrigated Region, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Mendonça, A.J.; Silva, A.A.R.d.; Lima, G.S.d.; Soares, L.A.d.A.; Nunes Oliveira, V.K.; Gheyi, H.R.; Lacerda, C.F.d.; Azevedo, C.A.V.d.; Lima, V.L.A.d.; Fernandes, P.D. Salicylic Acid Modulates Okra Tolerance to Salt Stress in Hydroponic System. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, K.; Singh, S. Effect of Gypsum Application on the Quality of Irrigation Waters. Madras Agric. J. 1967, 59, 646–647. [Google Scholar]
- Subba Rao, N. Seasonal Variation of Groundwater Quality in a Part of Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol. 2006, 49, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Y.; Ullah, S.F.; Akhter, G.; Aslam, A.Q. Groundwater Quality Evaluation by Electrical Resistivity Method for Optimized Tubewell Site Selection in an Ago-Stressed Thal Doab Aquifer in Pakistan. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.; Angami, M. Hydrochemistry and Evaluation of Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes in the Markandeya River Basin, Belgaum District, Karnataka State, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 459–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, A.M.; Shukla, M.K.; Schutte, B.J.; Picchioni, G.; Daniel, D. Physiologic Response of Six Plant Species Grown in Two Contrasting Soils and Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and RO Concentrate. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2017, 31, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water; US Geological Survey; Department of the Interior: Reston, VA, USA, 1985; Volume 2254. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, N.S.; Rao, P.S.; Reddy, G.V.; Nagamani, M.; Vidyasagar, G.; Satyanarayana, N. Chemical Characteristics of Groundwater and Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Varaha River Basin, Visakhapatnam District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 5189–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narsimha, A.; Sudarshan, V. Assessment of Fluoride Contamination in Groundwater from Basara, Adilabad District, Telangana State, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, M. Hydrogeochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Surface Water Quality of Pratapgarh District, Uttar Pradesh, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.W.; Heathcote, J. Natural Inorganic Hydrochemistry in Relation to Ground Water; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- McNeal, B.; Layfield, D.; Norvell, W.; Rhoades, J. Factors Influencing Hydraulic Conductivity of Soils in the Presence of Mixed-salt Solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1968, 32, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaraja, C.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Prasanna, M.; Thivya, C.; Thilagavathi, R.; Sarathidasan, J. Hydrochemistry of Groundwater in a Coastal Region and Its Repercussion on Quality, a Case Study—Thoothukudi District, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, M.N. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater in Moro Area, Kwara State, Nigeria. Environ. Geol. 1994, 24, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Mondal, G.; Kumar, S.; Singh, T.; Tewary, B.; Sinha, A. Major Ion Chemistry, Weathering Processes and Water Quality Assessment in Upper Catchment of Damodar River Basin, India. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneen, L. Notes on Water Quality in Agriculture Published as a Water Science and Engineering; Department of Water Sciences and Engineering, Paper 4001; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.D.-U.; Majumder, R.K.; Uddin, M.J.; Khalil, M.I.; Ferdous Alam, M. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in Patuakhali District, Southern Coastal Region of Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davraz, A.; Özdemir, A. Groundwater Quality Assessment and Its Suitability in Çeltikçi Plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1167–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.M.; Kumar, A.; Agrawal, N. Assessment of the Irrigation Water Quality of River Ganga in Haridwar District. Rasayan J. Chem. 2009, 2, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.; Ramkumar, K.; Chandrasekar, N.; Magesh, N.; Kaliraj, S. Groundwater Quality and Its Suitability for Drinking and Irrigational Use in the Southern Tiruchirappalli District, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, S.; Thirumurugan, M.; Elango, L. An Integrated Approach for Assessment of Groundwater Quality in and around Uranium Mineralized Zone, Gogi Region, Karnataka, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, V.; Brindha, K.; Sithole, B.; Lakshmanan, E. Spatial Interpolation Methods and Geostatistics for Mapping Groundwater Contamination in a Coastal Area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11601–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Sakizadeh, M. Comparison of Interpolation Methods for the Estimation of Groundwater Contamination in Andimeshk-Shush Plain, Southwest of Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Niazi, B.A.; Masoud, M.H. Evaluation of a Brackish Groundwater Resource in the Wadi Al-Lusub Basin, Western Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drought Feeding and Management of Sheep A Guide for Farmers and Land Managers, 2015th ed.; Victorian Government Department of Primary Industries: Melbourne, Australia, 1997.
- Scarlett, T.; Carberry, P. Drought Feeding of Goats. New South Wales Agricultrue: Sydney. Available online: http//www.agric.nsw.gov.au/reader/5337 (accessed on 22 February 2002).
- Maplecroft Climate Change and Environmental Risk. Available online: http://maplecroft.com (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Second Addendum. Vol. 1, Recommendations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; ISBN 92-4-154760-X. [Google Scholar]
- Ladeiro, B. Saline Agriculture in the 21st Century: Using Salt Contaminated Resources to Cope Food Requirements. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 310705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalling, J.W.; Davis, A.S.; Schutte, B.J.; Elizabeth Arnold, A. Seed Survival in Soil: Interacting Effects of Predation, Dormancy and the Soil Microbial Community. J. Ecol. 2011, 99, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiffer, C.H.; Ungar, I.A. Germination and Establishment of Halophytes on Brine-affected Soils. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 39, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.M.S.; Lacerda, C.F.; Neves, A.L.R.; de Sousa, C.H.C.; de Albuquerque Ribeiro, A.; Bezerra, M.A.; da Silva Araújo, I.C.; Gheyi, H.R. Ecophysiology of the Tall Coconut Growing under Different Coastal Areas of Northeastern Brazil. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.D.A.; Lacerda, C.F.; Rocha Neves, A.L.; Sousa, C.H.C.D.; Braz, R.D.S.; Oliveira, A.C.D.; Pereira, J.M.G.; Ferreira, J.F.D.S. Uses and Losses of Nitrogen by Maize and Cotton Plants under Salt Stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 67, 1119–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, P.R.M.; de Souza, E.R.; Santos, M.A.d.; Lins, C.M.T.; Monteiro, D.R.; Paulino, M.K.S.S.; Schaffer, B. Stomatal Regulation and Osmotic Adjustment in Sorghum in Response to Salinity. Agriculture 2022, 12, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, S.; Flowers, T.; Lane, P.; Doyle, R.; Haros, G.; Shabala, S. Halophyte Agriculture: Success Stories. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 107, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.R.D.; Dubeux, J.C.B.; Mello, A.C.L.D.; Silva, M.D.C.; Santos, M.V.F.D.; Santos, D.C.D. Forage Production and Mineral Composition of Cactus Intercropped with Legumes and Fertilized with Different Sources of Manure. Ciênc. Rural 2019, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Brito, G.S.M.; Santos, E.M.; de Araújo, G.G.L.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Zanine, A.D.M.; Perazzo, A.F.; Campos, F.S.; de Oliveira Lima, A.G.V.; Cavalcanti, H.S. Mixed Silages of Cactus Pear and Gliricidia: Chemical Composition, Fermentation Characteristics, Microbial Population and Aerobic Stability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, C.I.N.; de Lacerda, C.F.; Cajazeiras, C.C.d.A.; Neves, A.L.R.; Lopes, F.B.; Silva, A.O.d.; Sousa, H.C.; Gheyi, H.R.; Nogueira, R.d.S.; Lima, S.C.R.V.; et al. Potential of Brackish Groundwater for Different Biosaline Agriculture Systems in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region. Agriculture 2023, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Gonzalez Cruz, M.; Hernandez, E.A.; Uddameri, V. A GIS-Based Fit for the Purpose Assessment of Brackish Groundwater Formations as an Alternative to Freshwater Aquifers. Water 2020, 12, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Williams, S.; Webster, C. Biomarkers and Surrogate End Points for Fit-for-purpose Development and Regulatory Evaluation of New Drugs. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 81, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalf, L.; Benn, S. The Corporation Is Ailing Social Technology: Creating a ‘Fit for Purpose’ Design for Sustainability. J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 111, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlimann, A.; McKay, J.M. What Attributes of Recycled Water Make It Fit for Residential Purposes? The Mawson Lakes Experience. Desalination 2006, 187, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M. Fit for Purpose: Taking Integrated Water Resource Management Back to Basics. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2010, 24, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrysøe, C.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Borup, M. Identifying Fit-for-Purpose Lumped Surrogate Models for Large Urban Drainage Systems Using GLUE. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, M.; Trotz, M.; Vairavamoorthy, K. ‘Fit-for-Purpose’ Sustainability Index: A Simplified Approach for US Water Utility Sustainability Assessment. Water Pract. Technol. 2016, 11, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconet, D.; Callegari, A.; Hlavínek, P.; Capodaglio, A.G. Membrane Bioreactors for Sustainable, Fit-for-Purpose Greywater Treatment: A Critical Review. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hötzl, H. Water resources management in the Middle East under aspects of climatic changes. In Climatic Changes and Water Resources in the Middle East and North Africa; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).