Influence of High-Frequency, Low-Voltage Alternating Electric Fields on Biofilm Development Processes of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Flow Cells and Electric Field Exposure Devices
2.3. Experimental Conditions
2.3.1. Exposure of Alternating Electric Fields during Biofilm Development Processes
2.3.2. Exposure of Alternating Electric Fields during Cell Detachment
2.3.3. Combination of Alternating Electric Fields and Hydrodynamic Shear
2.4. Quantification of Adhered Cell Numbers and Extracellular Polymeric Substances
2.5. Quantification of Total Biofilm Biomass via Crystal Violet Assay
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
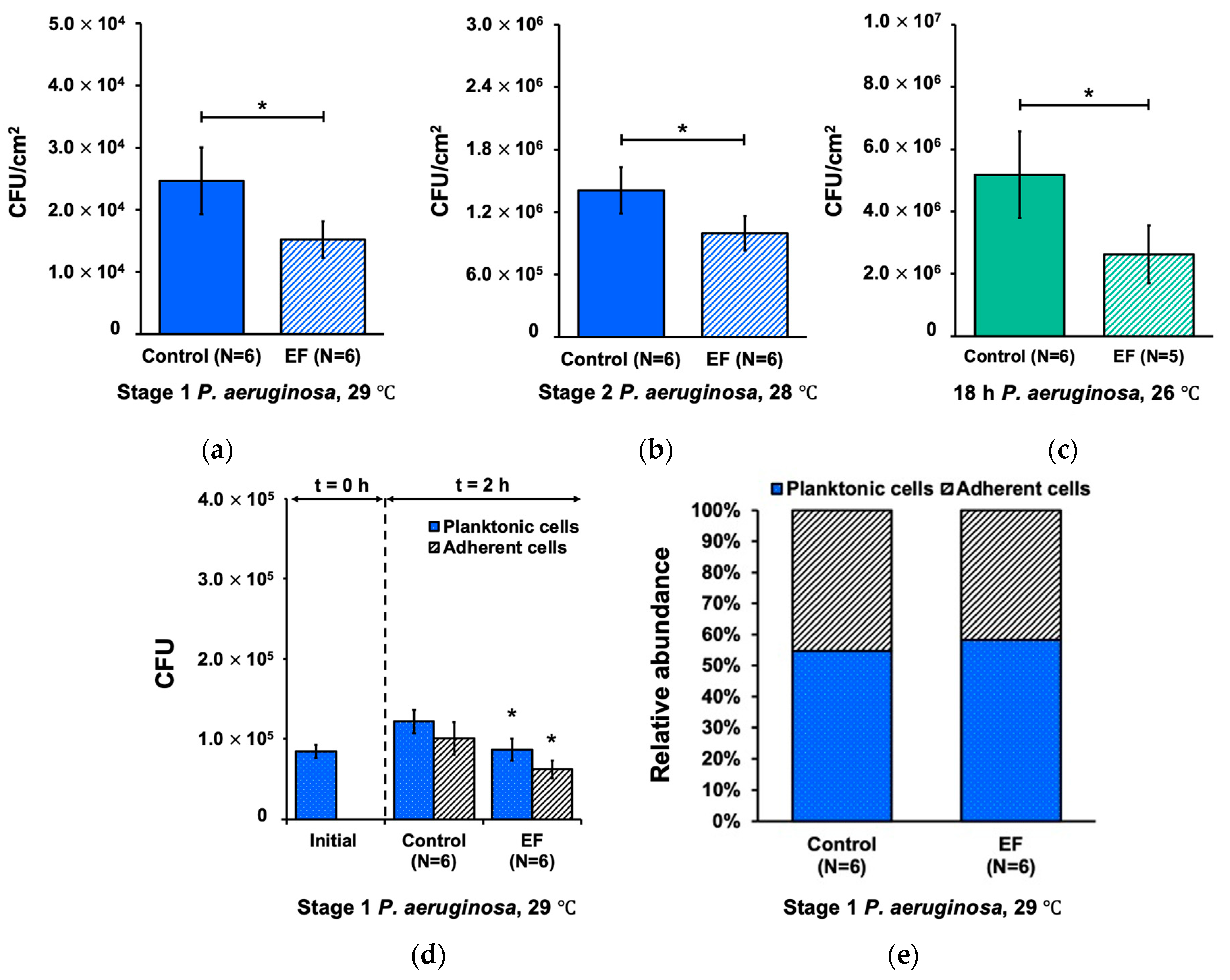
3.1. Effect of Alternating Electric Field on Biofilm Development Processes
3.2. Morphological Characteristics of the Adherent Cells
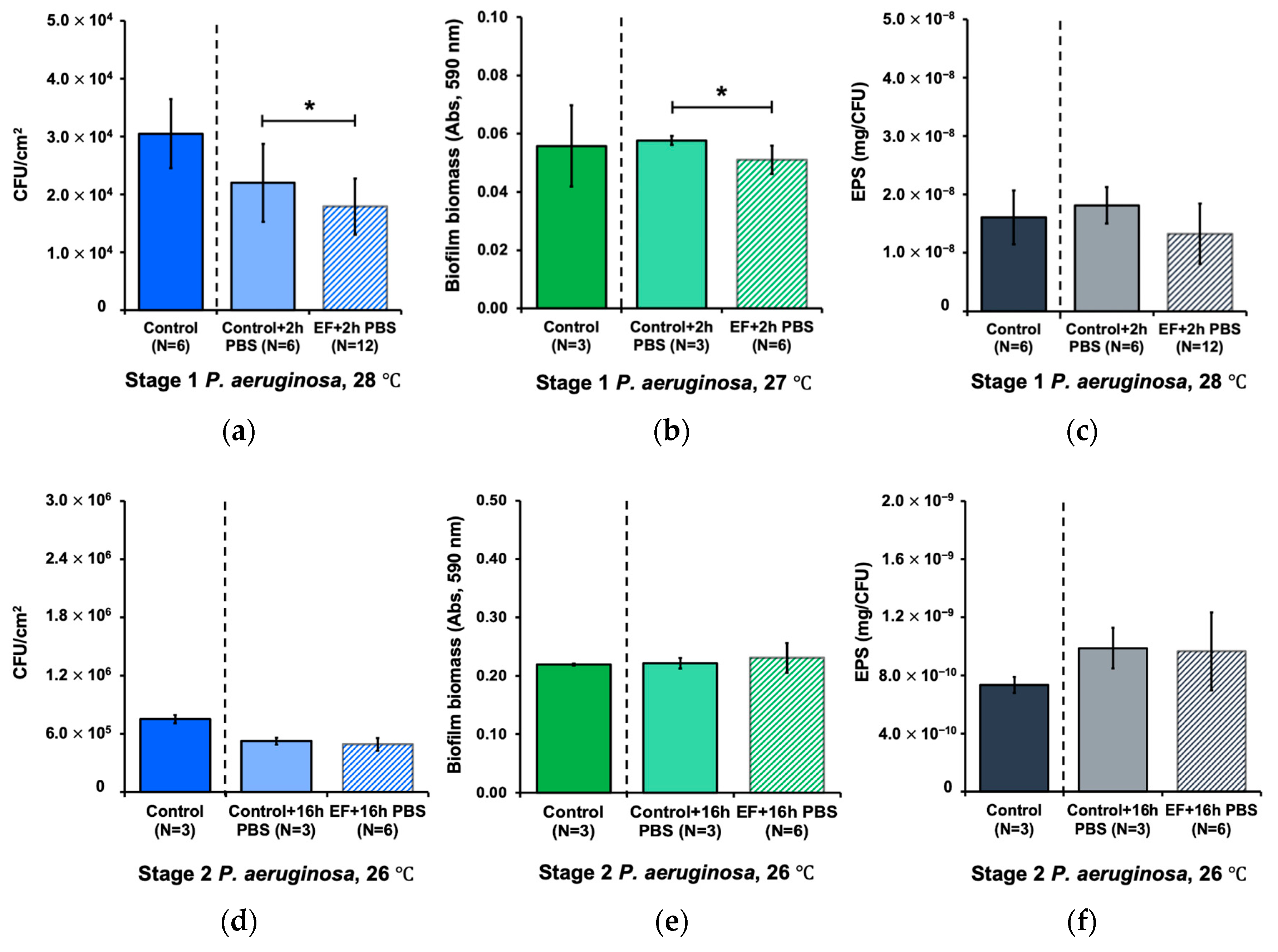
3.3. Effect of Alternating Electric Field on Biofilm Detachment
3.4. Combined Effect of Alternating Electric Field and Hydrodynamic Shear Forces
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butler, C.S.; Boltz, J. Biofilm Processes and Control in Water and Wastewater Treatment. In Comprehensive Water Quality and Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Tewari, S.; Dwivedi, J.; Sharma, V. Biofilm Mediated Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 1415–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, I.; Usman, T.M.; Varjani, S. Exploring the role of microbial biofilm for industrial effluents treatment. Bioengineered 2023, 13, 6420–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Kumar, K.; Gross, M.; Kunetz, T.; Wen, Z. Removal of total dissolved solids from wastewater using a revolving algal biofilm reactor. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitton, G. Drinking Water Distribution Systems: Biofilm Microbiology. In Microbiology of Drinking Water; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberg, M. Osmotic effects of biofouling in reverse osmosis (RO) processes: Physical and physiological measurements and mechanisms. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 15, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweity, A.; Oren, Y.; Ronen, Z.; Herzberg, M. The influence of antiscalants on biofouling of RO membranes in seawater desalination. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3389–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, J.; Fox, S.; Gilron, J. Interactions between biofilms and NF/RO flux and their implications for control—A review of recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 421–422, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Weigand, T.M.; Edalat, A. Reverse osmosis membrane biofouling: Causes, consequences and countermeasures. Npj Clean Water 2022, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Kiéné, L.; Lévi, Y. Chlorine demand of biofilms in water distribution systems. Water Res. 1999, 33, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; O’Connor, J.T.; Banerji, S.K. Biologically mediated corrosion and its effects on water quality in distribution systems. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1980, 72, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Griebe, T.; Schaule, G. Antifouling strategies in technical systems—A short review. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celmer, D.; Oleszkiewicz, J.; Cicek, N. Impact of ultrasound treatment and performance of a membrane biofilm reactor for tertiary hydrogen driven denitrification of municipal wastewater. In Proceedings of the Twentieth Jubilee-National, the Eighth Internatioanal and Technical Conference: Water Supply and Water Engineering, Warsaw, Poland, 15–18 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Shen, L. Advances in application of ultraviolet irradiation for biofilm control in water and wastewater infrastructure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Seyedi, S.; Wells, E.; McCarthy, D.; Crosbie, N.; Linden, K.G. Inactivation of biofilm-bound bacterial cells using irradiation across UVC wavelengths. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piasecka, A.; Bernstein, R.; Ollevier, F.; Meersman, F.; Souffreau, C.; Bilad, R.M.; Cottenie, K.; Vanysacker, L.; Denis, C.; Vankelecom, I. Study of biofilms on PVDF membranes after chemical cleaning by sodium hypochlorite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 141, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Wahman, D.G.; Bishop, P.L.; Pressman, J.G. Free Chlorine and Monochloramine Application to Nitrifying Biofilm: Comparison of Biofilm Penetration, Activity, and Viability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, K.M.; Gilg, M.R. Testing the relative effectiveness of traditional and non-traditional antifouling substrates on barnacle and macroalgae settlement. Mar. Biol. Res. 2014, 10, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.M.; Floerl, O.; Jones, L. Biosecurity risks associated with in-water and shore-based marine vessel hull cleaning operations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, L.D.; Weibel, D.B. Physicochemical regulation of biofilm formation. MRS Bull. 2011, 36, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. Antibacterial Activity of Electrospun Polymer Mats with Incorporated Narrow Diameter Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Giannelis, E.P.; Elimelech, M. Biocidal Activity of Plasma Modified Electrospun Polysulfone Mats Functionalized with Polyethyleneimine-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13159–13164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.T.; Babauta, J.T.; Beyenal, H. Electrochemical biofilm control: A review. Biofouling 2015, 31, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Ren, X.; Gao, M.; Jin, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, J.; She, Z. Enhanced aerobic granular sludge by static magnetic field to treat saline wastewater via simultaneous partial nitrification and denitrification (SPND) process. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 350, 126891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Kirchhoff, M.M. Origins, Current Status, and Future Challenges of Green Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Brown, M.R.; Elliott, T.S. Mechanisms of the bactericidal activity of low amperage electric current (DC). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 39, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Borden, A.; van der Mei, H.; Busscher, H. Electric block current induced detachment from surgical stainless steel and decreased viability of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6731–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Malan, S.M.; Karau, M.J.; Cede, J.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Brinkman, C.L.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Antibiofilm Activity of Low-Amperage Continuous and Intermittent Direct Electrical Current. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4610–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, A.; Jayaram, S.H. Effect of Electric Pulse Parameters on Releasing Metallic Particles From Stainless Steel Electrodes during PEF Processing of Milk. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataro, G.; Falcone, M.; Donsì, G.; Ferrari, G. Metal release from stainless steel electrodes of a PEF treatment chamber: Effects of electrical parameters and food composition. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 21, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzedakis, T.; Basseguy, R.; Comtat, M. Voltammetric and coulometric techniques to estimate the electrochemical reaction rate during ohmic sterilization. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1999, 29, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, J.; Roodenburg, B.; de Haan, S.W. Electrochemical reactions and electrode corrosion in pulsed electric field (PEF) treatment chambers. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2003, 4, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodaite-Riseviciene, R.; Saule, R.; Snitka, V.; Saulis, G. Release of Iron Ions From the Stainless Steel Anode Occurring during High-Voltage Pulses and Its Consequences for Cell Electroporation Technology. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Yu, C.; Xie, X. Locally enhanced electric field treatment (LEEFT) for water disinfection. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Lee, H.-M.; Chang, M.B. Inactivation of Aquatic Microorganisms by Low-Frequency AC Discharges. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2008, 36, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, G.; Cahen, G.; Sachyani, M.; Gileadi, E. The mechanism of low frequency a.c. electrochemical disinfection. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1982, 9, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosqueda-Melgar, J.; Raybaudi-Massilia, R.M.; Martín-Belloso, O. Influence of treatment time and pulse frequency on Salmonella Enteritidis, Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes populations inoculated in melon and watermelon juices treated by pulsed electric fields. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawioo, P.M.; Rweyemamu, A.; Garcia, H.A.; Hooijmans, C.M.; Brdjanovic, D. Evaluation of a microwave based reactor for the treatment of blackwater sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawki, M.M.; Gaballah, A. The effect of low AC electric field on bacterial cell death. Rom. J. Biophys. 2015, 25, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Ryu, S.; Kang, D.-H. Effect of Frequency and Waveform on Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium in Salsa by Ohmic Heating. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirson, E.D.; Gurvich, Z.; Schneiderman, R.; Dekel, E.; Itzhaki, A.; Wasserman, Y.; Schatzberger, R.; Palti, Y. Disruption of Cancer Cell Replication by Alternating Electric Fields. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3288–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaii, M.; Alfi, A.; Kasaeian, A.; Norozi, P.; Nasiri, M.; Sarokhalil, D.D.; Khoramrooz, S.S.; Fazli, M.; Davardoost, F. Antibacterial effect of alternating current against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeroginosa. Russ. Open Med. J. 2015, 4, e0203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Porat, Y.; Blatt, A.; Wasserman, Y.; Kirson, E.D.; Dekel, E.; Palti, Y. Microbial Growth Inhibition by Alternating Electric Fields. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3517–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunlasubpreedee, P.; Tobino, T.; Nakajima, F. Effects of high frequency-alternating electric fields on bacterial cell growth in planktonic and biofilm modes. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Symposium on Southeast Asian Water Environment, Bangkok, Thailand, 13–15 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Berbel, L.O.; Banczek, E.D.P.; Karousis, I.K.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Costa, I. Determinants of corrosion resistance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy dental implants in an In Vitro model of peri-implant inflammation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinzadeh, E.; Wei, C.; Farzadkia, M.; Rezaee, A. Effects of Low Frequency-Low Voltage Alternating Electric Current on Apoptosis Progression in Bioelectrical Reactor Biofilm. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdi, S.; Qamar, A.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Ghaffour, N. Biofilm removal efficacy using direct electric current in cross-flow ultrafiltration processes for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yin, X.; Li, J.; Carlos, C.; Du, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X. Effective anti-biofouling enabled by surface electric disturbance from water wave-driven nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirson, E.D.; Dbalý, V.; Tovaryš, F.; Vymazal, J.; Soustiel, J.F.; Itzhaki, A.; Mordechovich, D.; Steinberg-Shapira, S.; Gurvich, Z.; Schneiderman, R.; et al. Alternating electric fields arrest cell proliferation in animal tumor models and human brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10152–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poortinga, A.T.; Bos, R.; Busscher, H.J. Controlled electrophoretic deposition of bacteria to surfaces for the design of biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 67, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueshima, M.; Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, S.; Yamashita, K. Manipulation of bacterial adhesion and proliferation by surface charges of electrically polarized hydroxyapatite. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S. Antimicrobial Tolerance in Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 12, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoumelah, D.D.; Harnisch, F.; Kretzschmar, J. Benefits of Age–Improved Resistance of Mature Electroactive Biofilm Anodes in Anaerobic Digestion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8258–8266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Hieawy, A.; Shen, Y. Evaluation of extracellular polymeric substances matrix volume, surface roughness and bacterial adhesion property of oral biofilm. J. Dent. Sci. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Tay, F.R.; Niu, L.-N.; Chen, J.-H. Advancing antimicrobial strategies for managing oral biofilm infections. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.H.; Chan, K.-Y.; Xu, L.-C. Quantification of bacterial adhesion forces using atomic force microscopy (AFM). J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purevdorj, B.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Influence of Hydrodynamics and Cell Signaling on the Structure and Behavior of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4457–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Kaplan, L.A.; Newbold, J.D.; Cheng, X.; Hansen, C. Effects of Current Velocity on the Nascent Architecture of Stream Microbial Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5443–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.; Ochoa, J.C.; Pechaud, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liné, A. Effect of shear stress and growth conditions on detachment and physical properties of biofilms. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5499–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.; Simões, M.; Melo, L.; Mergulhão, F. The combined effects of shear stress and mass transfer on the balance between biofilm and suspended cell dynamics. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3348–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenkinsopp, S.A.; Khoury, A.E.; Costerton, J.W. Electrical enhancement of biocide efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3770–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Ellis, B.; Lam, K.; Johnson, F.; Khoury, A.E. Mechanism of electrical enhancement of efficacy of antibiotics in killing biofilm bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovitch, C.; Stewart, P.S. Removal and Inactivation of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms by Electrolysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6364–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Borden, A.J.; van der Werf, H.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Electric Current-Induced Detachment of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms from Surgical Stainless Steel. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6871–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareilleux, A.; Sicard, N. Lethal Effects of Electric Current on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 19, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelin, J.; Kavitha, M. Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karygianni, L.; Ren, Z.; Koo, H.; Thurnheer, T. Biofilm Matrixome: Extracellular Components in Structured Microbial Communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.-S. Causes and control of filamentous growth in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Guo, T.; Feng, H.; Yan, A.; Ni, Y.; Li, J. Filamentous Bacteria and Stalked Ciliates for the Stable Structure of Aerobic Granular Sludge Treating Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
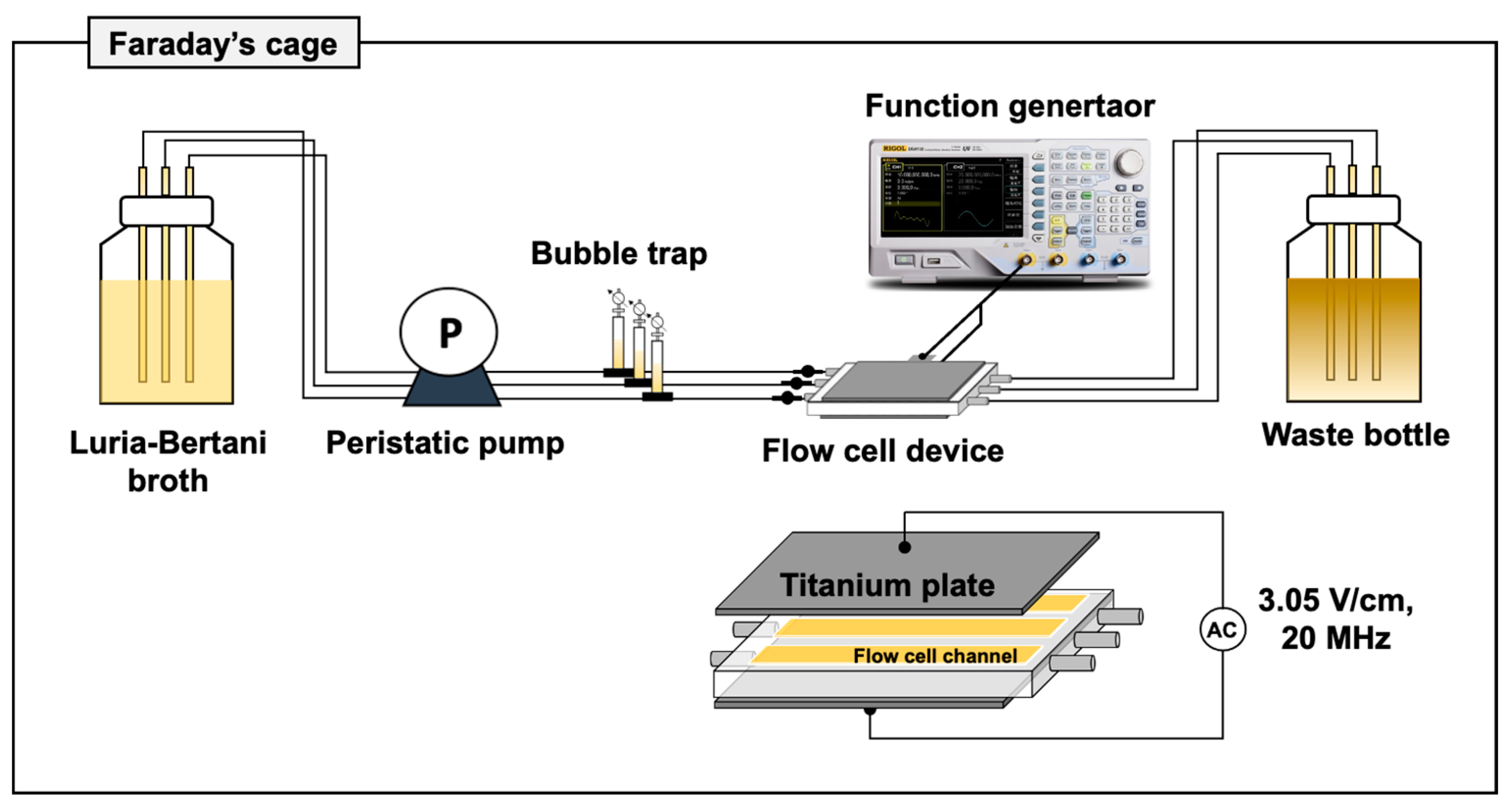



| Flow Rate (mL/min) | Velocity (mm/s) | Reynolds Number | Shear Rate (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.08 | 0.33 | 0.60 | 0.002 |
| 0.2 | 0.83 | 1.5 | 0.004 |
| 0.4 | 1.7 | 3.0 | 0.009 |
| 0.6 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 0.013 |
| Condition | Mean Cell Length (µm) | Volume Per Cell (µm3) | Total Adherent Cells (Cells/Channel) | Total Volume (µm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control cells | 1.47 | 1.15 | 106 | 106 |
| Treated cells | 2.39 | 1.88 | 106 | 106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunlasubpreedee, P.; Tobino, T.; Nakajima, F. Influence of High-Frequency, Low-Voltage Alternating Electric Fields on Biofilm Development Processes of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water 2023, 15, 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173055
Kunlasubpreedee P, Tobino T, Nakajima F. Influence of High-Frequency, Low-Voltage Alternating Electric Fields on Biofilm Development Processes of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water. 2023; 15(17):3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173055
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunlasubpreedee, Patthranit, Tomohiro Tobino, and Fumiyuki Nakajima. 2023. "Influence of High-Frequency, Low-Voltage Alternating Electric Fields on Biofilm Development Processes of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Water 15, no. 17: 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173055
APA StyleKunlasubpreedee, P., Tobino, T., & Nakajima, F. (2023). Influence of High-Frequency, Low-Voltage Alternating Electric Fields on Biofilm Development Processes of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water, 15(17), 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173055








