Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution under the Influence of Multiple Anthropogenic Activities in Karst Aquifers, Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Climatic Characteristics, Hydrogeological Setting and Functional Areas
2.1. Geographical, Climatic, and Hydrogeological Setting
2.2. Functional Areas
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Data Acquirement
3.2. Statistical Procedures and Geochemical Analysis
3.3. Water Quality for Health
3.4. Source Apportionment Based on PCA
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics
4.1.1. Groundwater Chemistry along Flow Paths
4.1.2. Hydrochemical Variation across the Functional Areas
4.2. Hydrogeological Processes Governing Water Chemistry
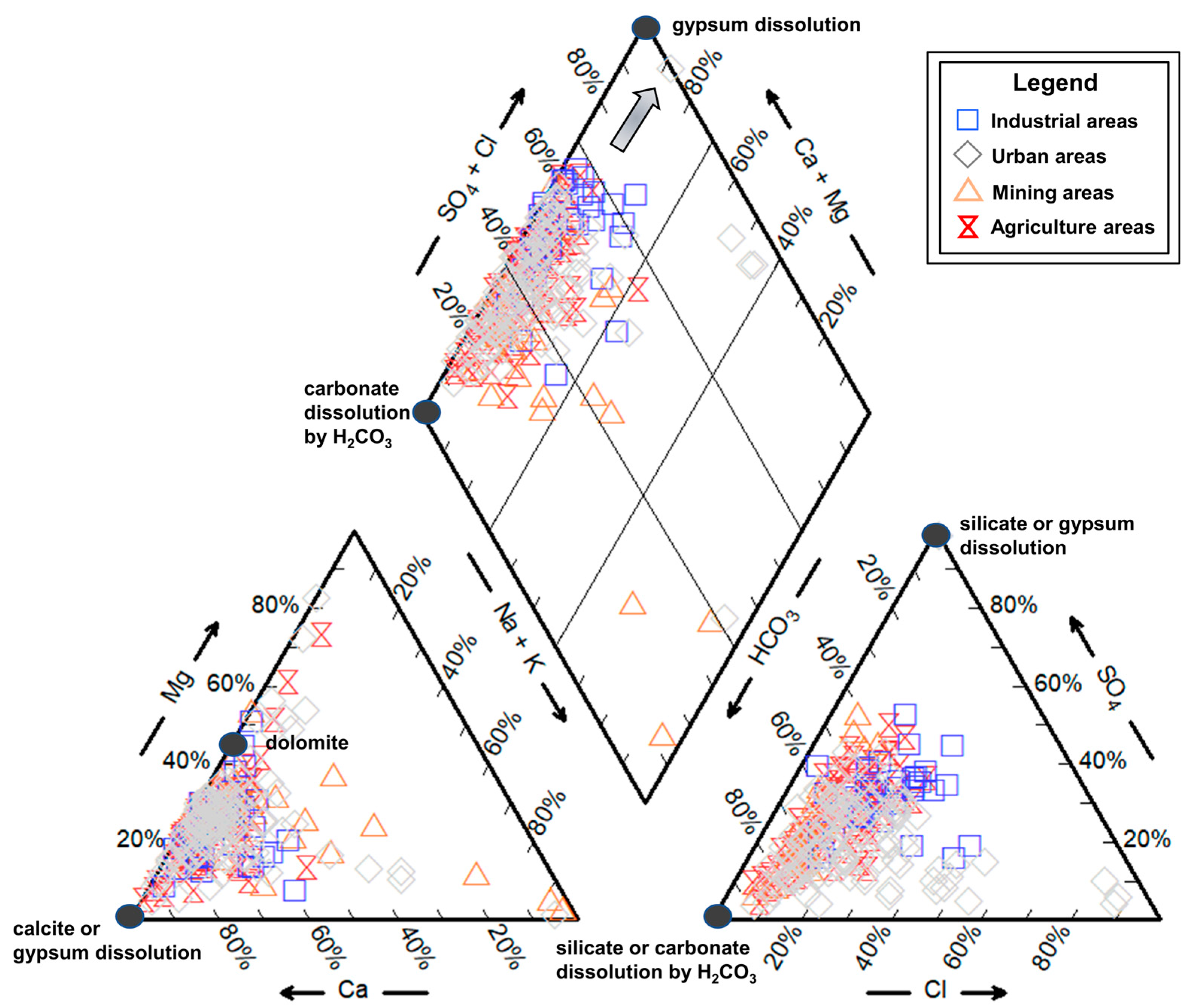
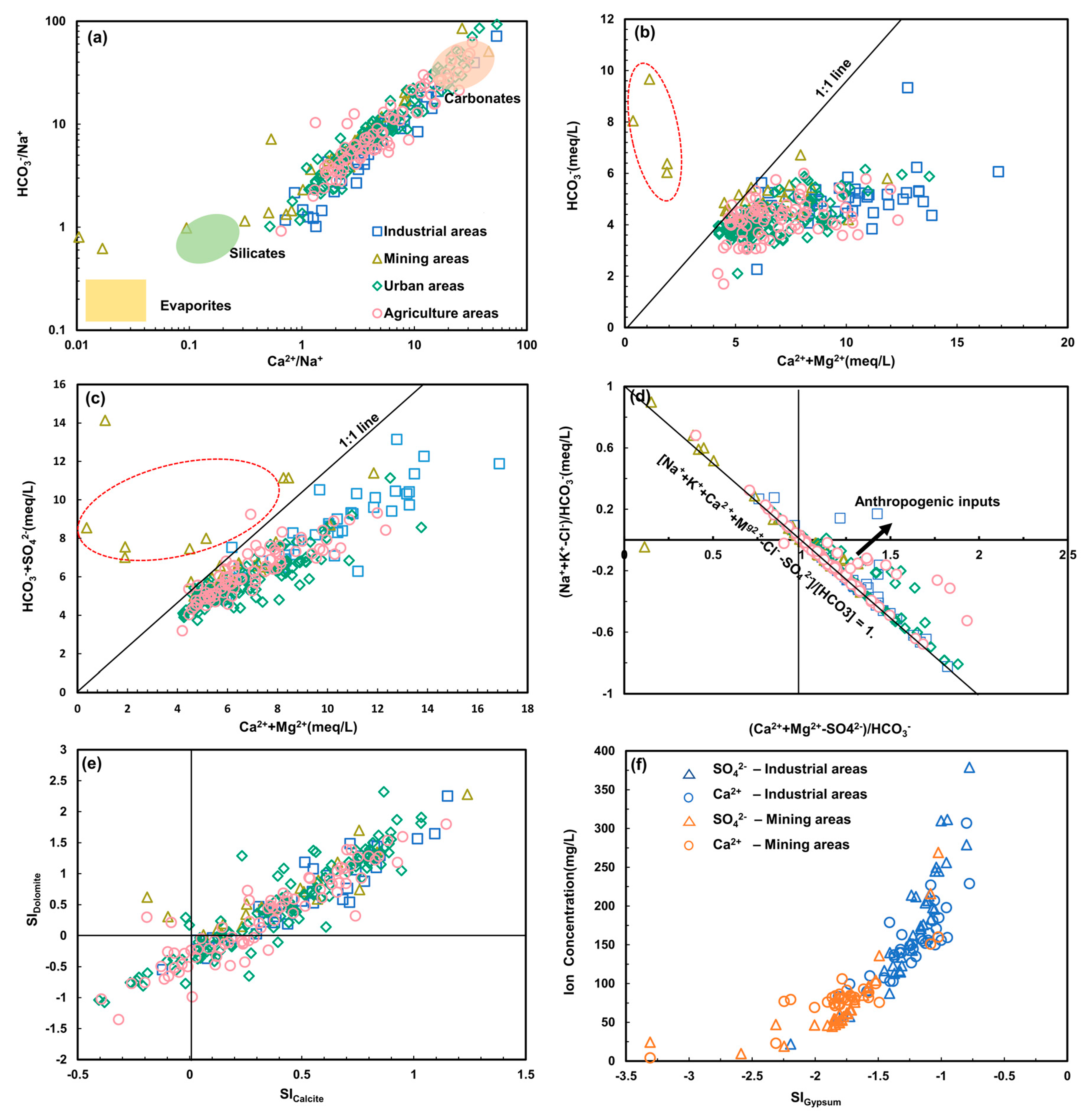
4.2.1. Water-Rock Interaction
4.2.2. Ion Exchange
4.3. Anthropogenic Activities and Potential Source Quantification
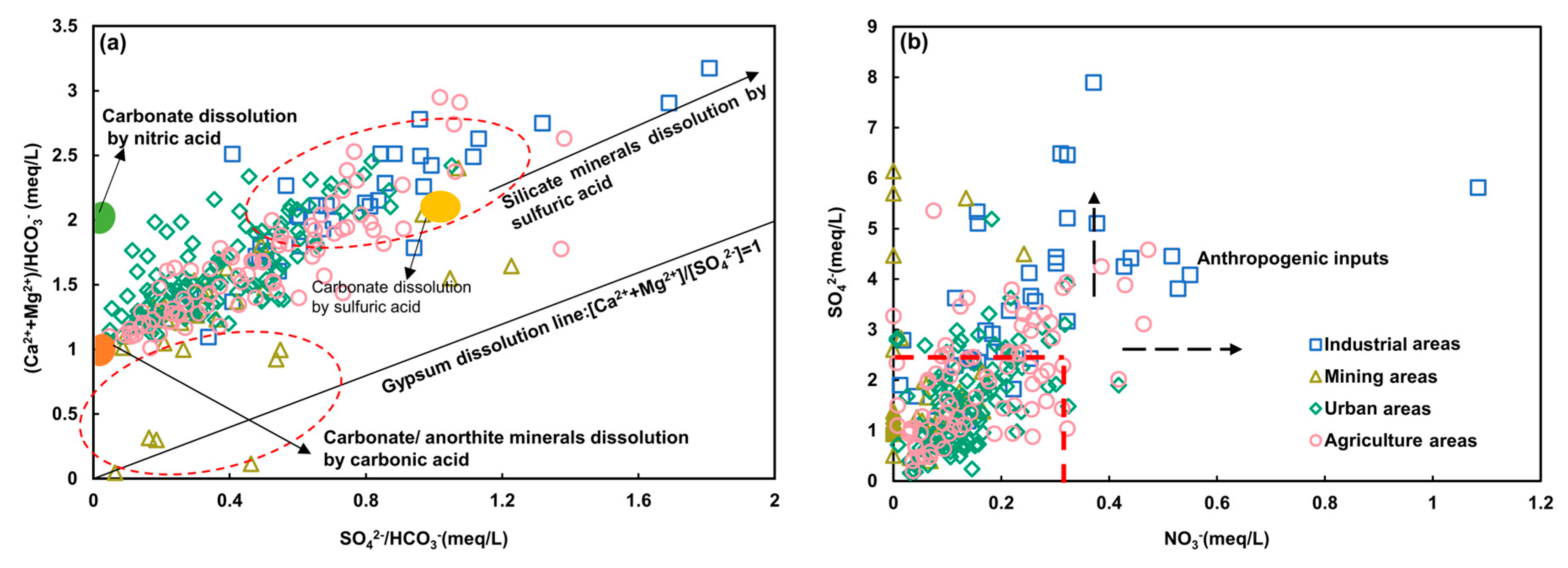
4.3.1. Anthropogenic Inputs
4.3.2. Potential Source Quantification
4.4. Environmental Implication
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campanale, C.; Losacco, D.; Triozzi, M.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. An Overall Perspective for the Study of Emerging Contaminants in Karst Aquifers. Resources 2022, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhor, K.; Ghasemizadeh, R.; Rajic, L.; Alshawabkeh, A. Assessment of groundwater quality and remediation in karst aquifers: A review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Strosnider, W.H.J.; Kogure, T.; Wang, B.; Wu, P.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Z. Identification and quantification of contributions to karst groundwater using a triple stable isotope labeling and mass balance model. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Ghasemizadeh, R.; Padilla, I.; Irizarry, C.; Kaeli, D.; Alshawabkeh, A. Spatiotemporal changes of CVOC concentrations in karst aquifers: Analysis of three decades of data from Puerto Rico. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Chang, L.; Ham, B.; Song, L.; Groves, C. Nitrate sources and biogeochemical processes in karst underground rivers impacted by different anthropogenic input characteristics. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggieri, R.; Forti, P.; Antoci, M.L.; De Waele, J. Accidental contamination during hydrocarbon exploitation and the rapid transfer of heavy-mineral fines through an overlying highly karstified aquifer (Paradiso Spring, SE Sicily). J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Goeppert, N.; Ohmer, M.; Goldscheider, N. Sulfate variations as a natural tracer for conduit-matrix interaction in a complex karst aquifer. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco Castro, R.; Pacheco Ávila, J.; Ye, M.; Cabrera Sansores, A. Groundwater Quality: Analysis of Its Temporal and Spatial Variability in a Karst Aquifer. Groundwater 2018, 56, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, P.J.; Martin, J.B.; Screaton, E.J. Geochemical and statistical evidence of recharge, mixing, and controls on spring discharge in an eogenetic karst aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Marquez, J.M.; Andreo, B.; Mudarra, M. Combining hydrodynamics, hydrochemistry, and environmental isotopes to understand the hydrogeological functioning of evaporite-karst springs. An example from southern Spain. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Luo, W.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y. Multiple isotope geochemistry and hydrochemical monitoring of karst water in a rapidly urbanized region. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 218, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebreen, H.; Banning, A.; Wohnlich, S.; Niedermayr, A.; Ghanem, M.; Wisotzky, F. The Influence of Karst Aquifer Mineralogy and Geochemistry on Groundwater Characteristics: West Bank, Palestine. Water 2018, 10, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, P.W.; Newell, C. The New Potential for Understanding Groundwater Contaminant Transport. Groundwater 2014, 52, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Chen, D.; White, R.E. Spatial variability of shallow groundwater level, electrical conductivity and nitrate concentration, and risk assessment of nitrate contamination in North China Plain. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Fan, Y.; Long, Y.; Pang, Z. Quantitative calculation for the contribution of acid rain to carbonate weathering. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Niu, Y. Effects of coal mining on the evolution of groundwater hydrogeochemistry. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2245–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Groves, C.; Hong, A. Coupled hydrogeochemical evaluation of a vulnerable karst aquifer impacted by septic effluent in a protected natural area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J. Distributions and origins of nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium in various aquifers in an urbanized coastal area, south China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Source apportionment of water pollutants in the upstream of Yangtze River using APCS-MLR. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3795–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, L.C.; Kalin, R.M.; Phoenix, V. Isotope Hydrology and Hydrogeochemical Signatures in the Lake Malawi Basin: A Multi-Tracer Approach for Groundwater Resource Conceptualisation. Water 2024, 16, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L.J.S.o.t.T.E. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, D.; Asare, E.A.; Wahi, R.; Ngaini, Z.; Klutse, N.A.B.; Asamoah, A. Deciphering groundwater pollution in the Lower Anayari Catchment: Insights from using δ2H, δ18O, PMF, and APCS-MLR receptor model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 27099–27116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X. Study on Numerical Simulation of Groundwater Dynamic Characteristics in Feicheng Basin. Master’s Thesis, University of Jinan, Jinan, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, W.; Wan, W.; Wu, Y.; Hou, D. Optimization and rationalization of karst groundwater resource in Feicheng Basin, China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhang, B.; Fan, M.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Ww, Q.; Liu, J. Research on the Evolution Law of Groundwater Hydrochemistry in Feicheng Basin. Yellow River 2015, 37, 75–79, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. The Characteristics of Shallow Groundwater Quality Evolution and Water Resources Protection in Feicheng Basin. Master’s Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. Research on the Numerical Simulation of Karst Groundwater in Feicheng Basin. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2015, 11, 59–64, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Huo, D. Sustainable Utilization of Karst Groundwater in Feicheng Basin, Shandong Province, China. In Proceedings of the Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst, San Antonio, TX, USA, 24–28 September 2005; pp. 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Water Environmental Assessment in Feicheng City Mining Area. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, 2004. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Y.; Qu, X.; Liu, T. Evaluation of water inrush from underlying aquifers by using a modified water-inrush coefficient model and water-inrush index model: A case study in Feicheng coalfield, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2105–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, C.; Ma, T.; Prommer, H. Geochemical evolution of groundwater in carbonate aquifers in Taiyuan, northern China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Tobin, B.W.; Schwartz, B.F. Using periodic hydrologic and geochemical sampling with limited continuous monitoring to characterize remote karst aquifers in the Kaweah River Basin, California, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3361–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Jing, J.; Li, L. A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, A.; Karami, G.H.; Hunkeler, D.; Taheri, A. Isotopic and hydrogeochemical evaluation of springs discharging from high-elevation karst aquifers in Lar National Park, northern Iran. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N.; Sunitha, B.; Adimalla, N.; Chaudhary, M. Quality criteria for groundwater use from a rural part of Wanaparthy District, Telangana State, India, through ionic spatial distribution (ISD), entropy water quality index (EWQI) and principal component analysis (PCA). Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Cravotta Iii, C.A.; Hu, W.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Hydrogeochemical evolution of Ordovician limestone groundwater in Yanzhou, North China. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ren, H.; Wu, Y.; Cao, F.; Jia, F.; Qu, P. The evolution of hydrogeochemical characteristics of a typical piedmont karst groundwater system in a coal-mining area, Northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xie, X.; Qian, Y.; Hou, Q.; Han, D.; Song, J.; Huang, G. Groundwater sulfate in the Pearl River Delta driven by urbanization: Spatial distribution, sources and factors. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 156, 105766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Hydrochemistry and coal mining activity induced karst water quality degradation in the Niangziguan karst water system, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6286–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Groves, C.; Yuan, D.; Kambesis, P. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2009, 109, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Sun, Y. Hydro-geochemical processes of the deep Ordovician groundwater in a coal mining area, Xuzhou, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2231–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Strosnider, W.H.J.; Kogure, T.; Wu, P.; Cao, X. Tracing and quantifying contributions of end members to karst water at a coalfield in southwest China. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetelat, B.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.L. Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin rivers: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4254–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, M.; Wan, L.; Wang, J.; Gan, Y.; Zhou, H. Accumulation, conversion and storage of solute from sinkholes to karst spring under concentrated recharge conditions. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N.; Marghade, D.; Dinakar, A.; Chandana, I.; Sunitha, B.; Ravindra, B.; Balaji, T. Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of chemical composition of groundwater in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P.; Pauwels, H.; Chabaux, F. Characterizing multiple water-rock interactions in the critical zone through Sr-isotope tracing of surface and groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 93, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Han, G. Major ions and δ34SSO4 in Jiulongjiang River water: Investigating the relationships between natural chemical weathering and human perturbations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Martinez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Mahlknecht, J. Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkeltaub, T.; Kurtzman, D.; Dahan, O. Real-time monitoring of nitrate transport in the deep vadose zone under a crop field-implications for groundwater protection. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Plazas, M.; Sanabria, J.; Junca, H. A composite taxonomical and functional framework of microbiomes under acid mine drainage bioremediation systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A.K.M.; Pelinson, N.d.S.; Elis, V.R.; Wendland, E. Long-term geophysical monitoring of an abandoned dumpsite area in a Guarani Aquifer recharge zone. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2020, 230, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Tang, C.; Song, X.; Yuan, R.; Han, Z.; Pan, Y. Factors contributing to nitrate contamination in a groundwater recharge area of the North China Plain. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Kang, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J. Assessing Groundwater Quality and Health Risks of Nitrogen Pollution in the Shenfu Mining Area of Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. Expo. Health 2017, 10, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zou, J.; Jia, R.; Yang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution under the Influence of Multiple Anthropogenic Activities in Karst Aquifers, Northern China. Water 2024, 16, 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121656
Zhang C, Zhang B, Zhang W, Zou J, Jia R, Yang Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution under the Influence of Multiple Anthropogenic Activities in Karst Aquifers, Northern China. Water. 2024; 16(12):1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121656
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chao, Baoxiang Zhang, Wenqing Zhang, Junyu Zou, Ruoyu Jia, and Yuesuo Yang. 2024. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution under the Influence of Multiple Anthropogenic Activities in Karst Aquifers, Northern China" Water 16, no. 12: 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121656
APA StyleZhang, C., Zhang, B., Zhang, W., Zou, J., Jia, R., & Yang, Y. (2024). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution under the Influence of Multiple Anthropogenic Activities in Karst Aquifers, Northern China. Water, 16(12), 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16121656





