Leakages in Water Distribution Networks: Estimation Methods, Influential Factors, and Mitigation Strategies—A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Water Losses Estimation Methodologies
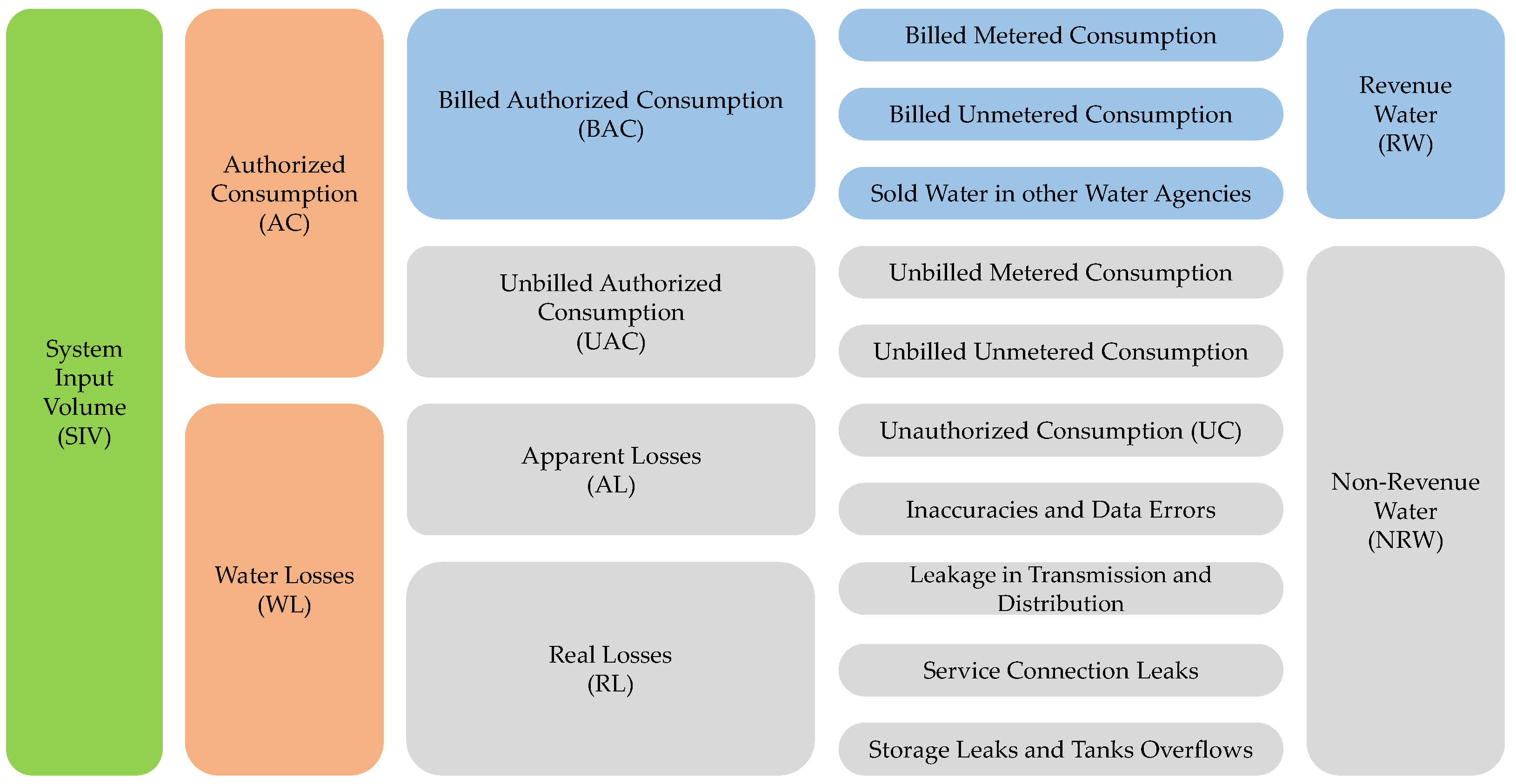
2.1. Water Balance (Top-Down) Approach
2.2. Burst and Background Estimates (BABE) Approach
2.3. Minimum Night Flow (Bottom-Up) Approach
2.4. Comparison
3. Leakage Related Factors
3.1. Structural Factors and Physical Pipe Properties
3.1.1. Diameter and Wall Thickness of the Pipeline
3.1.2. Pipeline Material and Aging
3.1.3. Connections per Unit Length of Pipeline Grid
3.2. Environmental Factors and Physical Pipe Properties
3.2.1. Soil Condition
3.2.2. Temperature
3.2.3. External Loads
3.3. Internal (Hydraulic) Factors
3.3.1. Velocity
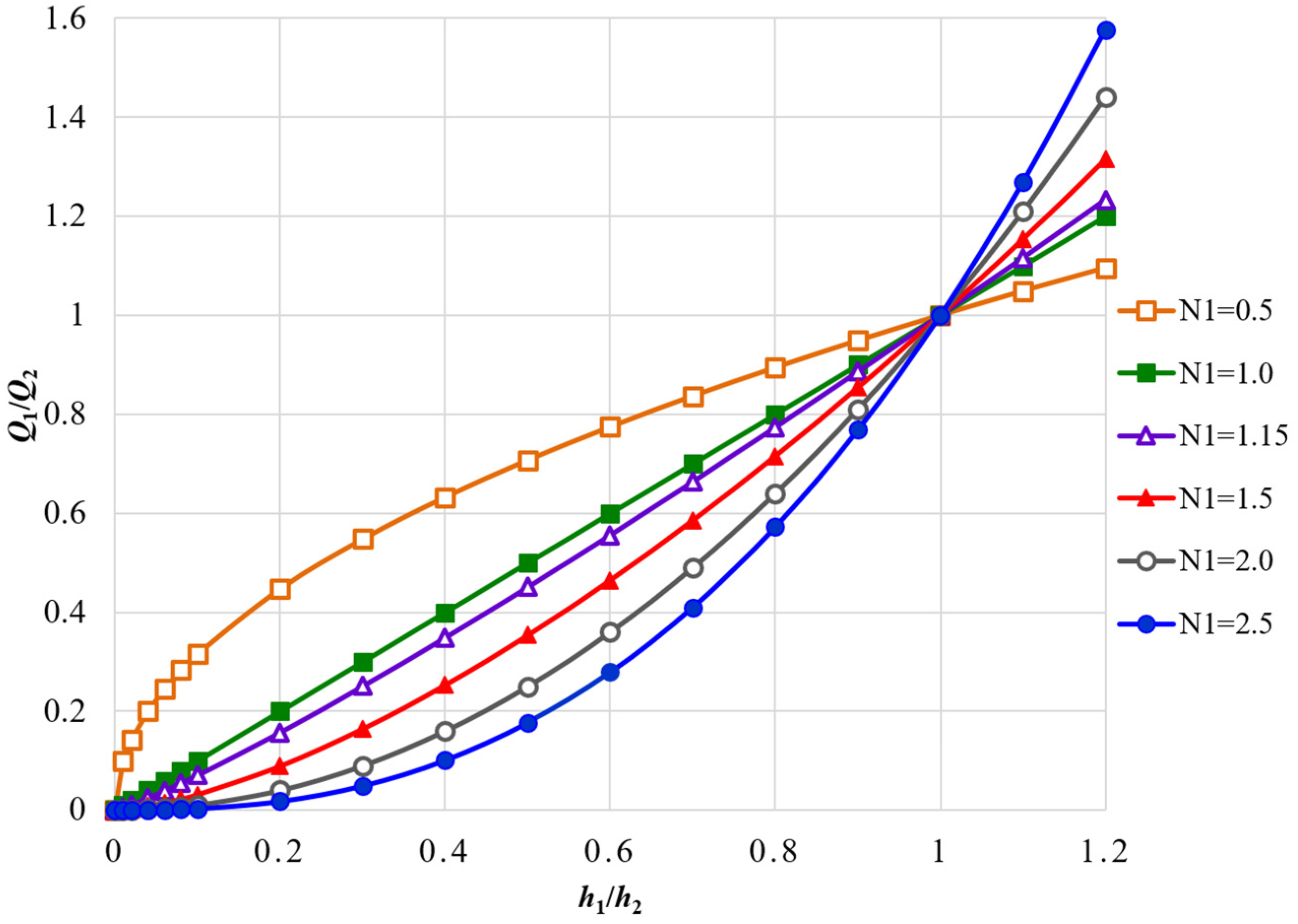
3.3.2. Pressure
3.4. Design, Maintenance, and Repair of the Pipeline Network
4. Leakage Reduction Technics
4.1. Pipe Repair and Replacement
4.2. Partitioning of Water Dinstribution Networks
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wittfogel, K.A. Oriental Despotism: A Comparative Study of Total Power; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1957; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2027/heb03224.0001.001 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Crouch, D.P. Water Management in Ancient Greek Cities; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L. Ancient Water Technologies; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 978-90-481-8631-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P. Elementary Hydrology; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1992; ISBN 9780132493840. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, J.; Cheng, A.H.D.; Sorek, S.; Ouazar, D.; Herrera, I. Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: Concepts, Methods and Practices; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Boston, MA, USA; Kluwer Academic Publisher: London, UK, 1999; p. 625. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, J.M.; Mainuddin, M.; Mpelasoka, F.; Ahmad, M.D.; Palash, W.; Quadir, M.E.; Shah-Newaz, S.M.; Hossain, M.M. The impact of climate change on regional water balances in Bangladesh. Clim. Change 2016, 135, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, G.; Hannah, D.M.; Watts, G. Climate change and water in the UK: Recent scientific evidence for past and future change. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2017, 41, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E.; Liang, S. Global atmospheric evaporative demand over land from 1973 to 2008. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 8353–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G. Estimation of global irrigation water use by the integration of multiple satellite observations. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Lalonde, A. Using practical predictions of Economic Intervention Frequency to calculate Short-run Economic Leakage Level, with or without Pressure Management. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialised Conference ‘Leakage 2005’, Halifax, NS, Canada, 12–14 September 2005; Available online: https://www.leakssuitelibrary.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/LambertLalondeHalifaxSep2005.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Gomes, R.; Marques, J.A.S.; Sousa, J. Estimation of the benefits yielded by pressure management in water distribution systems. Urban Water J. 2011, 8, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzolani, G.; Berardi, L.; Laucelli, D.; Martino, R.; Simone, A.; Giustolisi, O. A Methodology to Estimate Leakages in Water Distribution Networks Based on Inlet Flow Data Analysis. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroulias, N.; Foufeas, D.; Bougoulia, E. Estimating Water Losses and Assessing Network Management Intervention Scenarios: The Case Study of the Water Utility of the City of Drama in Greece. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes-Miquel, V.S.; Arrieta-Pastrana, A.; Coronado-Hernández, O.E. Analyzing Water Leakages in Parallel Pipe Systems with Rapid Regulating Valve Maneuvers. Water 2024, 16, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, P.F.; Aboujaoude, A.S. Managing leaks using flow step-testing, network modeling, and field measurement. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2011, 103, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutikanga, H.E.; Sharma, S.K.; Vairavamoorthy, K. Methods and Tools for Managing Losses in Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Hirner, W. Losses from Water Supply Systems: A Standard Terminology and Recommended Performance Measures; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.; Charalambous, B.; Fantozzi, M.; Kovac, J.; Rizzo, A.; Galea, S. 14 years experience of using IWA best practice water balance and water loss performance indicators in Europe. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialized Conference: Water Loss, Vienna, Austria, 30 March–2 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Farley, M. Leakage Management and Control: A Best Practice Training Manual. World Health Organization, Water, Sanitation and Health Team & Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council. 2001. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/66893 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Lambert, A. International Report: Water losses management and techniques. Water Supply 2002, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuken, R.H.S.; Lavooij, C.S.W.; Bosch, A.; Schaap, P.G. Low Leakage in the Netherlands Confirmed. In Proceedings of the Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liemberger, R.; Wyatt, A. Quantifying the global non-revenue water problem. Water Supply 2018, 19, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosetlhe, T.C.; Hamam, Y.; Du, S.; Monacelli, E. Appraising the Impact of Pressure Control on Leakage Flow in Water Distribution Networks. Water 2021, 13, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanek, M.; Suchorab, P. Fractal Characteristics of Water Outflows on the Soil Surface after a Pipe Failure. Water 2024, 16, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.; Trow, S. Calculating economic levels of leakage. In Proceedings of the IWA Water Loss 2005 Conference, Halifax, NS, Canada, 12–14 September 2005; Available online: http://rash.apanela.com/tf/leakage/Calculating%20Economic%20Levels%20of%20Leakage.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Papadopoulou, A. Integrating the Carbon and Water Footprints’ Costs in the Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC Full Water Cost Recovery Concept: Basic Principles Towards Their Reliable Calculation and Socially Just Allocation. Water 2012, 4, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.; Sánchez-Romero, F.-J.; López-Jiménez, P.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Leakage Management and Pipe System Efficiency. Its Influence in the Improvement of the Efficiency Indexes. Water 2021, 13, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heryanto, T.; Sharma, S.; Daniel, D.; Kennedy, M. Estimating the Economic Level of Water Losses (ELWL) in the Water Distribution System of the City of Malang, Indonesia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, C.; Hope, V. Environmental valuation and the economic level of leakage. Urban. Water 2001, 3, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Gonelas, K. The Optimal Balance Point between NRW Reduction Measures, Full Water Costing and Water Pricing in Water Distribution Systems. Alternative Scenarios Forecasting the Kozani’s WDS Optimal Balance Point. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Mocholí-Arce, M.; Sala-Garrido, R. Estimating the environmental and resource costs of leakage in water distribution systems: A shadow price approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D. Standard Definitions for Water Losses; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9781789060881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A. Accounting for Losses: The Bursts and Background Concept. Water Environ. J. 1994, 8, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Washali, T.; Sharma, S.; Kennedy, M. Methods of Assessment of Water Losses in Water Supply Systems: A Review. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4985–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liemberger, R.; Farley, M. Developing a nonrevenue water reduction strategy Part 1: Investigating and assessing water losses. In Proceedings of the IWA WWC 2004 Conference, Marrakech, Morocco, 19–24 September 2004; Available online: https://sswm.info/sites/default/files/reference_attachments/LIEMBERGER%20FARLEY%202004%20Developing%20a%20NRW%20Reduction%20Strategy.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Lambert, A.; Taylor, R. Water Loss Guidelines–Water New Zealand; Water New Zealand: Wellington, New Zealand, 2010; ISBN 978-0-9941243-2-6. [Google Scholar]
- Horbatuck, K.H.; Beruvides, M.G. Water Infrastructure System Leakage Analysis: Evaluation of Factors Impacting System Performance and Opportunity Cost. Water 2024, 16, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AWWA. Water Audits and Loss Control Programs Manual of Water Supply Practices, M36; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-58321-631-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mutikanga, H.E.; Sharma, S.K.; Vairavamoorthy, K. Assessment of apparent losses in urban water systems. Water Environ. J. 2011, 25, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seago, C.; Bhagwan, J.; McKenzie, R. Benchmarking leakage from water reticulation systems in South Africa. Water SA 2004, 30, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arregui, F.; Cabrera, E.; Cobacho, R.; García-Serra, J. Reducing Apparent Losses Caused By Meters Inaccuracies. Water Pract. Technol. 2006, 1, wpt2006093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, H.; Baptista, J.M.; Cabrera, E.; Cubillo, F.; Duarte, P.; Hirner, W.; Merkel, W.; Parena, R. Performance Indicators for Water Supply Services, 2nd ed.; Water Intelligence Online; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; Volume 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.; Sturm, R.; Kunkel, G. Water Loss Control, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Farley, M.R. District Metering. Part 1-System Design and Installation; WRc: Swindon, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.; Brown, T.G.; Takizawa, M.; Weimer, D. A review of performance indicators for real losses from water supply systems. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 1999, 48, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; McKenzie, R.D. Practical Experience in using the Infrastructure Leakage Index. In Proceedings of the International Water Association Conference ‘Leakage Management: A Practical Approach’, Lemesos, Cyprus, November 2002; Available online: https://www.geocities.ws/kikory2004/4_Lambert.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Lambert, A. Ten years experience in using the UARL formula to calculate infrastructure leakage index. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialized Conference: Water Loss 2009, Cape Town, South Africa, 26–29 April 2009; pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Washali, T.; Sharma, S.; Lupoja, R.; Al-Nozaily, F.; Haidera, M.; Kennedy, M. Assessment of water losses in distribution networks: Methods, applications, uncertainties, and implications in intermittent supply. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 152, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunaidi, O.; Brothers, K. Night flow analysis of pilot DMAs in Ottawa. In Proceedings of the Water Loss Specialist Conference, International Water Association, Bucharest, Romania, 23 September 2007; pp. 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Tabesh, M.; Yekta, A.H.A.; Burrows, R. An integrated model to evaluate losses in water distribution systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.B.; Girol, G.V.; Abe, N.; Propato, M. Night flow analysis and modeling for leakage estimation in a water distribution system. In Integrating Water Systems (CCWI 2010); Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-415-54851-9. [Google Scholar]
- Karadirek, I.E.; Kara, S.; Yilmaz, G.; Muhammetoglu, A. Implementation of Hydraulic Modelling for Water-Loss Reduction Through Pressure Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer, J.; Mirats-Tur, J.M.; Cembrano, G.; Puig, V.; Quevedo, J.; Pérez, R.; Sanz, G.; Ibarra, D. A decision support system for on-line leakage localization. Environ. Model Softw. 2014, 60, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkasseh, J.M.A.; Adlan, M.N.; Abustan, I.; Aziz, H.A.; Hanif, A.B.M. Applying Minimum Night Flow to Estimate Water Loss Using Statistical Modeling: A Case Study in Kinta Valley, Malaysia. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1439–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Washali, T.; Sharma, S.; Al-Nozaily, F.; Haidera, M.; Kennedy, M. Modelling the Leakage Rate and Reduction Using Minimum Night Flow Analysis in an Intermittent Supply System. Water 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, R.; Kaggwa, R.; Malebo, A. Utility Management Series for Small Towns, Leakage Control Manual 5; UN-Habitat Lake Victoria Water and Sanitation Initiative Team and National Water and Sewerage Corporation Team; UN-Habitat, 2012; ISBN 978-92-1-132537-9. [Google Scholar]
- Adlan, M.N.; Alkasseh, J.M.A.; Abustan, H.I.; Hanif, A.B.M. Identifying the appropriate time band to determine the minimum night flow: A case study in Kinta Valley, Malaysia. Water Supply 2013, 13, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, D.; Cima, E.; Ferrante, M.; Brunone, B.; Meniconi, S. The dependence of district minimum night flow on pressure head: The case study of Lenola. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammetoglu, A.; Albayrak, Y.; Bolbol, M.; Enderoglu, S.; Muhammetoglu, H. Detection and assessment of post meter leakages in public places using smart water metering. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 2989–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakogiannis, A.; Tzamtzis, A. Modeling of District Metered Areas with Relatively High Leakage Rate. The Case Study of Kalipoli’s DMA, CUNY Academic Works. 2014. Available online: https://academicworks.cuny.edu/cc_conf_hic/384 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Hamilton, S.; McKenzie, R. Water Management and Water Loss; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; p. 250. [Google Scholar]
- Makaya, E. Predictive leakage estimation using the cumulative minimum night flow approach. Am. J. Water. Resour. 2017, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.J.; Ben-Ephraim, Y. System leakage by night flow analysis: A case study in Guyana. Water Manag. 2012, 165, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, E.; Shahrour, I. Leakage detection using smart water system: Combination of water balance and automated minimum night flow. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4821–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WSAA. Guidelines Relating to the Subject of Targeting Leakage Using Nightflow Measurements; Wide Bay Water Corporation, Australia and Water Loss Research & Analysis Ltd.: UK; Water Services Association of Australia: Melbourne, Australia.
- Quevedo, J.; Pérez, R.; Pascual, J.; Puig, V.; Cembrano, G.; Peralta, A. Methodology to detect and isolate water losses in water hydraulic networks: Application to Barcelona water network. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2012, 45, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic estimation of minimum night flow in water distribution networks: Large-scale application to the city of Patras in western Greece. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.; Tooms, S.; Rogers, D. DMA Management Guidance Notes; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, R.S.; Wegelin, W.A.; Meyer, N. Water Demand Management Cookbook; Rand Water: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2003; ISSN 062030734X. [Google Scholar]
- Fallis, P.; Hübschen, K.; Oertlé, E.; Ziegler, D.; Klingel, P.; Baader, A.J.; Trujillo, R.; Laures, C. Guidelines for Water Loss Reduction: A Focus on Pressure Management; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Eschborn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, T.; Lambert, A.; McKenzie, R. Applying the IWA approach to water loss performance indicators in Australia. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Suresh, M.A.; Smith, L.; Ostfeld, A.; Stoleru, R.; Rasekh, A.; Banks, M.K. Mobile sensor networks for optimal leak and backflow detection and localization in municipal water networks. Environ. Model Softw. 2016, 80, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettler, A.J.; Goutler, I.C. An analysis of pipe breakage in urban water distribution networks. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1985, 12, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, S.A.; Marks, D.H.; Clark, R.M. A new methodology for modelling break failure patterns in deteriorating water distribution systems: Theory. Adv. Water Resour. 1987, 10, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tolikas, D. The role of leaks and breaks in water networks: Technical and economical solutions. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2001, 50, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, S.; Agathokleous, A.; Charalambous, B.; Adamou, A. Proactive risk-based integrity assessment of water distribution networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2001, 24, 3715–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langousis, A.S.; Fourniotis, N.T. Elements of Design of Water Supply and Sewerage Works; GOTSIS Publications: Patras, Greece, 2020; 722p, ISBN 978-960-9427-89-0. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Makar, J.; Desnoyers, R.; Mcdonald, S. Failure modes and mechanisms in gray cast iron pipe. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Underground Infrastructure Research 2001, Ontario, ON, Canada, 10–13 June 2001; pp. 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafodin, S.; Latifi, M. Experimental Investigation of Leakage Flow Rate and Fluidisation beneath Polyethylene Pipes in Non-Uniform Soils. Water 2024, 16, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutler, I.C.; Kazemi, A. Spatial and temporal groupings of water main pipe breakage in Winnipeg. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1989, 15, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoye, W.W. Controlling the cost of system maintenance. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1980, 72, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walski, T.M.; Pelliccia, A. Economic analysis of water main breaks. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1982, 74, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantokratoras, A. City Water Distribution Networks; Epikentro: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2015; ISBN 978-960-458-522-9. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Shamir, U.; Howard, C.D.D. An analytic approach to scheduling pipe replacement. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1979, 71, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.M.; Stafford, C.L.; Goodrich, J.A. Water Distribution Systems: A Spatial and Cost Evaluation. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1982, 108, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, S. Validation of the long life of PVC pipes. In Proceedings of the 17th Plastic Pipes Conference 2014, Chicago, IL, USA, 22–24 September 2014; pp. 1–9. Available online: https://www.teppfa.eu/wp-content/uploads/validation-of-the-long-life-of-pvc-pipes_steven-folkman_forum2015.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Lancashire, S.J. In-Service Durability of uPVC Water Mains. In Proceedings of the Plastics Pipes VI Conference, University of York, 26–28 March 1985; Available online: https://pvc4pipes.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/In-Service-Durability-of-uPVC-Water-Mains-Lancashire-PPVI-1985.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Alferink, F.; Janson, L.E.; Holloway, L. Old PVC-U Water Pressure Pipes: Investigation into Design and Durability. In PVC 1996 Conference Proceedings; 42C382 Institute of Materials: Brighton, UK, 1996; pp. 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Stahmer, M.W.; Whittle, A.J. Long Term Performance of PVC Pressure Pipes in a Large Rural Water Supply Scheme. In Proceedings of the Plastics Pipes XI Conference 2001, Munich, Germany, 3–6 September 2001; Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:201798775 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Çakmakcı, M.; Uyak, V.; Öztürk, İ.; Aydın, A.F.; Soyer, E.; Akça, L. The dimension and significance of water losses in Turkey. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialist Conference on Water Loss 2007, Bucharest, Romania, 23–26 September 2007; pp. 464–473. [Google Scholar]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic framework for the parametric modeling of leakages in water distribution networks: Large scale application to the City of Patras in Western Greece. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 2022, 36, 3617–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V. A troubleshooting manual for handling operational problems in water pipe networks. AQUA 2004, 53, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.P. The service pipe—A forgotten asset in leak detection. In Proceedings of the IWA Specialist Conference ‘Leakage 2005’, Halifax, NS, Canada, 12–14 September 2005; pp. 1–9. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:55477819 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Saghi, H.; Aval, A.A. Effective Factors in Causing Leakage in Water Supply Systems and Urban Water Distribution Networks. Am. J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 3, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbeis, P.; Le Gauffre, P.; Saegrov, S. Water Infrastructure Management: An Overview of European Models and Databases. In Chaper 16 in Urban Water Supply Handbook, 1st ed.; Mays, L.W., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Available online: https://www.accessengineeringlibrary.com/content/book/9780071371605/chapter/chapter16 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Al-Hashem, H.A.S.; Al-Naeem, M.A.H. Effect of Temperature on the Stiffness of Polyvinyl Chloride and Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride Joints Under Bending. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 7, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Gold, L.W. Ground Temperatures; Canadian Building Digest; No. CBD-180; National Research Council Canada: Ottawa, ON Canada, 1967; p. 6. ISSN 0008-3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florides, G.; Kalogirou, S. Annual ground temperature measurements at various depths. In Proceedings of the CLIMA 2005, Lausanne, Switzerland, 9–12 October 2005; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.14279/2490 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Griffith, P. Watter Hammer, Thermopedia. 2011. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1615/AtoZ.w.water_hammer (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Avallone, E.A.; Baumeister, T., III. Marks’ Standard Handbook for Mechanical Engineers, 9th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1987; ISBN 0-07-004127-X. [Google Scholar]
- Perdios, A.; Kokosalakis, G.; Fourniotis, N.T.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Statistical framework for the detection of pressure regulation malfunctions and issuance of alerts in water distribution networks. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.O. What do we know about Pressure: Leakage Relationships in Distribution Systems? In Proceedings of the IWA Conference on System Approach to Leakage Control and Water Distribution Systems Management, Brno, Czech Republic, 16–18 May 2001; ISBN 80-7204-197-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.O. International Report on Water Losses Management and Techniques. In Proceedings of the IWA Berlin Congress, Berlin, Germany, 15–19 October 2001; Available online: http://www.studiomarcofantozzi.it/IntRepWaterLossesMan%26TechniquesBerlin.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Farley, M.R.; Trow, S. Losses in Water Distribution Networks, a Practitioner’s Guide to Assessment, Monitoring and Control; IWA: London, UK, 2003; pp. 146–149. ISBN 1-900222-11-6. [Google Scholar]
- Van Zyl, J.E.; Clayton, C.R.I. The effect of pressure on leakage in water distribution systems. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2007, 160, 109–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J. Theoretical Modeling of Pressure and Leakage in Water Distribution Systems. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassa, A.M.; van Zyl, J.E.; Laubscher, R.F. A numerical investigation into the effect of pressure on holes and cracks in water supply pipes. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M. Experimental Investigation of the Effects of Pipe Material on the Leak Head-Discharge Relationship. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic Minimum Night Flow Estimation in Water Distribution Networks and Comparison with the Water Balance Approach: Large-Scale Application to the City Center of Patras in Western Greece. Water 2022, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V. Statistical Estimation of Water Losses in the Water Distribution Network (WDN) of the City of Patras. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Patras, Patra, Greece, 2018; p. 275. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Water Loss Estimation and Associated Financial Cost in Water Distribution Networks: Large Scale Application to the City of Patras in Western Greece. In Proceedings of the IWA World Water Congress & Exhibition 2022, Copenhagen, Denmark, 11–15 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Karathanasi, I.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Langousis, A. Practical Estimation of Minimum Night Flow in Water Distribution Networks: Large-Scale Application to the City of Patras in Western Greece. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Online, 19–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Parametric model for probabilistic estimation of water losses in water distribution networks: A large scale real world application to the city of Patras in western Greece. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria & Online, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langousis, A.; Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Karathanasi, I. Probabilistic water losses estimation in water distribution networks and comparison with the top down—Water balance approach: A large-scale application to the city center of Patras in western Greece. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria & Online, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M.; Milici, B. Leakage Estimation in Water Distribution Network: Effect of the Shape and Size Cracks. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1167–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, R.; Chen, Q.; Li, R. Review on water leakage control in distribution networks and the associated environmental benefits. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, Y.; Adams, B.J.; Rogers, J.S. Selection and scheduling of rehabilitation alternatives for water distribution systems. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dridi, L.; Mailhot, A.; Parizeau, M.; Villeneuve, J.P. Multiobjective Approach for Pipe Replacement Based on Bayesian Inference of Break Model Parameters. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 2009, 135, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halhal, D.; Walters, G.A.; Ouazar, D.; Savic, D.A. Water network rehabilitation with structured messy genetic algorithm. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 1997, 123, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Loganathan, G.V. Methodology for economically optimal replacement of pipes in water distribution systems: 1. Theory. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2002, 6, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.P.; Garrett, J.H., Jr.; Soibelman, L. A density-based spatial clustering approach for defining local indicators of drinking water distribution pipe breakage. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2010, 25, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.I.; Lin, M.D.; Lo, S.L. Use of a GIS-based hybrid artificial neural network to prioritize the order of pipe replacement in a water distribution network. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 166, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, H.T.; Fujiwara, O. Fund allocation model for pipe repair maintenance in water distribution networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 136, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, H.T.; Nagarur, N.N. Optimal maintenance policy and fund allocation in water distribution networks. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 2005, 131, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindi, K.S.; Hamam, Y.M. Pressure control for leakage minimization in water supply networks Part 1: Single period models. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1991, 22, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, L.S.; Ramos, H.; Coelho, S.T. Pressure Control for Leakage Minimization in Water Distribution Systems Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, S.-S.; Bui, Q.-N. Leak Prediction Model for Water Distribution Networks Created Using a Bayesian Network Learning Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2719–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.R.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Yoyo, S. Parameter-Less Remote Real-Time Control for the Adjustment of Pressure in Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2017, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abe, B.T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Towards Achieving a Reliable Leakage Detection and Localization Algorithm for Application in Water Piping Networks: An Overview. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20272–20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Impact of Pressure-Driven Demand on Background Leakage Estimation in Water Supply Networks. Water 2019, 11, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, L.; Giustolisi, O. Calibration of Design Models for Leakage Management of Water Distribution Networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 2537–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.-F.; Pan, B.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, Y. State-of-the-art review on the transient flow modeling and utilization for urban water supply system (UWSS) management. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2020, 69, 858–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Perdios, A.; Fourniotis, N.T.; Langousis, A. Towards More Efficient Hydraulic Modeling of Water Distribution Networks Using the EPANET Software Engine. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, G. Committee Report: Applying worldwide BMPs in water loss control. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2003, 95, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Todini, E. Looped water distribution networks design using a resilience index based heuristic approach. Urban Water 2000, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UKWIR. Effect of District Meter Areas on Water Quality; UK Water Industry Research Limited: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Korkana, P.; Kanakoudis, V.; Patelis, M.; Gonelas, K. Forming District Metered Areas in a Water Distribution Network Using Genetic Algorithms. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Sousa, J.; Marques, A.S. Influence of Future Water Demand Patterns on the District Metered Areas Design and Benefits Yielded by Pressure Management. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.; Savic, D. Economic Performance of DMAs in Water Distribution Systems. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paola, F.; Fontana, N.; Galdiero, E.; Giugni, M.; degli Uberti, G.S.; Vitaletti, M. Optimal Design of District Metered Areas in Water Distribution Networks. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, D.; Ferrari, G. Design and Performance of District Metering Areas in Water Distribution Systems. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhu, N.; Hou, D.; Chen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H. Real-Time Burst Detection in District Metering Areas in Water Distribution System Based on Patterns of Water Demand with Supervised Learning. Water 2018, 10, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa Bui, X.; Marlim, M.S.; Kang, D. Water Network Partitioning into District Metered Areas: A State-of-the-Art Review. Water 2020, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Lobba, A.; Becciu, G. Elementary DMA Design of Looped Water Distribution Networks with Multiple Sources. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04016011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRc. The Effects of System Operation on Water Quality in Distribution; WRc: Swindon, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grayman, W.M.; Murray, R.; Savic, D.A. Effects of Redesign of Water Systems for Security and Water Quality Factors. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2009, Kansas City, MO, USA, 17–21 May 2009; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Rauch, W. Automated Creation of District Metered Area Boundaries in Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Musmarra, D.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Simone, A. Water Distribution System Clustering and Partitioning Based on Social Network Algorithms. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Tzatchkov, V.G.; Alcocer-Yamanaka, V.H. Performance indices for water network partitioning and sectorization. Water Supply 2014, 15, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudicianni, C.; Herrera, M.; di Nardo, A.; Adeyeye, K. Automatic Multiscale Approach for Water Networks Partitioning into Dynamic District Metered Areas. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Shu, S.; Li, D.A. A Unified Spatial-Pressure Sensitivity Partitioning and Leakage Detection Method within a Deep Learning Framework. Water 2024, 16, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, L.S.; Allen, M.; Preis, A.; Iqbal, M.; Whittle, A.J. Automated sub-zoning of water distribution systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Greco, R.; Santonastaso, G.F. Weighted spectral clustering for water distribution network partitioning. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2017, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzatchkov, V.G.; Alcocer-Yamanaka, V.H.; Bourguett Ortíz, V. Graph Theory Based Algorithms for Water Distribution Network Sectorization Projects. In Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium 2006; American Society of Civil Engineers: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2008; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, L.; Ostfeld, A. Topological clustering for water distribution systems analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Marques, J.A.S.; Sousa, J. Decision support system to divide a large network into suitable District Metered Areas. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvisi, S.; Franchini, M. A heuristic procedure for the automatic creation of district metered areas in water distribution systems. Urban Water J. 2013, 11, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.; Izquierdo, J.; Montalvo, I.; Ilaya-Ayza, A.E.; Pérez-García, R.; Tavera, M. A flexible methodology to sectorize water supply networks based on social network theory concepts and multi-objective optimization. J. Hydroinform. 2015, 18, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.; Izquierdo, J.; Montalvo, I.; Pérez-García, R. A Novel Water Supply Network Sectorization Methodology Based on a Complete Economic Analysis, Including Uncertainties. Water 2016, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karypis, G.; Kumar, V. Multilevelk-way Partitioning Scheme for Irregular Graphs. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 1998, 48, 96–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Tzatchkov, V.; Varela, J.M.R.; Yamanaka, V.H.A. Water Supply Network Partitioning Based on Simultaneous Cost and Energy Optimization. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempewo, J.; Pathirana, A.; Vairavamoorthy, K. Spatial Analysis Tool for Development of Leakage Control Zones from the Analogy of Distributed Computing. In Water Distribution Systems Analysis 2008; American Society of Civil Engineers: Kruger National Park, South Africa, 2009; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alvisi, S. A New Procedure for Optimal Design of District Metered Areas Based on the Multilevel Balancing and Refinement Algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4397–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Fast algorithm for detecting community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 066133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.; Ayala-Cabrera, D.; Izquierdo, J.; Pérez-García, R.; Tavera, M. Water Supply Network Sectorization Based on Social Networks Community Detection Algorithms. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaponi, C.; Murari, E.; Todeschini, S. Modularity-Based Procedure for Partitioning Water Distribution Systems into Independent Districts. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2021–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, R. Spectral Clustering and Multicriteria Decision for Design of District Metered Areas. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, J.; Herrera, M.; Montalvo, I.; Pérez-García, R. Division of Water Supply Systems into District Metered Areas Using a Multi-agent Based Approach. In Software and Data Technologies. ICSOFT 2009. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Cordeiro, J., Ranchordas, A., Shishkov, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Izquierdo, J.; Pérez-García, R.; Montalvo, I. Multi-agent adaptive boosting on semi-supervised water supply clusters. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 50, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajebi, S.; Barrett, S.; Clarke, A.; Clarke, S. Multi-agent simulation to support water distribution network partitioning. In Proceedings of the Modelling and Simulation 2013-European Simulation and Modelling Conference, ESM 2013, Lancaster, UK, 23–25 October 2013; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Fourniotis, N.T.; Langousis, A. Combining Statistical Clustering with Hydraulic Modeling for Resilient Reduction of Water Losses in Water Distribution Networks: Large Scale Application Study in the City of Patras in Western Greece. Water 2022, 14, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Fourniotis, N.T.; Langousis, A. Large-scale application of a statistically rigorous and user unbiased algorithmic approach for reduction of leakages in the water distribution networks. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting 2022, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 December 2022. id. H45I-1487. 2022AGUFM.H45I1487S. [Google Scholar]
- Serafeim, A.V. Probabilistic Modeling and Optimization of Leakages in Water Distribution Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 2022. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10889/24051 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Serafeim, A.V.; Kokosalakis, G.; Deidda, R.; Fourniotis, N.T.; Karathanasi, I.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic modelling of water distribution networks and resilient reduction of leakages: Large scale application to the city of Patras in western Greece. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 April 2023. EGU23-5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowby, R.B.; Walski, T.M. Reconnecting Water Resources Research and Practice. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2021, 147, 02521004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, R.; Hellies, M.; Langousis, A. A critical analysis of the shortcomings in spatial frequency analysis of rainfall extremes based on homogeneous regions and a comparison with a hierarchical boundaryless approach. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 2021, 35, 2605–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, K.; Mehmet, C.D.; Osman, A.B. Hydrologic homogeneous regions using monthly streamflow in Turkey. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2008, 12, 181–193. [Google Scholar]
- Modarres, R.; Sarhadi, A. Statistically-based regionalization of rainfall climates of Iran. Glob. Planet. Change 2011, 75, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.G.; Ping, F. Regional Rainfall Frequency Analysis for the Luanhe Basin—By Using L-moments and Cluster Techniques. APCBEE Procedia 2012, 1, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.H.; Othman, I.R.; Deni, S.M. Hierarchical Cluster Approach for Regionalization of Peninsular Malaysia based on the Precipitation Amount. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 423, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
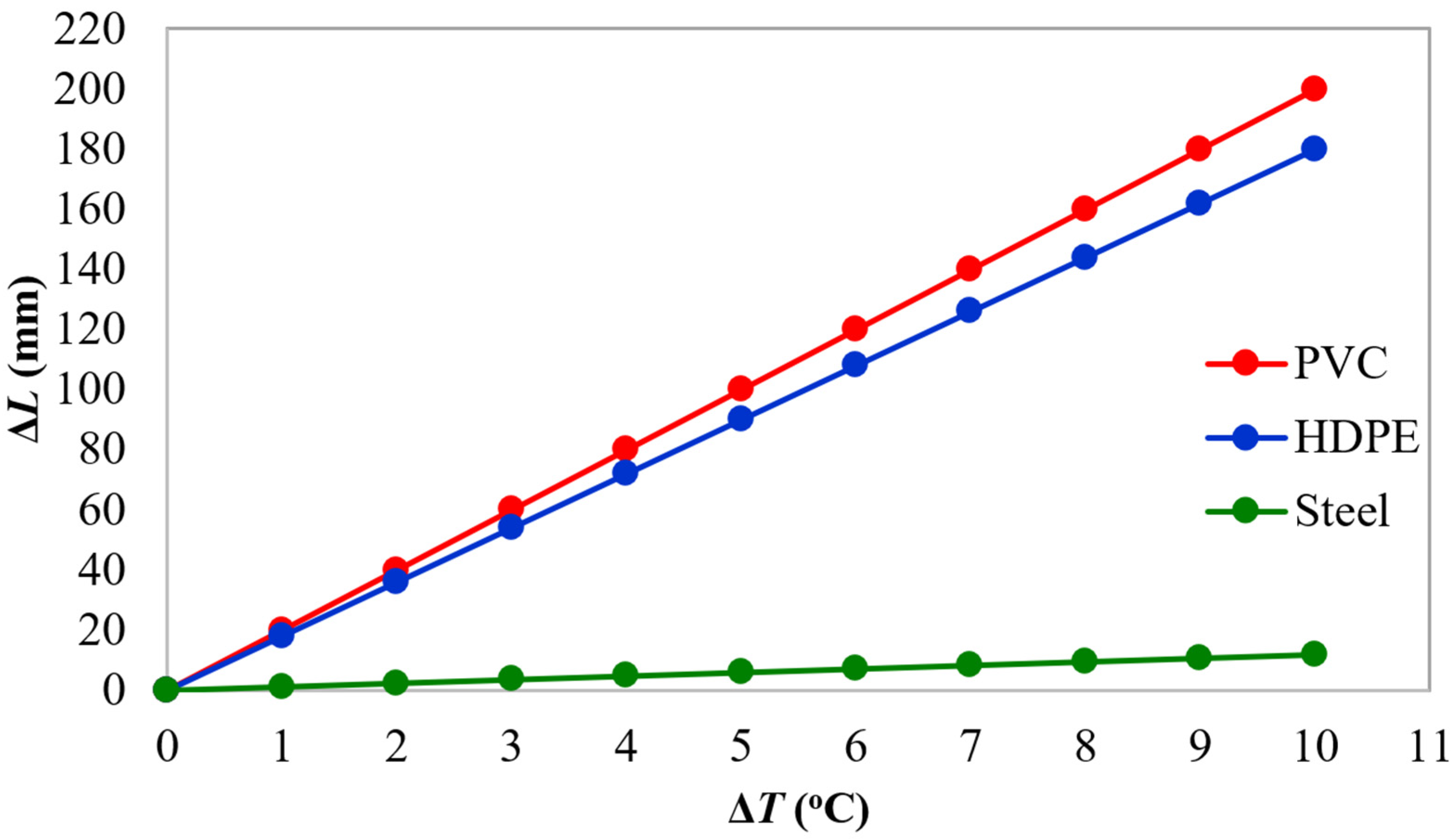
| Pipe Material | a (mm/m/°C) |
|---|---|
| PVC | 0.200 |
| HDPE | 0.180 |
| Steel | 0.012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serafeim, A.V.; Fourniotis, N.T.; Deidda, R.; Kokosalakis, G.; Langousis, A. Leakages in Water Distribution Networks: Estimation Methods, Influential Factors, and Mitigation Strategies—A Comprehensive Review. Water 2024, 16, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111534
Serafeim AV, Fourniotis NT, Deidda R, Kokosalakis G, Langousis A. Leakages in Water Distribution Networks: Estimation Methods, Influential Factors, and Mitigation Strategies—A Comprehensive Review. Water. 2024; 16(11):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111534
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerafeim, Athanasios V., Nikolaos Th. Fourniotis, Roberto Deidda, George Kokosalakis, and Andreas Langousis. 2024. "Leakages in Water Distribution Networks: Estimation Methods, Influential Factors, and Mitigation Strategies—A Comprehensive Review" Water 16, no. 11: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111534
APA StyleSerafeim, A. V., Fourniotis, N. T., Deidda, R., Kokosalakis, G., & Langousis, A. (2024). Leakages in Water Distribution Networks: Estimation Methods, Influential Factors, and Mitigation Strategies—A Comprehensive Review. Water, 16(11), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111534








