Abstract
The main aim of this research was to determine the physiological response of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (V. natans) to black water with a foul odor. V. natans was chosen as the experimental plant species to investigate the morphological response and ecophysiological adaptation methods in response to varying light depths and black-odorous water. V. natans was planted in tap water (D), two types of black-odorous water (E and F), and under three distinct light conditions (low light, medium light, and high light). In the high-light condition with black-odorous water (E), the biomass content of V. natans declined from 1.78 g on the 14th day to 1.49 g on the 28th day, demonstrating that the black-odorous water inhibited the growth of V. natans. Under the stress of black-odorous water, the chlorophyll content of V. natans increased greatly in the early period but reduced during the latter experimental period. However, on the 21st day, maximum chlorophyll content of 1.30 mg/g (E) and 1.18 mg/g (F) was observed. In addition, the malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) activity was monitored and reported under black-odorous water stress in V. natans. The experimental results of this work demonstrated conclusively that odorous black water exerts a certain stress on the physiological development of V. natans. Future research should incorporate the evaluation of several plant species and vary the process and environmental conditions to produce field-relevant, dependable results.
1. Introduction
With the rapid rise of China’s economy, a substantial amount of domestic sewage, agricultural wastewater, and industrial effluent are released into natural water bodies, resulting in the deterioration of the water environment/aquatic ecosystem, thereby causing significant water-related environmental issues [1,2,3,4]. However, in heavily polluted water, such as municipal/domestic sewage, aquaculture wastewater, and agricultural effluent, the concentrations of some pollutants exceed the self-purification capacity of the water body and the decomposition of organic pollutants will consume a large amount of dissolved oxygen (DO) from the water body [5,6]. These conditions promote and stimulate the emergence of algal blooms, which eventually produce odor-causing chemicals such as methylmercury. Therefore, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China suggested remediating black-odorous water in rural areas and eliminating vast areas of black-odorous water by the year 2025 [7,8].
Submerged plants are the most important primary producers in shallow lakes and play a significant role in maintaining the structure and function of shallow lake ecosystems, as well as in the remediation and purification of polluted water bodies [9,10,11,12,13]. Stressed by environmental contamination, the physiological growth of submerged plants undergoes certain modifications. According to previous studies, the biomass and plant height of submerged plants vary in response to low light or excessive nutritional stress [14,15,16]. In addition, the chlorophyll content/concentration and antioxidant enzyme activity of submerged plants can more precisely indicate the stress-induced state of the plants, The chlorophyll content of V. natans was different under different environmental conditions. For example, the chlorophyll content of V. natans under 8 mL/L ammonia nitrogen stress was lower than that under 4 mL/L ammonia nitrogen stress [17]. In another work, the chlorophyll content of Coontail increased from 1 mg/L to 15 mg/L as the Zn content increased, and the antioxidant enzyme activity indirectly reflected the reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative stress in plants [18,19].
V. natans is a submerged herb belonging to the family Hydrocharitaceae with unisexual flowers and dioecious plants. V. natans possesses typical submerged plant traits, including well-developed aeration tissues, longer pedicels with flowers kept above water, and spreading proliferation of grape stems, which are compatible with any aquatic environment. The unusual physiological structure of V. natans makes it an ideal species for water purification and aquatic ecological restoration [9,20]. In a recent study that compared the tolerance of five submerged plants to various ammonia nitrogen concentrations, it was observed that V. natans could survive at concentrations as high as 16 mg/L (NH4+-N) [21]. Jiaojiao et al. [22] demonstrated that V. natans exhibited growth-related inhibition but not extinction under the combined stress of less than 30% light intensity and a DO concentration of less than 5.5 mg/L. Zhang et al. [23] reported that V. natans decreased the C, N, and P concentrations in black-odorous water sediments by 0.28, 0.08, and 0.83 g/kg, respectively, compared to the control group. Although several research studies focus on the water purification efficiency of submerged plants in black-odorous water [21,24], there are no studies that have reported their physiological growth response. The primary purpose of this study was to examine the physiological and biochemical properties and responsiveness of V. natans under various light conditions for the treatment of black-odorous water and demonstrate its efficacy for the restoration/purification of black-odorous water.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
Experiments were carried out at Hunan Agricultural University’s YunYuan Base in Hunan Province, China. The test vats were placed in an open, well-ventilated experimental shed that received sufficient sunlight. The testing period lasted from November to December of 2021, and the test plants were acquired from a field garden located in Hunan Province, China. The soil was gathered from the base of Hunan Agricultural University’s Cultivation Garden, whereas the black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F) were collected from Jingang Town, Wangcheng District, Changsha City, Hunan Province (Figure 1). Before the start of the experiment, healthy V. natans were selected, intercepted to a leaf length of 14.5 (±0.5) cm, root length of 3.0 (±0.5) cm, and the number of leaves was 10 in each plant. One plant was placed in each plastic cup and they were pre-cultured for 15 days (Figure 2).

Figure 1.
Photographic images of (A) black-odorous water (E), and (B) black-odorous water (F).

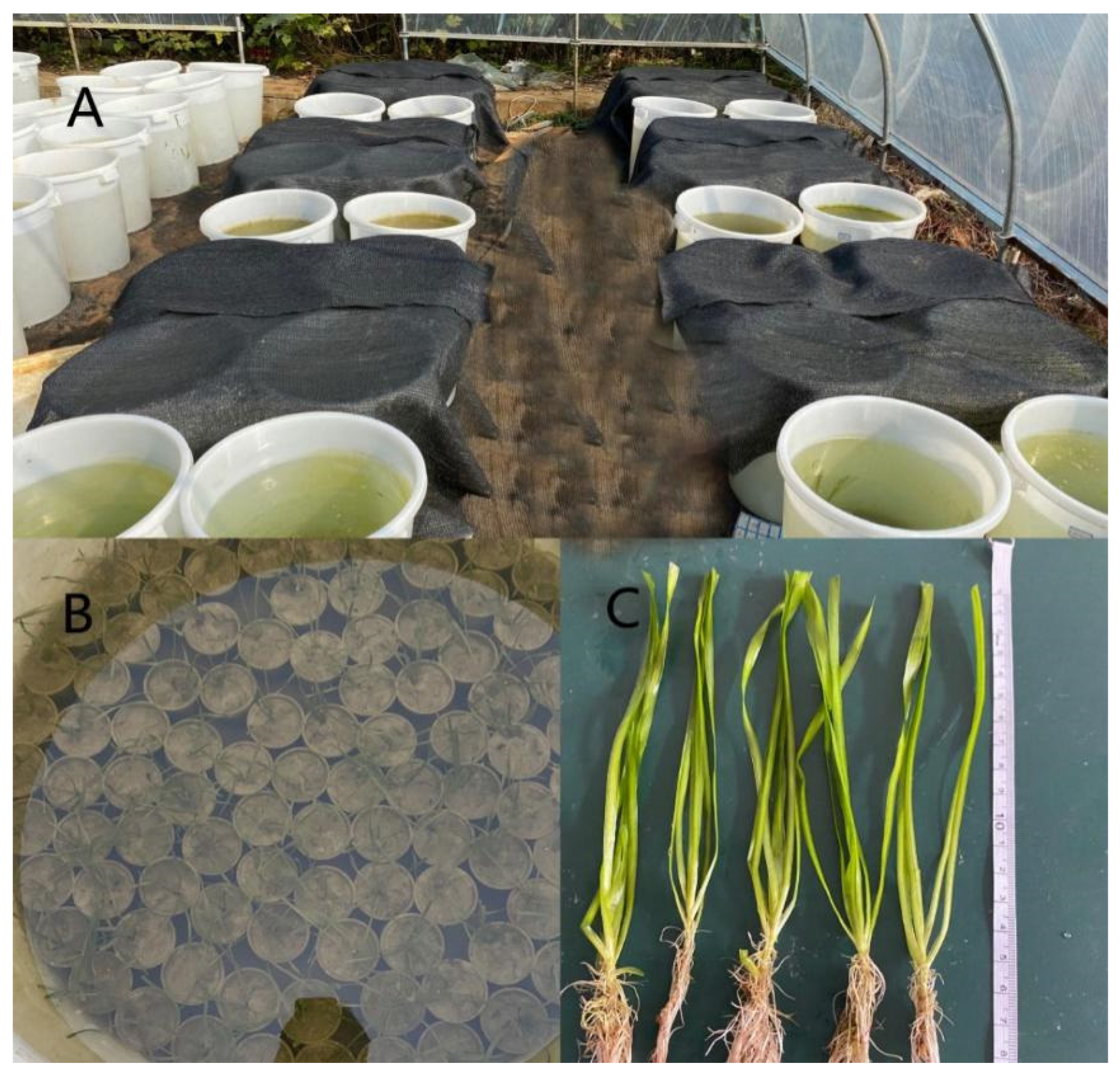
Figure 2.
Photographic images of (A) the test site, (B) the pre-cultivation of plants, and (C) before the pre-cultivation of V. natans.
2.2. Experimental Design
In the experiment, three light intensities were established: bright light (no shade treatment (A)), medium light (one layer of shade net treatment (B)), and low light (double-shade net treatment (C)). Three distinct water environments were prepared: tap water (D), black-odorous water (E), and black-odorous water (F). Each condition was assigned four sets of replicates, resulting in a total of 36 experimental units. Eight cups were planted in each of the 40 L polyethylene buckets in which the pretreated V. natans was planted. During the 28-day experimental period (temperature ~20 °C), samples were collected and the different parameters were measured on days 1, 4, 7, 14, and 28, respectively, and a cup of V. natans was taken each time. Before beginning the experiment, the light intensity was measured as follows: 100% natural light, 56% natural light, and 15% natural light for the high-light group (no shade treatment (A)), the medium-light group (one layer of shade net treatment (B)), and the low-light group (double-shade net treatment (C)), respectively.
The following water-quality parameters were measured: (a) tap water (D) with NH4+-N 0.262 mg/L, dissolved oxygen (DO) 9.6 mg/L, redox potential 226 mV; (b) black-odorous water (E) with NH4+-N 5.098 mg/L, DO 3.6 mg/L, transparency 13.6 cm, redox potential −161 mV, total phosphorus 0.2016 mg/L; and (c) black-odorous water (F) with NH4+-N 4.329 mg/L, DO 2.4 mg/L, transparency 14.7 cm, redox potential −153 mV, total phosphorus 0.1785 mg/L. The sediment characteristics were as follows: pH 6.63, organic matter 19.26 mg/g, and total nitrogen (TN) 1.93 mg/g.
2.3. Analytical Techniques
After sampling, the samples were rinsed three times, weighed using a precision balance, and the biomass, height, root length, number of branches, number of leaves, and weight of the underground sections were recorded. After collection, 0.2 g of fresh sample was taken for determining the chlorophyll content and the remainder of V. natans was frozen at −80 °C and stored in the refrigerator. The chlorophyll concentration was measured using the ethanol technique [25].
All biochemical assays were conducted at 4 °C. Approximately 0.5 g of fresh plants were homogenized in liquid nitrogen using a cooled mortar and pestle before being extracted with 5 mL of 20 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing 0.5 mM EDTA and 0.15 M NaCl. The crude extract was centrifuged at 15,000× g and 4 °C for 5 min and the supernatant was used to measure the antioxidant enzyme activity. MDA was measured using the thiobarbituric acid method [26], SOD was measured using the nitrogen blue tetrazolium photochemical reduction method [27], POD was measured using the guaiacol method [28], and CAT was measured using the sodium thiosulfate titration method [29].
Before beginning the experiment, 200 mL of each type of experimental water and 200 g of experimental soil were collected for analysis. NH4+-N, DO, transparency, redox potential, and total phosphorus concentration were measured in different water environments using the phenol method [30], using a portable dissolved oxygen meter (model: JPB-607A, Qingdao Jinghong Environmental Protection Technology Co., Qingdao, China), Sechs disc method, portable redox potential meter (model: CT-8010, Shenzhen Ke Didi Electronic Co., Shenzhen, China), and the ammonium molybdate method, respectively. The soil organic matter and total nitrogen were determined using the potassium dichromate external heating method [31] and Kjeldahl’s nitrogen method [32], respectively. An illuminance meter was used to measure the light intensity.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Microsoft Excel 2016 was utilized for storing the experimental data, whereas SPSS statistics 22 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used to perform descriptive statistical analysis. The graphs were plotted using the Origin 2021 software (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Index
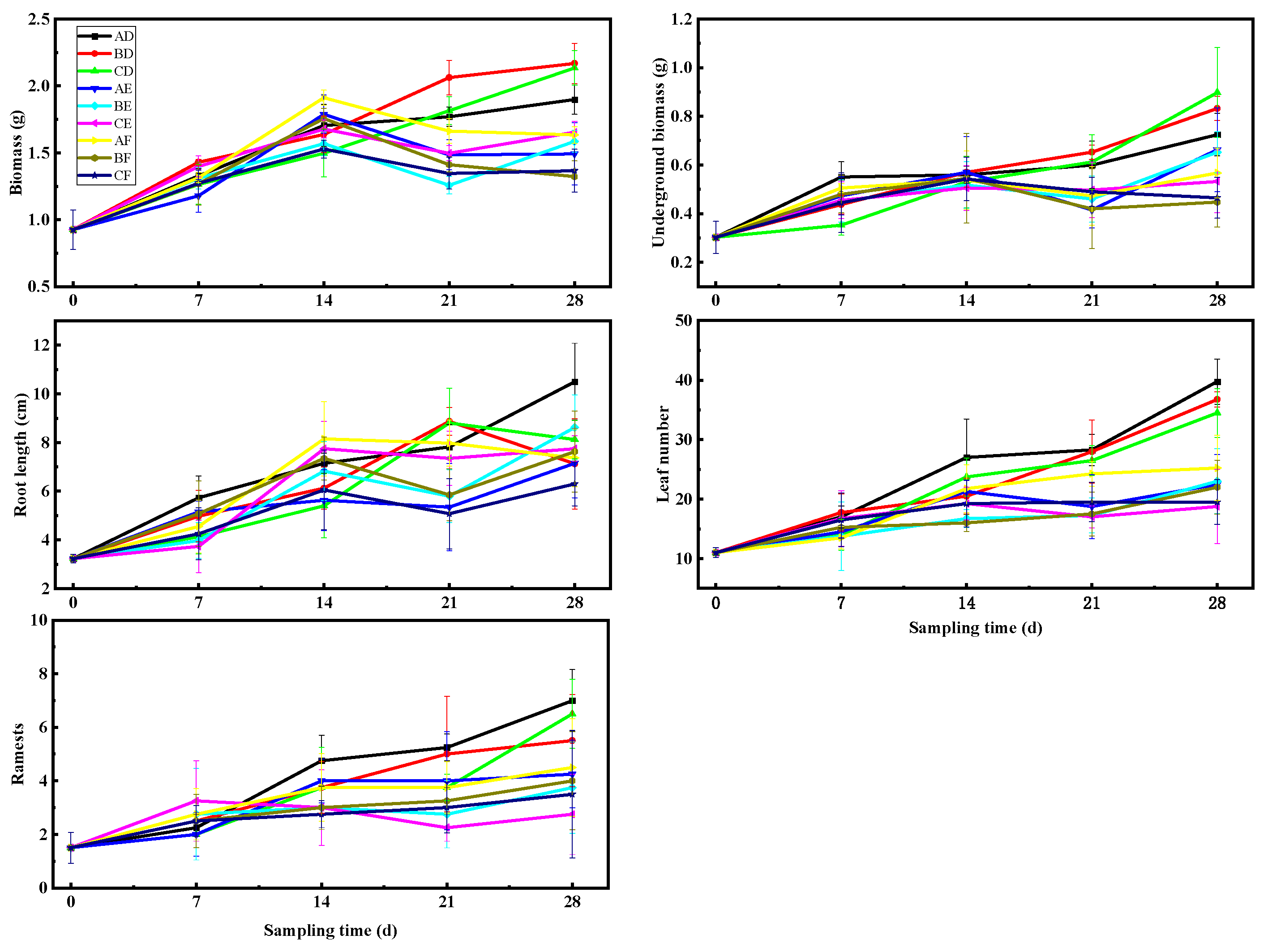
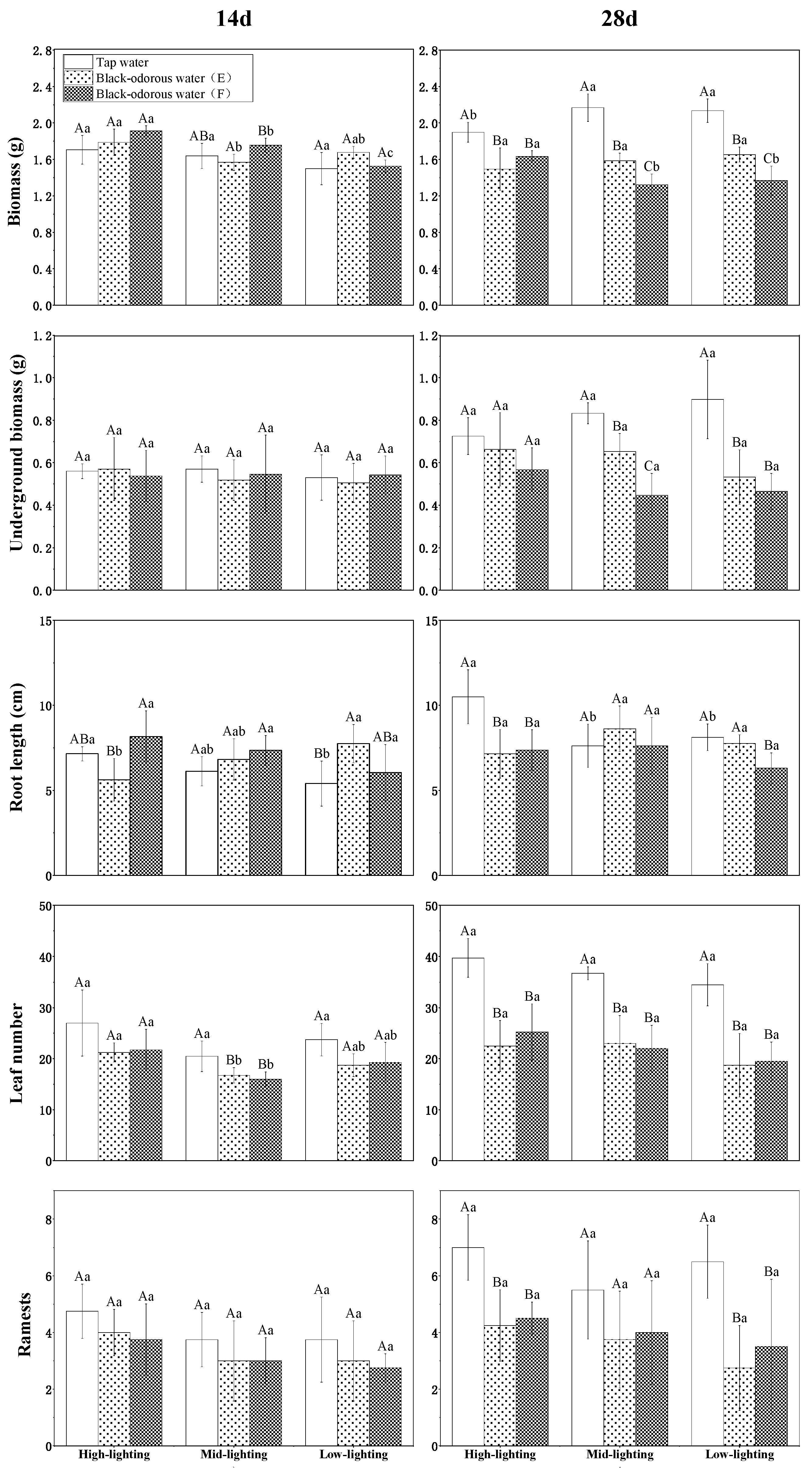
The biomass of V. natans was significantly impacted by the interactions between the varied water quality and variable water quality and light (p ≤ 0.05; Table 1). The biomass of V. natans under high-light conditions was marginally greater than that of the medium- and low-light groups in both black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F); however, the biomass appeared to increase and then decrease in both the black-odorous water environments (Figure 3). For example, under the high-light condition of black-odorous water (E), it decreased from 1.784 ± 0.144 g on the 14th day to 1.492 ± 0.233 g on the 28th day. On day 14, the biomass of V. natans did not substantially differ, irrespective of the different water environments, but from the 28th day’s results, the biomass of V. natans in tap water (D) was significantly higher than that in black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F) (Figure 4).

Table 1.
The results of multivariate bivariate ANOVA of biomass tiller number, root length, weight of the underground parts, and total leaf number of V. natans with different water qualities and light conditions on the 28th day of the experiment.
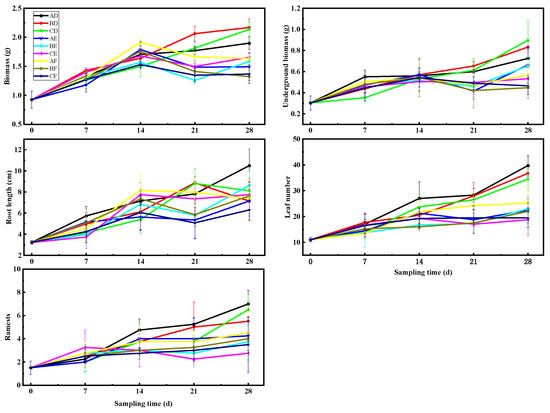
Figure 3.
The morphological changes of V. natans at different sampling times: bright light (A), medium light (B), low light (C), laboratory tap water (D), black-odorous water (E), and black-odorous water (F).
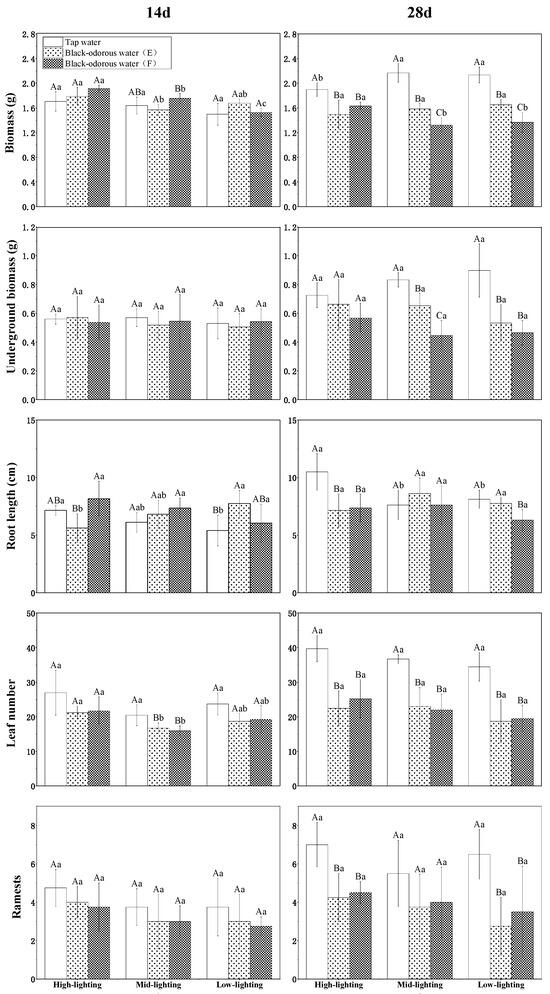
Figure 4.
The morphological index values of V. natans on the 14th and 28th days of the experiment under different light intensities and water environments. The uppercase letters represent the differences between the water quality and the lowercase letters represent the differences between the lighting conditions.
The different water quality had a substantial impact on the subterranean biomass of V. natans (p ≤ 0.05; Table 1). The underground biomass of V. natans in tap water (D) steadily grew over time, whereas the subterranean biomass measured 0.897 ± 0.184 g under low-light-intensity conditions. However, the subsurface biomass in the black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F) showed an increase, followed by a declining phase over time (Figure 3).
The root length of V. natans was significantly impacted by the interaction of the varied water quality and varying water quality with light (p ≤ 0.05; Table 1). V. natans’ root length was longer under higher light-intensity conditions in tap water (D) (Figure 3). The root length of V. natans in black-odorous water (E) under high light was significantly shorter than that under the treatment with tap water (D) and black-odorous water (F) (day 14). However, on day 28, the root length of V. natans in tap water (D) under high light was significantly different from that under medium- and low-light conditions (Figure 4).
Different light and water quality had a significant impact on the number of leaves in V. natans (p ≤ 0.05; Table 1). Although the quantity of V. natans leaves in tap water (D) grew over time and with increased light intensity, the quantity of V. natans leaves in the black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F) increased steadily over time (Figure 3). The number of V. natans leaves in the tap-water (D) treatment was substantially higher on the 14th day than on the 28th day in the medium-light samples of the black-odorous water (E) and the black-odorous water (F) (Figure 4).
The ramets of V. natans were significantly affected by the varying water quality (p ≤ 0.05; Table 1). Under different water environments, the ramets of V. natans gradually became higher with increasing light intensity (Figure 3). There was no discernible difference between the ramets of V. natans in the different water qualities based on the results from the 14th day. However, on the 28th day, the ramets of V. natans in tap water (D) were significantly higher in the high-light treatment than in the low-light treatment in the black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F) (Figure 4).
There was a significant effect of the different water qualities on the ramets of V. natans (p ≤ 0.05; Table 1). The ramets of V. natans became progressively higher with increasing light intensity in the different water qualities (Figure 3). In the results on the 14th day, there was no significant difference in the ramets of V. natans in the different water qualities, but in the results on the 28th day, the ramets of V. natans in tap water (D) were significantly higher in high-light versus low-light treatment than in black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F) (Figure 4).
3.2. Photosynthetic Index
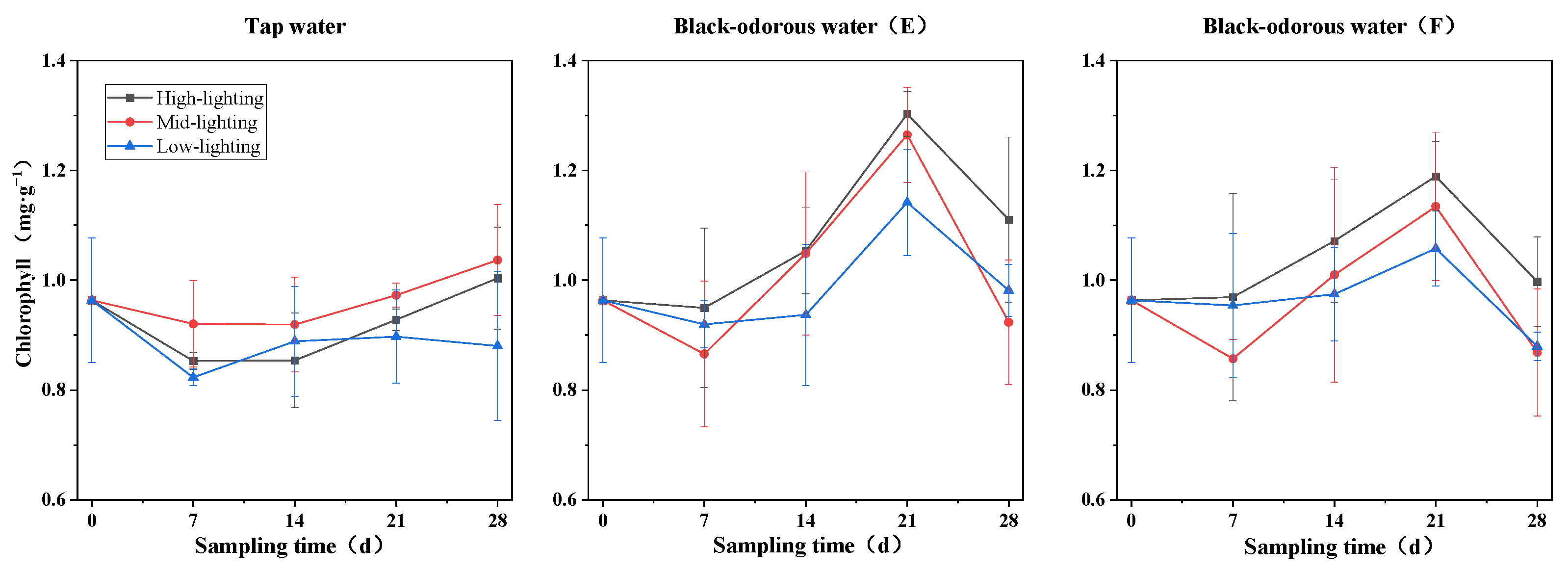
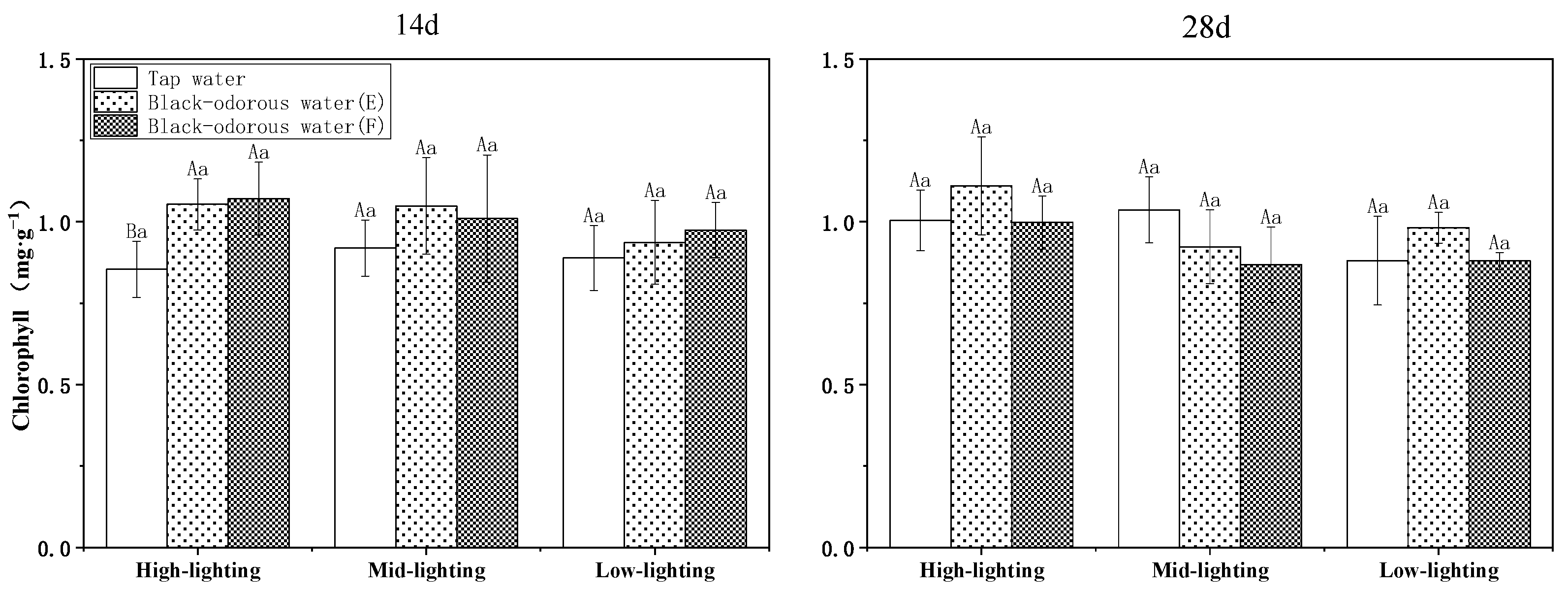
On the 14th and 28th days of the experiment, the different water environments and light conditions significantly affected the amount of chlorophyll in V. natans (p ≤ 0.05; Table 2). In tap water (D), the chlorophyll content under medium-light conditions was higher than the chlorophyll content under high-light conditions and lower than the chlorophyll content under low-light conditions. In black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F), the chlorophyll content peaked on the 21st day at 1.303 ± 0.041 mg/g and 1.189 ± 0.063 mg/g, respectively (Figure 5). In comparison to black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (F), tap water (D) had no discernible impact on the chlorophyll content of V. natans on the 14th and 28th days of experimentation (Figure 6).

Table 2.
The results of multivariate two-way analysis of variance between the total chlorophyll content of V. natans and different water qualities and light conditions on the 14th and 28th days of the experiment.
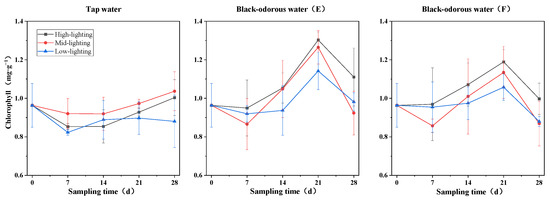
Figure 5.
Changes in the chlorophyll content of V. natans at different sampling times.
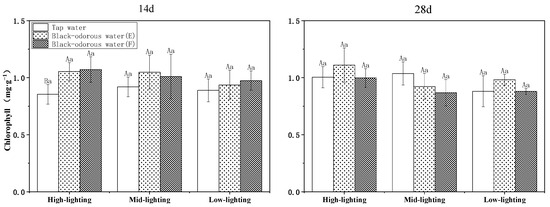
Figure 6.
Chlorophyll content of V. natans under different light and water-quality conditions on the 14th and 28th days of experiments.
3.3. MDA and Antioxidant System Indexes
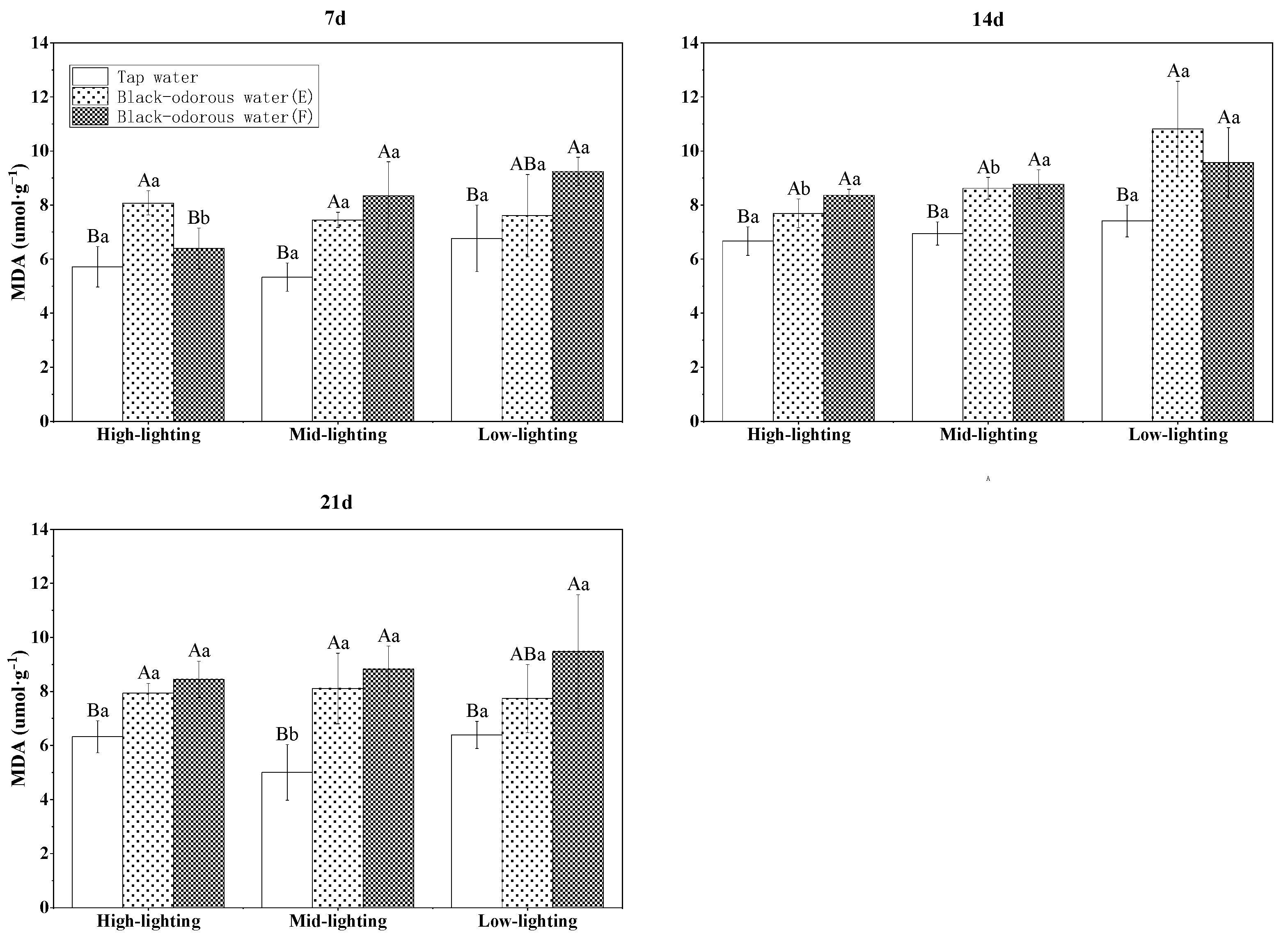
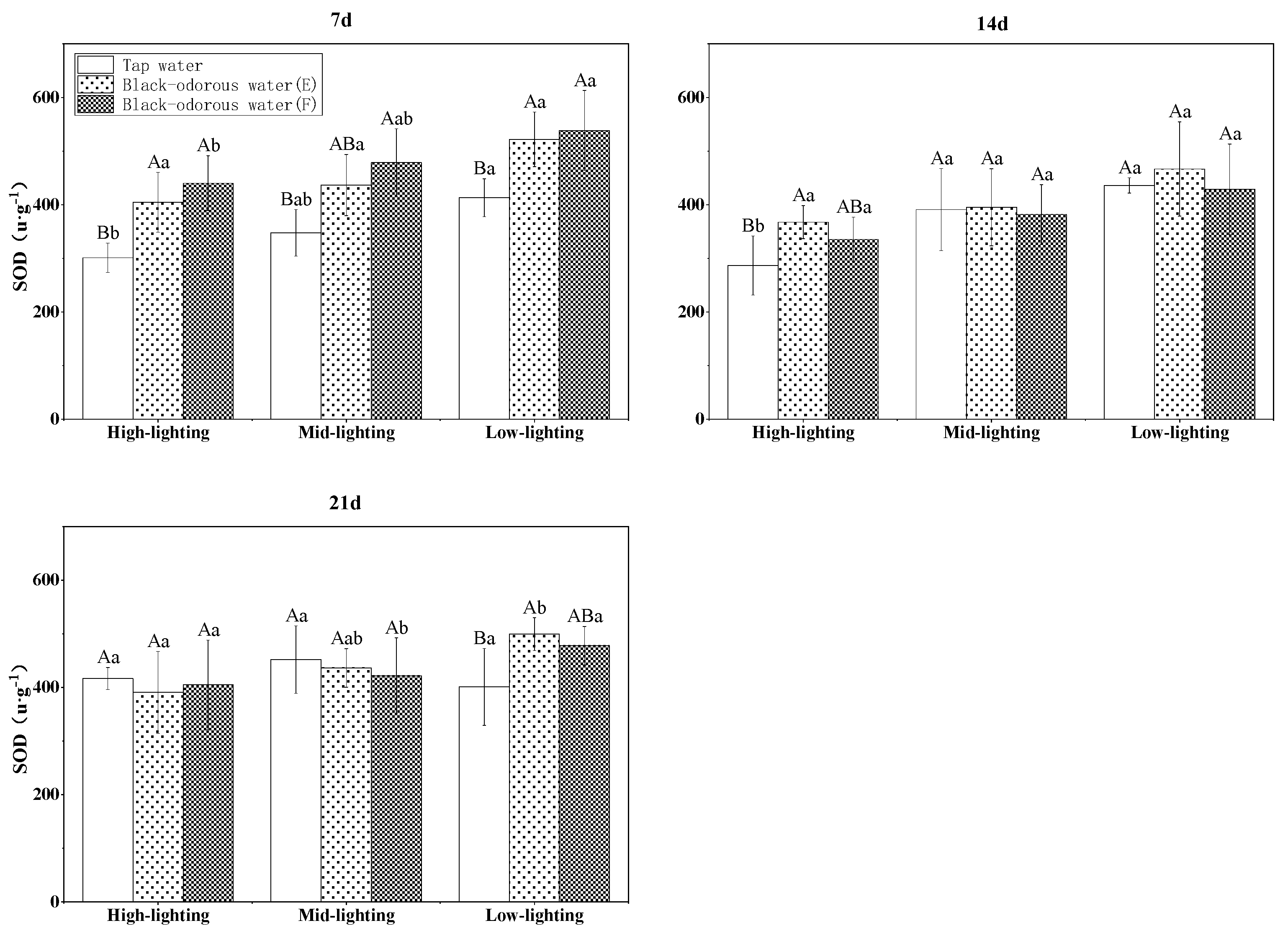
The malondialdehyde (MDA) content of V. natans was significantly affected by changes in the light, water quality/environment, time, and their interactions (p ≤ 0.05; Table 3). On days 7, 14, and 21, the tap water (D)’s MDA level of V. natans was considerably lower than that of the two black-odorous water samples (p ≤ 0.05; Figure 7). In addition, it was also observed that light had no discernible influence on the MDA content of V. natans (Figure 7). The superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme activity of the black-odorous water was significantly affected (p ≤ 0.05; Table 3) under the different light conditions, water quality, time, and interaction of water quality and time. On the 7th day, there was a significant difference between the SOD content of V. natans in tap water (D) and black-odorous water (E) and black-odorous water (B) depending on the light intensity (F). However, as time progressed, the SOD activity of V. natans decreased in comparison to the 7th day and did not significantly differ from that of tap water (D) (Figure 8).

Table 3.
Multivariate ternary ANOVA results of different antioxidant enzyme activity values (MDA, SOD, CAT, and POD) under the influence of different water environments, light conditions, and time.
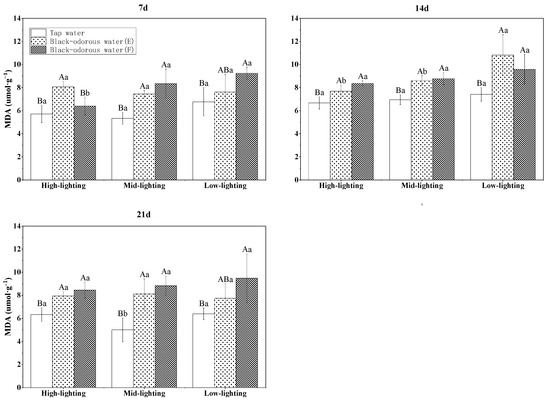
Figure 7.
MDA content of V. natans on the 7th, 14th, and 21st days of experiments.
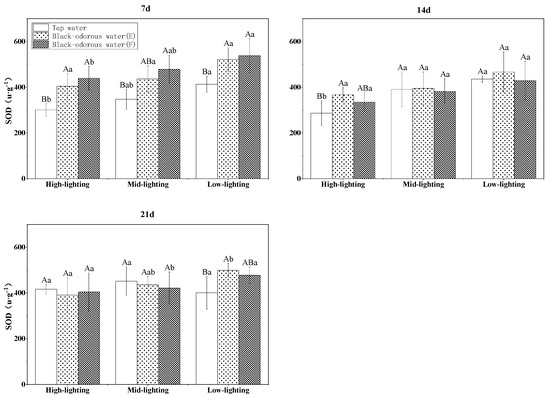
Figure 8.
SOD enzyme activity of V. natans on the 7th, 14th, and 21st days of experiments.
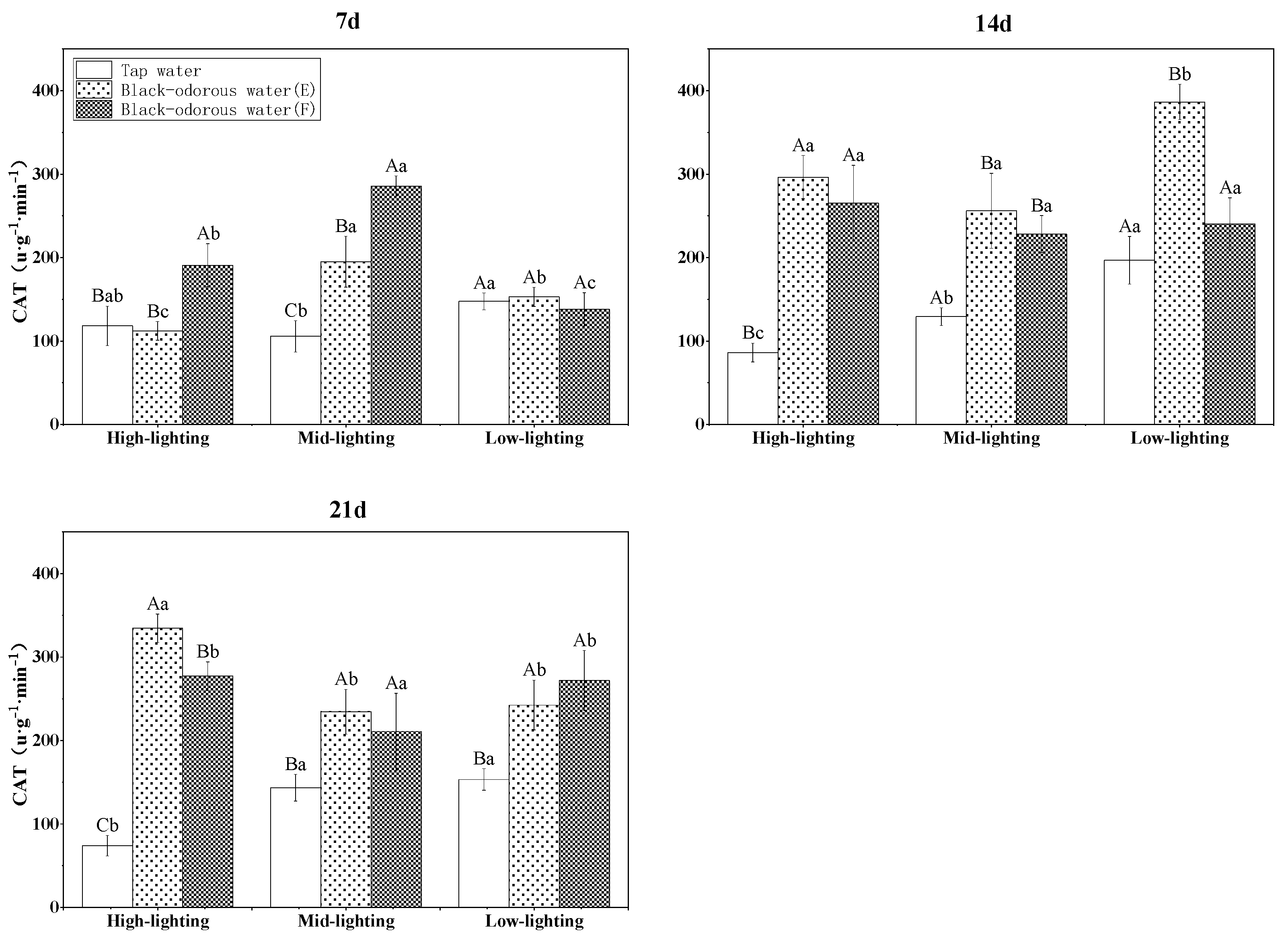
On the other hand, the different light conditions, time, water quality, and their interactions significantly (p ≤ 0.05; Table 3) altered the catalase (CAT) enzyme activity of V. natans. On the 7th day of the experiment, V. natans in tap water (D) under medium-light conditions displayed considerably lower CAT enzyme activity than the two black-odorous water samples. On the 14th and 21st days of the experiments, the CAT enzyme activity levels of V. natans in tap water (D) were significantly lower than those in the two black-odorous water samples. However, under the other two light conditions, the CAT enzyme activity of V. natans in different water environments was essentially the same (Figure 9).
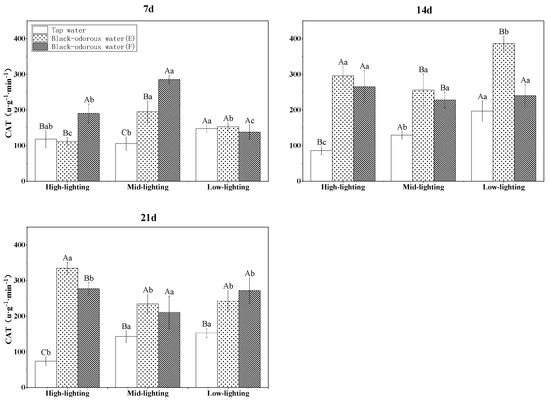
Figure 9.
CAT enzyme activity of V. natans on the 7th, 14th, and 21st days of experiments.
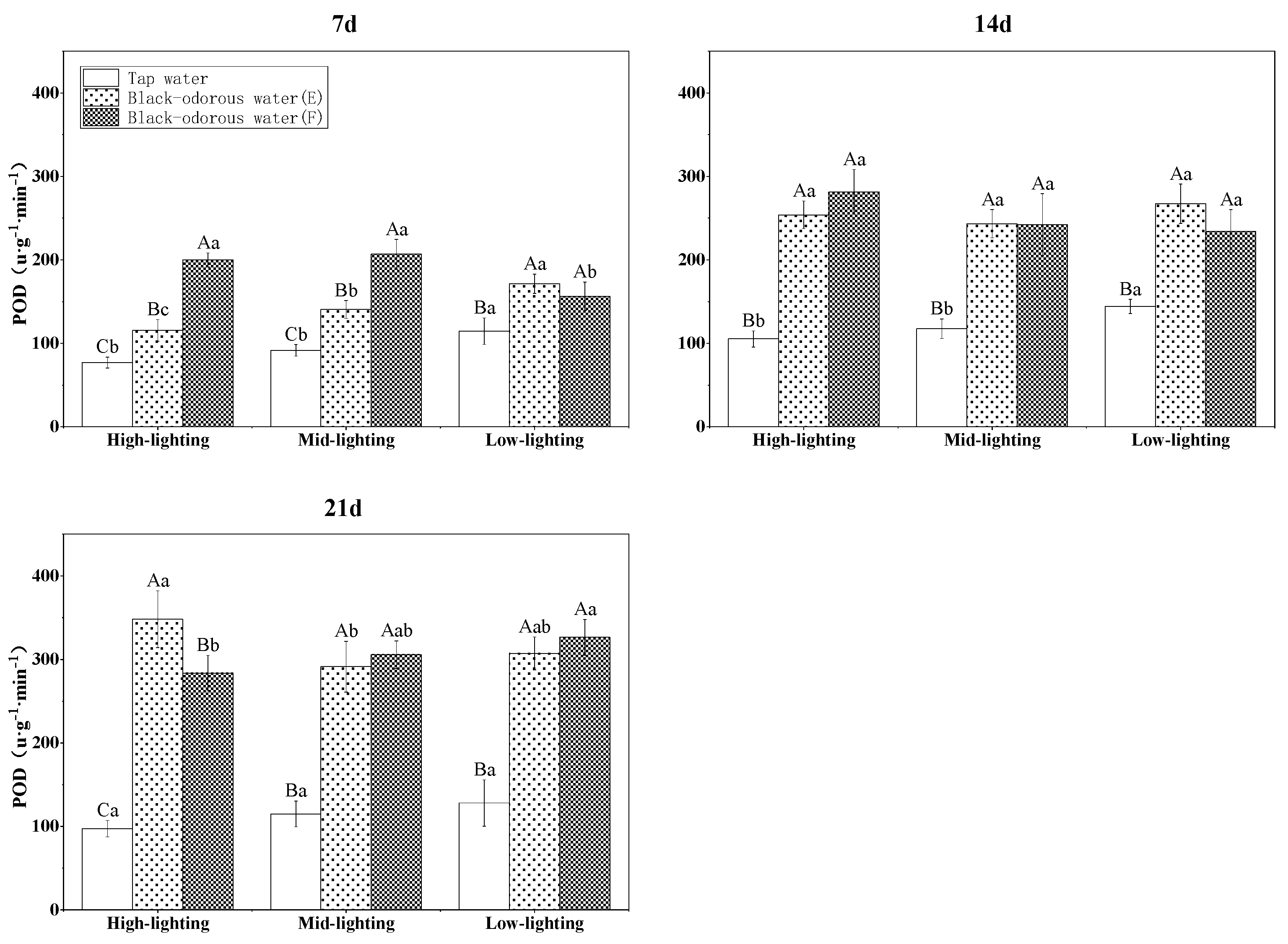
The peroxidase (POD) of V. natans was significantly affected by the interactions of (a) water quality, time, and light; (b) water quality and time; and (c) water quality and light (p ≤ 0.05; Table 3). Although the POD enzyme activity increased with the experimental time, the POD enzyme activity in tap water (D) was significantly lower on days 7, 14, and 24 than that observed in the two black-odorous waters (Figure 10).
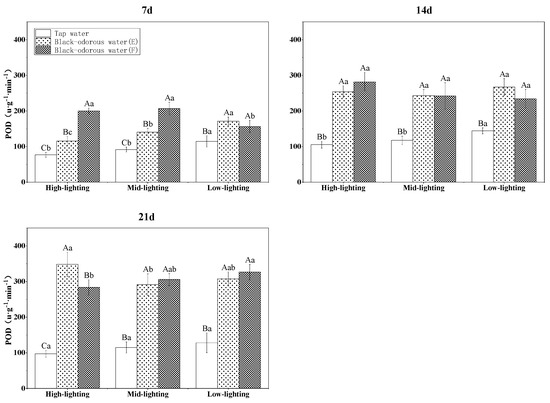
Figure 10.
POD enzyme activity of V. natans on the 7th, 14th, and 21st days of sampling.
3.4. Discussion
The measurement of the changes in plant biomass under the stress of black-odorous water can also reflect the extent of plant tolerance to black-odorous water [33]. The biomass of V. natans is an important indicator of the efficiency of phytoremediation [33]. In this study, it was observed that black-odorous water inhibited the growth of V. natans and that the biomass of V. natans first exhibited an increasing trend before exhibiting a reverse biomass growth. This finding may be explained by the fact that in the short term, V. natans did not absorb excessive pollutants and was able to show normal biomass growth (i.e., mostly in the subsurface portion of V. natans). According to the literature [34,35], black-odorous water inhibits the growth of V. natans. Zhu et al. [36] revealed that the biomass of V. natans under the combined stress of low light, high-ammonia nitrogen, and sulfide likewise displayed an increasing growth followed by a reverse growth. It has also been demonstrated that by controlling its shape or morphological features, V. natans avoids/tolerates adverse environmental stress [37].
In this study, V. natans had fewer leaves in the black-odorous water than in the tap water (D). However, there was no discernible variation in root length, which may be explained by the fact that V. natans increases root vigor to withstand stress [38,39]. However, it is noteworthy to mention that these observations are not consistent with the results of an experiment where light had a significant impact on the growth of V. natans. One possible explanation for this phenomenon is the low transparency of the black-odorous water, which affects its sensitivity to light and makes the shade have little impact on it.
The amount of chlorophyll in a plant can represent how well it is absorbing and utilizing light energy. Chlorophyll is involved in the conversion and transport of energy inside the plant’s body. Thus, the growth state of the plant can be assessed by measuring its chlorophyll content since changes in the environment, such as light, water quality, and temperature, can impact the amount of chlorophyll present and, consequently, the rate at which the leaves synthesize oxygen [25,35,40,41,42]. The chlorophyll content of V. natans in the tap water (D) showed an increasing trend over time, whereas the chlorophyll content of V. natans in the black-odorous water (E) and the black-odorous water (F) showed an increasing and then a decreasing trend. The increasing trend was also noticeably greater than the chlorophyll content of V. natans in the tap water (D), which peaked on the 21st day of the experiment. These results indicate that the chlorophyll content of V. natans in the black-odorous water was higher than that observed in the tap water (D). This difference was likely caused by the low transparency and low-light intensity of the black-odorous water, which required V. natans to produce more chlorophyll to promote photosynthesis.
Cao et al. [43] reported that V. natans adapts to the environment by synthesizing more chlorophyll under low light. In another study, Hu et al. [44] showed that the synthesis of chlorophyll in V. natans was inhibited under metal (Cu2+) stress because the Cu2+ entering the plant caused an imbalance of chloroplast enzyme activity, resulting in accelerated chlorophyll decomposition. This suggests that the decrease in the chlorophyll content of V. natans in the black-odorous water in the later stage of the experiment may have been caused by the gradual increase in the pollutants present in the black-odorous water. When plants are used to treat ammonia-nitrogen-containing water, they experience photoinhibition, or inhibition of photosynthesis, which is thought to be caused by excessive light and manifests as chloroplast inactivation of the photosystem, a decrease in the chlorophyll content, the destruction of reaction center proteins, and changes in the lutein cycle [21,24,45].
MDA is the end product of membrane lipid peroxidation, which is one of the key indications of membrane-system damage. Its level can reflect the degree of stress injury to plants and its buildup signals a decline in tissue protection [46,47]. Under conditions of stress, the regulating function of reactive oxygen metabolism in plant cells is disturbed, resulting in an increase in free radicals and triggering an oxidative stress response in the plant body in order to adjust to the polluted environment [48]. In this study, the MDA concentration in the black-odorous water was substantially higher than in the tap water (D), showing that the important activities of V. natans are hampered in the presence of black-odorous water.
Antioxidant enzymes are essential defensive mechanisms in plants [49] and the activity of antioxidant enzymes changes when plants are subjected to external environmental stressors [1,50,51]. The antioxidant enzymes include superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), etc. The SOD scavenges the superoxide anion radicals; it is essential for the oxidative and antioxidant balance of plants and serves as the first line of defense in the antioxidant system [52]. In this study, the SOD activity of V. natans in the black-odorous water was significantly greater than that in the tap water (D) on the 7th day of the experiment but showed a declining trend with no significant difference from the tap water (D) in a later stage. This was presumably because the stress was beyond the tolerance range of V. natans to inhibit SOD activity. Catalase is one of the essential enzymes of the biodefense system that can degrade excess H2O2, thus protecting the cells from the harmful effects of H2O2 and mitigating peroxidative damage [53]. The CAT activity of V. natans in the black-odorous water was considerably higher than in the tap water (D), which showed that V. natans increased CAT activity in response to black-odorous-water stress. Wang et al. [54] reported that the CAT activity of V. natans under high-ammonia-nitrogen stress (2.8 mM) was much higher than under other mild-ammonia-nitrogen stresses.
Peroxidase is a class of oxidoreductases extensively found in plants, animals, and microbes that employs H2O2 and analogs as oxidants to create H2O [26,55]. Peroxidase is one of the most essential enzymes in the plant antioxidant protection enzyme system [56]. In this study, the POD activity in the black-odorous water was substantially higher than in the tap water (D) and it increased significantly with the experimental time. Therefore, it appears that V. natans responds to the stress of black-odorous water by boosting the activity of antioxidant enzymes.
In general, under severe environmental stress, plants produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals that are detrimental to the cells [57,58]. Antioxidant enzymes, such as V. natans’ defense mechanism, protect plants by scavenging ROS and free radicals [59,60,61]. SOD generates H2O2 and oxygen from ROS via the catalytic disproportionation processes. Although H2O2 causes damage to the plants, CAT and POD degrade H2O2 into innocuous byproducts. After 14 days, the SOD in V. natans was essentially unchanged, indicating that the removal of ROS and free radicals in the plant had not been completed to the extent that they were toxic to V. natans. These findings also corroborate the decrease in the biomass of V. natans after 14 days of experimental time [12,62]. The steady increase in CAT and POD activity over the course of the experiment suggested that the protective enzyme system in V. natans was activated to combat the oxidative damage produced by environmental stress. V. natans adapted to the adverse environmental stress by increasing its CAT and POD activity, which responded better to the stress of the black-odorous water than the SOD activity. Thus, future research should focus on current real-life case studies on sustainability and/or water quality in order to achieve the universal continuous black and odorous water index (CBOWI) by determining the role of different N species, fertilizers, and sulfur transformation (e.g., speciation and its precipitation mechanism with iron and manganese) and conducting microbial community structure analysis to determine the dominant genera in the plant biofilm [63,64,65,66,67,68].
4. Conclusions
The changes in the morphological and physiological characteristics of V. natans under the stress of black-odorous water were tested in this study. The growth and morphology of V. natans were not significantly influenced by the intensity of the light. The MDA and antioxidant enzymes of V. natans were able to respond to the black-odorous water stress. The CAT and POD activity of V. natans responded better than the SOD activity. V. natans thrived in the environment of black-odorous water and its high tolerance capacity suggests that it may have applications in the ecological restoration of black-odorous water. In this study, the experimental trial period was too brief and only one plant species was evaluated. In future research, the duration of the experiment should be lengthened and a wide range of submerged plants should be tested under varied concentrations of polluted water and different environmental conditions in order to ascertain the treatment efficiency of black-odorous water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.W. and Z.H. (Zhenrong Huang); methodology, M.W.; software, M.W.; validation, M.W., T.P. and Z.H. (Zhenrong Huang); formal analysis, M.W.; investigation, Z.H. (Ziyun He); resources, Z.H. (Zhenrong Huang); data curation, Z.H. (Zhenrong Huang); writing—original draft preparation, E.R.R.; writing—review and editing, Z.H. (Zhenrong Huang); visualization, Y.G.; supervision, T.P.; project administration, H.H.; funding acquisition, D.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (China) (No. 2019JJ40122) and the Scientific Research Project from the Education Department of Hunan Province (No. 22B0203) provided financial support to carry out this experimental study. The IHE Delft Institute for Water Education (The Netherlands) provided Eldon R. Rene with staff time and infrastructural assistance for his collaboration with Chinese scholars (Project: Support to Society).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Funding statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Yin, J.; Fan, P.; Zhong, G.; Wu, Z. Responses of Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara to the combined effects of Mn and pH. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.; Xie, P.; Li, Z.; Ni, L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J. Physiological stress of high NH4+ concentration in water column on the submersed macrophyte Vallisneria Natans L. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Opportunities for phytoremediation and bioindication of arsenic contaminated water using a submerged aquatic plant: Vallisneria natans (lour.) Hara. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2015, 17, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasri, M.A.; Suthindhiran, K. Effect of zinc and lead on the physiological and biochemical properties of aquatic plant Lemna minor: Its potential role in phytoremediation. Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 7, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, D.; Xu, M.; Shen, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S. A critical review of the appearance of black-odorous waterbodies in China and treatment methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S. The river runs black. The environmental challenge to China’s future. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 58, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing and Construction. Ministry of Environmental Protection issued guidelines for the remediation of urban black-odorous waterbodies. Urban Roads Bridges Flood Control 2016, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. MEP Adopts in Principle the Programmes of Action for “Green Shield 2018”, Environmental Protection of Centralized Drinking Water Sources, and Treatment of Black and Odorous Waters. News Release, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, The People’s Republic of China. 2018. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/News_service/news_release/201802/t20180227_431831.shtml (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Mustafa, H.M.; Hayder, G. Recent studies on applications of aquatic weed plants in phytoremediation of wastewater: A review article. Ain. Shams. Eng. J. 2021, 12, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Gupta, A.; Chandra, H. Managing water quality with aquatic macrophytes. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2008, 7, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Deng, J.; Zhou, Y. Aquatic vegetation in response to increased eutrophication and degraded light climate in Eastern Lake Taihu: Implications for lake ecological restoration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiao, L.X.; Yang, S.; Jin, X.; Yi, W. Effects of organic matter and submerged macrophytes on variations of alkaline phosphatase activity and phosphorus fractions in lake sediment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, P.; Xie, D. Effects of ammonia nitrogen and sediment nutrient on growth of the submerged plant Vallisneria natans. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.L. Response of Submerged Plant Vallisneria spinulosa to Changes of Heavy Copper and Water Level in Poyang Lake. Master’s Thesis, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, R. Effect of Light Conditions on Growth Characteristic of Two Submersed Macrophyte. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Study on the Response of Ammonium Nitrogen Stress in Water by Themyriophyllum verticillatum of Submerged Plant. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hak, K.; Ritchie, R.J.; Dummee, V. Bioaccumulation and physiological responses of the Coontail, Ceratophyllum demersum exposed to copper, zinc and in combination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 110049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Liu, C.; Ke, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wu, Z. Growth and physiological responses in a submerged clonal aquatic plant and multiple-endpoint assessment under prolonged exposure to ciprofloxacin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, H.; Chu, Z. Advance in antioxidative enzyme system of submerged macrophytes under ammonia stress. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 39, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, W. Naming history, classification and characteristics of species from the genus Vallisneria in China. Plant Sci. J. 2019, 37, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.-Y.; Zhu, W.-J.; Liu, X.-B.; Lan, Y.-Q.; Mo, J.-N.; Shen, W.-G. Effects of different concentrations of ammonia nitrogen on the growth of five submerged plant species. HydroEcology 2019, 40, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.J.; Zhang, M.; Quan, S.-Q.; Liu, Z.-G.; Chen, H.-W.; Yin, Q.; Ouyang, C.-Y. Integrated effects of hypoxia, high ammonia and low light on the growth and physiological C-N metabolism indices of Vallisneria natans. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Effects of Root Growth of vallisnerio natans on the Black and Odorous Water. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, X. Research on the Restoration Effect of Three Kinds of Aquatic Plants on the Repair of Black and Odorous Water. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Song, S.; Yan, Y.; Li, P.; Jeelani, N.; Wang, P.; An, S.; Leng, X. Combined effects of light reduction and ammonia nitrogen enrichment on the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, L.-L.; Li, J.; He, X.-J.; Cai, J.-C. Bioaccumulation and tolerance characteristics of a submerged plant (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) exposed to toxic metal lead. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.-W.; Wang, D.-X.; Liu, R.-J.; Zhang, C.-M. The Suitable conditions for assaying SOD activity by nitrogen blue tetrazolium photoreduction method on Alopine Forage. Grassl. Turf. 2000, 42, 3206–3211. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, I.Y.; Bautista, G.A. Variation of peroxidase activity in cacao beans during their ripering, fermentation and drying. Food Chem. 1999, 65, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeyer, H.U. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, A.E.; Rhodes, T.R.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.P. Evaluation of uncertainty of soil organic matter measured by potassium dichromate outside heating method. Constr. Des. Eng. 2017, 16, 101–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Øien, A. Determination of Kjeldahl nitrogen and exchangeable ammonium in soil by the indophenol method. Acta Agric. Scand. 1986, 36, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Ren, W.; Yuan, C.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cao, T.; Ni, L.; Jeppesen, E. Phenotypic responses of a submerged macrophyte (Vallisneria natans) to low light combined with water depth. Aquat. Bot. 2022, 176, 103462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Song, S.; Li, P.; Jeelani, N.; Wang, P.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, J.; An, S.; Leng, X. Growth and physiological responses of submerged plant Vallisneria natans to water column ammonia nitrogen and sediment copper. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Luo, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J. Responses of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans to a water depth gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.P. Study on the Growth and Physiology Mechanism of Vallisneria spinulosa in Response to the Complex Stress of Sulfide, High Ammonia and Low Light. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Yuan, G.; Fu, H.; Peng, H.; Ge, D.; Lou, Q.; Zhong, J. Effects of ammonium pulse on the growth of three submerged macrophytes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.H. Study on the Effects of Substrates and Arsenic Stress on the Growth of Vallisneria natans. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Yang, T.; Wen, Z.-H.; Zhang, X.-L.; Cao, T.; Ni, L.-Y.; Yuan, C.-B. Growth and physiological response of vallisneria natans under extreme low light and two substrate conditions. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 652–662. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Han, F.; Bai, G.; Kong, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; He, F.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y. The promotion effects of silicate mineral maifanite on the growth of submerged macrophytes Hydrilla verticillata. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.C.; Yates, D.F.; Macauley, J.M.; Quarles, R.L.; Genthner, F.J.; Chancy, C.A.; Devereux, R. Effects of light reduction on growth of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria americana and the community of root-associated heterotrophic bacteria. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 291, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Ni, L.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M. Effects of moderate ammonium enrichment on three submersed macrophytes under contrasting light availability. Freshwater Biol. 2011, 56, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Ni, L.; Xie, P. Acute biochemical responses of a submersed macrophyte, Potamogeton crispus L., to high ammonium in an aquarium experiment. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2004, 19, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Pu, H.; Chen, L.; Cheng, S. Effects of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) and cupic hydroxide [Cu(OH)2] on activity of antioxidase and contentof chlorophyll in Vallisneria natans. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2011, 27, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Zhu, T.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, T.; Ni, L.; Hilt, S. Littoral slope, water depth and alternative response strategies to light attenuation shape the distribution of submerged macrophytes in a mesotrophic lake. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yuan, G.; Cao, T.; Ni, L.; Li, W.; Zhu, G. Relationships between relative growth rate and its components across 11 submersed macrophytes. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2012, 27, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Fu, H.; Zhong, J.; Cao, T.; Ni, L.; Zhu, T.; Li, W.; Song, X. Nitrogen/carbon metabolism in response to NH4+ pulse for two submersed macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 2015, 121, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona, R. Advanced lipoxidation end-products. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2011, 192, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrut, B.; Shahid, M.; Douay, F.; Dumat, C.; Pinelli, E. Molecular mechanisms involved in lead uptake, toxicity and detoxification in higher plants. In Heavy Metal Stress in Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Cao, T.; Fu, H.; Ni, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Song, X.; Xie, P.; Jeppesen, E. Linking carbon and nitrogen metabolism to depth distribution of submersed macrophytes using high ammonium dosing tests and a lake survey. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Chen, K.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X. Impact of water depth and sediment type on root morphology of the submerged plant Vallisneria natans. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2014, 30, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manquián-Cerda, K.; Escudey, M.; Zúñiga, G.; Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Molina, M.; Cruces, E. Interactive effects of aluminum and cadmium on phenolic compounds, antioxidant enzyme activity and oxidative stress in blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) plantlets cultivated in vitro. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jin, P.; Bishop, P.L.; Li, F. Upgrade of three municipal wastewater treatment lagoons using a high surface area media. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2011, 6, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, P.F.; Hou, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.J. Metabolic adaptations to ammonia-induced oxidative stress in leaves of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadary, A.A. Kinetic Studies of Catalase And Peroxidase Enzymes Extracted From Garlic Cloves (Allium sativum L.). Egypts Pres. Spec. Counc. Educ. Sci. Res. 2021, 59, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, R.; Tao, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y. The effect of Alternaria leaf spot on the antioxidant system of cucumber seedlings. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 164, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Sun, K.; Su, X.; Pan, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Wang, X.-P. Physiological responses and tolerance mechanisms to Pb in two xerophils: Salsola passerina Bunge and Chenopodium album L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 205–206, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampeetong, A.; Brix, H. Effects of NaCl salinity on growth, morphology, photosynthesis and proline accumulation of Salvinia natans. Aquat. Bot. 2009, 91, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gechev, T.; Gadjev, I.; Van Breusegem, F.; Inzé, D.; Dukiandjiev, S.; Toneva, V.; Minkov, I. Hydrogen peroxide protects tobacco from oxidative stress by inducing a set of antioxidant enzymes. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, R.S.; Kalpana; Sharma, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Reactive oxygen species (ros): A self-generated necessary devil in the cell. In Emerging Challenges for Human Health Sustainability and Interventions in Pharmaceutical, Microbiology and Medical Sciences, Futuristic Innovative Approaches; Learning Media Publication: Meerut, India, 2021; pp. 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Matés, J.M. Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology 2000, 153, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jiang, H.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y. Growth, pigment composition, chlorophyll fluorescence and antioxidant defenses in the red alga Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) under light stress. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 100, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yang, P.; Kong, M. Effects of nitrate dosing on the migration of reduced sulfur in black odorous river sediment and the influencing factors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, N.; Lu, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Lei, P. In situ high-resolution measurement of phosphorus, iron and sulfur by diffusive gradients in thin films in sediments of black-odorous rivers in the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chow, A.T.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Vallisneria natans on H2S and S2− releases in black-odorous waterbody under additional nitrate: Comprehensive performance and microbial community structure. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, Y.; Boyd, C.E. A sodium-nitrate-based, water-soluble, granular fertilizer for sport fish ponds. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2001, 63, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, Y.; Boyd, C.E. Nitrogen fertilization of Golden Shiner ponds. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2002, 64, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Wan, Y.; Ni, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, T. A new method for continuous monitoring of black and odorous water body using evaluation parameters: A case study in Baoding. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).